The Gyrotrons as Promising Radiation Sources for THz Sensing and Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Advantages of the Gyrotrons as Powerful Radiation Sources for Sensing and Imaging
3. Illustrative Applications of Gyrotrons to Advanced Spectroscopic Techniques, Imaging, and Inspection
3.1. Advanced Spectroscopic Techniques
3.1.1. DNP-NMR and ESR Spectroscopy
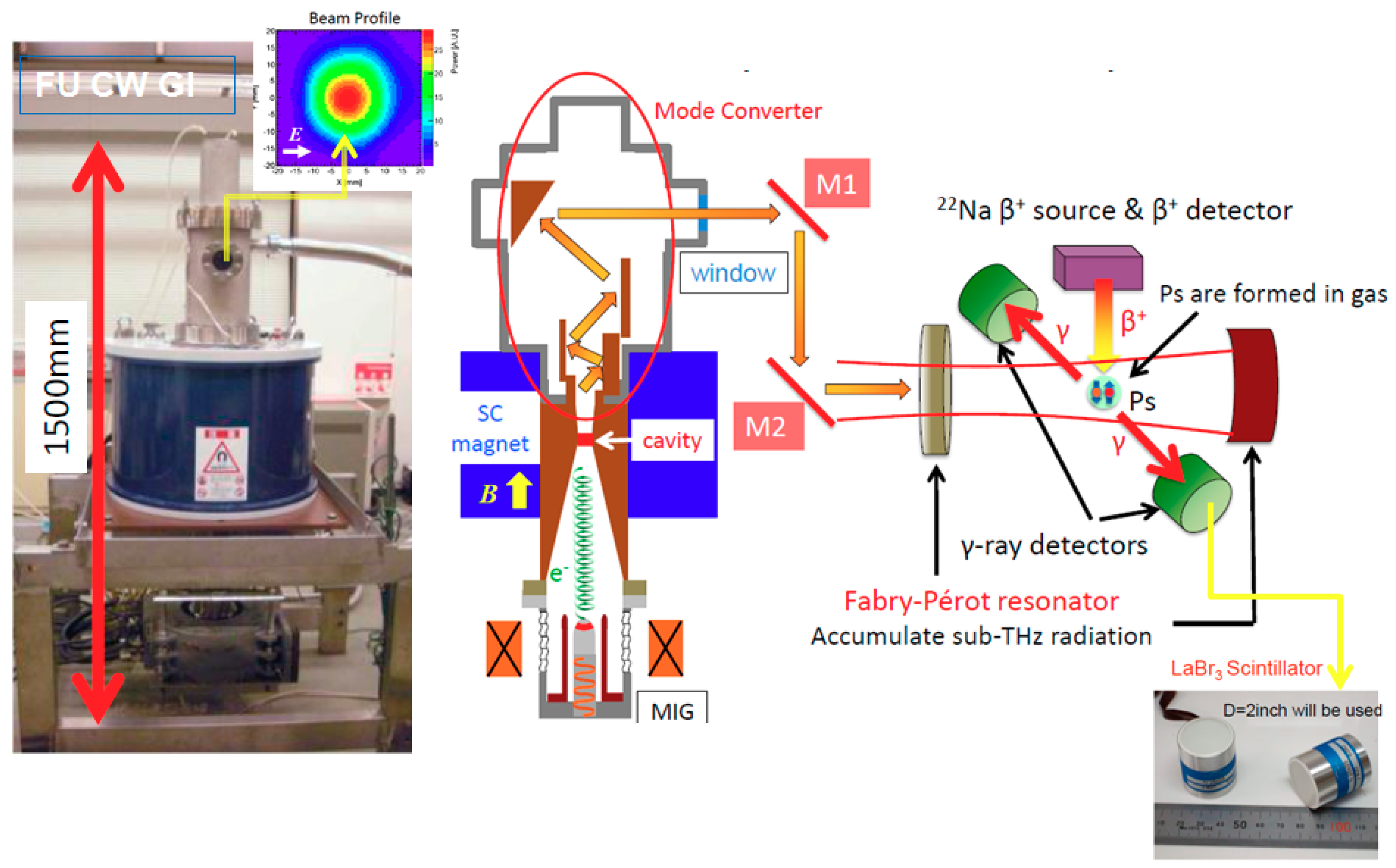
3.1.2. Measurement of the Hyperfine Splitting (HFS) of Positronium
3.1.3. X-ray Detected Magnetic Resonance (XDMR) Spectroscopy
3.1.4. Radioacoustic Spectroscopy Using Gyrotron Radiation
3.2. Remote Atmosphere Sensing Using Gyrotrons
3.3. Remote Detection of Concealed Radioactive Materials
3.4. Imaging, Food Inspection, and Quality Control Using Gyrotron Radiation
3.5. Active Thermal Imaging Using Gyrotrons
3.6. A High-Sensitivity Technique for Time-Resolved Imaging and Measurement of 2D Intensity Profiles of Millimeter-Wave Radiation
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, D.; Zhang, X.-C. Scanning the Issue: T-Ray Imaging, Sensing and Retection. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bründermann, E.; Hübers, H.-W.; Kimmitt, M.F. Terahertz Techniques; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-J.; Nagatsuma, T. Handbook of Terahertz Technologies: Devices and Applications; Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peiponen, K.Z.; Zeitler, A.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M. (Eds.) Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, P.H. THz technology: An overview. Int. J. High Speed Electron. Syst. 2003, 13, 351–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, T.; Kawase, K. Terahertz applications in tomographic imaging and material spectroscopy: A review. In Handbook of Terahertz Technology for Imaging, Sensing and Communications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials: Number 34; Saeedkia, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 493–546. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.-H. Terahertz bio-sensing techniques. In Handbook of Terahertz Technology for Imaging, Sensing and Communications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials: Number 34; Saeedkia, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Ng, B.W.-H.; Abbott, D. Terahertz Imaging for Biomedical Applications: Pattern Recognition and Tomographic Reconstruction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ferguson, B.; Abbott, D. T-ray Imaging and Tomography. J. Biol. Phys. 2003, 29, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickwell, E.; Wallace, V.P. Biomedical applications of terahertz technology (Topical Review). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, R301–R310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-C.; Jin, B.B. Terahertz applications in the pharmaceutical industry. In Handbook of Terahertz Technology for Imaging, Sensing and Communications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials: Number 34; Saeedkia, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 579–614. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-H.; Lee, W. Food inspection system using Terahertz imaging. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2014, 56, 1211–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsah-Hejri, L.; Hajeb, P.; Ara, P.; Ehsani, R.J. A Comprehensive Review on Food Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1563–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Lee, S.; Rao, R.M.; Slamani, M.-L.; Varshney, P.K. Imaging for concealed weapon detection: A tutorial overview of development in imaging sensors and processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.A. A review of terahertz sources. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 374001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizov, F.; Rogalski, A. THz detectors. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2010, 34, 278–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.S.; Vitiello, M.S.; Linfield, E.H.; Davies, A.G.; Hoffmann, M.C.; Booske, J.; Paoloni, C.; Gensch, M.; Weightman, P.; Williams, G.P.; et al. The 2017 terahertz science and technology roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.S.; Schwarz, M. Accelerator-Based THz Radiation Sources. In Synchrotron Light Sources and Free-Electron Lasers; Jaeschke, E., Khan, S., Schneider, J., Hastings, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 83–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booske, J.H. Plasma physics and related challenges of millimeter wave-to-terahertz and high power microwave generation. Phys. Plasmas 2008, 15, 055502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idehara, T.; Saito, T.; Ogawa, I.; Mitsudo, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Sabchevski, S. The potential of the gyrotrons for development of the sub-terahertz and the terahertz frequency range—A review of novel and prospective applications. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumm, M. State-of-the-art of high power gyro-devices and free electron masers. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2020, 41, 1–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, U.; Singh, T.P.; Sinha, A.K. A Review on the Applications of High Power, High Frequency Microwave Source: Gyrotron. J. Fusion Energy 2011, 30, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Mitsudo, S.; Sabchevski, S.; Glyavin, M.; Ogawa, I. Gyrotron FU series—Current status of development and applications. Int. J. Vac. 2001, 62, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, R.J. Development of terahertz gyrotrons for spectroscopy at MIT. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyavin, M.Y.; Idehara, T.; Sabchevski, S.P. Development of THz Gyrotrons at IAP RAS and FIR UF and Their Applications in Physical Research and High-Power THz Technologies. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Sabchevski, S.P. Development and Application of Gyrotrons at FIR UF. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2018, 46, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Ogawa, I.; Shimizu, Y.; Tatsukawa, T. Higher Harmonic Operations of Submillimeter Wave Gyrotrons (Gyrotron FU Series). Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 1998, 19, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, M.K.; Bajaj, V.S.; Griffin, R.G.; Temkin, R.J. Continuous-wave operation of a 460-GHz second harmonic gyrotron oscillator. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2006, 34, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kartikeyan, M.V.; Borie, E.; Thumm, M. A 250 GHz, 50 W, CW second harmonic gyrotron. Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2007, 28, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozkin, M.V.; Glyavin, M.Y.; Denisov, G.G.; Luchinin, A.G. A high-efficiency second-harmonic gyrotron with a depressed collector. Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2008, 29, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Yamada, N.; Ikeuti, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Ikeda, R.; Ogawa, I.; Idehara, T.; Manuilov, V.N.; Shimozuma, T.; et al. Generation of high power sub-terahertz radiation from a gyrotron with second harmonic oscillation. Phys. Plasmas 2012, 19, 063106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatematsu, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Idehara, T.; Kawase, T.; Ichioka, R.; Ogawa, I.; Saito, T.; Fujiwara, T. Development of second harmonic gyrotrons, Gyrotron FU CW GII and Gyrotron FU CW GIII, equipped with internal mode converters. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2014, 35, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratman, V.L.; Kalynov, Y.K.; Manuilov, V.N. Large-orbit gyrotron operation in the terahertz frequency range. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalynov, Y.; Manuilov, V.; Fiks, A.; Zavolskiy, N. Powerful continuous-wave sub-terahertz electron maser operating at the 3rd cyclotron harmonic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 213502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Ogawa, I.; Mitsudo, S.; Iwata, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Itakura, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Zapevalov, V.E.; et al. A high harmonic gyrotron with an axis-encircling electron beam and a permanent magnet. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2004, 32, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapevalov, V.E.; Manuilov, V.N.; Malygin, O.V.; Tsimring, S.E. High-power twin-beam gyrotrons operating at the second gyrofrequency harmonic. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 1994, 37, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyavin, M.Y.; Luchinin, A.G.; Golubiatnikov, G.Y. Generation of 1.5-kW, 1-THz Coherent Radiation from a Gyrotron with a Pulsed Magnetic Field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Ogawa, I.; Mori, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Mitsudo, S.; Saito, T. A THz Gyrotron FU CW III with a 20 T superconducting magnet. J. Plasma Fusion Res. Ser. 2009, 8, 1508–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Glyavin, M.Y.; Ginzburg, N.S.; Goldenberg, A.L.; Luchinin, A.G.; Denisov, G.G.; Manuilov, V.N.; Vladimir, E.; Zapevalov, V.E.; Zotova, I.V. THz Gyrotrons: Status and Possible Optimizations. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.T.; Griffin, R.G.; Hu, K.N.; Joo, C.G.; Joye, C.D.; Mastovsky, I.; Shapiro, M.A.; Sirigiri, J.R.; Temkin, R.J.; Torrezan, A.C.; et al. Continuous-wave Submillimeter-wave Gyrotrons. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2006, 6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.T.; Griffin, R.G.; Hu, K.N.; Joo, C.G.; Joye, C.D.; Sirigiri, J.R.; Temkin, R.J.; Torrezan, A.C.; Woskov, P.P. Spectral characteristics of a 140-GHz long-pulsed gyrotron. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2007, 35, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glyavin, M.Y.; Chirkov, A.V.; Denisov, G.G.; Fokin, A.P.; Kholoptsev, V.V.; Kuftin, A.N.; Luchinin, A.G.; Golubyatnikov, G.Y.; Malygin, V.I.; Morozkin, M.V.; et al. Experimental tests of a 263 GHz gyrotron for spectroscopic applications and diagnostics of various media. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 054705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, S.; Braunmueller, F.; Tran, T.M.; Hogge, J.-P.; Genoud, J.; Tran, M.Q. High-Power THz-Waves using gyrotrons: New physics results. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Idehara, T.; Mitsudo, S.; Ogawa, I. Development of High-Frequency, Highly Stable Gyrotrons as Millimeter to Submillimeter Wave Radiation Sources. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2004, 32, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, A.; Tsvetkov, A.; Manuilov, V.; Sedov, A.; Bozhkov, V.; Genneberg, V.; Movshevich, B.; Glyavin, M. Control of sub-terahertz gyrotron frequency by modulation-anode voltage: Comparison of theoretical and experimental results. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 124705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Matsuki, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Tatematsu, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Idehara, T. Further Characterization of 394-GHz Gyrotron FU CW GII with Additional PID Control System for 600-MHz DNP-SSNMR Spectroscopy. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2016, 37, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryan, E.M.; Idehara, T.; Kuleshov, A.N.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Matsuki, Y.; Fujiwara, T. Stabilization of Gyrotron Frequency by PID Feedback Control on the Acceleration Voltage. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryan, E.M.; Idehara, T.; Kuleshov, A.N.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Matsuki, Y.; Fujiwara, T. Simultaneous Stabilization of Gyrotron Frequency and Power by PID Double Feedback Control on the Acceleration and Anode Voltages. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2017, 38, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, A.; Glyavin, M.; Golubiatnikov, G.; Lubyako, L.; Morozkin, M.; Movschevich, B.; Tsvetkov, A.; Denisov, G. High-power sub-terahertz source with a record frequency stability at up to 1 Hz. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brand, F.G. Tunable gyrotrons. In Infrared and Millimeter Waves; Button, K.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 14, pp. 371–408. [Google Scholar]
- Sabchevski, S.P.; Idehara, T. A Numerical Study on Finite-Bandwidth Resonances of High-Order Axial Modes (HOAM) in a Gyrotron Cavity. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 628–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabchevski, S.; Idehara, T. Resonant Cavities for Frequency Tunable Gyrotrons. Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2008, 29, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.D.; Brand, G.F.; Idehara, T. A 150–600 GHz step-tunable gyrotron. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 5250–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Tatsukawa, T.; Brand, G.F. Rapid frequency step-switching in submillimeter wave gyrotrons (Gyrotrons FU III and FU IV). Phys. Plasmas 1999, 6, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapevalov, V.E.; Bogdashov, A.A.; Chirkov, A.V.; Denisov, G.G.; Kuftin, A.N.; Lygin, V.K.; Moiseev, M.A. Optimization of the frequency step tunable 105–170 GHz 1 MW gyrotron prototype. In Proceedings of the Twenty Seventh International Conference on Infrared and Millimeter Waves, San Diego, CA, USA, 26 September 2002; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samartsev, A.; Avramidis, K.A.; Gantenbein, G.; Dammertz, G.; Thumm, M.; Jelonnek, J. Efficient Frequency Step-Tunable Megawatt-Class D-Band Gyrotron. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 327–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, M.K.; Bajaj, V.S.; Griffin, R.G.; Kreischer, K.E.; Mastovsky, I.; Shapiro, M.A.; Sirigiri, J.R.; Temkin, R.J. Second harmonic operation at 460 GHz and broadband continuous frequency tuning of a gyrotron oscillator. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2005, 52, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, T.H.; Idehara, T.; Ogawa, I.; Agusu, L.; Kobayashi, S. Frequency tunable gyrotron using backward wave components. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 063304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrezan, A.C.; Han, S.-T.; Mastovsky, I.; Shapiro, M.A.; Sirigiri, J.R.; Temkin, R.J.; Barnes, A.B.; Griffin, R.G. Continuous—Wave Operation of a Frequency-Tunable 460-GHz Second-Harmonic Gyrotron for Enhanced Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2010, 38, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Kosuga, K.; Agusu, L.; Ikeda, R.; Ogawa, I.; Saito, T.; Matsuki, Y.; Ueda, K.; Fujiwara, T. Continuously Frequency Tunable High Power Sub-THz Radiation Source-Gyrotron FU CW VI for 600-MHz DNP-NMR Spectroscopy. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2010, 31, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, Y.; Idehara, T.; Fukazawa, J.; Fujiwara, T. Advanced instrumentation for DNP-enhanced MAS NMR for higher magnetic fields and lower temperatures. J. Magn. Resonance 2016, 264, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thankamony, A.S.L.; Wittmann, J.J.; Kaushik, M.; Corzilius, B. Dynamic nuclear polarization for sensitivity enhancement in modern solid-state NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Resonance Spectrosc. 2017, 102, 120–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.; Soundararajan, M.; Cuanillon, P.H.; Braunmueller, F.; Alberti, S.; Ansermet, J.-P.H. Dynamic nuclear polarization by frequency modulation of a tunable gyrotron of 260 GHz. J. Magn. Resonance 2016, 262, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idehara, T.; Pereyaslavets, M.; Nishida, N.; Yoshida, K.; Ogawa, I. Frequency Modulation in a Submillimeter-Wave Gyrotron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Khutoryan, E.M.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kuleshov, A.N.; Dumbrajs, O.; Matsuki, Y.; Fujiwara, T. High-speed frequency modulation of a 460-GHz gyrotron for enhancement of 700-MHz DNP-NMR spectroscopy. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, L.R.; Gerfen, G.J.; Temkin, R.J.; Singel, D.J.; Griffin, R. Dynamic Nuclear Polarization with a Cyclotron Resonance Maser at 5 T. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 3561–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Sabchevski, S. Development and Applications of High-Frequency Gyrotrons in FIR FU Covering the sub-THz to THz Range. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 33, 667–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehara, T.; Sabchevski, S.P. Gyrotrons for High-Power Terahertz Science and Technology at FIR UF. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2017, 38, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruker Announces World’s First 1.2 GHz High-Resolution Protein NMR Data. Available online: https://ir.bruker.com/press-releases/press-release-details/2019/Bruker-Announces-Worlds-First-12-GHz-High-Resolution-Protein-NMR-Data/default.aspx (accessed on 14 December 2019).
- Idehara, T.; Glyavin, M.; Kuleshov, A.; Sabchevski, S.; Manuilov, V.; Zaslavsky, V.; Zotova, I.; Sedov, A. A novel THz-band double-beam gyrotron for high-field DNP-NMR spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 094708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudo, S.; Glyavin, M.; Khutoryan, E.; Bandurkin, I.; Saito, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Manuilov, V.; Zotova, I.; Fedotov, A.; Kuleshov, A.; et al. An Experimental Investigation of a 0.8 THz Double-Beam Gyrotron. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2019, 40, 1114–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudo, S.; Umegaki, C.; Hiiragi, K.; Narioka, M.; Fujii, Y.; Tatematsu, Y. Development of a millimeter wave pulsed ESR system by using a gyrotron as a light source. In Proceedings of the 2016 41st International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz waves (IRMMW-THz), Copenhagen, Denmark, 25–30 September 2016; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Suehara, T.; Namba, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Saito, H.; Idehara, T.; Ogawa, I.; Sabchevski, S. Direct Measurement of Positronium Hyper Fine Structure—A New Horizon of Precision Spectroscopy Using Gyrotrons. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 3, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Suehara, T.; Namba, T.; Asai, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Saito, H.; Ogawa, I.; Idehara, T.; Sabchevski, S. Direct observation of the hyperfine transition of ground-state positronium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 253401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogalev, A.; Goulon, J.; Goujon, J.; Wilhelm, F.; Ogawa, I.; Idehara, T. X-ray detected magnetic resonance at sub-THz frequencies using a high-power gyrotron source. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 33, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulon, J.; Rogalev, A.; Wilhelm, F.; Goujon, G. X-ray detected magnetic resonance: A new spectroscopic tool. In Magnetism and Synchrotron Radiation; Beaurepaire, E., Bulou, H., Scheurer, F., Jean-Paul, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 191–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshelev, M.A.; Tsvetkov, A.I.; Morozkin, M.V.; Glyavin, M.Y.; Tretyakov, M.Y. Molecular gas spectroscopy using radioacoustic detection and high-power coherent subterahertz radiation sources. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 2017, 331, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manheimer, W. A role for high power millimeter wave sources in atmospheric remote sensing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Plasma Sciences (ICOPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–9 June 1993; p. 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novel Gyro-TWA Amplifier for High Power Mm-Wave Radar Remote Sensing. Available online: https://gtr.ukri.org/projects?ref=ST%2FK006673%2F1 (accessed on 14 December 2019).
- He, W.; Donaldson, C.R.; Zhang, L.; McElhinney, F.; Yin, H.; Garner, J.R.; Ronald, K.; Cross, A.W.; Phelps, A.D.R. Experimental test of a W-band gyro-TWA for cloud radar applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 46th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), London, UK, 4–6 October 2016; pp. 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granatstein, V.L.; Nusinovich, G.S. Detecting excess ionizing radiation by electromagnetic breakdown of air. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 063304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusinovich, G.S.; Pu, R.; Antonsen, T.M.; Sinitsyn, O.V.; Rodgers, J.; Mohamed, A.; Silverman, J.; Al-Sheikhly, M.; Dimant, Y.S.; Milikh, G.M.; et al. Development of THz-range gyrotrons for detection of concealed radioactive materials. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2011, 32, 380–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyavin, M.Y.; Luchinin, A.G.; Bogdashov, A.A.; Manuilov, V.N.; Morozkin, M.V.; Rodin, Y.V.; Denisov, G.G.; Kashin, D.; Rogers, G.; Romero-Talamas, C.A.; et al. Experimental Study of the Pulsed Terahertz Gyrotron with Record-Breaking Power and Efficiency Parameters. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2014, 56, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusinovich, G.S.; Sprangle, P.; Romero-Talamas, C.A.; Granatstein, V.L. Range, resolution and power of THz systems for remote detection of concealed radioactive materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 083303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusinovich, G.S.; Sprangle, P.; Semenov, V.E.; Dorozhkina, D.S.; Glyavin, M.Y. On the sensitivity of terahertz gyrotron based systems for remote detection of concealed radioactive materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 124912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyavin, M.Y.; Luchinin, A.G.; Manuilov, V.N.; Morozkin, M.V.; Bogdashov, A.A.; Gachev, I.G.; Sedov, A.S.; Pu, P.; Nusinovich, G.S.; Granatshtein, V.L. Development of a high-power pulsed subterahertz gyrotron for remote detection of sources of ionizing radiation. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2012, 54, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, U.; Kumar, A.; Sinha, A.K. A Feasibility Study of Beam-Wave Interaction in 670 GHz Gyrotron for Radioactive Material Detection Application. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 076705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yu, D.; Sawant, A.; Choe, M.S.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, E. Remote detection of radioactive material using high-power pulsed electromagnetic radiation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawase, M. Application of Terahertz Waves to Food Science. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.K.; Choi, S.W.; Han, S.T.; Woo, D.H.; Chun, H.S. Detection of foreign bodies in foods using continuous wave terahertz imaging. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, A.; Zahid, A.; Fan, D.; Yang, X.; Imran, M.A.; Alomainy, A.; Abbasi, Q.H. State-of-the-art in terahertz sensing for food and water security–A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.-T.; Torrezan, A.C.; Sirigiri, J.R.; Shapiro, M.A.; Temkin, R.J. Active real-time imaging system employed with a CW 460-GHz gyrotron and a pyroelectric array camera. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz 2009), Busan, Korea, 21–25 September 2009; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.T.; Park, W.K.; Chun, H.S. Development of a compact sub-terahertz gyrotron and its application to t-ray real-time imaging for food inspection. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz 2012), Wollongong, Australia, 23–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S. Compact sub-THz gyrotrons for real-time T-ray imaging. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 14th International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IVEC), Paris, France, 21–23 May 2013; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.T.; Torrezan, A.C.; Sirigiri, J.R.; Shapiro, M.A.; Temkin, R.J. Real-time, T-ray imaging using a sub-terahertz gyrotron. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2012, 60, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.T.; Lee, W.J.; Park, K.S.; Choi, S.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Yoo, J.S. Application of T-ray gyrotron developed for real-time non-destructive inspection to enhanced regeneration of cells. In Proceedings of the 2015 40th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz waves (IRMMW-THz 2015), Hong Kong, China, 23–28 August 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Kim, J.I.; Jeon, S.G.; Kim, J.; Park, K.K.; Oh, C.H. Enhanced continuous-wave terahertz imaging with a horn antenna for food inspection. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 33, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.P.; Ko, H.; Kim, N.; Lee, W.H.; Moon, K.; Lee, I.M.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, W.; Han, S.T.; et al. Real-time continuous-wave terahertz line scanner based on a compact 1× 240 InGaAs Schottky barrier diode array detector. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 28977–28983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, R.; Fliflet, A.; Smith, G.; Andreadis, T.; Hornstein, M.K.; Lombardi, M.; Bowles, J.; Gold, S.; Lewis, D.; Kidwell, D. Long-range thermal imaging using a millimeter-wave source. In Proceedings of the 33rd IEEE International Conference on Plasma Science (ICOPS 2006), Traverse City, MI, USA, 4–8 June 2006; p. 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, M.K.; Hubbard, R.F.; Smith, G.; Fliflet, A.W.; Lombardi, M.; Gold, S.H.; Lewis, D., III; Andreadis, T.D. Demonstration experiments for active thermal imaging using a millimeter-wave source (ATIMS). In Proceedings of the 33rd IEEE International Conference on Plasma Science (ICOPS 2006), Traverse City, MI, USA, 4–8 June 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitlin, M.S.; Glyavin, M.Y.; Fedotov, A.E.; Tsvetkov, A.I. Imaging of Spatial Distributions of the Millimeter Wave Intensity by Using the Visible Continuum Radiation from a Discharge in a Cs–Xe Mixture. Part II: Demonstration of Application Capabilities of the Technique. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2017, 43, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitlin, M.S.; Golovanov, V.V.; Spivakov, A.G.; Tsvetkov, A.I.; Zelenogorskiy, V.V. Time-resolved imaging of millimeter waves using visible continuum from the positive column of a Cs–Xe dc discharge. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 063301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

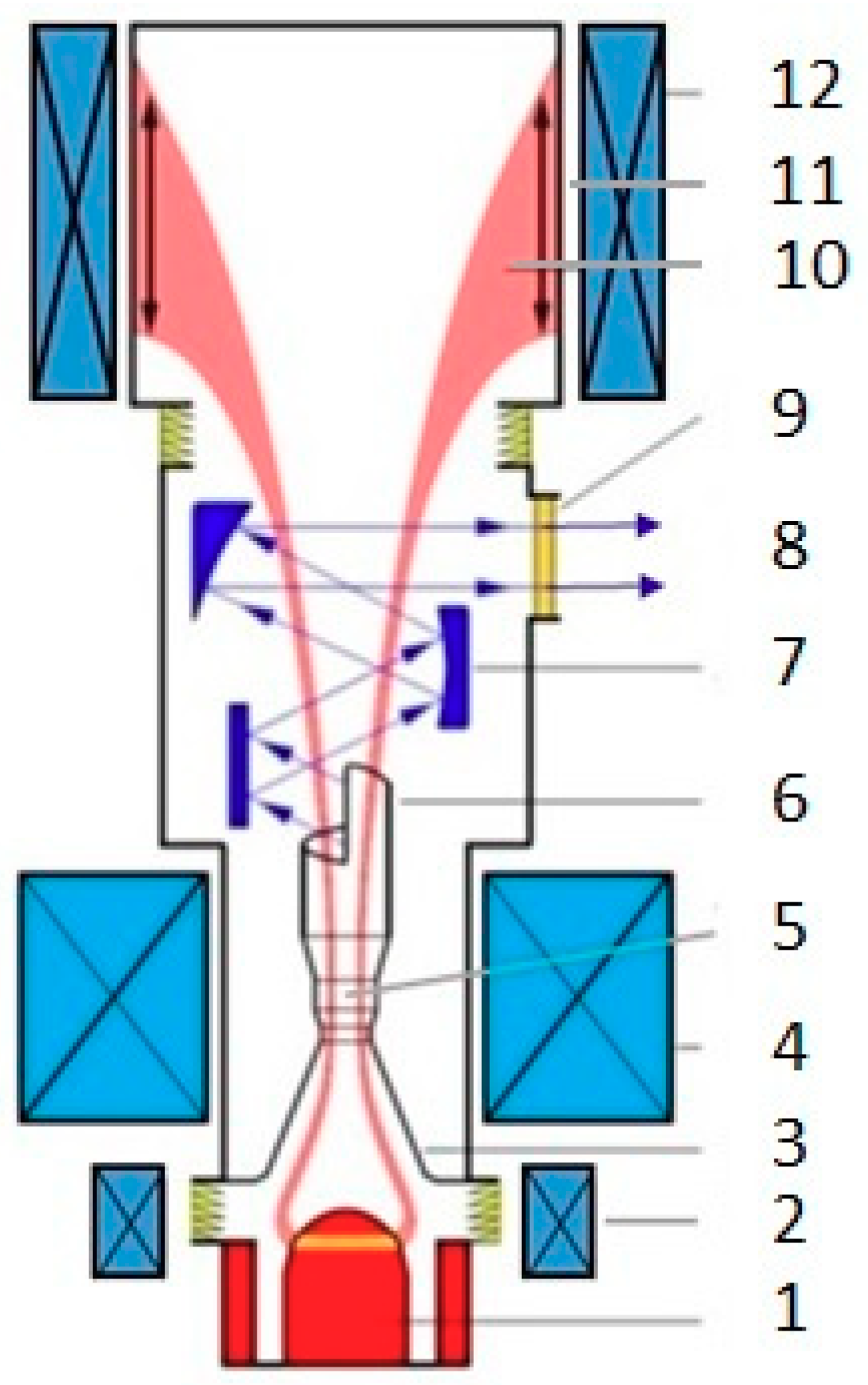






| Characteristic Features of the Gyrotrons and Their Radiation |
|---|
| High-power (from Watts to kW) 1 radiation in both pulsed and CW (continuous wave) regimes. |
| Coherent radiation with stable spectral characteristics (narrow spectral line width; small down- and up-shift of the frequency during the pulse and long operation times; possibilities for phase locking). |
| Stable output parameters (power and frequency) through appropriate stabilization (e.g., PID control) |
| Step-wise and smooth continuous frequency tunability in wide frequency bands. |
| Possibility to modulate the output power and frequency. |
| Possibility to deliver Gaussian beam output using internal or external quasi-optical converters. |
| Possibility for transmission of the generated radiation by waveguides (e.g., corrugated waveguides with low losses) or quasi-optical system of reflectors and phase-correcting mirrors. |
| Possibility to focus and steer the generated wave beam by quasi-optical elements. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idehara, T.; Sabchevski, S.P.; Glyavin, M.; Mitsudo, S. The Gyrotrons as Promising Radiation Sources for THz Sensing and Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030980
Idehara T, Sabchevski SP, Glyavin M, Mitsudo S. The Gyrotrons as Promising Radiation Sources for THz Sensing and Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030980
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdehara, Toshitaka, Svilen Petrov Sabchevski, Mikhail Glyavin, and Seitaro Mitsudo. 2020. "The Gyrotrons as Promising Radiation Sources for THz Sensing and Imaging" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030980
APA StyleIdehara, T., Sabchevski, S. P., Glyavin, M., & Mitsudo, S. (2020). The Gyrotrons as Promising Radiation Sources for THz Sensing and Imaging. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030980







