Abstract
In this study, we measured neuronal activation in the primary somatosensory area (S1) and Brodmann area 3 (BA3) using 3T functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) while presenting a 250-Hz high-frequency vibrational stimulus to each of three phalanges (distal, intermediate, and proximal) of four fingers of the right hand (index, middle, ring, and little). We compared the nerve activation area between each finger and each phalange. Ten healthy male college students (26.6 ± 2.5 years old) participated in this study. One session consisted of three blocks: a rest (30 s), stimulation (30 s), and response phase (9 s). In the rest phase, the vibrational stimulus was not presented. In the stimulation phase, the vibrational stimulation was presented at any one of the three phalanges of the selected finger. In the response phase, subjects were instructed to press a button corresponding to the phalange that they thought had received the vibration. The subtraction method was used to extract the activation area. The activation area in the S1 was the largest when the little finger was stimulated (for the finger comparison), and largest when the second phalange was stimulated (for the phalange comparison). The BA3 showed similar trends, and there was no statistically significant difference.
1. Introduction
Several studies have used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), electroencephalogram (EEG), and magnetoencephalogram (MEG) to investigate the level of nerve activation in regions that respond to vibrations, such as the primary somatosensory area (S1) and Brodmann area 3 (BA3). A considerable degree of activation has been noted in these areas after stimulation with low-frequency vibration (<80 Hz), particularly in Meissner’s corpuscle. Some studies have also compared the degree of activation on applying low-frequency vibration stimulation to the first phalange of a given finger [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. It was reported that the activation area of the little finger was larger than that of other fingers, and that the activation area of the index finger was larger than that of the middle and ring fingers. In addition, several studies have compared the level of brain activation in response to low-frequency vibration stimulation applied to the first phalange of all five fingers [9,10,11,12,13]. In these studies, from the analysis of peak coordinates for the activation area, the distance increased in radial form for each finger based on the distal phalanx (P1) of the thumb. The distance between the distal phalanx (P1) of the thumb and P1 of the little finger was the largest. From these results, it was derived that the activation distance corresponding to each finger could be observed. One study compared the level of activation by presenting vibration stimulation to all phalanges of all five fingers [14]. In these studies, peak coordinates at BA3 were formed in the order of index finger, middle finger, and hand finger in the lateral to medial direction and inferior to superior direction for each finger. For each phalanx, it was reported that the peak coordinates in BA3 appeared only in the index and handhelds in the order of P1, intermediate (P2), and proximal (P3) in the anterior to posterior direction. Thus, several studies have reported the characteristics of neuronal activation in the S1 and BA3 regions in response to low-frequency vibration stimulation on all fingers and phalanges. The difference in the number of voxels in the activated somatosensory area according to the vibration stimulation is used in most tactile studies because it allows visually intuitive expression and quantitative analysis of the position, area, and size of the activation for each finger and phalanx.
Studies have been also conducted to observe the level of neural activation in the S1 and BA3 areas when the fingers are presented with high-frequency (>100 Hz) vibrational stimuli sensitive to the Pacinian corpuscle. Namely, one study compared activation characteristics of these areas when presenting the high-frequency vibration stimulus to all phalanges of the index finger [15], and another study compared the degree of activation when applying the high-frequency vibration stimulus to the first phalange of the index finger and the little finger [16]. In these previous studies, the activation area of the little finger was larger than that of other fingers, and the activation area of the second finger was larger than that of the first and third nodes. For each finger, peak coordinates at BA3 were formed in the order of index finger, middle finger, ring finger, and hand finger in the lateral to medial direction. For each phalange, peak coordinates were shown in BA3 from anterior to posterior and inferior to superior in the order of P1, P2, and P3 for all fingers. Compared with a low-frequency vibration stimulus, studies using high-frequency vibration stimulation have only been conducted on a specific finger or phalange; thus, there is a need for more research on the effects of high-frequency vibration stimulation on various fingers and phalanges.
In tactile studies, BA3 is referred to as the primary somatosensory cortex, and it has been reported that it is activated by most tactile stimuli such as vibration and pressure stimulation [17,18]. It has been reported that BA2 is mainly activated by pressure sensation, joint position, and complex touch, while BA1 is reported to have a response mainly to vibrating touch [17,18]. Therefore, in this study, the region of interest (ROI) analysis was performed by selecting BA3, which responds predominantly to vibrational stimuli and can observe a distinct activation pattern. Additionally, in previous studies, when presenting the vibration stimulus the somatosensory area was not divided into sub-areas of BA1, 2, and 3, and the results for the entire area (S1) were extracted. Thus, in this study, for direct comparison with previous studies, the activation area for S1 was extracted. To this aim, we investigated the level of neural activation upon high-frequency vibration stimulation in a number of fingers and phalanges. First, high-frequency vibration (250 Hz), which is known to stimulate the Pacinian corpuscle, was administered to three phalanges (distal, intermediate, and proximal) on four fingers (index, middle, ring, and little) of the right hand. The resulting neuronal activation in the S1 and BA3 regions was measured using fMRI. Second, the activation area of each finger and each phalange was compared.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
Ten healthy male college students (mean age = 26.6 ± 2.5 years) participated in this study. All subjects were right-handed as evaluated by the revised Edinburgh test [19]. No subjects had a history of psychiatric or neurological disorders or brain damage. Detailed experimental procedures were explained to all subjects before initiating the study, and subjects were only permitted to participate after they had completely understood these. The protocol for the research project was approved by the Institutional Review Committee of Konkuk University and the study conforms to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki. All experimental procedures were approved by and performed under the regulations of the Institutional Review Committee of Korea University (KU-IRB-11-46-A-1).
2.2. MR-Compatible Vibrotactile Stimulator
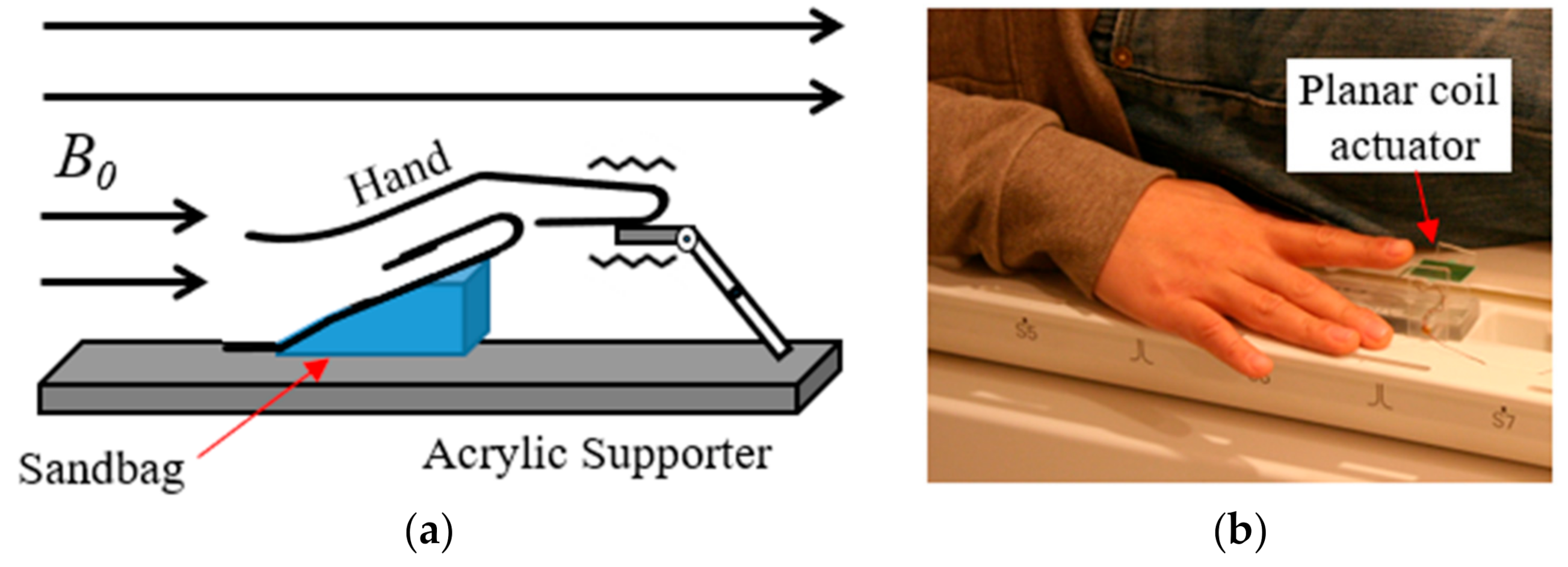
Vibration stimulation was applied using an MR-compatible vibrotactile stimulator developed by our team [20]. This device generates vibrations by using the current flowing in the static magnetic field of the MR scanner (B0) and in the planar coil. It can stimulate an area of 1 × 1 cm2 and weighs 11 g. The stimulation parameter was controlled using E-Prime S/W (Psychology Software Tools, Inc., Sharpsburg, PA, USA). The MR scanner and MR-compatible vibrotactile stimulator were synchronized using a trigger signal from the LPT-1 printer port of the computer onto which the E-Prime software had been installed [20]. Brain images were acquired while applying the constant high-frequency vibration stimulation (250 Hz; intensity = 8 psi) to the three phalanges (distal (P1), intermediate (P2), and proximal (P3) phalanx) of four fingers (index, middle, ring, and little) of the right hand. During the experiment, the entire hand was placed on the acrylic supporter and the sandbag was placed under the palm so that the stimulation location did not change and the hand was kept in a comfortable state (Figure 1).
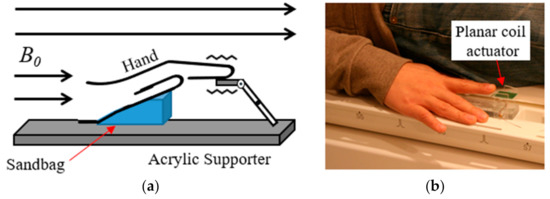
Figure 1.
MR-compatible vibrotactile stimulator. (a) Conceptual diagram of operation; (b) actual view of stimulator (sandbag is under the hand).
2.3. Experimental Design
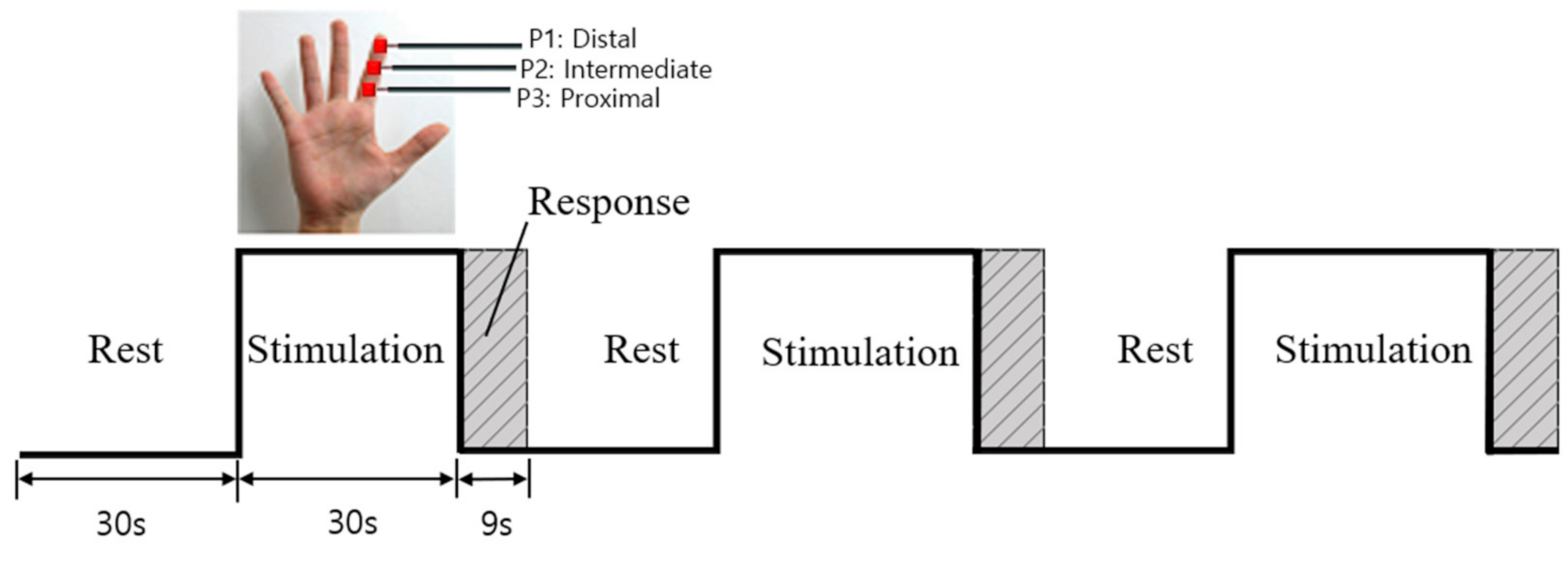
Three vibrotactile stimulators were attached to three phalanges (P1, P2, and P3) of a randomly selected finger (index, middle, ring, or little finger) of the right hand before starting the experiment. One session comprised three blocks (Figure 2), each of which included a rest (30 s), stimulation (30 s), and response phase (9 s). During the rest phase, subjects were asked to sit comfortably with their eyes closed, and did not receive any vibration stimulus. In the stimulation phase, subjects received 30 s of vibration stimulation to one of the randomly selected phalanges (P1, P2, or P3) on a specific finger (index, middle, ring, or little). Since there were three stimulation phases per session, all three phalanges could be sequentially stimulated. During the response phase, a response button was placed in the subjects’ left hand and they were asked to press the button corresponding to the phalange that had been stimulated. This was to confirm whether the subject had correctly identified the stimulated location. This session was repeated three times for each of the selected fingers, during which all three phalanges of the selected finger were stimulated three times each. This procedure was repeated for the remaining three fingers. The order of finger/phalange stimulation was counterbalanced to prevent repetitive effect and carryover effect; additionally, there was a 5-min break between sessions. With three sessions per finger, all participants completed a total of 12 sessions (3 sessions/finger × 4 fingers = 12 sessions). According to the subjects’ responses, which were recorded in the response phase, functional images of the eight subjects (age = 26.6 ± 2.9 years) that demonstrated a 100% correct response rate were analyzed.
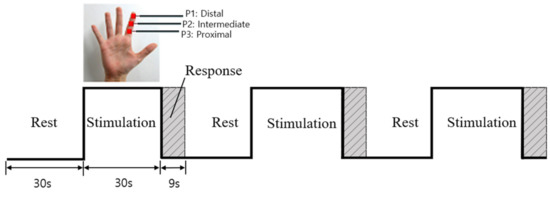
Figure 2.
Experimental design.
2.4. Image Acquisition
Brain imaging was performed using a 3T MRI system (Magnetom TrioTim, Siemens Medical Systems, Erlangen, Germany) at Korea University Brain Imaging Center. Anatomical images were obtained using a T1-weighted 3D MPRAGE sequence with the following parameters: repetition time (TR) = 1900 ms, echo time (TE) = 2.48 ms, flip angle = 9°, field of view (FOV) = 200 mm, and spatial resolution = 0.8 × 0.8 × 1 mm3. Functional images were recorded with the T2-weighted gradient echo-planar imaging sequence with the following parameters: TR = 3000 ms, TE = 30 ms, flip angle = 90°, FOV = 192 mm, slice thickness = 2 mm, and in-plane resolution = 1.5 × 1.5 mm2. To exclude any auditory and visual factors, all subjects were provided with headsets and their eyes were closed during the experiment. The subjects were also asked to minimize hand and head movements.
2.5. Image Analysis
The fMRI data were analyzed using SPM 8 (Wellcome Department of Cognitive Neurology, London, UK). All functional images were aligned with the anatomical images obtained during the study using transformation routines that were built into SPM 8. The realigned scans were co-registered to each participant’s anatomical images obtained within each session and normalized to the template image obtained by SPM 8, which used the space defined by the Montreal Neurologic Institute. Motion correction was implemented using Sinc interpolation. Time-series data were filtered with a 240-s high-pass filter to remove artifacts associated with cardiorespiratory and other cyclical influences. The functional map was subsequently smoothed with a 3-mm isotropic Gaussian kernel prior to statistical analysis. Statistical analysis was done both individually and as a group using a general linear model and the Gaussian random field theory, which were implemented in SPM 8 [21]. Statistical parametric maps were computed using the t-statistic. Comparisons made within individual subjects were considered as significant at a threshold of p < 0.05 and were corrected for multiple comparisons. We used random effect analysis to compute group activation.
Region of interest (ROI) analysis was applied to specifically observe the activated regions of the S1 and BA3 in the left hemisphere of the activated area of the brain. The PICKATLAS Tool of the Wake Forest University PickAtlas 3.0 S/W was used for ROI masking of each region [22]. The subtraction method (stimulation phase–rest phase) was used to estimate the area of activation of the S1 and BA3 regions after administering the vibration stimulation in each finger and phalange [23]. Among the SPM analysis tools, the number of activated voxels for each finger and joint was extracted for each subject using small volume correction (SVC). In addition, images acquired for each experimental phase were averaged to increase the spatial resolution. The area of activation was calculated by counting the number of activated voxels and multiplying it by the in-plane resolution of 1.5 × 1.5 mm2.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using PASW statistics 18 (IBM Corporation) to determine the presence or absence of statistically significant differences in the activated area in the S1 and BA3 regions after vibration stimulation. A two-way repeated measures ANOVA was performed with finger (index, middle, ring, and little) and phalange (P1, P2, and P3) as independent variables. Bonferroni analysis, a form of pairwise analysis, was also used to identify significant differences in the measured area activated by the stimulation.
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data
Functional imaging data from the eight participants who demonstrated a 100% correct response rate were used. The correct answer rates of the other two subjects were 94.4% and 97.2%, respectively.
3.2. Activation Area
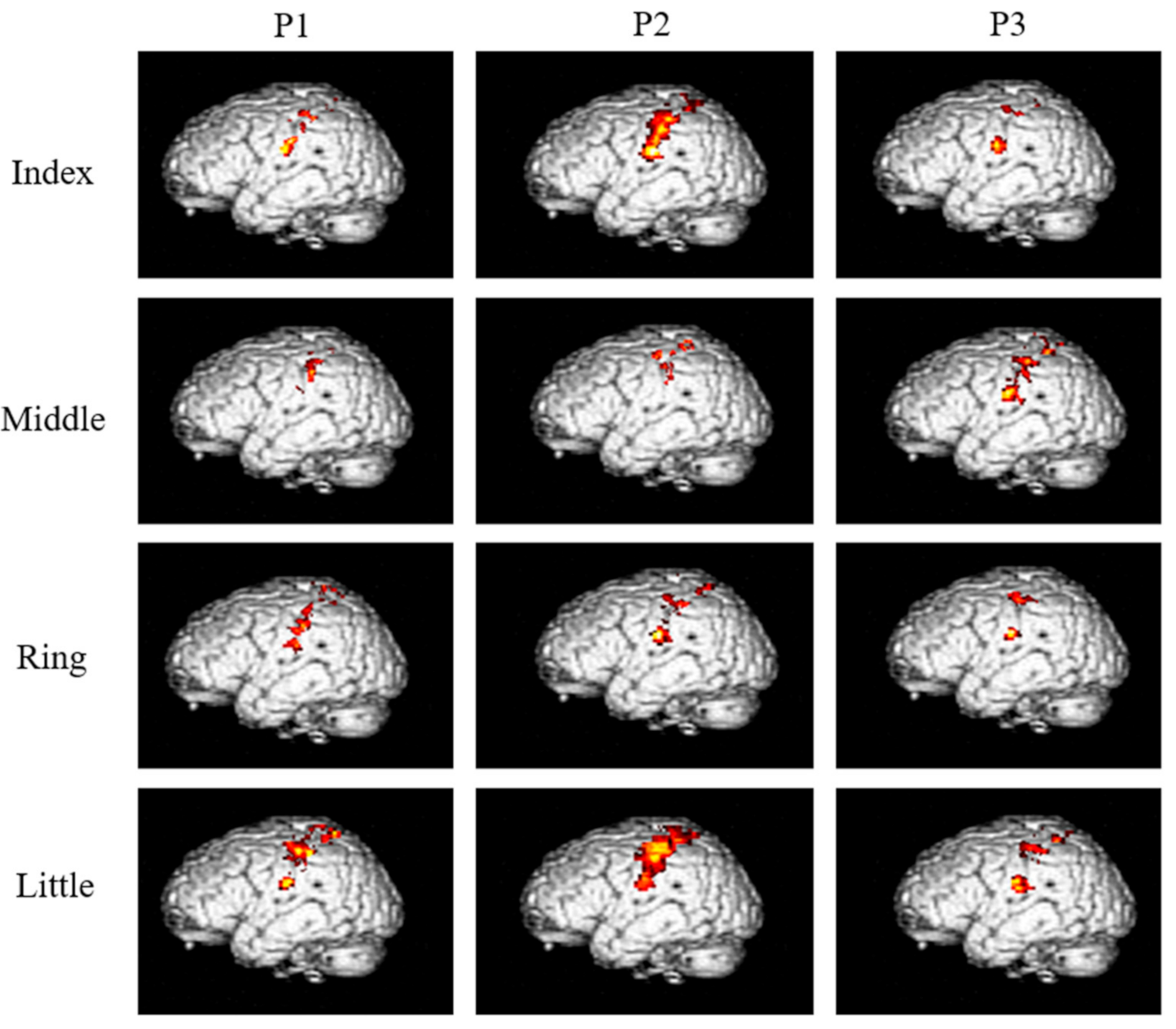
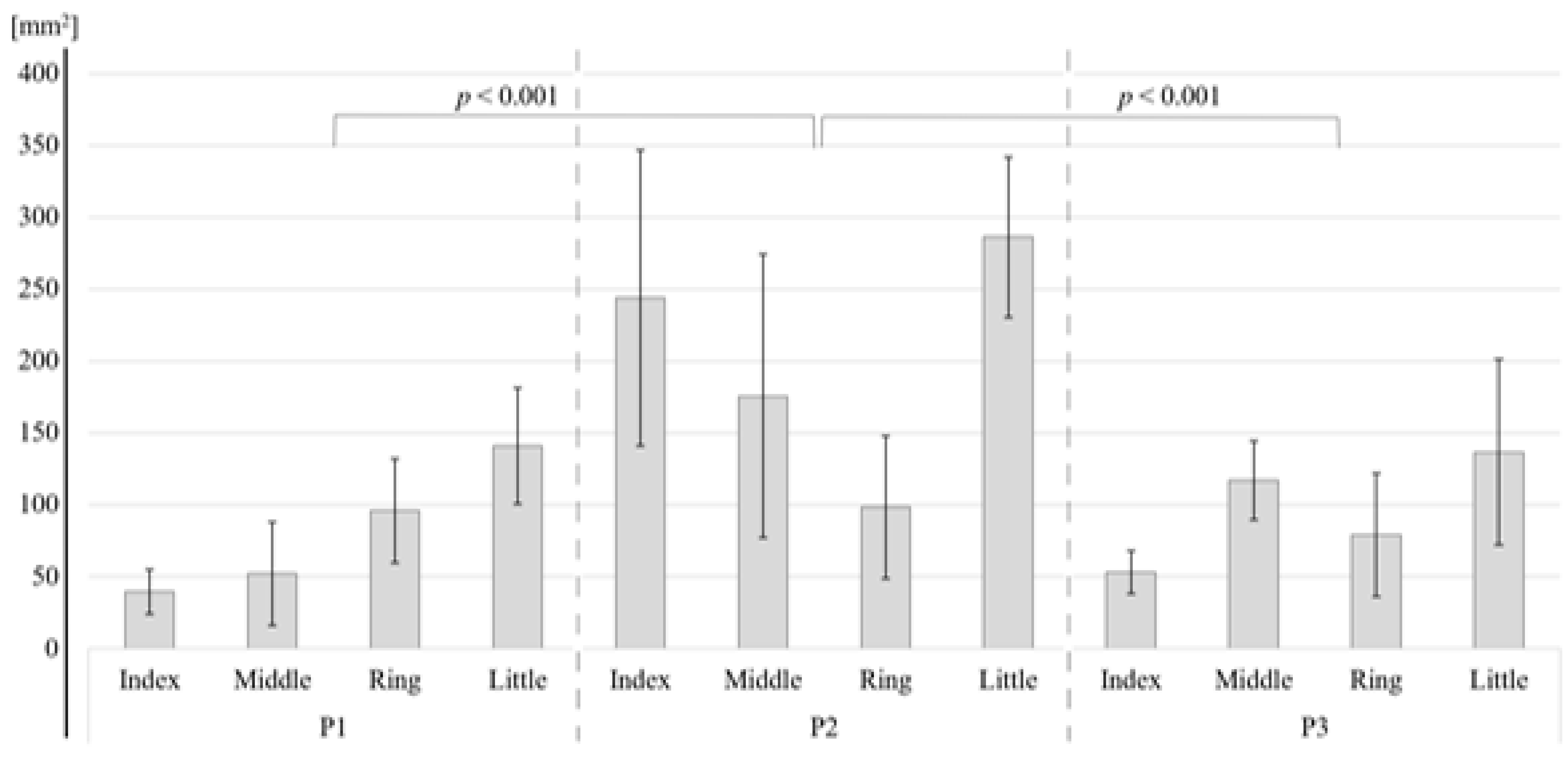
The neural activation resulting from the vibration stimuli are shown for each finger and phalange in Figure 3, and the area of activation in the S1 and BA3 (mm2) is shown in Table 1.
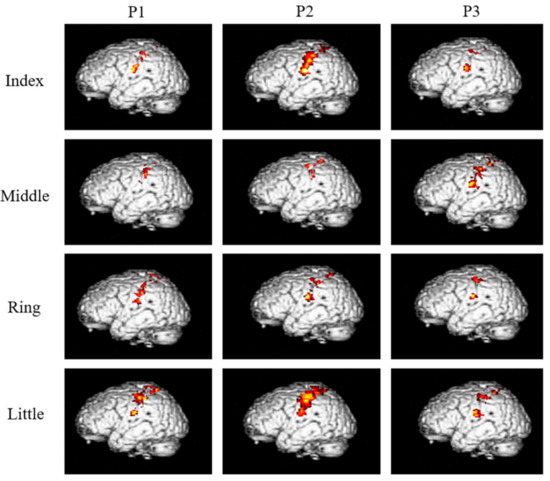
Figure 3.
Areas activated after applying high-frequency vibration stimulation to each of the three phalanges of the four fingers of the right hand (group analysis, corrected p < 0.05).

Table 1.
Activated area (mm2) in the primary somatosensory area (S1) and Brodmann area 3 (BA3) regions after applying high-frequency vibration stimulation to each of the three phalanges on the four fingers of the right hand.
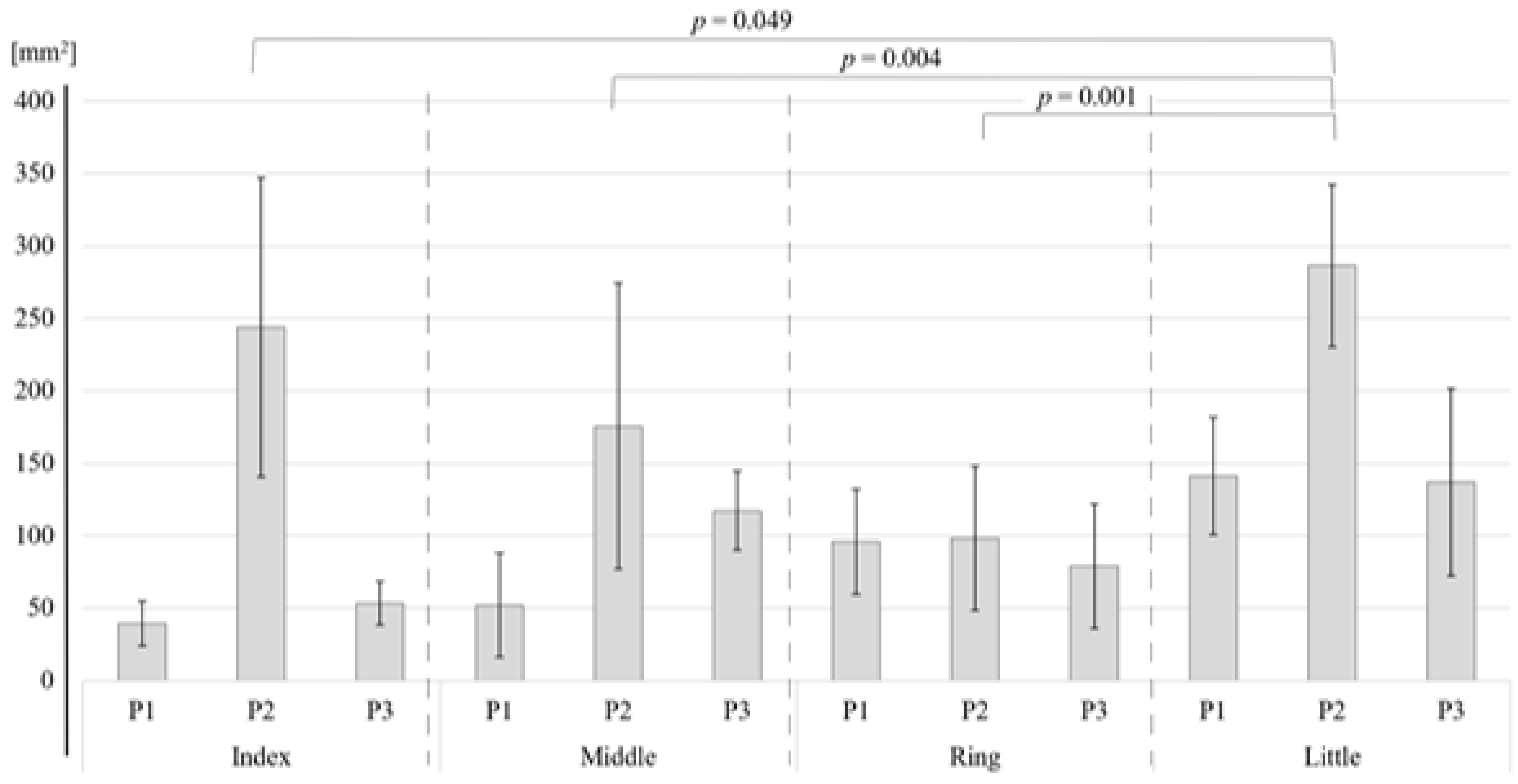
As shown in Table 2, for the S1, the two-way ANOVA revealed a significant difference in the activation area between the four fingers (p < 0.001) and between the three phalanges (p < 0.001). Bonferroni tests showed that the areas of activation of the index finger (p = 0.049), middle finger (p = 0.004), and ring finger (p = 0.001) were significantly smaller than that of the little finger (Figure 4). There were no other significant differences. Bonferroni tests for each phalange showed that the activation areas of the first (p < 0.001) and the third (p < 0.001) phalange were significantly smaller than those of the second phalange (Figure 5). For BA3, the little finger and the second phalange had the largest area of activation (Table 1), but there were no significant differences between the four phalanges (Table 2).

Table 2.
Two-way ANOVA results of the area of activation in the S1 and BA3 regions after applying high-frequency vibration stimulation to each of the three phalanges of the four fingers of the right hand.
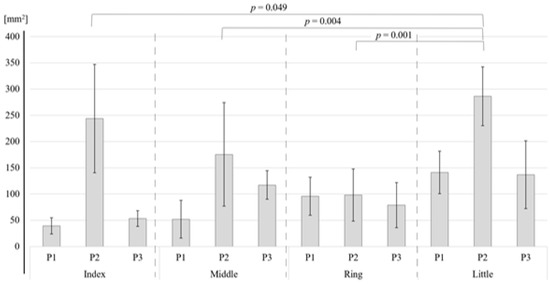
Figure 4.
Difference in the area of activation by finger in the S1 region.
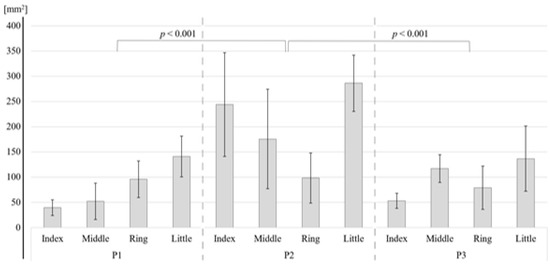
Figure 5.
Difference in area of activation by phalange in the S1 region.
4. Discussion
This study used fMRI to analyze the difference in the area of activation in the S1 and BA3 regions when the three phalanges of the right four fingers were stimulated with 250 Hz of high-frequency vibration. In the S1 region, stimulation of the little finger and the second node resulted in the largest area of activation. The BA3 region showed similar trends to that of the S1 region, but there were no significant differences.
Several studies have reported the brain activation associated with low-frequency vibration stimulation of each finger; the highest levels of activation have frequently been found in the S1 and BA3 regions on stimulation of the index finger [2,6,9,12,16], and a few studies have reported similar results after stimulation of the little finger [1,7]. Generally, the greatest level of activation has been reported to occur for stimulation of the index finger, which has a large distribution of sensory receptors. However, many studies have reported that a smaller finger size corresponds to a denser arrangement of sensory receptors. This could be one reason for the greater activation seen when stimulating the little finger [24]. In this study, the highest level of activation was observed in the little finger following a high-frequency vibration stimulus. Although there is a need for further research, the results reported in this study may also be elucidated with the reason previously given in cases of low-frequency stimulus [24].
Several studies have compared the level of activation in the S1 and the BA3 regions after stimulation between each phalange [7,14,15,25]. Many previous studies have demonstrated that the highest degree of activation occurs after low-frequency vibration stimulation to the first phalange; this may be because the first node contains a large number of Meissner’s corpuscles that are sensitive to low-frequency stimuli [26]. However, in the present study, the largest area of activation was observed when the second phalange was stimulated with a high-frequency vibration stimulus. Pacinian corpuscles, which are sensitive to high-frequency vibration stimuli, are known to have a much larger receptive field than Meissner’s corpuscles [27,28,29]. Considering this, even after stimulating the second phalange, the receptors of the adjacent regions (either the first or the third phalanges) may have also been stimulated due to their large receptive field, subsequently leading to a large area of activation. That is, it is thought that more receptors are recruited when stimulating the second phalange compared to the first and third phalanges. However, further research needs to confirm this interpretation.
Although there was no significant difference, the order of activation area sizes in the BA3 region was similar to that of the S1. This is attributed to the low signal-to-noise ratio of the acquired brain images: BA3 has a smaller absolute area and a smaller activation area than S1. Further experimental or validation studies are necessary.
5. Conclusions
This study compared the area of brain activation after the presentation of high-frequency vibration stimuli to three phalanges of the four right fingers. Our results provide basic data for neuroscience research related to tactile sensation. The limitations of this study and future studies are described below. Since the TR for image acquisition was 3 s, detailed activation analysis according to temporal change in time series aspect could not be performed. Additionally, in this paper, an experiment was performed on only one high-frequency vibration stimulation of 250 Hz. Of course, brain activation was confirmed in S1 and BA3, but it is insufficient to analyze the neurological connectivity between digit-specific brain areas and mechanoreceptors. For this, first, an additional experiment using various low and high frequencies in the range that humans can perceive is required. Second, by performing BOLD response analysis, detailed analysis of BA1, 2, 3a, 3b, S1, and S2 for vibration stimulation should be performed. Third, a comparative study on the actual feeling of the subject in response to the vibration stimulation is also needed. Fourth, in terms of neurophysiology and neurology, comparative studies on rapidly adapting (RA) and slowly adapting (SA) will be needed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-S.K. and S.-C.C.; methodology, H.-S.K., J.-H.J. and S.-C.C.; formal analysis, J.-H.L., J.-J.J., and K.-H.K.; investigation, J.-H.L., J.-J.J., and K.-H.K.; resources, J.-S.A. and M.-H.C.; data curation, J.-S.A., Y.-J.K., and M.-H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-S.K.; writing—review and editing, H.-S.K. and S.-C.C.; visualization, H.-S.K. and J.-H.J.; project administration, S.-C.C.; funding acquisition, S.-C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was written as part of Konkuk University’s research support program for its faculty on sabbatical leave in 2019. This work was also supported by a Mid-Career Researcher Program Grant through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) (No. 2017R1A2B2004629).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gelnar, P.A.; Krauss, B.R.; Szeverenyi, N.M.; Apkarian, A.V. Fingertip Representation in the Human Somatosensory Cortex: An fMRI Study. NeuroImage 1998, 7, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, S.T.; Kelly, E.F.; Bowtell, R.; Dunseath, W.J.R.; Folger, S.E.; McGlone, F. fMRI of the Responses to Vibratory Stimulation of Digit Tips. NeuroImage 2000, 11, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlone, F.; Kelly, E.F.; Trulsson, M.; Francis, S.T.; Westling, G.; Bowtell, R. Functional neuroimaging studies of human somatosensory cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 135, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.J.; Staines, W.R.; Nelson, A.; Plewes, D.B.; Mcllroy, W.E. New devices to deliver somatosensory stimuli during functional MRI. Magn. Reason. Med. 2001, 46, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.J.; Staines, W.R.; Graham, S.J.; McIlroy, W.E. Activation in SI and SII; the influence of vibrotactile amplitude during passive and task-relevant stimulation. Cogn. Brain Res. 2004, 19, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Panchuelo, R.M.; Francis, S.; Bowtell, R.; Schluppeck, D. Mapping Human Somatosensory Cortex in Individual Subjects With 7T Functional MRI. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweisfurth, M.A.; Schweizer, R.; Frahm, J. Functional MRI indicates consistent intra-digit topographic maps in the little but not the index finger within the human primary somatosensory cortex. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyasagar, R.; Folger, S.E.; Parkes, L.M. Re-wiring the brain: Increased functional connectivity within primary somatosensory cortex following synchronous co-activation. NeuroImage 2014, 92, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldjian, J.A.; Gottschalk, A.; Patel, R.S.; Pincus, D.; Detre, J.A.; Alsop, D.C. Mapping of secondary somatosensory cortex activation induced by vibrational stimulation: An fMRI study. Brain Res. 1999, 824, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westen, D.; Fransson, P.; Olsrud, J.; Rosén, B.; Lundborg, G.; Larsson, E.M. Finger somatotopy in area 3b: An fMRI-study. BMC Neurosci. 2004, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, R.; Voit, D.; Frahm, J. Finger representations in human primary somatosensory cortex as revealed by high-resolution functional MRI of tactile stimulation. NeuroImage 2008, 42, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.J.; Chen, R. Digit Somatotopy within Cortical Areas of the Postcentral Gyrus in Humans. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Breitwieser, C.; Kaiser, V.; Neuper, C.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Stability and distribution of steady-state somatosensory evoked potentials elicited by vibro-tactile stimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2012, 50, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweisfurth, M.A.; Frahm, J.; Schweizer, R. Individual fMRI maps of all phalanges and digit base of all fingers in human primary somatosensory cortex. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, I.; Mashiko, T.; Kimura, T.; Imada, T. Are there discrete distal-proximal representations of the index finger and palm in the human somatosensory cortex? A neuromagnetic study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalberlah, C.; Villringer, A.; Pleger, B. Dynamic causal modeling suggests serial processing of tactile vibratory stimuli in the human somatosensory cortex—An fMRI study. NeuroImage 2013, 74, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, M. Receptive fields of neurons in Areas 3b and 1 of somatosensory cortex in monkeys. Brain Res. 1980, 198, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, V.; Spezioc, M.L.; Etzela, J.A.; Castelli, F.; Adolphsd, R.; Keysers, C. Primary somatosensory cortex discriminates affective significance in social touch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1657–E1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Choi, M.H.; Chung, Y.G.; Kim, S.P.; Jun, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yi, J.H.; Park, J.R.; Lim, D.W.; Chung, S.C. Development of a simple MR-compatible vibrotactile stimulator using a planar-coil-type actuator. Behav. Res. Method 2013, 45, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, W.D.; Friston, K.J.; Ashburner, J.T.; Kiebel, S.J.; Nichols, T.E. Statistical Parametric Mapping: The Analysis of Functional Brain Images, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Maldjian, J.A.; Laurienti, P.J.; Kraft, R.A.; Burdette, J.H. An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. NeuroImage 2003, 19, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.C.; Sohn, J.H.; Lee, B.S.; Tack, G.R.; Yi, J.H.; You, J.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.Y. A comparison of the mean signal change method and the voxel count method to evaluate the sensitivity of individual variability in visuospatial performance. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 418, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.M.; Hackeman, E.; Goldreich, D. Diminutive Digits Discern Delicate Details: Fingertip Size and the Sex Difference in Tactile Spatial Acuity. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15756–15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlushchuk, Y.; Forss, N.; Hari, R. Distal-to-proximal representation of volar index finger in human area 3b. NeuroImage 2004, 21, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbo, A.B.; Johansson, R.S. The tactile sensory innervation of the glabrous skin of the human hand. In Active Touch: The Mechanism of Recognition of Objects by Manipulation, 1st ed.; Gordon, G., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1978; pp. 29–54. [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo, A.B.; Johansson, R.S. Properties of cutaneous mechanoreceptors in the human hand related to touch sensation. Hum. Neurobiol. 1984, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mountcastle, V.B. Medical Physiology, Sensory Receptors and Neural Encoding: Introduction to Sensory Processes, 1st ed.; The CV Mosby Co.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Siedentopf, C.M.; Heubach, K.; Ischebeck, A.; Gallasch, E.; Fend, M.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Koppelstaetter, F.; Haala, I.A.; Krause, B.J.; Felber, S.; et al. Variability of BOLD response evoked by foot vibrotactile stimulation: Influence of vibration amplitude and stimulus waveform. NeuroImage 2008, 41, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).