Artificial Intelligence for Student Assessment: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Current revision of the state of the art.
- The most recent applications of AI to assess students.
- Based on our analysis, we suggest the main ways to improve education using AI and make some predictions on the future of this field of research.
2. Educational Applications of AI
2.1. AI for Tutoring
2.2. AI for Educational Assessment
2.3. Other Educational Uses of AI
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Questions and Objectives
- RO1.
- Identifying the main studies around student assessment based on AI in the last decade (2010–2020), using a systematic review.
- RO2.
- Analyzing the impact that education and/or technology have on this field of research.
- RO3.
- Analyzing the type of educational assessment which is being improved with AI.
3.2. Eligibility Criteria
3.3. Information Sources
3.4. Search Strategy
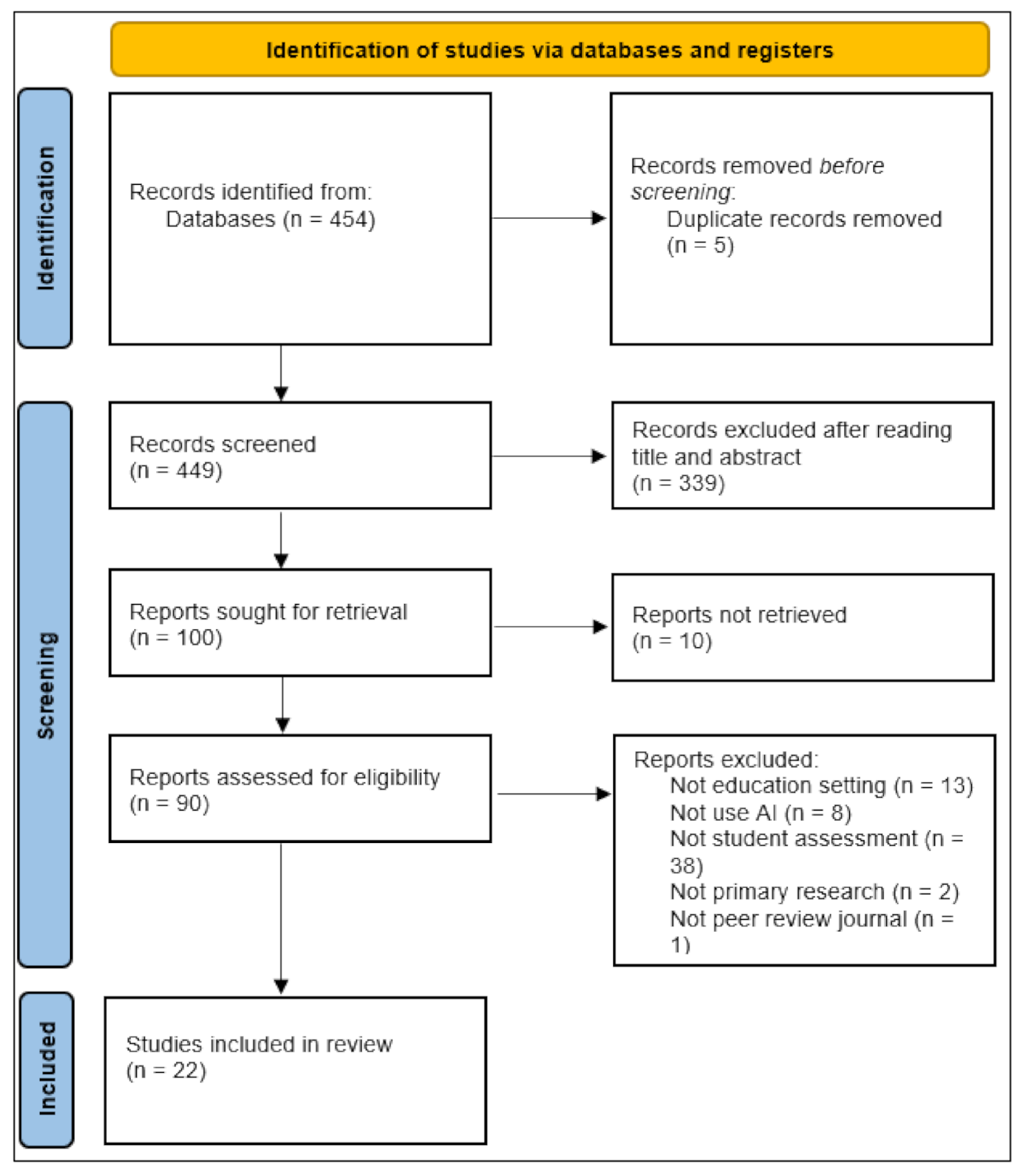
3.5. Study Selection
3.6. Coding, Data Extraction and Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Understanding of AI
4.2. Pedagogical Model Used
4.3. Formative Evaluation as the Reason for the Use of AI
4.4. Automated Scoring
4.5. Comparison between IA Use and Non-Use
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNESCO. Elaboration of a Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/artificial-intelligence/ethics (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- United Nations Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development/Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- Janpla, S.; Piriyasurawong, P. The Development of an Intelligent Multilevel Item Bank Model for the National Evaluation of Undergraduates. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 4163–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendes Espinosa, M.P.; Cerdán Cartagena, F. Tecnologías avanzadas para afrontar el reto de la innovación educativa. RIED. Rev. Iberoam. Educ. Distancia 2020, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.S.; Wang, X.; Xu, C. An extended theory of planned behavior for the modelling of chinese secondary school students’ intention to learn artificial intelligence. Mathematics 2020, 8, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugurullo, F. Urban Artificial Intelligence: From Automation to Autonomy in the Smart City. Front. Sustain. Cities 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, B.; Kalantzis, M.; Searsmith, D. Artificial intelligence for education: Knowledge and its assessment in AI-enabled learning ecologies. Educ. Philos. Theory 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korteling, J.E.; van de Boer-Visschedijk, G.C.; Blankendaal, R.A.M.; Boonekamp, R.C.; Eikelboom, A.R. Human-versus Artificial Intelligence. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, S.; Ahad, M.; Tripathi, G.; Feroz, N.; Casalino, G. Enabling Technologies for Urban Smart Mobility: Recent Trends, Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors 2021, 21, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Song, Y.; Kim, J. Evaluation of AI-Assisted Telemedicine Service Using a Mobile Pet Application. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchi, N.; Bissonnette, V.; Yilmaz, R.; Ledwos, N.; Winkler-Schwartz, A.; Del Maestro, R.F. The Virtual Operative Assistant: An explainable artificial intelligence tool for simulation-based training in surgery and medicine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houwink, E.J.F.; Kasteleyn, M.J.; Alpay, L.; Pearce, C.; Butler-Henderson, K.; Meijer, E.; van Kampen, S.; Versluis, A.; Bonten, T.N.; van Dalfsen, J.H.; et al. SERIES: eHealth in primary care. Part 3: eHealth education in primary care. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 26, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña-Fernández, Y.; Valenzuela-Fernández, L.A.; Garro-Aburto, L.L. Inteligencia artificial y sus implicaciones en la educación superior. Propósitos y Represent. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Tudela, P.A.; Prendes-Espinosa, M.P.; Solano-Fernández, I.M. Smart learning environments and ergonomics: An approach to the state of the question. J. New Approaches Educ. Res. 2020, 9, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, E. Teaching Machine Dichotomy: Skinner vs. Pressey. Psychol. Rep. 1960, 6, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Beijing Consensus on Artificial Intelligence and Education; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, E.; Chua, X.N. Robotic Chinese language tutor: Personalising progress assessment and feedback or taking over your job? Horizont 2020, 28, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, J.; Conejo, R.; Guzmán, E. Statistical Techniques to Explore the Quality of Constraints in Constraint-Based Modeling Environments. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2013, 23, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narciss, S.; Sosnovsky, S.; Schnaubert, L.; Andrès, E.; Eichelmann, A.; Goguadze, G.; Melis, E. Exploring feedback and student characteristics relevant for personalizing feedback strategies. Comput. Educ. 2014, 71, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, K.H.; Jones, K.A.; Jones, G.W.; Amiel, J.; Barron, B.; Elhadad, N. Machine learning to extract communication and history-taking skills in OSCE transcripts. Med. Educ. 2020, 54, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, O.C.; Boticario, J.G. Involving Users to Improve the Collaborative Logical Framework. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakou, M.; Fylladitakis, E.D.; Karolidis, D.; Früh, W.-G.; Hatziapostolou, A.; Athinaios, S.S.; Grigoriadou, M. Evaluation of an intelligent open learning system for engineering education. Knowl. Manag. E-Learning Int. J. 2016, 8, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saplacan, D.; Herstad, J.; Pajalic, Z. Feedback from digital systems used in higher education: An inquiry into triggered emotions two universal design oriented solutions for a better user experience. In Transforming Our World through Design, Diversity and Education: Proceedings of Universal Design and Higher Education in Transformation Congress 2018; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 256, pp. 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Ascaso, A.; Boticario, J.G.; Finat, C.; Petrie, H. Setting accessibility preferences about learning objects within adaptive elearning systems: User experience and organizational aspects. Expert Syst. 2017, 34, e12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Li, K.; Wu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Predicting student achievement based on temporal learning behavior in MOOCs. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, K.K. Adoption of artificial intelligence in higher education: A quantitative analysis using structural equation modelling. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 3443–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, L. Automated Scoring of Chinese Engineering Students’ English Essays. Int. J. Distance Educ. Technol. 2017, 15, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Individualized AI Tutor Based on Developmental Learning Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 27927–27937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Arias-Navarrete, A.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Proposal of an Architecture for the Integration of a Chatbot with Artificial Intelligence in a Smart Campus for the Improvement of Learning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, M.; Yi, H. Building an efficient artificial intelligence model for personalized training in colleges and universities. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2021, 29, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón, O.D.; Sarache, W.; Ruiz-Herrera, S. Predicción del rendimiento académico por medio de técnicas de inteligencia artificial. Form. Univ. 2020, 13, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.; Oliver, S.; Thomas, J. An Introduction to Systematic Reviews; SAGE: Los Angeles, LA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, C. Co-word analysis applied to highly cited papers in Library and Information Science (2007–2017). Transinformacao 2018, 30, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhienmora, P.; Haddawy, P.; Khanal, P.; Suebnukarn, S.; Dailey, M.N. A virtual reality simulator for teaching and evaluating dental procedures. Methods Inf. Med. 2010, 49, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhienmora, P.; Haddawy, P.; Suebnukarn, S.; Dailey, M.N. Intelligent dental training simulator with objective skill assessment and feedback. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 52, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouguengay, Y.A.; El Faddouli, N.-E.; Bennani, S. A neuro-fuzzy inference system for the evaluation of reading/writing competencies acquisition in an e-learning environnement. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2015, 81, 600–608. [Google Scholar]
- Kaila, E.; Kurvinen, E.; Lokkila, E.; Laakso, M.-J. Redesigning an Object-Oriented Programming Course. ACM Trans. Comput. Educ. 2016, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanta, C.; Walton, D. The Use of Argument Maps as an Assessment Tool in Higher Education. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2016, 79, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perikos, I.; Grivokostopoulou, F.; Hatzilygeroudis, I. Assistance and Feedback Mechanism in an Intelligent Tutoring System for Teaching Conversion of Natural Language into Logic. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2017, 27, 475–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.K.; Joyner, D.A. Using AI to Teach AI: Lessons from an Online AI Class. AI Mag. 2017, 38, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grivokostopoulou, F.; Perikos, I.; Hatzilygeroudis, I. An Educational System for Learning Search Algorithms and Automatically Assessing Student Performance. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2017, 27, 207–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.; Hastings, P.; Blaum, D.; Jaeger, A.J.; Hughes, S.; Wallace, P.; Griffin, T.D.; Britt, M.A. Different Approaches to Assessing the Quality of Explanations Following a Multiple-Document Inquiry Activity in Science. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2017, 27, 758–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.R.; Mir, R.R.; Farhan, M.; Rafiq, T.; Aslam, M. Student Query Trend Assessment with Semantical Annotation and Artificial Intelligent Multi-Agents. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicher, K.R.; Zimmerman, L.; Wilcox, B.; Liston, B.; Cronau, H.; Macerollo, A.; Jin, L.; Jaffe, E.; White, M.; Fosler-Lussier, E.; et al. Using virtual standardized patients to accurately assess information gathering skills in medical students. Med. Teach. 2019, 41, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Anbarasan, M.; Praveen Kumar, D. Design of online intelligent English teaching platform based on artificial intelligence techniques. Comput. Intell. 2020, 12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jesus, F.; Castelli, M.; Oliveira, T.; Mendes, R.; Nunes, C.; Sa-Velho, M.; Rosa-Louro, A. Using artificial intelligence methods to assess academic achievement in public high schools of a European Union country. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Nguyen-Huy, T.; Langlands, T.A.M.; Galligan, L. Modern Artificial Intelligence Model Development for Undergraduate Student Performance Prediction: An Investigation on Engineering Mathematics Courses. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 136697–136724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnce, M.; Yiğit, T.; Hakan Işik, A. A Novel Hybrid Fuzzy AHP-GA Method for Test Sheet Question Selection. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2020, 19, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulum, Ö.G. A critical deconstruction of computer-based test application in Turkish State University. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 4883–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; McClenen, C. Development of adaptive formative assessment system using computerized adaptive testing and dynamic bayesian networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazos, C.A.; Gutiérrez, F.L.; Gallardo, J.; Ortega, M.; Fardoun, H.M.; Molina, A.I. Descriptive theory of awareness for groupware development. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019, 10, 4789–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig-Vila, R.; Moreno-Isac, V. El pensamiento computacional en Educación. Análisis bibliométrico y temático. Rev. Educ. Distancia 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Álvarez-Herrero, J.-F. Diseño y validación de un instrumento para la taxonomía de los robots de suelo en Educación Infantil. Pixel-Bit Rev. Medios Educ. 2020, 60, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González González, C.S. Estrategias para la enseñanza del pensamiento computacional y uso efectivo de tecnologías en educación infantil: Una propuesta inclusiva. Rev. Interuniv. Investig. Tecnol. Educ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio Caride, S. Experiencias robóticas en infantil. Rev. Interuniv. Investig. Tecnol. Educ. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabero-Almenara, J.; Romero-Tena, R.; Palacios-Rodríguez, A. Evaluation of Teacher Digital Competence Frameworks Through Expert Judgement: The Use of the Expert Competence Coefficient. J. New Approaches Educ. Res. 2020, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendes Espinosa, M.P.; González-Calatayud, V. Interactive environments for involvement and motivation for learning. In Video Games for Teachers: From Research to Action; Payá, A., Mengual-Ándres, S., Eds.; Mcragw Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2019; pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Díaz, E.; Gutiérrez Esteban, P.; Fernández Olaskoaga, L. University-School Scenarios and Voices from Classrooms. Rethinking Collaboration within the Framework of an Interuniversity Project. J. New Approaches Educ. Res. 2019, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkle, M.; Cobo, C. Redefining Knowledge in the Digital Age. J. New Approaches Educ. Res. 2018, 7, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Published 2010–2020 | Published before 2010 |
| English or Spanish language | Not in English or Spanish |
| Empirical research | Not empirical (e.g., review) |
| Peer review journal | Not peer review journal |
| Use of artificial intelligence to assess learners | Not artificial intelligence |
| Not learning setting | |
| Not for assessment |
| Authors | Year | Journal | Country | Author Affiliation | Subject or Educational Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhienmora et al. [35] | 2010 | Methods of information in medicine | Thailand | Engineering and dentistry | Dental study |
| Phattanapon et al. [36] | 2011 | Artificial intelligence in medicine | Thailand | Computer science and Dentistry | Dental study |
| Gálvez et al. [18] | 2013 | International journal of artificial intelligence in education | Spain | Computer engineering | Computer science |
| Santos & Boticario [21] | 2014 | The scientific world journal | Spain | Computer science | Secondary education and University |
| Ouguengay et al. [37] | 2015 | Journal of theoretical and applied information technology | Morocco | Computer science | Amazigh Language |
| Samarakou et al. [22] | 2016 | Knowledge Management & E-Learning | Greece and UK | Engineering | Heat transfer |
| Kaila et al. [38] | 2016 | ACM Transactions on Computing Education | Finland | Information technology | Computer science, mathematics, and physics |
| Rapanta & Walton [39] | 2016 | International Journal of educational research | Portugal and Canada | Philosophy | Business and Education |
| Liu et al. [27] | 2017 | International Journal of Distance Education Technologies | China | Computer and information Science | English language |
| Perikos et al. [40] | 2017 | International journal of artificial intelligence in education | Greece | Computer engineering and informatics | Logic |
| Goel & Joyner [41] | 2017 | AI Magazine | USA | Interactive computing | Artificial intelligence |
| Grivokostopoulo et al. [42] | 2017 | International journal of artificial intelligence in education | Greece | Computer engineering | Artificial intelligence |
| Wiley et al. [43] | 2017 | International journal of artificial intelligence in education | USA | Psychology, Artificial intelligence | Secondary education, global warming |
| Malik et al. [44] | 2017 | EURASIA Journal of Mathematics Science and Technology Education | Pakistan | Information technology | English |
| Maicher et al. [45] | 2019 | Medical teacher | USA | Medicine | Medicine |
| Sun et al. [46] | 2020 | Computer intelligence | China and India | Engineering | English |
| Cruz-Jesus et al. [47] | 2020 | Heliyon | Portugal | Information management | Secondary education |
| Deo et al. [48] | 2020 | IEEE Access | Australia, Vietnam y Sweden | Engineering | Mathematics |
| Ince et al. [49] | 2020 | International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making | Turkey | Vocational school of technical Science, Computer engineering | Mathematics |
| Ulum [50] | 2020 | Education and information technologies | Turkey | English language | English |
| Jani et al. [20] | 2020 | Medical education | USA | Medicine | Medicine |
| Choi & McClenen [51] | 2020 | Applied sciences | Korea and Canada | Adolescent coaching counselling, Computer science | Statistics |
| Country | Number of Contributions |
|---|---|
| USA | 4 |
| Greece | 3 |
| Thailand | 2 |
| Spain | 2 |
| Portugal | 2 |
| Chine | 2 |
| Canada | 2 |
| Turkey | 2 |
| Morocco | 1 |
| UK | 1 |
| Finland | 1 |
| Pakistan | 1 |
| Australia | 1 |
| Vietnam | 1 |
| Sweden | 1 |
| Korea | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Calatayud, V.; Prendes-Espinosa, P.; Roig-Vila, R. Artificial Intelligence for Student Assessment: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125467
González-Calatayud V, Prendes-Espinosa P, Roig-Vila R. Artificial Intelligence for Student Assessment: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(12):5467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125467
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Calatayud, Víctor, Paz Prendes-Espinosa, and Rosabel Roig-Vila. 2021. "Artificial Intelligence for Student Assessment: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 11, no. 12: 5467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125467
APA StyleGonzález-Calatayud, V., Prendes-Espinosa, P., & Roig-Vila, R. (2021). Artificial Intelligence for Student Assessment: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 11(12), 5467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125467








