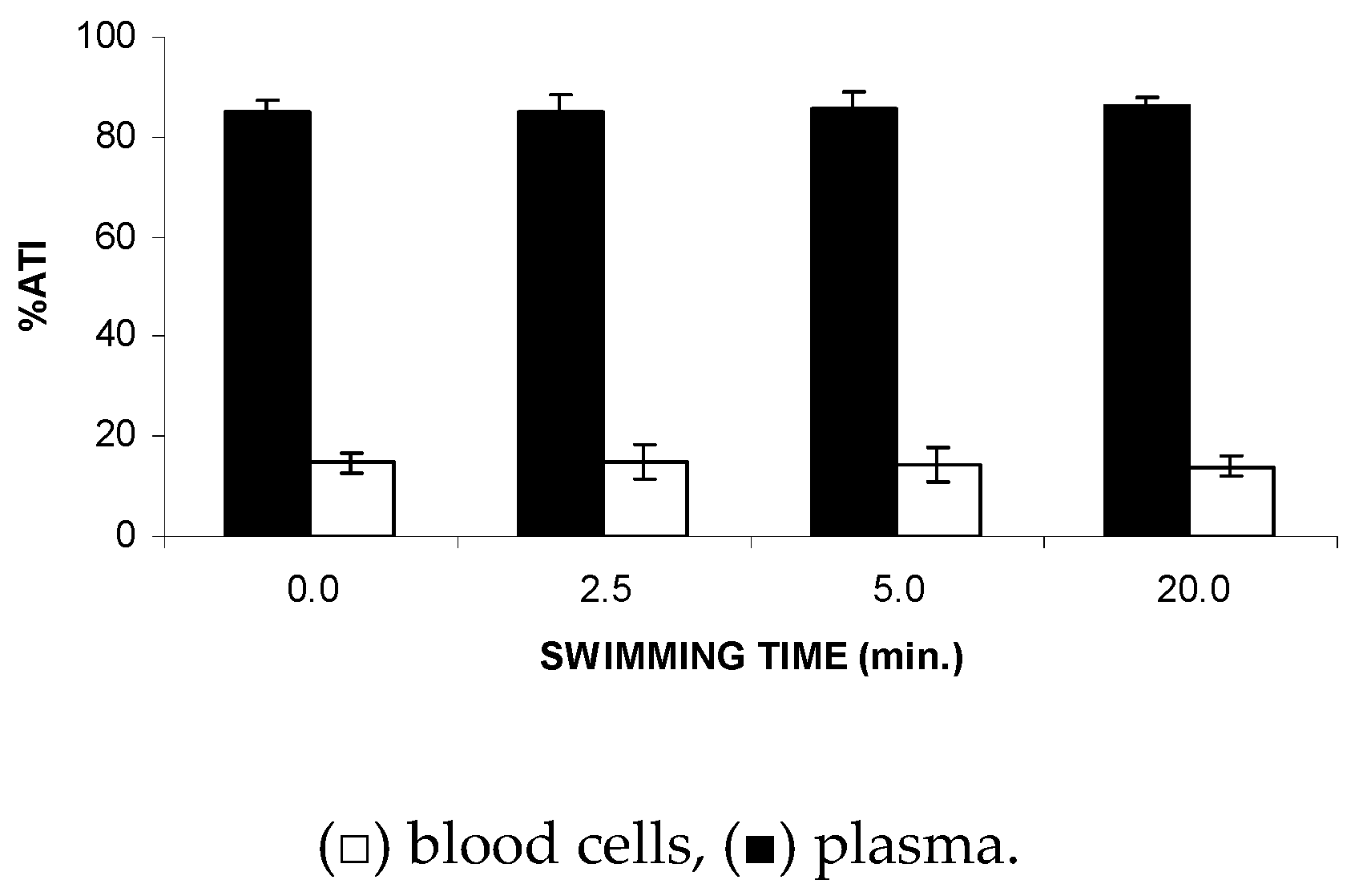Abstract
The present study investigated the effects of forced swimming on the technetium-99m (99mTc) labeling of blood constituents (BloCs). Rats (Wistar) were submitted to forced swim. In previous experiments, swimming animals would recover for different periods of time. Animals not submitted to swimming were used as control. Blood samples were obtained and the 99mTc labeling of BloCs was carried out. Blood cells (BCs), plasma (P), insoluble fractions (IF-P and IF-BCs), and soluble fractions (SF-P and SF-BC) were isolated. Radioactivity was determined, and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated in each fraction. Results showed that forced swimming decreased the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) in IF-P (p < 0.05). It is suggested that the 99mTc labeling of BloCs could be used to verify the effects of the stress conditions on BloCs and that the radionuclide fixation on plasma proteins might be altered in rats submitted to acute stress induced by forced swimming, returning to control levels after recovery.
1. Introduction
Individuals under biological stress respond negatively to a stress stimulus while they have sufficient reserves. Important alterations to the behavior, metabolic pathways, physiological responses, and the effects of drugs have been described [1,2,3,4,5]. Following the NPR/Robert Wood Johnson Foundation/Harvard School of Public Health Burden of Stress in America Survey (2014), the most common effects on health among those with a great deal of stress are undesirable effects, such as problems with (i) sleep (56%); (ii) emotional well-being (63%); and (iii) difficulty in concentrating, thinking, or making decisions (50%) (http://www.rwjf.org/en/library/research/2014/07/the-burden-of-stress-in-america.html). Consequently, it is highly desirable to develop evidence-based methods that minimize the impact of stress [5]. An experimental model such as forced swimming (FS) could be used to better understand the mechanisms that underlie stress.
FS is utilized for inducing stress in rodents [6,7,8]. Acute stress can be induced by a unique swimming session in a large water tank where the animals are forced to swim wall-to-wall distances, moving the extremities while keeping their nose above the water [9]. Following acute FS stress in C57BL/6J mice, it was reported that a decrease in the circulating and brain concentrations of (3α,5α)-3-hydroxy-pregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) could be due to modifications in the biosynthesis/metabolism or changes in the regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis [10]. Some behavioral, biochemical, and physiological parameters are modified in animals under this condition, such as social behavior [6,11], learning and memory [12], liver glycogen content [7], and the angiotensin II receptor [13]. Souza et al. [14] showed that the biodistribution of the radiopharmaceutical 99m-technetium (99mTc) methylene diphosphonate was altered due to the FS.
99mTc is used to label different radiopharmaceuticals, and it is the main radionuclide utilized in nuclear medicine and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) [15]. Functional images of different organs, tissues, and systems are obtained [16,17,18] and alterations to the 99mTc radiopharmaceutical can be also associated with a disturbance in the metabolism [19].
99mTc red blood cells (99mTc RBCs) can be obtained by in vivo, in vitro, and combined in vitro/in vivo methods. In general, the basic mechanism of this radiolabeling process is almost the same. RBCs are “pre-tinned” (stannous ions) for some minutes before the addition of the 99mTc as sodium 99mTc-pertechnetate. Stannous ions (Sn++) enter into the cell and are strongly bound to cellular components. Pertechnetate, as 99mTc, diffuses freely across the erythrocyte membrane and is reduced in the presence of Sn++ inside the cell and binds to the β chain of the hemoglobin [15,20].
99mTc RBCs have been used for evaluating volemia [21] and cardiac function [22] and detecting gastrointestinal bleeding sites [23]. In one case report, 99mTc RBCs were used to localize intrathoracic bleeding [24].
Authors reported that synthetic and natural medications might alter the bioavailability of radiopharmaceuticals [25,26], as well as the radiolabeling of blood constituents [25,27,28,29,30].
99mTc RBCs obtained by an in vitro technique can be used to determine the blood and red cell volume [31], to detect gastrointestinal blood loss and hemangioma, for gated blood pool studies [15], and to obtain selective imaging of the splenic tissue (when RBCs are heat-damaged or heat-denatured) in a variety of clinical scenarios [32].
Plasma proteins have been used as Tc-99m-labeled macro-aggregated albumin to measure pulmonary perfusion in mice [33], as 99mTc-albumin nanocolloid in abdominal and pelvic region scintigraphy [34], and as 99mTc-human serum albumin to determine the plasma volume [35].
Considering that in vitro blood constituent labeling with 99mTc can be modified by medications, an experimental assay to try to verify the effects of drugs was developed [27,28,29,30].
The cardiac function has been evaluated in stressful situations such as exercise by radiopharmaceutical ventriculography [36,37]. Gwozdzinski et al. [38] reported: (i) a significant decrease in membrane thiols after exercise (60 min), with an increase in plasma thiols immediately after and 60 min after the exercise; (ii) a significant decrease in the level of ascorbic acid in the erythrocytes after exercise; and that (iii) a single-bout of exercise can mobilize defensive antioxidant components in blood against oxidative stress. Considering these findings and the undesirable effects of stress on health [39], the aim of this work was to evaluate the effects of stress induced by FS on in vitro blood constituent labeling with 99mTc.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Wistar rats (male, 3–4 months, 250–300 g) were housed (six animals per cage) in controlled conditions with 12 h light/12 h dark cycles, light at 6:00 am, and controlled temperature (25 ± 2 °C). Food and water were freely accessed by all animals. The Committee on animal research of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (UERJ) had approved the protocols used in this current study (CEA/122/2006).
2.2. Forced Swimming and Recovery
Rats were removed from their home cages and immediately submitted to FS in an aquarium (70 × 50 × 40 cm, 25 ± 2 °C) with water filled to 30 cm high for different periods of time (2.5, 5, or 20 min). Following Souza et al. [14], with slight modifications, the animals were forced to swim (CS) and not interrupt their swimming or place their feet or tails on the walls or bottom of the aquarium.
A study related to the recovery from FS was also performed, where animals rested for different amounts of time (5, 20, or 60 min) after 2.5 min of swimming before the blood constituent radiolabeling procedure.
Animals not submitted to swimming were used as control (NS).
2.3. In-Vitro Blood Constituent Radiolabeling
The experiments were performed according to a previously published protocol [40].
All the tubes (vials) utilized were closed (rubber cap) and, to try to eliminate the air from the tubes (vacuum), a syringe was used in the various steps of the procedure.
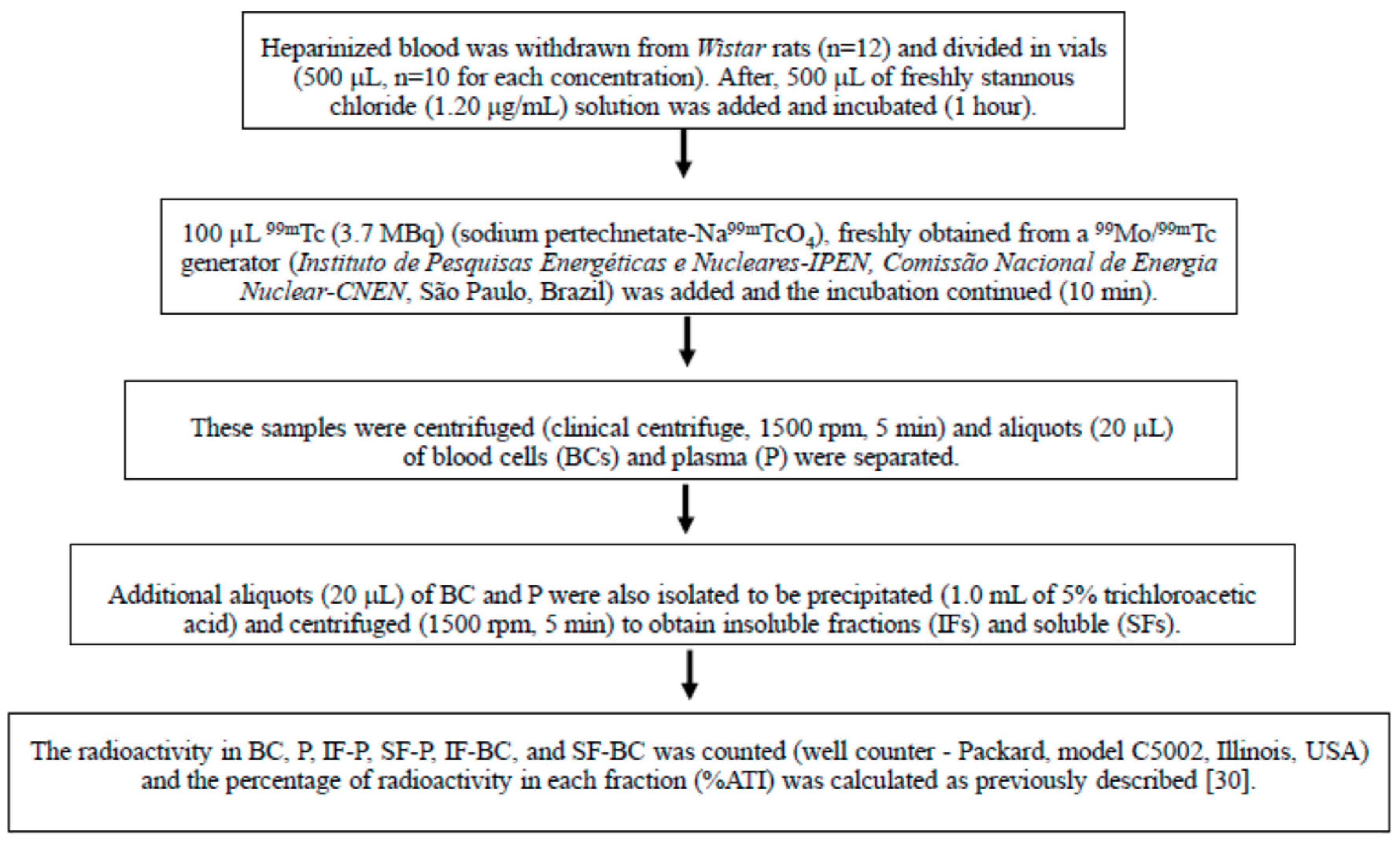
Figure 1 briefly summarize all the steps of the radiolabeling procedure.
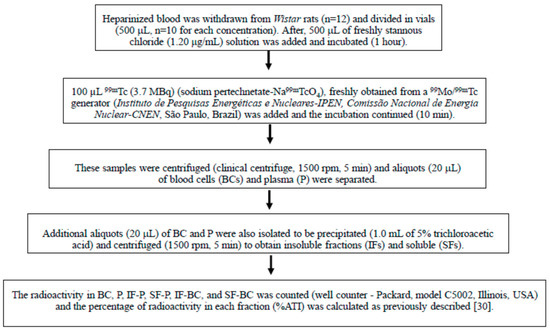
Figure 1.
The 99mTc (99m-technetium) labeling of blood constituents withdrawn from Wistar rats.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SD of the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) from the labeling assay (n = 10 for each FS time or recovery). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to verify statistical significance. Statistical post-test (Bonferroni) was used to verify the p-value (p < 0.05) and to compare the control group (treated with 0.9% NaCl) with each treatment. InStat GraphPad software was used to perform the statistical analysis (GraphPad InStat version 3.0 for Windows 95, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. The Distribution (ATI%) of P and BC Compartments from the Blood Isolated from Animals Submitted to FS
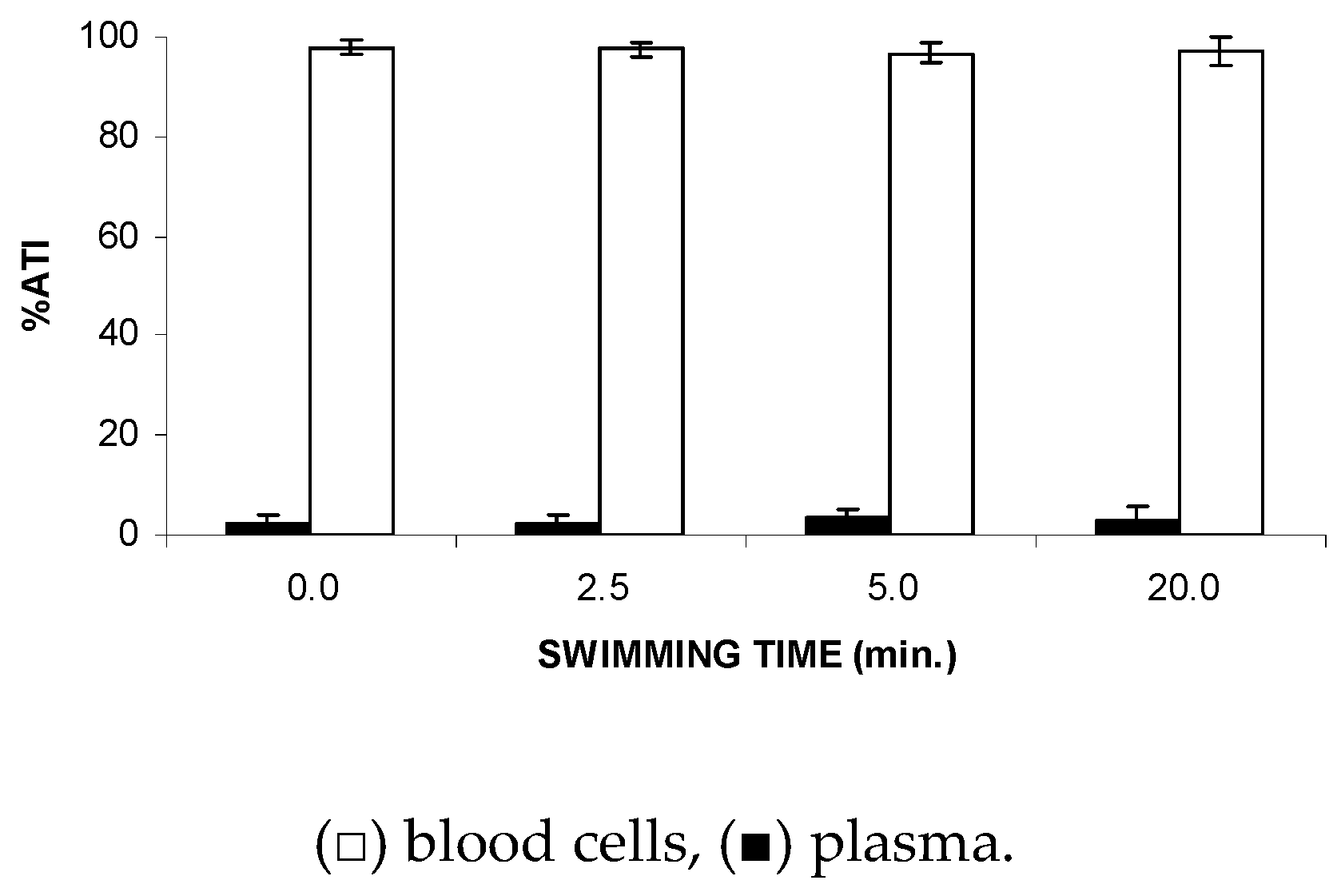
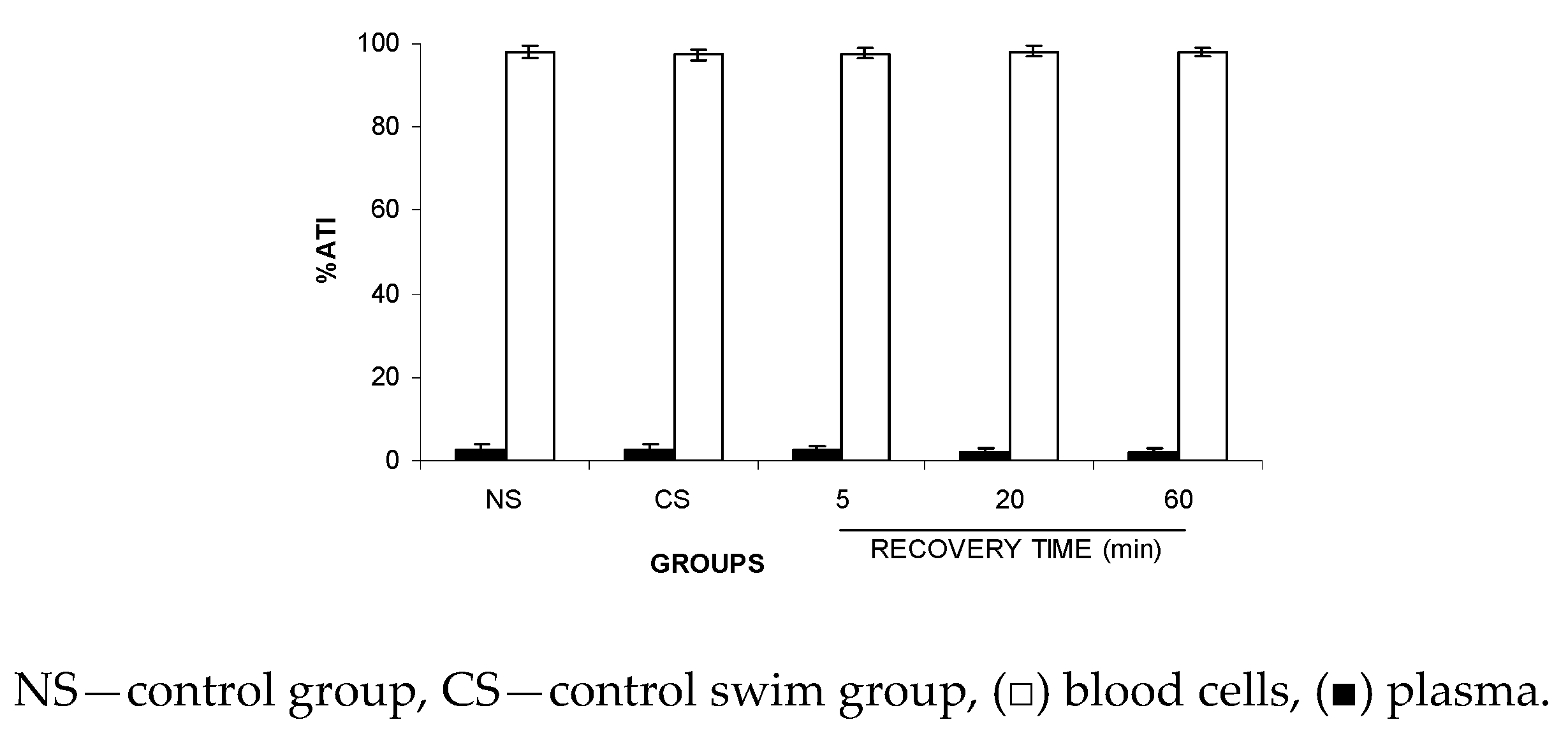
Figure 2 shows no significant (p > 0.5) alteration to the ATI% in plasma (P) and blood cells (BCs), suggesting that FS might not modify the distribution of the 99mTc between the plasma and cellular compartments.
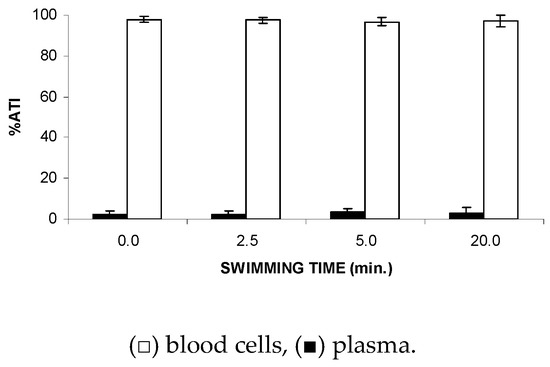
Figure 2.
Effect of the forced swimming (FS) on the distribution of 99mTc between the cellular and plasma compartments. Wistar rats were submitted to FS, blood samples were withdrawn, and the labeling of blood constituents with 99mTc procedure was carried out. Blood cells and plasma were separated by centrifugation. The radioactivity in blood cells and plasma was measured and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated.
3.2. The Fixation (ATI%) on Soluble and Insoluble Fractions Isolated from Blood Cells Obtained from Wistar Rats Submitted to FS
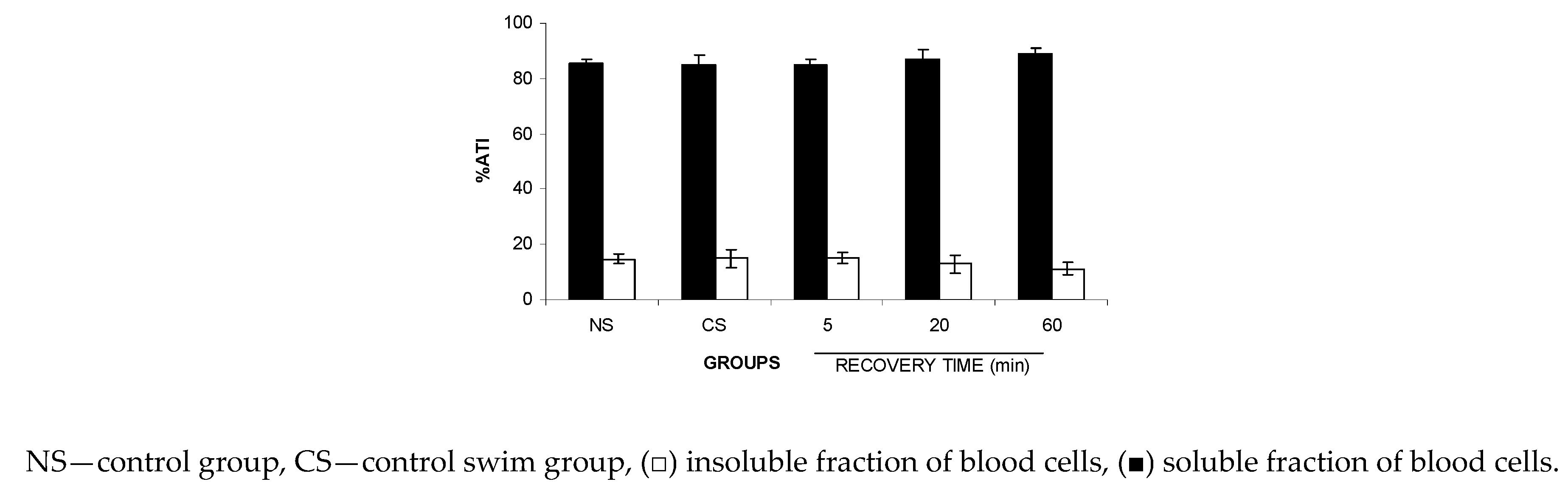
Similarly, based on the results obtained with the blood compartments, Figure 3 shows no significant (p > 0.05) alteration to the ATI% of the insoluble fraction isolated from blood cells (IF-BCs) in the blood from the animals submitted to FS, suggesting no modification of the 99mTc fixation on the cellular proteins in the studied stress condition.
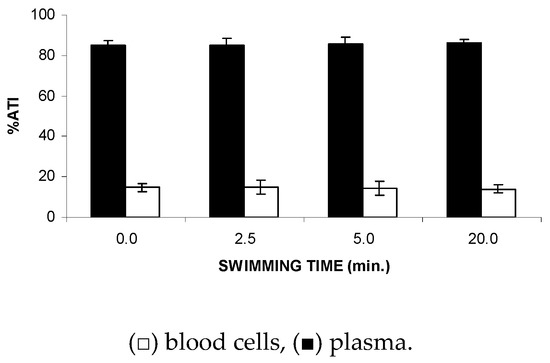
Figure 3.
Effect of the forced swimming (FS) on the distribution of 99mTc between the cellular and plasma compartments. Wistar rats were submitted to FS, blood samples were withdrawn, and the labeling of blood constituents with 99mTc procedure was carried out. Blood cells and plasma were separated by centrifugation. The radioactivity in blood cells and plasma was measured and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated.
3.3. The Fixation (ATI%) on Soluble and Insoluble Fractions Isolated from the Plasma Obtained from Wistar Rats Submitted to FS
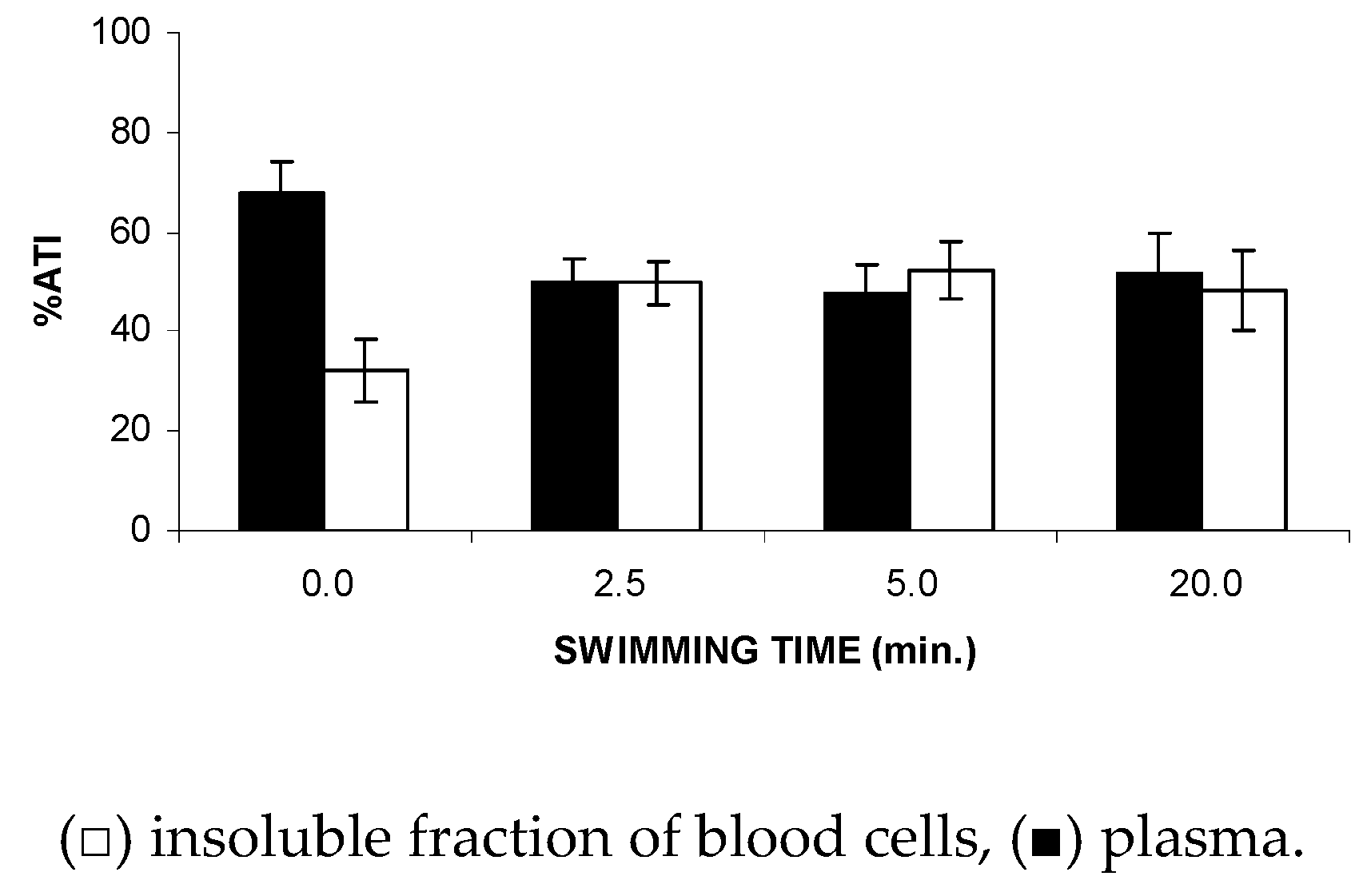
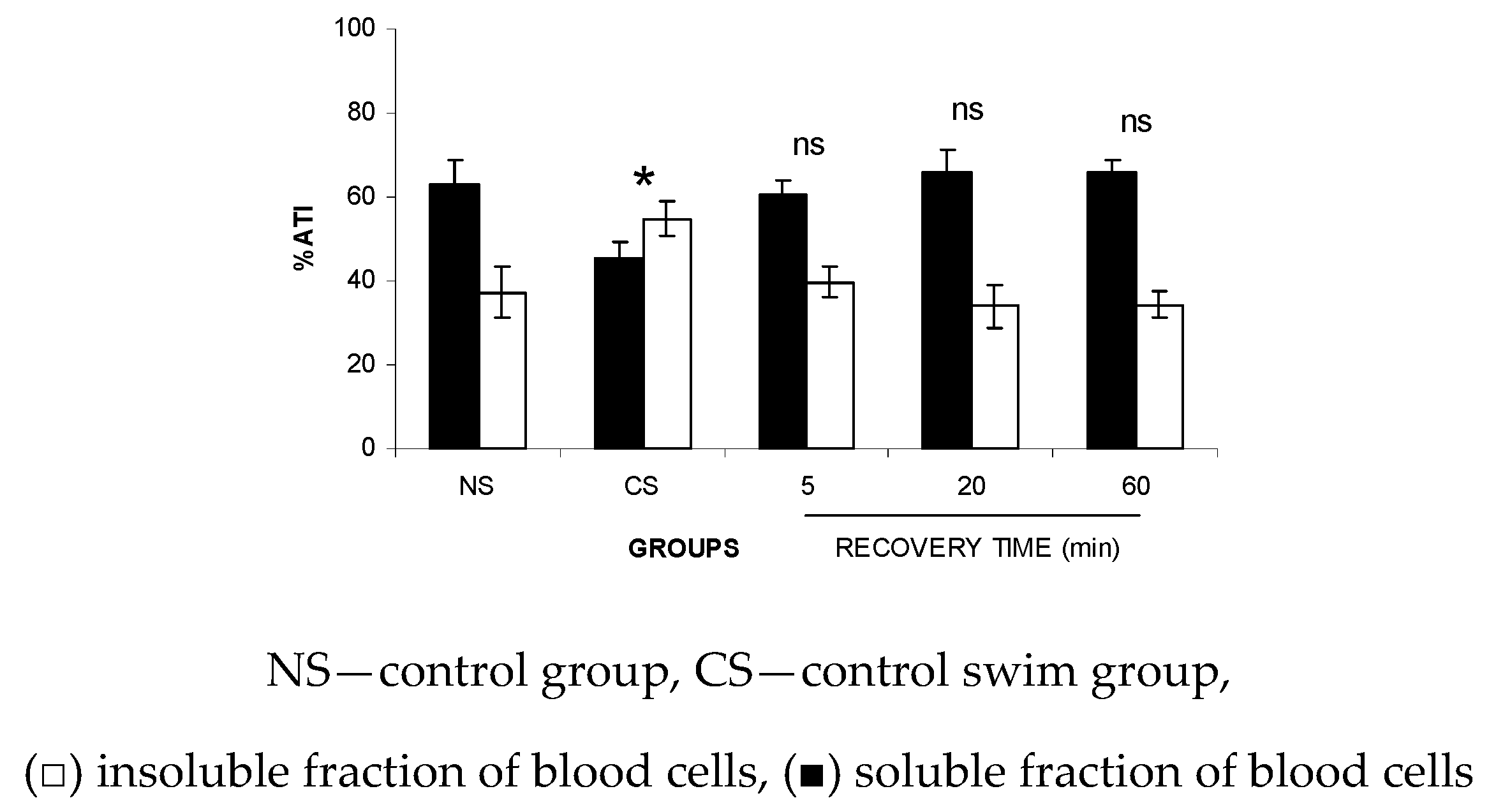
Figure 4 shows that the FS significantly (p < 0.05) altered the fixation (ATI%) of the 99mTc on the soluble and insoluble fractions obtained from plasma (SF-P and IF-P, respectively) at all of the time periods evaluated (2.5 to 20 min), suggesting a reduction in the 99mTc fixation on the plasma proteins from the animals submitted to the studied stress condition.
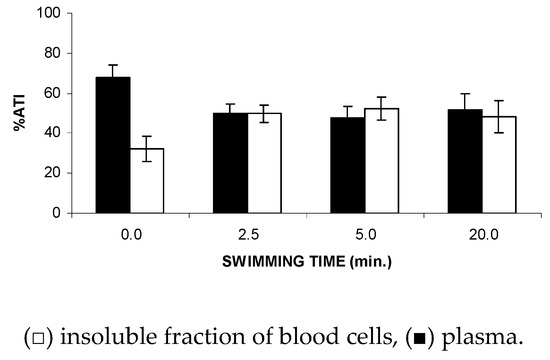
Figure 4.
Effect of the forced swimming (FS) on the distribution of 99mTc between the cellular and plasma compartments. Wistar rats were submitted to FS, blood samples were withdrawn, and the labeling of blood constituents with the 99mTc procedure was carried out. Blood cells and plasma were separated by centrifugation. The radioactivity in blood cells and plasma was measured and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated.
3.4. The Fixation (ATI%) in P and BC Compartments of Wistar Rats after Recovery from FS
Data of the ATI% on P and BCs in Figure 5 suggest no significant alteration (p > 0.05) to the distribution of the 99mTc between the cellular and plasma compartments after recovery from FS.
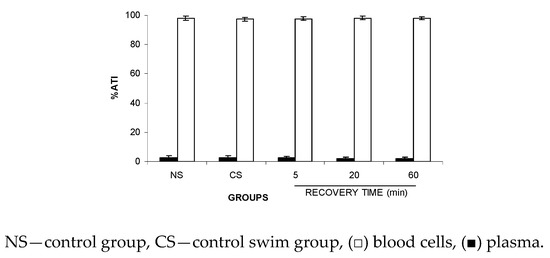
Figure 5.
ATI% in the blood cells and plasma from Wistar rats after recovery from the forced swimming. Wistar rats were submitted to forced swimming for 2.5 min, and recovery was followed for different periods of time. After that, blood samples were withdrawn and the labeling of blood constituents with the 99mTc procedure was carried out. Blood cells and plasma were separated by centrifugation. The radioactivity in blood cells and plasma was measured and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated.
3.5. The Fixation (ATI%) in SF-BC and IF-BC Fractions Isolated from Wistar Rats after Recovery from the FS
Similarly, based on the results obtained with BCs and P, data of the %ATI on SF-BCs and IF-BCs in Figure 6 indicate no significant alteration (p > 0.05) in the fixation of 99mTc on cellular proteins after recovery from the FS.
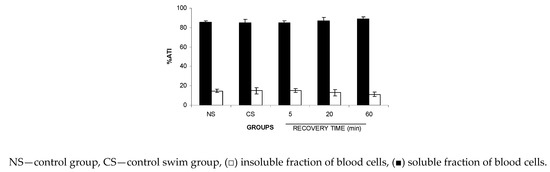
Figure 6.
ATI% in the soluble and insoluble fractions of the blood cells from Wistar rats after recovery from the forced swimming (FS). Wistar rats were submitted to FS for 2.5 min and recovery was followed for different periods of time. After that, blood samples were withdrawn and the labeling of blood constituents with the 99mTc procedure was carried out. Blood cells were separated by centrifugation and insoluble and soluble fractions of blood cells were isolated by precipitation in trichloroacetic acid centrifugation. The radioactivity in each fraction was measured and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated.
3.6. The Fixation (ATI%) in SF-P and IF-P Fractions Isolated from Wistar Rats after Recovery from the FS
Figure 7 indicates that after 5 min of recovery from a 2.5-min FS, the ATI% in SF-P and IF-P presented the same value obtained with the NS group. Similar data were obtained with the highest time of recovery (20 and 60 min).
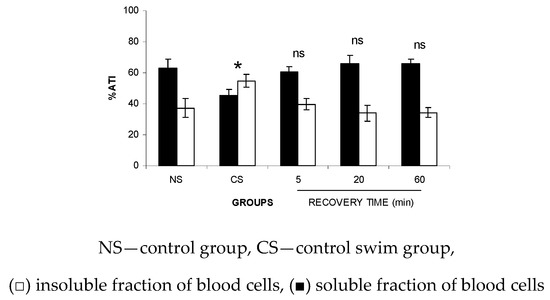
Figure 7.
ATI% in the soluble and insoluble fractions of the blood cells from Wistar rats after recovery from the forced swimming (FS). Wistar rats were submitted to FS for 2.5 min and recovery was followed for different periods of time. After that, blood samples were withdrawn and the labeling of blood constituents with the 99mTc procedure was carried out. Plasma was separated by centrifugation and insoluble and soluble fractions of plasma were isolated by precipitation in trichloroacetic acid centrifugation. The radioactivity in each fraction was measured and the percentage of 99mTc incorporated (%ATI) was calculated.
4. Discussion
Several studies have related metabolic disorders to stress in different organs and body systems. Heart, circulatory, gastrointestinal, immunological, and nervous systems can present altered function in individuals with stressful lifestyles [5,41,42,43,44]. In some conditions, the stress can be desirable, as in the cardiac evaluations with radiopharmaceuticals [36,37].
Changes in blood parameters have been evaluated in physical activities such as cycling [38], whole-body vibration exercise [45], and FS-induced [6,7,8] stress.
Plasma proteins and RBCs labeled with 99mTc have been used to evaluate various clinical applications [32,34,35] and in experimental models [25,26,27,28,29,30,36].
In the current work, the effects of FS on the in-vitro 99mTc blood constituent labeling were assessed. The data analysis showed that the FS for different amounts of time (2.5, 5, or 20 min) did not alter the allocation of radioactivity between BC and P compartments (Figure 2). The presence of the radionuclide 99mTc on the cellular proteins (blood cells) was not modified (Figure 3). No alteration was verified after different periods of recovery from FS (Figure 5 and Figure 6). These data agree with other studies that obtained no alterations in RBC radiolabeling in patients after dipyridamole-thallium stress testing [46] without interference in the pathways and chemical actions of the Sn++ and pertechnetate ions [31]. Antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase are highly active and present at high concentrations in RBCs, constituting the most important components of the antioxidant defense system of blood [47,48]. This could be related to the absence of alterations to the RBC radiolabeling from animals submitted to FS. Vierck et al. [49] reported that running and cycling (moderate and high intensity) reduce the carotenoid levels in the skin, whereas sports and both exercise intensities had comparable findings. Moreover, it is suggested that above a determined threshold, physical activity also induces oxidative stress on the surface of the body (skin) associated with a reduction in the antioxidant level.
Authors suggested that medications could interfere with the fixation of 99mTc in blood on the same sites as blood constituents, inducing alterations in the erythrocyte membrane structure or altering the Sn++ and pertechnetate ion transport into cells, inhibiting (via chelating action) the Sn++ and pertechnetate ions, and oxidizing or generating free radicals that might oxidize the Sn++ [27,40]. The influence of stress conditions on such radiolabeling has yet to be evaluated. Regarding the plasma proteins, the oxidative status of a plasma compartment could be an important factor in altering the fixation of 99mTc on plasma proteins. Indeed, studies have demonstrated that different stressful situations could induce alterations to the plasma antioxidant systems in animals and human beings [50,51,52,53,54].
Our findings suggest that the binding of 99mTc to plasma proteins from rats might be altered after FS (Figure 4). Moreover, the data indicate that the swimming-induced alteration to the fixation of 99mTc on plasma proteins is not time-dependent, returning to control level after 5 or 20 min of recovery. These data suggest that this assay could be used to assess the effects of stress on the blood constituents. Stressful situations such as the hemodialysis procedure have been related to increases of oxidative stress and the alteration/damage of the antioxidant defense [54]. Other authors have demonstrated that the amount of a reduced form of human albumin and glutathione peroxidase are increased after hemodialysis [55,56], while catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione-S-transferase, and glutathione peroxidase experimentally induce myocardial infarction (rats) [57]. Finkler et al. [58] reported that the negative consequences of exercise are generally related to the difference between the number of antioxidants (antioxidant enzymes and low-molecular-weight antioxidants) and the free radicals (reactive nitrogen and oxygen species) during physical exercise. In plasma, oxidative stress could lead to the excessive production of free radicals and/or a reduction in the antioxidant defenses, with an uncontrolled redox status of the cell. This imbalance could be by-passed with the production or activation of these antioxidant enzymes, as well as endogenous substances such as glutamine. These defense mechanisms could require some time to appear and block the oxidative stress effects, explaining the data obtained with the fixation of 99mTc on plasma proteins from rats submitted to swimming after recovery (Figure 7). Moreover, some oxidative stress markers in plasma and RBCs could also sustain and justify this finding.
The limitations of the current research were related to the number of animals utilized in this work and the time used for the recovery from FS. Moreover, the scarcity of publications evaluating the effect of stress on blood constituent labeling limited the discussion of the results. Although there were some limitations in the current investigation, some important findings were observed.
5. Conclusions
The 99mTc labeling of blood constituents could be used to evaluate the effects of stress conditions on the blood constituents related to FS. Moreover, the fixation of radionuclides on plasma proteins might be altered in rats submitted to acute stress induced by FS, returning to control levels after the recovery time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.d.F., M.O.P., G.S.R., and M.B.-F.; methodology, A.S.d.F., M.O.P., G.S.R., and M.B.-F.; formal analysis, A.S.d.F., M.O.P., G.S.R., and M.B.-F.; investigation, A.S.d.F., A.L.B.D.C., E.H.F.F.F., C.S.-F., T.E.-S., M.A.S.G., M.C.M.-F., D.B.-S., and A.G.M.; resources, A.S.F., M.O.P., G.S.R., and M.B.-F.; data curation, A.S.d.F., M.O.P., G.S.R., N.R.A., and M.B.-F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.d.F., A.L.B.D.C., E.H.F.F.F., and L.L.P.-D.; writing—review and editing, D.B.-S., L.L.P.-D., D.C.S.-C., R.T., N.R.A., and M.B.-F.; visualization, D.C.S.-C., E.H.F.F.F., R.T., and M.B.-F.; supervision, A.S.d.F., D.C.S.-C., R.T., N.R.A., and M.B.-F.; project administration, A.S.d.F., R.T., N.R.A., and M.B.-F.; funding acquisition, A.S.d.F., N.R.A., and M.B.-F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), and Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (UERJ).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support of the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Martin, B.; Golden, E.; Carlson, O.D.; Egan, J.M.; Mattson, M.P.; Maudsley, S. Caloric restriction: Impact upon pituitary function and reproduction. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygula, R.; Abumaria, N.; Havemann-Reinecke, U.; Rüther, E.; Hiemke, C.; Zernig, G.; Fuchs, E.; Flügge, G. Pharmacological validation of a chronic social stress model of depression in rats: Effects of reboxetine, haloperidol and diazepam. Behav. Pharmacol. 2008, 19, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mällo, T.; Matrov, D.; Kõiv, K.; Harro, J. Effect of chronic stress on behavior and cerebral oxidative metabolism in rats with high or low positive affect. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcculloch, P.F.; Dinovo, K.M.; Connolly, T.M. The cardiovascular and endocrine responses to voluntary and forced diving in trained and untrained rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R224–R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, B.S.; Chamine, I.; Wakeland, W. A systems approach to stress, stressors and resilience in humans. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 282, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The forced swim test as a model of depressive-like behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akil, M.; Bicer, M.; Kilic, M.; Avunduk, M.C.; Mogulkoc, R.; Baltaci, A.K. Effect of intraperitoneal selenium administration on liver glycogen levels in rats subjected to acute forced swimming. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 139, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitychoutis, P.M.; Sanoudou, D.; Papandreou, M.; Nasias, D.; Kouskou, M.; Tomlinson, C.R.; Tsonis, P.A.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z. Forced swim test induces divergent global transcriptomic alterations in the hippocampus of high versus low novelty-seeker rats. Hum. Genom. 2014, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shors, T.J. Acute stress and re-exposure to the stressful context suppress spontaneous unit activity in the basolateral amygdala via NMDA receptor activation. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 2811–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Devincci, A.M.; Beattie, M.C.; Morrow, D.H.; McKinley, R.E.; Cook, J.B.; O’Buckley, T.K.; Morrow, A.L. Reduction of circulating and selective limbic brain levels of (3α,5α)-3-hydroxy-pregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) following forced swim stress in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2014, 231, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tõnissaar, M.; Herm, L.; Eller, M.; Kõiv, K.; Rinken, A.; Harro, J. Rats with high or low sociability are differently affected by chronic variable stress. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, L.; Groenewald, I.; Stein, D.J.; Wegener, G.; Harvey, B.H. Stress and re-stress increases conditioned taste aversion learning in rats: Possible frontal cortical and hippocampal muscarinic receptor involvement. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 586, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreanez, A.; Arcaya, J.L.; Carrizo, E.; Mosquera, J. Forced swimming test increase superoxide anion positive cells and angiotensin II positive cells in the cerebrum and cerebellum of the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 71, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, D.E.; Pereira, M.O.; Brito, L.C.; Souza, R.S.S.; Almeida, M.C.; Fonseca, A.S.; Santos-Filho, S.D.; Vaisberg, M.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Does acute swimming exercise alter the bioavailability of the radiopharmaceutical technetium-99m methylenediphosphonate (99mTc-MDP) in Wistar rats? Anim. Biol. 2011, 61, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, G.B. Fundamentals of Nuclear Pharmacy, 5th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, M.; Monzen, H.; Futai, R.; Inagaki, K.; Shimoyama, H.; Morikawa, M.; Tomioka, N.; Konishi, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Yuki, R.; et al. Reduction of infracardiac intestinal activity by a small amount of soda water in technetium-99m tetrofosmin myocardial perfusion scintigraphy with adenosine stress. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2008, 15, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, N.D.; Rondogianni, P.E.; Pianou, N.K.; Karampina, P.A.; Vlontzou, E.A.; Datseris, I.E. 99mTc-depreotide in the evaluation of bone infection and inflammation. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2008, 29, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.D.; Freeman, L.M.; Sostman, H.D.; Goodman, L.R.; Woodard, P.K.; Naidich, D.P.; Gottschalk, A.; Bailey, D.L.; Matta, F.; Yaekoub, A.Y.; et al. SPECT in acute pulmonary embolism. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgazzar, A.H. Synopsis of Nuclear Medicine Pathophysiology, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Chan, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Amir, N.; Durr-E-Sabih; Bin Asad, M.H.; Rahim, M.K.; Hussain, M.S.; Murtaza, G.; Shah, S.N. Preparation and radiochemical control of 99mTc labeled blood pool agent for in vivo labelling of the red blood cells. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2014, 71, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Mccommis, K.S.; Goldstein, T.A.; Zhang, H.; Misselwitz, B.; Gropler, R.J.; Zheng, J. Quantification of myocardial blood volume during dipyridamole and doubtamine stress: A perfusion CMR study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2007, 9, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engvall, C.; Ryding, E.; Wirestam, R.; Holtås, S.; Ljunggren, K.; Ohlsson, T.; Reinstrup, P. Human cerebral blood volume (CBV) measured by dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI and 99mTc-RBC SPECT. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2008, 20, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, G.D.; Cooper, G.S.; Chak, A.; Sivak, M.V.J.R.; Chitale, A.A.; Wong, R.C. The yield of bleeding scans in acute lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 39, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, K.; Charest, M. Detection of intrathoracic bleeding by 99mTc-labeled red blood cell SPECT/CT after wedge biopsy of pulmonary angiosarcoma. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2016, 44, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhajosula, S.; Killeen, R.P.; Osborne, J.R. Altered biodistribution of radiopharmaceuticals: Role of radiochemical/pharmaceutical purity, physiological, and pharmacologic factors. Semin Nucl. Med. 2010, 40, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Perales, J.L.; Martínez, A.A. A portable database of adverse reactions and drug interactions with radiopharmaceuticals. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2013, 41, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroz, M.O.; Fonseca, A.S.; Rocha, G.S.; Frydman, J.N.; Rocha, V.C.; Pereira, M.O.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Cinnamomum zeylanicum extract on the radiolabeling of blood constituents and the morphometry of red blood cells: In vitro assay. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007, 66, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydman, J.N.G.; Rocha, V.C.; Benarroz, M.O.; Rocha, G.S.; Pereira, M.O.; Fonseca, A.S.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Assessment of effects of a Cordia salicifolia extract on the radiolabeling of blood constituents and on the morphology of red blood cells. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic, B.; Muftuler, F.Z.; Kilcar, A.Y.; Ichedef, C.; Unak, P. Effects of broccoli extract on biodistribution and labeling blood components with 99mTc-GH. Acta Cir. Bras. 2011, 26, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garcia-Pinto, A.B.; Santos-Filho, S.D.; Carvalho, J.J.; Pereira, M.J.; Fonseca, A.S.; Bernardo-Filho, M. In vitro and in vivo studies of an aqueous extract of Matricaria recutita (German chamomile) on the radiolabeling of blood constituents, on the morphology of red blood cells and on the biodistribution of the radiopharmaceutical sodium pertechnetate. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2013, 9 (Suppl. 1), S49–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). The Radiopharmacy: A Technologist’s Guide. Available online: http://www.eanm.org/content-eanm/uploads/2016/11/tech_radiopharmacy.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2017).
- Sammartano, A.; Scarlattei, M.; Migliari, S.; Baldari, G.; Ruffini, L. Validation of in vitro labeling method for human use of heat-damage red blood cells to detect splenic tissue and hemocateretic function. Acta Biomed. 2019, 90, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M.; Tashiro, M.; Nishi, K.; Mishima, M.; Kawano, K.; Takazono, T.; Saijo, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Imamura, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; et al. Detection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in mice using lung perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography with [99mTc] MAA. Med. Mycol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, F.; Frantellizzi, V.; Drudi, F.M.; Maghella, F.; Liberatore, M. Locally vascularized pelvic accessory spleen. J. Ultrasound 2015, 19, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eeeee-Bonfils, P.K.; Damgaard, M.; Stokholm, K.H.; Nielsen, S.L. 99mTc-albumin can replace 125I-albumin to determine plasma volume repeatedly. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladapo, J.A.; Blecker, S.; Elashoff, M.R.; Federspiel, J.J.; Vieira, D.L.; Sharma, G.; Monane, M.; Rosenberg, S.; Phelps, C.E.; Douglas, P.S. Clinical implications of referral bias in the diagnostic performance of exercise testing for coronary artery disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, O.; Pascual, T.N.; Mercuri, M.; Acampa, W.; Burchert, W.; Flotats, A.; Kaufmann, P.A.; Kitsiou, A.; Knuuti, J.; Underwood, S.R.; et al. Nuclear cardiology practice and associated radiation doses in Europe: Results of the IAEA Nuclear Cardiology Protocols Study (INCAPS) for the 27 European countries. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwozdzinski, K.; Pieniazek, A.; Brzeszczynska, J.; Tabaczar, S.; Jegier, A. Alterations in red blood cells and plasma properties after acute single bout of exercise. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 168376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NPR/Robert Wood Johnson Foundation/Harvard School of Public Health. The Burden of Stress in America. Available online: http://www.rwjf.org/en/library/research/2014/07/the-burden-of-stress-in-america.html (accessed on 8 April 2017).
- Fonseca, A.S.; Frydman, J.N.; Rocha, V.C.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Acetylsalicylic acid decreases the labeling of blood constituents with technetium-99m. Acta Biol. Hung. 2007, 58, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbout, J.P.; Glaser, R. Stress-induced immune dysregulation: Implications for wound healing, infectious disease and cancer. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006, 1, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, K.A.; Edenfield, T.M.; Blumenthal, J.A. Exercise as a treatment for depression and other psychiatric disorders: A review. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2007, 27, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, S.M.; Macaulay, T.E.; Winstead, P.S.; Smith, K.M. Stress-related mucosal disease: Considerations of current medication prophylaxis. Orthopedics 2007, 30, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsugi, M.; Saijo, Y.; Yoshioka, E.; Sato, T.; Horikawa, N.; Gong, Y.; Kishi, R. Relationship between two alternative occupational stress models and arterial stiffness: A cross-sectional study among Japanese workers. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 82, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.R.; Ng, G.Y.; Jones, A.Y.; Pang, M.Y. Cardiovascular stress ınduced by whole-body vibration exercise in ındividuals with chronic stroke. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, R.J.; Eu, P.; Arkles, L.B. Efficiency of labelling of red blood cells with technetium-99m after dipyridamole infusion for thallium-201 stress testing. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 19, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadjeva, V.; Dimov, A.; Georgieva, N. Influence of therapy on the antioxidant status in patients with melanoma. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2008, 33, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şekeroğlu, M.R.; Huyut, Z.; Him, A. The susceptibility of erythrocytes to oxidation during storage of blood: Effects of melatonin and propofol. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierck, H.B.; Darvin, M.E.; Lademann, J.; Reisshauer, A.; Baack, A.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. The influence of endurance exercise on the antioxidative status of human skin. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 3361–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.T.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, K.T.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, N.Y. Protective effects of L-arginine on pulmonary oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses during exhaustive exercise in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.Y.; Lim, S.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Ann, E.S.; Yoon, S. A combination of soy isoflavone supplementation and exercise improves lipid profiles and protects antioxidant defense-systems against exercise-induced oxidative stress in ovariectomized rats. Biofactors 2007, 29, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.A.; Gordon, M.E.; Betros, C.L.; Mckeever, K.H. Apoptosis and antioxidant status are influenced by age and exercise training in horses. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.; Karlsen, A.; Blomhoff, R.; Raastad, T.; Kadi, F. Plasma antioxidant responses and oxidative stress following a soccer game in elite female players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morena, M.; Cristol, J.P.; Senecal, L.; Leray-Moragues, H.; Krieter, D.; Canaud, B. Oxidative stress in hemodialysis patients: Is NADPH oxidase complex the culprit? Kidney Int. Suppl. 2002, 61, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxborough, H.E.; Mercer, C.; Mcmaster, D.; Maxwell, A.P.; Young, I.S. Plasma glutathione peroxidase activity is reduced in haemodialysis patients. Nephron 1999, 81, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soejima, A.; Matsuzawa, N.; Hayashi, T.; Kimura, R.; Ootsuka, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Yamada, A.; Nagasawa, T.; Era, S. Alteration of redox state of human serum albumin before and after hemodialysis. Blood Purif. 2004, 22, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farvin, K.H.S.; Anandan, R.; Kumar, S.H.S.; Shiny, K.S.; Sankar, T.V.; Thankappan, T.K. Effect of squalene on tissue defense system in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 50, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Finkler, M.; Lichtenberg, D.; Pinchuk, I. The relationship between oxidative stress and exercise. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).