Combining a Universal OBD-II Module with Deep Learning to Develop an Eco-Driving Analysis System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A universal OBD-II module is developed to collect driving information from various car models.
- Three deep learning methods are combined with the universal OBD-II module to predict fuel consumption.
- Three different car models are used to evaluate fuel consumption.
- An intuitive driving graphic user interface is designed for the eco-driving assistant system.
2. Related Research
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Development of Universal OBD-II Hardware
3.2. Heterogenous Communication Protocol Identification in the CAN Bus
3.3. Data Unit Standardization
3.4. User Interface Development
3.5. Neural Network Algorithm
3.5.1. Data and Preprocessing
3.5.2. Neural Network Model Selection and Processing
3.6. Driving Test
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Somayajula, D.; Meintz, A.; Ferdowsi, M. Designing efficient hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2009, 4, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, E. Independent driving pattern factors and their influence on fuel-use and exhaust emission factors. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2001, 6, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robuschi, N.; Salazar, M.; Viscera, N.; Braghin, F.; Onder, C.H. Minimum-fuel energy management of a hybrid electric vehicle via iterative linear programming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 14575–14587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachimczyk, B.; Dziak, D.; Czapla, J.; Damps, P.; Kulesza, W.J. IOT on-board system for driving style assessment. Sensors 2018, 18, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagberg, F.; Selpi; Piccinini, G.F.B.; Engstrom, J. A review of research on driving styles and road safety. Hum. Factors 2015, 57, 1248–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamson, S.L.; Hibberd, D.L.; Jamson, A.H. Drivers’ ability to learn eco-driving skills; effects on fuel efficient and safe driving behaviour. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 58, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezipour, A.; Rakotonirainy, A.; Haworth, N.; Delhomme, P. Enhancing eco-safe driving behaviour through the use of in-vehicle human-machine interface: A qualitative study. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 100, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Hu, Y.F.; Gao, B.Z. Sequential optimization of eco-driving taking into account fuel economy and emissions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 130841–130853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.C.; Ko, K.H.; Jeung, I.S. Optimal fuel-cut driving method for better fuel economy. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2013, 14, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, Q.Y.; Guo, Y.S.; Fu, R.; Yuan, W. Improving the User Acceptability of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems Based on Different Driving Styles: A Case Study of Lane Change Warning Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 4196–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Tang, L.H.; Lei, Y. Controller area network node reliability assessment based on observable node information. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2017, 18, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J. A real-time embedded system for monitoring of cargo vehicles using controller area network (CAN). IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 15031: Road Vehicles—Communication between Vehicle and External Equipment for Emissions-Related Diagnostics; ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 27145: Road Vehicles—Implementation of World-Wide Harmonized On-Board Diagnostics (WWH-OBD) Communication Requirements; ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- SAE International. SAE J1939 Standards Collection; SAE International: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, F.; Azevedo, I.M.L. What are the best combinations of fuel-vehicle technologies to mitigate climate change and air pollution effects across the United States? Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F.; Ashok, A.; Waitz, I.A.; Yim, S.H.L.; Barrett, S.R.H. Air pollution and early deaths in the United States. Part I: Quantifying the impact of major sectors in 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettinger, G. EU Energy Policy Achievements and the Way Forward; Energy and Climate—What Strategies for Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Husnjak, S.; Forenbacher, I.; Bucak, T. Evaluation of eco-driving using smart mobile devices. Promet Traffic Transp. 2015, 27, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivak, M.; Schoettle, B. Eco-driving: Strategic, tactical, and operational decisions of the driver that influence vehicle fuel economy. Transp. Policy 2012, 22, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Carballeira, O.; Diaz-Rodriguez, M.; del Campo, I.; Martinez, V. An intelligent system-on-a-chip for a real-time assessment of fuel consumption to promote eco-driving. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois, D.; Wang, Y.; Boggio-Marzet, A.; Monzon, A. Multivariate analysis of fuel consumption related to eco-driving: Interaction of driving patterns and external factors. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 72, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, C.; Baptista, P.; Duarte, G.; Farias, T.; Pereira, J. Real-time feedback impacts on eco-driving behavior and influential variables in fuel consumption in a lisbon urban bus operator. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz, K.; Cavallaro, F.; Nocera, S.; Willenbrock, R. Reducing fuel consumption and carbon emissions through eco-drive training. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2017, 46, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, V.C.; Munoz-Organero, M. Artemisa: A personal driving assistant for fuel saving. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2016, 15, 2437–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meseguer, J.E.; Toh, C.K.; Calafate, C.T.; Cano, J.C.; Manzoni, P. DrivingStyles: A mobile platform for driving styles and fuel consumption characterization. J. Commun. Netw. 2017, 19, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, R.; Fallon, S.; Jacob, P.; O’Dwyer, D. Vehicle telematics and its role as a key enabler in the development of smart cities. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 11713–11724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fafoutellis, P.; Mantouka, E.G.; Vlahogianni, E.I. Eco-driving and its impacts on fuel efficiency: An overview of technologies and data-driven methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimpas, D.; Papadakis, A.; Samarakou, M. OBD-II sensor diagnostics for monitoring vehicle operation and consumption. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Liu, C.; Rong, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Dong, Z.N.; Su, Y.L. Vehicle fuel consumption prediction method based on driving behavior data collected from smartphones. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 9263605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Rakha, H.; Trani, A.; Van Aerde, M. Estimating vehicle fuel consumption and emissions based on instantaneous speed and acceleration levels. J. Transp. Eng. 2002, 128, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, P.; Qin, W.H.; Xu, Y.; Miyajima, C.; Takeda, K. Impact of driver behavior on fuel consumption: Classification, evaluation and prediction using machine learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78515–78532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.V.; Bansal, H.O.; Singh, D. Fuzzy logic and Elman neural network tuned energy management strategies for a power-split HEVs. Energy 2021, 225, 120152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, B.D. AVR-Based Fuel Consumption Gauge. Circuit Cellar Mag. 2005, 183, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Elman, J.L. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, C.; Rong, J. Modeling of individual vehicle safety and fuel consumption under comprehensive external conditions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, E.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Tamminen, S.; Pirttikangas, S.; Roning, J.; Riekki, J. Personalised assistance for fuel-efficient driving. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 58, 681–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.C.; Zhu, L.; Gonder, J.; Young, S.; Walkowicz, K. Data-driven fuel consumption estimation: A multivariate adaptive regression spline approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 83, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walnum, H.J.; Simonsen, M. Does driving behavior matter? An analysis of fuel consumption data from heavy-duty trucks. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 36, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara Togun, N.; Baysec, S. Prediction of torque and specific fuel consumption of a gasoline engine by using artificial neural networks. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

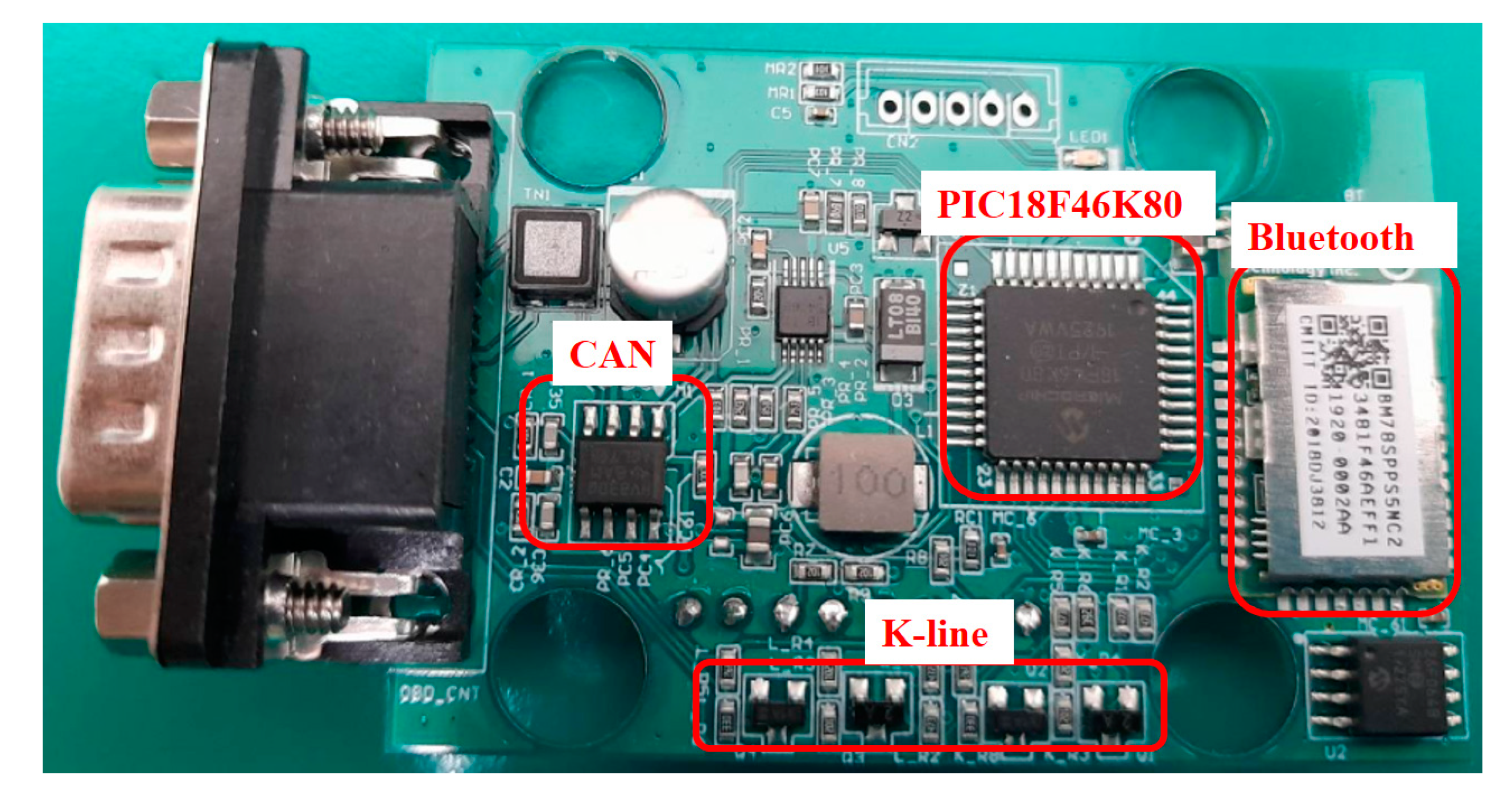
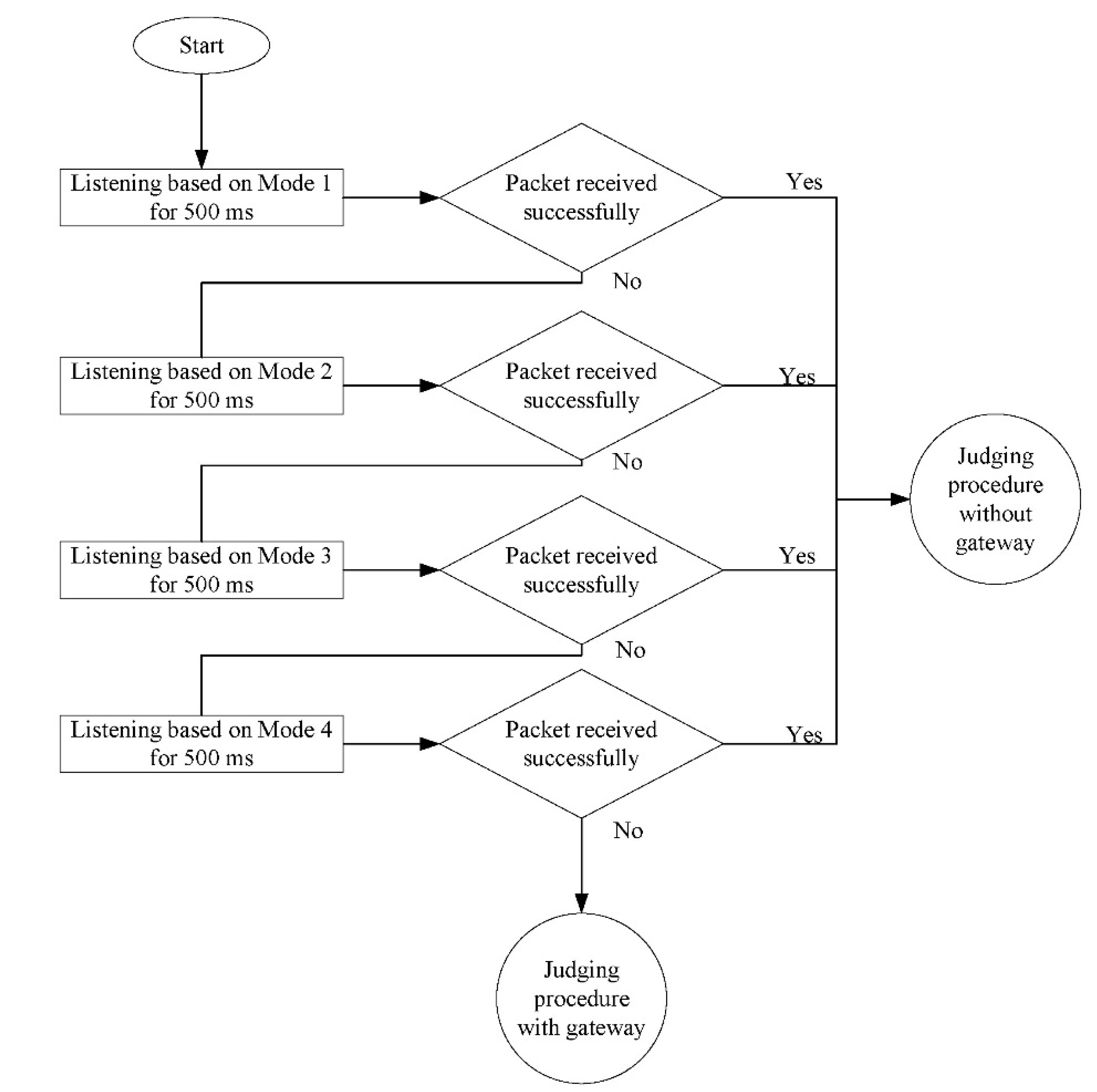
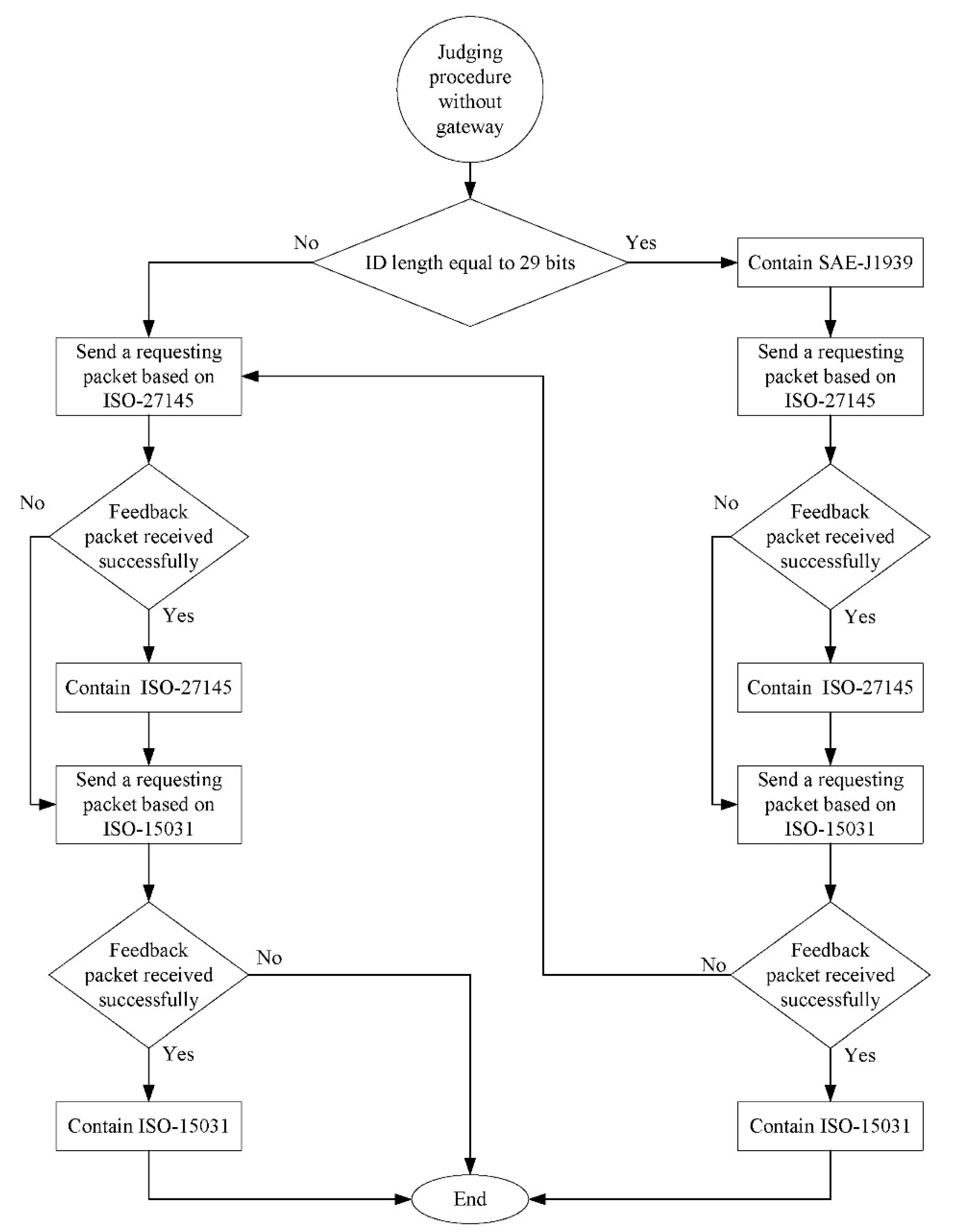
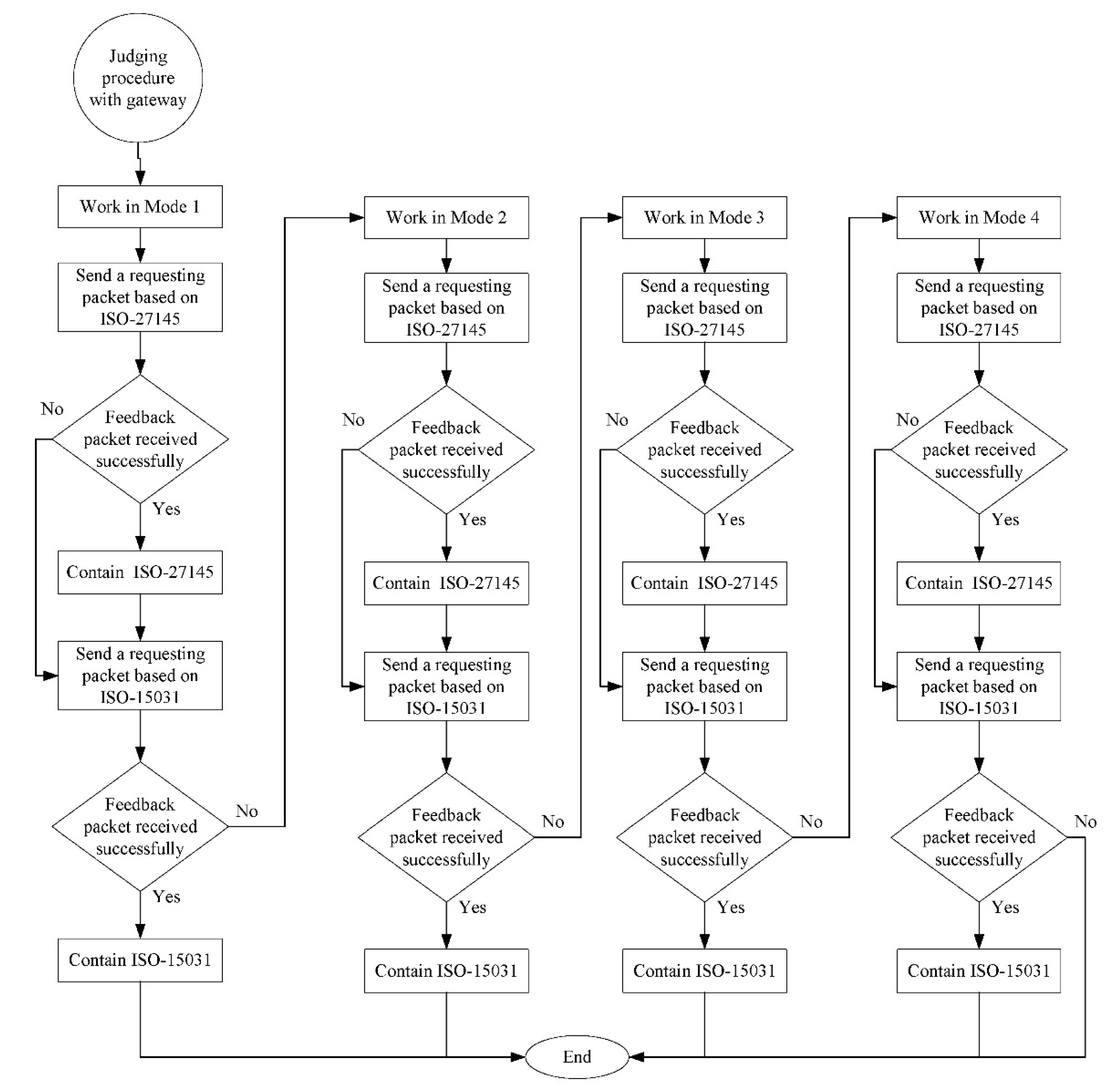
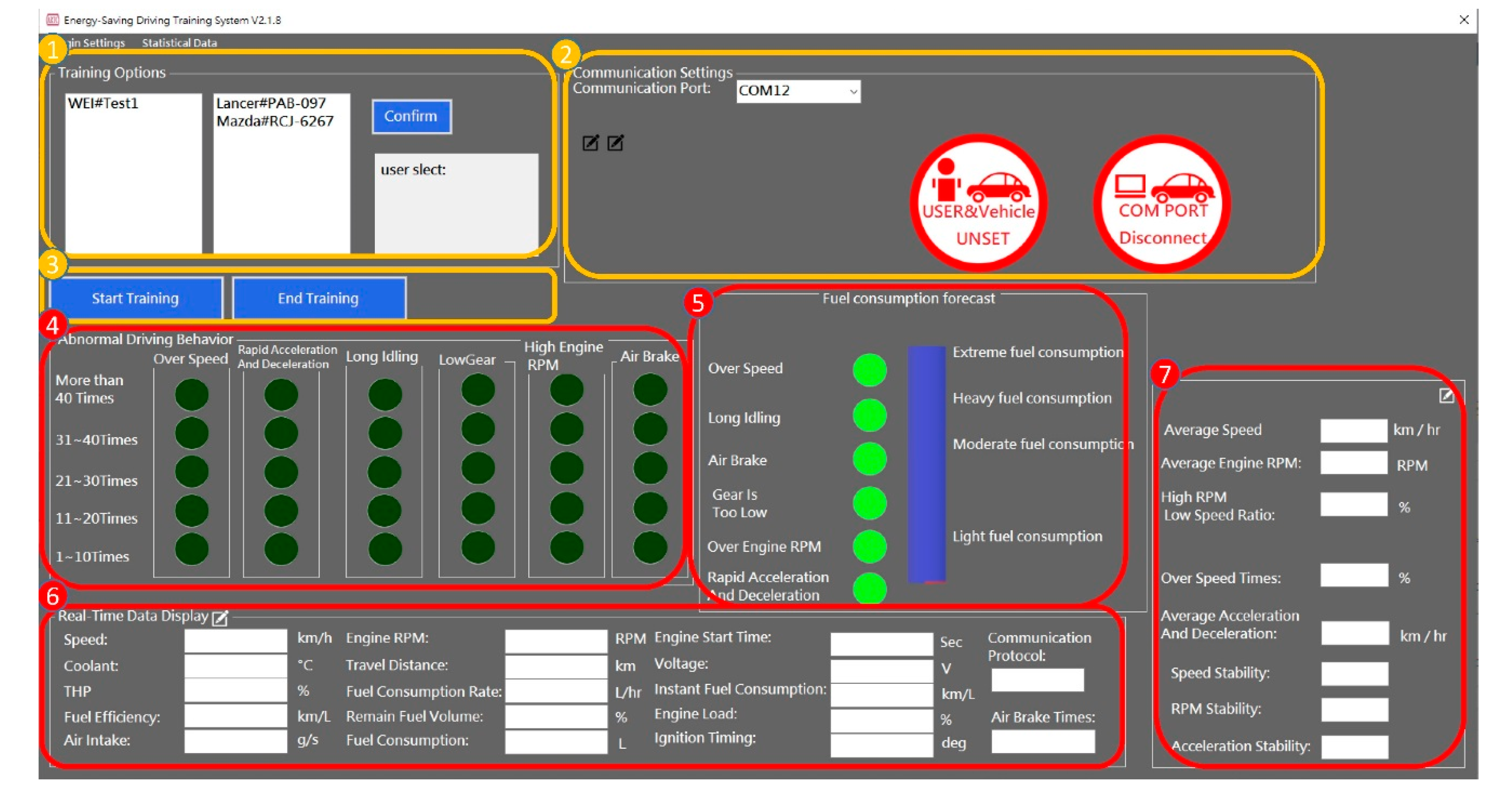

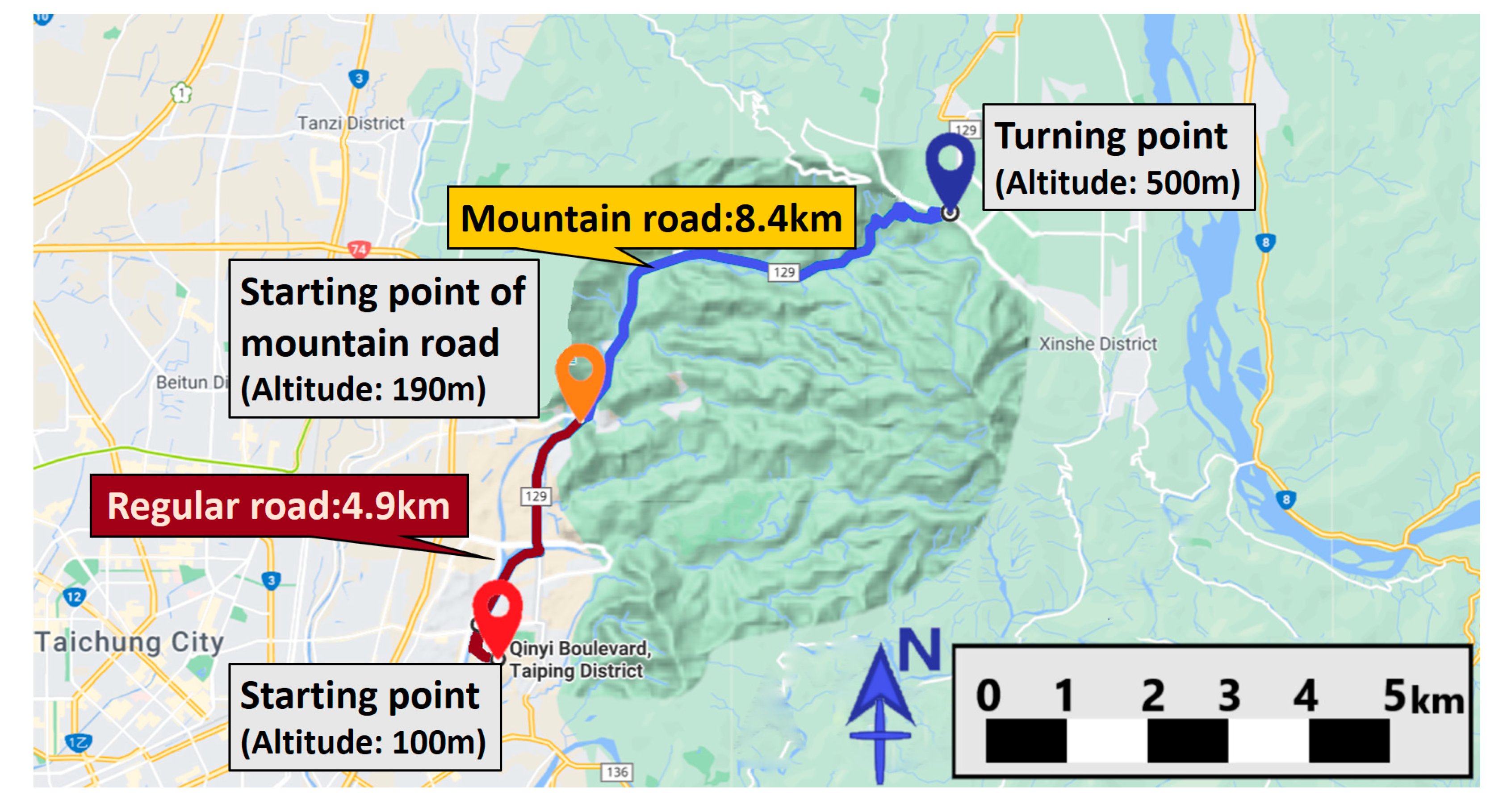
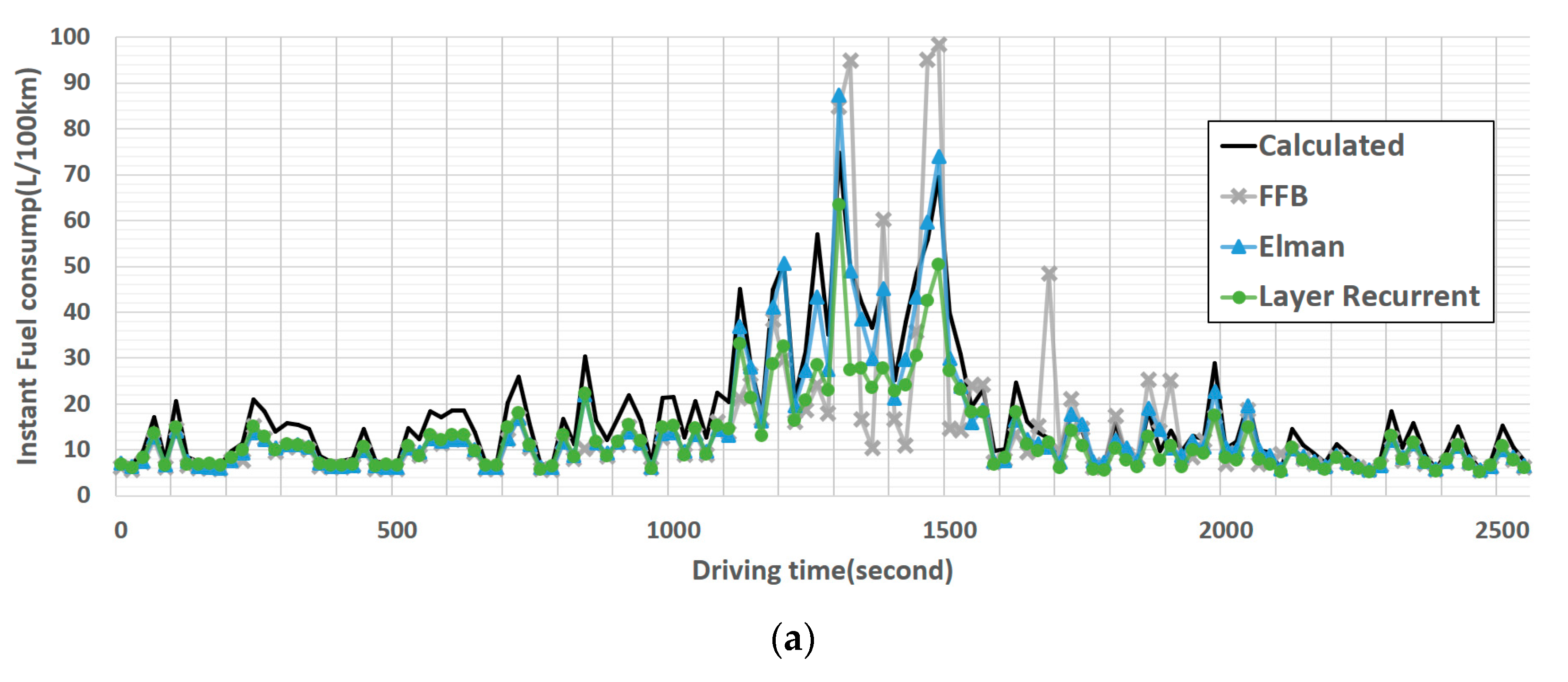
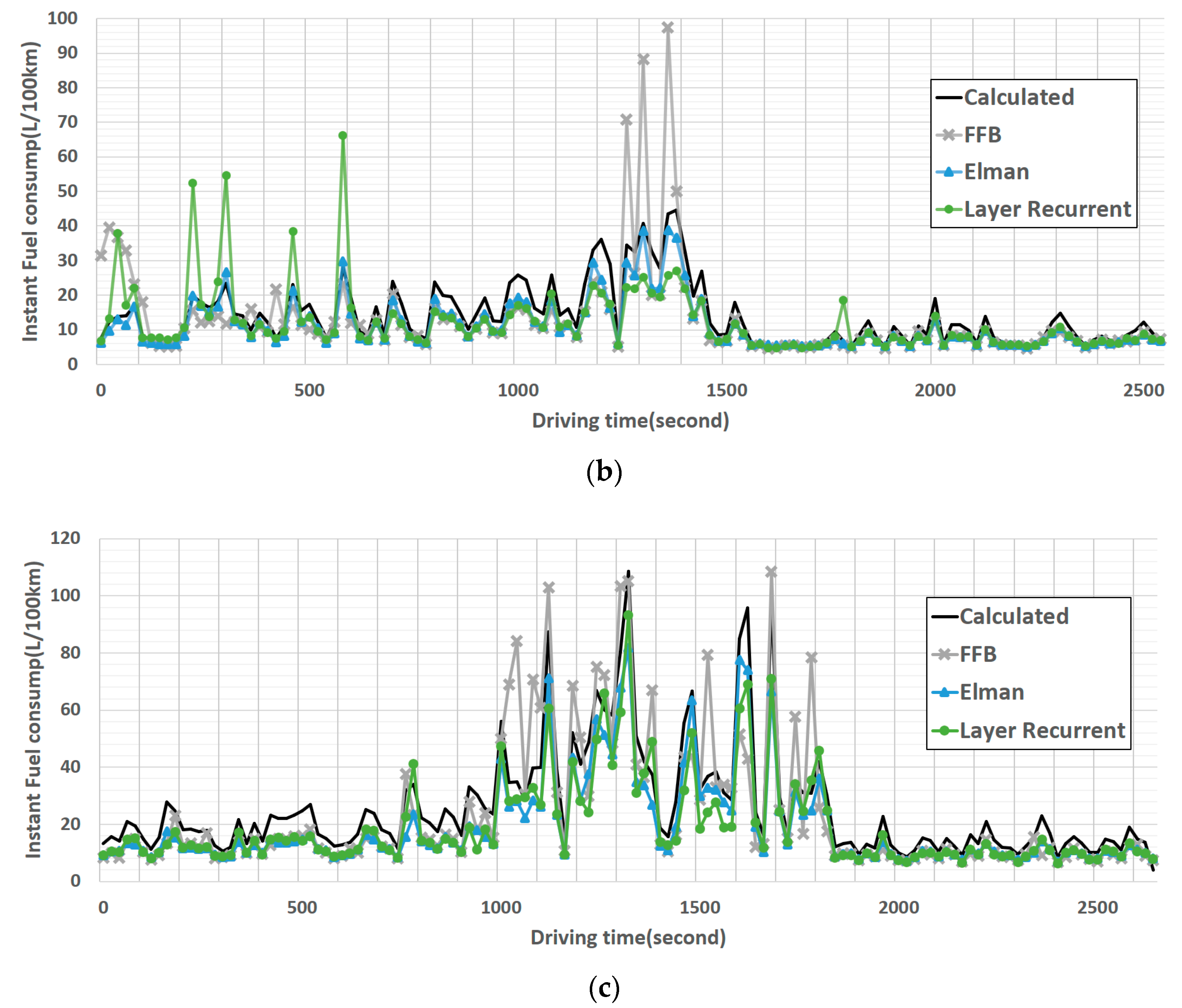

| Brand | Module | Engine Displacement (c.c.) | Engine Torque | Fuel Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mazda | Mazda 3 | 1999 | 21.7 kgm/4000 rpm | 0.87 |
| Mitsubishi | Lancer1.8 | 1798 | 17.9 kgm/4200 rpm | 1.17 |
| Toyota | Vios | 1496 | 14.3 kgm/4200 rpm | 1.48 |
| Parameter Name | Unit | Range of Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Engine displacement | c.c. | 0~16,383.75 |
| Air flow rate | g/s | 0~655.35 |
| Engine coolant temperature | °C | −40~215 |
| Engine load | % | 0~100 |
| Ignition timing | ° | 0~655.35 |
| Engine rotations | rpm | 0~16,383.75 |
| Vehicle speed | km/h | 0~255 |
| Throttle position | % | 0~100 |
| Control module voltage | V | 0~65.535 |
| RPM Range | Weight |
|---|---|
| RPM < 1000 | 2 |
| 1000 ≤ RPM < 1500 | (RPM-1000)/500 + 2 |
| 1500 ≤ RPM < 2000 | (RPM-1500)/250 + 3 |
| 2000 ≤ RPM < 2300 | (RPM-2000)/100 + 5 |
| 2300 ≤ RPM < 2600 | (RPM-2300)/50 + 8 |
| 2600 ≤ RPM < 2900 | (RPM-2600)/25 + 14 |
| 2900 ≤ RPM < 3200 | (RPM-2900)/25 + 26 |
| 3200 ≤ RPM < 3500 | (RPM-3200)/20 + 38 |
| 3500 ≤ RPM | (RPM-3500)/20 + 53 |
| Model | Training Times (s) | RMSE | γ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lancer | Mazda | Vios | Lancer | Mazda | Vios | ||
| Elman backprop | 29 | 4.077 | 3.672 | 8.24 | 0.9696 | 0.967 | 0.9827 |
| Layer recurrent | 42 | 6.369 | 7.737 | 9.266 | 0.9771 | 0.6616 | 0.9556 |
| Feed-forward backprop | 25 | 9.742 | 9.504 | 12.685 | 0.7933 | 0.718 | 0.8471 |
| Route Type | Parameter Name | Lancer | Mazda | Vios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mountain road | Average calculated fuel consumption (L/100 km) | 35.8852 | 22.4482 | 45.3746 |
| Average RPMWeight | 5.5158 | 4.2622 | 7.7183 | |
| Regular road | Average calculated fuel consumption (L/100 km) | 11.8218 | 9.5756 | 9.2630 |
| Average RPMWeight | 3.1779 | 2.7708 | 2.3384 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, M.-H.; Tian, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-C. Combining a Universal OBD-II Module with Deep Learning to Develop an Eco-Driving Analysis System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104481
Yen M-H, Tian S-L, Lin Y-T, Yang C-W, Chen C-C. Combining a Universal OBD-II Module with Deep Learning to Develop an Eco-Driving Analysis System. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104481
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Meng-Hua, Shang-Lin Tian, Yan-Ting Lin, Cheng-Wei Yang, and Chi-Chun Chen. 2021. "Combining a Universal OBD-II Module with Deep Learning to Develop an Eco-Driving Analysis System" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104481
APA StyleYen, M.-H., Tian, S.-L., Lin, Y.-T., Yang, C.-W., & Chen, C.-C. (2021). Combining a Universal OBD-II Module with Deep Learning to Develop an Eco-Driving Analysis System. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4481. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104481






