Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
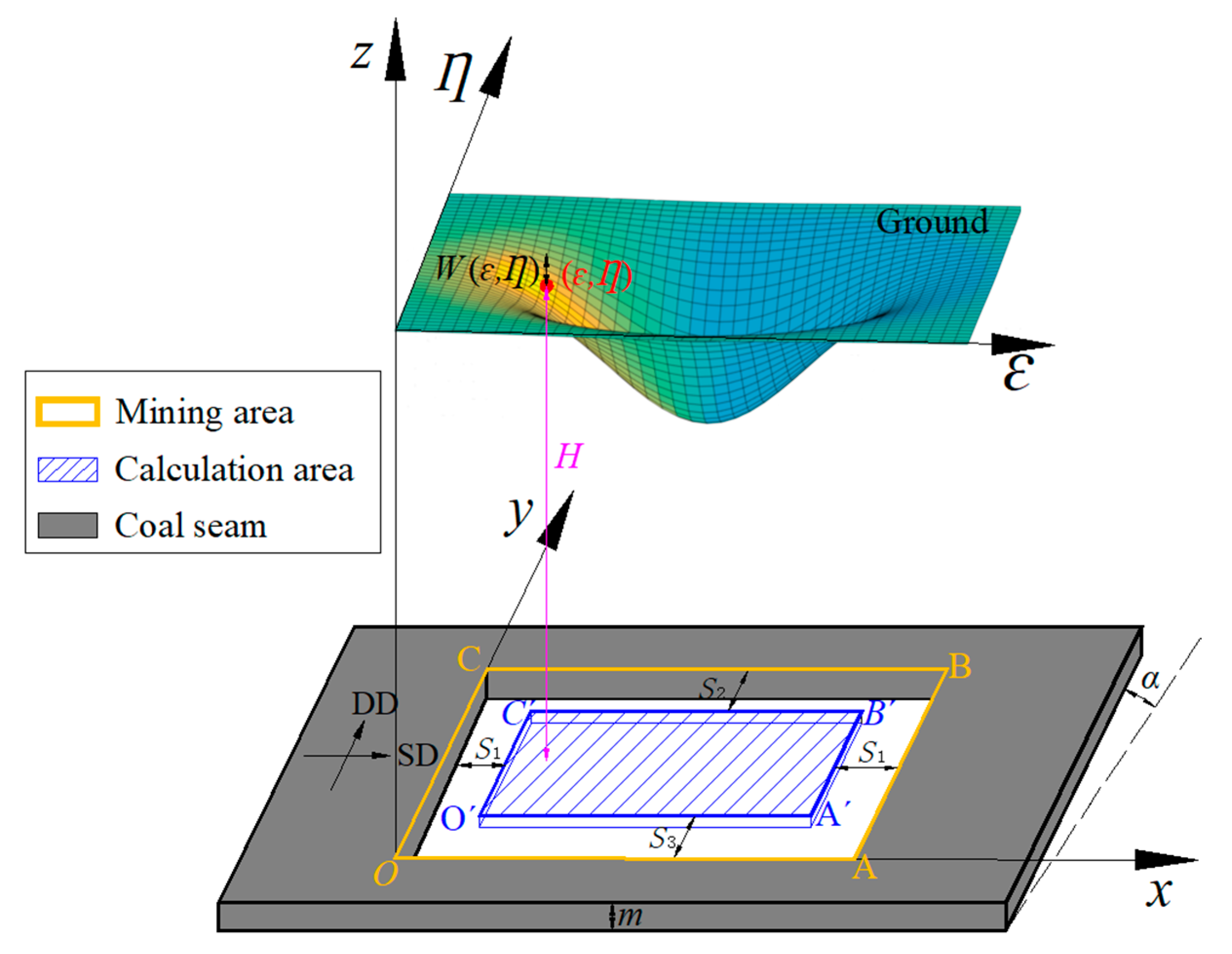
2. Fundamental of PIM-Based Ground Subsidence Prediction
3. Proposed Ground Subsidence Prediction Method
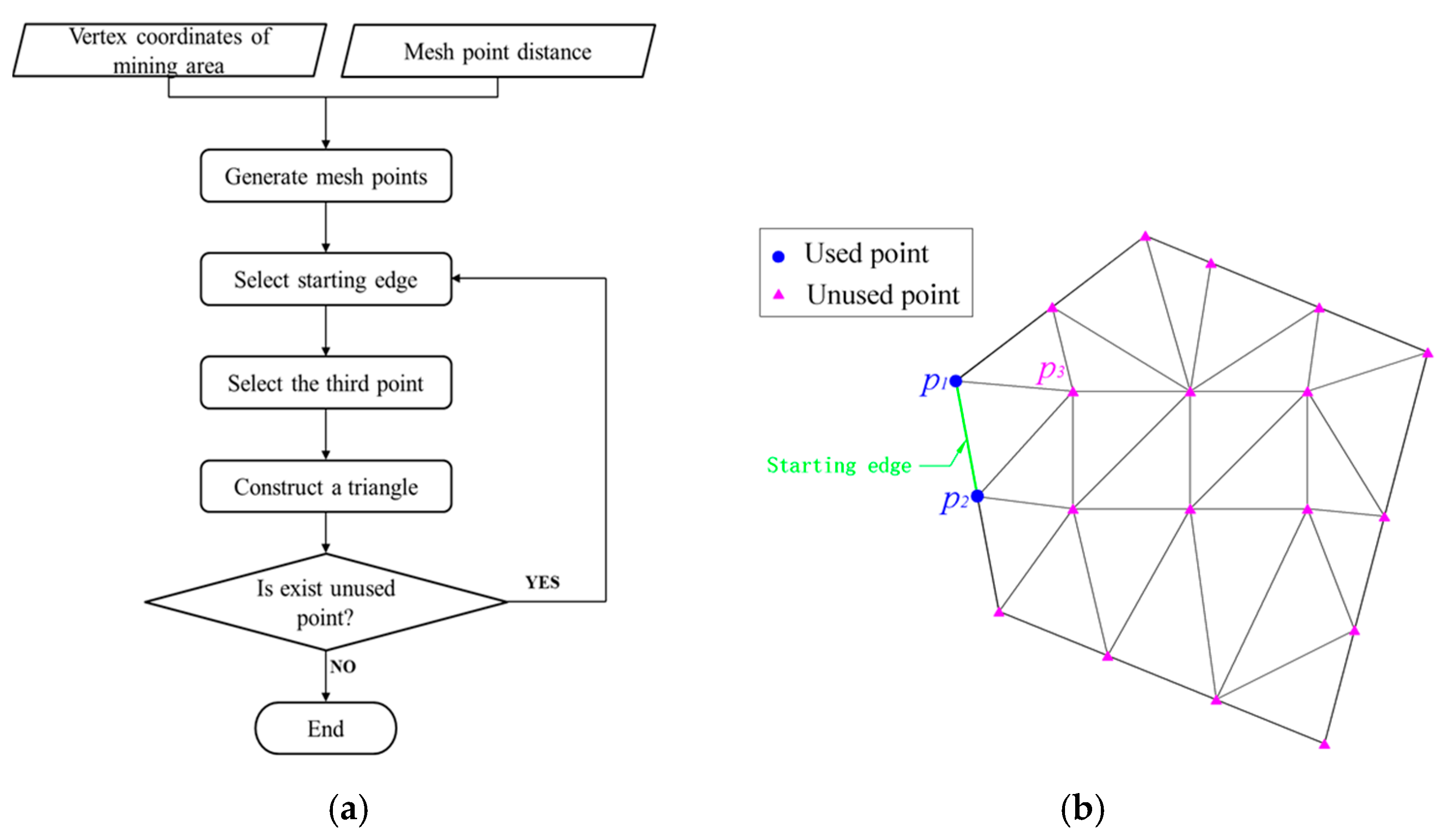
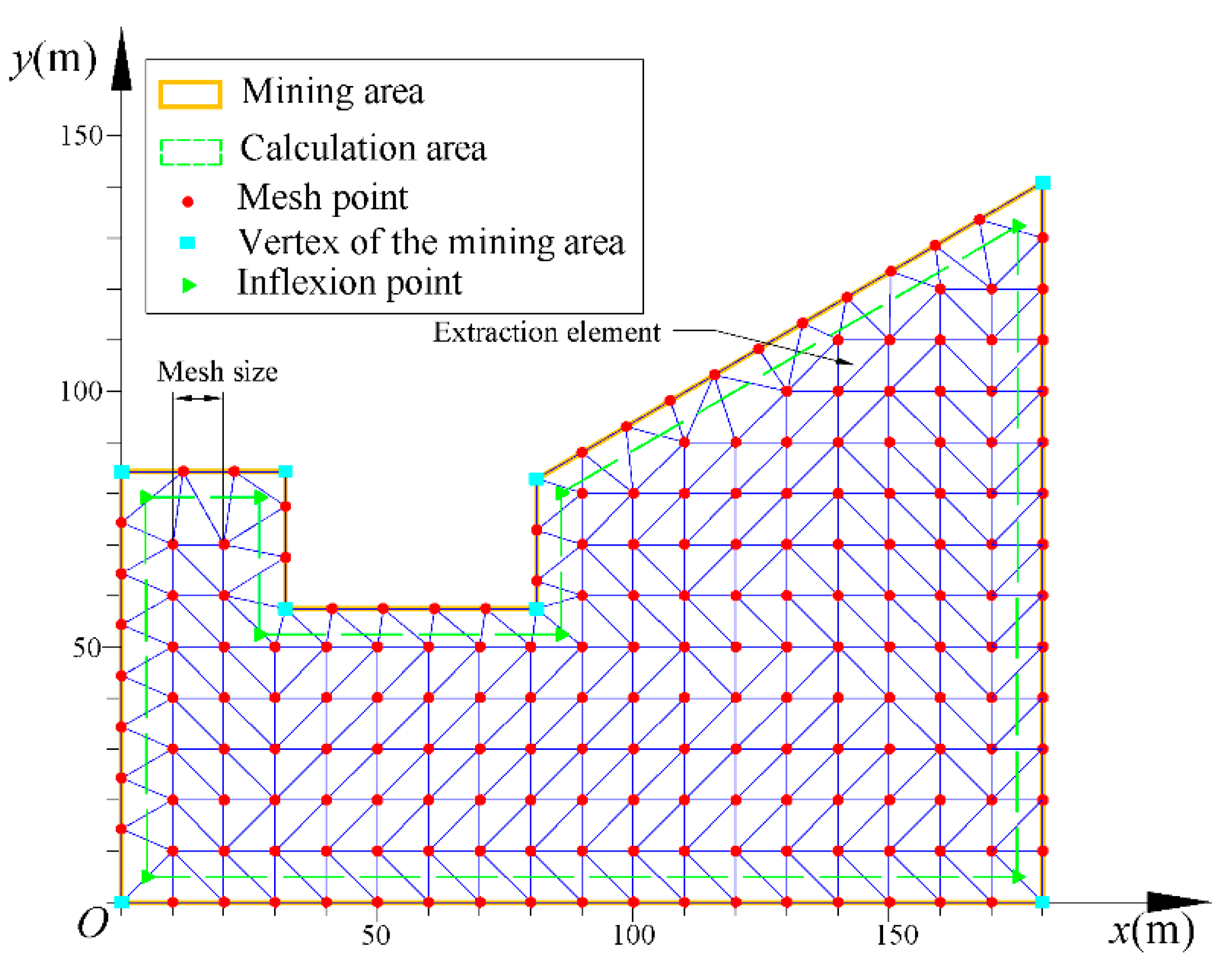
3.1. Irregularly Shaped Mining Area Segmentation Using DTM
- (a)
- Search for a point p3i from unused points. If the point satisfiesthen add the point into the point set P. Repeat the search for each unused point;
- (b)
- Select a point, p3i, from P constructing two vectors and , then calculate the angle between these two vectors (α3i). Add the angle into an angle set Λ. Repeat the selection and calculation for each point in the point set P;
- (c)
- Search the maximum angle from Λ. Assuming the maximum angle is calculated based on vectors of and , p3k is the third point (p3) of a Delaunay triangle.
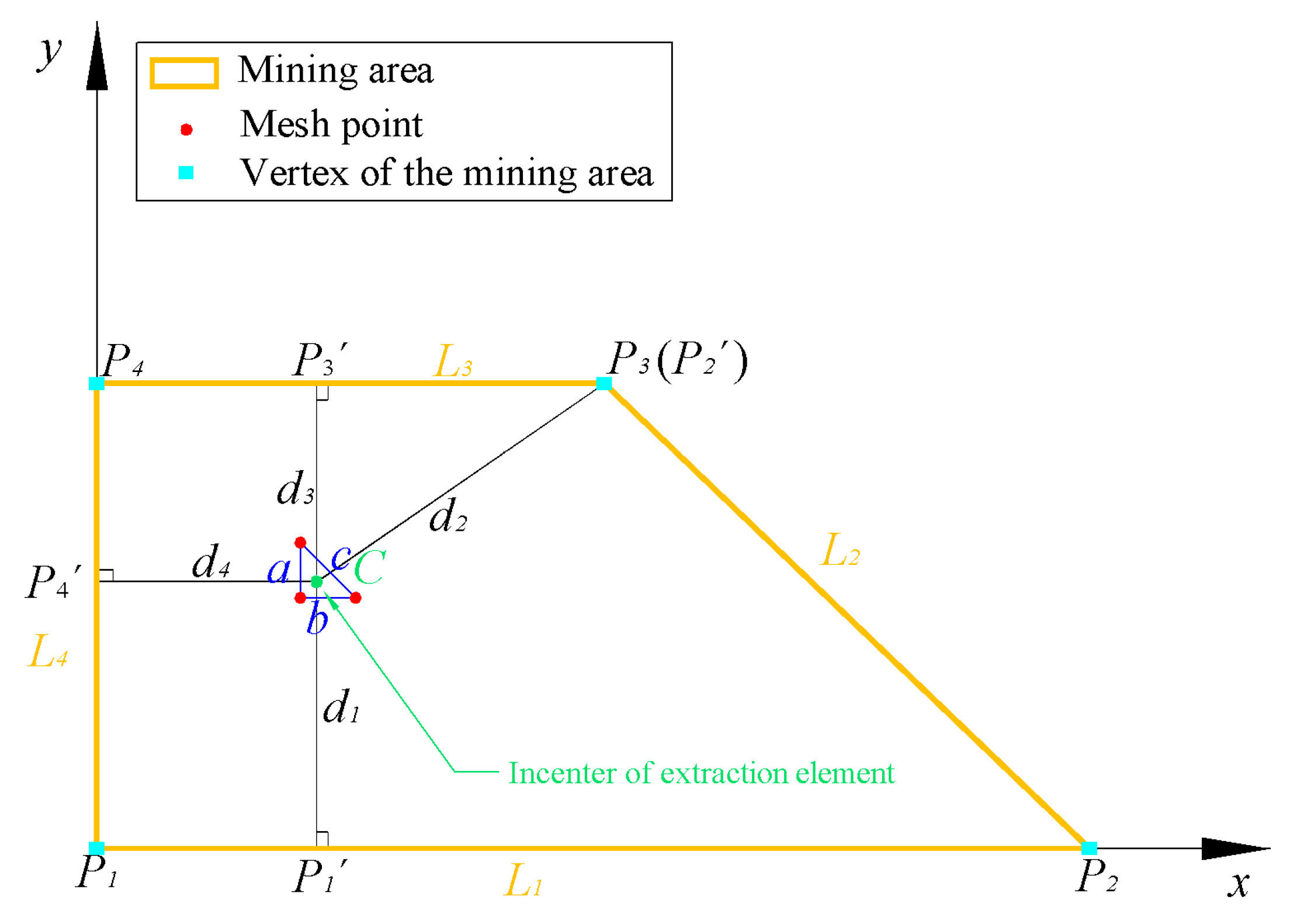
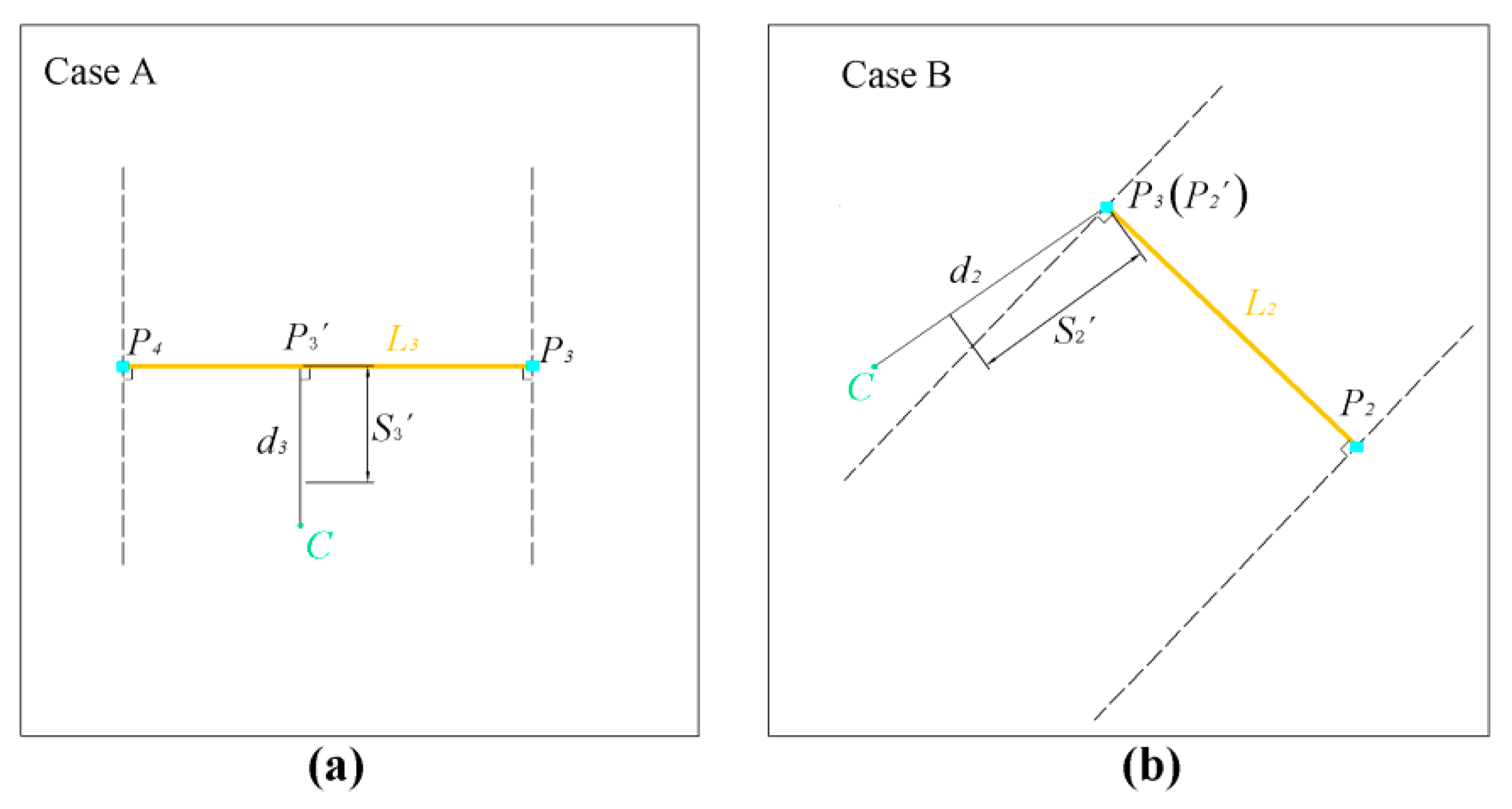
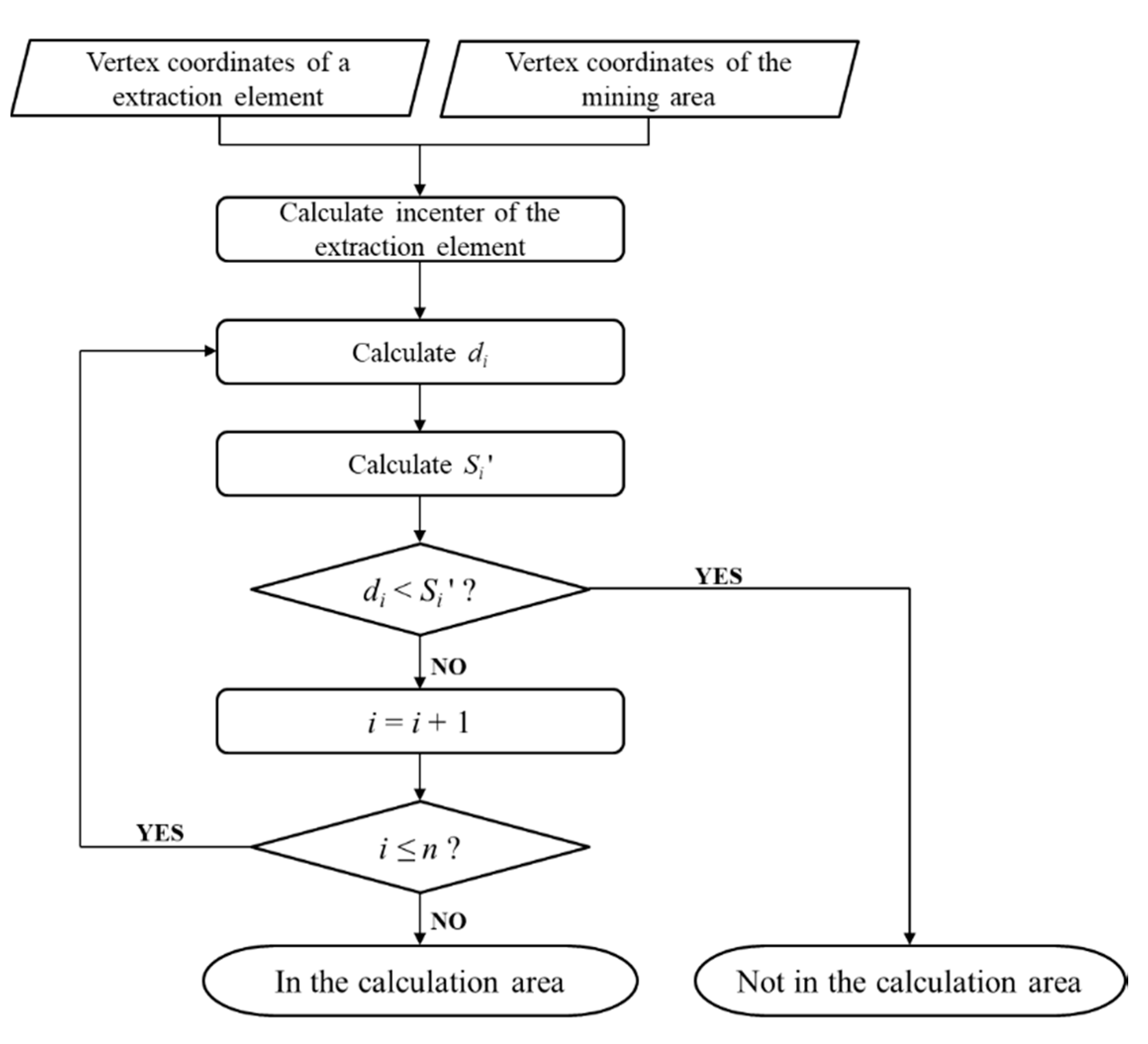
3.2. Selection of Extraction Elements within the Calculation Area
- (a)
- Input vertex coordinates of a triangular extraction element and the vertex coordinates of the mining area;
- (b)
- Calculate the incenter of the extraction element by Equation (6);
- (c)
- Determine the relative position of the incenter and the i-th mining boundary line by Equation (7) and Equation (8); then calculate the BD (di) and BP for the i-th mining boundary line;
- (d)
- Calculate the deviation of the inflection point on the BP, that is, Si’;
- (e)
- Compare di and Si’. If the former is smaller than the latter, the extraction element is not in the calculation area. Otherwise, make i equal to i + 1, and repeat (c)–(e) for the (i + 1)-th mining boundary line;
- (f)
- If di is greater than or equal to Si’ for each mining boundary line, the extraction area is in the calculation area.
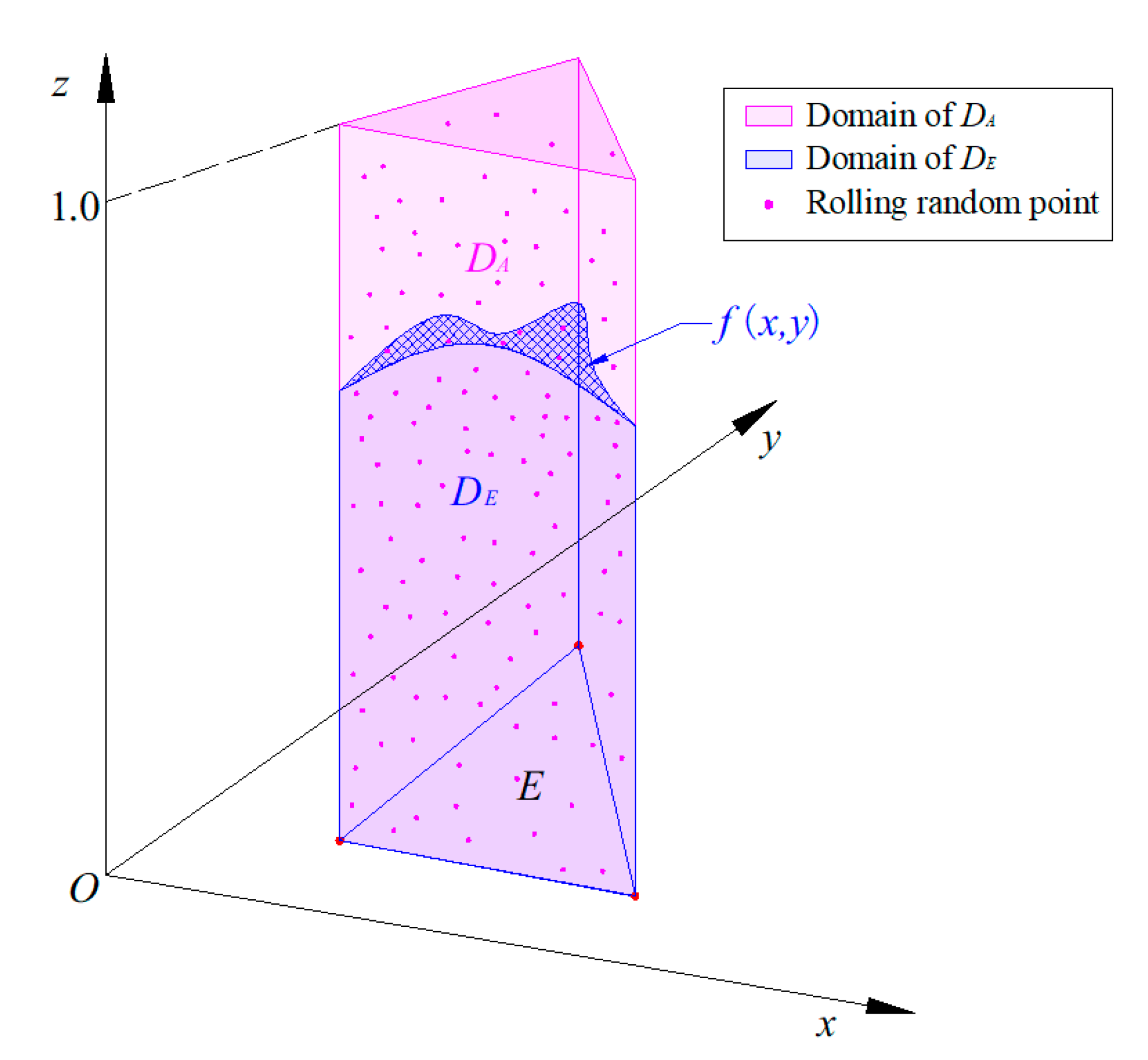
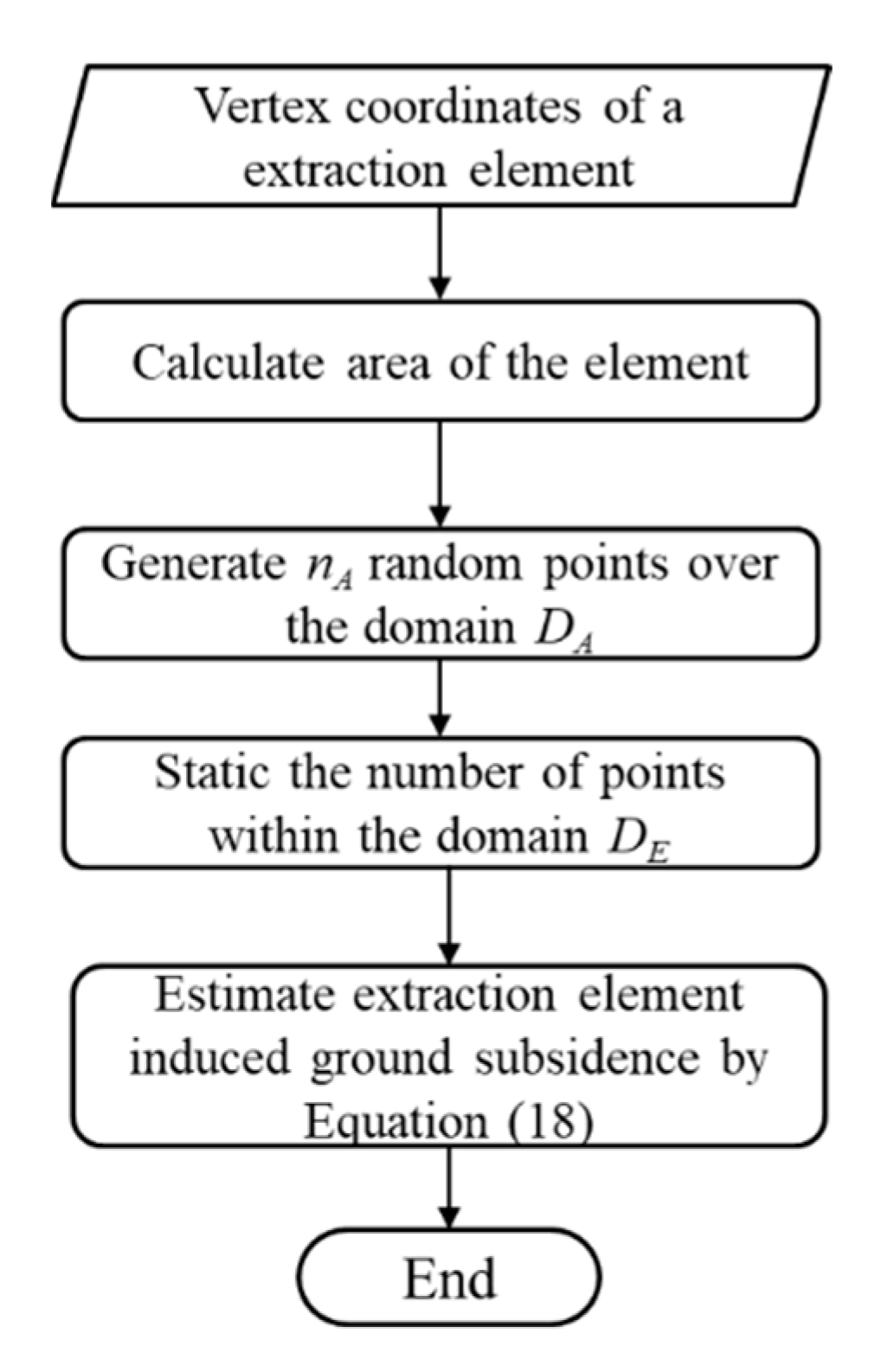
3.3. Extraction Element-Induced Subsidence Prediction Based on the Monte Carlo Method
- (a)
- Input the vertex coordinates of a triangular extraction element;
- (b)
- Calculate the area of the element by Equation (18);
- (c)
- Generate nA random points over the domain DA;
- (d)
- Calculate the number of points within the domain DE. The random point (xi,yi,zi) within the domain can be determined by
- (e)
- Estimate the extraction element-induced ground subsidence by Equation (18).
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Simulation Result
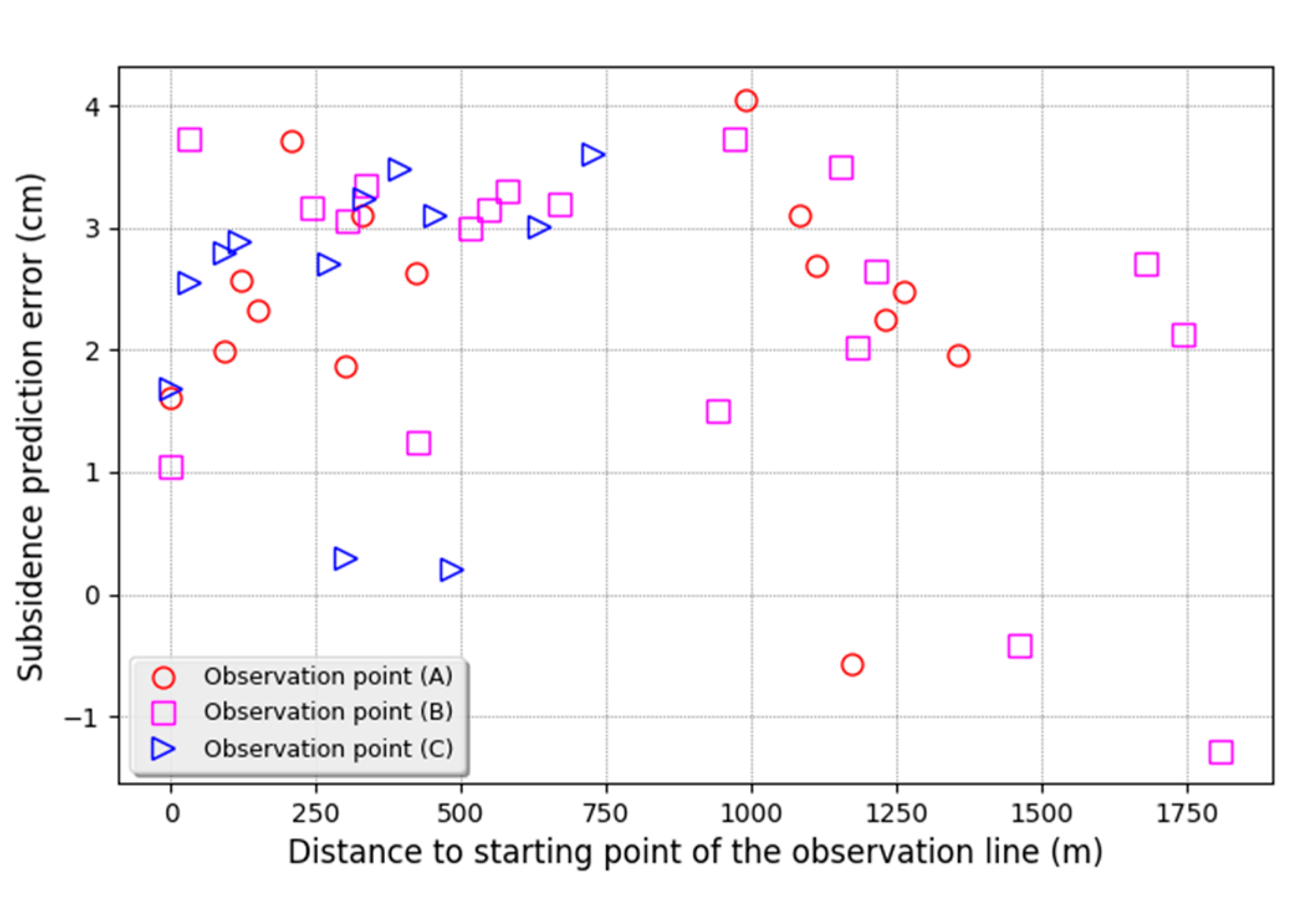
4.2. Validation Using Direct Leveling Based Subsidence Observations
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unlu, T.; Akcin, H.; Yilmaz, O. An integrated approach for the prediction of subsidence for coal mining basins. Eng. Geol. 2013, 166, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Kan, W.; Dawei, Z. AutoCAD-based prediction of 3D dynamic ground movement for underground coal mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 71, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Guoquan, Z.; Jixian, C. Mining under Buildings; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1983; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Jinzhuang, W.; Weimin, M.; Mengxun, N.; Xueli, F. Strata and Surface Movement in Coal Mine; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1981; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, A.; Shakhriar, K.; Goshtasbi, K. Profiling Function for Surface Subsidence Prediction in Mining Inclined Coal Seams. J. Min. Sci. 2004, 40, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, P.P.; Srivastava, A.M.C.; Saxena, N.C. A critical review of mine subsidence prediction methods. Min. Sci. Technol. 1991, 13, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. An improved influence function method for predicting subsidence caused by longwall mining operations in inclined coal seams. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Meng, F.; Chen, J. Numerical simulation analysis of surface subsidence under thick loose mining conditions. Coal Eng. 2014, 46, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Qi, Z.; Yuanzhong, L.; Xiaoping, Z. A study of surface subsidence and coal pillar safety for strip mining in a deep mine. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 627–639. [Google Scholar]
- Alejano, L.R.; Ramirez-Oyanguren, P.; Taboada, J. FDM predictive methodology for subsidence due to flat and inclined coal seam mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1999, 36, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqiang, G.; Guangli, G. A Data-Intensive FLAC3D Computation Model: Application of Geospatial Big Data to Predict Mining Induced Subsidence. Comput. Modeling Eng. Sci. 2019, 5, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Abouzar, V.; John, A.; William, G. Mine-Scale Numerical Modeling of Longwall Operations. In Proceedings of the 2010 Underground Coal Operators’ Conference, Wollongong, Australia, 11–12 February 2010; pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, K.; Ross, S.; Naj, A. Numerical Modelling of Mining Subsidence. In Proceedings of the 2006 Coal Operators’ Conference, Wollongong, Australia, 6–7 July 2006; pp. 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Knothe, S. Observations of surface movements under influence of mining and their theoretical interpretation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Ground Movement, Berlin, Germany, 19 February 1957; pp. 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Keinhorst, H. Considerations on the problem of mining damage. Glukauf 1934, 70, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzsch, H. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983; p. 543. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, B.N.; Reddish, D.J. Subsidence: Occurrence, Prediction and Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; p. 528. [Google Scholar]
- Hejmanowski, R. Zur Vorausberechnung Förderbedingter Bodensenkungen über Erdöl-und Erdgaslagerstätten; TU Clausthal: Berlin, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Malinowska, A.; Hejmanowski, R.; Dai, H. Ground movements modeling applying adjusted influence function. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejmanowski, R.; Malinowska, A.; Kwinta, A.; Ulmaniec, P. Modeling of land subsidence caused by salt cavern convergence applying Knothe’s theory. Markscheidewesen 2018, 25, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett, J. Where and why artificial neural networks are applicable in civil engineering. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 1994, 8, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafie, M.; Samimi Namin, F. Prediction of subsidence risk by FMEA using artificial neural network and fuzzy inference system. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishro, M.; Khosravi, S.; Tehrani, S.M.; Mousavi, S.R. Modeling and zoning of land subsidence in the southwest of Tehran using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Hum. Cap. Urban. Manag. 2016, 1, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Tien Bui, D.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Chapi, K.; Pradhan, B.; Chen, W.; Khosravi, K.; Panahi, M.; Bin Ahmad, B.; Saro, L. Land subsidence susceptibility mapping in south Korea using machine learning algorithms. Sensors 2018, 18, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nefeslioglu, H.; Gokceoglu, C.; Sonmez, H. An assessment on the use of logistic regression and artificial neural networks with different sampling strategies for the preparation of landslide susceptibility maps. Eng. Geol. 2008, 97, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, S. Study on artificial neural network method for ground subsidence prediction of metal mine. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2011, 2, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sroka, A.; Knothe, S.; Tajdus, K.; Misa, R. Underground exploitation inside safety pillar shafts considering the effective use of a coal deposit. Mineral. Resour. Manag. 2015, 31, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwinta, A.; Gradka, R. Mining exploitation influence range. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, G.; Li, S. Predicting underground strata movements model with considering key strata effects. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baochen, L.; Guohua, L. The Basic Rule of Surface Movement of Coal Mine; Chinese Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- National Coal Bureau of P.R.C. Regulation of Mining and Pillar Leaving under Building, Water-Body, Railway and Main Underground Engineer; Coal Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 81–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peixian, L.; Zhixiang, T.; Kazhong, D. Calculation of maximum ground movement and deformation caused by mining. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 2011, 21, 562–569. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.T.; Schachter, B.J. Two Algorithms for Constructing a Delaunay Triangulation. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 1980, 9, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoqun, W.; Kaitai, F. The effective dimension and quasi-Monte Carlo integration. J. Complex. 2003, 19, 101–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, A.; McCullagh, P.; Meng, X.L.; Nicolae, D.; Tan, Z. A Theory of Statistical Models for Monte Carlo Integration. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2003, 65, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, X.F.; Zheng, F.D. Simulation of fully coupled finite element analysis of nonlinear hydraulic properties in land subsidence due to groundwater pumping. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4191–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
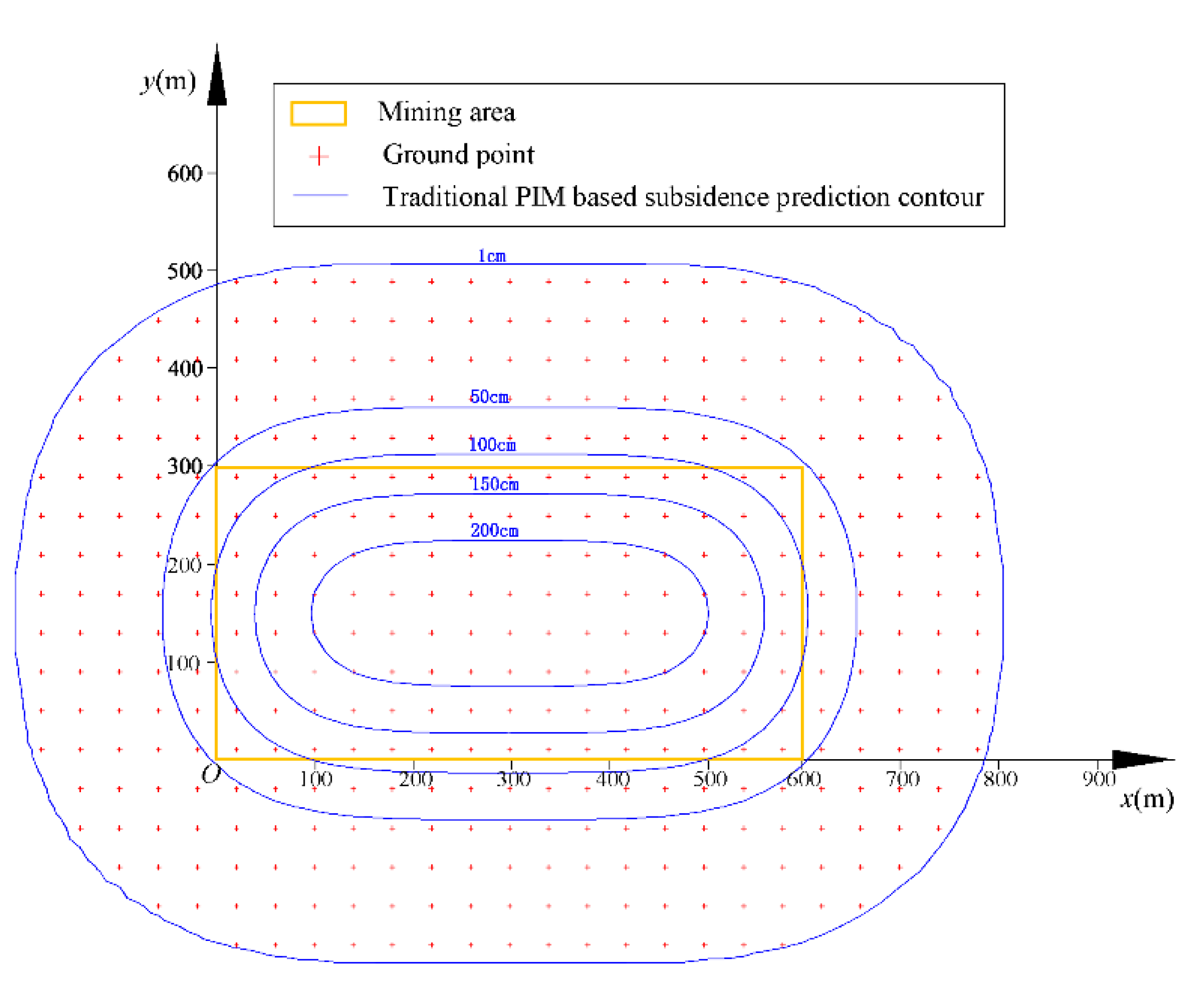
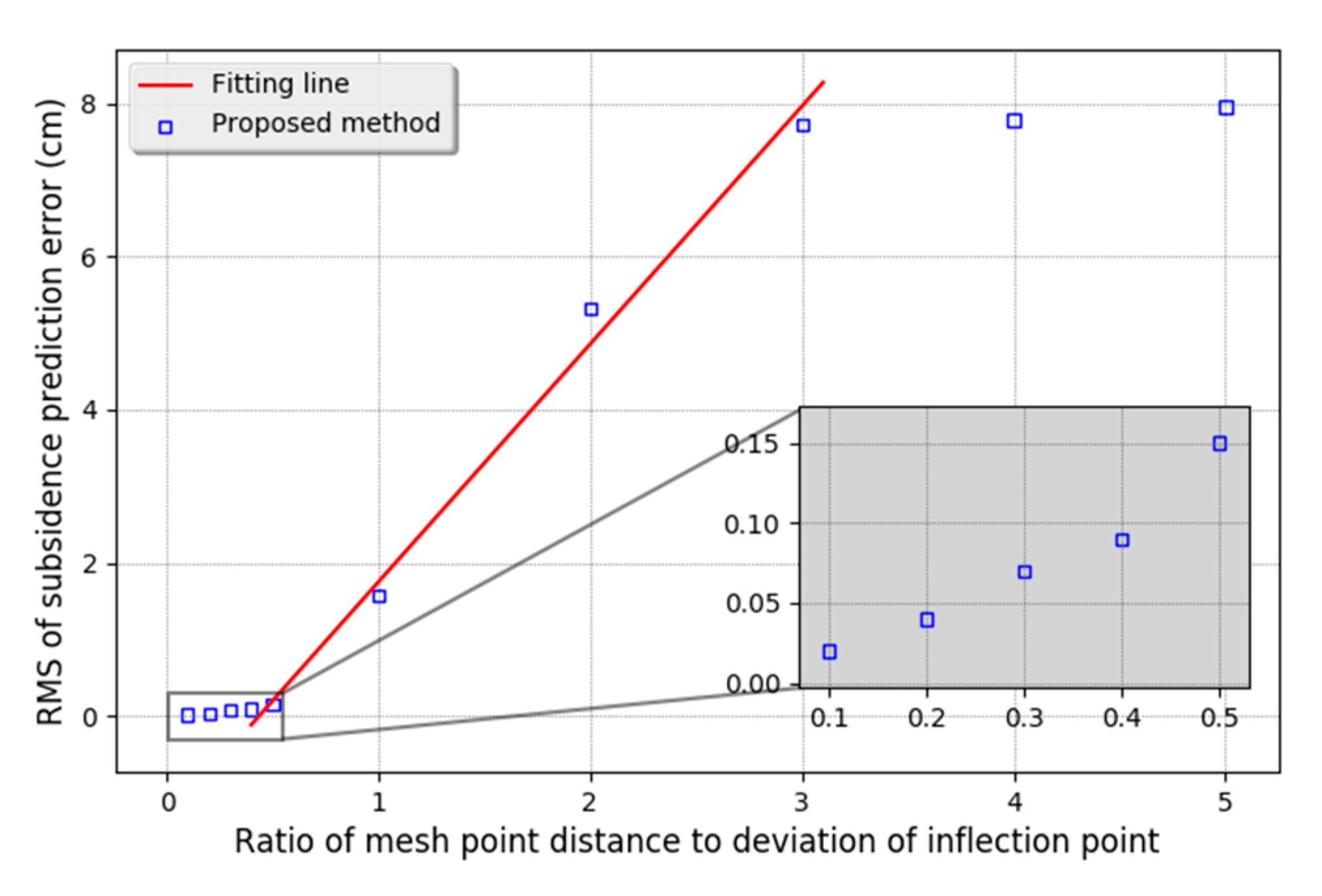

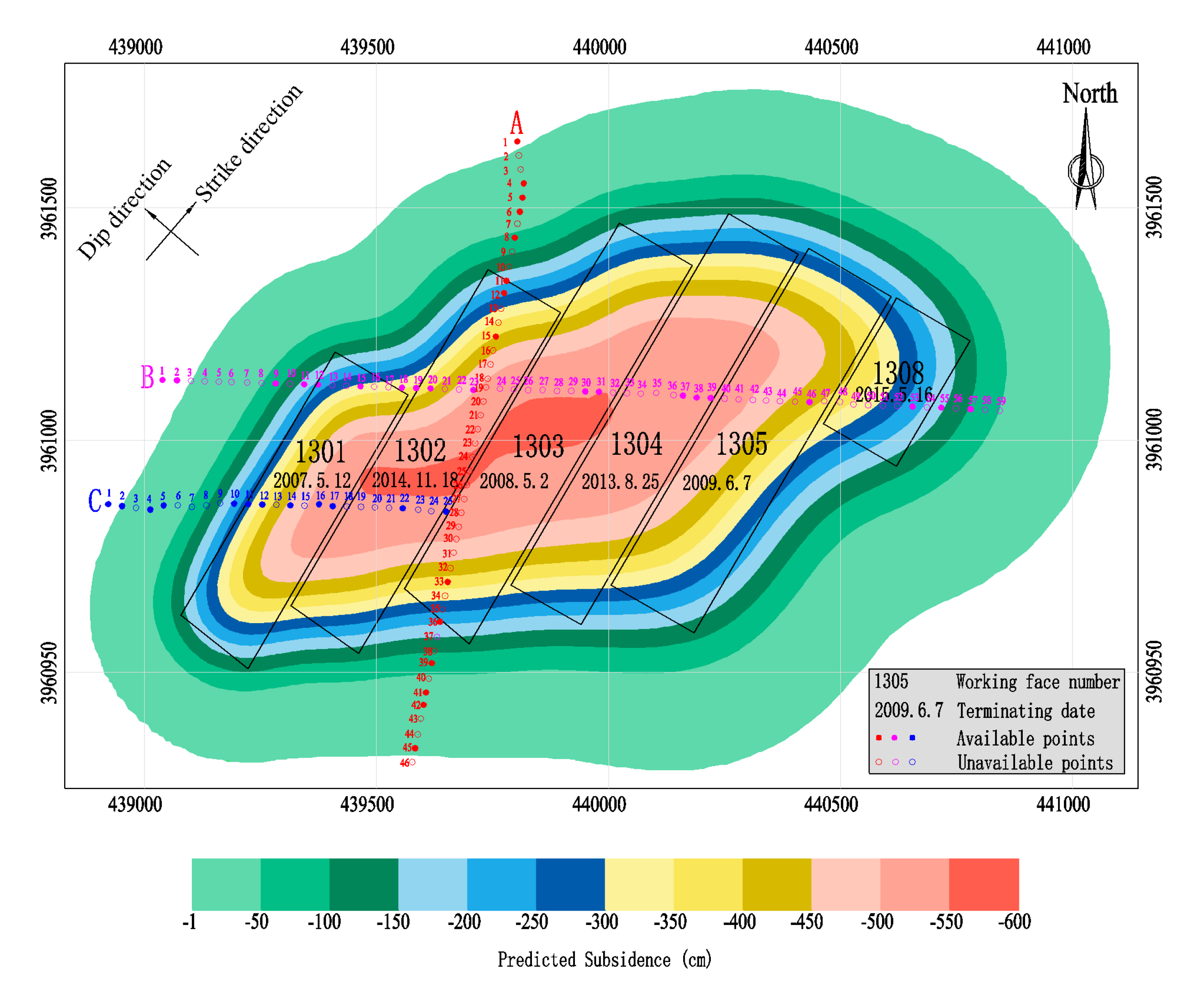
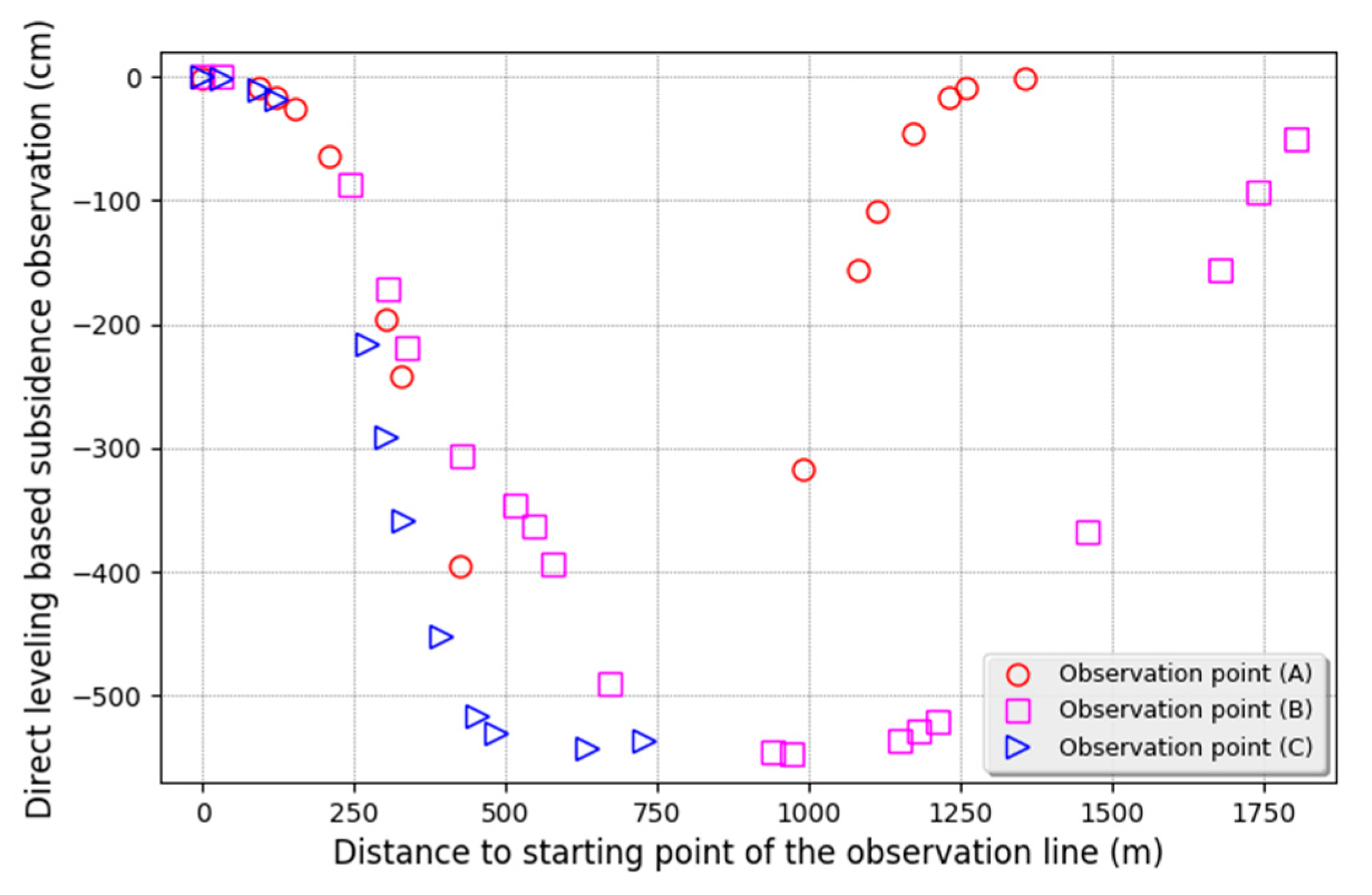
| Length on x Direction (m) | Length on y Direction (m) | α (°) | H (m) | M (cm) | q | tanβ | k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 300 | 0 | −700 | 300 | 0.85 | 2.2 | 0.05 |
| Ratio | Mean (cm) | STD (cm) | RMSE (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 0.2 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 0.3 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 0.4 | −0.03 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| 1.0 | 1.10 | 1.12 | 1.57 |
| 2.0 | 4.03 | 3.48 | 5.32 |
| 3.0 | 5.84 | 5.04 | 7.72 |
| 4.0 | 5.86 | 5.11 | 7.78 |
| 5.0 | 5.90 | 5.33 | 7.95 |
| Ratio | Mean (cm) | STD (cm) | RMSE (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.45 | 23.68 | 23.81 |
| 200 | −1.76 | 10.17 | 10.32 |
| 300 | −0.53 | 5.77 | 5.79 |
| 400 | 0.32 | 2.13 | 2.15 |
| 500 | 0.18 | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| 600 | −0.15 | 0.75 | 0.76 |
| 700 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.27 |
| 800 | −0.01 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 900 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| 1000 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Observation Line | Mean (cm) | STD (cm) | RMSE (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.38 | 1.06 | 2.61 |
| B | 2.35 | 1.39 | 2.73 |
| C | 2.47 | 1.14 | 2.72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, X.; Song, B.; Bo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Lu, G. Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186623
Tan X, Song B, Bo H, Li Y, Wang M, Lu G. Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(18):6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186623
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Xianfeng, Bingzhong Song, Huaizhi Bo, Yunwei Li, Meng Wang, and Guohong Lu. 2020. "Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method" Applied Sciences 10, no. 18: 6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186623
APA StyleTan, X., Song, B., Bo, H., Li, Y., Wang, M., & Lu, G. (2020). Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method. Applied Sciences, 10(18), 6623. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186623





