Highly Active Ruthenium Catalyst Supported on Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
2.2. Materials
2.3. Synthesis of Hydrophobic Magnetite Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oleic Acid (MNP-OA)
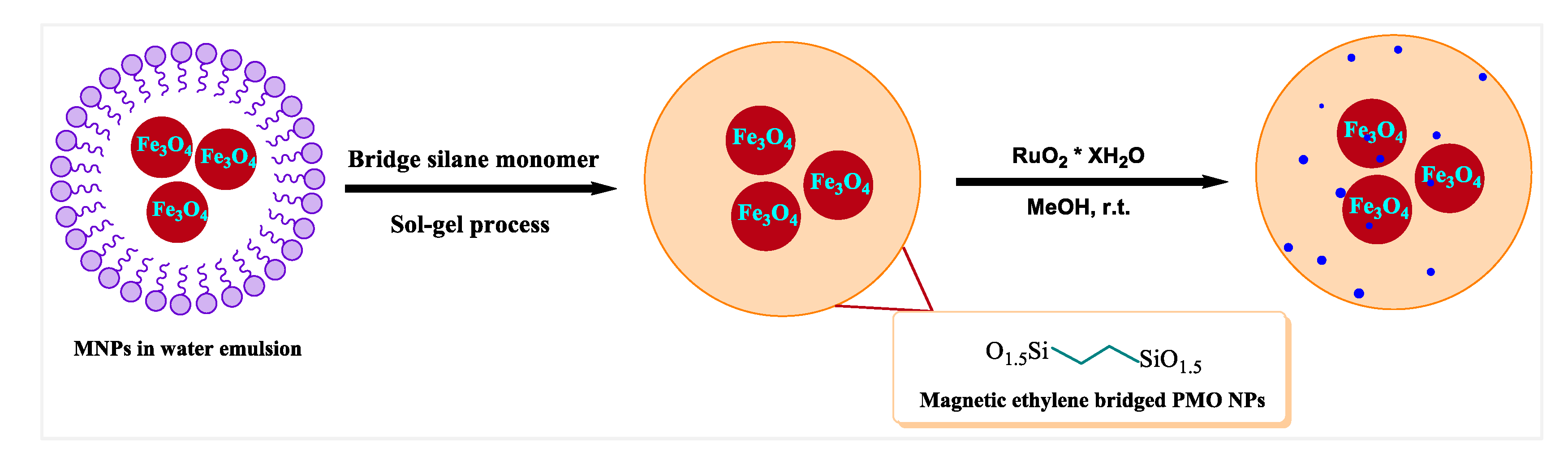
2.4. Synthesis of the Magnetic PMO Nanoparticles (Magnetic PMO NPs)
2.5. Supporting Ruthenium Oxide Nanoparticles on the Magnetic Ethylene-PMO NPs
2.6. General Procedure for the Hydrogenation of Aromatic Compounds Mediated by Ru@M-Ethylene PMO NPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Catalytic Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles with Ruthenium Metal Nanoparticles
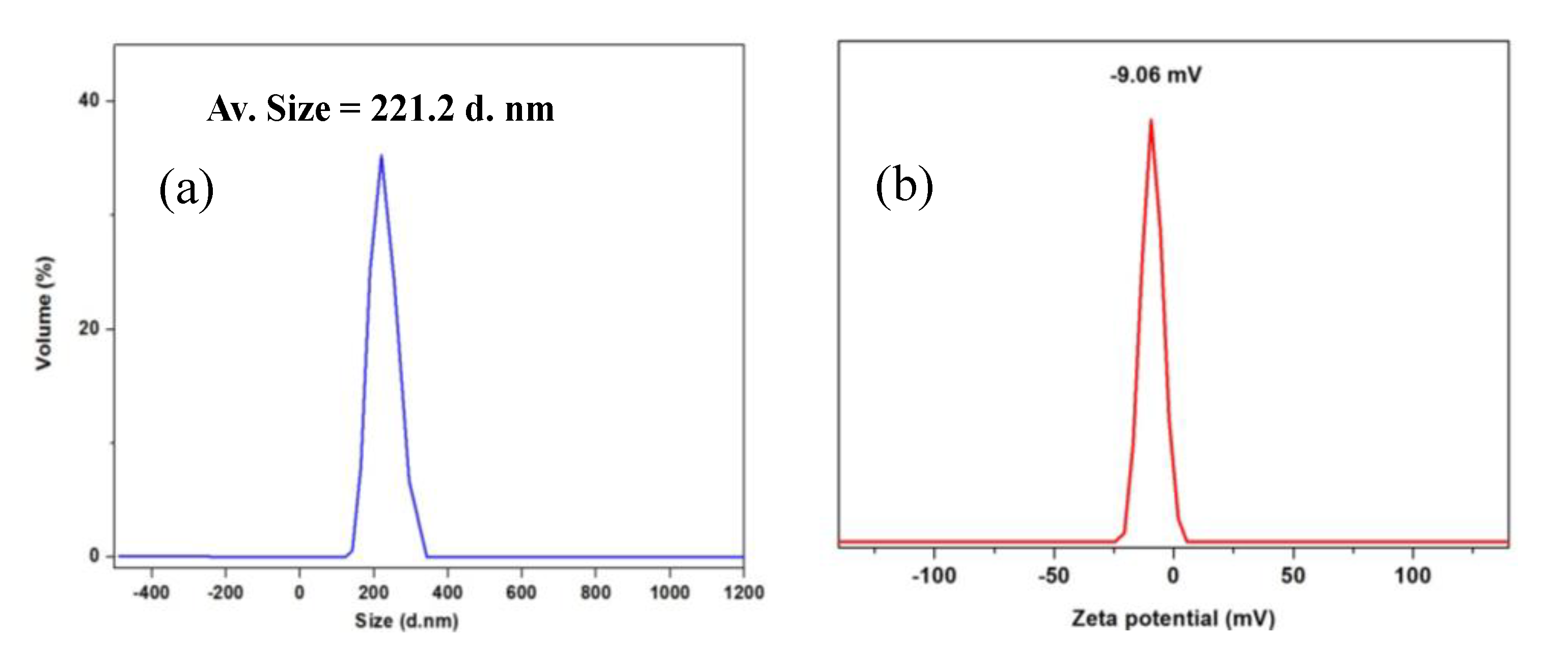
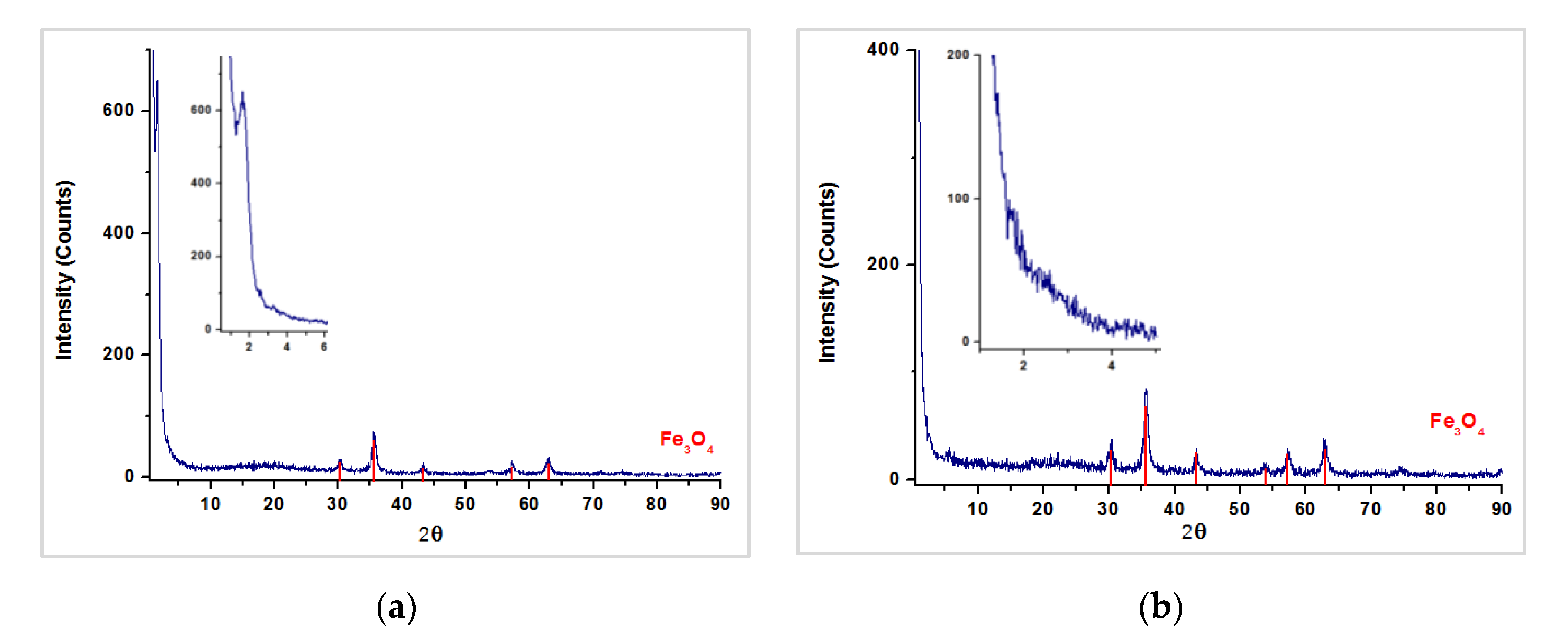
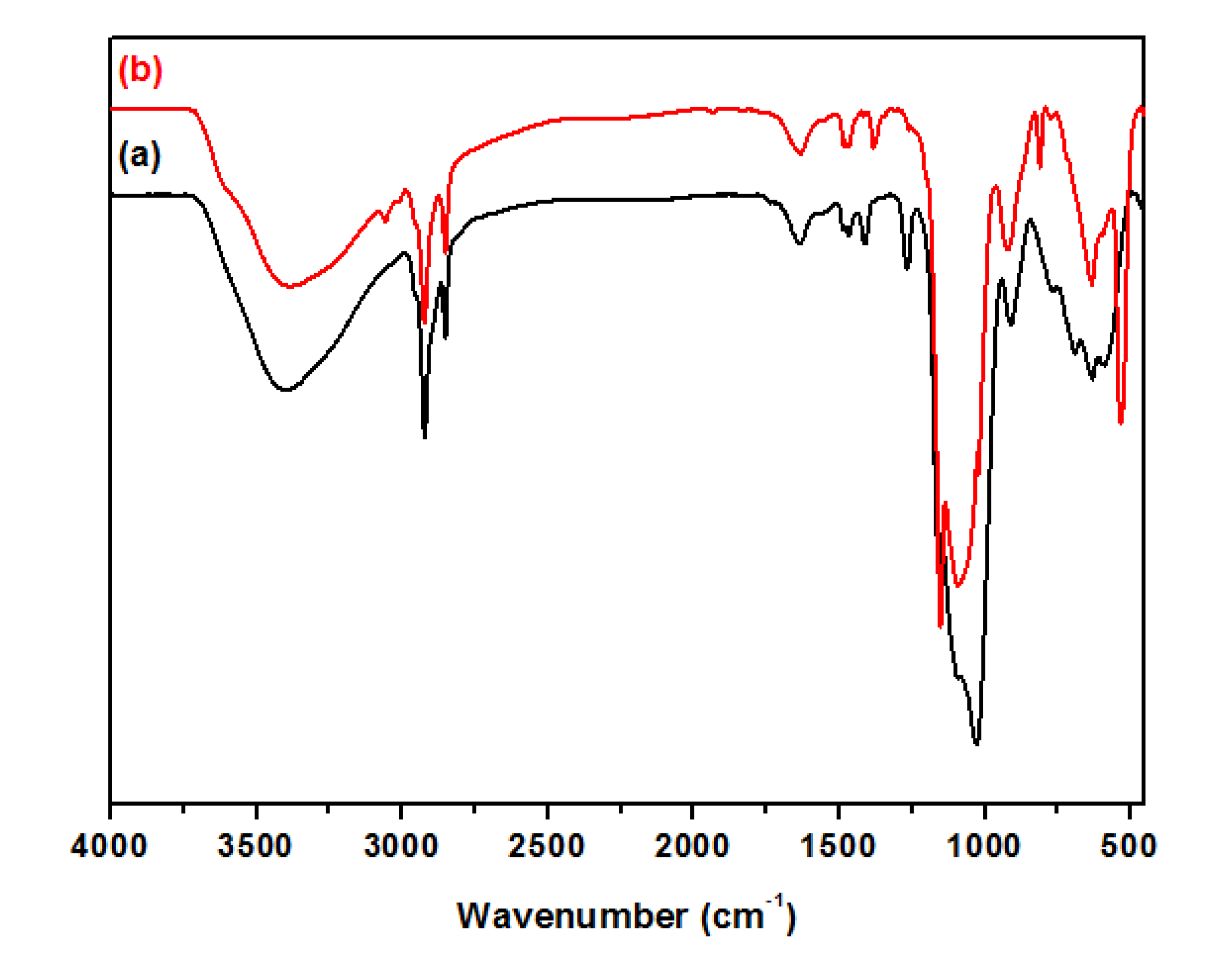
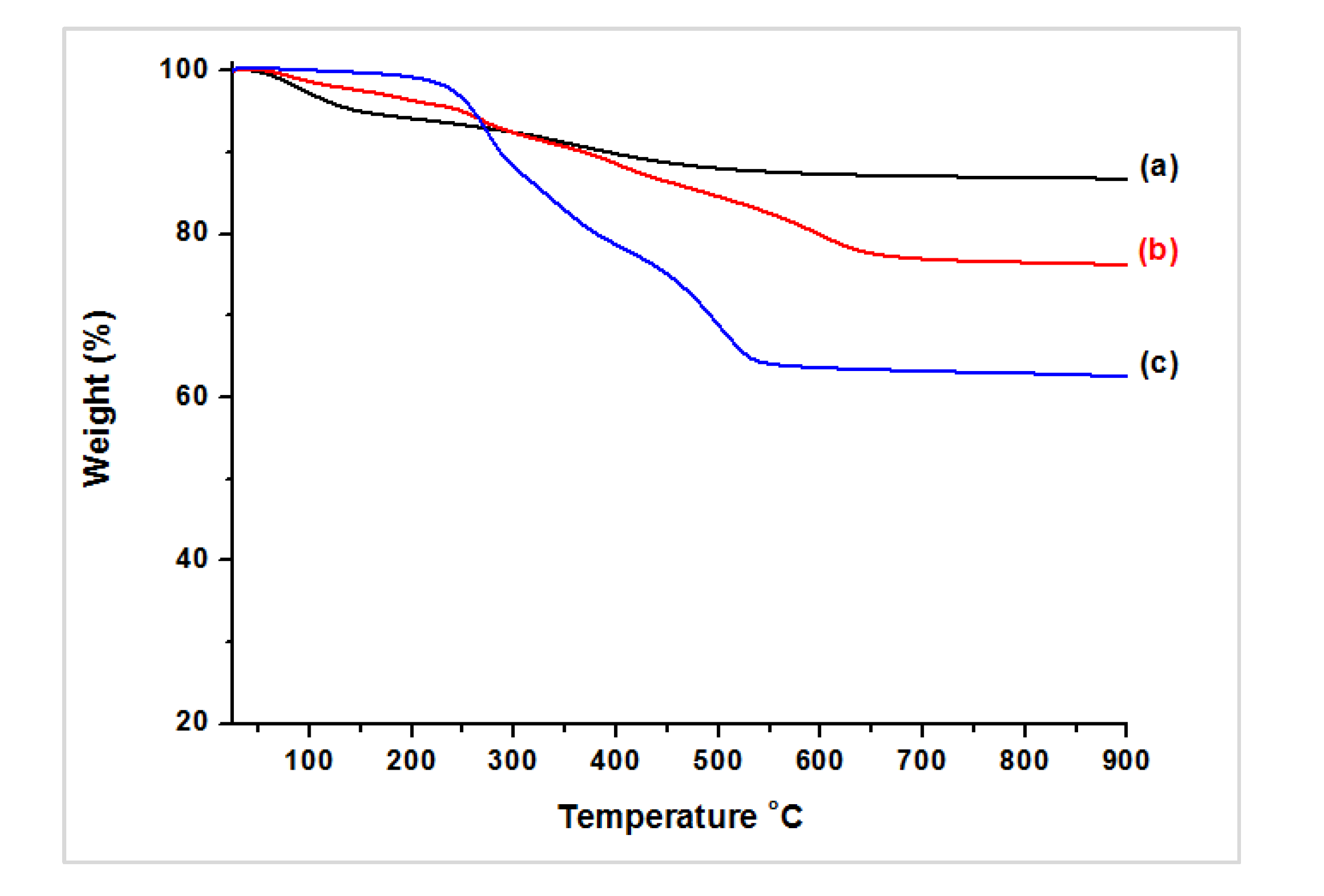
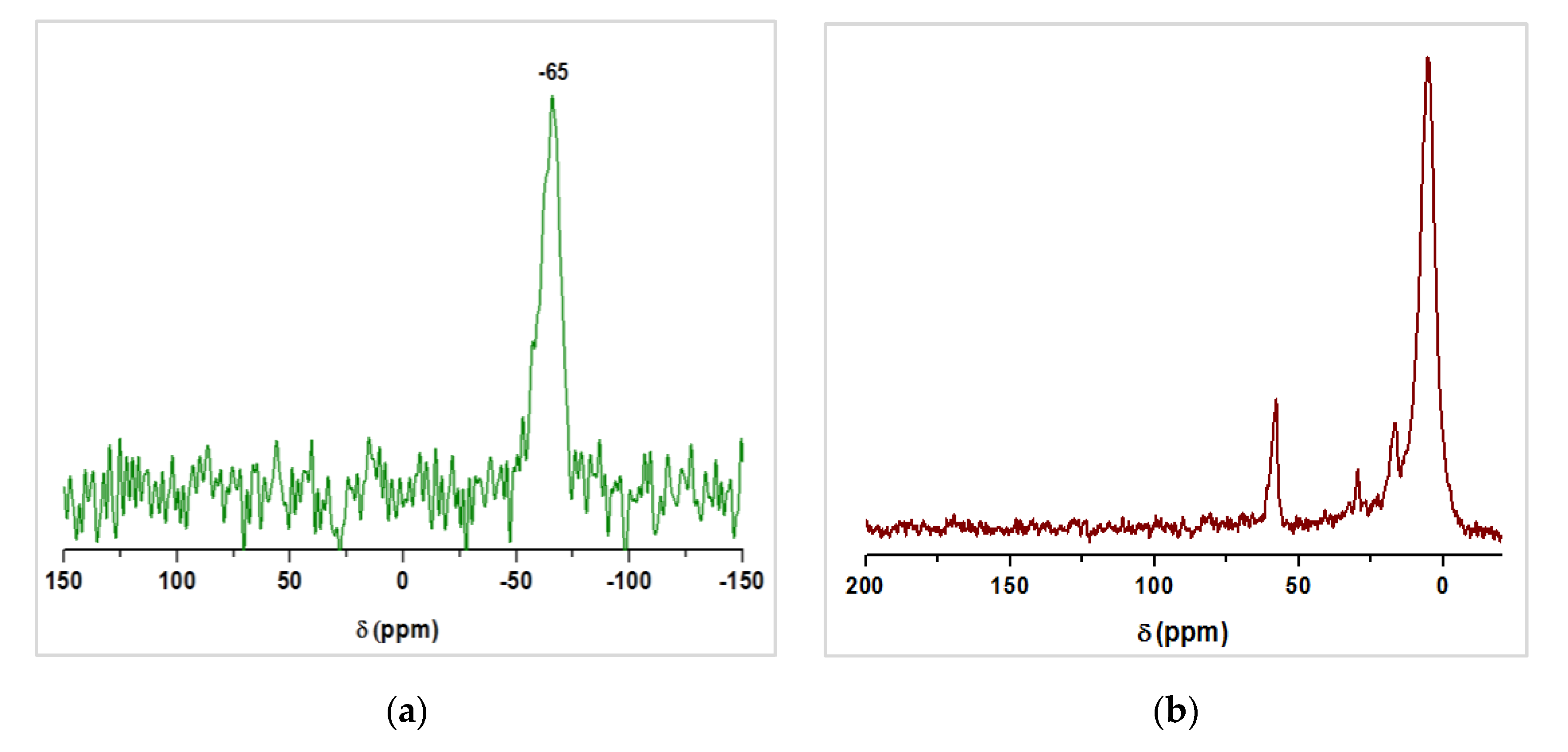
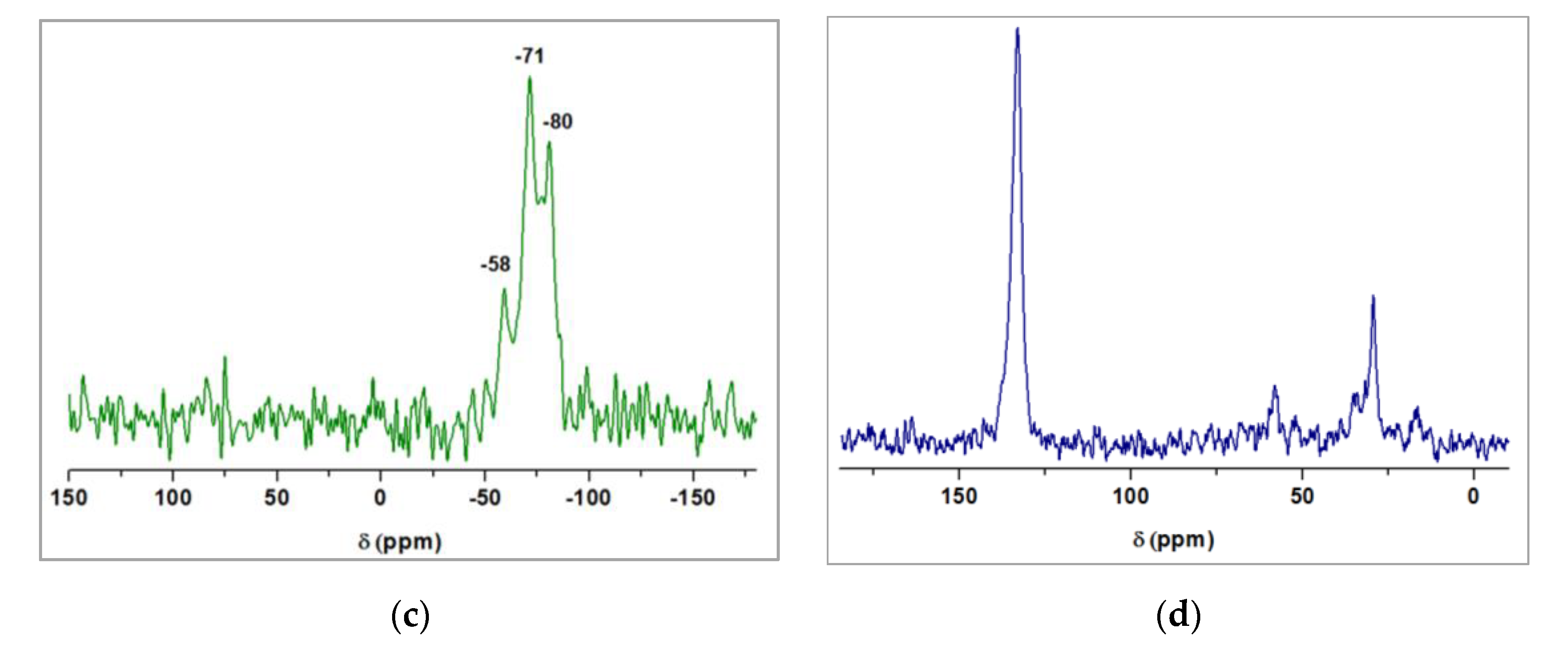
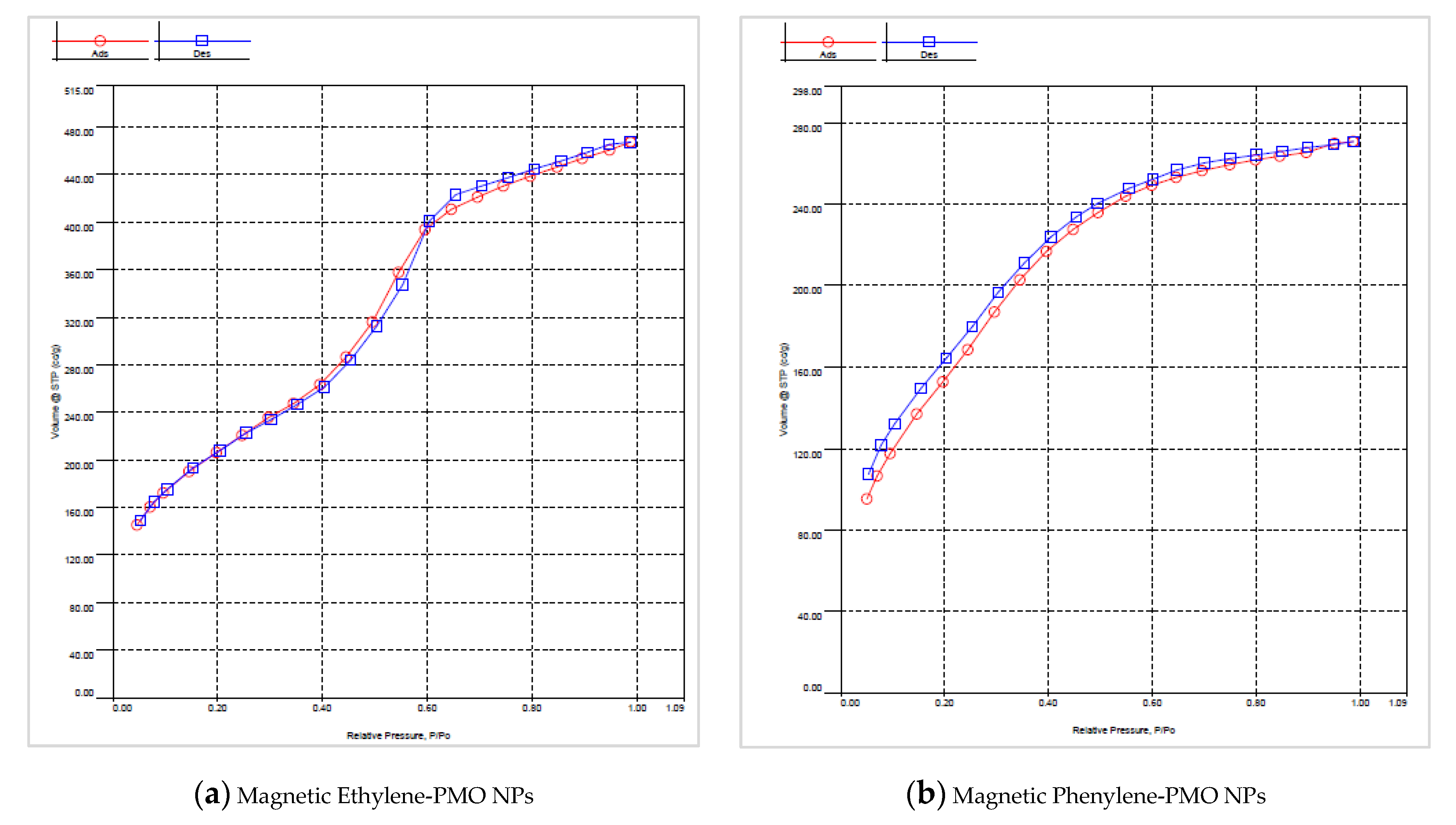
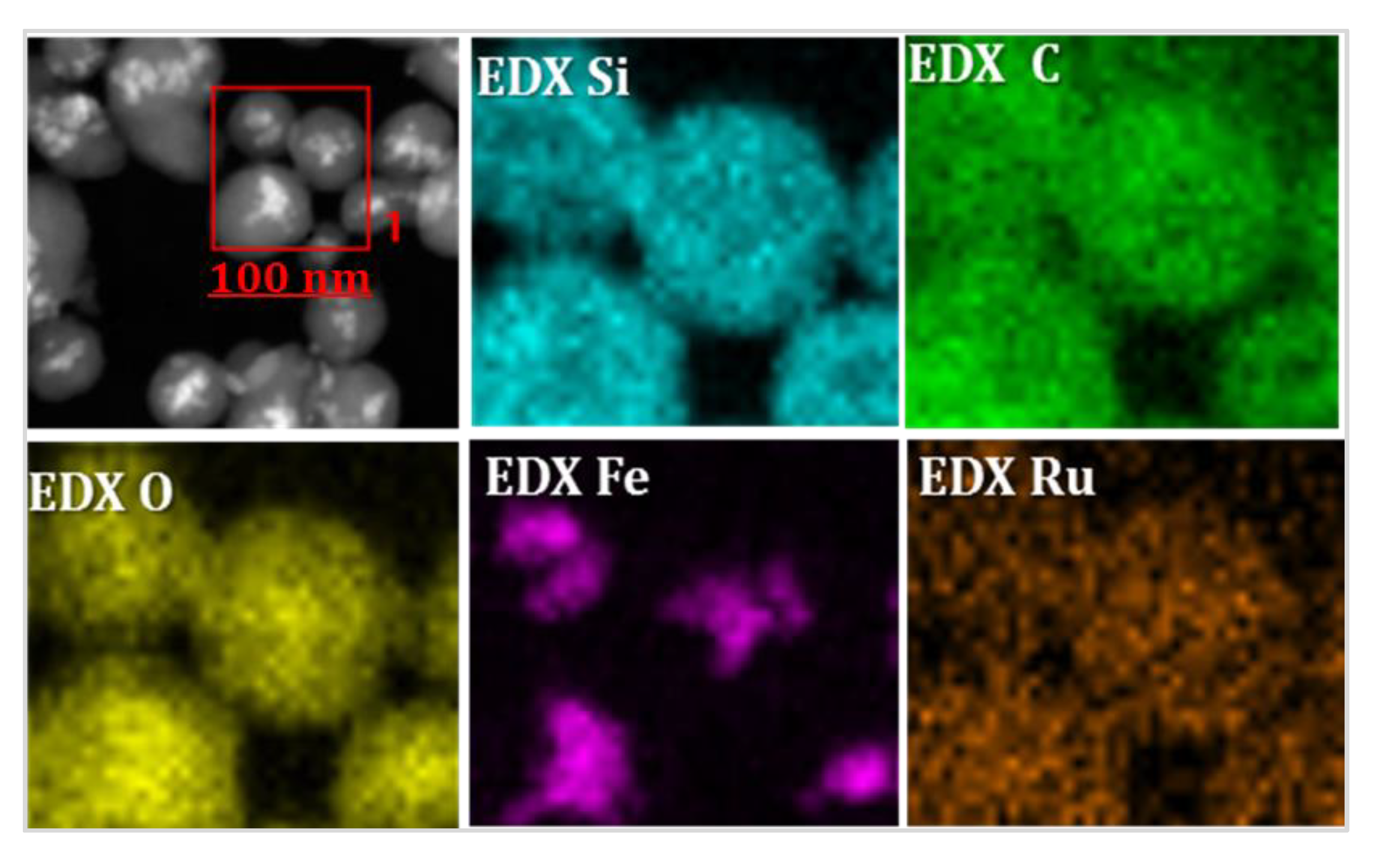
3.2. Characterization of Magnetic PMO Nanoparticle Systems
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetic Ethylene-PMO NP Catalytic Systems
3.4. Catalysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melde, B.J.; Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Stein, A. Mesoporous sieves with unified hybrid inorganic/organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3302–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Guan, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Ohsuna, T.; Terasaki, O. Novel mesoporous materials with a uniform distribution of organic groups and inorganic oxide in their frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9611–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, T.; MacLachlan, M.J.; Coombs, N.; Ozin, G.A. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas with organic groups inside the channel walls. Nature 1999, 402, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boury, B.; Corriu, R.J.P. Adjusting the porosity of a silica-based hybrid material. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, K.J.; Loy, D.A. Bridged polysilsesquioxanes. Molecular-engineered hybrid organic−inorganic materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3306–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunks, W.J.; Ozin, G.A. Challenges and advances in the chemistry of periodic mesoporous organosilicas (PMOs). J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3716–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercaemst, C.; De Jongh, P.E.; Meeldijk, J.D.; Goderis, B.; Verpoort, F.; Van Der Voort, P. Ethenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas with ultra-large mesopores. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, M.; Manchanda, A.S.; Zhuang, J.; Kruk, M. Face-centered-cubic large-pore periodic mesoporous organosilicas with unsaturated and aromatic bridging groups. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8737–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.V.; Jain, A.; George, S.J. Organic–inorganic light-harvesting scaffolds for luminescent hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3055–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, B.; Landskron, K.; Whitnall, W.; Perovic, D.; Ozin, G.A. Past, present, and future of periodic mesoporous organosilicas the PMOs. Accounts Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waki, M.; Mizoshita, N.; Tani, T.; Inagaki, S. Periodic mesoporous organosilica derivatives bearing a high density of metal complexes on pore surfaces. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11871–11875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.R.; Kruk, M.; Mercuri, L.P.; Jaroniec, M.; Asefa, T.; Coombs, N.; Ozin, G.A.; Kamiyama, T.; Terasaki, O. Periodic mesoporous organosilica with large cagelike pores. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1903–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Ha, C.S. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas for advanced applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Voort, P.; Esquivel, D.; De Canck, E.; Goethals, F.; Van Driessche, I.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: From simple to complex bridges; a comprehensive overview of functions, morphologies and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3913–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, M.A.; Beltramini, J.N. Recent advances in hybrid periodic mesostructured organosilica materials: Opportunities from fundamental to biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79129–79151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descalzo, A.B.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Hoffmann, K.; Rurack, K. The supramolecular chemistry of organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5924–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoshita, N.; Tani, T.; Inagaki, S. Syntheses, properties and applications of periodic mesoporous organosilicas prepared from bridged organosilane precursors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, J.; Wolter, G.; Fröba, M. Synthesis and characterization of highly ordered thiophene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilicas with large pores. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.S.; Zhou, C.H. (Clayton); Tong, D.S.; Lin, C.X. Synthesis chemistry and application development of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. J. Porous Mater. 2009, 17, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lofgreen, J.E.; Ozin, G.A. Why PMO? Towards functionality and utility of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Small 2010, 6, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, F.; Li, Y.; Löbermann, F.; Döblinger, M.; Schuster, J.; Peter, L.M.; Trauner, D.; Bein, T. A Zinc Phthalocyanine based periodic mesoporous organosilica exhibiting charge transfer to fullerenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14971–14975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Cui, Y.; Ren, Z.; Qiao, Z.-A.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Highly ordered periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with controllable pore structures. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6588–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djojoputro, H.; Zhou, X.F.; Qiao, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Lu, G. Periodic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres with tunable wall thickness. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6320–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Cattoen, X.; Man, M.W.C.; Durand, J.O.; Khashab, N.M. Syntheses and applications of periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20318–20334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J.L. Chemistry of mesoporous organosilica in nanotechnology: Molecularly organic-inorganic hybridization into frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3235–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Tan, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Quan, X.; Liu, J. Clickable periodic mesoporous organosilicas: Synthesis, click reactions, and adsorption of antibiotics. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 20, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Takeda, H.; Yui, T.; Ueda, Y.; Koike, K.; Inagaki, S.; Ishitani, O. Efficient light harvesting via sequential two-step energy accumulation using a Ru–Re5 multinuclear complex incorporated into periodic mesoporous organosilica. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, M.; De Canck, E.; Van Driessche, I.; Lynen, F.; Van Der Voort, P. Developing a new and versatile ordered mesoporous organosilica as a pH and temperature stable chromatographic packing material. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5546–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, R.; Shi, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S. One-dimensional periodic mesoporous organosilica helical nanotubes with amphiphilic properties for the removal of contaminants from water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Ling, Y.; El-Toni, A.M.; Zhao, D. Periodic mesoporous organosilica nanocubes with ultrahigh surface areas for efficient CO2 adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, M.; Nakashima, K.; Gunawardhana, N.; Yokoi, T.; Ito, M.; Inoue, M.; Yusa, S.I.; Yoshio, M.; Tatsumi, T. Periodic organosilica hollow nanospheres as anode materials for lithium ion rechargeable batteries. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4768–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Auras, F.; Löbermann, F.; Döblinger, M.; Schuster, J.; Peter, L.M.; Trauner, D.; Bein, T. A photoactive porphyrin-based periodic mesoporous organosilica thin film. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18513–18519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroki, M.; Asefa, T.; Whitnal, W.; Kruk, M.; Yoshina-Ishii, C.; Jaroniec, M.; Ozin, G.A. Synthesis and Properties of 1,3,5-Benzene Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica (PMO): Novel Aromatic PMO with Three Point Attachments and Unique Thermal Transformations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13886–13895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; Jeremias, F.; Ernst, S.-J.; Henninger, S.K. Synthesis, functionalization and evaluation of ethylene-bridged PMOs as adsorbents for sorption dehumidification and cooling systems. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2017, 244, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Cattoën, X.; Man, M.W.C.; Gallud, A.; Raehm, L.; Trens, P.; Maynadier, M.; Durand, J.O. Biodegradable ethylene-bis(propyl)disulfide-based periodic mesoporous organosilica nanorods and nanospheres for efficient in-vitro drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6174–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.L. Hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: A generic intelligent framework-hybridization approach for biomedicine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16326–16334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wang, W.; Kong, W.; Chen, Y. Hollow periodic mesoporous organosilicas for highly efficient HIFU-based synergistic therapy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17950–17958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giret, S.; Man, M.W.C.; Carcel, C. Mesoporous-silica-functionalized nanoparticles for drug delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13850–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guan, B.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Z.A.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Mesostructured TiO2 gated periodic mesoporous organosilica-based nanotablets for multistimuli-responsive drug release. Small 2015, 11, 5907–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Salles, D.; Maynadier, M.; Mongin, O.; Hugues, V.; Blanchard-Desce, M.; Cattoën, X.; Man, M.W.C.; Gallud, A.; Garcia, M.; et al. Mixed periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles and core–shell systems, application to in vitro two-photon imaging, therapy, and drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 7214–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaweera, I.; Hong, J.; D’Souza, A.; Balkus, K.J., Jr. Novel wrinkled periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for hydrophobic anticancer drug delivery. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Huo, W.-L.; Xu, J.; Meng, X.; Yang, J. A one-step method for pore expansion and enlargement of hollow cavity of hollow periodic mesoporous organosilica spheres. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 52, 2868–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wang, W.; Kong, W.; Chen, Y. Organic-inorganic hybrid hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for efficient ultrasound-based imaging and controlled drug release. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Omar, H.; Anjum, D.H.; Gurinov, A.A.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I.; Khashab, N.M. Periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with controlled morphologies and high drug/dye loadings for multicargo delivery in cancer cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 9607–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.X.; Qiao, S.; Yu, C.; Ismadji, S.; Lu, G. Periodic mesoporous silica and organosilica with controlled morphologies as carriers for drug release. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parambadath, S.; Mathew, A.; Barnabas, M.J.; Ha, C.S. A pH-responsive drug delivery system based on ethylenediamine bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2015, 215, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.M.; Croissant, J.G.; Maynadier, M.; Cattoën, X.; Man, M.W.C.; Vergnaud, J.; Chaleix, V.; Sol, V.; Garcia, M.; Gary-Bobo, M.; et al. Porphyrin-functionalized mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for two-photon imaging of cancer cells and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3681–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Tian, Y.; Tian, W.; Huang, P.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Smart cancer cell targeting imaging and drug delivery system by systematically engineering periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Ha, C.-S. Periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) for catalytic applications. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponchia, G.; Marin, R.; Freris, I.; Marchiori, M.; Moretti, E.; Storaro, L.; Canton, P.; Lausi, A.; Benedetti, A.; Riello, P. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable pore size for tailored gold nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esquivel, D.; De Canck, E.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Van Der Voort, P.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Periodic Mesoporous organosilicas as catalysts for organic reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 1280–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of Janus Au@periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) nanostructures with precisely controllable morphology: A seed-shape defined growth mechanism. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4826–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.Q.; Kleitz, F.; Chen, Z.G.; Yang, T.; Strounina, E.; Lu, G.; Qiao, S. Yolk-Shell Hybrid materials with a periodic mesoporous organosilica shell: Ideal nanoreactors for selective alcohol oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 22, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, M.J.; Silva, F.P.; Kiyohara, P.K.; Rossi, L.M.; Landers, R. Catalyst recovery and recycling facilitated by magnetic separation: Iridium and other metal nanoparticles. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. Fast-growing field of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6949–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.J.; Lee, W.; Oh, Y.S.; Lee, J.K. Magnetic nanoparticles as a catalyst vehicle for simple and easy recycling. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrówczyński, R.; Nan, A.; Liebscher, J. Magnetic nanoparticle-supported organocatalysts – an efficient way of recycling and reuse. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5927–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polshettiwar, V.; Luque, R.; Fihri, A.; Zhu, H.; Bouhrara, M.; Basset, J.M. Magnetically recoverable nanocatalysts. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3036–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Lee, I.S. Magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst systems for the organic reactions. Nano Today 2010, 5, 412–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, C.; Sun, Z.; Wu, L.Z.; Tung, C.; Zhang, T. Magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts (MRNCs): A versatile integration of high catalytic activity and facile recovery. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6244–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Varma, R.S. Magnetically retrievable catalysts for organic synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shylesh, S.; Schünemann, V.; Thiel, W.R. Magnetically separable nanocatalysts: Bridges between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3428–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalidindi, S.B.; Jagirdar, B.R. Nanocatalysis and prospects of green chemistry. ChemSusChem 2011, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawande, M.B.; Branco, P.S.; Varma, R.S. Nano-magnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for recyclable catalysts in the development of sustainable methodologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3371–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, B.; Mansouri, F.; Mirzaei, H.M. ChemInform abstract: Recent applications of magnetically recoverable nanocatalysts in C-C and C-X coupling reactions. ChemCatChem 2015, 46, 1736–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudr, J.; Haddad, Y.; Richtera, L.; Heger, Z.; Cernak, M.; Adam, V.; Zitka, O. Magnetic nanoparticles: From design and synthesis to real world applications. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Davaran, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schuth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Rezaee, M. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, H.H.P.; Keane, M.A. Enzyme-magnetic nanoparticle hybrids: New effective catalysts for the production of high value chemicals. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, K.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Barkhi, M.; Baharifar, H.; Poor-Akbar, E.; Zari, N.; Stamatis, H.; Bordbar, A.K. Immobilization of cellulase enzyme onto magnetic nanoparticles: Applications and recent advances. Mol. Catal. 2017, 442, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, C.; Tertis, M.; Galatus, R.V. Magnetic nanoparticles for antibiotics detection. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijs, M.A.M.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.; Ko, S.; Kim, I.; Huang, Y.; Mohanty, K.K.; Huh, C.; Maynard, J.A. Recent advances incorporating superparamagnetic nanoparticles into immunoassays. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, J.; Rosenzweig, N.; Rosenzweig, Z. Superparamagnetic Fe2O3Beads−CdSe/ZnS quantum dots core−shell nanocomposite particles for cell separation. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Mehrjardi, M. Fe3O4@silica sulfuric acid: An efficient and heterogeneous nanomagnetic catalyst in organic reactions. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2017, 14, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Stubbs, L.P.; Ho, F.; Liu, R.; Ship, C.P.; Maguire, J.A.; Hosmane, N.S. Magnetic nanocomposites: A new perspective in catalysis. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.M.; Costa, N.J.S.; Silva, F.P.; Wojcieszak, R. Magnetic nanomaterials in catalysis: Advanced catalysts for magnetic separation and beyond. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2906–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.W.; Chang, S.H. Magnetic nanoparticles and their heterogeneous persulfate oxidation organic compound applications. Springer Proc. Phys. 2015, 175, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, G.K.; Farr, W.; Hunyadi Murph, S.E. Multifunctional Fe2O3-au nanoparticles with different shapes: Enhanced catalysis, photothermal effects, and magnetic recyclability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 15162–15172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schätz, A.; Reiser, O.; Stark, W.J. Nanoparticles as semi-heterogeneous catalyst supports. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8950–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Gao, Y. Nanoparticle-supported catalysts and catalytic reactions—A mini-review. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2006, 1, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulahmetovic, E.; Hargaden, G.C. Recent advances in the development of magnetic catalysts for the Suzuki reaction. Rev. J. Chem. 2017, 7, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.M.; Garcia, M.A.S.; Vono, L.L.R. Recent advances in the development of magnetically recoverable metal nanoparticle catalysts. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, V.F.; Francesko, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Bañobre-Lopez, M.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Advances in magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Health Mater. 2017, 7, 1700845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, K.; Gu, H.; Zheng, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Xu, B. Dopamine as a robust anchor to immobilize functional molecules on the iron oxide shell of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9938–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedernikova, I.A. Magnetic nanoparticles: Advantages of using, methods for preparation, characterization, application in pharmacy. Rev. J. Chem. 2015, 5, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zverev, V.; Pyatakov, A.; Shtil, A.; Tishin, A. Novel applications of magnetic materials and technologies for medicine. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, T.; Schöpf, B.; Hofmann, H.; Hofmann, M.; Von Rechenberg, B. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Possibilities and limitations of a new drug delivery system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosayebi, J.; Kiyasatfar, M.; Laurent, S. Synthesis, functionalization, and design of magnetic nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Adv. Health Mater. 2017, 6, 1700306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, S.; Jin, Y.G.; Chen, Z.G.; Gu, H.C.; Lu, G. Magnetic hollow spheres of periodic mesoporous organosilica and Fe3O4 nanocrystals: Fabrication and structure control. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, D. Magnetic spherical cores partly coated with periodic mesoporous organosilica single crystals. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, F.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, G.; Hao, S.; Zhang, X. Ru nanoparticles dispersed on magnetic yolk–shell nanoarchitectures with Fe3O4 core and sulfoacid-containing periodic mesoporous organosilica shell as bifunctional catalysts for direct conversion of cellulose to isosorbide. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.X.; Li, Z.; Brumbley, S.; Petrasovits, L.; McQualter, R.B.; Yu, C.; Lu, G. Synthesis of magnetic hollow periodic mesoporous organosilica with enhanced cellulose tissue penetration behaviour. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7565–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Hu, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, K.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z. Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4/PMMA/SiO2 nanorattles with periodic mesoporous shell for lysozyme adsorption. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2264–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Elzatahry, A.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Al-Dahyan, D.; Zhao, D. A versatile in situ etching-growth strategy for synthesis of yolk–shell structured periodic mesoporous organosilica nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 51470–51479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Guan, Y.P.; Liu, H.Z. Synthesis of magnetic silica nanospheres with metal ligands and application in affinity separation of proteins. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 275, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Mayers, B.T.; Xia, Y. Modifying the surface properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles through a sol−gel approach. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Tapec, R.; Theodoropoulou, N.; Dobson, J.; Hebard, A.; Tan, W. Synthesis and characterization of silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in microemulsion: The effect of nonionic surfactants. Langmuir 2001, 17, 2900–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R. Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1981, 17, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axet, M.; Philippot, K. Catalysis with colloidal ruthenium nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1085–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakers, L.; Martínez-Prieto, L.M.; López-Vinasco, A.M.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B.; Glorius, F.; Van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. Ruthenium nanoparticles ligated by cholesterol-derived NHCs and their application in the hydrogenation of arenes. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7070–7073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novio, F.; Monahan, D.; Coppel, Y.; Antorrena, G.; Lecante, P.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B. Surface chemistry on small ruthenium nanoparticles: Evidence for site selective reactions and influence of ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafter, E.; Gutmann, T.; Löw, F.; Buntkowsky, G.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B.; Van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. Secondary phosphineoxides as pre-ligands for nanoparticle stabilization. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, P.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B. ChemInform abstract: Organometallic ruthenium nanoparticles: A comparative study of the influence of the stabilizer on their characteristics and reactivity. ChemCatChem 2013, 44, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gálvez, D.; Nolis, P.; Philippot, K.; Chaudret, B.; Van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. Phosphine-stabilized ruthenium nanoparticles: The effect of the nature of the ligand in catalysis. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Entry | Substrate | H2 Pressure | Reaction Time (h) | Temperature | Products | Yield (%) [b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 100 psi | 1 | 80 °C |  | >99 |
| 2 | 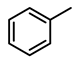 | 100 psi | 1 | 80 °C |  | >99 |
| 3 | 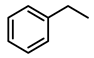 | 400 psi | 2 | 120 °C | 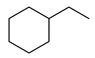 | >99 |
| 4 |  | 400 psi | 4 | 120 °C |  | >99 |
| 5c | 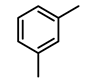 | 400 psi | 12 | 120 °C | 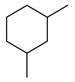 | >99 |
| 6c | 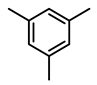 | 400 psi | 12 | 120 °C | 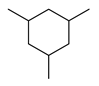 | >99 |
| 7 | 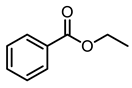 | 400 psi | 12 | 120 °C | 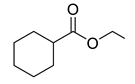 | >99 |
| 8 | 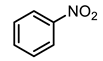 | 400 psi | 12 | 120 °C | 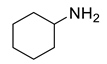 | >99 |
| Entry. | Substrate | S/C Ratio | Reaction Time (h) | Conversion (%) [b] | TON | TOF (h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 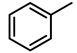 | 1000 | 0.5 | 99.6 | 996 | 1992 |
| 2 | 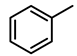 | 2000 | 1 | 100 | 2000 | 2000 |
| 3 |  | 5000 | 1 | 99.8 | 4992 | 4992 |
| 4 | 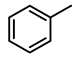 | 10,000 | 1 | 97.2 | 9783 | 9783 |
| 5 |  | 50,000 | 1 | 9.5 | 4750 | 4750 |
| 6 | 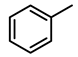 | 100,000 | 1 | 2 | 2000 | 2000 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omar, S.; Abu-Reziq, R. Highly Active Ruthenium Catalyst Supported on Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175769
Omar S, Abu-Reziq R. Highly Active Ruthenium Catalyst Supported on Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(17):5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175769
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmar, Suheir, and Raed Abu-Reziq. 2020. "Highly Active Ruthenium Catalyst Supported on Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles" Applied Sciences 10, no. 17: 5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175769
APA StyleOmar, S., & Abu-Reziq, R. (2020). Highly Active Ruthenium Catalyst Supported on Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences, 10(17), 5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175769






