The Generalized Skin Depth for Polarized Porous Media Based on the Cole–Cole Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Calculation of the Generalized Skin Depth of Polarized Media
2.1. The Cole–Cole Model
2.2. Calculation of the Generalized Skin Depth with Polarized Media
3. Generalized Skin Depth Characteristic Analysis Based on the Cole–Cole Model
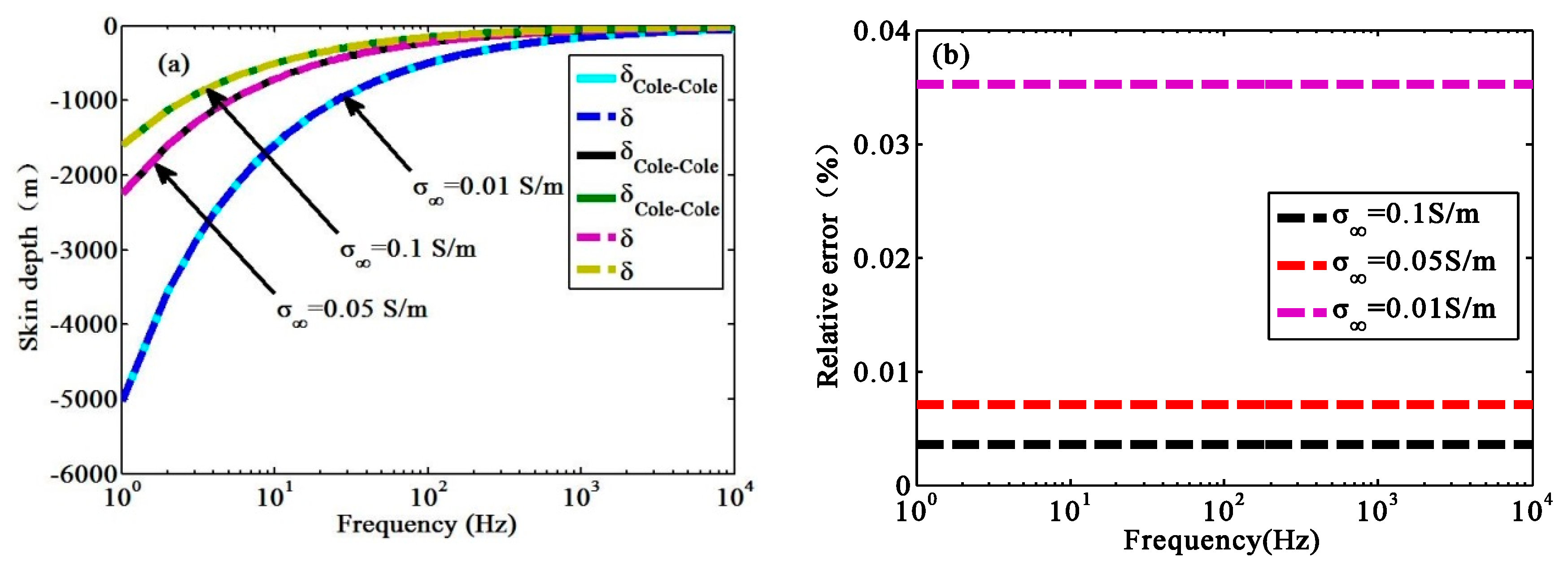
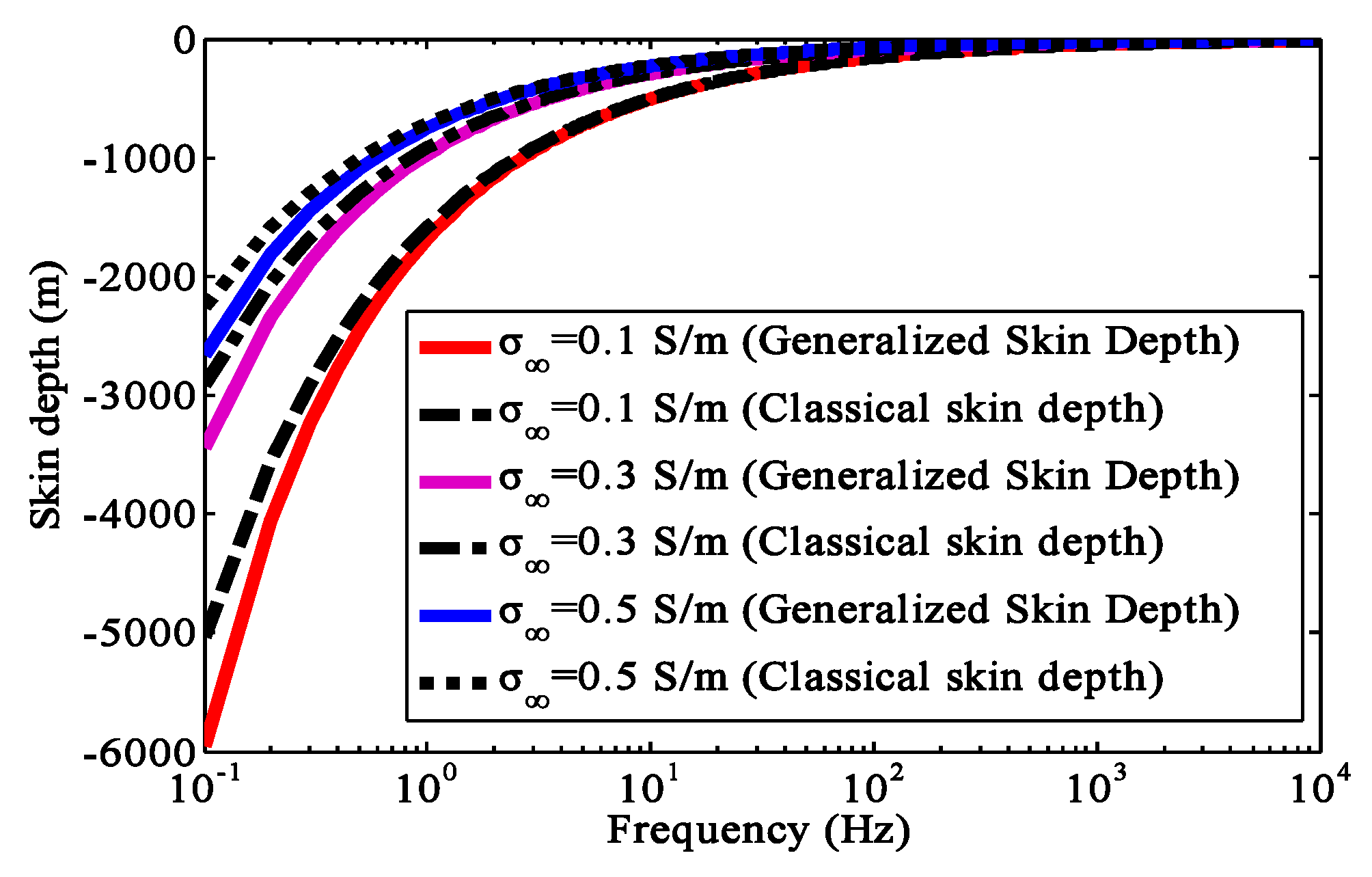
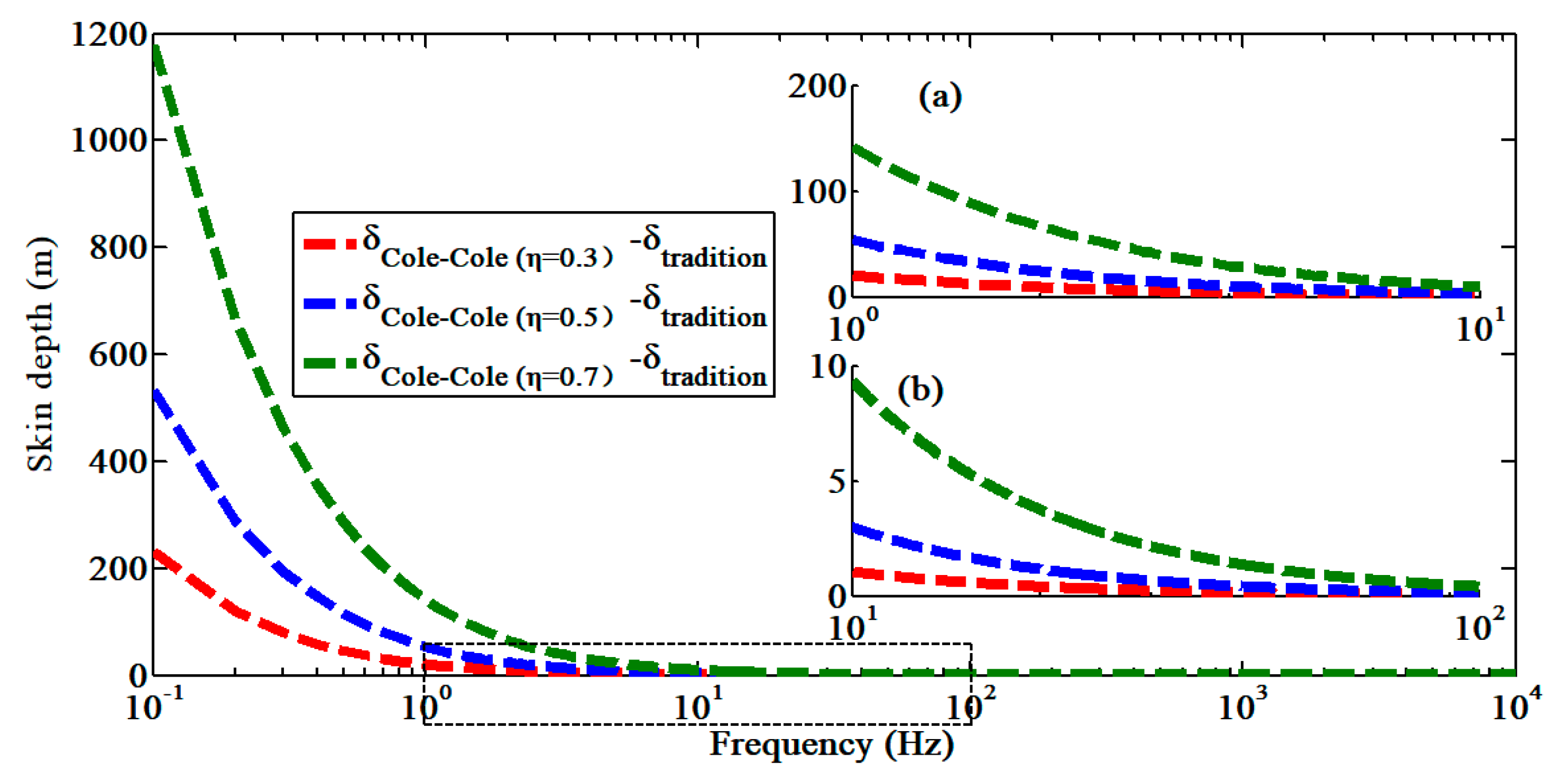
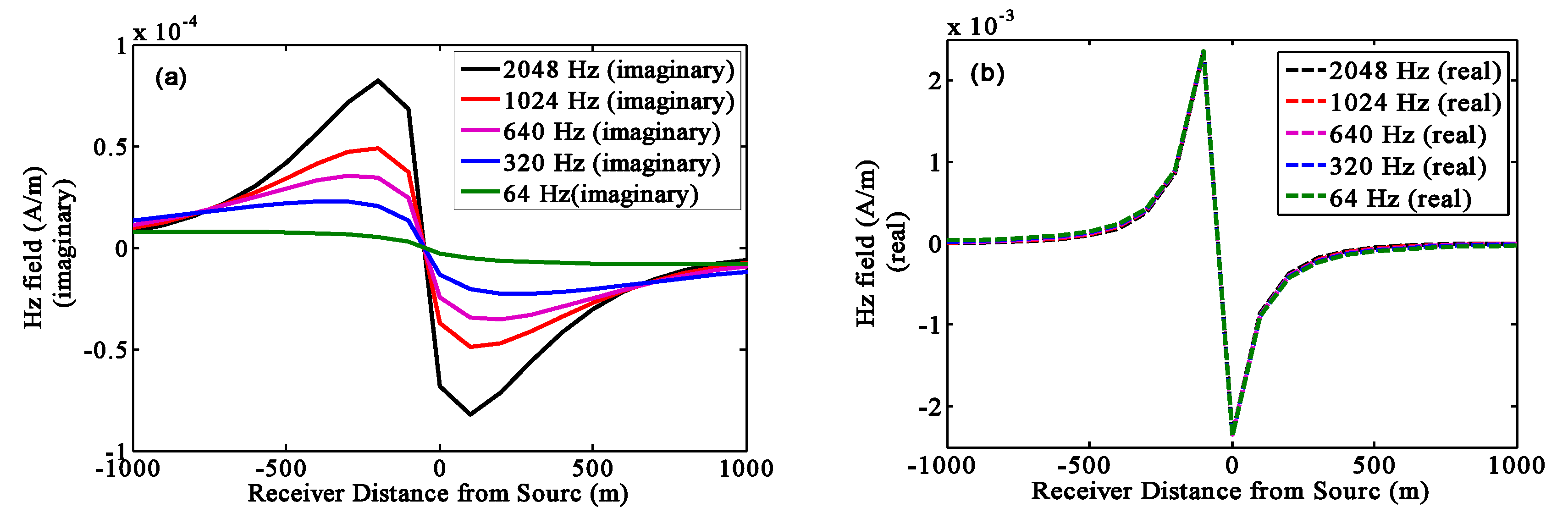
3.1. Verification of the Generalized Skin Depth Formula
3.2. Effect of the Polarization Parameters on the Generalized Skin Depth
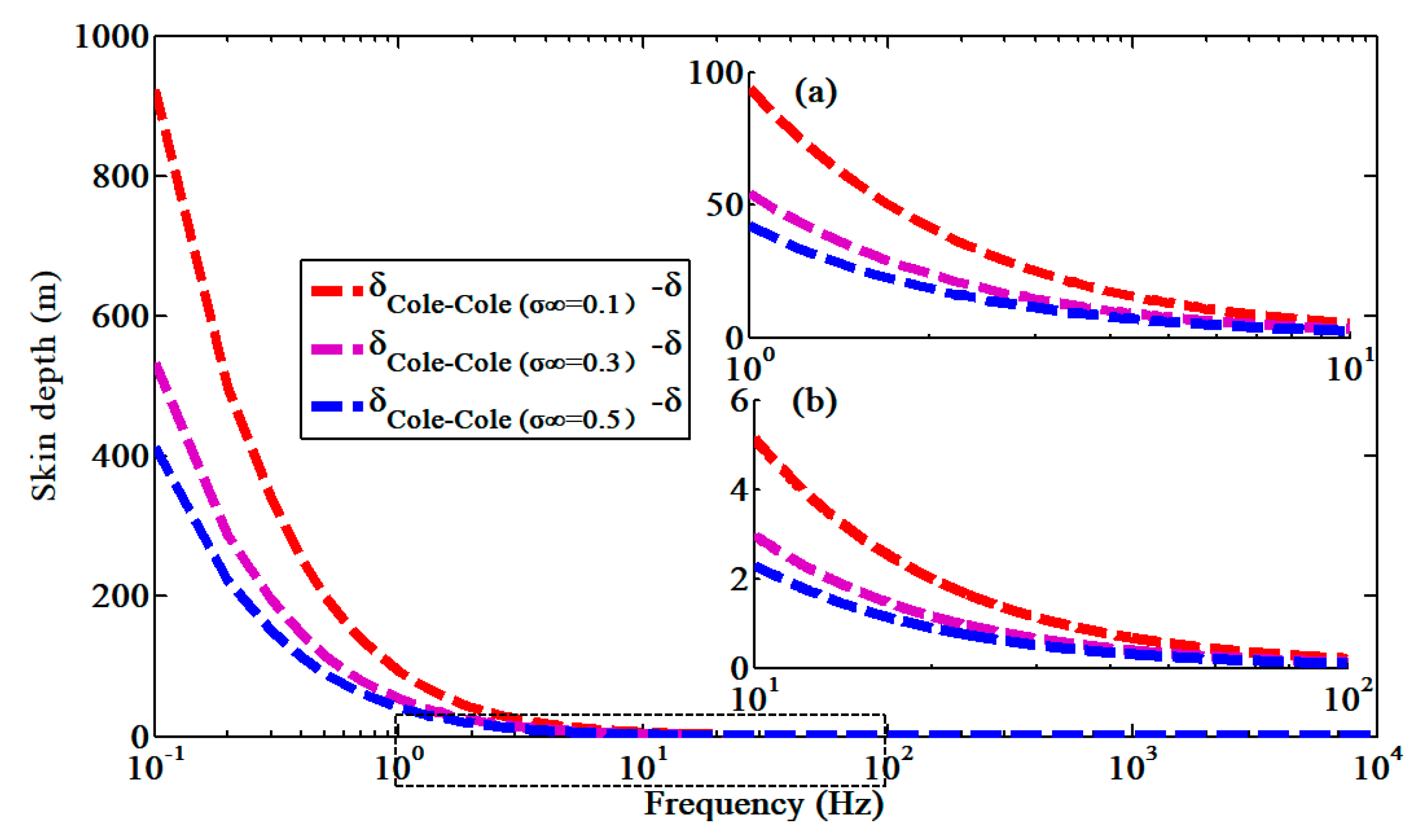
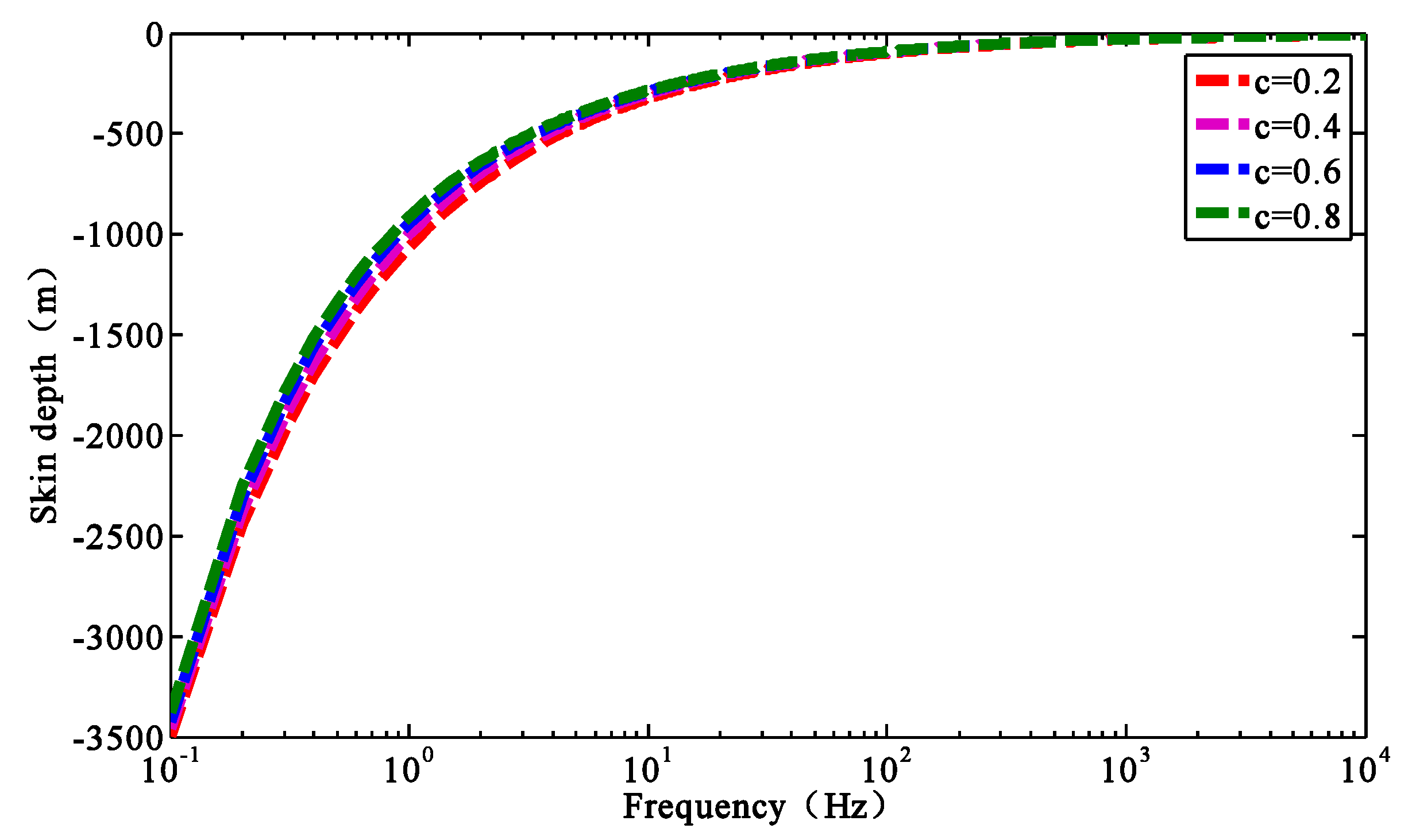
3.2.1. Influence of the Conductivity on the Generalized Skin Depth
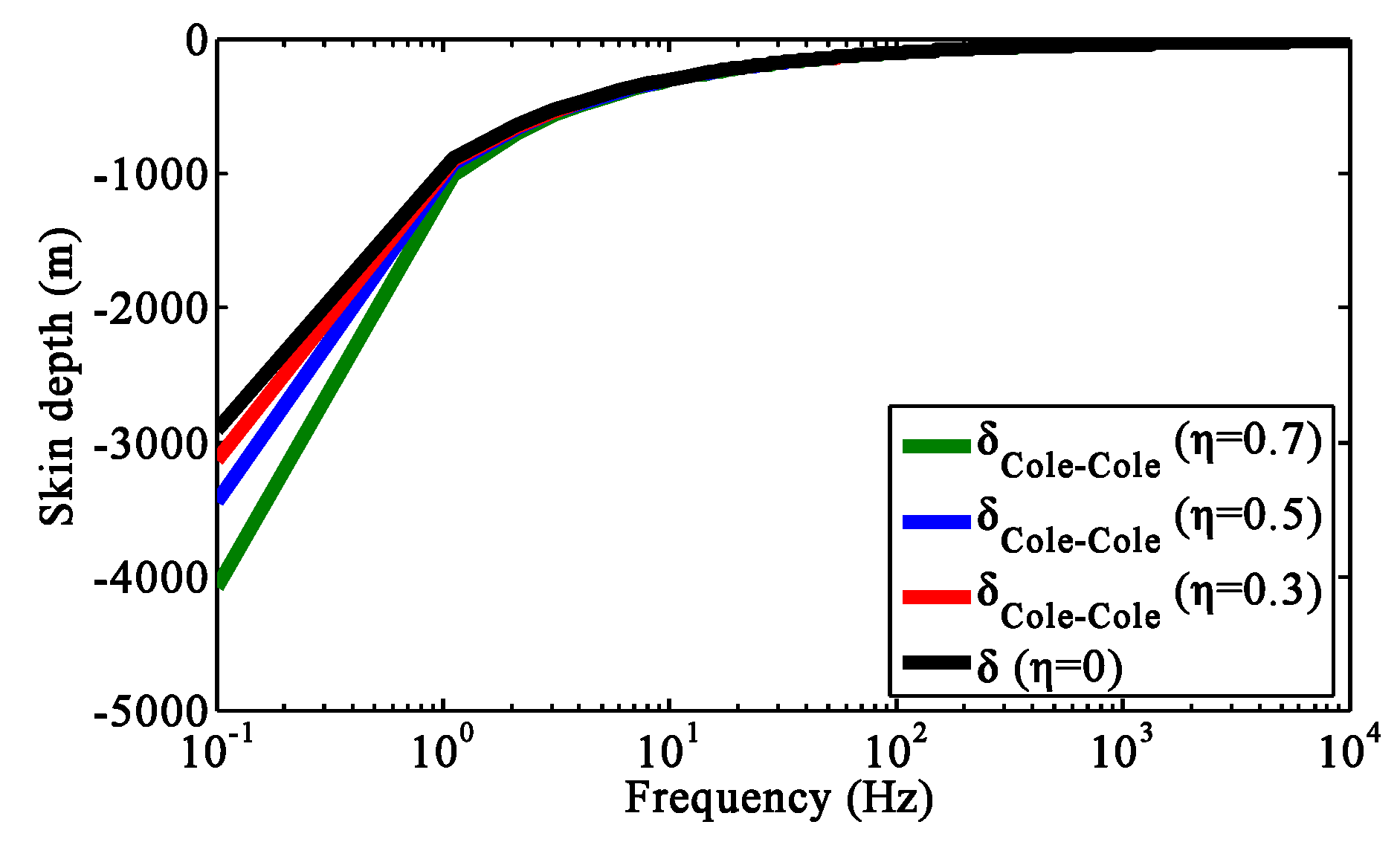
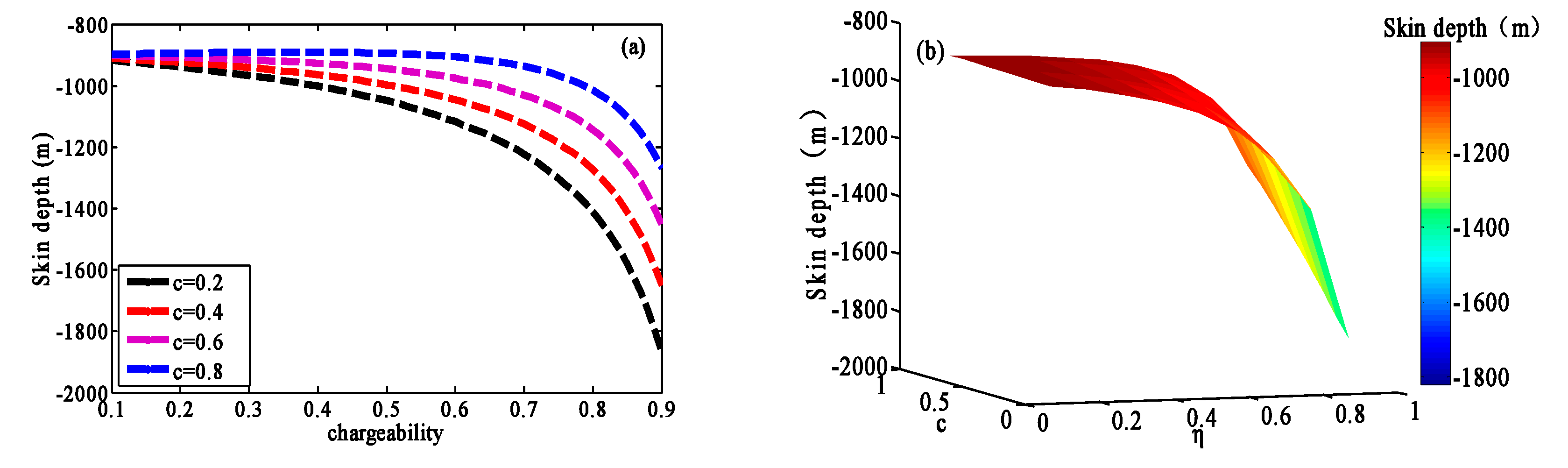
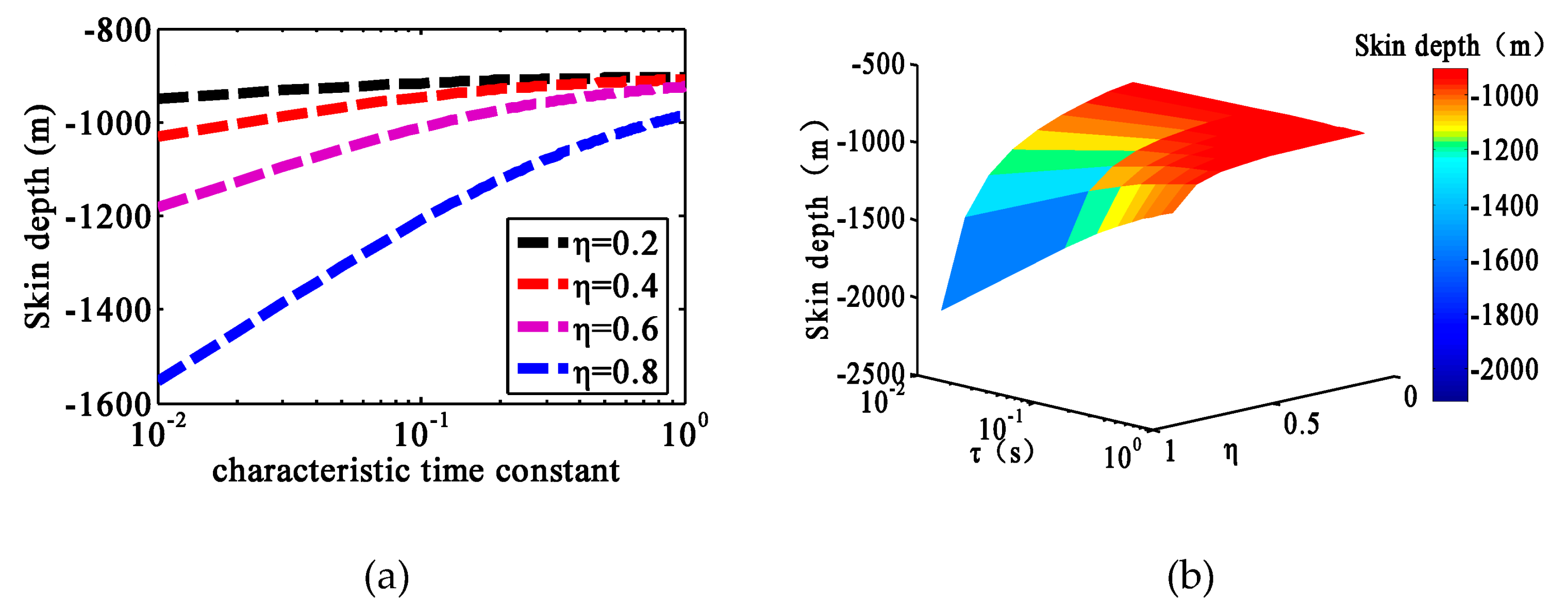
3.2.2. Effect of the Chargeability on the Generalized Skin Depth
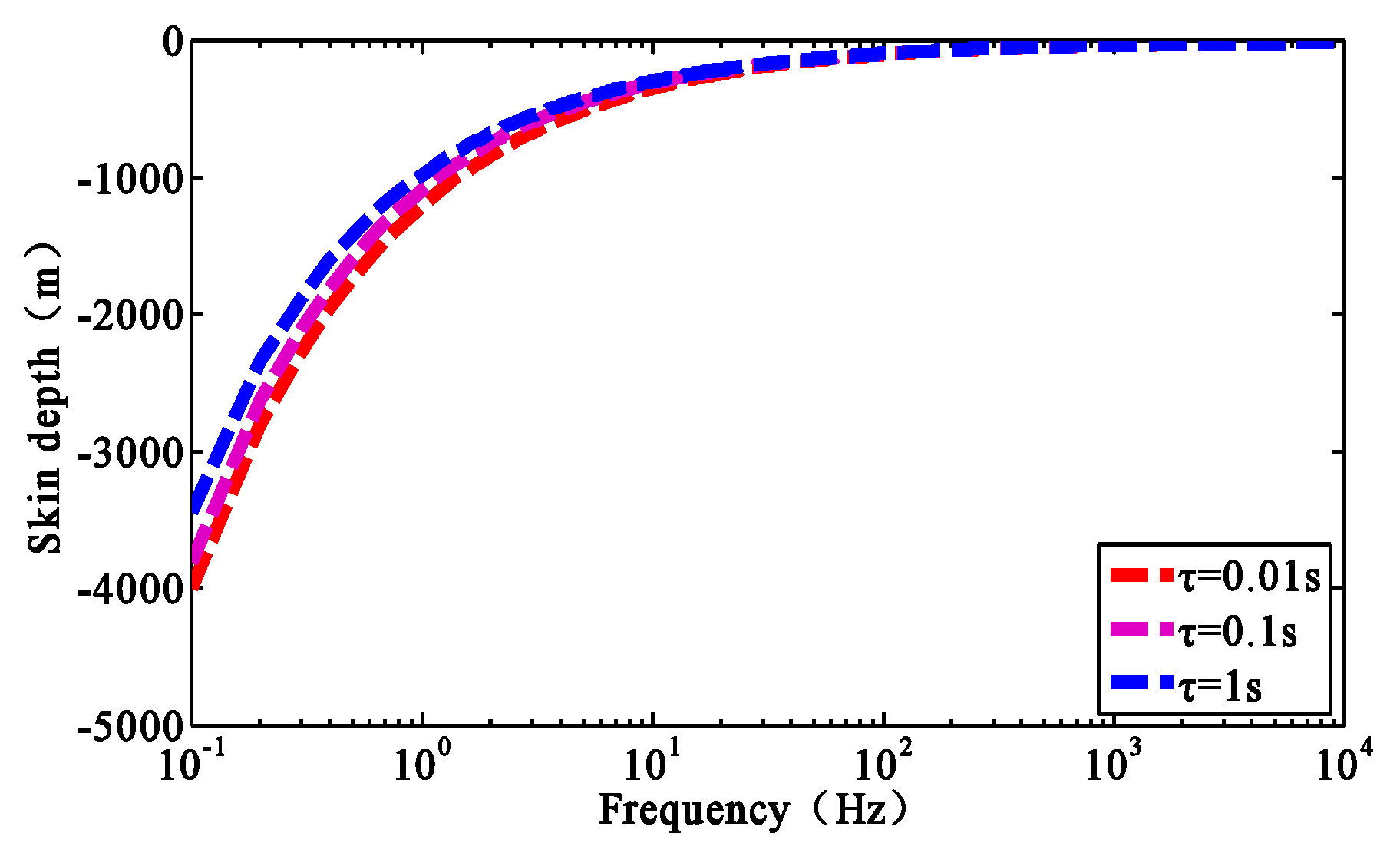
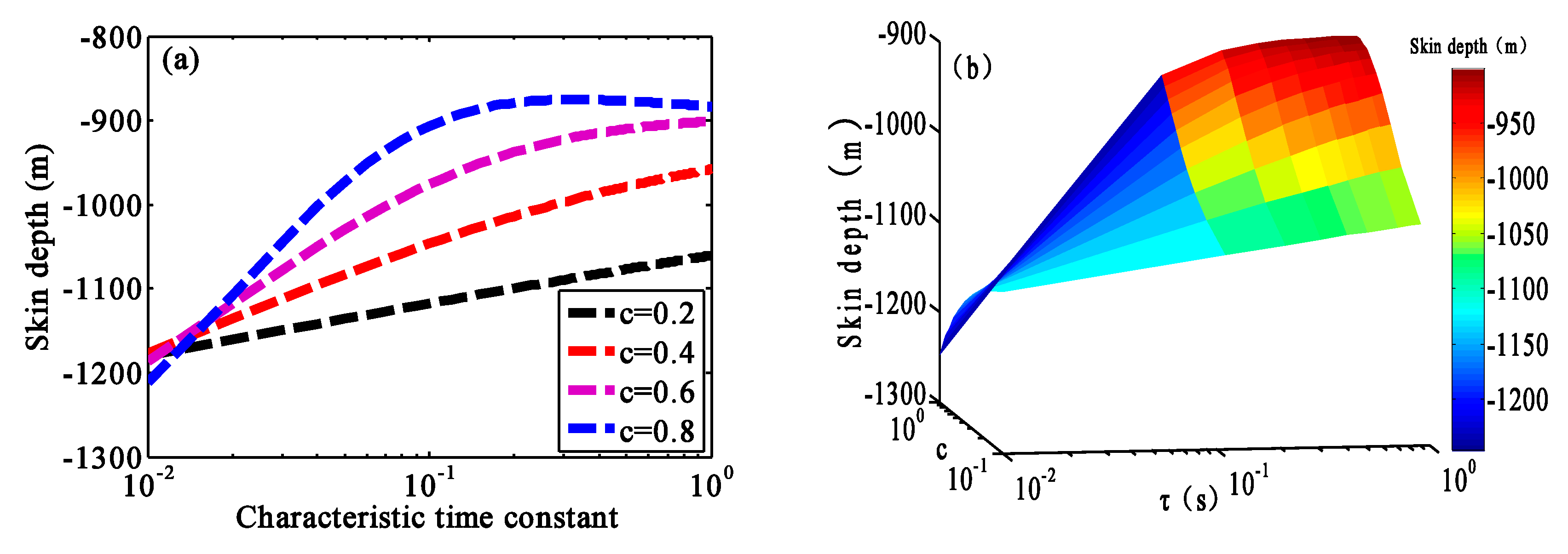
3.2.3. Influence of the Frequency Dependence and Characteristic Time Constant on the Generalized Skin Depth
3.3. Characteristic Analysis of the Generalized Skin Depth at Low Frequency
4. Skin Depth of Porous Media with Metallic Particles
5. Skin Depth Imaging of Polarized Porous Media
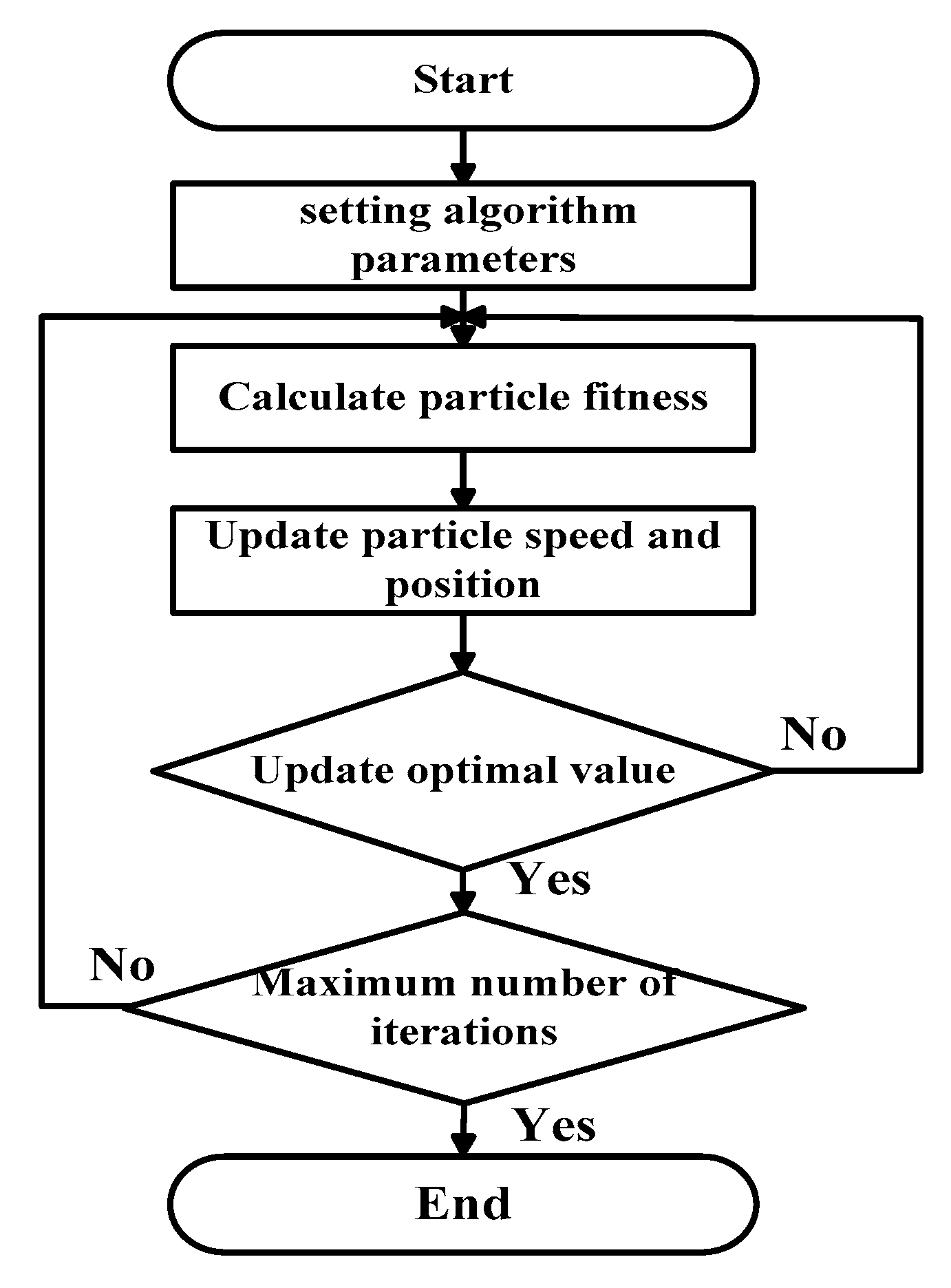
5.1. Polarization Parameter Extraction Based on Particle Swarm Optimization
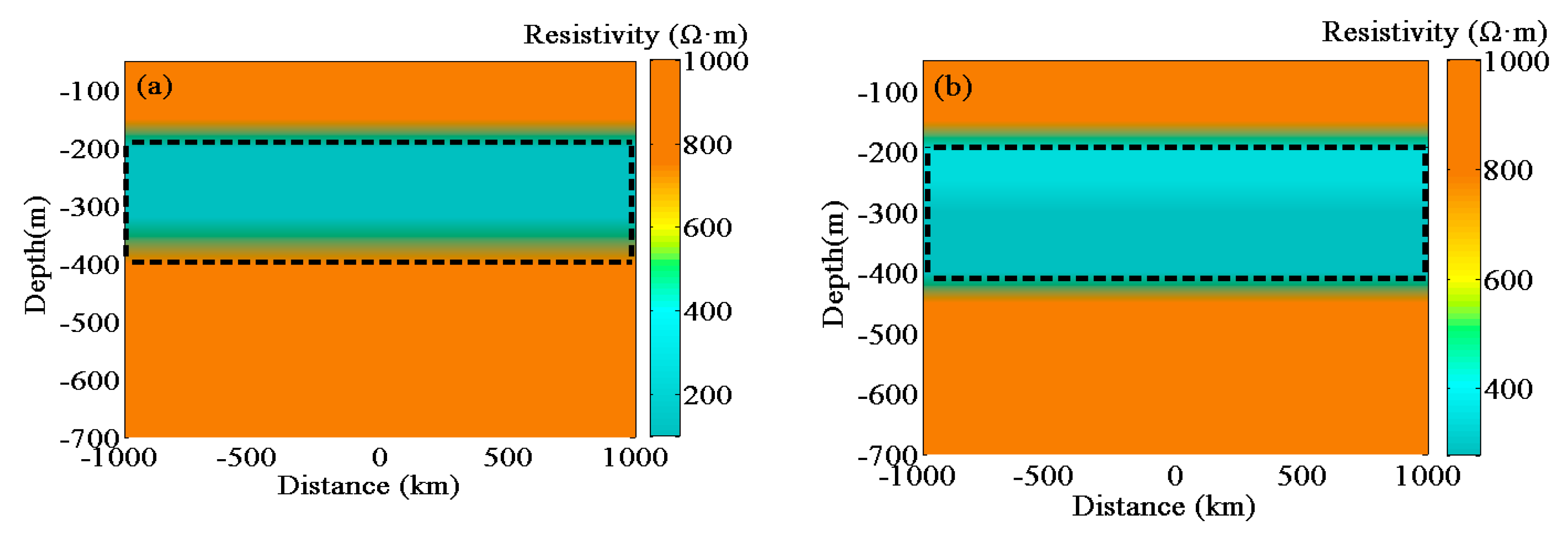
5.2. Skin Depth Imaging of Layered Model for Polarized Medium
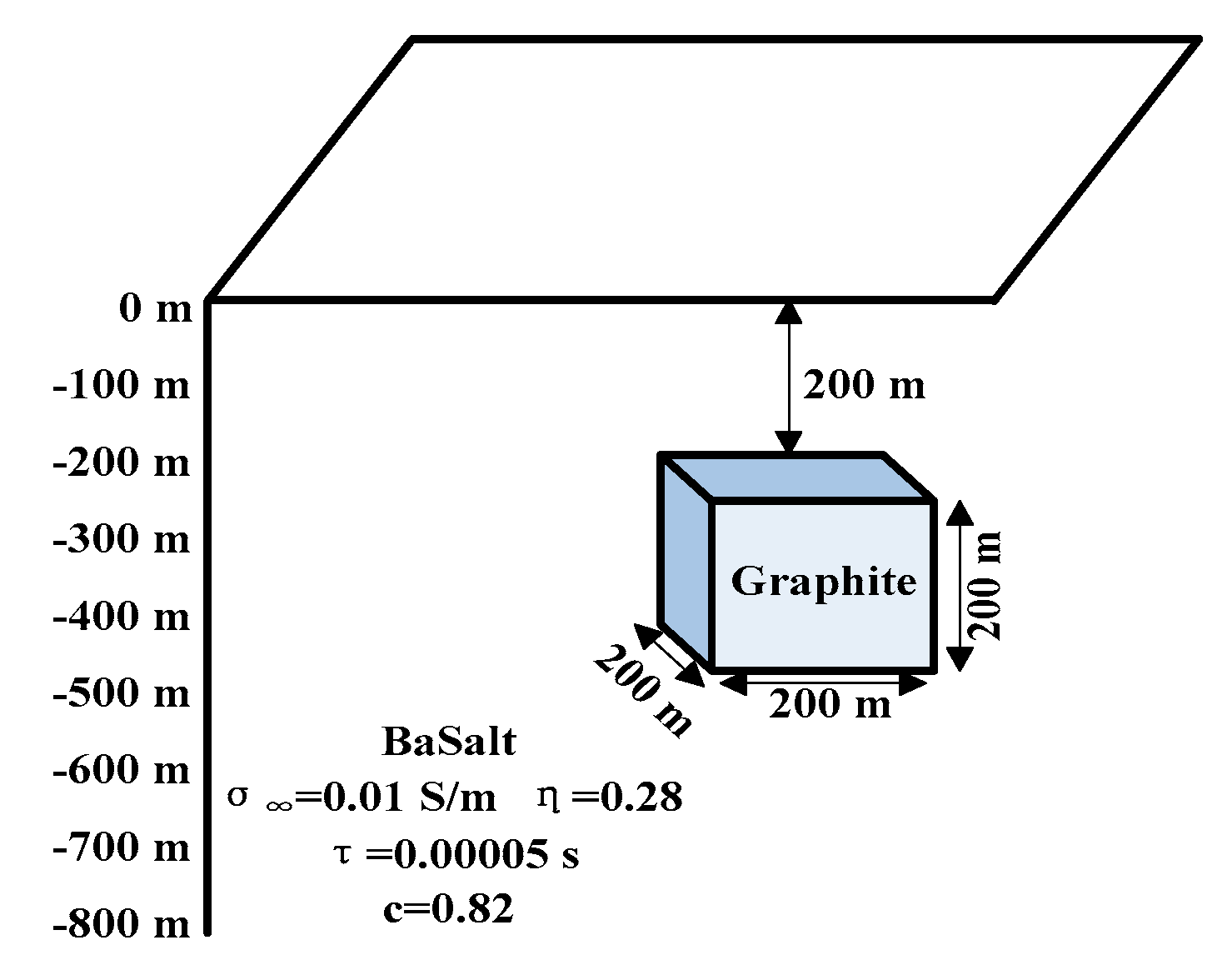
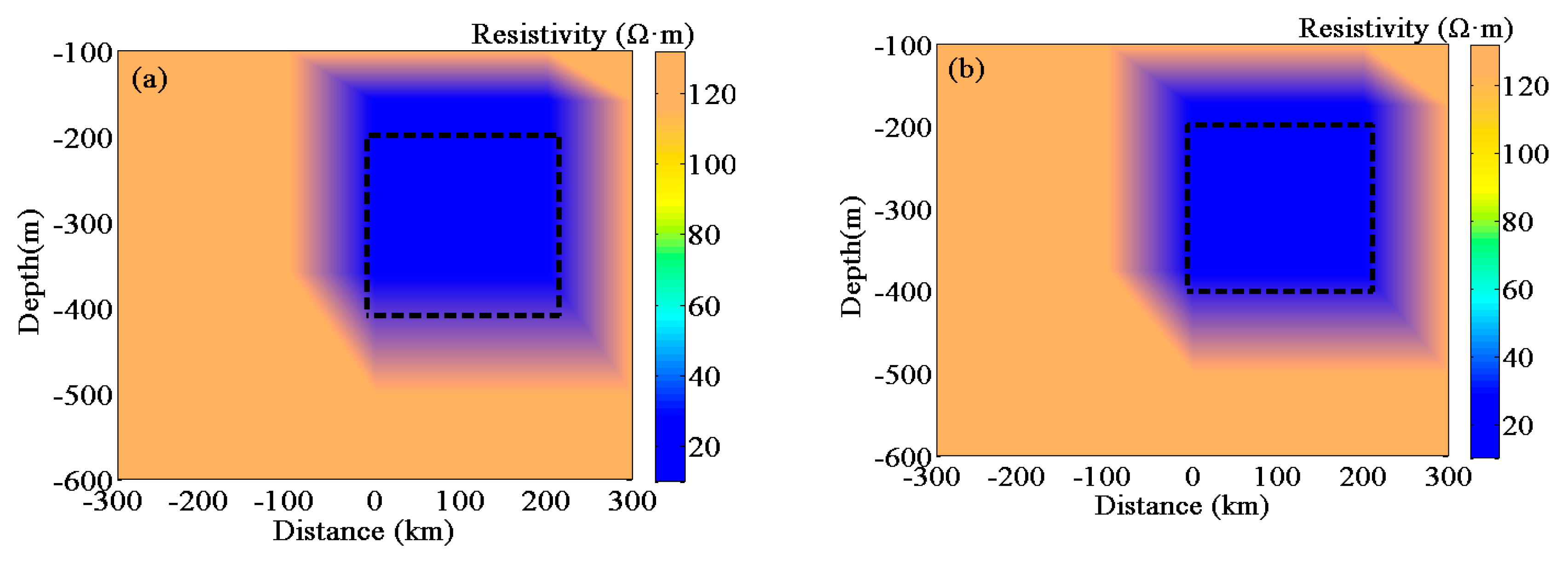
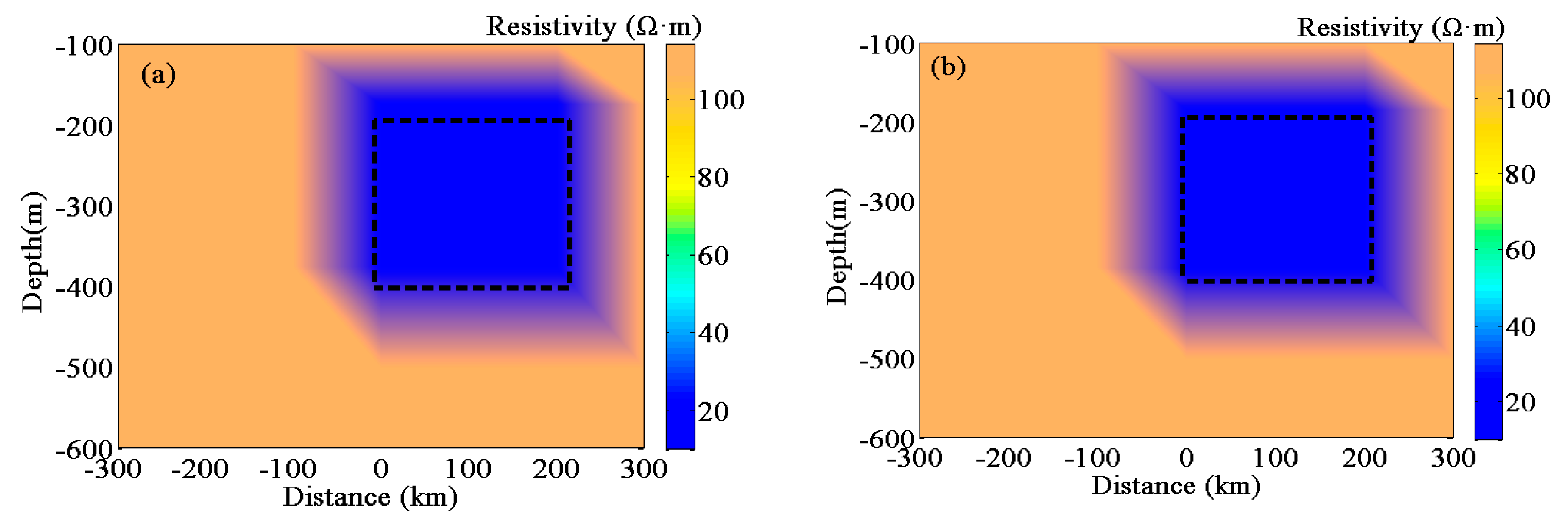
5.3. Depth Interpretation of a Three-Dimensional Chargeable Body
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.P.; Mogi, T. Effective skin depth of EM fields due to large circular loop and electric dipole sources. Earth Planets Space 2003, 55, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, R.L. The existence of a region inaccessible to magnetotelluric sounding. Geophys. J. Int. 1982, 68, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiping, W. Electromagnetic Response Character of Helicopter Frequency Domain EM System above Uniform Half Space and Its Prospecting Depth. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2003, 24, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, J.E.; Macnae, J.C. Doubling the effective skin depth with a local source. Geophysics 1990, 64, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Mogi, T. Effective Skin Depth with a Local Source and Its Application to Survey Design and Data Interpretation. Seg Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 2002, 21, 684. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, D. Airborne EM skin depths. Geophys. Prospect. 2004, 52, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Xue, G.-Q. Effective skin depth of whole EM field due to a grounded wire source. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.; Zhou, N.; Chen, W. Research on the Application of a 3-m Transmitter Loop for TEM Surveys in Mountainous Areas. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2014, 19, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, H. Analysis and application of the detection depth of electrical source Short-offset TEM. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 57, 631. [Google Scholar]
- Debye, P.; Falkenhagen, H. Dispersion of the conductivity and dielectric constants of strong electrolytes. Phys. Z. 1928, 29, 401–426. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics. I. Alternating current characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani, A.; Cosenza, P.; Revil, A.; Zamora, M.; Schmutz, M.; Florsch, N.; Jougnot, D. Non-invasive monitoring of water content and textural changes in clay-rocks using spectral induced polarization: A laboratory investigation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvillard, P.A.; Revil, A.; Qi, Y.; SoueidAhmed, A.; Coperey, A.; Ravanel, L. Three-dimensional electrical conductivity and induced polarization tomography of a rock glacier. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 9528–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, W.H.; Ward, S.H.; Hallof, P.G.; Sill, W.R.; Nelson, P.H. Mineral discrimination and removal of inductive coupling with multi-frequency IP. Geophysics 1978, 43, 588–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, J.A. Electromagnetic Theory; McGraw-Hill Book CO.: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Spies, B.R. Depth of investigation in electromagnetic sounding methods. Geophysics 1989, 54, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Mao, D.; Shao, Z. Induced polarization response of porous media with metallic particles—Part 6: The case of metals and semimetals. Geophysics 2016, 82, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikov, N.O.; Antonov, E.Y. Fast-decaying inductively induced polarization in frozen ground: A synthesis of results and models. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 82, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN′95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.H.; Eberhart, R.C. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimizer. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Proceedings. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Alaska, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Mukherjee, V.; Ghoshal, S.P. Particle swarm optimization with an aging leader and challengers algorithm for the solution of optimal power flow problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabi, A.; Fini, M.H. Adaptive underfrequency load shedding using particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2017, 15, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Srivastava, G.M.S. Genetic Algorithm Enabled Particle Swarm Optimization (PSOGA) based Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing Environment. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2018, 17, 1237–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, D.Q.; Jiang, F.B. A two-stage CO-PSO minimum structure inversion using CUDA for extracting IP information from MT data. J. Cent. South Univ. 2018, 25, 1195–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundations of Geophysical Electromagnetic Theory and Methods Electromagnetic Migration. Available online: https://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040120116010_f94e.html (accessed on 19 February 2020).
- Zhdanov, M.S. Electromagnetic methods in the frequency and time domains. Methods Geochem. Geophys. 2009, 43, 649–693. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, G.A. Frequency-domain modeling of airborne electromagnetic responses using staggered finite differences. Geophys. Prosp. 1995, 43, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

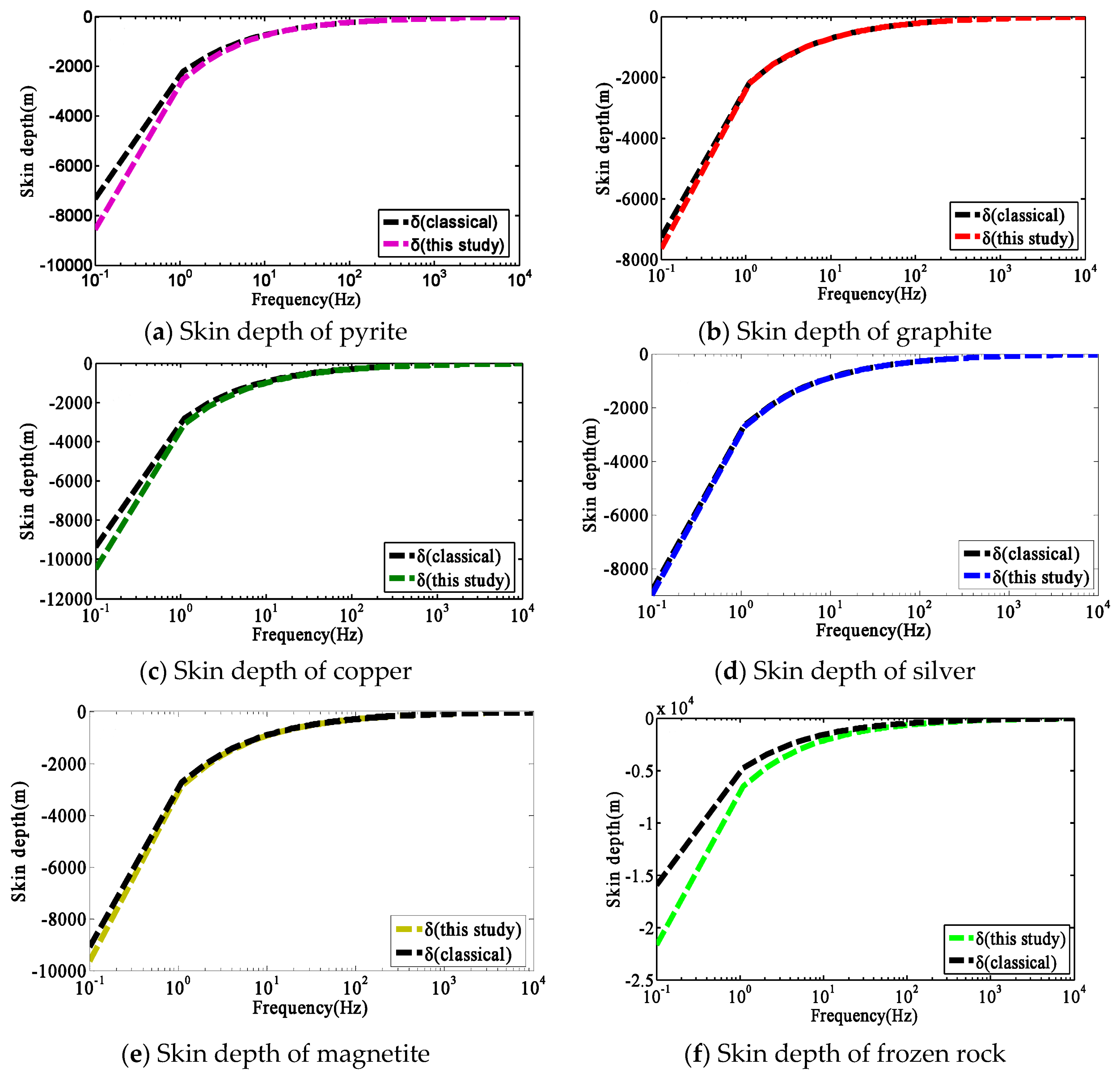


| Metallic Particles | Chargeability η | Conductivity at Infinite Frequency σ∞ (S/m) | Frequency Dependence c | Characteristic Time Constant τ(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | 0.308 | 0.0479 | 0.6 | 2 |
| Pyrite | 0.275 | 0.0472 | 0.78 | 0.0155 |
| Silver | 0.037 | 0.0325 | 0.62 | 0.004 |
| Copper | 0.221 | 0.0289 | 0.41 | 0.0042 |
| Magnetite | 0.13 | 0.0307 | 0.38 | 0.01 |
| Frozen rocks | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.8 | 0.00005 |
| IP Parameters | Theoretical Model | Extraction Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| (S/m) | 0.01 | 0.0096 |
| 0.46 | 0.4612 | |
| 0.8 | 0.8001 | |
| (s) | 0.0000 | 0.000056 |
| IP Parameters | Theoretical Model | Extraction Parameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basalt | Graphite | Basalt | Graphite | |
| (S/m) | 0.01 | 0.0479 | 0.0135 | 0.0491 |
| 0.82 | 0.6 | 0.8155 | 0.57 | |
| 0.28 | 0.308 | 0.2498 | 0.334 | |
| (s) | 0.00005 | 2 | 0.00005 | 1.93 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Y.; Meng, X.; Shao, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q. The Generalized Skin Depth for Polarized Porous Media Based on the Cole–Cole Model. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041456
Ji Y, Meng X, Shao J, Wu Y, Wu Q. The Generalized Skin Depth for Polarized Porous Media Based on the Cole–Cole Model. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(4):1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041456
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Yanju, Xiangdong Meng, Jingya Shao, Yanqi Wu, and Qiong Wu. 2020. "The Generalized Skin Depth for Polarized Porous Media Based on the Cole–Cole Model" Applied Sciences 10, no. 4: 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041456
APA StyleJi, Y., Meng, X., Shao, J., Wu, Y., & Wu, Q. (2020). The Generalized Skin Depth for Polarized Porous Media Based on the Cole–Cole Model. Applied Sciences, 10(4), 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041456




