Prediction of Optimized Color Design for Sports Shoes Using an Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Kansei Engineering
2.2. ANNs
2.3. GA
2.4. Hybrid GA-Based ANN
3. Implementation Methods
3.1. Selection of Representative Form Types and Color Schemes to Build the Experimental Sample Images
3.2. Linguistic Variable Selection for Affective Responses
3.3. Definition of Experimental Color Index for Sports Shoes
3.4. Semantic Meaning Questionnaires to Determine Affective Responses
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Definition of Design Factors for Modeling
4.2. Description of the ANN Model
4.3. GA Optimization Search Mechanism
4.4. Hybrid Learning of ANN
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berkowitz, M. The influence of shape on product preferences. In NA—Advances in Consumer Research; Wallendorf, M., Anderson, P., Eds.; Association for Consumer Research: Provo, UT, USA, 1987; Volume 14, p. 559. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, D. Watches Tell More Than Time: Product Design, Information, and the Quest for Elegance; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X. When the shape of the glass influences the flavour associated with a coloured beverage: Evidence from consumers in three countries. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 39, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.C. Automatic design support and image evaluation of two-coloured products using colour association and colour harmony scales and genetic algorithm. Comput. Aided Des. 2007, 39, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniani, M.; Yamamoto, S. A comparative study on correlation between personal background and interior color preference. Color Res. Appl. 2015, 40, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, S. Colour scheme supporting technique based on hierarchical scene structure for exterior design of urban scenes in 3D. Color Res. Appl. 2010, 37, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X. Consumer preferences for color combinations: An empirical analysis of similarity-based color relationships. J. Consum. Psychol. 2010, 20, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H. Red-Colored products enhance the attractiveness of women. Displays 2014, 35, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Guess your size: A hybrid model for footwear size recommendation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 36, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Wang, M.J. Taiwanese adult foot shape classification using 3d scanning data. Ergonomics 2015, 58, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, E.; Artacho, M.A.; Gonzalez, J.C.; Garcia, A.C. Application of product semantics to footwear design. Part I—Identification of footwearsemantic space applying differential semantics. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2005, 35, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.A.; Lin, M.C.; Leonard, M.S.; Occena, L.G. Building an expert system for the design of sports shoes. Comput. Ind. Eng. 1988, 15, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudta, P.; Kanchan, K.; Chantrapornchai, C. Children shoes suggestion system using data mining. Int. J. Database Theory Appl. 2012, 5, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bornholdt, S.; Graudenz, D. General asymmetric neural networks and structure design by genetic algorithms. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, M.D.; Yeh, Y.E. Developing a design support system for the exterior form of running shoes using partial least squares and neural networks. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 65, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamachi, M.; Senuma, I.; Iwashige, R. A study of emotion-technology. Jpn. J. Ergon. 1974, 10, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, S.W.; Chiu, F.Y.; Lu, S.H. Product-Form design model based on genetic algorithms. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2010, 40, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, C.H.; Khoo, L.P. Products classification in emotional design using a basic-emotion based semantic differential method. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2012, 42, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Yeh, C.H.; Wei, C.H. User-Oriented design for the optimal combination on product design. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2006, 100, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Hong, S.W. A systematic approach for coupling user satisfaction with product design. Ergonomics 2003, 46, 1441–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Fu, S.H. The relationships between automobile head-up display presentation images and drivers’ Kansei. Displays 2011, 32, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lai, H.H.; Yeh, C.H. Consumer-Oriented product form design based on fuzzy logic: A case study of mobile phones. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2007, 37, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, M.D.; Yeh, Y.E.; Huang, C.L. Eliciting design knowledge from affective responses using rough sets and Kansei engineering system. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2016, 7, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Yeh, Y.E. A study on extraction of consumer affective factor for Kansei engineering. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2015, 18, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Optimization of indoor climate conditioning with passive and active methods using GA and CFD. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.W.; Tsai, H.C. Applying a hybrid approach based on fuzzy neural network and genetic algorithm to product form design. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2005, 35, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, I. Deciding the financial health of dot-coms using rough sets. Inf. Manag. 2006, 43, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, S.I. Neural Network Learning and Expert Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Shieh, M.D.; Yeh, Y.E. Comparative study on perceptual evaluations of sports shoe exterior colors in Taiwan. Color Res. Appl. 2015, 40, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.C. An image evaluation approach for parameter-based product form and color design. Comput. Aided Des. 2006, 38, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.W.; Wang, M.F.; Lee, D.J.; Chen, C.W. A study on the application of an artificial neural algorithm in the color matching of Taiwanese cultural and creative commodities. Color Res. Appl. 2015, 40, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Yeh, C.H. Form design of product image using grey relational analysis and neural network models. Comput. Oper. Res. 2005, 32, 2689–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Yeh, C.H.; Wei, C.C. How will the use of graphics affect visual aesthetics a user-centered approach for web page design. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2013, 71, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, K. Modelling of colour perception of different age groups using artificial neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks and Learning Machines, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yuste, A.J.; Dorado, M.P. A neural network approach to simulate biodiesel production from waste olive oil. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourquin, J.; Schmidli, H.; Hoogevest, P.V.; Leuenberger, H. Basic concepts of artificial neural networks (ANN) modeling in the application to pharmaceutical development. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1997, 2, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Shieh, M.D.; Chen, K.H.; Lin, P.J. Product form feature selection for mobile phone design using LS-SVR and ARD. In Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction: Context Diversity; Stephanidis, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, G. The improvement of BP algorithm and its application. J. Sichuan Univ. Eng. Sci. Ed. 2000, 32, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.T. The determination of the number of the hidden cells and the variable selection of the neural network. Stat. Inf. Forum 2007, 22, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems, 1st ed.; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Vico, F.J.; Veredas, F.J.; Bravo, J.M.; Almaraz, J. Automatic design synthesis with artificial intelligence techniques. Artif. Intell. Eng. 1999, 13, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampinen, J. Cam shape optimisation by genetic algorithm. Comput. Aided Des. 2003, 35, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems, 2nd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jadav, K.; Panchal, M. Optimizing weights of artificial neural networks using genetic algorithms. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Electron. Eng. 2012, 1, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mistuo, G.; Runwei, C. Genetic Algorithms & Engineering Design; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Beale, R. Supporting serendipity: Using ambient intelligence to augment user exploration for data mining and web browsing. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2007, 65, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saemi, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Varjani, A.Y. Design of neural networks using genetic algorithm for the permeability estimation of the reservoir. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 59, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.R.; Dandy, G.C.; Murphy, L.J. Genetic algorithms compared to other techniques for pipe optimization. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1994, 120, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, L.D. Practical Handbook of Genetic Algorithms: Complex Coding Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Y.; Fung, K.Y. Product form design using customer perception evaluation by a combined superellipse fitting and ANN approach. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2013, 27, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, M.S.; Hung, Y.C. An integrated neuro-genetic approach incorporating the Taguchi method for product design. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2014, 29, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Shoe Name | Form Type | Color Scheme 1 | Color Scheme 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basketball shoes |  |  |  |
| Jogging shoes |  |  |  |
| Casual Shoes |  |  |  |
| Running Shoes |  |  |  |
| Unmodified |  |  |  |
PCCS-based 24-color color wheel | Hue Code | Hue Name | Hue Code in the Munsell Color System | Hue Code | Hue Name | Hue Code in the Munsell Color System |
| 1:pR | purplish red | 10RP | 13:bG | bluish green | 9G | |
| 2:R | red | 4R | 14:BG | blue green | 5BG | |
| 3:yR | yellowish red | 7R | 15:BG | bluie green | 10BG | |
| 4:r0 | redish orange | 10R | 16:gB | greenish blue | 5B | |
| 5:0 | orange | 4YR | 17:B | Blue | 10B | |
| 6:y0 | yellowish orange | 8YR | 18:B | Blue | 3PB | |
| 7:rY | redish yellow | 2Y | 19:pB | purplish blue | 6PB | |
| 8:Y | yellow | 5Y | 20:V | Violet | 9PB | |
| 9:gY | greenish yellow | 8Y | 21:bP | bluish purple | 3P | |
| 10:YG | Yellow green | 3GY | 22:P | Purple | 7P | |
| 11:yG | yellowish green | 8GY | 23:rP | redish purple | 1RP | |
| 12:G | green | 3G | 24:RP | Red purple | 6RP |
| NO | Sample | R.G.B | NO | Sample | R.G.B | NO | Gradient Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 230.0.51 | 14 |  | 0.160.193 | 27 |  |
| 2 |  | 229.0.79 | 15 |  | 0.158.150 | 28 |  |
| 3 |  | 229.0.106 | 16 |  | 0.155.107 | 29 |  |
| 4 |  | 228.0.127 | 17 |  | 0.153.68 | 30 |  |
| 5 |  | 190.0.129 | 18 |  | 34.172.56 | 31 |  |
| 6 |  | 146.7.131 | 19 |  | 143.195.31 | 32 |  |
| 7 |  | 96.25.134 | 20 |  | 207.0.219 | 33 |  |
| 8 |  | 29.32.136 | 21 |  | 255.251.0 | 34 |  |
| 9 |  | 0.71.157 | 22 |  | 252.200.0 | 35 |  |
| 10 |  | 0.104.183 | 23 |  | 243.152.0 | 36 |  |
| 11 |  | 0.134.209 | 24 |  | 235.97.0 | ||
| 12 |  | 0.160.233 | 25 |  | 230.0.18 | ||
| 13 |  | 26 |  |
| Design Factors | Design Factor Levels | |
|---|---|---|
| X1: Form type (Data type: discrete) | X11 Basketball shoes X12 Jogging Shoes X13 Running Shoes X14 Casual Shoes X15 Other type | |
| X2: Number of colors (Data type: continuous) | Single Color Two Colors | |
| X3: Direction of color gradient | Horizontal Gradient Vertical Gradient | |
| : Sole color | White Black | |
| : Experimental color index Body color | Color index | , …, X526 26 Experimental color index |
| Red (R) Green (G) Blue (B) | ||
| Model | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | Adj. 1 | Adj. 2 | Adj. 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X21 | X22 | X31 | X32 | X41 | X42 | Ave. | StdDev | Ave. | StdDev | Ave. | StdDev | ||||
| typa_g01 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 255 | 251 | 0 | 0.14 | 3.11 | 0.75 | 2.96 | 1.81 | 3.03 |
| Typa01 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 230 | 0 | 18 | −0.83 | 3.13 | 1.10 | 2.26 | 0.52 | 3.18 |
| typb_g01 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 255 | 251 | 0 | −1.00 | 3.05 | 0.00 | 2.83 | 1.22 | 3.21 |
| typb01 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 230 | 0 | 18 | −1.46 | 2.44 | −0.21 | 2.15 | 0.00 | 2.45 |
| typc_g01 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 255 | 251 | 0 | −2.48 | 2.53 | −0.10 | 2.86 | −0.48 | 3.36 |
| typc01 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 230 | 0 | 18 | −1.11 | 2.13 | 0.61 | 1.81 | −0.25 | 2.46 |
| typd_g01 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 255 | 251 | 0 | −0.90 | 3.23 | −0.53 | 2.42 | 0.47 | 2.89 |
| typd01 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 230 | 0 | 18 | −1.39 | 3.32 | −0.19 | 2.99 | −0.55 | 3.77 |
| type_g01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 255 | 251 | 0 | −1.58 | 2.98 | −1.00 | 2.89 | 0.58 | 3.30 |
| type01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 230 | 0 | 18 | −2.03 | 2.80 | −0.76 | 2.72 | −0.07 | 3.23 |
| typf_g01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 255 | 251 | 0 | −1.92 | 2.71 | −0.81 | 2.42 | 0.81 | 3.45 |
| typf01 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 230 | 0 | 18 | −1.29 | 2.31 | −1.07 | 2.05 | −0.39 | 2.45 |
| Population size | 100 |
| Maximum number of generations | 100 |
| Termination criterion | Meet the maximum number of generations (100) or tolerance (10−6) |
| Selection function | Roulette wheel |
| Crossover function | Discrete method (0.65 probability of crossover) |
| Mutation function | Real valued (0.05 probability of mutation) |
| Models | Hidden Layers | Hidden Nodes | MSE | R2 | Overal R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adj1 | Adj2 | Adj3 | Adj1 | Adj2 | Adj3 | ||||
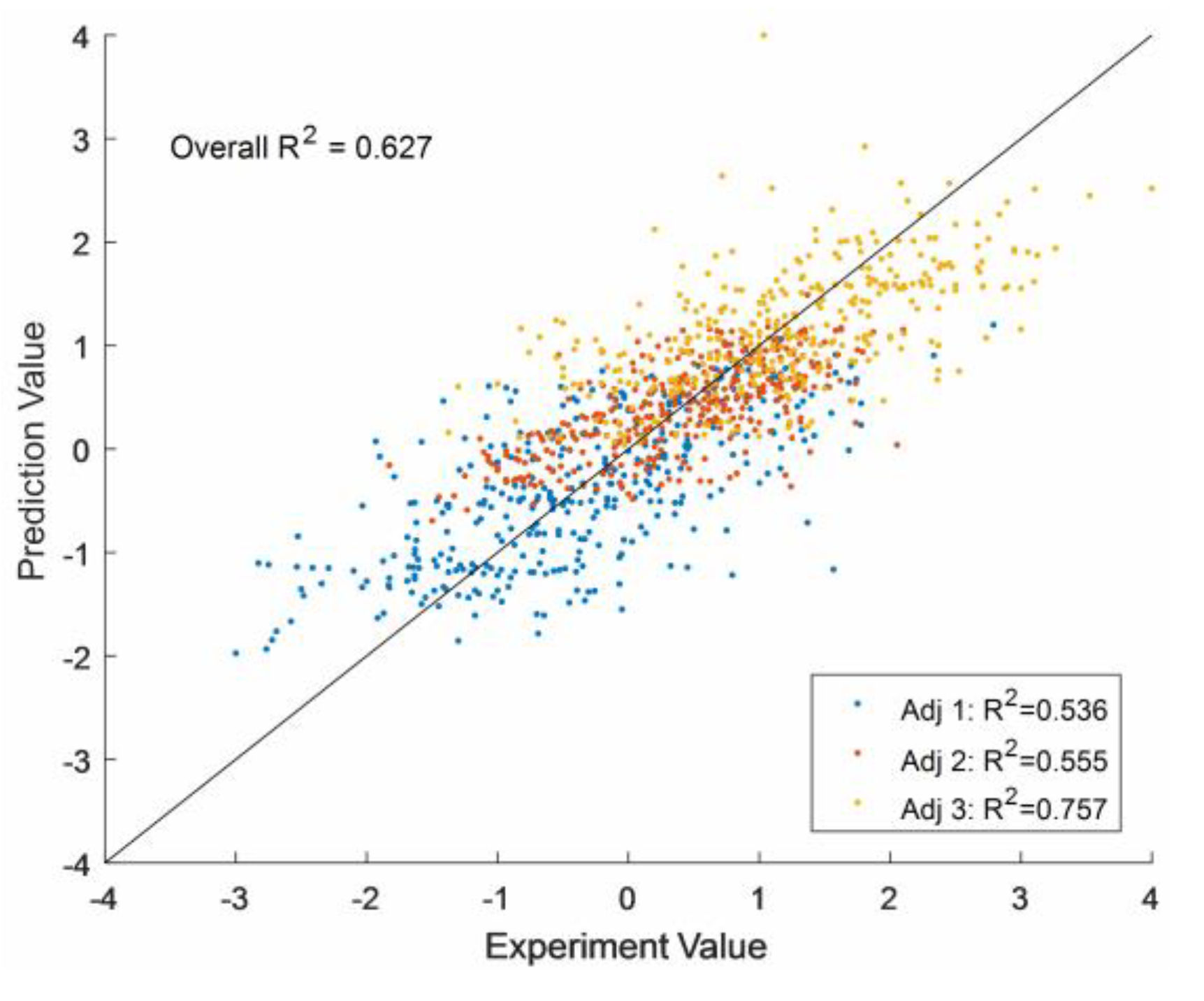
| ANN | 2 | 10 × 10 | 0.549 | 0.308 | 0.536 | 0.536 | 0.555 | 0.757 | 0.627 |
| ANN | 2 | 50 × 50 | 0.524 | 0.259 | 0.469 | 0.550 | 0.619 | 0.782 | 0.662 |
| ANN | 2 | 100 × 50 | 0.690 | 0.340 | 0.552 | 0.441 | 0.496 | 0.755 | 0.569 |
| ANN | 2 | 50 ×100 | 0.828 | 0.417 | 0.967 | 0.34 | 0.4 | 0.61 | 0.357 |
| ANN | 3 | 50 × 50 × 50 | 0.480 | 0.312 | 0.531 | 0.61 | 0.51 | 0.72 | 0.624 |
| GA-ANN | 1 | 16 | 0.419 | 0.231 | 0.403 | 0.633 | 0.665 | 0.824 | 0.713 |
| GA-ANN | 2 | 35 × 5 | 0.393 | 0.222 | 0.417 | 0.652 | 0.683 | 0.829 | 0.724 |
| GA-ANN | 3 | 28 × 38 × 19 | 0.381 | 0.239 | 0.367 | 0.668 | 0.674 | 0.843 | 0.733 |
| GA-ANN | 4 | 30 × 46 × 30 × 46 | 0.360 | 0.209 | 0.472 | 0.699 | 0.703 | 0.806 | 0.720 |
| Shoe Form Type | Color Quantity | Gradient or Color Index | Optimal Shoecolor Schematic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opt. Value | Questionnaire Average Score | |||
 | 2 | Horizontal | −0.05, 0.25, 1.45 | −0.12, 0.39, 1.43 |
 | 2 | 2 229.0.79 | −0.69, 0.86, −0.07 | −0.72, 0.47, 0.73 |
 | 2 | Vertical | −0.57, 1.03, 1.13 | −0.43, 0.96, 1.27 |
 | 2 | 16 0.155.107 | −0.60, 0.17, 0.80 | −0.17, 0.04, 0.99 |
 | 2 | 8 29.32.136 | −0.46, −0.54, 1.43 | −0.88, −0.57, 1.21 |
 | 2 | 15 0.158.150 | −0.46, −0.43, 0.82 | −0.67, −0.11, 0.76 |
 | N | Horizontal | −1.92, −0.81, 0.81 | −0.24, −0.75, 0.76 |
 | 2 | 15 0.158.150 | −0.03, 0.30, 0.97 | 0.16, 0.54, 0.94 |
 | 2 | 4 228.0.127 | 0.71, 0.61, 1.48 | −0.54, 1.68, 0.37 |
| Shoe Form Type | Color Quantity | Gradient or Color Index | Optimal Shoe Color Schematic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opt. Value | Questionnaire Average Score | |||
 | 1 | 17 0.158.68 | 0.71, 1.29, 1.45 | 1.71, 1.14, 3.00 |
 | 1 | 22 252.200.0 | −0.60, −0.07, 1.87 | −0.60, 3.44, 0.61 |
 | 1 | 8 29.32.136 | 2.33, 1.75, 2.17 | 1.81, 1.43, 2.13 |
 | 1 | 16 0.155.107 | −0.60, 0.17, 0.80 | −0.17, 0.04, 0.99 |
 | 1 | 6 146.7.131 | −0.46, −0.54, 1.43 | −0.88, −0.57, 1.21 |
 | 1 | 21 29.32.136 | −1.05, 0.40, 1.00 | 0.95, 1.65, 2.07 |
 | 1 | Horizontal | −1.17, 0.24, 0.86 | −2.56, −1.34, -0.56 |
 | 1 | Horizontal | −0.29, 0.57, 1.43 | 0.35, 0.25, 1.22 |
 | 1 | Horizontal | 0.45, 0.62, 0.41 | 1.91, 2.37, 2.13 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, Y.-E. Prediction of Optimized Color Design for Sports Shoes Using an Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051560
Yeh Y-E. Prediction of Optimized Color Design for Sports Shoes Using an Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(5):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051560
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Yu-En. 2020. "Prediction of Optimized Color Design for Sports Shoes Using an Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm" Applied Sciences 10, no. 5: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051560
APA StyleYeh, Y.-E. (2020). Prediction of Optimized Color Design for Sports Shoes Using an Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 10(5), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051560




