A Fast Calculation Method of Far-Field Intensity Distribution with Point Spread Function Convolution for High Energy Laser Propagation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Model
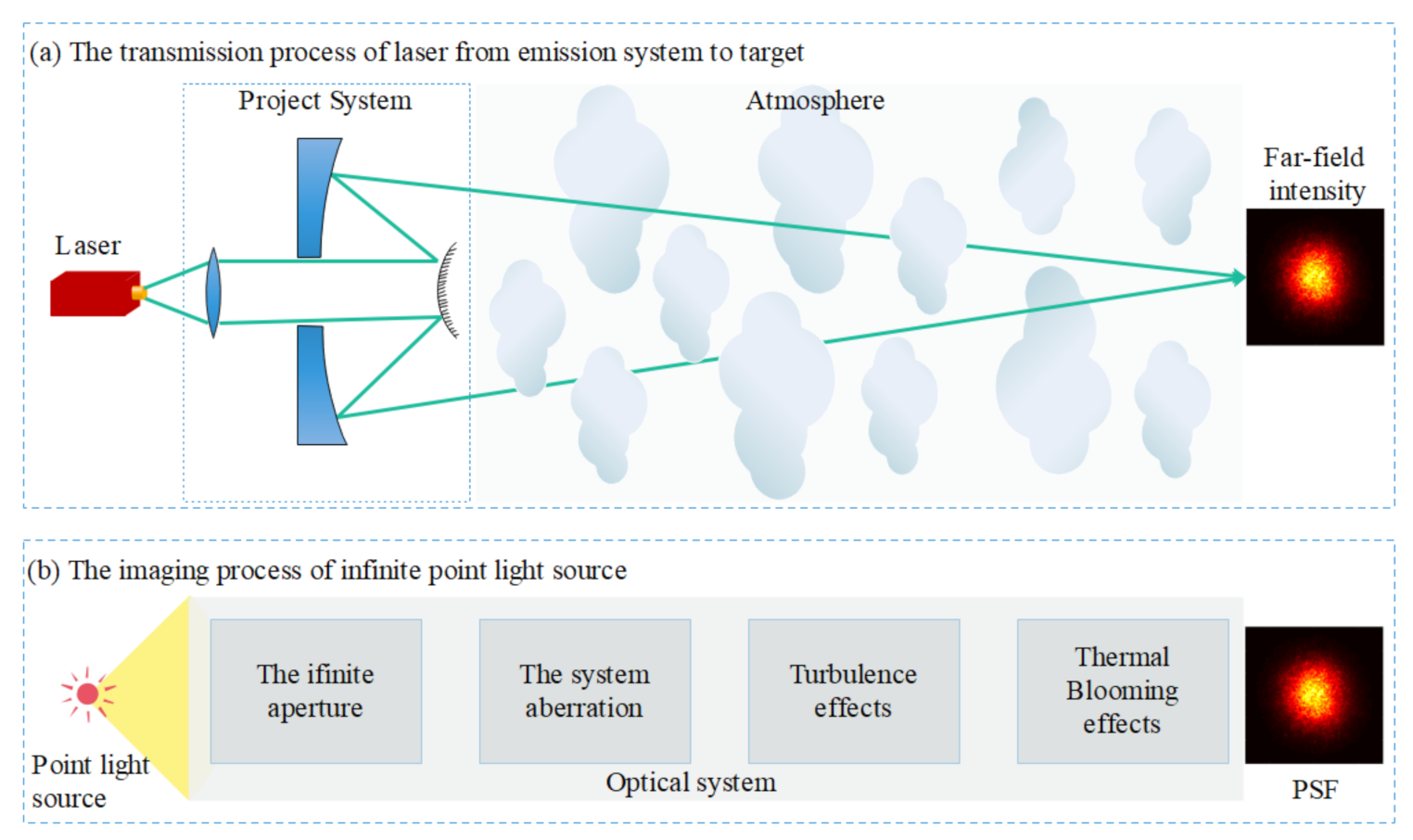
2.1. Fast Calculation of Far-Field Intensity Distribution with PSF Convolution
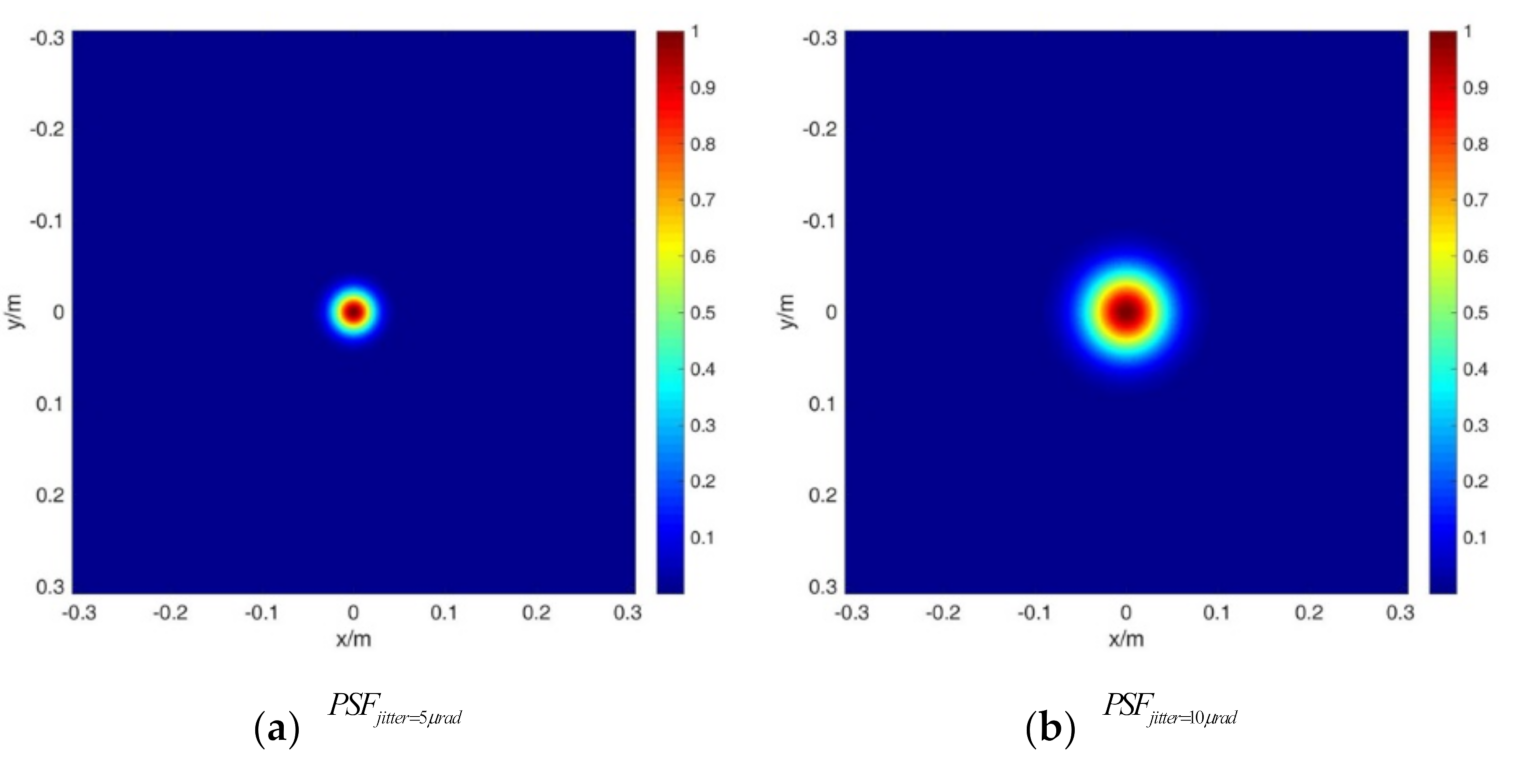
2.2. PSF Calculation for Jitter Effect
2.3. PSF Calculation for Turbulence Effect
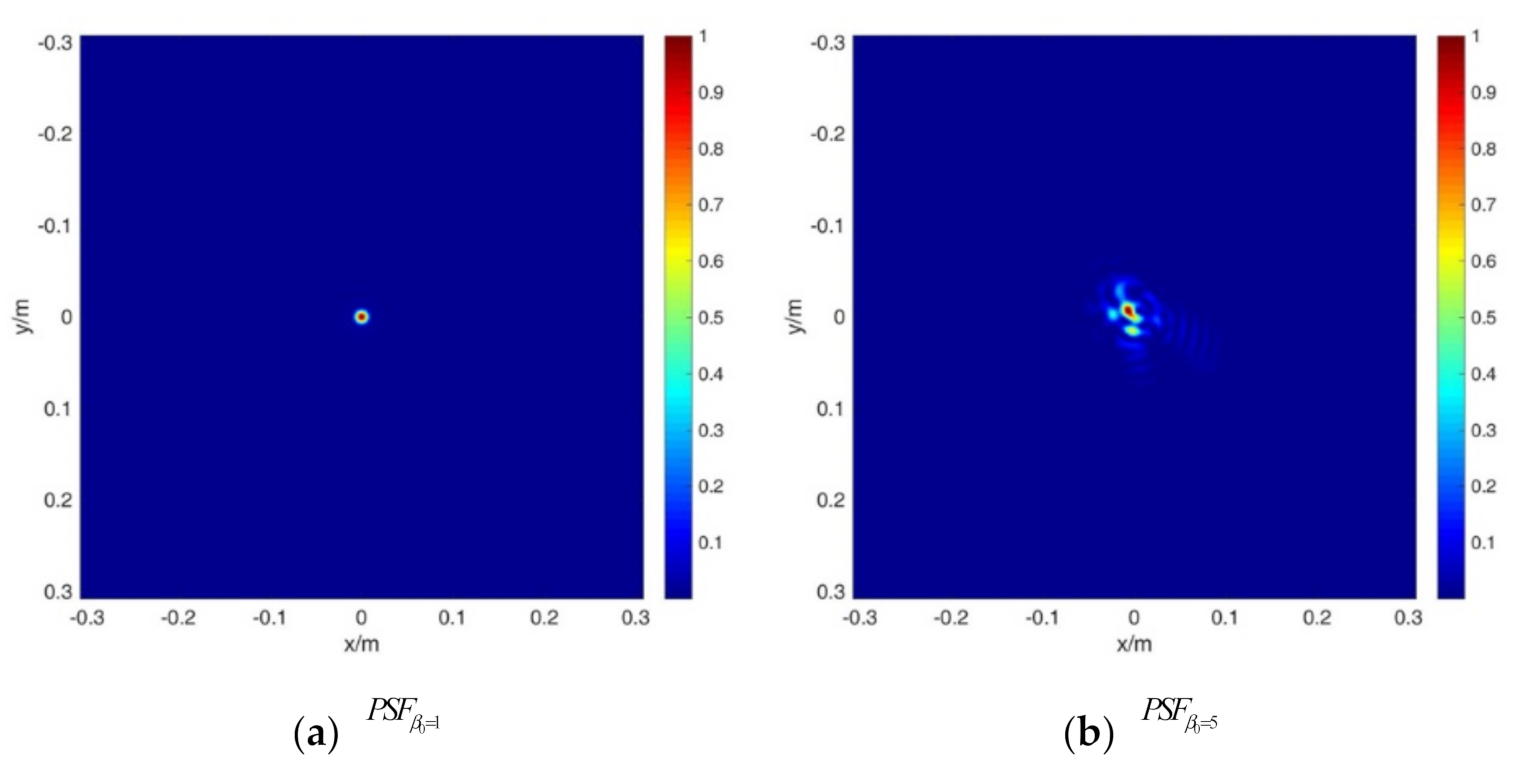
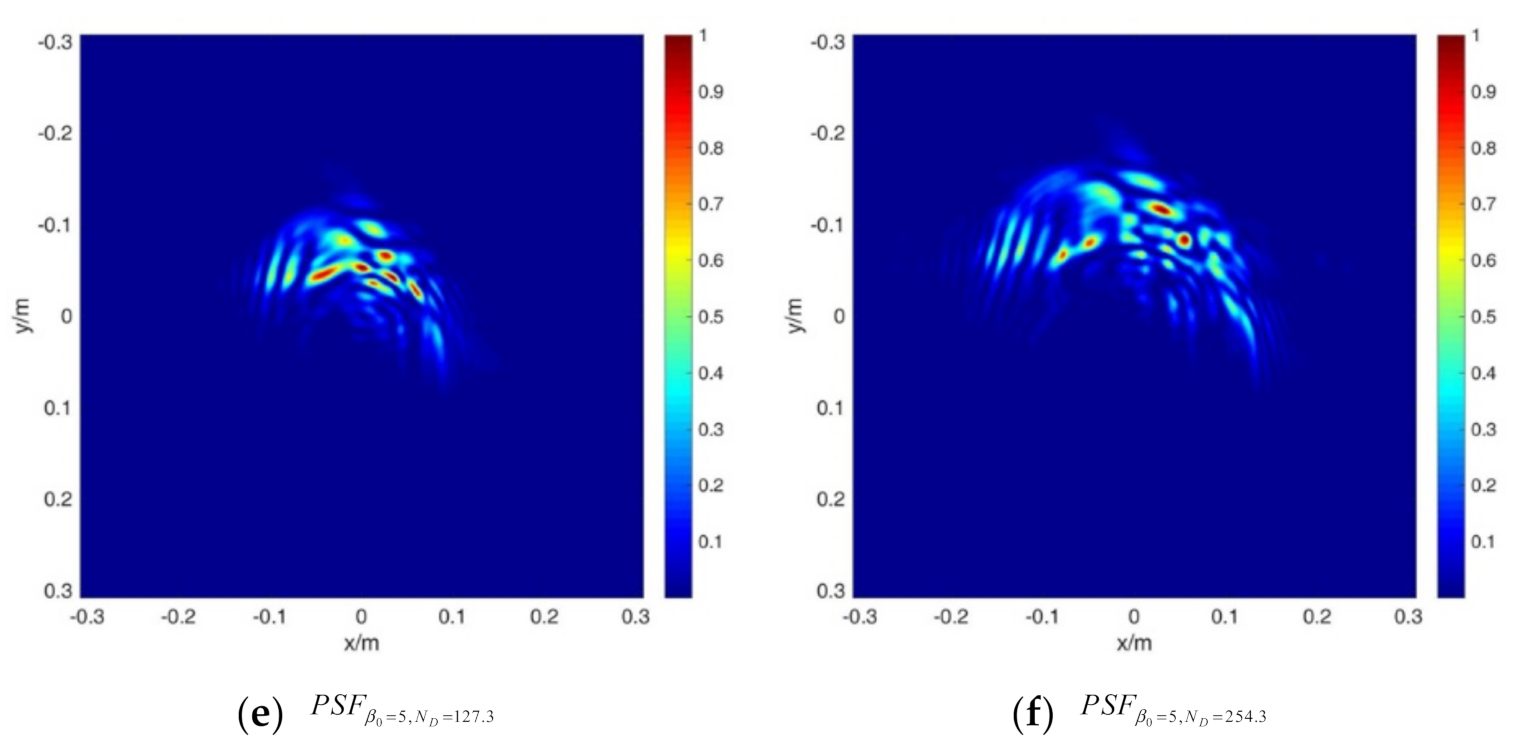
2.4. PSF Calculation for Thermal Blooming Effect with Aberrations and Finite Aperture Effect
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calculation Parameter Setting
3.2. PSF Calculation for Different Effects
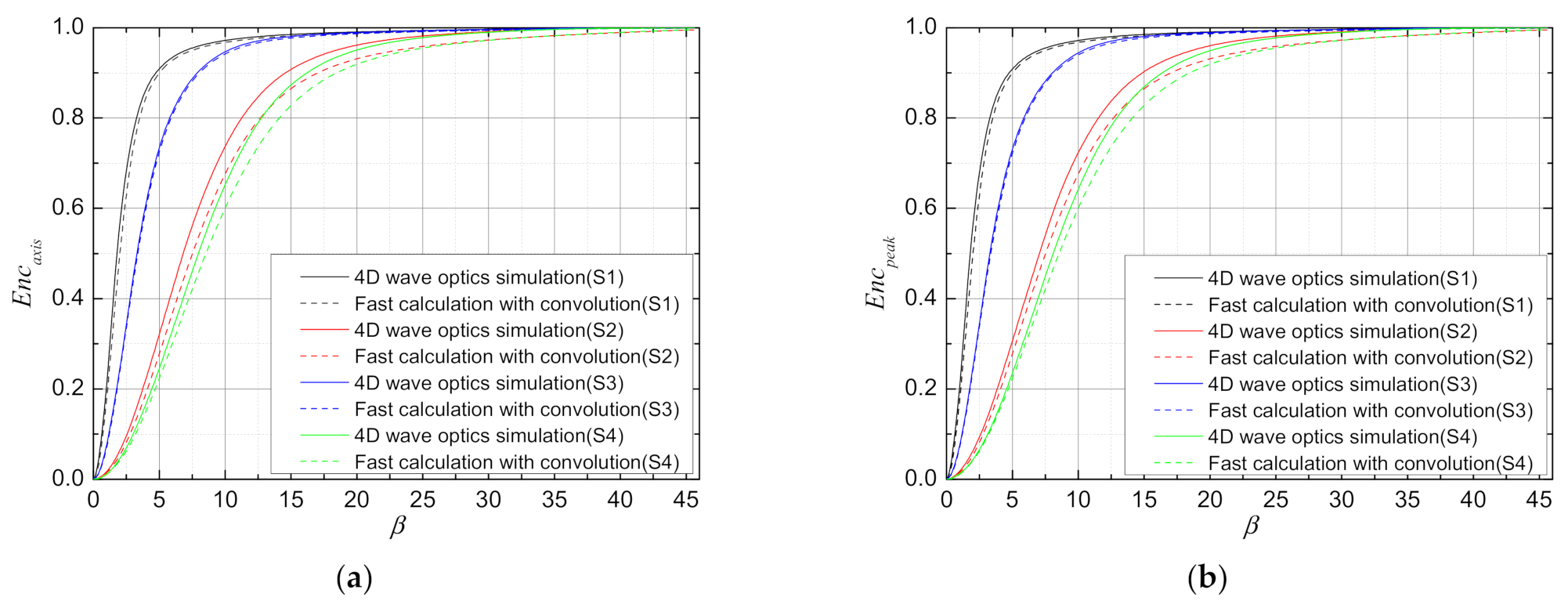
3.3. Verification of the Fast Calculation Model with PSF Convolution
3.3.1. Results for Turbulence-Only Effects
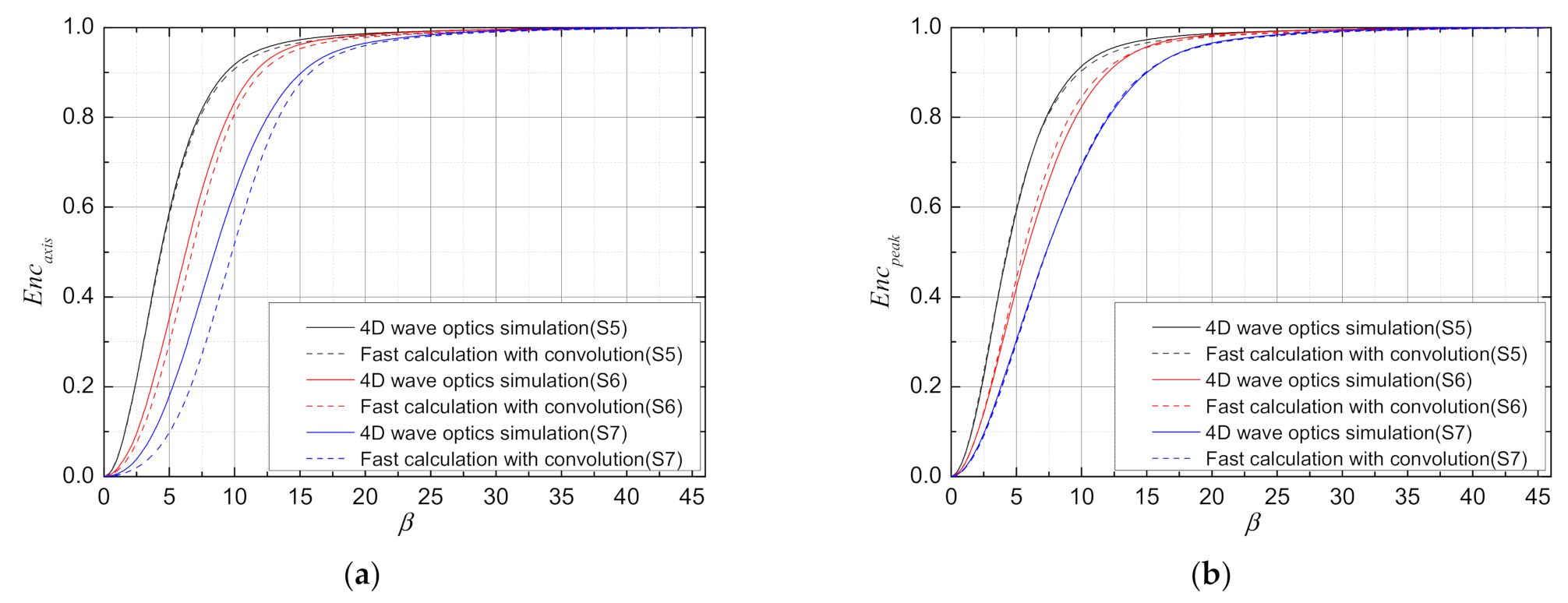
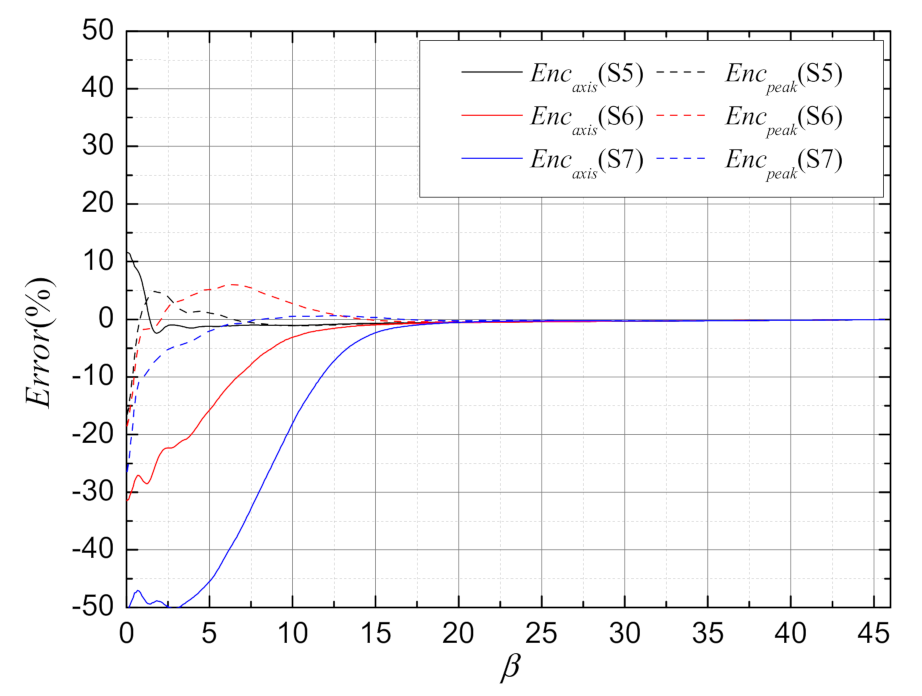
3.3.2. Results for Turbulence and Thermal Blooming Effects
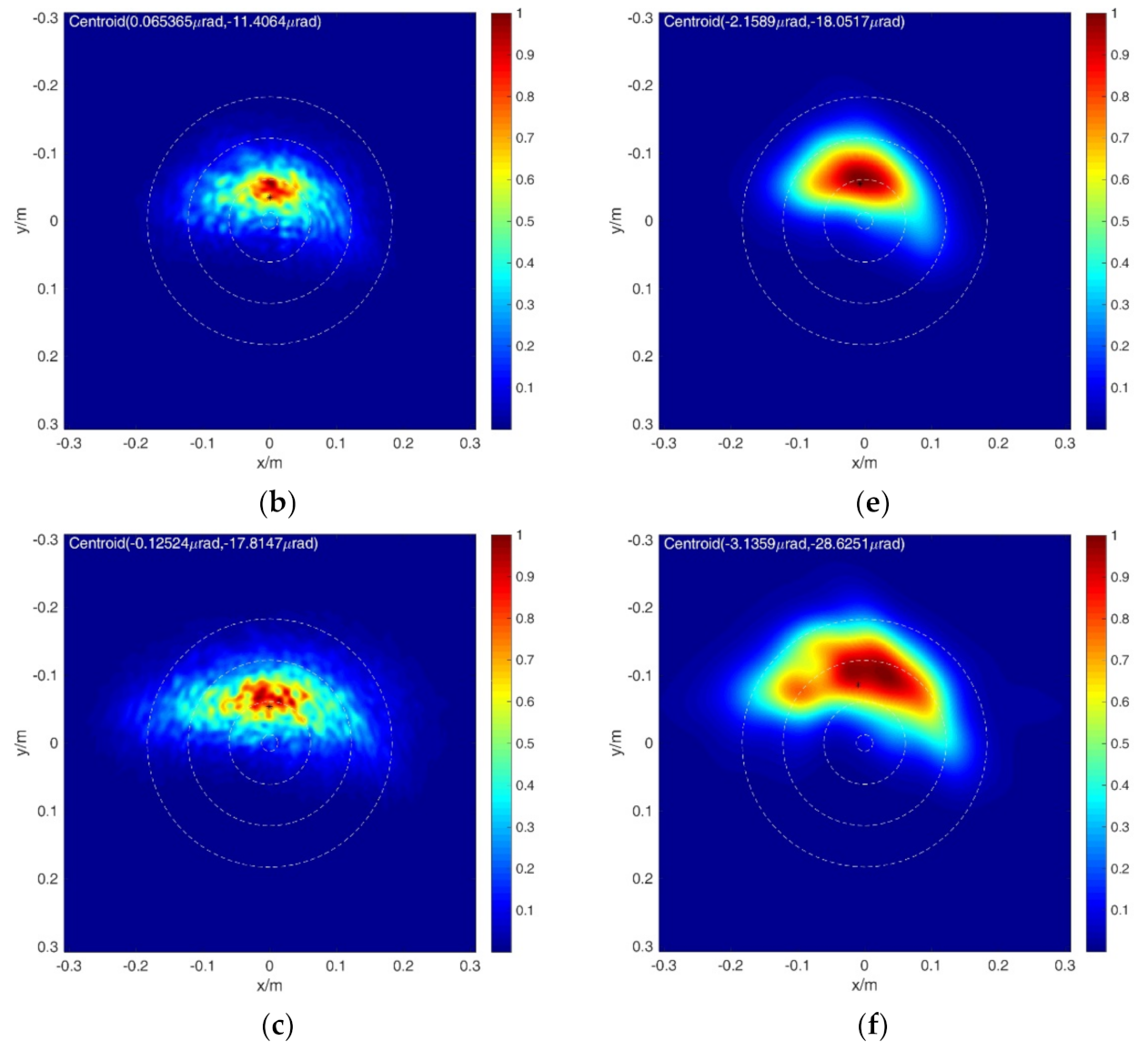
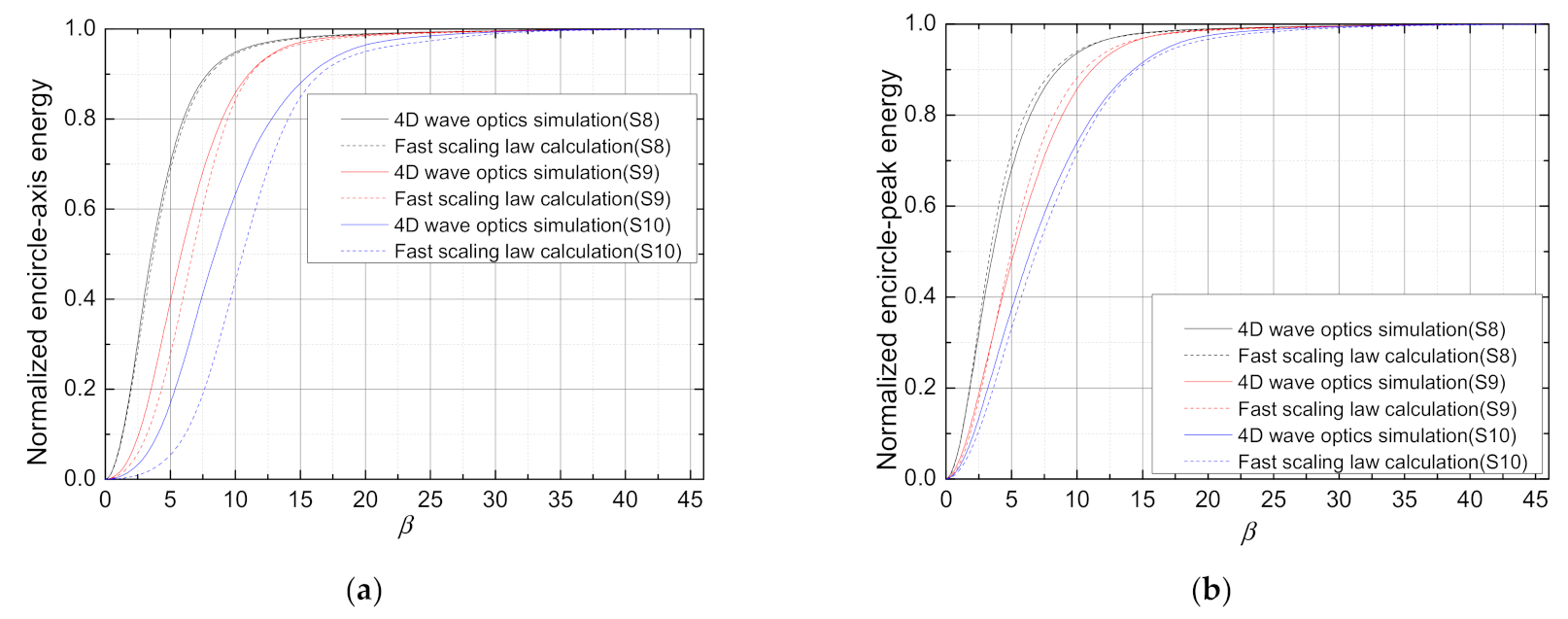
3.3.3. Results Verification of Uplink Transmission Scenario Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, L.C.; Phillips, R.L. Laser Beam Propagation through Random Media; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sprangle, P.; Hafizi, B.; Ting, A.; Fischer, R. High-power lasers for directed-energy applications. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, F201–F209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Thermal blooming effect of laser beams propagating through seawater. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 5861–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Ji, X. Thermal blooming effect of Hermite–Gaussian beams propagating through the atmosphere. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 2019, 36, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, B.F.; Reeger, J.A. Numerical simulation of thermal blooming with laser-induced convection. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2019, 33, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Eyyuboğlu, H.T.; Ji, G.; Jia, X. Propagation of an Airy beam through the atmosphere. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 2154–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, F.G. High power laser propagation. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.C. High-power laser propagation: Thermal blooming. Proc. IEEE 1977, 65, 1679–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin-Bo, H.; Ying-Jian, W. Numerical analysis of the scaling laws about focused beam spreading induced by the atmosphere. J. Phys. 2006, 55, 6715–6719. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, L.; Herrmann, J. Phase compensation for thermal blooming. IEEE J. Quantum Electron 1973, 13, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, R.D. High energy laser scaling laws. In Proceedings of the Directed Energy Modeling and Simulation Conference, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 25 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ngwele, A.M. Scaling Law Modeling of Thermal Blooming in Wave Optics. 2006. Available online: https://www.mza.com/publications/NgweleDEPSNov2006.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Long, S.N. Characterizing Effects and Benefits of Beam Defocus on High Energy Laser Performance under Thermal Blooming and Turbulence Conditions for Air-To-Ground Engagements. Air Force Inst. Technol. 2008, 5, 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, C.; Fan, C.; Wang, Y. Scaling laws about DF high energy laser propagation in real atmosphere. Chin. J. Lasers 2007, 37, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Qiao, C.; Cheng, F.; Yingjian, W. Scaling laws of high energy laser propagation through atmosphere. Chin. J. Lasers 2010, 19, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R. Combined effect of turbulence and thermal blooming of laser propagation in atmosphere. Infrared Laser Eng. 2006, 35, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Shakir, S.A.; Dolash, T.M.; Spencer, M.; Berdine, R.; Cargill, D.S.; Carreras, R. General wave optics propagation scaling law. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 2016, 33, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A.; Bingham, S.P.; Van Zandt, N.R.; Spencer, M.F. Wave-optics comparisons to a scaling-law formulation. Unconv. Indirect. Imaging Image Reconstr. Wavefront Sens. 2018, 10772, 1077202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zandt, N.R.; Fiorino, S.T.; Keefe, K.J. Enhanced fast-running scaling law model of thermal blooming and turbu-lence effects on high energy laser propagation. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 14789–14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbring, E.; Faber, S.M.; Hinkley, S.; MacIntosh, B.A.; Gavel, D.; Gates, E.L.; Christou, J.C.; Le Louarn, M.; Raschke, L.M.; Severson, S.A.; et al. Characterizing the adaptive optics off-axis point-spread function. I. A semiempirical method for use in natural guide star observations. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2002, 114, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Britton, M.C. The Anisoplanatic Point-Spread Function in Adaptive Optics. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2006, 118, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fétick, R.J.L.; Fusco, T.; Neichel, B.; Mugnier, L.M.; Beltramo-Martin, O.; Bonnefois, A.; Petit, C.; Milli, J.; Vernet, J.; Oberti, S.; et al. Physics-based model of the adaptive-optics corrected point-spread-function. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 628, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, S.A.; Clark, T.T.; Cargill, D.S.; Carreras, R. Far-field propagation of partially coherent laser light in random mediums. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 15609–15622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W.; Cox, M.E. Introduction to Fourier Optics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W.; Narducci, L.M. Statistical Optics Robotica; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, D.L. Optical Resolution Through a Randomly Inhomogeneous Medium for Very Long and Very Short Exposures. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1966, 56, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, V.P.; Fortes, B.V. Adaptive Beaming and Imaging in The Turbulent Atmosphere; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Frehlich, R. Simulation of laser propagation in a turbulent atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohbehn, J. Laser Beam Propagation in The Atmosphere; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Fleck, J.A.; Morris, J.R.; Feit, M.D. Time-dependent propagation of high energy laser beams through the atmosphere. Appl. Phys. 1976, 10, 129–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.; Kovadlo, P.; Lukin, V.; Nosov, V.; Kiselev, A.; Kolobov, D.; Kopylov, E.; Shikhovtsev, M.; Avdeev, F. Statistics of the Optical Turbulence from the Micrometeorological Measurements at the Baykal Astrophysical Observatory Site. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jicha, O.; Pechac, P.; Zvanovec, S.; Grabner, M.; Kvicera, V. Long-term measurements of refractive index structure constant in atmospheric boundary layer. Optics in Atmospheric Propagation & Adaptive Systems XV. Int. Soc.Opt. Photonics 2012, 8535, 853509. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, P.B. PROP-I: An Efficient Implicit Algorithm for Calculating Nonlinear Scalar Wave Propagation in The Fresnel Approximation; Naval Research Lab: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, M.F. Wave-optics investigation of turbulence thermal blooming interaction: I. Using steady-state simulations. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 081804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, P.B. Hufnagel-Valley Profiles for Specified Values of The Coherence Length and Isoplanatic Angle; MA-TN-88-013; W.J. Schafer Associates: Livermore, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Tofsted, D.H.; O’Brien, S.G.; Vaucher, G.T. An Atmospheric Turbulence Profile Model for Use in Army Wargaming Applications I; ARL-TR-3748; U.S. Army Research Laboratory: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.G.; Zieske, P.L. Turbulence Environmental Characterization; RADC-TR-79-131; Rome Air Development Center: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Trinquet, H.; Vernin, J. A statistical model to forecast the profile of the index structure constant CN2. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2007, 7, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, H.W. The possibility of compensating astronomical seeing. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1953, 65, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, R.R. In Laser Wavefront Control. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 1989, 1000, 101. [Google Scholar]






| Parameter | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Grid number, N | 1024 × 1024 |
| Grid sampling interval of the emission plane, Δx | 0.0012 m |
| Number of phase screen, Nps | 40 |
| Wavelength, λ | 1 μm |
| Transmitting aperture, D | 0.3 m |
| Propagation distance, L | 3 km |
| Initial aberration of the laser emission system, β0 | 1.0 and 5.0 times diffraction limit aberration |
| Turbulence structure constant, Cn2 | 5.0 × 10−14 m−2/3, 1.0 × 10−14 m−2/3, 5.0 × 10−15 m−2/3 |
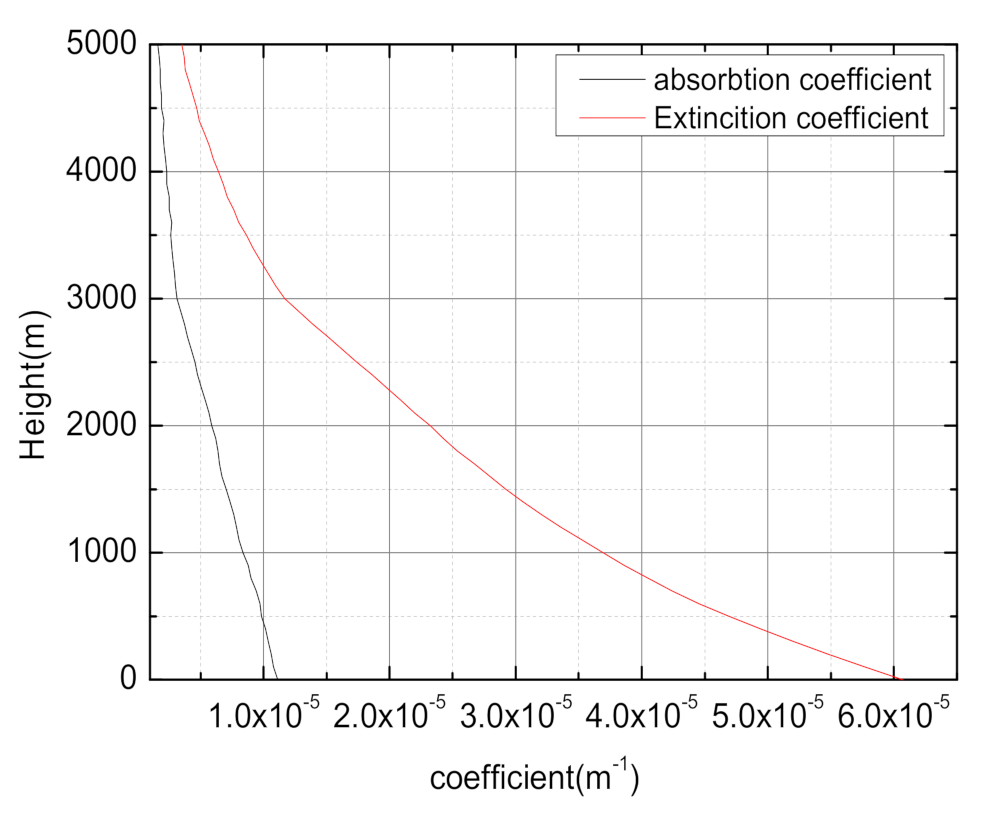
| Absorption coefficient, α | 1.1 × 10−5 m−1 |
| Extinction coefficient, ξ | 6.1 × 10−5 m−1 |
| Wind speed, v | 2 m/s |
| Angular velocity of light beam scanning, ω | 0 rad/s |
| Scenario | Cn2 | D/r0 | jitter | β0 | P | ND |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 5.0 × 10−15 m−2/3 | 4.0 | 0 | 1 | - | - |
| S2 | 5.0 × 10−14 m−2/3 | 16.1 | 0 | 1 | - | - |
| S3 | 5.0 × 10−15 m−2/3 | 4.0 | 5 μrad | 5 | - | - |
| S4 | 5.0 × 10−14 m−2/3 | 16.1 | 10 μrad | 5 | - | - |
| S5 | 1.0 × 10−14 m−2/3 | 6.13 | 5 μrad | 5 | 10 kW | 25.5 |
| S6 | 1.0 × 10−14 m−2/3 | 6.13 | 5 μrad | 5 | 50 kW | 127.3 |
| S7 | 1.0 × 10−14 m−2/3 | 6.13 | 5 μrad | 5 | 100 kW | 254.3 |
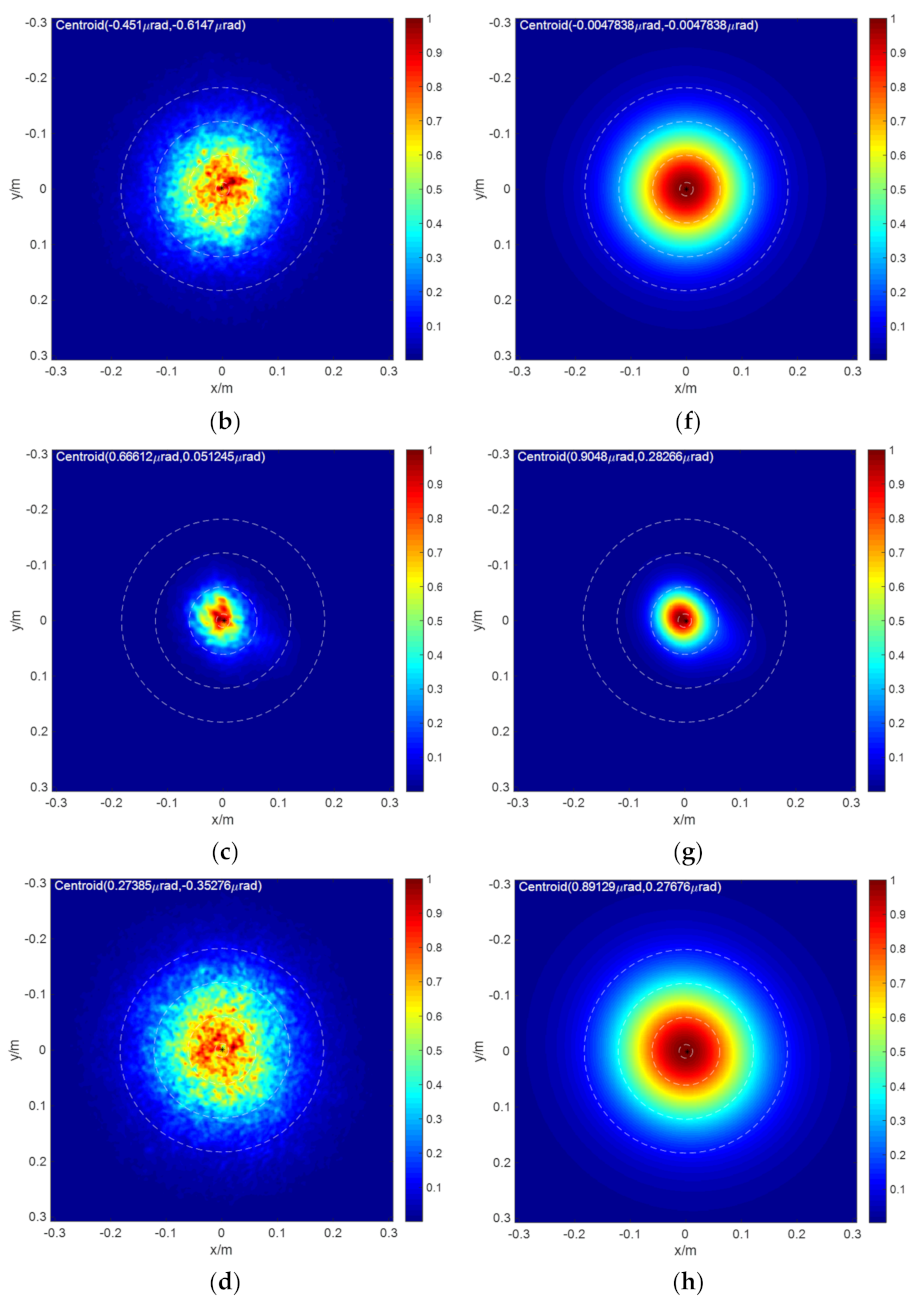
| Scenario | Parameters | Fast Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | ||
| S2 | ||
| S3 | ||
| S4 |
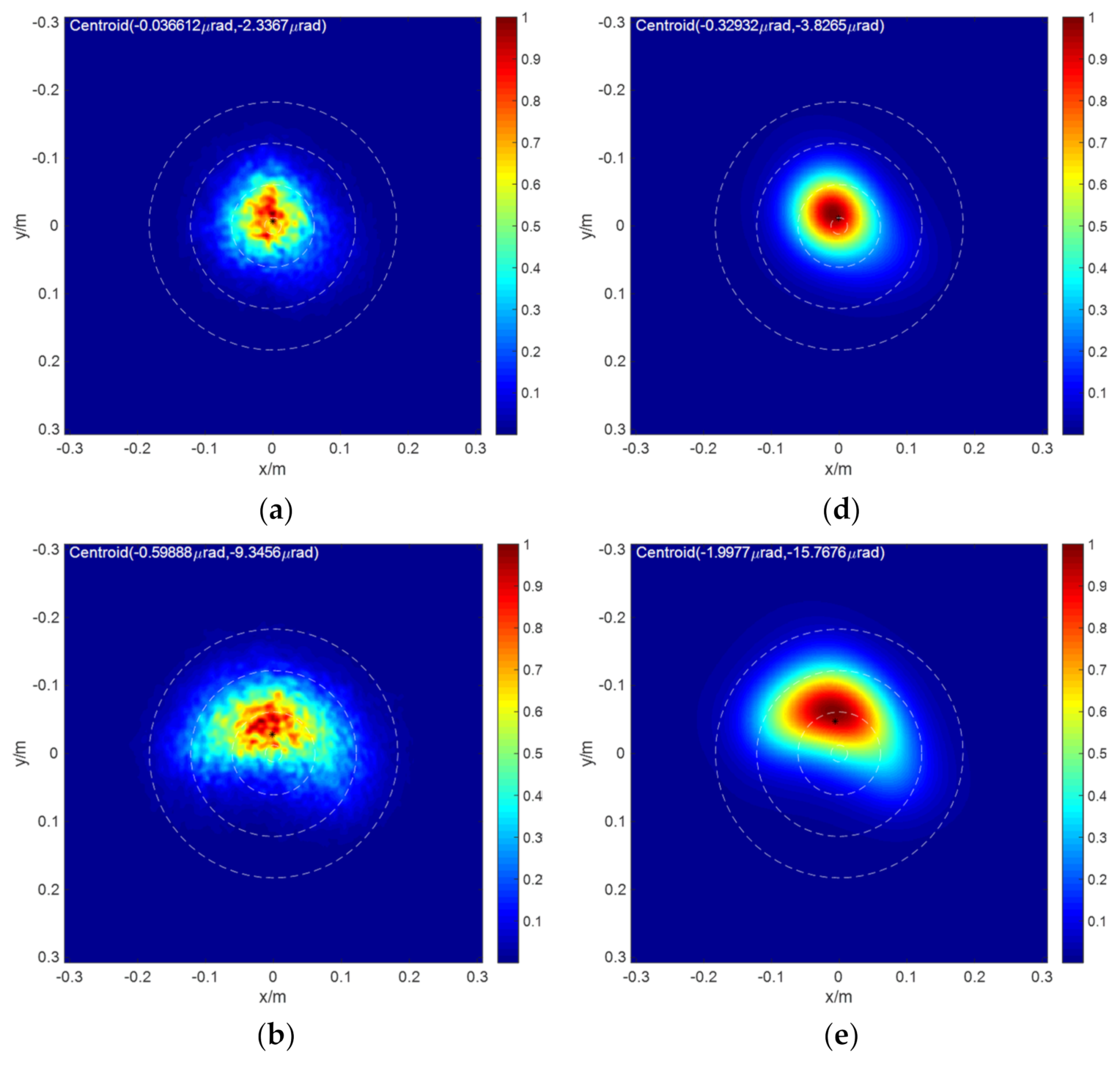
| Scenario | Parameters | Fast Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| S5 | ||
| S6 | ||
| S7 |
| Scenario | Parameters | Fast Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| S8 | ||
| S9 | ||
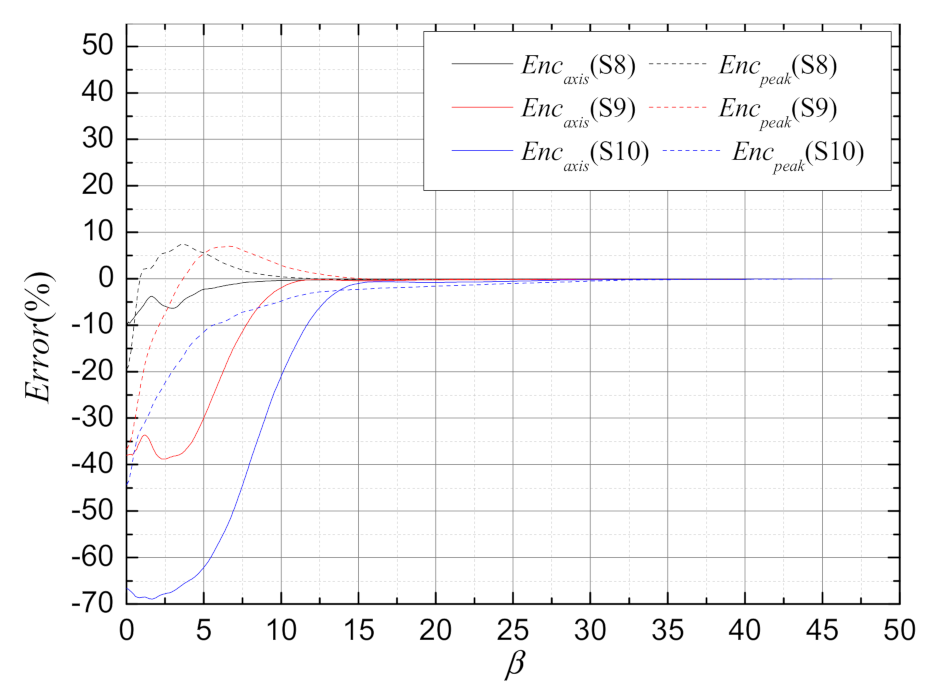
| S10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Fan, C.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. A Fast Calculation Method of Far-Field Intensity Distribution with Point Spread Function Convolution for High Energy Laser Propagation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104450
Ma H, Zhang P, Zhang J, Liu H, Fan C, Qiao C, Zhang W, Li X. A Fast Calculation Method of Far-Field Intensity Distribution with Point Spread Function Convolution for High Energy Laser Propagation. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104450
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Huimin, Pengfei Zhang, Jinghui Zhang, Haiqiu Liu, Chengyu Fan, Chunhong Qiao, Weiwei Zhang, and Xiaohong Li. 2021. "A Fast Calculation Method of Far-Field Intensity Distribution with Point Spread Function Convolution for High Energy Laser Propagation" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104450
APA StyleMa, H., Zhang, P., Zhang, J., Liu, H., Fan, C., Qiao, C., Zhang, W., & Li, X. (2021). A Fast Calculation Method of Far-Field Intensity Distribution with Point Spread Function Convolution for High Energy Laser Propagation. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104450






