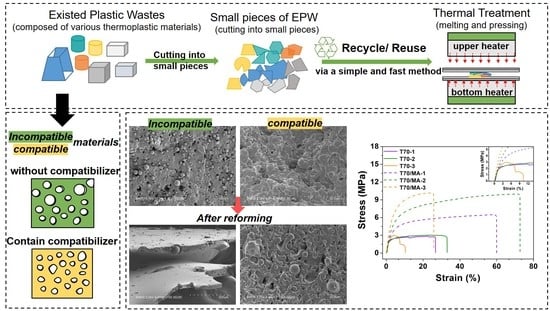
Effect of Melting–Recycling Cycles and Mechanical Fracture on the Thermoplastic Materials Composed of Thermoplastic Polyurethane and Polypropylene Waste Blends
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
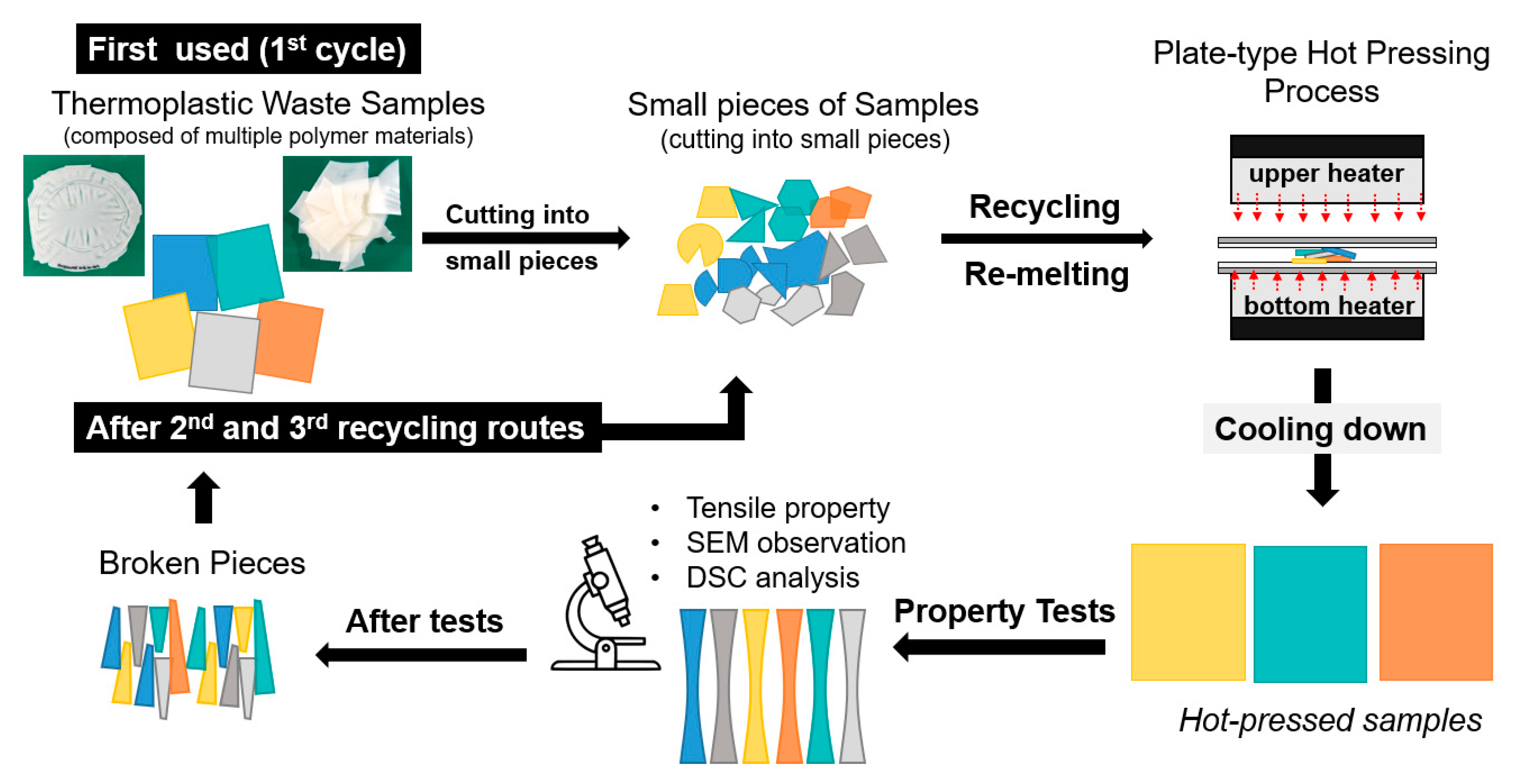
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Tests
2.3.1. SEM Observation
2.3.2. Tensile Properties
2.3.3. DSC Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
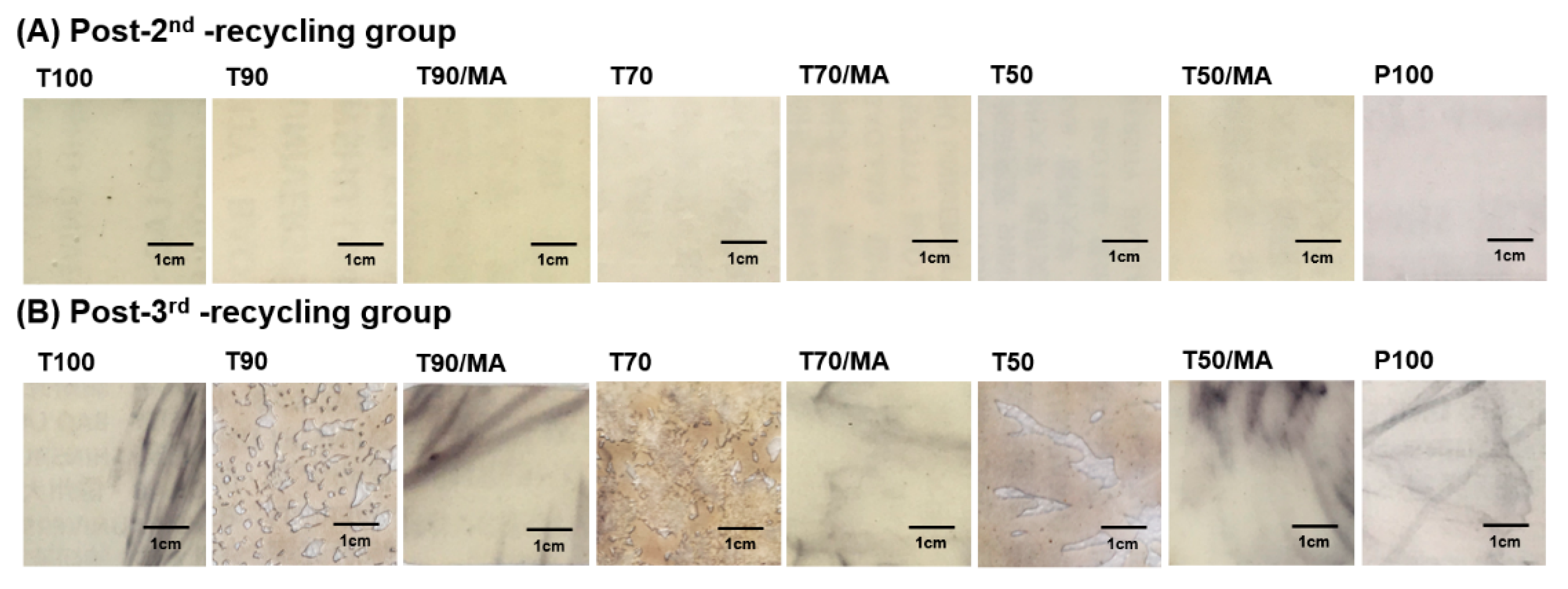
3.1. Surface Observation
3.1.1. Microscope Observation
3.1.2. SEM Observation
3.2. Tensile Properties
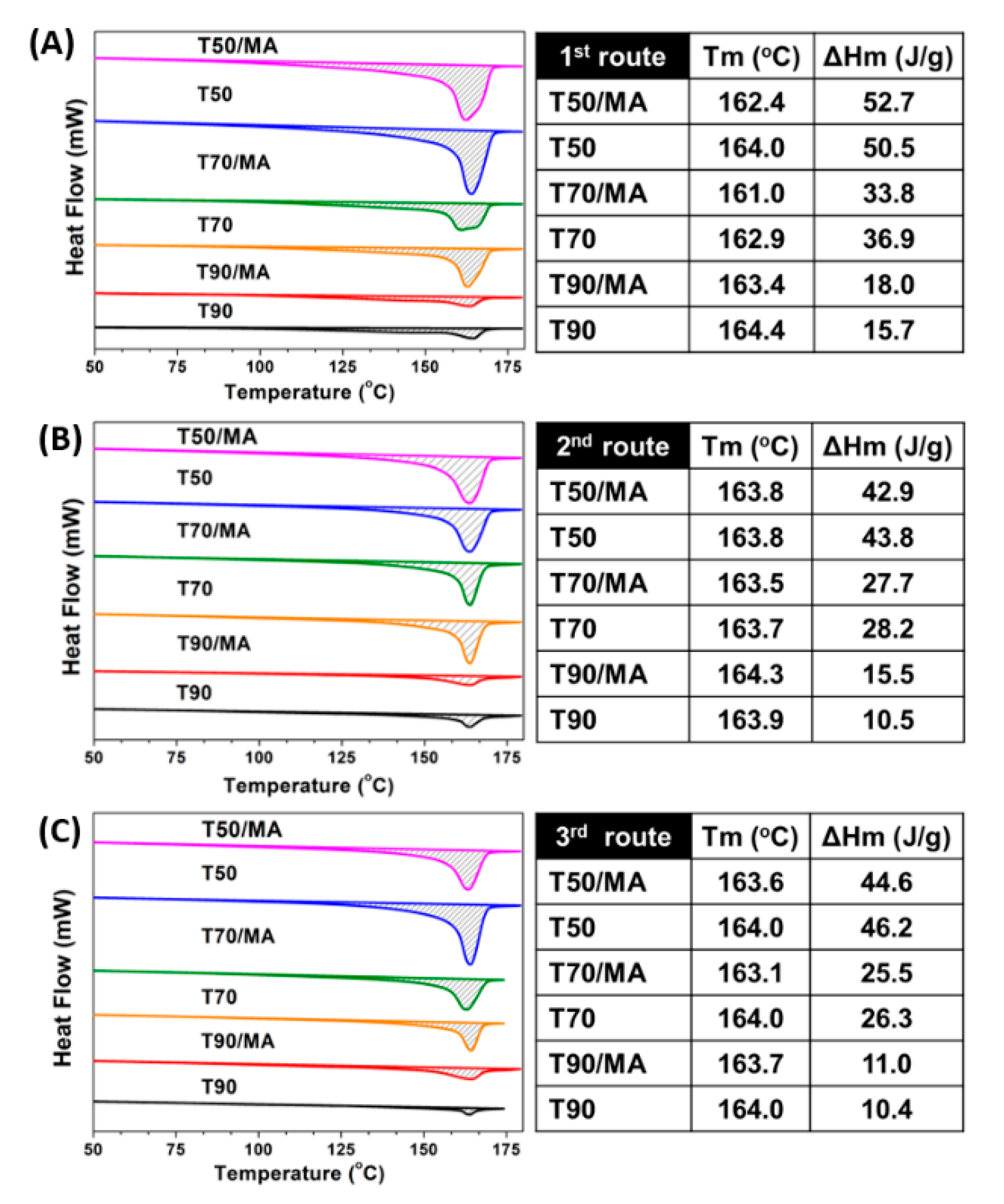
3.3. DSC Analysis
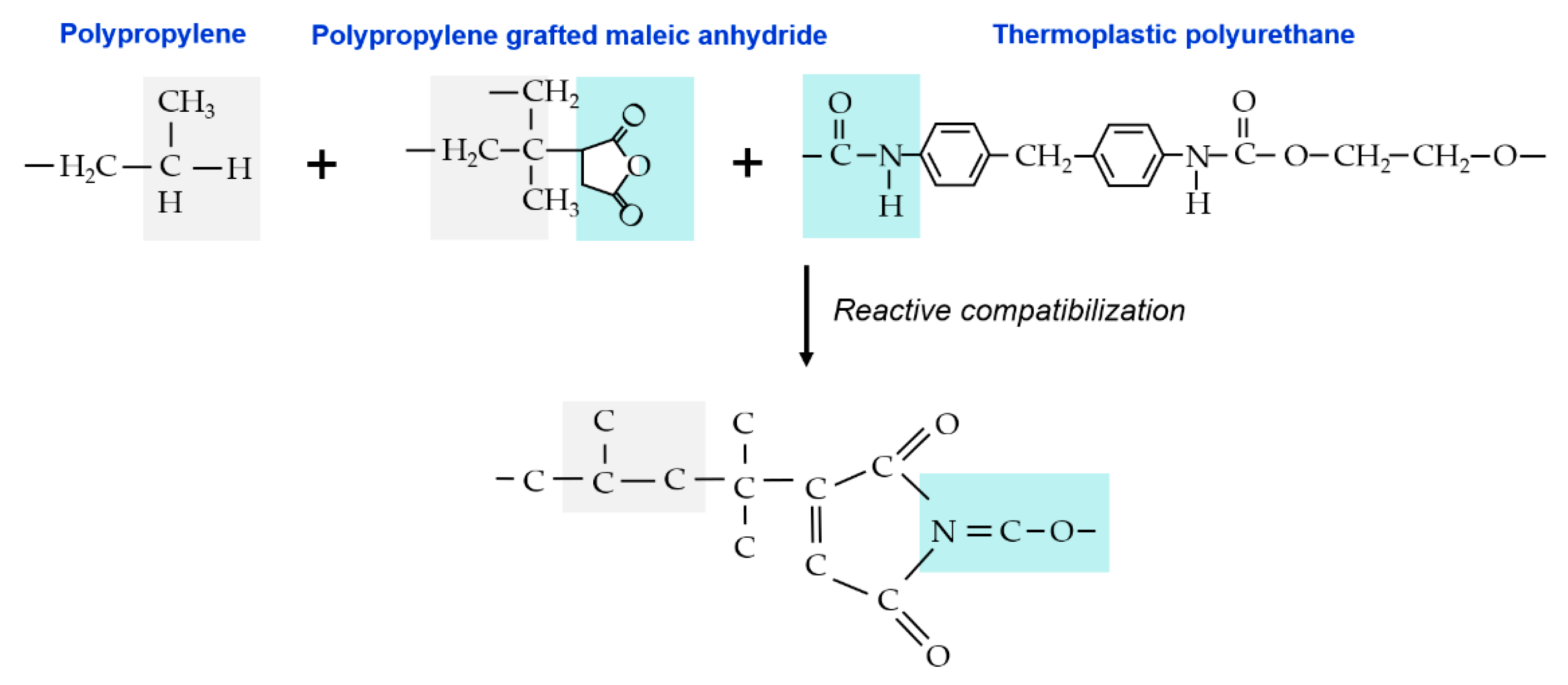
3.4. Differentiation Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashwani, K.S.; Raman, B.; Balbir, S.K. Mechanical properties of composite materials based on waste plastic—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Faraca, G.; Astrup, T. Plastic waste from recycling centres: Characterisation and evaluation of plastic recyclability. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, Y. Recent progress on preparation and properties of nanocomposites from recycled polymers: A review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, J.; Bourdon, S.; Brossard, J.M.; Cauret, L.; Fontaine, L.; Montembault, V. Mechanical recycling: Compatibilization of mixed thermoplastic wastes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 147, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-de Hita, P.; Perez-Galvez, F.; Morales-Conde, M.J.; Pedreno-Rojas, M.A. Reuse of plastic waste of mixed polypropylene as aggregate in mortars for the manufacture of pieces for restoring jack arch floors with timber beams. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, D.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Murray, R.E.; Samaniuk, J.R.; Stebner, A.P. Recycling glass fiber thermoplastic composites from wind turbine blades. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumi-Larbi, A.; Yunana, D.; Kamsouloum, P.; Webster, M.; Wilson, D.C.; Cheeseman, C. Recycling waste plastics in developing countries: Use of low-density polyethylene water sachets to form plastic bonded sand blocks. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenkamer, D.A.; Sullivan, J.L. On the recyclability of a cyclic thermoplastic composite material. Compos. Part B Eng. 1998, 29, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripornsawat, B.; Saiwari, S.; Nakason, C. Thermoplastic vulcanizates based on waste truck tire rubber and copolyester blends reinforced with carbon black. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.H. Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Encycl. Renew. Sustain. Mater. 2020, 5, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Urreaga, J.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, C.; Martinez-Aguirre, A.; Fonseca-Valero, C.; Acosta, J.; de la Orden, M.U. Sustainable eco-composites obtained from agricultural and urban waste plastic blends and residual cellulose fibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, A.; Rochman, A. Characterization of TPU-elastomers by thermal analysis (DSC). Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrockiene, V.; Zukiene, K.; Jankauskaite, V.; Baltusnikas, A.; Petraitiene, S. Properties of mechanically recycled polycaprolactone-based thermoplastic polyurethane/polycaprolactone blends and their nanocomposites. J. Elastom. Plast. 2016, 48, 266–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirkova, M.; Brozova, L.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusova, J.; Krejcikova, S.; Zhigunov, A.; Pavlicevic, J. Recyclable polyurethane/nanoclay films. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 4079–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.Q.; Bai, J.M.; Chua, C.K.; Zhou, K.; Wei, J. Characterization of creeping and shape memory effect in laser sintered thermoplastic polyurethane. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2016, 16, 041007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.M.; Jiang, H.Z.; Chen, X.L. Reutilization of abandoned molecular sieve as flame retardant and smoke suppressant for thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 3905–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchimon, S.Z.; Tausif, M.; Goswami, P.; Cheung, V. Polyamide 6 and thermoplastic polyurethane recycled hybrid Fibres via twin-screw melt extrusion. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somdee, P.; Lassu-Kuknyo, T.; Konya, C.; Szabo, T.; Marossy, K. Thermal analysis of polyurethane elastomers matrix with different chain extender contents for thermal conductive application. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.Q.; Liu, C.K.; Zhou, K.Q.; Xuan, X.; Shi, C.L. Synergistic effect between solid wastes and intumescent flame retardant on flammability and smoke suppression of thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2020, 31, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, N.; Zhang, X.W.; Zheng, M.Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.B.; Maharaj, C.; Dear, J.P.; Yan, Y. Microstructure and tensile properties of injection molded thermoplastic polyurethane with different melt temperatures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kang, B.K.; Kim, H.D.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Huh, J.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, D.J. Effect of hot pressing/melt mixing on the properties of thermoplastic polyurethane. Macromol. Res. 2009, 17, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazim, N.H.; Samat, N. The influence of irradiated recycled polypropylene compatibilizer on the impact fracture behavior of recycled polypropylene/microcrystalline cellulose composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, E24–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiziltas, E.E.; Kiziltas, A.; Lee, E.C. Structure and properties of compatibilized recycled polypropylene/recycled polyamide 12 blends with cellulose fibers addition. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 3556–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.N.; Nie, S.B.; Huang, X.H.; Ding, G.X.; Zhu, J.B. Thermoplastic blends of PP and waste rubber powder: Effects of compatibilizer on tensile properties, thermal behavior and decomposition kinetics. Int. Polym. Proc. 2018, 33, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirawan, R. Recyclability of natural fiber-filled thermoplastic composites. Encycl. Renew. Sustain. Mater. 2020, 5, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, D.; Maji, P.K. Recycling of plastic wastes with poly (ethylene-co-methacrylic acid) copolymer as compatibilizer and their conversion into high-end product. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.S.; Ahmad, S.; Gan, S. Characterization of recycled thermoplastics-based nanocomposites: Polymer-clay compatibility, blending procedure, processing condition, and clay content effects. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 131, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, U.; Yang, L.; Kao, C.C.; Thomason, J.L. Effects of thermal recycling temperatures on the reinforcement potential of glass fibers. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.R.; Lin, T.A.; Lin, M.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Impact resistance of fiber reinforced sandwich-structured nonwoven composites: Reinforcing effect of different fiber length. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.C.; Lin, J.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, T.A.; Lou, C.W. Fabrication, properties, and failure of composite sandwiches made with sheet extrusion method. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2020, 22, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Guermazi, N.; Elleuch, K.; Ayedi, H.F. Study of UV-aging of thermoplastic polyurethane material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, D.; Rosu, L.; Cascaval, C.N. IR-change and yellowing of polyurethane as a result of UV irradiation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaranpillai, J.; Joseph, G.; Jose, S.; Hameed, N. Phase morphology, thermomechanical, and crystallization behavior of uncompatibilized and PP-g-MAH compatibilized polypropylene/polystyrene blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchimon, S.Z.; Tausif, M.; Goswami, P.; Cheung, V. From hybrid fibers to microfibers: The characteristics of polyamide 6/polypropylene blend via one-step twin-screw melt extrusion. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.A.; Lin, J.H.; Bao, L.M. Polypropylene/thermoplastic polyurethane blends: Mechanical characterizations, recyclability and sustainable development of thermoplastic materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5304–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Ismail, H.; Jaafar, M. Recycled polypropylene/peanut shell powder (RPP/PSP) composites: Property comparison before and after electron beam irradiation. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strankowski, M.; Strankowska, J.; Gazda, M.; Piszczyk, L.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jurga, S. Thermoplastic polyurethane/(organically modified montmorillonite) nanocomposites produced by in situ polymerization. Express Polym. Lett. 2012, 6, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample Codes | Compositions | Hot-Pressing Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (T) (wt %) | Polypropylene (P) (wt %) | Maleic Anhydride Grafted Polypropylene (MA) (wt %) | Temperature (°C) | |
| P100 | - | 100 | - | 185 |
| T100 | 100 | - | - | 160 |
| T90 | 90 | 10 | 0 | 170 |
| T90/MA | 90 | 10 | 5 | 170 |
| T70 | 70 | 30 | 0 | 170 |
| T70/MA | 70 | 30 | 5 | 170 |
| T50 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 185 |
| T50/MA | 50 | 50 | 5 | 185 |
| Post-2nd-Recycling (Groups) | Tensile Stress at Break (MPa) | Tensile Strain at Break (%) | Tensile Stress at Yield Point (MPa) | Tensile Strain at Yield Point (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P100 | 29.3 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.9 | 31.1 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 0.2 |
| T100 | 13.7 ± 0.9 | 280.3 ± 27.3 | 14.0 ± 1.0 | 279.2 ± 28.4 |
| T90 | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 144.1 ± 25.4 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 139.8 ± 29.9 |
| T90/MA | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 212.4 ± 25.1 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 210.7 ± 26.0 |
| T70 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 21.4 ± 10.2 | - | - |
| T70/MA | 9.0 ± 1.3 | 72.7 ± 7.7 | 9.3 ± 1.0 | 70.4 ± 6.2 |
| T50 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 8.9 ± 4.6 | - | - |
| T50/MA | 8.0 ± 0.9 | 39.9 ± 5.3 | 8.4 ± 0.9 | 31.2 ± 3.7 |
| Post-3rd-Recycling (Groups) | Tensile Stress at Break (MPa) | Tensile Strain at Break (%) | Tensile Stress at Yield Point (MPa) | Tensile Strain at Yield Point (%) |
| P100 | 23.6 ± 1.4 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 25.1 ± 1.5 | 3.1 ± 0.2 |
| T100 | 10.8 ± 0.5 | 252.1 ± 24.7 | 11.1 ± 0.6 | 250.6 ± 26.2 |
| T90 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 0.04 | - | - |
| T90/MA | 7.4 ± 0.5 | 170.0 ± 23.7 | 7.7 ± 0.3 | 167.5 ± 24.8 |
| T70 | 1.7 ± 1.2 | 6.6 ± 3.4 | - | - |
| T70/MA | 9.2 ± 0.4 | 29.6 ± 5.2 | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 25.2 ± 3.1 |
| T50 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 7.00 ± 1.2 | - | - |
| T50/MA | 7.1 ± 0.3 | 20.9 ± 1.8 | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, T.A.; Lin, J.-H.; Bao, L. Effect of Melting–Recycling Cycles and Mechanical Fracture on the Thermoplastic Materials Composed of Thermoplastic Polyurethane and Polypropylene Waste Blends. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175810
Lin TA, Lin J-H, Bao L. Effect of Melting–Recycling Cycles and Mechanical Fracture on the Thermoplastic Materials Composed of Thermoplastic Polyurethane and Polypropylene Waste Blends. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(17):5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175810
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ting An, Jia-Horng Lin, and Limin Bao. 2020. "Effect of Melting–Recycling Cycles and Mechanical Fracture on the Thermoplastic Materials Composed of Thermoplastic Polyurethane and Polypropylene Waste Blends" Applied Sciences 10, no. 17: 5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175810
APA StyleLin, T. A., Lin, J.-H., & Bao, L. (2020). Effect of Melting–Recycling Cycles and Mechanical Fracture on the Thermoplastic Materials Composed of Thermoplastic Polyurethane and Polypropylene Waste Blends. Applied Sciences, 10(17), 5810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175810