Biomechanical Comparison of a Novel Implant and Commercial Fixation Devices for AO/OTA 43-C1 Type Distal Tibial Fracture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
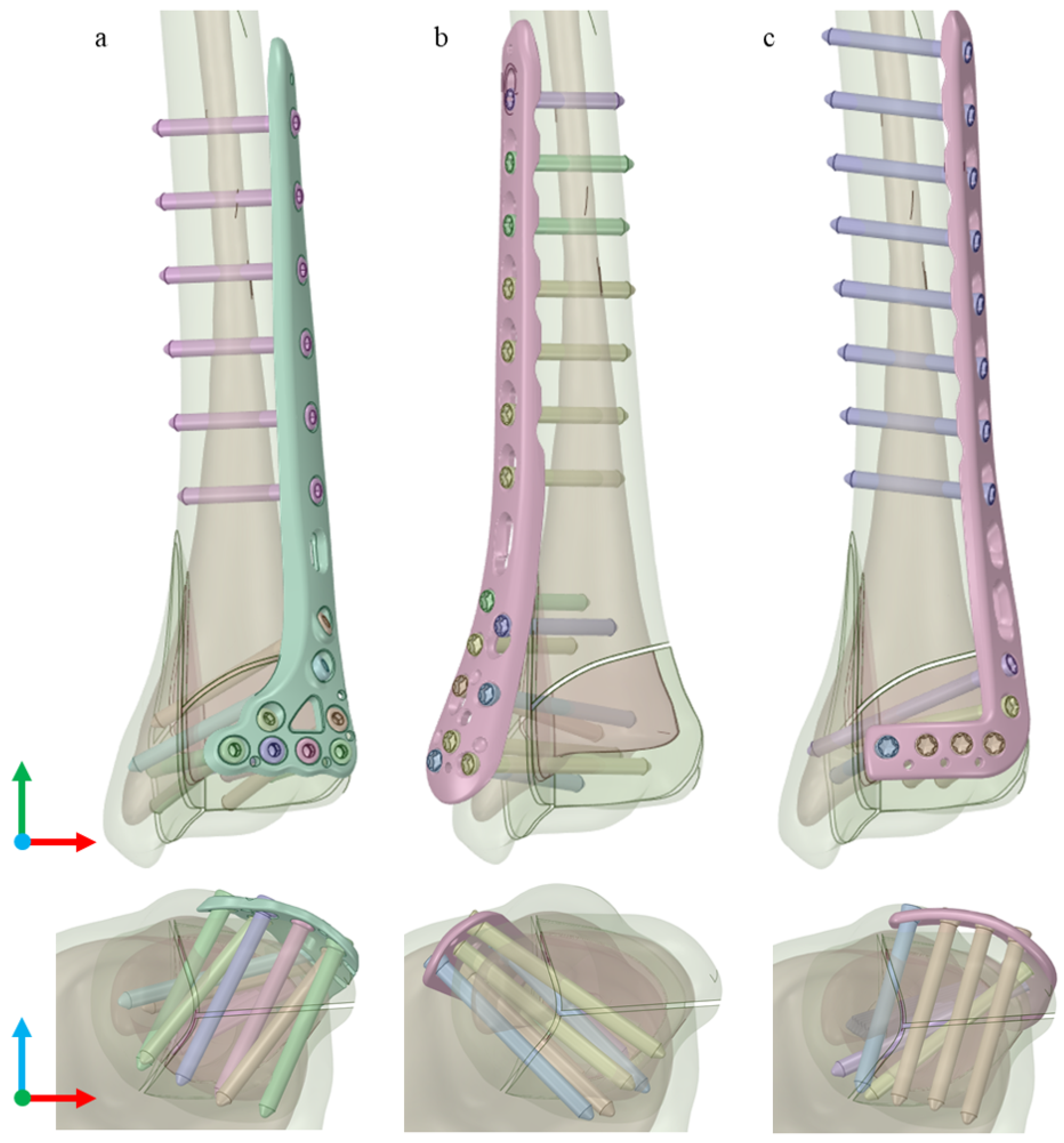
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, C.W.; Kyung, H.S.; Park, I.H.; Kim, P.T.; Ihn, J.C. Distal tibia metaphyseal fractures treated by percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 408, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinge, C.; Sanders, R.; DiPasquale, T. Treatment of complex tibial periarticular fractures using percutaneous techniques. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2000, 375, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfet, D.L.; Shonnard, P.Y.; Levine, D.; Borrelli, J., Jr. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury 1997, 28, A42–A48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, D.J.; Syed, S.U.; Davies, S.J. Fractures of the distal tibia:minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury 2004, 35, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deangelis, J.P.; Deangelis, N.A.; Anderson, R. Anatomy of the superficial peroneal nerve in relation to fixation of tibia fractures with the less invasive stabilization system. J. Orthop. Trauma 2004, 18, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizat, R.M.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Ab Rahman, S.; Md Shihabudin, T.M.T.; Robson, N.; Kamarul, T. Biomechanical Comparative Analyses Between the Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates in Treating Complex Distal Tibial Fracture: A Finite Element Study. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2013, 3, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirolo, J.M.; Behn, A.W.; Abrams, G.D.; Bishop, J.A. Anterolateral Versus Medial Plating of Distal Extra-articular Tibia Fractures: A Biomechanical Model. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e760–e765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aneja, A.; Luo, T.D.; Liu, B.; Domingo, M.; Danelson, K.; Halvorson, J.J.; Carroll, E.A. Anterolateral distal tibia locking plate osteosynthesis and their ability to capture OTAC3 pilon fragments. Injury 2018, 49, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, H.S.; Oh, J.K.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, H.R. Anatomically Precontoured Locked Plates in Pilon Fractures: A Computed Tomography Based and Cadaveric Study. Indian J. Orthop. 2018, 52, 665–671. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.L.; Slongo, T.F.; Agel, J.; Broderick, J.S.; Creevey, W.; Decoster, T.A.; Prokuski, L.; Sirkin, M.S.; Ziran, B.; Henley, B.; et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium-2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J. Orthop. Trauma 2007, 21, S1-133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffel, K.; Dieter, U.; Stachowiak, G.; Gächter, A.; Kuster, M.S. Biomechanical testing of the LCP–how can stability in locked internal fixators be controlled? Injury 2003, 34, B11-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglen, J.O. Early outcome of hybrid external fixation for fracture of the distal tibia. J. Orthop. Trauma 1999, 13, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.F.; Pandy, M.G. Static and dynamic optimization solutions for gait are practically equivalent. J. Biomech. 2001, 34, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Chang, S.H.; Son, D.S. Finite element analysis of the effect of bending stiffness and contact condition of composite bone plates with simple rectangular cross-section on the bio-mechanical behaviour of fractured long bones. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Wei, H.W.; Lin, K.P.; Chen, W.C.; Tsai, C.L.; Lin, K.J. Biomechanical effect of the configuration of screw hole style on locking plate fixation in proximal humerus fracture with a simulated gap: A finite element analysis. Injury 2016, 47, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.T.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, H.L.; Zobitz, M.E.; Chen, W.P.; Lai, K.A.; An, K.A. The number of screws, bone quality, and friction coefficient affect acetabular cup stability. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingo-Robinet, J.; López-Durán, L.; Galetoe, J.E.; Martinez-Cervell, C. Ankle fractures with posterior malleolar fragment: Management and results. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2011, 50, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoníček, J.; Rammelt, S.; Klika, D.; Naňka, O.; Tuček, M.; Kostlivý, K.; Vaněček, V. Classification of posterior malleolar fractures in ankle fractures. Rozhl. Chir. 2018, 97, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Huebner, E.J.; Iblher, N.; Kubosch, D.C.; Suedkamp, N.P.; Strohm, P.C. Distal tibial fractures and pilon fractures. Acta Chir. Orthop. Traumatol. Cech. 2014, 81, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Assal, M.; Ray, A.; Stern, R. Strategies for surgical approaches in open reduction internal fixation of pilon fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, H.; Rosseels, W.; Rammelt, S.; Nijs, S. Direct fixation of fractures of the posterior pilon via a posteromedial approach. Injury 2017, 48, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hak, D.J. Anterolateral approach for tibial pilon fractures. Orthopedics 2012, 35, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacLeod, A.R.; Serrancoli, G.; Fregly, B.J.; Toms, A.D.; Gill, H.S. The effect of plate design, bridging span, and fracture healing on the performance of high tibial osteotomy plates: An experimental and finite element study. Bone Jt. Res. 2018, 7, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, T.; Nigrelli, V.; Pecorella, D.; Bragonzoni, L.; Ricotta, V. Influence of the Screw Positioning on the Stability of Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: A Numerical Approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.S.; Chen, C.F.; Lee, O.K. Benefits of opposite screw insertion technique in medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: A virtual biomechanical study. J. Orthop. Translat. 2020, 20, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.R.; Ziran, B.H.; Anglen, J.O.; Stahel, P.F. Locking plates: Tips and tricks. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlee, M.H.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Murali, M.R.; Kamarul, T. Finite element analysis of three commonly used external fixation devices for treating Type III pilon fractures. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, S.; Miramini, S.; Richardson, M.; Mendis, P.; Zhang, L. Effects of dynamic loading on fracture healing under different locking compression plate configurations: A finite element study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 94, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benli, S.; Aksoy, S.; Havitcioğlu, H.; Kucuk, M. Evaluation of bone plate with low-stiffness material in terms of stress distribution. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 3229–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xiu, K.; Duan, H.; Zhang, M. Biomechanical and histological evaluation of the application of biodegradable poly-L-lactic cushion to the plate internal fixation for bone fracture healing. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaham, R.M.A.R.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Rashid, A.H.A.; Hossain, M.G.; Kamarul, T. Finite element analysis of Puddu and Tomofix plate fixation for open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Injury 2012, 43, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Model Part | Young’s Modulus (Mpa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical bone | 17,500 | 0.3 |
| Cancellous bone | 1500 | 0.12 |
| Titanium alloy (Plate and screw) | 110,000 | 0.3 |
| Bone Plate Type | Maximum Bone Plate von Mises Stress (MPa) | Stiffness (N/mm) |
|---|---|---|
| ADT | 228.82 | 52.12 |
| MDT | 181.00 | 1576.58 |
| ADLT | 144.15 | 1219.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-P.; Lin, K.-J.; Hsu, C.-E.; Chen, C.-P.; Shih, C.-M.; Lin, K.-P. Biomechanical Comparison of a Novel Implant and Commercial Fixation Devices for AO/OTA 43-C1 Type Distal Tibial Fracture. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104395
Wang S-P, Lin K-J, Hsu C-E, Chen C-P, Shih C-M, Lin K-P. Biomechanical Comparison of a Novel Implant and Commercial Fixation Devices for AO/OTA 43-C1 Type Distal Tibial Fracture. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104395
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shun-Ping, Kun-Jhih Lin, Cheng-En Hsu, Chao-Ping Chen, Cheng-Min Shih, and Kang-Ping Lin. 2021. "Biomechanical Comparison of a Novel Implant and Commercial Fixation Devices for AO/OTA 43-C1 Type Distal Tibial Fracture" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104395
APA StyleWang, S.-P., Lin, K.-J., Hsu, C.-E., Chen, C.-P., Shih, C.-M., & Lin, K.-P. (2021). Biomechanical Comparison of a Novel Implant and Commercial Fixation Devices for AO/OTA 43-C1 Type Distal Tibial Fracture. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104395






