Interior Sound Quality Prediction of Pure Electric Vehicles Based on Transfer Path Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PEV Transfer Path Analysis
2.2. PEV Transfer Path Synthesis
2.3. Psychoacoustic Parameters of SQ
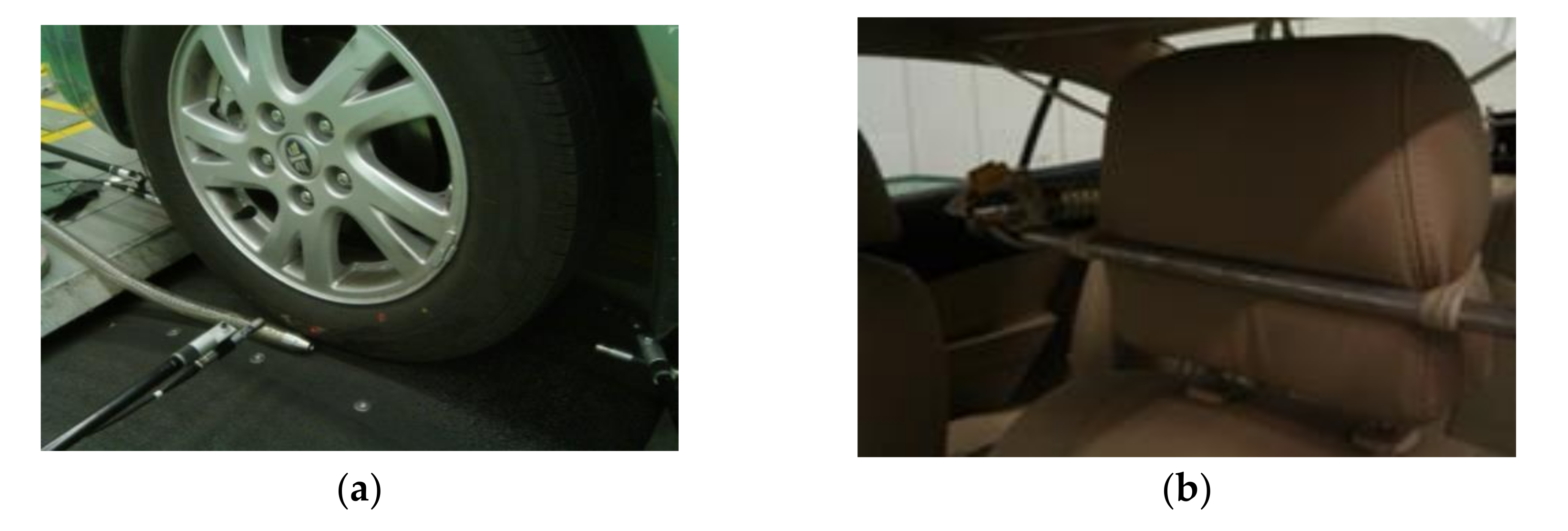
3. Measurements
3.1. Transfer Function Measurements
3.1.1. Airborne Noise Transfer Function Measurements
3.1.2. Structure-Borne Noise Transfer Function Measurements
3.2. Noise Source Excitation Measurements
3.2.1. Airborne Noise Source Excitation Measurements
3.2.2. Structure-Borne Noise Source Excitation Measurements
4. Interior Sound Quality Synthesis
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, K.; Hou, Z.; Sun, D.; Wu, P.; Luo, R.; Kuang, K. Objective evaluation of noise in electric vehicles during acceleration based on psychoacoustics. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; Volume 261, pp. 2863–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, L.; Altinsoy, M.E. Prediction of annoyance evaluations of electric vehicle noise by using artificial neural networks. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 145, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zuo, S. Electromagnetic Vibration and Noise of the Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors for Electric Vehicles: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 5, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, D.; Bekker, A.; Bienert, J. The subjective dimensions of sound quality of standard production electric vehicles. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 129, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Hou, Z.; Sun, D. Sound Quality Estimation of Electric Vehicles Based on GA-BP Artificial Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.B.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, X.R.; Yang, M.L.; Ding, W.P. The development of a deep neural network and its application to evaluating the interior sound quality of pure electric vehicles. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 120, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, J.; Kueppers, T.; Skoda, S. Psychological factors influencing the evaluation of electric vehicle interior noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Hou, Z. Intelligent evaluation of the interior sound quality of electric vehicles. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.K. Prediction of interior noise by excitation force of the powertrain based on hybrid transfer path analysis. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2008, 9, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Lee, S.-K. Prediction of Interior Noise Based on Hybrid TPA. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars-Mech. Syst. 2009, 2, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reising, M.; Küçükay, F.; Eulert, S.; Decker, H.; Luehrs, G.-F. Hybrid acoustic synthesis–Assessment of rear final drives in an early stage of development, on the basis of transfer path analyses and test bench measurements. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 80, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkus, D.; Tcherniak, D.; Brunskog, J. Application of vibro-acoustic operational transfer path analysis. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 154, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, S.; Hou, L.; Zhang, P.; Bu, X.; Xiang, J.; Tang, H.; Lin, J. Transfer path analysis and its application in low-frequency vibration reduction of steering wheel of a passenger vehicle. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 157, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Hu, F.; Zeng, F.; Wei, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J. Research of transfer path analysis based on contribution factor of sound quality. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comesana, D.F.; Korbasiewicz, M. Evaluation of electric vehicle interior noise focused on sound source identification and transfer path analysis. In Proceedings of the Aachen Acoustics Colloquium, Aachen, Germany, 23 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Hou, H. Electric Vehicle Interior Noise Contribution Analysis. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 2016, 2016-01-1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Ibarbia, A.; Battarra, M.; Palenzuela, J.; Cervantes, G.; Walsh, S.; De-La-Cruz, M.; Theodossiades, S.; Gagliardini, L. Comparison between transfer path analysis methods on an electric vehicle. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 118, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albers, A.; Fischer, J.; Landes, D.; Behrendt, M. Method for Measuring and Analyzing the Transfer Path of Acoustic Phenomena into the Driver Cabin of a Battery Electric Vehicle. SAE Int. J. Engines 2014, 7, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Qian, K.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Q. Interior noise and vibration prediction of permanent magnet synchronous motor. J. Vibroeng. 2018, 20, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.-H.; Jen, M.U.; de Klerk, D. Noise Source Separation in Electric Vehicles Using Operational Transfer Path Analysis. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; Volume 258, pp. 1687–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki, H.; Iwanaga, Y.; Ito, H.; Takahashi, Y. Interior Noise evaluation of Electric Vehicle: Noise source contribution analysis. In Proceedings of the 1st International Electric Vehicle Technology Conference, Troy, MI, USA, 17 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Hou, Z.; Sun, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, R.; Sun, D. Sound quality evaluation in the VIP lounge of an EMU train based on psychoacoustic parameters. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; Volume 261, pp. 2935–2945. [Google Scholar]
- Fastl, H.; Zwicker, E. Loudness; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 203–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastl, H.; Zwicker, E. Sharpness and Sensory Pleasantness. In Psychoacoustics: Facts and Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastl, H.; Zwicker, E. Roughness. In Psychoacoustics: Facts and Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Hou, Z.; Sun, Q.; Gao, Y.; Sun, D.; Liu, R. Evaluation and optimization of sound quality in high-speed trains. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 174, 107830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Shin, T.J.; Lee, S.K. Sound Source Identification Based on Acoustic Source Quantification by Measuring the Particle Velocity Directly. In Proceedings the FISITA 2012 World Automotive Congress, Berlin, Germany, 27–30 November 2013; pp. 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, Y.J.; Kang, K.-T.; Kwon, O.J.; Hong, J.-C. The Mathematical Model on Crosstalk Effect of Airborne Noise Sources and Verification based on Comparison between Transfer Path Analysis Methods. Trans. Korean Soc. Noise Vib. Eng. 2008, 18, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.K. Prediction of structure-borne noise caused by the powertrain on the basis of the hybrid transfer path. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2009, 223, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]























| No. | Equipment | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microphone | B&K 4189-A-021 |
| 2 | Acoustic calibrator | B&K 4231 |
| 3 | Data collector | LMS SC316W |
| 4 | Medium-high frequency volume source | LMS SN5114 |
| 5 | Laptop | Dell 5511 |
| No. | Equipment | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microphone | B&K 4189-A-021 |
| 2 | Acceleration sensor | KISTLER 8762A |
| 3 | Miniature shaker | LMS A78 |
| 4 | Data collector | LMS SC316W |
| 5 | Power amplifier | LMS SN2249 |
| 6 | Acoustic calibrator | B&K 4231 |
| 7 | Laptop | Dell 5511 |
| No. | Equipment | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microphone | B&K 4189-A-021 |
| 2 | Acoustic calibrator | B&K 4231 |
| 3 | Acceleration sensor | KISTLER 8734A |
| 4 | Data collector | LMS SC316W |
| 5 | Laptop | Dell 5511 |
| No. | Equipment | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microphone | B&K 4189-A-021 |
| 2 | Acceleration sensor | KISTLER 8762A |
| 3 | Acoustic calibrator | B&K 4231 |
| 4 | Data collector | LMS SC316W |
| 5 | Laptop | Dell 5511 |
| Contribution | Suspension | Mount | Electric Drive System | Tire |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound pressure level/dB(A) | 57.8 | 50.3 | 52.7 | 49.1 |
| Loudness/sone | 11.4 | 5.1 | 6.5 | 4.5 |
| Sharpness/acum | 0.712 | 0.691 | 0.783 | 0.753 |
| Roughness/asper | 0.439 | 0.629 | 0.677 | 0.513 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, K.; Hou, Z.; Liang, J.; Liu, R.; Sun, D. Interior Sound Quality Prediction of Pure Electric Vehicles Based on Transfer Path Synthesis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104385
Qian K, Hou Z, Liang J, Liu R, Sun D. Interior Sound Quality Prediction of Pure Electric Vehicles Based on Transfer Path Synthesis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104385
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Kun, Zhichao Hou, Jie Liang, Ruixue Liu, and Dengke Sun. 2021. "Interior Sound Quality Prediction of Pure Electric Vehicles Based on Transfer Path Synthesis" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104385
APA StyleQian, K., Hou, Z., Liang, J., Liu, R., & Sun, D. (2021). Interior Sound Quality Prediction of Pure Electric Vehicles Based on Transfer Path Synthesis. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104385







