Semantic Matching Based on Semantic Segmentation and Neighborhood Consensus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Representation for Semantic Matching
2.2. Spatial Context for Semantic Matching
3. Approach
3.1. Network Architecture
3.2. Feature Extraction
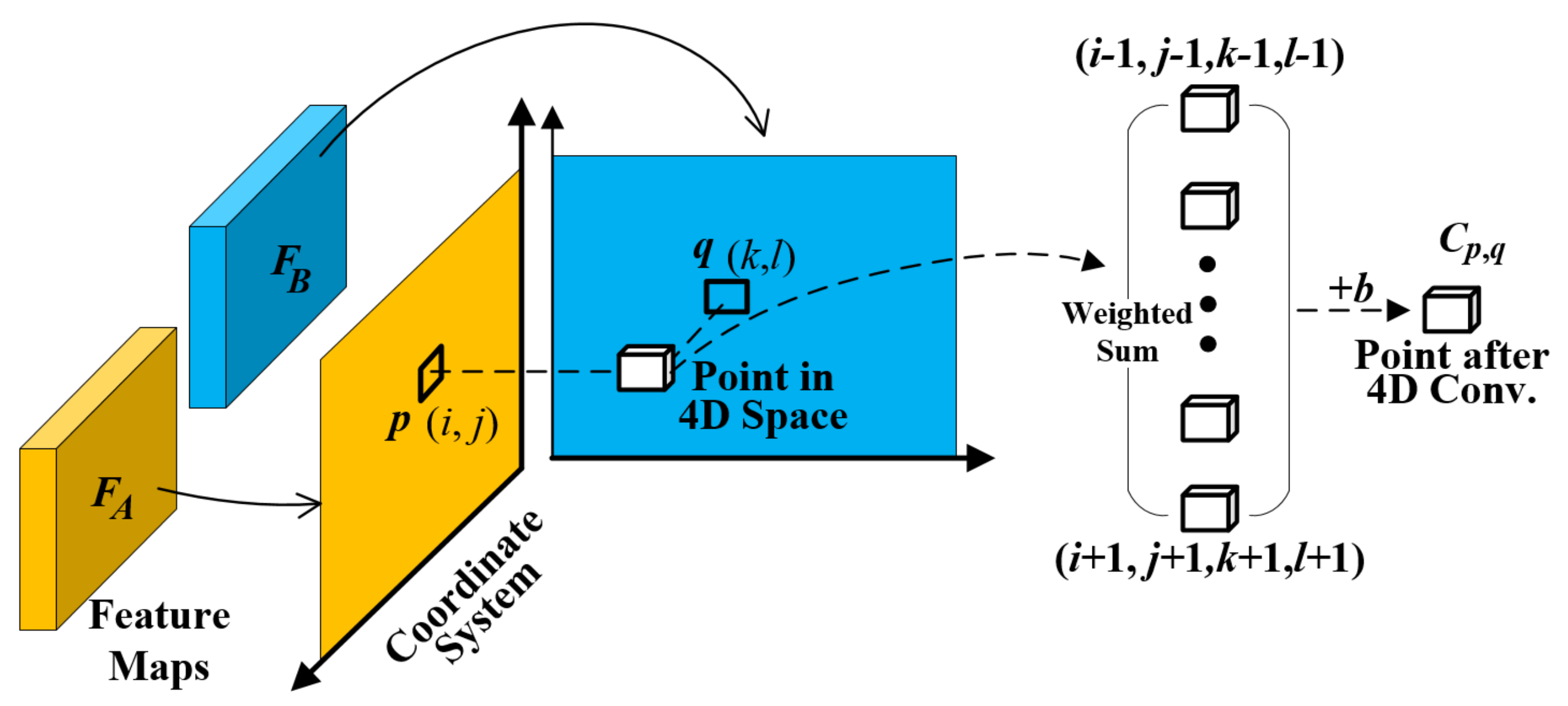
3.3. Four-Dimensional Convolution
3.4. Objective Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Quantitative Results
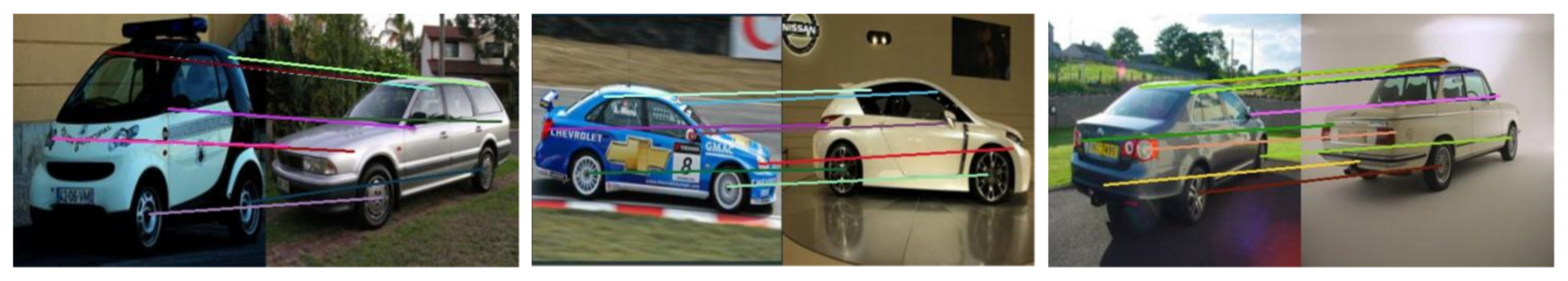
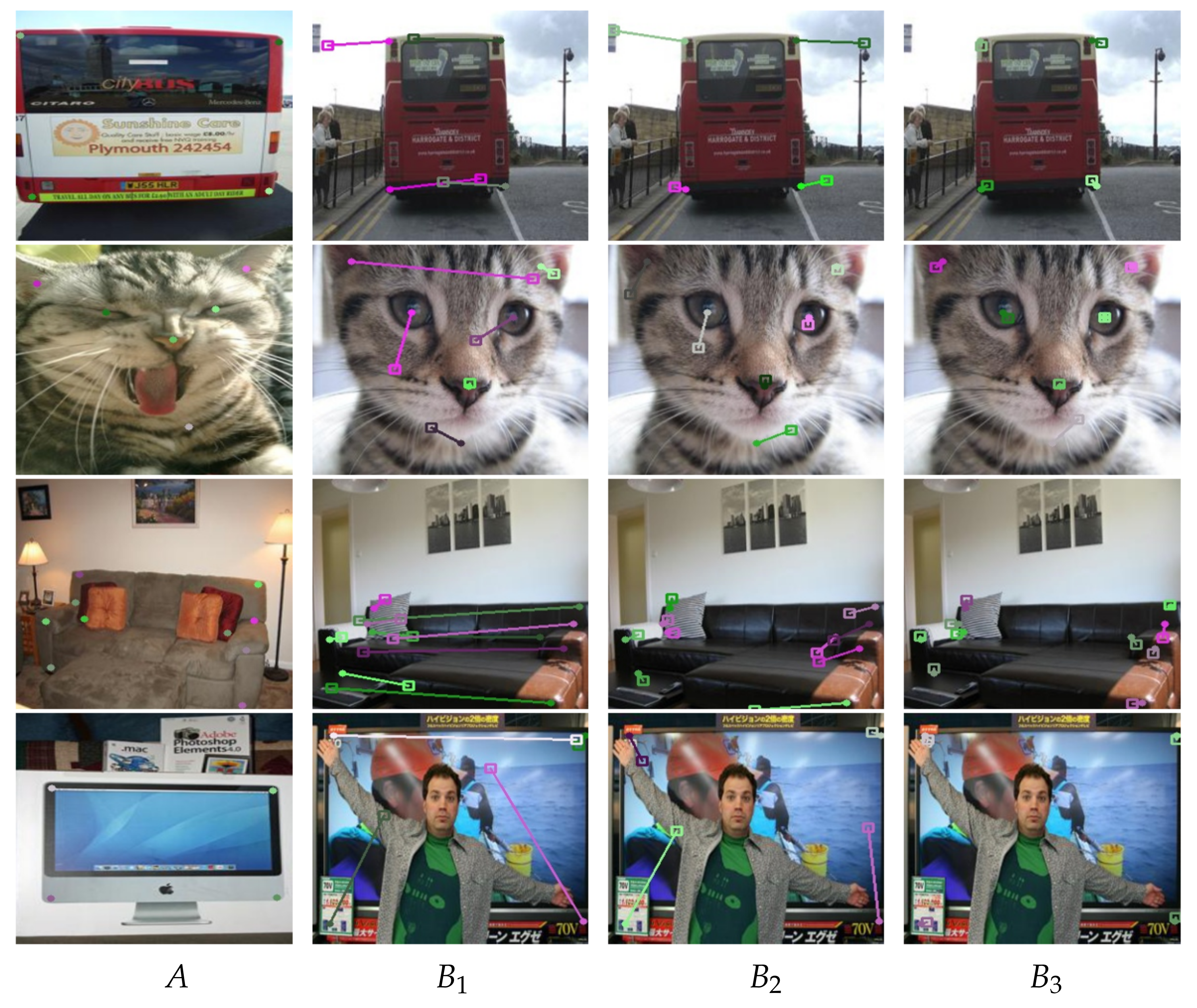
4.3. Qualitative Results
4.4. Ablation Study
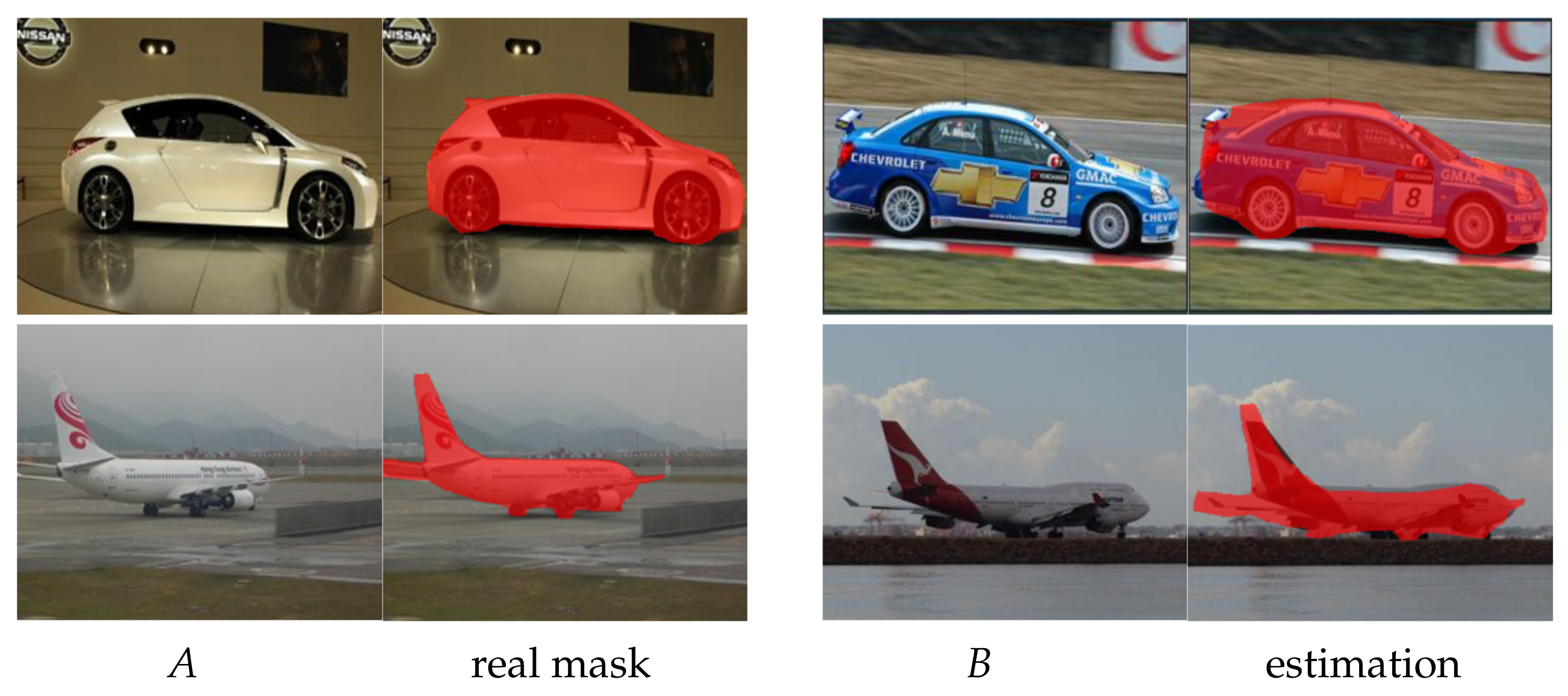
4.5. Limitation
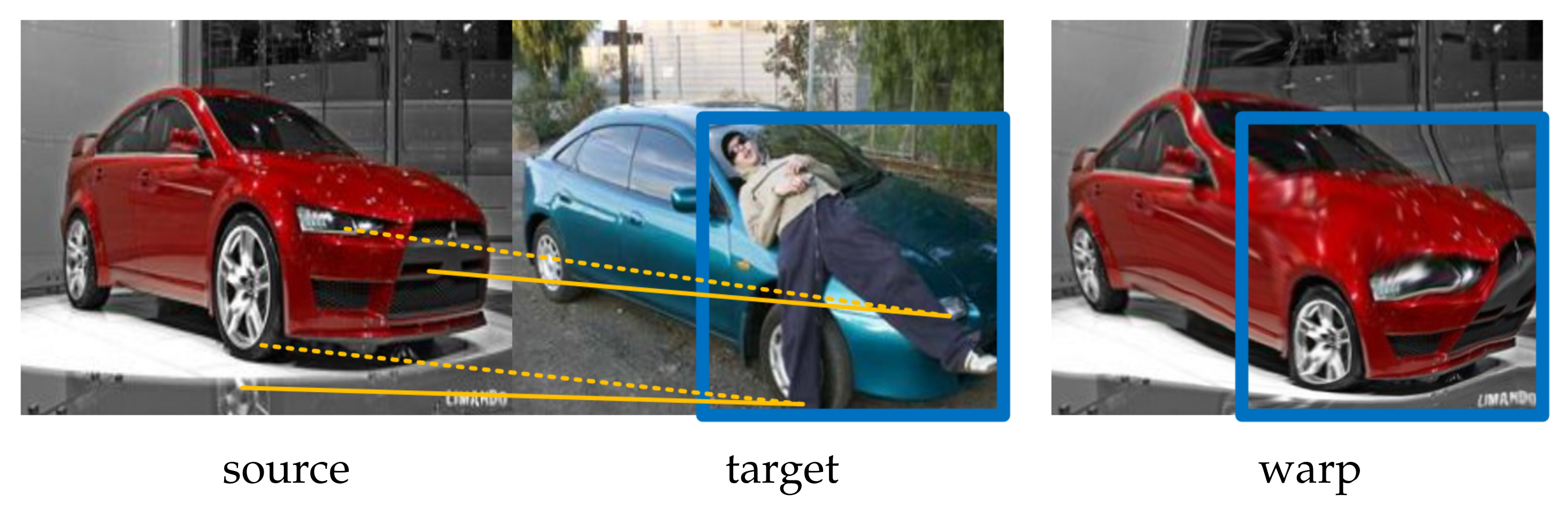
4.6. Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 47, 7–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, R.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X. Improved Cost Computation and Adaptive Shape Guided Filter for Local Stereo Matching of Low Texture Stereo Images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Ren, S.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H. Crosspatch-based rolling label expansion for dense stereo matching. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 63470–63481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brox, T.; Bruhn, A.; Papenberg, N.; Weickert, J. High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Szech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, B.K.; Schunck, B.G. Determining optical flow. Artif. Intell. 1981, 17, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.L.; Zhang, N.; Darrell, T. Do convnets learn correspondence? In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 1601–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, A.; Jacobs, D.W.; Chandraker, M. Warpnet: Weakly supervised matching for single-view reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3253–3261. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, C.B.; Gwak, J.; Savarese, S.; Chandraker, M. Universal correspondence network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03558. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, B.; Cho, M.; Schmid, C.; Ponce, J. Proposal flow: Semantic correspondences from object proposals. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, S.; Min, D.; Sohn, K. Parn: Pyramidal affine regression networks for dense semantic correspondence. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Hua, G.; Kang, S.B. Visual attribute transfer through deep image analogy. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.01088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yuen, J.; Torralba, A. Sift flow: Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 978–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberman, K.; Liao, J.; Shi, M.; Lischinski, D.; Chen, B.; Cohen-Or, D. Neural best-buddies: Sparse cross-domain correspondence. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2018, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, D.; Liao, J.; Sander, P.V.; Yuan, L. Deep exemplar-based colorization. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2018, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Sheikh, Y.; Ramanan, D. Pixelnn: Example-based image synthesis. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.05349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, B.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Wen, F. Cross-domain correspondence learning for exemplar-based image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5143–5153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Qi, H. Image super-resolution by neural texture transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7982–7991. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tola, E.; Lepetit, V.; Fua, P. Daisy: An efficient dense descriptor applied to wide-baseline stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 32, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Aubry, M.; Huang, Q.; Efros, A.A. Learning dense correspondence via 3d-guided cycle consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Min, D.; Ham, B.; Jeon, S.; Lin, S.; Sohn, K. Fcss: Fully convolutional self-similarity for dense semantic correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–27 July 2017; pp. 6560–6569. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, B.; Cho, M.; Schmid, C.; Ponce, J. Proposal flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3475–3484. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffalitzky, F.; Zisserman, A. Automated scene matching in movies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval, London, UK, 18–19 July 2002; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 186–197. [Google Scholar]
- Sivic, J.; Zisserman, A. Video Google: A text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA; Volume 3, p. 1470. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, T.; Leibe, B.; Kobbelt, L. SCRAMSAC: Improving RANSAC’s efficiency with a spatial consistency filter. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 2090–2097. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Lin, W.Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Yeung, S.K.; Nguyen, T.D.; Cheng, M.M. Gms: Grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra-robust feature correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4181–4190. [Google Scholar]
- Rocco, I.; Cimpoi, M.; Arandjelović, R.; Torii, A.; Pajdla, T.; Sivic, J. Neighbourhood consensus networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.10510. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, D.; Larlus, D.; Vedaldi, A. Anchornet: A weakly supervised network to learn geometry-sensitive features for semantic matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5277–5286. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yan, S.; He, X. Dynamic context correspondence network for semantic alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 2010–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ponce, J.; Ham, B. Sfnet: Learning object-aware semantic correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2278–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Rezende, R.S.; Ham, B.; Wong, K.Y.K.; Cho, M.; Schmid, C.; Ponce, J. Scnet: Learning semantic correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1831–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Shechtman, E.; Irani, M. Matching local self-similarities across images and videos. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 18–23 June 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Min, D.; Lin, S.; Sohn, K. Deep self-correlation descriptor for dense cross-modal correspondence. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 679–695. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Min, D.; Ham, B.; Ryu, S.; Do, M.N.; Sohn, K. DASC: Dense adaptive self-correlation descriptor for multi-modal and multi-spectral correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2103–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Min, D.; Lin, S.; Sohn, K. Dctm: Discrete-continuous transformation matching for semantic flow. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4529–4538. [Google Scholar]
- Rocco, I.; Arandjelovic, R.; Sivic, J. Convolutional neural network architecture for geometric matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6148–6157. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2012 (VOC2012) Results. Available online: http://www.pascal-network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2012/workshop/index.html (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G.; Yang, E.; DeVito, Z.; Lin, Z.; Desmaison, A.; Antiga, L.; Lerer, A. Automatic Differentiation in Pytorch. 2017. Available online: http://https://pytorch.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2011 (VOC2011) Results. Available online: http://www.pascal-network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2011/workshop/index.html (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Kim, S.; Lin, S.; Jeon, S.R.; Min, D.; Sohn, K. Recurrent transformer networks for semantic correspondence. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 6126–6136. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, P.H.; Lee, J.; Jung, D.; Han, B.; Cho, M. Attentive semantic alignment with offset-aware correlation kernels. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Rocco, I.; Arandjelović, R.; Sivic, J. End-to-end weakly-supervised semantic alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6917–6925. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Min, D.; Kim, S.; Sohn, K. Joint learning of semantic alignment and object landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7294–7303. [Google Scholar]





| Methods | PF-PASCAL ( img) | PF-WILLOW ( bbox) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCN-ST [8] | 0.299 | 0.556 | 0.740 | 0.241 | 0.540 | 0.665 |
| SCNet [35] | 0.362 | 0.722 | 0.820 | 0.386 | 0.704 | 0.853 |
| A2Net [46] | 0.428 | 0.708 | 0.833 | 0.363 | 0.688 | 0.844 |
| CNNGeo [40] | 0.460 | 0.758 | 0.884 | 0.382 | 0.712 | 0.858 |
| SFNet [34] | - | 0.787 | - | - | 0.740 | - |
| Weakalign [47] | 0.490 | 0.748 | 0.840 | 0.370 | 0.702 | 0.799 |
| CAT-FCSS [22] | 0.336 | 0.689 | 0.792 | 0.362 | 0.546 | 0.692 |
| RTNs [45] | 0.552 | 0.759 | 0.852 | 0.413 | 0.719 | 0.862 |
| SAOLD [48] | 0.528 | 0.727 | 0.792 | - | - | - |
| NCNet [31] | 0.542 | 0.789 | 0.860 | 0.440 | 0.727 | 0.854 |
| Ours | 0.555 | 0.842 | 0.932 | 0.454 | 0.747 | 0.863 |
| Semantic Segment | 4D Convolution | PF-PASCAL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | 0.306 | 0.499 | 0.612 |
| × | ✓ | 0.409 | 0.740 | 0.865 |
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.555 | 0.842 | 0.932 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, H. Semantic Matching Based on Semantic Segmentation and Neighborhood Consensus. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104648
Xu H, Chen X, Cai H, Wang Y, Liang H, Li H. Semantic Matching Based on Semantic Segmentation and Neighborhood Consensus. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104648
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Huaiyuan, Xiaodong Chen, Huaiyu Cai, Yi Wang, Haitao Liang, and Haotian Li. 2021. "Semantic Matching Based on Semantic Segmentation and Neighborhood Consensus" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104648
APA StyleXu, H., Chen, X., Cai, H., Wang, Y., Liang, H., & Li, H. (2021). Semantic Matching Based on Semantic Segmentation and Neighborhood Consensus. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104648






