Shape Optimization Design for a Centrifuge Structure with Multi Topological Configurations Based on the B-Spline FCM and GCMMA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Extend the B-Spline FCM for structure shape optimization design into engineering applications;
- (2)
- Develop a complete shape optimization process of the basket of a geotechnical centrifuge based on the competitive weighted B-Spline FCM and the GCMMA, which settles the light-weighting design of the basket with multi topological configurations whilst also meeting the requirement of the geotechnical centrifuge strength.
2. Review on the Weighted B-Spline FCM
2.1. The Implicit Level Set Function
2.2. The B-Spline Finite Cell Method
2.3. The Weighted Dirichlet Boundary Conditions
3. Geometric Representation and Mechanical Analysis
3.1. Geometric Representation Based on Level-Set Function
3.2. Grid Identification
3.3. Topological Configurations and Related Design Variables
3.4. Mechanical Analysis
4. Shape Optimization
4.1. Shape Optimization Model
4.2. The Flowchart of Shape Optimization
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Optimization Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.Y.; Hong, J.Z.; Wu, W.K. Design and research of a new kind balance adjusting system of centrifuge. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2012, 6, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Health and Safety and Risk Management. Available online: http://www.ehs.cornell.edu/lrs/centrifuge/centrifugeDamages.htm (accessed on 16 December 1998).
- Xuan, H.J.; Song, J. Failure analysis and optimization design of a centrifuge rotor. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo, A.; Heredero, F.; Fargas, G. Failure investigation of a centrifuge duplex stainless steel basket. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 2165–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, W.W.N.G. The state-of-the-art centrifuge modeling of geotechnical problems at HKUST. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2015, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, N.R.; Choo, Y.W.; Cho, G.C. A newly developed state-of-the-art geotechnical centrifuge in Korea. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 17, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, I.S.; Seo, M.W.; Jung, W.S.; Kim, H.S. Development of a large scale geotechnical centrifuge in KOWACO. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Physical Modeling in Geotechnics, Hong Kong, China, 4–6 August 2006; pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Francavilla, A.; Ramakrishnan, C.V.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. Optimization of shape to minimize stress concentration. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 1975, 10, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. Shape optimization of structures: A literature survey. Comput. Struct. 1986, 24, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, J.; Makinen, R.A.E. Introduction to Shape Optimization: Theory, Approximation and Computation; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Shapiro, V.; Suresh, K.; Tsukanov, I. Shape optimization with topological changes and parametric control. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2007, 71, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Cai, S.Y. Shape optimization of Dirichlet boundaries based on weighted B-spline finite cell method and level-set function. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 294, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabago, J.F.T.; Azegami, H. An improved shape optimization formulation of the Bernoulli problem by tracking the Neumann date. J. Eng. Math. 2019, 117, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Beckers, P.; Fleury, C. A unified parametric design approach to structural shape optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1995, 38, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Campbell, J.S. Shape optimization and sequential linear programming. In Optimum Structural Design; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Wang, D.; Yang, J. A parametric mapping method for curve shape optimization on 3d panel structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2010, 84, 485–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, E.; Ruess, M.; Kollmannsberger, S.; Schillinger, D.; Düster, A. Geometric modeling, isogeometric analysis and the finite cell method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2012, 249, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.A.; Botkin, M.E. Structural shape optimization with geometric description and adaptive mesh refinement. AIAA J. 1982, 23, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Bruns, T.; Tortorelli, D. A gradient-based, parameter-fee approach to shape optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizian, J.; Düster, A.; Rank, E. Finite cell method. Comput. Mech. 2007, 41, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, D.; Ruess, M. The finite cell method: A review in the context of higher-order structural analysis of CAD and image-based geometric models. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2015, 22, 391–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Chen, L. A fast analysis method for the CAD model based on the boundary representation in fixed grid. ActaAeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2019, 40, 222693. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Huang, Q.Q. Unification of parametric and implicit methods for shape sensitivity analysis and optimization with fixed mesh. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2017, 109, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhu, J.H.; Gao, T. Stress constrained shape and topology optimization with fixed mesh: A B-spline finite cell method combined with level set function. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 278, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Fedkiw, R. Level set method and dynamic implicit surfaces. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2003, 57, B15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapior, V. Theory of R-Functions and Applications: A Primer; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Svanberg, K. A globally convergent version of MMA without line search. In Proceedings of the First World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, Goslar, Germany, 28 May–2 June 1995; Volume 28, pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Höllig, K.; Reif, U.; Wipper, J. Weighted extended b-spline approximation of dirichlet problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2001, 39, 442–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovcic, Y.; Remouchamps, A. BOSS QUATTRO: An open system for parametric design. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2002, 23, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




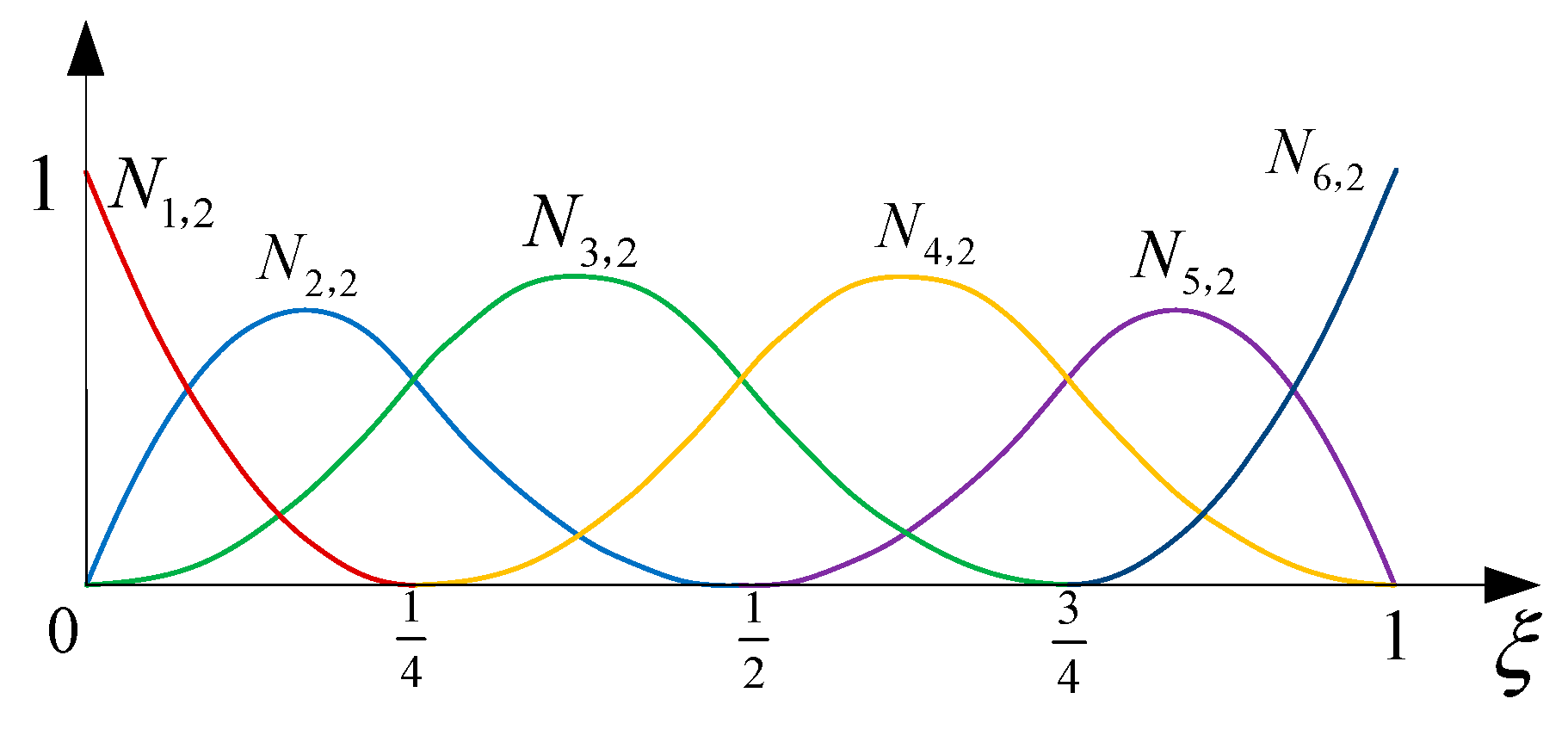



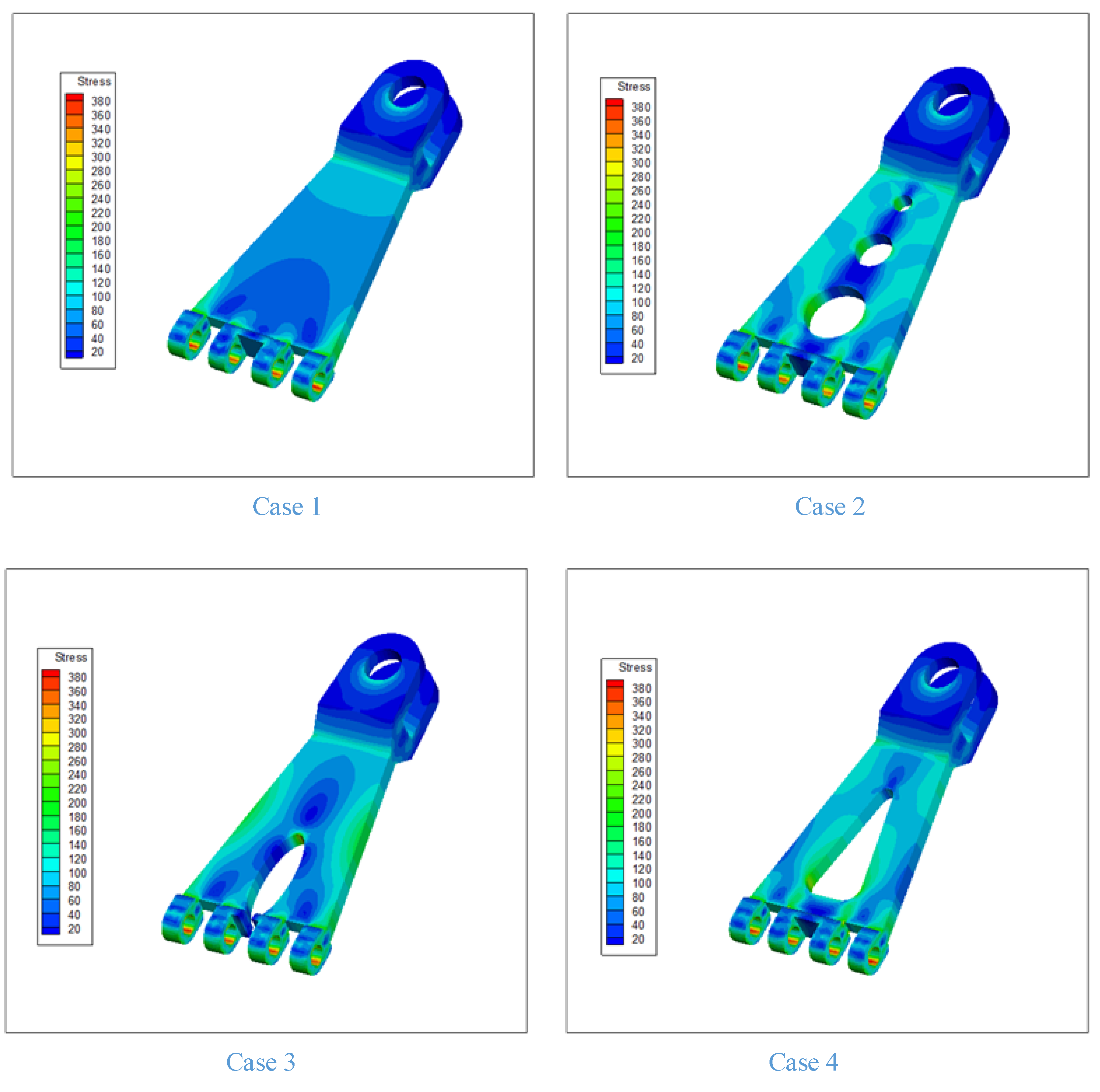





| Maximum Von-Mises Stress/MPa | Mass/kg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |
| Case 1 | 396.95 | 398.25 | 987.51 | 915.20 |
| Case 2 | 390.03 | 399.32 | 909.86 | 819.76 |
| Case 3 | 394.68 | 399.68 | 921.60 | 827.51 |
| Case 4 | 390.34 | 398.72 | 874.57 | 781.82 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; He, L. Shape Optimization Design for a Centrifuge Structure with Multi Topological Configurations Based on the B-Spline FCM and GCMMA. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020620
Li X, He L. Shape Optimization Design for a Centrifuge Structure with Multi Topological Configurations Based on the B-Spline FCM and GCMMA. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(2):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020620
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyao, and Liangli He. 2020. "Shape Optimization Design for a Centrifuge Structure with Multi Topological Configurations Based on the B-Spline FCM and GCMMA" Applied Sciences 10, no. 2: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020620
APA StyleLi, X., & He, L. (2020). Shape Optimization Design for a Centrifuge Structure with Multi Topological Configurations Based on the B-Spline FCM and GCMMA. Applied Sciences, 10(2), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020620




