Gemini Surfactant as a Template Agent for the Synthesis of More Eco-Friendly Silica Nanocapsules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Nanocapsules Synthesis and Characterization
2.2.2. Ecotoxicity Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
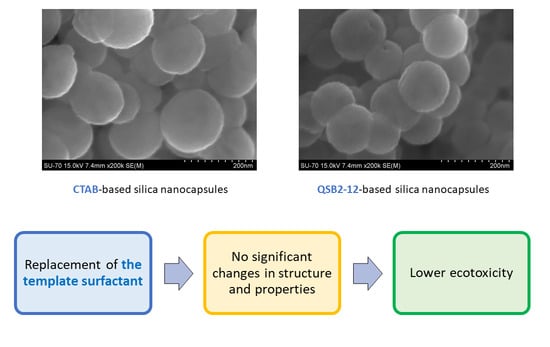
3.2. Characterization of Silica Nanocapsules
3.3. Ecotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirmohseni, A.; Akbari, M.; Najjar, R.; Hosseini, M. Self-healing waterborne polyurethane coating by pH-dependent triggered-release mechanism. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, D.; Hu, Z. A smart anticorrosion coating based on hollow silica nanocapsules with inorganic salt in shells. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, T.L.P.; Sousa, I.; Wilhelm, M.; Carneiro, J.; Opršal, J.; Kukačková, H.; Špaček, V.; Maia, F.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Tedim, J.; et al. Improving the functionality and performance of AA2024 corrosion sensing coatings with nanocontainers. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheludkevich, M.L.; Tedim, J.; Ferreira, M.G.S. “Smart” coatings for active corrosion protection based on multi-functional micro and nanocontainers. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 82, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Chen, J.-F.; Yun, J. Direct encapsulation of water-soluble drug into silica microcapsules for sustained release applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 3374–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadzadeh, M.; Boura, S.H.; Peikari, M.; Kasiriha, S.M.; Ashrafi, A. A review on self-healing coatings based on micro/nanocapsules. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 68, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Thareja, S. In vitro and in vivo characterization of pharmaceutical nanocarriers used for drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, C.; Vaidya, F.U.; Pandey, S.M. Mechanism for Development of Nanobased Drug Delivery System. In Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 35–67. ISBN 978-0-12-814029-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; He, J.; Tang, H.; Yan, C. Porous Silica Nanocapsules and Nanospheres: Dynamic Self-Assembly Synthesis and Application in Controlled Release. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5894–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.; Oliveira, T.; Ferreira, V.; Sushkova, A.; Silva, S.; Carneiro, D.; Cardoso, D.; Goncalves, S.; Maia, F.; Rocha, C.; et al. Toxicity of innovative anti-fouling nano-based solutions in marine species. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, F.; Silva, A.P.; Fernandes, S.; Cunha, A.; Almeida, A.; Tedim, J.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Incorporation of biocides in nanocapsules for protective coatings used in maritime applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelelas, F.; Martins, R.; Oliveira, T.; Maia, F.; Malheiro, E.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S.; Tedim, J. Efficacy and Ecotoxicity of Novel Anti-Fouling Nanomaterials in Target and Non-Target Marine Species. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutner-Hoch, E.; Martins, R.; Oliveira, T.; Maia, F.; Soares, A.; Loureiro, S.; Piller, C.; Preiss, I.; Weis, M.; Larroze, S.; et al. Antimacrofouling Efficacy of Innovative Inorganic Nanomaterials Loaded with Booster Biocides. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, F.; Tedim, J.; Lisenkov, A.D.; Salak, A.N.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Silica nanocontainers for active corrosion protection. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.; Tuel, A. A Fast and Efficient Ion-Exchange Procedure to Remove Surfactant Molecules from MCM-41 Materials. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, C.; Duerkop, A.; Baeumner, A.J. Nanocontainers for Analytical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12840–12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brycki, B.E.; Kowalczyk, I.H.; Szulc, A.; Kaczerewska, O.; Pakiet, M. Multifunctional Gemini Surfactants: Structure, Synthesis, Properties and Applications. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants; Najjar, R., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3325-4. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M.T.; Kaczerewska, O.; Ribosa, I.; Brycki, B.; Materna, P.; Drgas, M. Hydrophilicity and flexibility of the spacer as critical parameters on the aggregation behavior of long alkyl chain cationic gemini surfactants in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goronja, J.; Janosevic-Lezaic, A.; Dimitrijevic, B.; Malenovic, A.; Stanisavljev, D.; Pejic, N. Determination of critical micelle concentration of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide: Different procedures for analysis of experimental data. Hem. Ind. 2016, 70, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.T.; Kaczerewska, O.; Ribosa, I.; Brycki, B.; Materna, P.; Drgas, M. Biodegradability and aquatic toxicity of quaternary ammonium-based gemini surfactants: Effect of the spacer on their ecological properties. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemicals Agency. Cetrimonium Bromide—Registration Dossier (EC Number: 200-311-3). 2020. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/brief-profile/-/briefprofile/100.000.283 (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Garcia, M.T.; Ribosa, I.; Kowalczyk, I.; Pakiet, M.; Brycki, B. Biodegradability and aquatic toxicity of new cleavable betainate cationic oligomeric surfactants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, F.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L. Quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs): A review on occurrence, fate and toxicity in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemicals Agency. Dodecyltrimethylammonium Chloride—Registration Dossier (EC Number: 203-927-0). 2020. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.003.570 (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Kaczerewska, O.; Martins, R.; Figueiredo, J.; Loureiro, S.; Tedim, J. Environmental behaviour and ecotoxicity of cationic surfactants towards marine organisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Poel, I.; Robaey, Z. Safe-by-Design: From Safety to Responsibility. Nanoethics 2017, 11, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nymark, P.; Bakker, M.; Dekkers, S.; Franken, R.; Fransman, W.; García-Bilbao, A.; Greco, D.; Gulumian, M.; Hadrup, N.; Halappanavar, S.; et al. Toward Rigorous Materials Production: New Approach Methodologies Have Extensive Potential to Improve Current Safety Assessment Practices. Small 2020, 16, 1904749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD Test No. 201: Freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 2011; ISBN 978-92-64-06992-3.
- ISO. ISO 10253 Water Quality—Marine Algal Growth Inhibition Test with Skeletonema sp. and Phaeodactylum tricornutum; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Férard, J.F.; Eullaffroy, P. Ecotoxicity of selected nano-materials to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, I.; Maia, F.; Silva, A.; Cunha, A.; Almeida, A.; Evtyugin, D.V.; Tedim, J.; Ferreira, M.G. A novel approach for immobilization of polyhexamethylene biguanide within silica capsules. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 92656–92663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Domka, L. Adsorption of the quaternary ammonium salts on montmorillonite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2004, 65, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Z. A Review: Fundamental Aspects of Silicate Mesoporous Materials. Materials 2012, 5, 2874–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutner-Hoch, E.; Martins, R.; Maia, F.; Oliveira, T.; Shpigel, M.; Weis, M.; Tedim, J.; Benayahu, Y. Toxicity of engineered micro- and nanomaterials with antifouling properties to the brine shrimp Artemia salina and embryonic stages of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwale, P.; Lampis, S.; Conti, G.; Caddeo, C.; Murgia, S.; Fadda, A.M.; Monduzzi, M. In Vitro Release of Lysozyme from Gelatin Microspheres: Effect of Cross-linking Agents and Thermoreversible Gel as Suspending Medium. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3186–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, I.; Quevedo, M.C.; Sushkova, A.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Tedim, J. Chitosan Microspheres as Carriers for pH-Indicating Species in Corrosion Sensing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 1900662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.E.-D.M.; Koller, M. Introductory Chapter: Principles of Green Chemistry. In Green Chemistry; Saleh, H.E.-D.M., Koller, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]







| Hydrodynamic Size [nm] | ζ [mV] | PdI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiNC_CTAB | 157.1 ± 18.3 731.2 ± 134.3 | 32.8 ± 1.1 | 0.68 |
| SiNC_QSB2-12 | 191.6 ± 37.1 662.1 ± 160.0 | 40.9 ± 6.8 | 0.56 |
| SBET [m2/g] | Pore Size [nm] | |
|---|---|---|
| SiNC_CTAB | 719 | 4.4 |
| SiNC_QSB2-12 | 603 | 5.9 |
| Marine Species | I/LC50 [mg/L] (95% CI) | t-Test | p-Value | F-Test to Compare Variances DFn, DFd | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiNC_CTAB | SiNC_QSB2-12 | |||||
| Nannochloropsis gaditana | 8.51 | 9.69 | 1.2230 | 0.2282 | 94.91 | <0.0001 |
| (6.76–10.7) | (9.48–9.91) | 20, 22 | ||||
| Tetraselmis chuii | 7.41 | 9.26 | 3.3437 | 0.0014 | 17.28 | <0.0001 |
| (7.37–7.45) | (8.97–9.55) | 19, 22 | ||||
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 2.37 | 8.30 | 2.1350 | 0.0386 | 14.84 | <0.0001 |
| (1.75–3.23) | (2.69–15.61) | 22, 20 | ||||
| Artemia salina | 23.0 | 25.4 | 0.6126 | 0.5451 | 8.42 | 0.0003 |
| (20.6–25.7) | (18.4–35.0) | 14, 14 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczerewska, O.; Sousa, I.; Martins, R.; Figueiredo, J.; Loureiro, S.; Tedim, J. Gemini Surfactant as a Template Agent for the Synthesis of More Eco-Friendly Silica Nanocapsules. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228085
Kaczerewska O, Sousa I, Martins R, Figueiredo J, Loureiro S, Tedim J. Gemini Surfactant as a Template Agent for the Synthesis of More Eco-Friendly Silica Nanocapsules. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(22):8085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228085
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczerewska, Olga, Isabel Sousa, Roberto Martins, Joana Figueiredo, Susana Loureiro, and João Tedim. 2020. "Gemini Surfactant as a Template Agent for the Synthesis of More Eco-Friendly Silica Nanocapsules" Applied Sciences 10, no. 22: 8085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228085
APA StyleKaczerewska, O., Sousa, I., Martins, R., Figueiredo, J., Loureiro, S., & Tedim, J. (2020). Gemini Surfactant as a Template Agent for the Synthesis of More Eco-Friendly Silica Nanocapsules. Applied Sciences, 10(22), 8085. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228085