In-Orbit Results and Attitude Analysis of the SNUGLITE Cube-Satellite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SNUGLITE CubeSat Project
2.2. Beacon and Telemetry Data
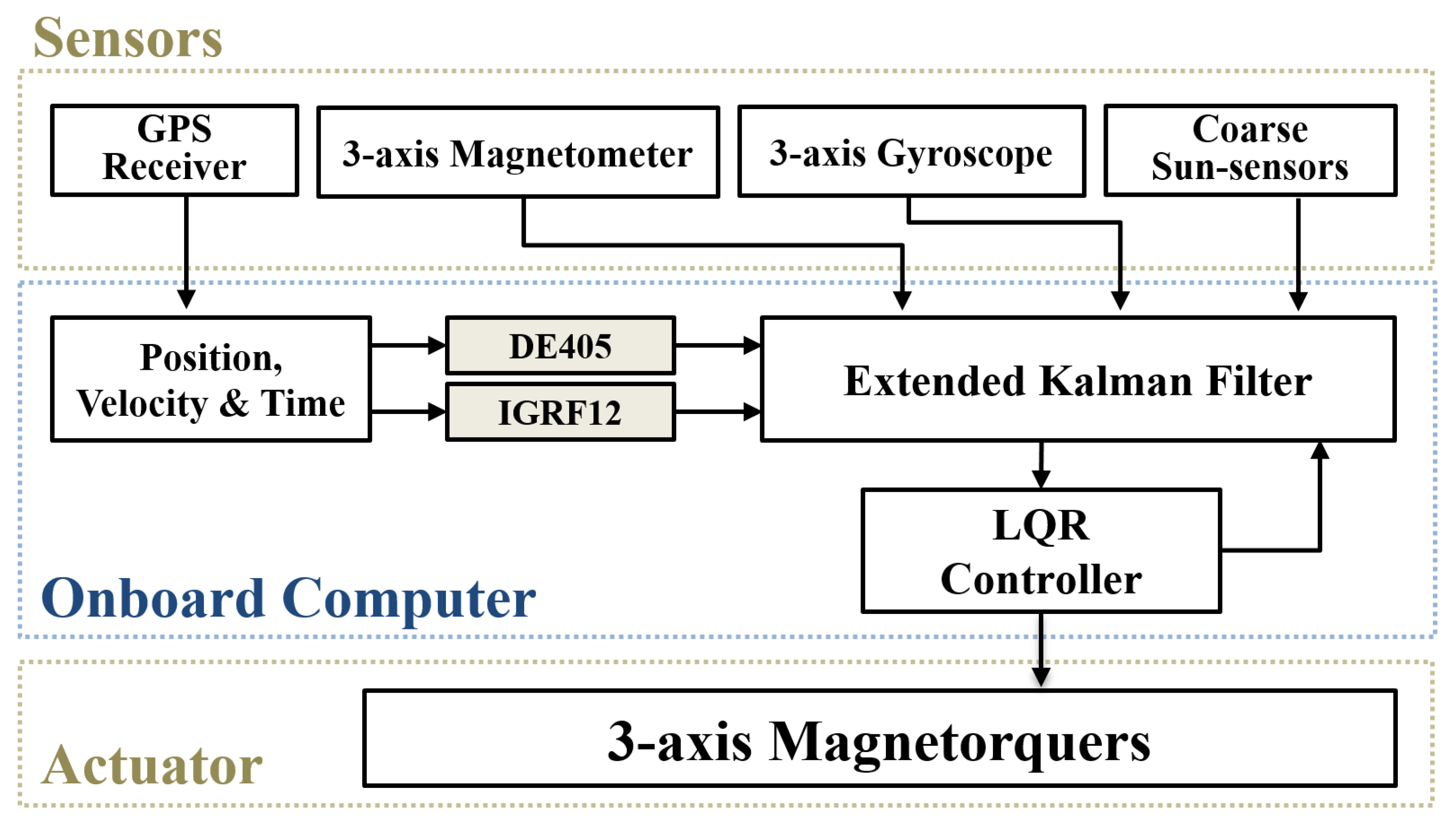
2.3. Attitude System of SNUGLITE
2.3.1. Attitude System Configuration
2.3.2. Onboard Attitude Determination Algorithm
2.3.3. Attitude Estimation Analysis Method
3. In-Orbit Results
3.1. Satellite Status
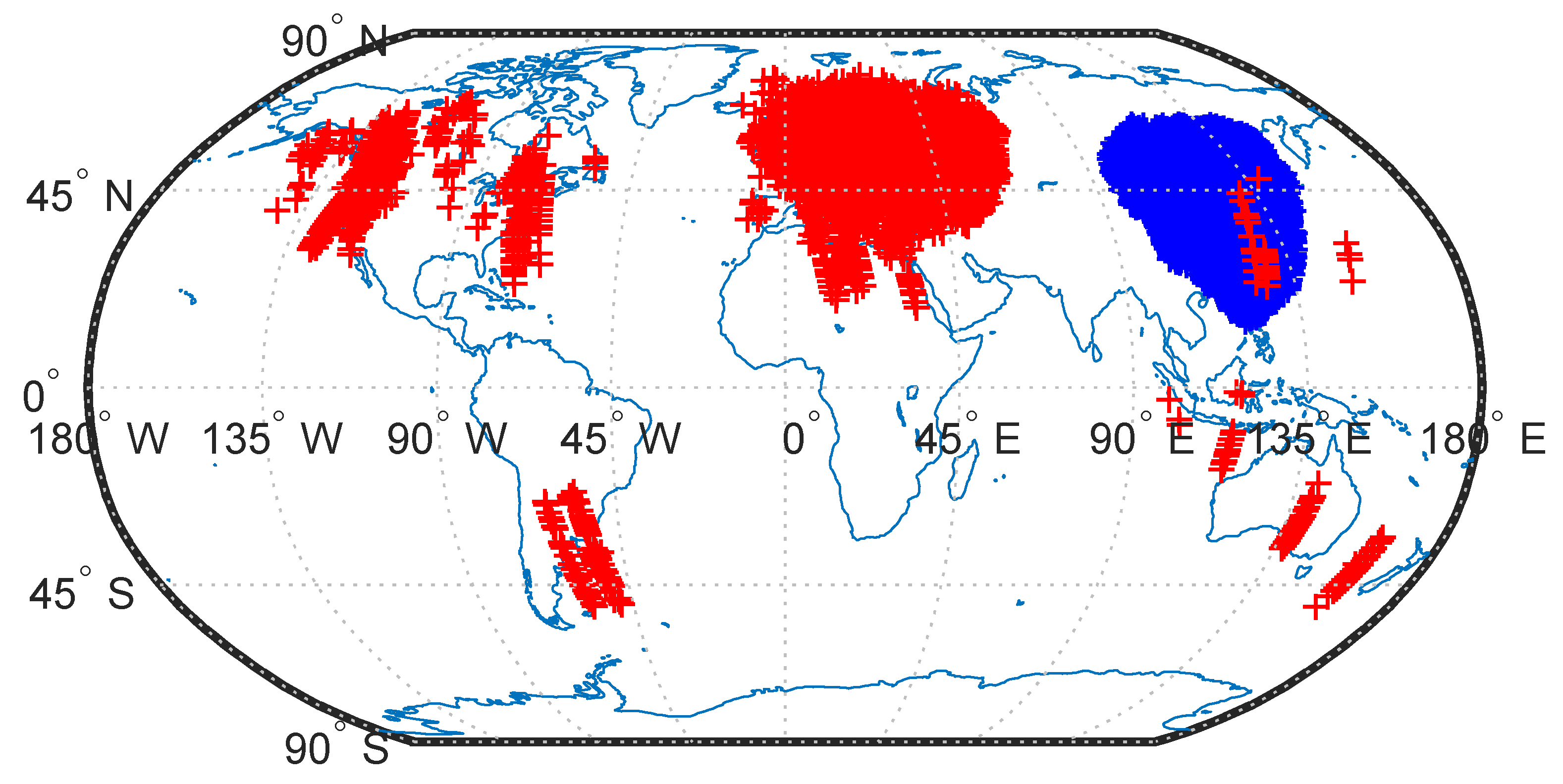
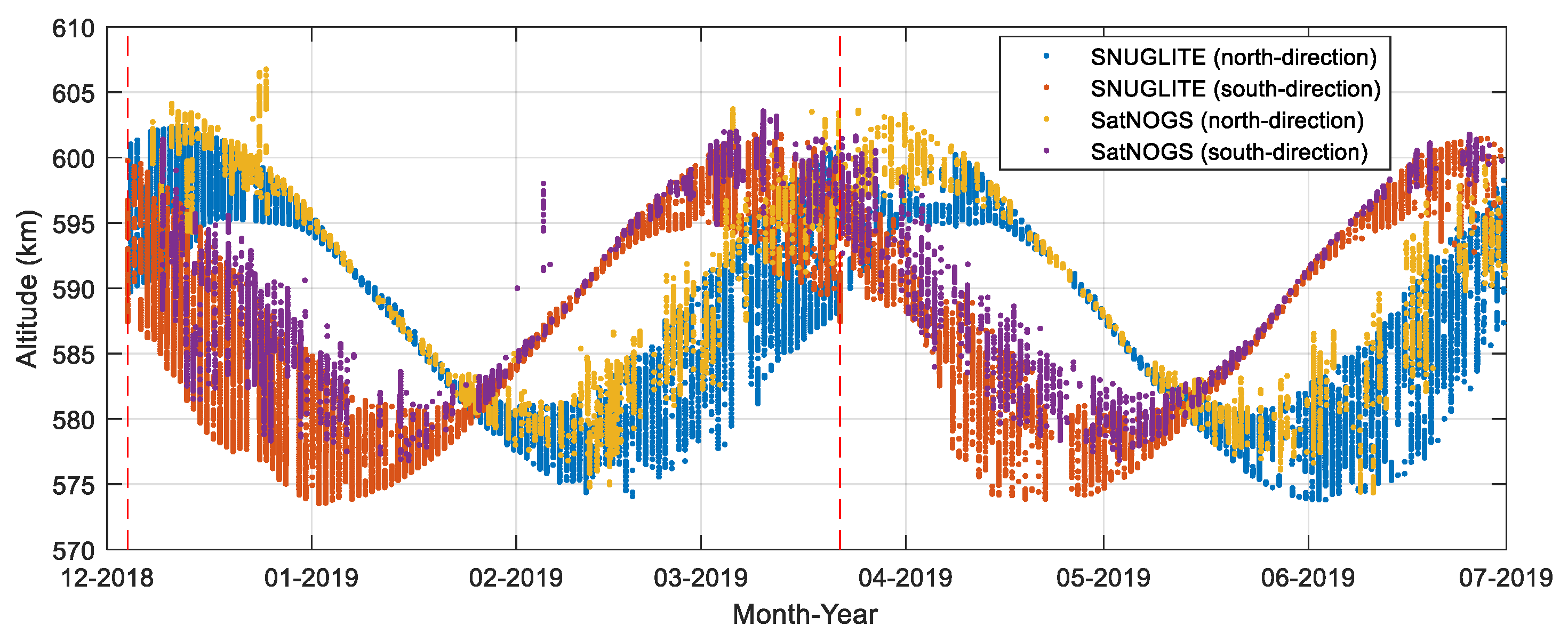
3.1.1. GPS Receiver Results
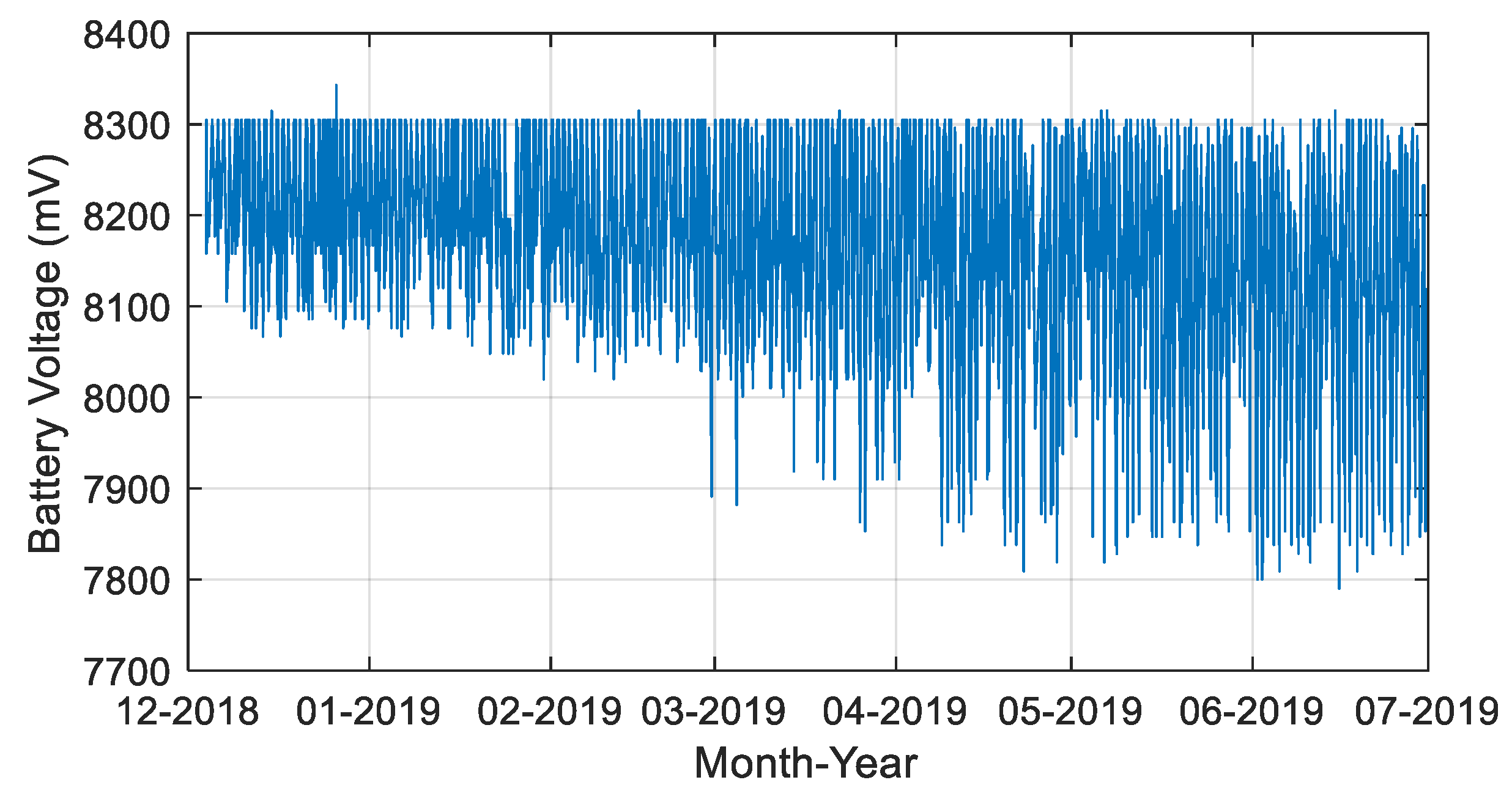
3.1.2. Battery Voltage
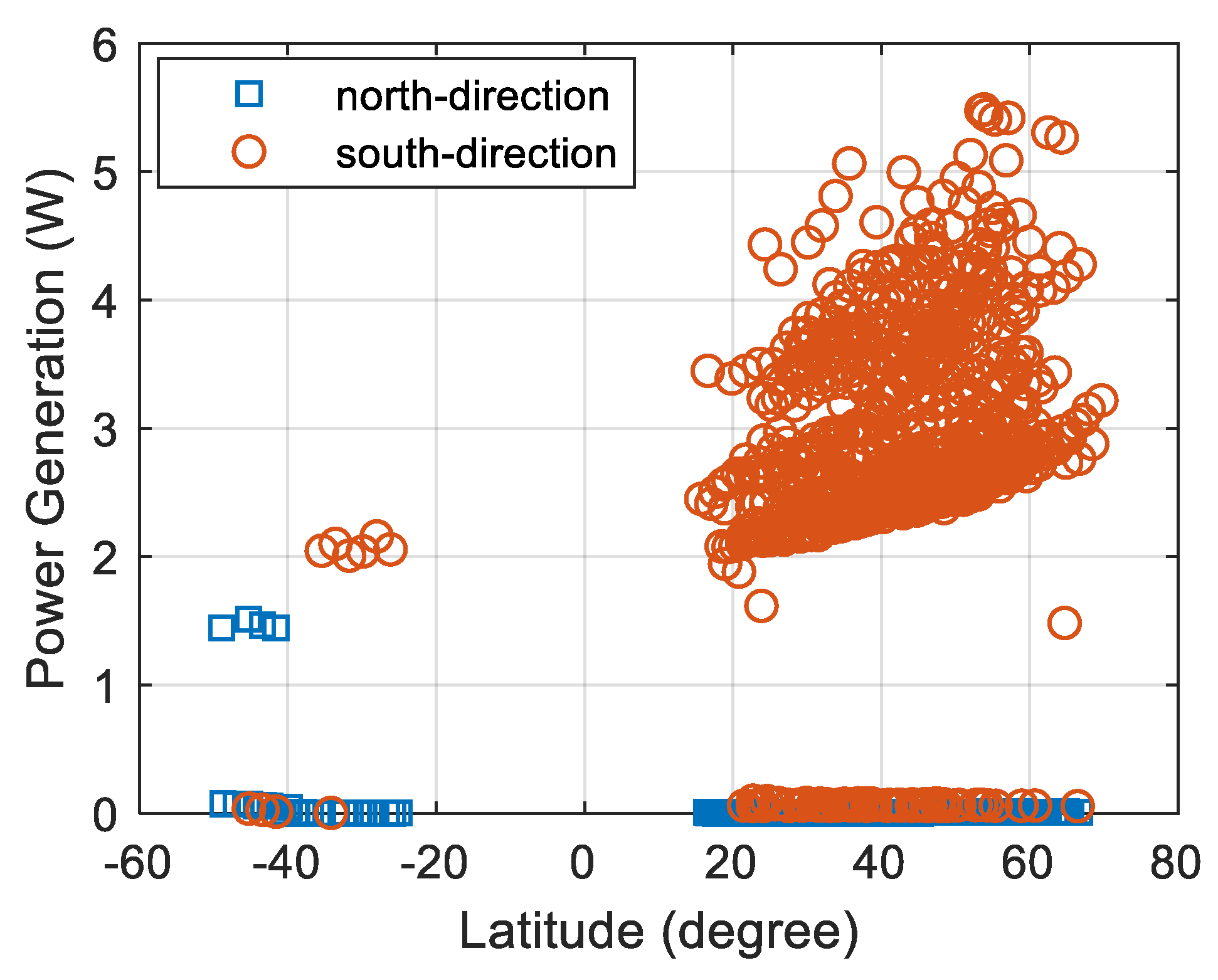
3.1.3. Power Generation
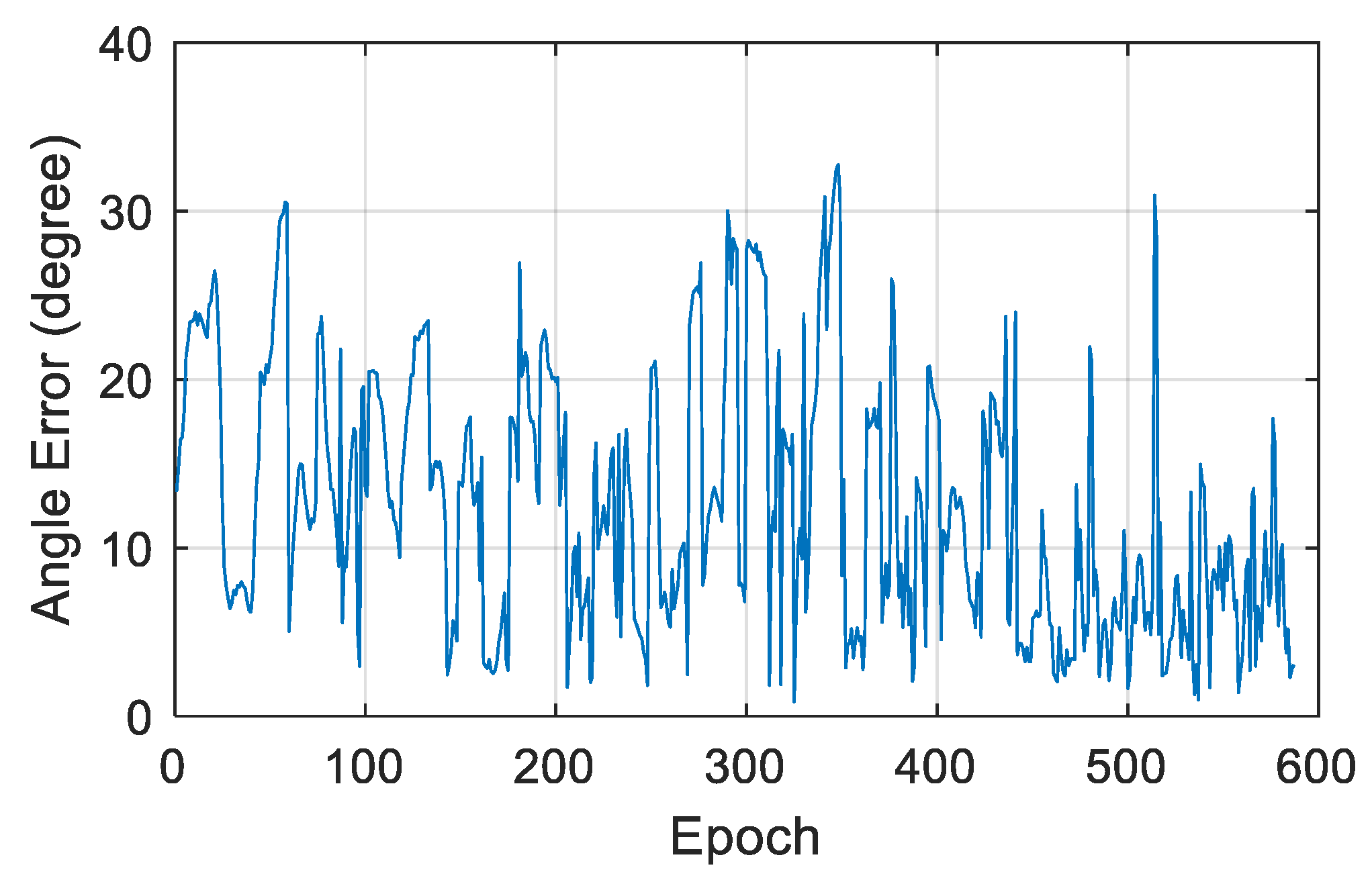
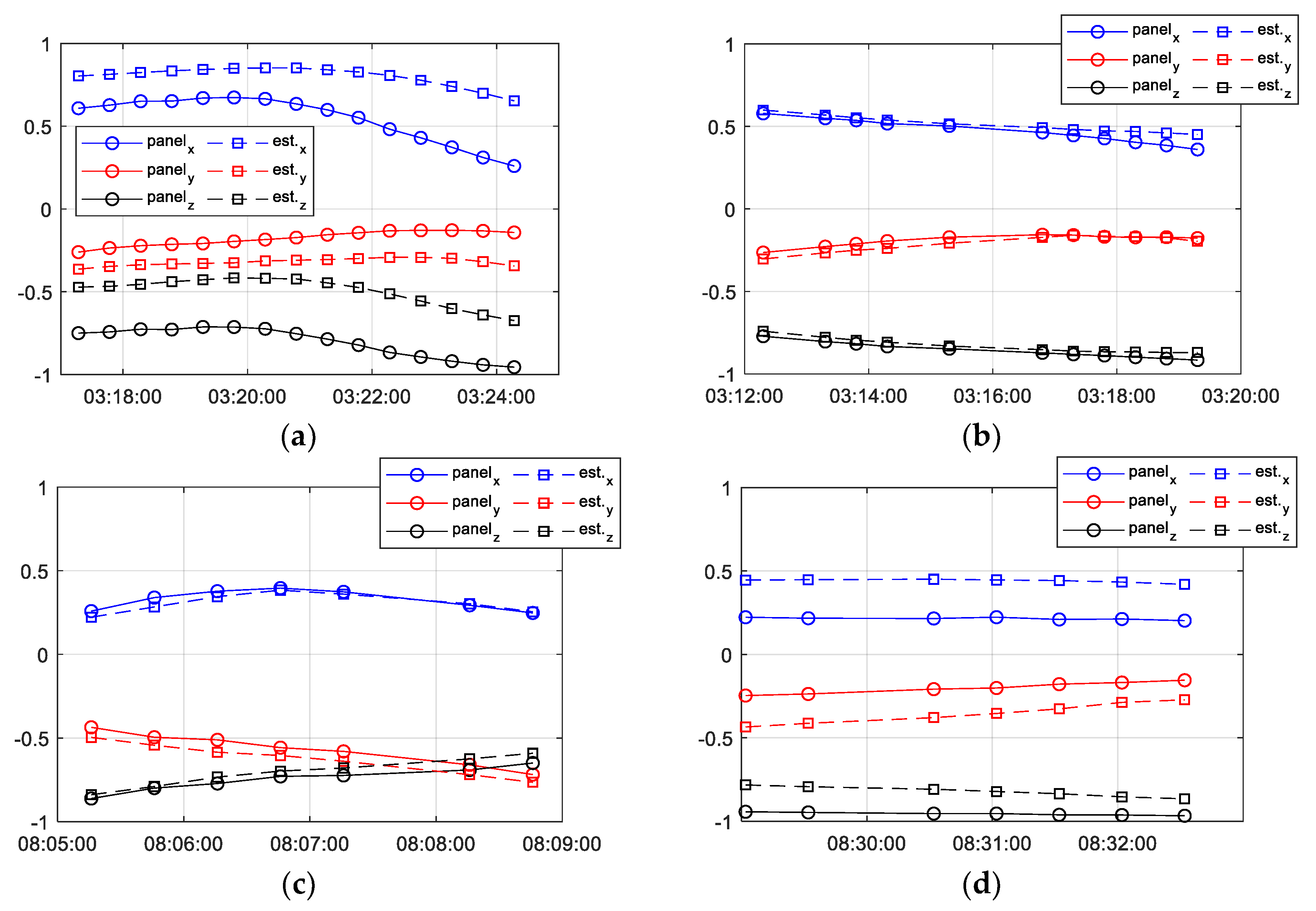
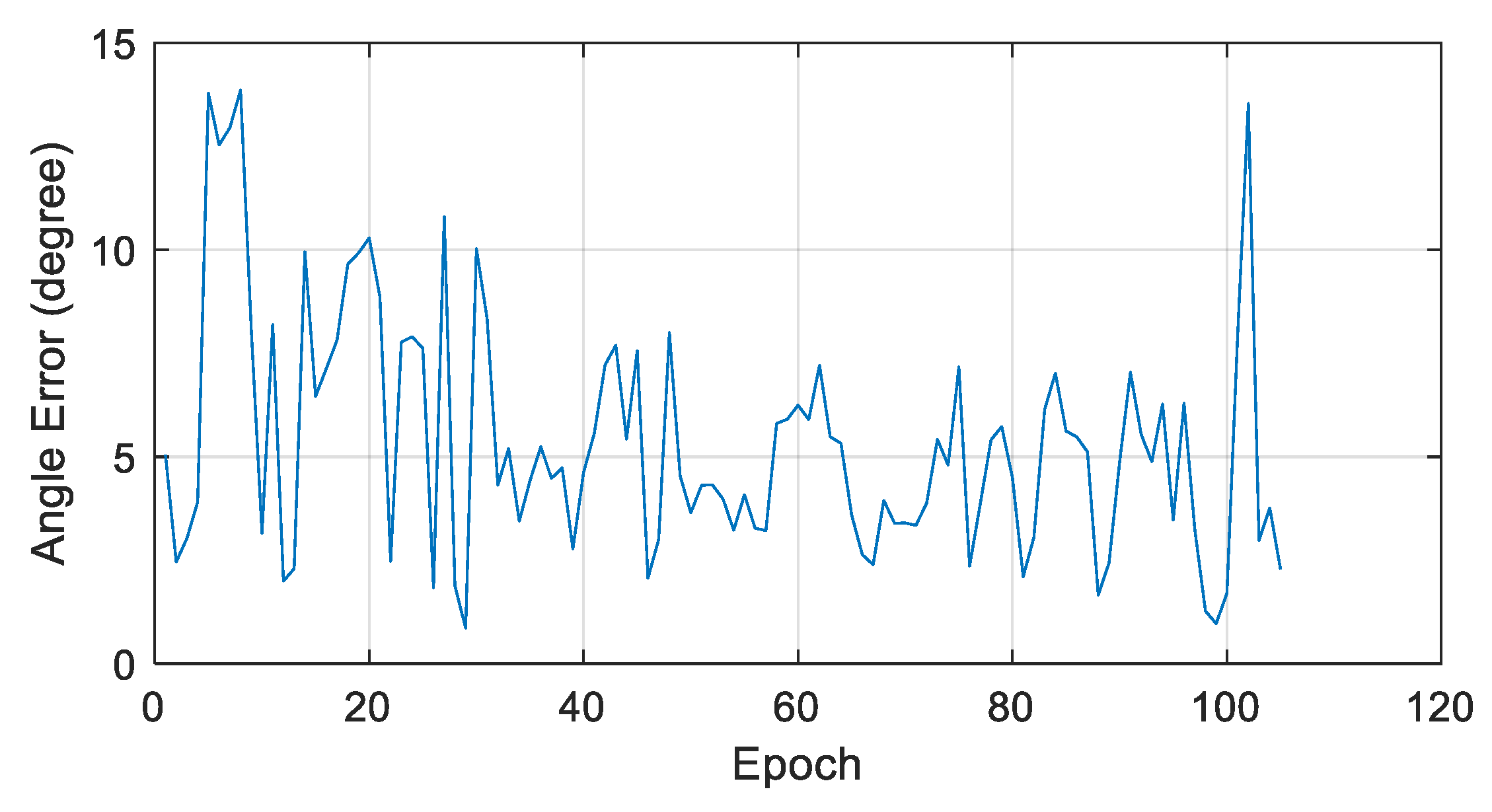
3.2. Satellite Attitude
- The z-component of the GPS velocity in Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) is negative.
- The total power generation is more than 2 W.
- The power generation on the –z side is more than 100 mW.
- Reverse direction cases of sun-pointing vector by slow temperature changes are excluded.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- California Polytechnic State University. CubeSat Design Specification; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, W.; Camps, A. Remote Sensing With Small Satellites. In Introduction to Satellite Remote Sensing, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 797–810. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Peroy, C.; Emami, M.R. CubeSat Mission: From Design to Operation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swartwout, M. CubeSats and Mission Success: 2017 Update. In Proceedings of the Electronic Technology Workshop, NASA Electronic Parts Packaging Program (NEPP) Electron, Greenbelt, MD, USA, 27 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, J.P.; Baumgart, M.; Rogler, B.; Downs, C.; Williams, M.; Woods, T.N.; Palo, S.; Chamberlin, P.C.; Solomon, S.; Jones, A.; et al. MinXSS-1 CubeSat On-Orbit Pointing and Power Performance. J. Small Satell. 2017, 6, 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- Taraba, M.; Rayburn, C.; Tsuda, A.; Macgillivray, C.S. Boeing’s CubeSat TestBed 1 Attitude Determination Design and On-Orbit Experience. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Springmann, J.C.; Sloboda, A.J.; Klesh, A.T.; Bennett, M.W.; Cutler, J.W. The attitude determination system of the RAX satellite. Acta Astronaut. 2012, 75, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springmann, J.C.; Cutler, J.W. Flight results of a low-cost attitude determination system. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 99, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavinskis, A.; Ehrpais, H.; Kuuste, H.; Sunter, I.; Viru, J.; Kutt, J.; Kulu, E.; Noorms, M. Flight Results of ESTCube-1 Attitude Determination System. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 29, 04015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boshuizen, C.; Mason, J.; Klupar, P.; Spanhake, S. Results from the Planet Labs Flock Constellation. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 2–7 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, D. Seizing Opportunity: Spire’s CubeSat Constellation of GNSS, AIS, and ADS-B Sensors. In Proceedings of the Stanford PNT Symposium 2018, Stanford, CA, USA, 8 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Post, M.; Wright, T.; Lee, R. Design of Attitude Control Systems for CubeSat-Class Nanosatellite. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2013, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libre Space Foundation. SatNOGS Database. Available online: https://db.satnogs.org/ (accessed on 30 September 2019).
- Gonzalez, O.R.; Kelkar, A.G. Robust Multivariable Control. In The Electrical Engineering Handbook, 1st ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 1037–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. Attitude Determination and Control of Cubesat Using Magnetic Torquer and LQR Controller. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J. Attitude Determination and Control System for Low Earth Orbit CubeSat Considering Operation Scenario. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, H. HILS Verification of Low Earth Orbit Cube-Satellite Attitude Determination and Control System Using Helmholtz Cage. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Kim, O.-J.; Bae, Y.; Shim, H.; Kee, C.; Han, S.; Choi, Y.; Choi, W.-S. Analysis of On-board GPS Receiver Navigation Solutions for SNUGLITE Cubesat. In Proceedings of the KSAS 2019 Spring Conference, Buan, Korea, 18 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Yu, S.; Kim, O.-J.; No, H.; Shim, H.; Kee, C. Development and Verification of Attitude Determination and Control Algorithm for SNUGLITE Cube Satellite. In Proceedings of the ITM/PTTI 2018, Reston, VA, USA, 30 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M. Sensor Calibration and Single-axis HIL Verification of ADCS for Low Earth Orbit Cube-Satellite. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.G.; Hwang, P.Y.C. The Discrete Kalman Filter, State-Space Modeling, and Simulation. In Introduction to Random Signals and Applied Kalman Filtering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 190–241. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Jang, J.; Yu, S.; Kim, O.-J.; Shim, H.; Kee, C. Single-axis Hardware in the Loop Experiment Verification of ADCS for Low Earth Orbit Cube-Satellite. JPNT 2017, 6, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Vallado, D.A.; Seago, J.H.; Seidelmann, P.K. Implementation Issues Surrounding the New IAU Reference Systems for Astrodynamics. In Proceedings of the 16th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 22–26 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vallado, D.A. Kepler’s Equation and Kepler’s Problem. In Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 49–136. [Google Scholar]
- Vallado, D.A. General Perturbation Techniques. In Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 605–724. [Google Scholar]
- CubeSatShop by Innovative Solutions in Space. Available online: https://www.cubesatshop.com (accessed on 14 March 2020).

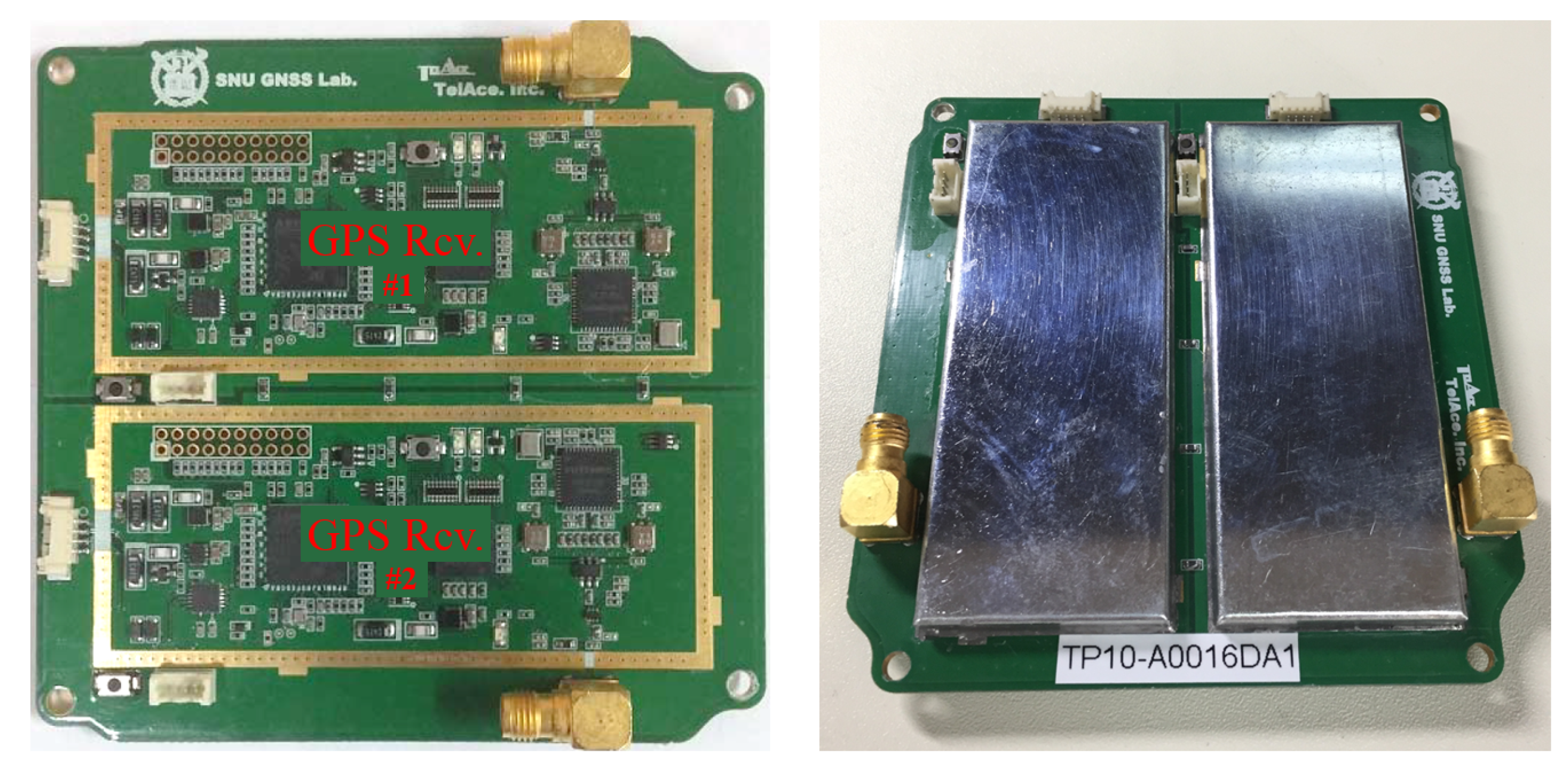

| Item | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| main payloads | dual-frequency L1/L2C Global Position System (GPS) receiver (2 units) | ||
| secondary payloads | 3-axis flux-gate magnetometer | ||
| satellite size | before deployment | 100 × 100 × 227 mm (2U) | |
| after deployment | 100 × 100 × 727 mm (boom deployment) | ||
| satellite weight | 1.87 kg | ||
| satellite communication | frequency | uplink | 437.275 MHz 1 (UHF 2) |
| downlink | 437.275 MHz 1 (UHF 2) | ||
| 2405 MHz 1 (S-band) | |||
| data rate | uplink | 9600 bps (UHF 2) | |
| downlink | 9600 bps (UHF 2) | ||
| 106,000 bps (S-band) | |||
| modulation | GMSK (UHF 2), DQPSK (S-band) | ||
| protocol | AX.25 (UHF 2) | ||
| orbit | sun-synchronous 575 km | ||
| Data | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| time | “YY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS” in UTC (GMT) | 6 × unsigned char |
| GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver | positioning flag (“0”: TLE (two line element set), “1”: GPS) | unsigned char |
| “X, Y, Z” position in Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) (cm) | 3 × signed int | |
| “X, Y, Z” velocity in ECEF (cm/s) | 3 × signed int | |
| power system | battery status flag (“0”: initial, “1”: under-voltage, “2”: safe-mode, “3”: nominal, “4”: full) | unsigned char |
| battery voltage (mV) | unsigned short | |
| battery current (mA) | unsigned short | |
| power-supply-switch flags for each module | unsigned char | |
| current consumption for each power-supply-switch (mA) | 6 × unsigned short | |
| solar-panel input voltage: “± X, ±Y, −Z 1” (mV) | 3 × unsigned short | |
| solar-panel input current: “± X, ±Y, −Z 1” (mA) | 3 × unsigned short | |
| attitude system | estimated attitude: “q0, q1, q2, q3” | 4 × float |
| estimated gyro bias: “roll, pitch, yaw” (rad/s) | 3 × float | |
| estimated angular rate: “roll, pitch, yaw” (rad/s) | 3 × float | |
| gyroscope measurements: “roll, pitch, yaw” (rad/s) | 3 × float | |
| attitude convergence flag and sun/eclipse flag | unsigned char | |
| attitude variance: “q0, q1, q2, q3” | 4 × float | |
| mode | current operation mode (“0”: init-mode, “1”: standby mode) | unsigned char |
| elapsed time of operation mode (min) | signed int | |
| temperature | solar panels (deg. Celsius) | 5 1 × unsigned char |
| onboard computer (deg. Celsius) | 2 × unsigned char | |
| power module (deg. Celsius) | 4 × unsigned char | |
| UHF module (deg. Celsius) | 2 × unsigned char | |
| deployment status | antenna release status flag and boom release status flag | unsigned char |
| number of trial for antenna release | unsigned char | |
| number of trial for boom release | unsigned char |
| Generated Power | Number of Valid Epoch | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Degree) | RMS (Degree) | ||
| >2 W | 587 | 12.6 | 14.7 |
| >3 W | 287 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
| >4 W | 105 | 5.4 | 6.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, O.-J.; Shim, H.; Yu, S.; Bae, Y.; Kee, C.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Han, S.; Choi, Y. In-Orbit Results and Attitude Analysis of the SNUGLITE Cube-Satellite. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072507
Kim O-J, Shim H, Yu S, Bae Y, Kee C, Kim H, Lee J, Han J, Han S, Choi Y. In-Orbit Results and Attitude Analysis of the SNUGLITE Cube-Satellite. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072507
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, O-Jong, Hanjoon Shim, Sunkyoung Yu, Yonghwan Bae, Changdon Kee, Hakdu Kim, Jungchul Lee, Jinhee Han, Sanghyuck Han, and Yeonju Choi. 2020. "In-Orbit Results and Attitude Analysis of the SNUGLITE Cube-Satellite" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072507
APA StyleKim, O.-J., Shim, H., Yu, S., Bae, Y., Kee, C., Kim, H., Lee, J., Han, J., Han, S., & Choi, Y. (2020). In-Orbit Results and Attitude Analysis of the SNUGLITE Cube-Satellite. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072507





