Specific Absolute Velocity Thresholds during Male Basketball Games Using Local Positional System; Differences between Age Categories
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Distances Covered
4.2. Specific Thresholds
4.3. Differences between Competitions
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narazaki, K.; Berg, K.; Stergiou, N.; Chen, B. Physiological demands of competitive basketball. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkrim, N.B.; El Fazaa, S.; El Ati, J. Time-motion analysis and physiological data of elite under-19-year-old basketball players during competition. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delextrat, A.; Badiella, A.; Saavedra, V.; Matthew, D.; Schelling, X.; Torres-Ronda, L. Match activity demands of elite Spanish female basketball players by playing position. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2015, 15, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, E.; Stojiljković, N.; Scanlan, A.T.; Dalbo, V.J.; Berkelmans, D.M.; Milanović, Z. The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basketball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, A.T.; Dascombe, B.J.; Reaburn, P.; Dalbo, V.J. The physiological and activity demands experienced by Australian female basketball players during competition. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2012, 15, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, D.; Delextrat, A. Heart rate, blood lactate concentration, and time-motion analysis of female basketball players during competition. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkrim, N.B.; Castagna, C.; Jabri, I.; Battikh, T.; El Fazaa, S.; El Ati, J. Activity profile and physiological requirements of junior elite basketball players in relation to aerobic-anaerobic fitness. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2330–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, M.; García-Rubio, J.; Ibáñez, S.J. Activity Demands and Speed Profile of Young Female Basketball Players Using Ultra-Wide Band Technology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulka, K.; Cuberek, R.; Svoboda, Z. Time–motion analysis of basketball players: A reliability assessment of Video Manual Motion Tracker 1.0 software. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 32, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Guerrero, J.; Fernández-Valdés, B.; Jones, B.; Moras, G.; Reche, X.; Sampaio, J. Changes in physical demands between game quarters of U18 elite official basketball games. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, A.T.; Tucker, P.S.; Dascombe, B.J.; Berkelmans, D.M.; Hiskens, M.I.; Dalbo, V.J. Fluctuations in activity demands across game quarters in proffesional and semiprofessional male basketball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 3006–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portes, R.; Navarro, R.M.; Sosa, C.; Trapero, J.J.; Jiménez, S.L. Monitoring and interpreting external load in basketball: A narrative review. Rev Psicol del Deport. 2019, 28, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Varley, M.C.; Jaspers, A.; Helsen, W.F.; Malone, J.J. Methodological Considerations When Quantifying High-Intensity Efforts in Team Sport Using Global Positioning System Technology. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferioli, D.; Schelling, X.; Bosio, A.; La Torre, A.; Rucco, D.; Rampinini, E. Match Activities in Basketball Games: Comparison Between Different Competitive Levels. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.; Reche, X. Carga Externa en Baloncesto Formativo y Profesional Durante Competición Oficial; Poster presented at ASEPREB Congress 2019, Barcelona. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Franc-Garcia/publication/334139194_CARGA_EXTERNA_EN_BALONCESTO_FORMATIVO_Y_PROFESIONAL_DURANTE_COMPETICION_OFICIAL/links/5d1a19a6299bf1547c8df7d1/CARGA-EXTERNA-EN-BALONCESTO-FORMATIVO-Y-PROFESIONAL-DURANTE-COMPETICION-OFICIAL.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Hodder, R.W.; Ball, K.A.; Serpiello, F.R. Criterion Validity of Catapult ClearSky T6 Local Positioning System for Measuring Inter-Unit Distance. Sensors 2020, 20, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, C.; Orr, R.; O’Connor, H. Global positioning systems (GPS) and microtechnology sensors in team sports: A systematic review. Sport Med. 2013, 43, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luteberget, L.S.; Spencer, M.; Gilgien, M. Validity of the Catapult ClearSky T6 Local Positioning System for Team Sports Specific Drills, in Indoor Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serpiello, F.R.; Hopkins, W.G.; Barnes, S.; Tavrou, J.; Duthie, G.M.; Aughey, R.J.; Ball, K. Validity of an ultra-wideband local positioning system to measure locomotion in indoor sports. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jennings, D.; Cormack, S.; Coutts, A.J.; Boyd, L.; Aughey, R.J. The validity and reliability of GPS units for measuring distance in team sport specific running patterns. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aughey, R.J.; Falloon, C. Real-time versus post-game GPS data in team sports. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.D.; O’Connor, F.; Pitchford, N.; Torres-Ronda, L.; Robertson, S.J. Relationships between internal and external training load in team-sport athletes: Evidence for an individualized approach. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, C.; Abián-Vicén, J.; Areces, F.; López, R.; Del Coso, J. Physical and physiological demands of experienced male basketball players during a competitive game. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeting, A.J.; Cormack, S.J.; Morgan, S.; Aughey, R.J. When is a sprint a sprint? A review of the analysis of team-sport athlete activity profile. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, A.C.; Anson, J.; Pyne, D. Physiologically based GPS speed zones for evaluating running demands in Women’s Rugby Sevens. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, J.D. Impact of maximum speed on sprint performance during high-level youth female field hockey matches: Female Athletes in Motion (FAiM) study. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, C.; Le Gall, F.; Dupont, G. Analysis of repeated high-intensity running performance in professional soccer. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, T.; Sullivan, C.; Bilsborough, J.C.; Cordy, J.; Coutts, A.J. Match-to-match variation in physical activity and technical skill measures in professional Australian Football. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, M.C.; Gabbett, T.; Aughey, R.J. Activity profiles of professional soccer, rugby league and Australian football match play. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 32, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, C.; Moran, A.; Piggott, D. Defining elite athletes: Issues in the study of expert performance in sport psychology. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2015, 16, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harriss, D.J.; Atkinson, G. Ethical Standards in Sport and Exercise Science Research: 2014 Update. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holme, B.R. Wearable Microsensor Technology to Measure Physical Activity Demands in Handball. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian School of Sport Sciences, Oslo, Norway, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rico-González, M.; Arcos, A.L.; Clemente, F.M.; Rojas-Valverde, D.; Pino-Ortega, J. Accuracy and reliability of local positioning systems for measuring sport movement patterns in stadium-scale: A systematic review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.J.; Watsford, M.L.; Kelly, S.J.; Pine, M.J.; Spurrs, R.W. Valisity and interunit reliability of 10 hz and 15 hz GPS units for assessing athlete movement demands. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luteberget, L.S.; Holme, B.R.; Spencer, M. Reliability of Wearable Inertial Measurement Units to Measure Physical Activity in Team Handball. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C.; Pyne, D.; Portus, M.; Dawson, B. Validity and Reliability of GPS Units to Monitor Cricket-Specific Movement Patterns. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2009, 4, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffield, R.; Reid, M.; Baker, J.; Spratford, W. Accuracy and reliability of GPS devices for measurement of movement patterns in confined spaces for court-based sports. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, M.W.; Baumgart, C.; Polglaze, T.; Freiwald, J. Validity and reliability of GPS and LPS for measuring distances covered and sprint mechanical properties in team sports. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varley, M.C.; Fairweather, I.H.; Aughey, R.J. Validity and reliability of GPS for measuring instantaneous velocity during acceleration, deceleration, and constant motion. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.T.; JScorr, T.; Kelly, V.G. The validity and reliability of global positioning systems in team sports: A brief review. J Strength Cond Res. 2016, 30, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.; Casamichana, D.; Calleja-González, J.; Román, J.S.; Ostojic, S.M. Reliability and Accuracy of 10 Hz GPS Devices for Short-Distance Exercise. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 233–234. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolella, D.P.; Torres-Ronda, L.; Saylor, K.J.; Schelling, X. Validity and reliability of an accelerometer-based player tracking device. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: Current use, calculations, and interpretation. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferioli, D.; Bosio, A.; Zois, J.; La Torre, A.; Rampinini, E. Seasonal changes in physical capacities of basketball players according to competitive levels and individual responses. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pino-Ortega, J.; Rojas-Valverde, D.; Gómez-Carmona, C.D.; Bastida-Castillo, A.; Hernández-Belmonte, A.; García-Rubio, J.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Ibáñez, S.J. Impact of Contextual Factors on External Load During a Congested-Fixture Tournament in Elite U’18 Basketball Players. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scanlan, A.; Dascombe, B.; Reaburn, P. A comparison of the activity demands of elite and sub-elite Australian men’s basketball competition. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, E.; Miranda, N.; Zhang, S.; Sosa, C.; Trapero, J.; Lorenzo, J.; Lorenzo, A. Peak Match Demands in Young Basketball Players: Approach and Applications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, J.L.; Conte, D.; Stanton, R.; McLean, B.; Scanlan, A.T. The Application of Accelerometer-Derived Moving Averages to Quantify Peak Demands in Basketball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020. In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, J.; McGarry, T.; Calleja-González, J.; Sáiz, S.L.J.; Del Alcázar, X.S.I.; Balciunas, M. Exploring Game Performance in the National Basketball Association Using Player Tracking Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, P.G.; Pyne, D.B.; Minahan, C.L. The Physical and Physiological Demands of Basketball Training and Competition. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McInnes, S.; Carlson, J.; Jones, C.; McKenna, M.J. The physiological load imposed on basketball players during competition. J. Sports Sci. 1995, 13, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.S.; Vescovi, J.D. Velocity Thresholds for Women’s Soccer Matches: Sex Specificity Dictates High-Speed-Running and Sprinting Thresholds—Female Athletes in Motion (FAiM). Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Hoshikawa, S.; Hirose, N. Longitudinal Age-Related Morphological and Physiological Changes in Adolescent Male Basketball Players. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 18, 751–757. [Google Scholar]
| Speed Zones | Speed |
|---|---|
| Zone 1 (Standing–Walking) | <7 Km h−1 |
| Zone 2 (Jogging) | 7–14 Km h−1 |
| Zone 3 (Running) | >14–18 Km h−1 |
| Zone 4 (High Speed Running) | >18.0 Km h−1 |
| Zone | Variables | N | Mean | SD | CV% | Shapiro–Wilk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Game | Total Distance (m) | 117 | 3188.84 | 808.37 | 25% | p = 0.055 |
| m·min | 117 | 83.95 | 7.24 | 8% | p = 0.181 | |
| Real Time (min, seg) | 117 | 38.02 | 10.00 | 26% | p = 0.036 | |
| Maximum Velocity (Km h−1) | 117 | 24.54 | 1.72 | 7% | p < 0.001 | |
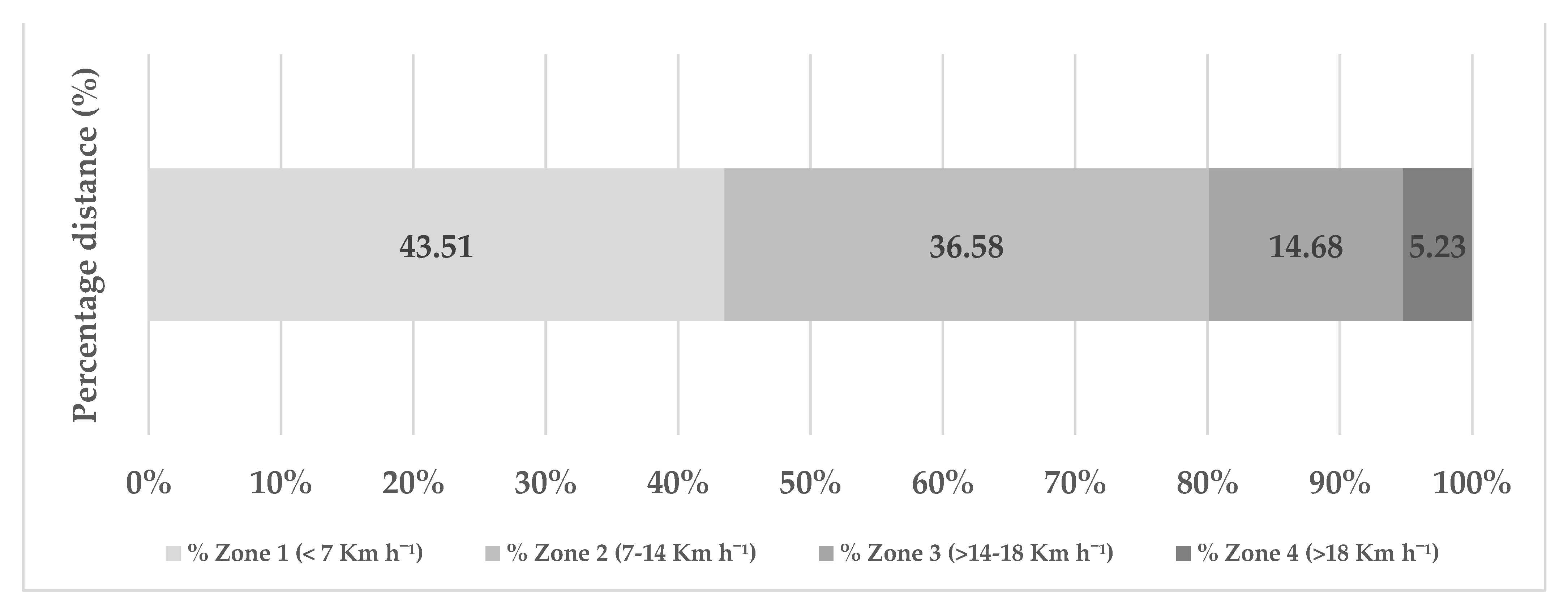
| Zone 1 (0–7.00 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 117 | 1364.57 | 376.84 | 27% | p = 0.024 |
| % Distance | 117 | 43.51 | 3.84 | 8% | p = 0.334 | |
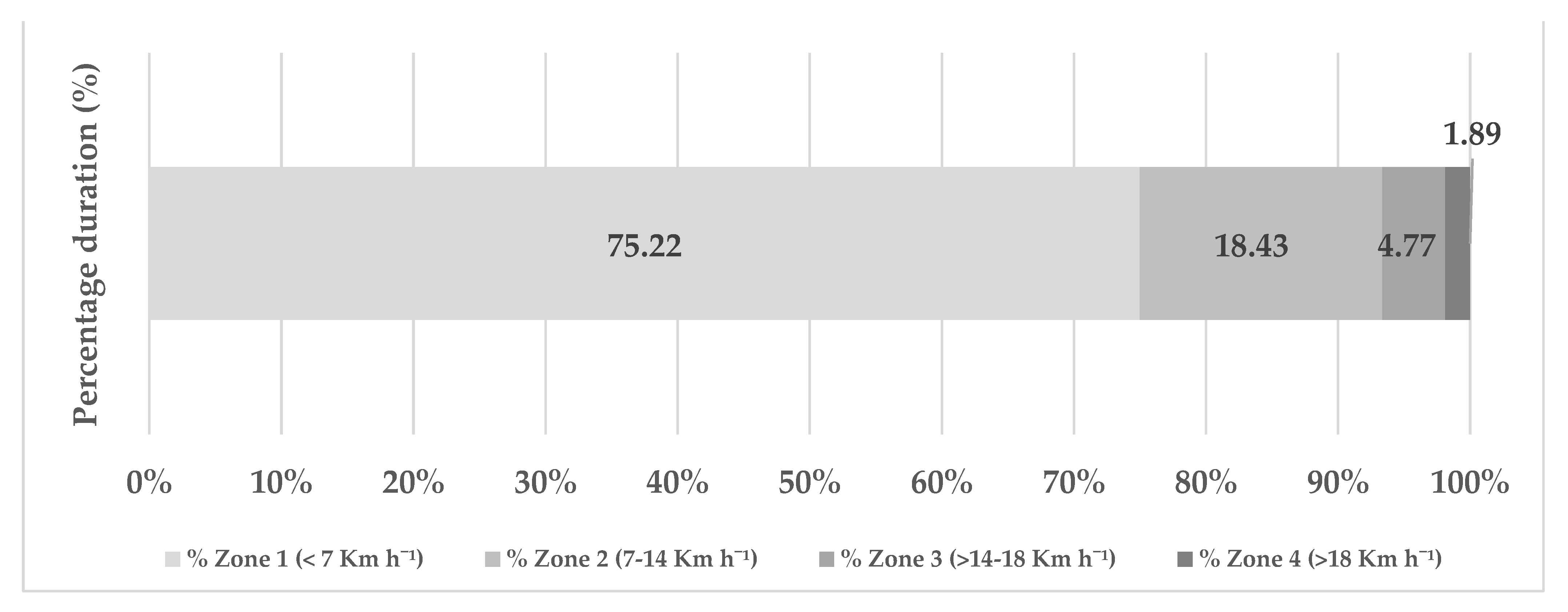
| % Duration | 117 | 75.22 | 3.00 | 3% | p = 0.359 | |
| Zone 2 (7.01–14 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 117 | 1163.80 | 302.32 | 25% | p = 0.173 |
| % Distance | 117 | 36.58 | 3.59 | 9% | p = 0.086 | |
| % Duration | 117 | 18.43 | 2.48 | 13% | p = 0.213 | |
| Zone 3 (14.01–18 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 117 | 469.07 | 144.99 | 30% | p = 0.096 |
| % Distance | 117 | 14.68 | 2.53 | 17% | p = 0.225 | |
| % Duration | 117 | 4.77 | 1.04 | 21% | p = 0.003 | |
| Zone 4 (>18.01 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 117 | 165.43 | 73.64 | 44% | p = 0.010 |
| % Distance | 117 | 5.23 | 2.16 | 41% | p < 0.001 | |
| % Duration | 117 | 1.89 | 1.19 | 62% | p < 0.001 |
| Parameter | Senior | Junior | F | P Tukey | Effect Size | Effect Size Magnitude | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||||
| Full Game | Total Distance (m) | 3325.14 | ±899.84 | 3029.82 | ±659.639 | 3.98 | 0.048 | 0.37 | Small |
| m·min | 81.65 | ±7.037 | 86.64 | ±6.574 | 15.55 | 0.001 | −0.73 | Moderate | |
| Real Time (min, seg) | 40.67 | ±10.96 | 34.93 | ±7.761 | 10.35 | 0.002 | 0.59 | Small | |
| Max Velocity (Km h−1) | 24.41 | ±1.34 | 24.59 | ±1.698 | 0.39 | 0.533 | −0.11 | Trivial | |
| Zone 1 (0–7.00 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 1455.04 | ±415.49 | 1259.02 | ±296.261 | 8.37 | 0.005 | 0.53 | Small |
| % Distance | 45.20 | ±3.19 | 41.54 | ±3.593 | 34.11 | 0.001 | 1.08 | Moderate | |
| % Duration | 76.24 | ±2.69 | 74.02 | ±2.922 | 18.22 | 0.001 | 0.79 | Moderate | |
| Zone 2 (7.01–14 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 1199.01 | ±3.37 | 1122.72 | ±3.741 | 1.87 | 0.175 | 0.25 | Small |
| % Distance | 342.40 | ±17.67 | 244.33 | ±19.3 | 3.59 | 0.061 | −0.35 | Small | |
| % Duration | 36.01 | ±2.26 | 37.25 | ±2.462 | 13.79 | 0.001 | −0.68 | Moderate | |
| Zone 3 (14.01–18 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 483.89 | ±2.51 | 451.78 | ±2.571 | 1.43 | 0.234 | 0.22 | Small |
| % Distance | 152.16 | ±4.59 | 135.50 | ±4.968 | 0.23 | 0.627 | −0.09 | Trivial | |
| % Duration | 14.58 | ±0.97 | 14.81 | ±1.081 | 3.76 | 0.055 | −0.35 | Small | |
| Zone 4 (>18.01 Km h−1) | Distance (m) | 139.83 | ±1.57 | 195.29 | ±2.152 | 19.06 | 0.001 | −0.81 | Moderate |
| % Distance | 58.90 | ±2.07 | 78.25 | ±1.676 | 40.02 | 0.001 | −1.17 | Moderate | |
| % Duration | 4.22 | ±1.50 | 6.40 | ±0.602 | 3.36 | 0.069 | −0.73 | Moderate | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sosa, C.; Lorenzo, A.; Trapero, J.; Ribas, C.; Alonso, E.; Jimenez, S.L. Specific Absolute Velocity Thresholds during Male Basketball Games Using Local Positional System; Differences between Age Categories. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104390
Sosa C, Lorenzo A, Trapero J, Ribas C, Alonso E, Jimenez SL. Specific Absolute Velocity Thresholds during Male Basketball Games Using Local Positional System; Differences between Age Categories. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104390
Chicago/Turabian StyleSosa, Carlos, Alberto Lorenzo, Juan Trapero, Carlos Ribas, Enrique Alonso, and Sergio L. Jimenez. 2021. "Specific Absolute Velocity Thresholds during Male Basketball Games Using Local Positional System; Differences between Age Categories" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104390
APA StyleSosa, C., Lorenzo, A., Trapero, J., Ribas, C., Alonso, E., & Jimenez, S. L. (2021). Specific Absolute Velocity Thresholds during Male Basketball Games Using Local Positional System; Differences between Age Categories. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104390










