Superhydrophobic Surfaces Enabled by Femtosecond Fiber Laser-Written Nanostructures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Materials and Conditions
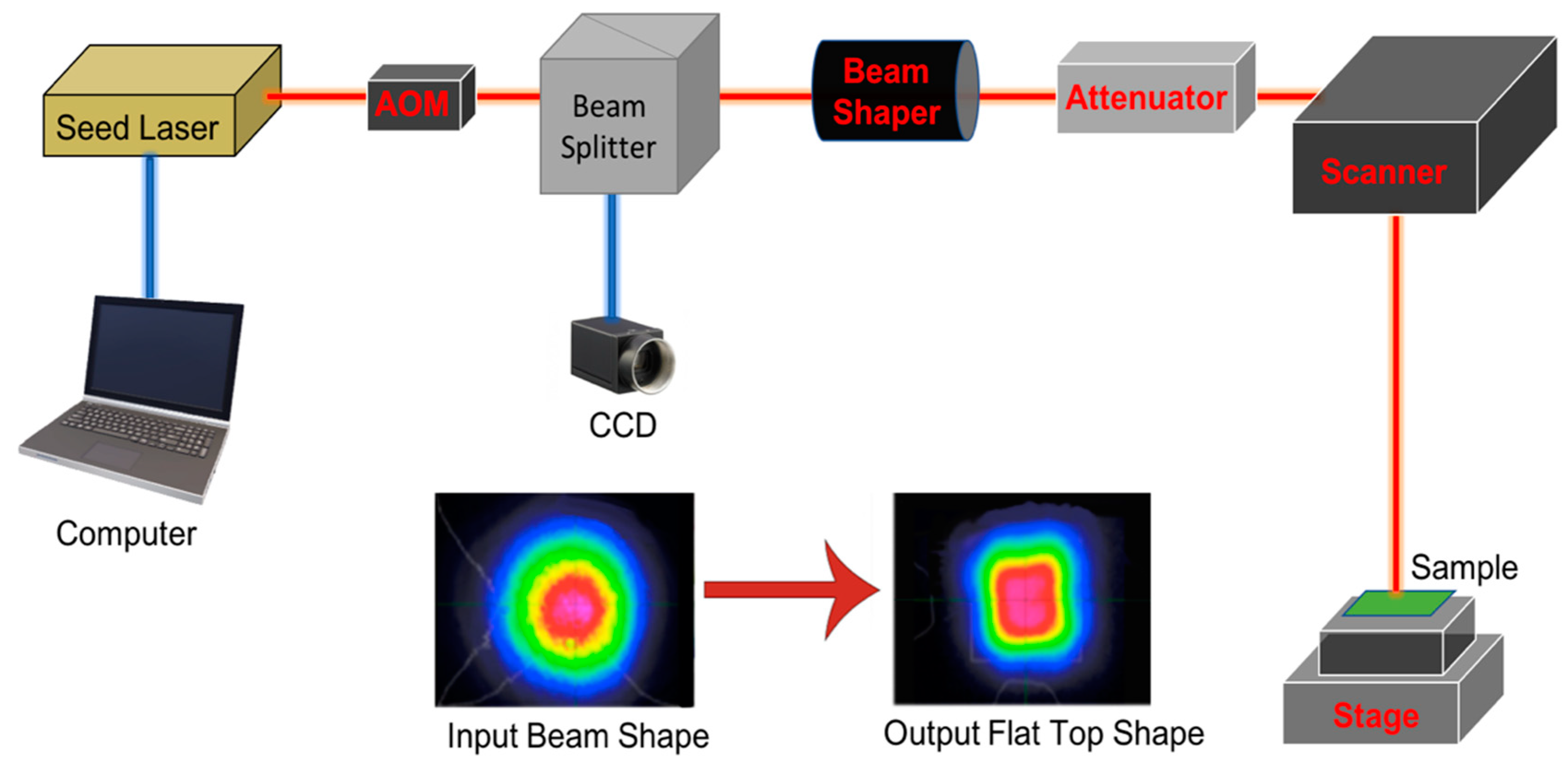
2.2. Laser System Setup
2.3. Characterization of Surface Structure
3. Results and Discussion
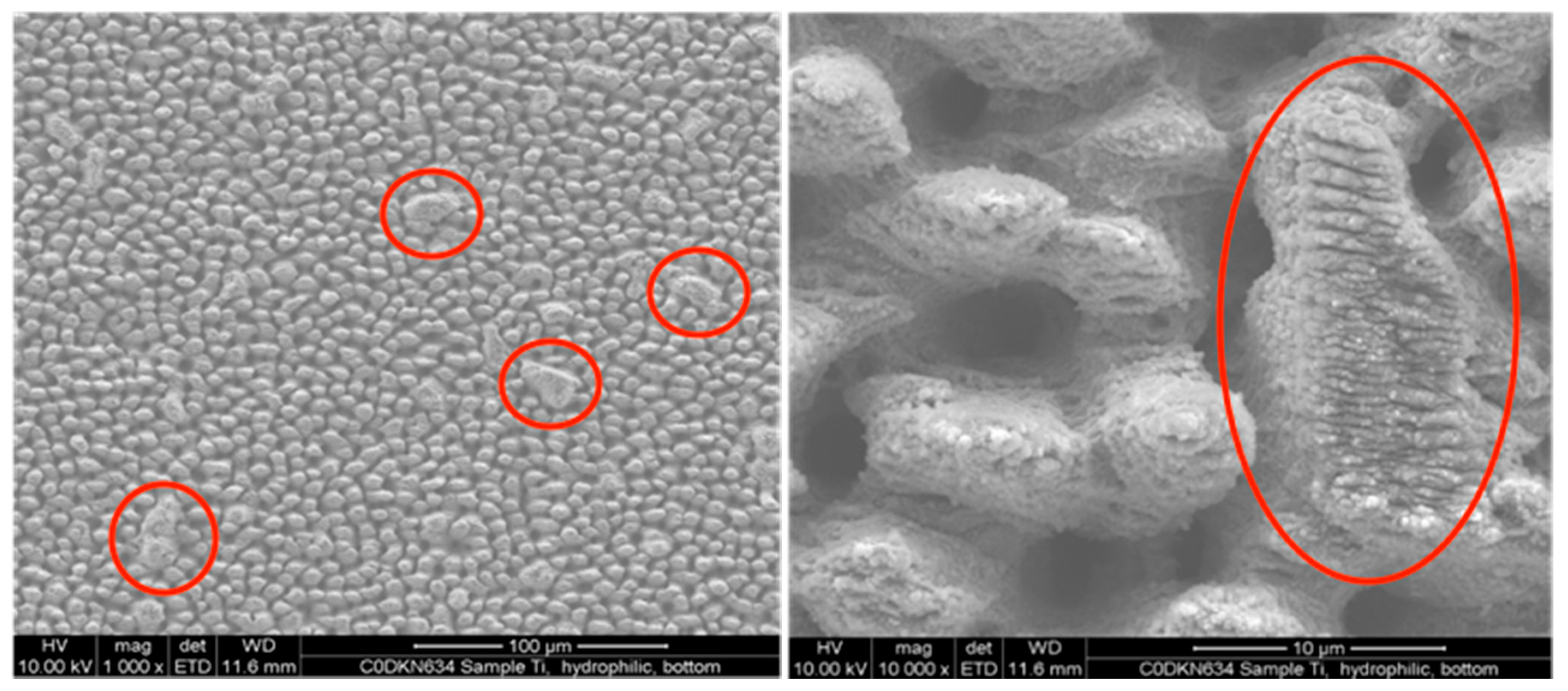
3.1. Effect of Laser Irradiation on Surface Morphology
3.2. Effect of Laser Irradiation on Metal Wettability
- (1)
- the PRR of 100 kHz (energy: 8, 16, 32, 55 µJ; scanning speed: 50, 100, 200, 500, 800 mm/s; pitch: 2, 5, 7 µm), and
- (2)
- the PRR of 200 kHz (energy: 8, 16, 32, 55 µJ; scanning speed: 50, 100, 200, 500, 800 mm/s; pitch: 2, 5, 7 µm).
3.3. Water-Repellent and Self-Cleaning Properties
3.4. Light-Trapping Effect
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Nosonovsky, M. The rose petal effect and the modes of superhydrophobicity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 4713–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.R.; Lawrence, C.R. Water capture by a desert beetle. Nature 2001, 414, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixler, G.D.; Bhushan, B. Bioinspired rice leaf and butterfly wing surface structures combining shark skin and lotus effects. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11271–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 667–677. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Rodak, D.E. Is the lotus leaf superhydrophobic? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 144101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, G. Considerations on the Use of Hydrophobic, Superhydrophobic or Icephobic Coatings as a Part of the Aircraft Ice Protection System; SAE Technical Paper Series; SAE International: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.G.; Xin, S.C.; Wu, C.W. Drag reduction of a miniature boat with superhydrophobic grille bottom. AIP Adv. 2011, 1, 032148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Kehr, Y.Z.; Horng, L.; Chang, K.; Kuo, L. An Experimental Study of Drag Reduction in a Pipe with Superhydrophobic Coating at Moderate Reynolds Numbers. EPJ Web Conf. 2010, 6, 19005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaels, A.D. Angioplasty versus bypass surgery for coronary artery disease. Circulation 2002, 106, e187–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishizaki, T.; Saito, N.; Takai, O. Correlation of Cell Adhesive Behaviors on Superhydrophobic, Superhydrophilic, and Micropatterned Superhydrophobic/Superhydrophilic Surfaces to Their Surface Chemistry. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8147–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.; Tirrell, D.A. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature 2004, 428, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, P.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Kumar, A. Superhydrophobic coatings for aluminium surfaces synthesized by chemical etching process. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2016, 7, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkleman, A.; Gotesman, G.; Yoffe, A.; Naaman, R. Immobilizing a drop of water: Fabricating highly hydrophobic surfaces that pin water droplets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, W.; Tatsuma, T. Conversion of a solid surface from super-hydrophobic to super-hydrophilic by photocatalytic remote oxidation and photocatalytic lithography. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 243, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lyu, S.; Fu, F.; Chang, H.; Wang, S. Preparation of superhydrophobic coating with excellent abrasion resistance and durability using nanofibrillated cellulose. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 106194–106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.C.; Zoubir, A.; Rivero, C.; Lopez, C.; Petit, L.C.; Richardson, K.A. Femtosecond Laser Microstructuring and Refractive Index Modification Applied to Laser and Photonic Devices. In Proceedings of the Micromachining Technology for Micro-Optics and Nano-Optics II, San Jose, CA, USA, 29 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.T.; Hunter, S.R.; Aytug, T. Superhydrophobic materials and coatings: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 086501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerse, C.; Kalaycıoğlu, H.; Elahi, P.; Çetin, B.; Kesim, D.K.; Akçaalan, Ö.; Yavaş, S.; Aşık, M.; Öktem, B.; Hoogland, H.; et al. Ablation-cooled material removal with ultrafast bursts of pulses. Nature 2016, 537, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Multifunctional surfaces produced by femtosecond laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 033103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2012, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Calderon, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Dias-Ponte, A.; Morant-Miñana, M.C.; Gómez-Aranzadi, M.; Olaizola, S.M. Femtosecond laser fabrication of highly hydrophobic stainless steel surface with hierarchical structures fabricated by combining ordered microstructures and LIPSS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, L. Laser-Generated Surface Structures Create Extremely Water-Repellent Metals. Available online: http://www.rochester.edu/newscenter/superhydrophobic-metals-85592/ (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Gaudiosi, D.M.; Gagnon, E.; Lytle, A.L.; Fiore, J.L.; Gibson, E.A.; Kane, S.; Squier, J.; Murnane, M.M.; Kapteyn, H.C.; Jimenez, R.; et al. Multi-kilohertz repetition rate Ti:sapphire amplifier based on down-chirped pulse amplification. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horley, R. The Fiber Advantage. Oemagazine, 1 September 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmed, K.M.; Grambow, C.; Kietzig, A.M. Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metals by Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. Micromachines 2014, 5, 1219–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Park, C.H. Superhydrophobic Textiles: Review of Theoretical Definitions, Fabrication and Functional Evaluation. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, C.D.; Brugnara, M.; Maniglio, D.; Siboni, S.; Wangdu, T. About the possibility of experimentally measuring an equilibrium contact angle and its theoretical and practical consequences. Contact Angle Wettability Adhes. 2006, 4, 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.B. Hierarchical micro/nano structures for super-hydrophobic surfaces and super-lyophobic surface against liquid metal. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2014, 2, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, T.J.; Her, E.K.; Shin, B.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, K.R.; Hong, B.K.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, K.H.; Moon, M.W. Water condensation behavior on the surface of a network of superhydrophobic carbon fibers with high-aspect-ratio nanostructures. Carbon 2012, 50, 5085–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, L.; Mazur, E.; Nolte, S.; Schaffer, C.B. Femtosecond Laser Micromachining. In Ultrafast Nonlinear Optics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.H.; Wang, Z.J. Modeling Cassie-Baxter State on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 37, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiponen, K.E.; Tsubo, T. Metal surface roughness and optical reflectance. Opt. Laser Technol. 1990, 22, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, C.; You, R.; Wu, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhu, L.; Feng, S. Superhydrophobic silver film as a SERS substrate for the detection of uric acid and creatinine. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4988–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, E.; Lee, H.J.; Lu, X. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Enabled by Femtosecond Fiber Laser-Written Nanostructures. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082678
Liu E, Lee HJ, Lu X. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Enabled by Femtosecond Fiber Laser-Written Nanostructures. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(8):2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082678
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Erin, Hyeong Jae Lee, and Xuejun Lu. 2020. "Superhydrophobic Surfaces Enabled by Femtosecond Fiber Laser-Written Nanostructures" Applied Sciences 10, no. 8: 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082678
APA StyleLiu, E., Lee, H. J., & Lu, X. (2020). Superhydrophobic Surfaces Enabled by Femtosecond Fiber Laser-Written Nanostructures. Applied Sciences, 10(8), 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082678





