Inheritance Coding with Gagné-Based Learning Hierarchy Approach to Developing Mathematics Skills Assessment Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosing Student Learning Problems by Applying Gagné Theory
3. Gagné-Based Learning Hierarchy Approach
- Step 1.
- Design test questions from each skill level in the learning hierarchy diagram. The number of selected skill levels is ρ.
- Step 2.
- Encode Xj in Equation (1). The value of xi is 0 or 1. Repeat ρ times, and produce a vector (x1, x2, …, xρ).
- Step 3.
- Repeat Step 2 ps times to produce ps feasible individuals for test questions.
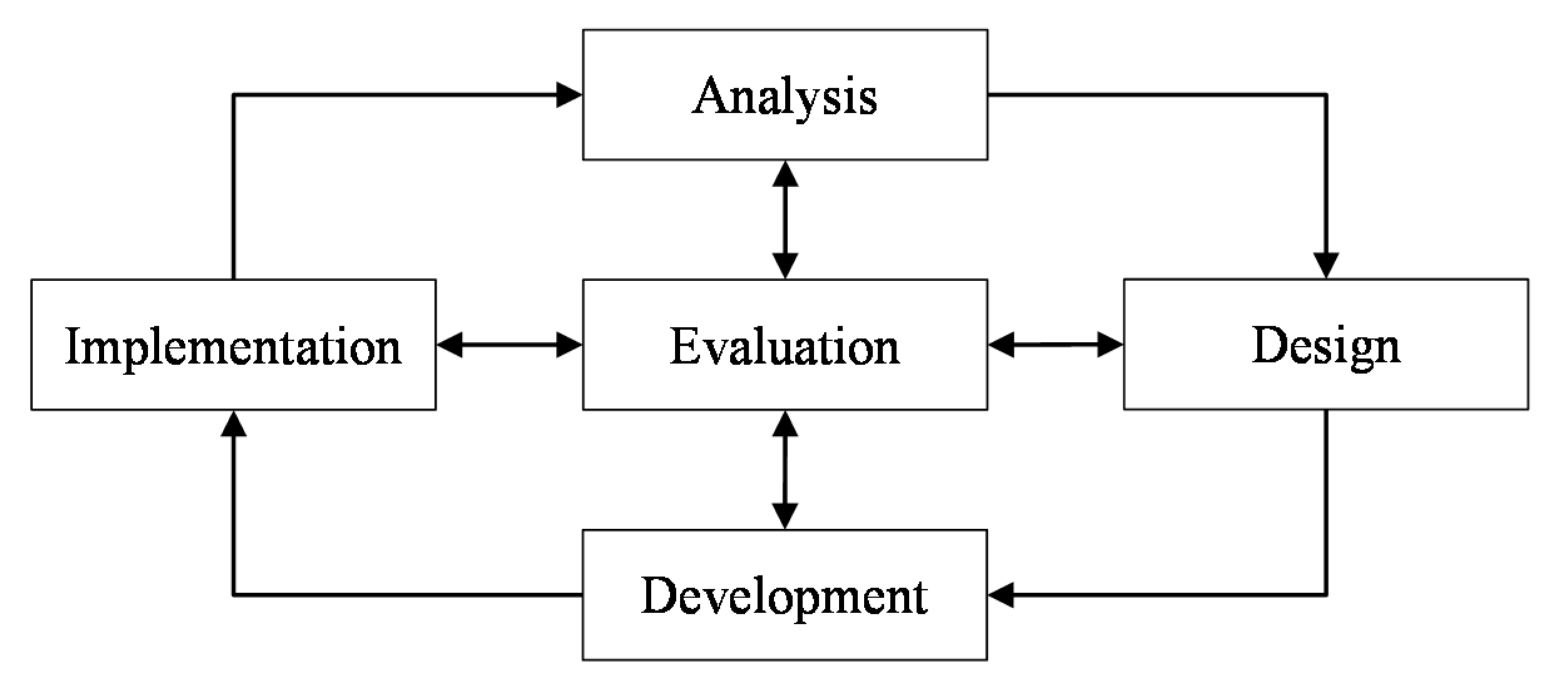
4. Developing Mathematics Skills Assessment Systems
4.1. Analysis Phase
4.2. Design Phase
4.3. Development Phase
4.4. Implementation Phase
4.5. Evaluation Phase
5. Actual Implementation of the GBLHA Mathematics Skills Assessment System for Diagnosing Student Learning Problems
5.1. Test Subject 1: Fractions Unit
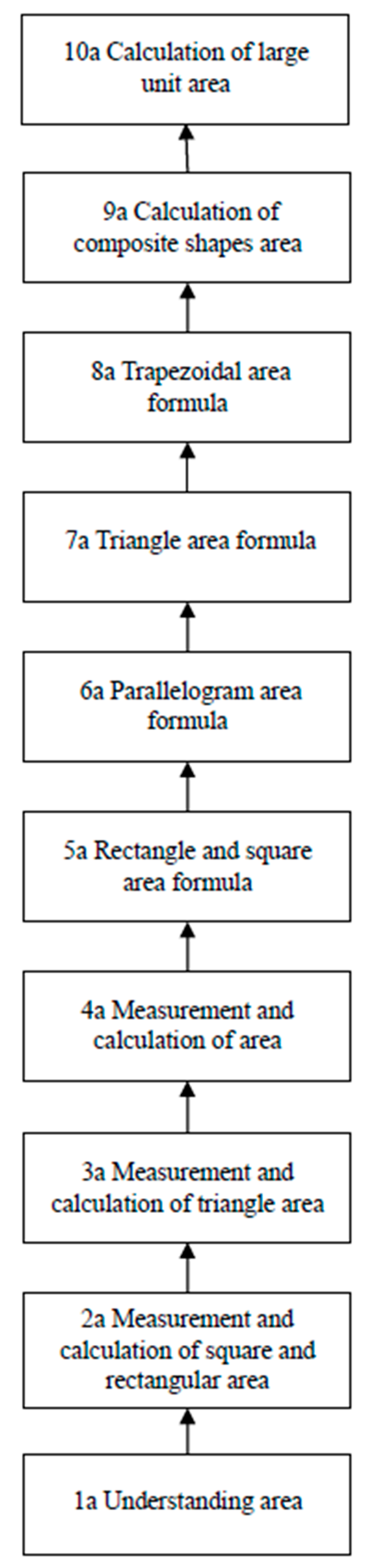
5.2. Test Subject 2: Area Computation Unit
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gagné, R.M.; Glaser, R. Foundations in learning research. In Instructional Technology: Foundations; Robert, M.G., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goodson, L.A.; Slater, D.; Zubovic, Y. Adding confidence to knowledge. J. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. 2015, 15, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, R.M.; Briggs, L.; Wager, W. Principles of Instructional Design; HBJ College Publishers: Fort Worth, TX, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, J.L. Cooperative learning and Gagné’s events of instruction: A syncretic view. Educ. Technol. 1992, 32, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, C.M. Evaluate Whether Uri Treisman’s Model of Collaborative Learning is Consistent and/or Supportive of Robert Gagné’s Learning Hierarchy (ERIC Report ED559985). Available online: http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED559985.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Gagné, R.M. The Conditions of Learning and Theory of Instruction; Holt, Rinehart & Winston: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, A.P.; Kumar, J. A framework for evaluation of e-learning applications in developing countries. Adv. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2015, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Shikuku, B.N.; Wasike, D.W. Problem based learning and its effect on Kenyan secondary school students learning outcomes in linear programming. J. Educ. Res. Behav. Sci. 2015, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, K.R.P. Role of problem solving ability on enhancing students’ achievement. Indian J. Res. 2016, 5, 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, R.M. Instructional Design: The ADDIE Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Molenda, M. In search of the elusive ADDIE Model. Perform. Improv. 2003, 42, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, G.R.; Ross, S.M.; Kalman, H.; Kemp, J.E. Designing Effective Instruction; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Arkün, S.; Akkoyunlu, B. A study on the development process of a multimedia learning environment according to the ADDIE model and students’ opinions of the multimedia learning environment. Interact. Educ. Multimed. 2008, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.C.; Lee-Hsieh, J.; Turton, M.; Cheng, S.F. Using the ADDIE model to develop online continuing education courses on caring for nurses in Taiwan. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2004, 45, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradmand, N.; Datta, A.; Oakley, G. The design and implementation of an educational multimedia mathematics software: Using ADDIE to guide instructional system design. J. Appl. Instr. Des. 2014, 4, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Azimi, K.; Ahmadigol, J.; Rastegarpour, H. A survey of the effectiveness of instructional design ADDIE and multimedia on learning key skills of futsal. J. Educ. Manag. Stud. 2015, 5, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tang, W.L.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, J.T. Development of e-materials on the complex graphics area unit for elementary school students. In Proceedings of the SICE 2014 Annual Conference, Sapporo, Japan, 9–12 September 2014; pp. 1899–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tang, W.L.; Tseng, S.H.; Tsai, J.T. Action research on the development of digital material in the mandarin character recognition learning course for an elementary school in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Education & International Development, Kobe, Japan, 3–6 April 2016; p. 22930. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.L.; Hsu, P.S.; Tsai, J.T. Study of instructional design for elementary school teachers applying digital materials to remedial instruction on mathematics in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Education & International Development, Kobe, Japan, 3–6 April 2016; p. 22928. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.L.; Kang, H.M.; Tsai, J.T. Action research of mathematical learning effects. In Proceedings of the SICE 2013 Annual Conference, Nagoya, Japan, 14–17 September 2013; pp. 873–875. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.L.; Tsai, J.T. Research on the development of mathematical digital materials on the fraction area unit for elementary school students. In Proceedings of the 2015 Asia-Pacific Conference on Education, Society, and Psychology, Seoul, Korea, 8–10 January 2015; p. 405. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.T.; Wu, Y.F.; Tang, W.L. Auto-reply system of questions and answers on mathematic speed unit for elementary school students. Curric. Instr. Q. 2012, 15, 179–210. [Google Scholar]
- Algraini, S.; McIntyre-Mills, J. Human development in Saudi education: A critical systemic approach. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2018, 31, 121–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Olaya, C. An engineering view for social systems: Agency as an operational principle for designing higher education access policies. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2017, 30, 627–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshaw, J.L. Systems thinking for systems making: Joining systems of thought and action. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.I. Improvements in introductory programming course: Action research insights and outcomes. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2018, 31, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. Intelligent web-based learning system with personalized learning path guidance. Comput. Educ. 2008, 51, 787–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterlin-Geller, L.R.; Yovanoff, P. Diagnostic assessments in mathematics to support instructional decision making. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2009, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ozyurt, H.; Ozyurt, O.; Baki, A. Architecture and design process of the individualized assessment system integrable to distance education. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2012, 13, 212–225. [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth, M.; Adamoli, A. Teaching Java programming with the Informa clicker system. Sci. Comput. Program. 2013, 78, 499–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.J.; Panjaburee, P.; Triampo, W.; Shih, B.Y. A group decision approach to developing concept effect models for diagnosing student learning problems in mathematics. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2013, 44, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C.; Hwang, G.J.; Yang, S.J.H.; Hwang, G.H. A two-tier test-based approach to improving students’ computer-programming skills in a web-based learning environment. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 198–210. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, E.R.; Kobrin, J.L.; DiCerbo, K.E.; Holland, L.R. Tracing the assessment triangle with learning progression-aligned assessments in mathematics. Meas. Interdiscip. Res. Perspect. 2017, 15, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, J.; Norton, A. Learning progression toward a measurement concept of fractions. Int. J. STEM Educ. 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reigeluth, C.M.; Curtis, R.V. Learning situations and instructional models. In Instructional Technology: Foundations; Robert, M.G., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, P.F. Job and task analysis. In Instructional Technology: Foundations; Robert, M.G., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K.; Cho, M.K. Design and implementation of integrated instruction of mathematics and science in Korea. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2014, 11, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Schenke, K.; Rutherford, T.; Lam, A.C.; Bailey, D.H. Construct confounding among predictors of mathematics achievement. AERA Open 2016, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.L.; Wilkins, J.L.M. Subitising activity relative to units construction: A case study. Res. Math. Educ. 2019, 21, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäder, J.; Lithner, J.; Sidenvall, J. Mathematical problem solving in textbooks from twelve countries. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Gagné, R.M.; Wager, W.W.; Golas, K.C.; Keller, J.M. Principles of Instructional Design, 5th ed.; Thomson/Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Takker, S.; Subramaniam, K. Knowledge demands in teaching decimal numbers. J. Math. Teach. Educ. 2019, 22, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Qj\Ci | C12 | C11 | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Q2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Q3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Q4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Q5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Q6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Q7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q28 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q29 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q30 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q31 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q32 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q33 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q34 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q35 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q36 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sum of concepts (mi) | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 |
| C12 | C11 | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 50% | 56% | 58% | 53% | 56% | 57% | 63% | 67% | 70% | 73% | 75% |
| C12 | C11 | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 33% | 56% | 50% | 53% | 61% | 67% | 63% | 67% | 70% | 73% | 75% |
| C12 | C11 | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 17 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 33% | 44% | 42% | 40% | 39% | 43% | 46% | 44% | 47% | 45% | 47% |
| C12 | C11 | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 29 | 32 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 |
| AR (%) | 67% | 67% | 67% | 67% | 73% | 78% | 81% | 83% | 85% | 87% | 88% | 89% |
| C12 | C11 | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 18 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 |
| AR (%) | 0% | 0% | 22% | 33% | 33% | 39% | 43% | 46% | 48% | 47% | 48% | 50% |
| Qj\Ci | C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Q2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Q3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Q4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Q5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Q6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Q7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q22 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q23 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q24 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q25 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q26 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q27 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q28 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q29 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Q30 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sum of concepts (mi) | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 33% | 33% | 42% | 47% | 50% | 57% | 63% | 67% | 70% |
| C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 23 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 33% | 44% | 50% | 60% | 61% | 67% | 71% | 74% | 77% |
| C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 16 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 50% | 44% | 50% | 53% | 56% | 52% | 54% | 52% | 53% |
| C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 2 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 25 | 28 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| AR (%) | 67% | 67% | 78% | 83% | 87% | 89% | 90% | 92% | 93% | 93% |
| C10 | C9 | C8 | C7 | C6 | C5 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of correct concepts | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| Sum of concepts | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| AR (%) | 33% | 33% | 33% | 33% | 40% | 39% | 43% | 42% | 44% | 47% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, W.-L.; Tsai, J.-T.; Huang, C.-Y. Inheritance Coding with Gagné-Based Learning Hierarchy Approach to Developing Mathematics Skills Assessment Systems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041465
Tang W-L, Tsai J-T, Huang C-Y. Inheritance Coding with Gagné-Based Learning Hierarchy Approach to Developing Mathematics Skills Assessment Systems. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(4):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041465
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Wei-Ling, Jinn-Tsong Tsai, and Ching-Ying Huang. 2020. "Inheritance Coding with Gagné-Based Learning Hierarchy Approach to Developing Mathematics Skills Assessment Systems" Applied Sciences 10, no. 4: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041465
APA StyleTang, W.-L., Tsai, J.-T., & Huang, C.-Y. (2020). Inheritance Coding with Gagné-Based Learning Hierarchy Approach to Developing Mathematics Skills Assessment Systems. Applied Sciences, 10(4), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10041465





