Effects of Complex Functional Strength Training on Balance and Shooting Performance of Rifle Shooters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
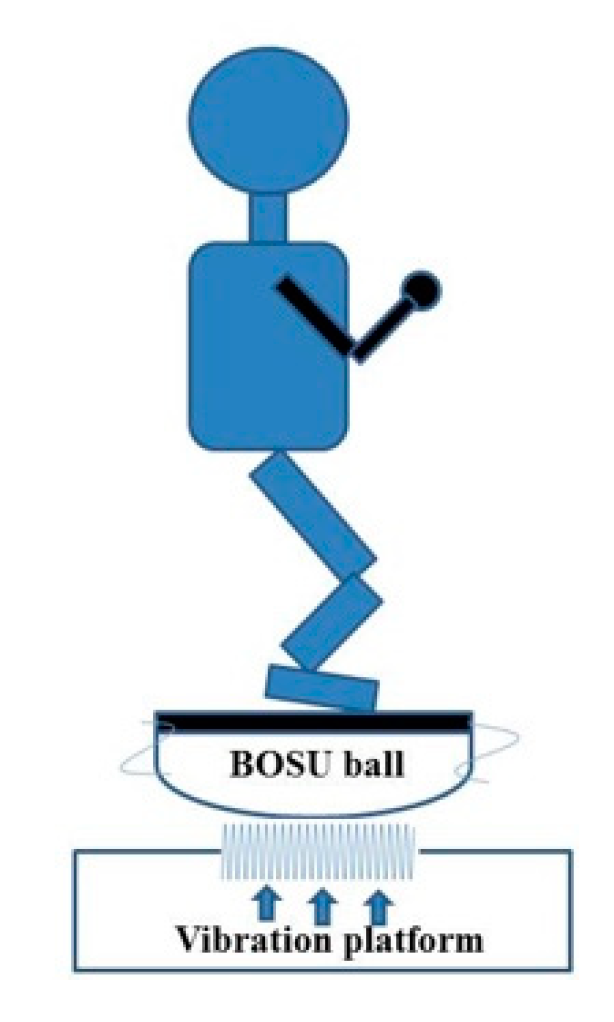
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Dependent Measures
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISSF Rules and Regulations. International Shooting Sport Federation Official Statutes Rules and Regulations. Available online: www.thenrai.in/PDF/0efbcf72-1db0-41b0-93e5-5bb8eb37b539.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2017).
- Zatsiorsky, V.M.; Aktov, A.V. Biomechanics of highly precise movements: The aiming process in air rifle shooting. J. Biomech. 1990, 23, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, N.; Lyytinen, H.; Viitasalo, J. Rifle-balancing in precision shooting: Behavioral aspects and psychophysiological implication. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 1998, 8, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, D.; Zakynthinaki, M.S.; Cordente, C.A.; Anton, A.M.; Jimenez, D.L. Validation of a dumbbell body sway test in Olympic air pistol shooting. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ball, K.; Best, R.; Wrigley, T. Body sway, aim point fluctuation and performance in rifle shooters: Inter-and intra-individual analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mononen, K.; Konttinen, N.; Viitasalo, J.; Era, P. Relationships between postural balance, rifle stability and shooting accuracy among novice rifle shooters. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2007, 17, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrysomallis, C. Balance ability and athletic performance. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karmali, F.; Goodworth, A.D.; Valko, Y.; Leeder, T.; Peterka, R.J.; Merfeld, D.M. The role of vestibular cues in postural sway. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 125, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, R.; Takakusaki, K.; Ota, J.; Yozu, A.; Haga, N. Human upright posture control models based on multisensory inputs; in fast and slow dynamics. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 104, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croix, G.; Chollet, D.; Thouvarecq, R. Effect of expertise level on the perceptual characteristics of gymnasts. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihalainen, S.; Kuitunen, S.; Mononen, K.; Linnamo, V. Determinants of elite-level air rifle shooting performance. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T.H.; Noé, F. Effect of expertise and visual contribution on postural control in soccer. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2006, 16, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, P.J.; Rhea, M.R. Effects of vibration training on muscle strength: A meta-analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilcock, I.M.; Whatman, C.; Harris, N.; Keogh, J.W. Vibration training: Could it enhance the strength, power, or speed of athletes? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delecluse, C.; Roelants, M.; Verschueren, S. Strength increase after whole-body vibration compared with resistance training. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2003, 35, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, H.S.; Cramer, J.T.; Bemben, D.A.; Shehab, R.L.; Anderson, M.A.; Bemben, M.G. Effects of a 6-week periodized squat training with or without whole-body vibration upon short-term adaptations in squat strength and body composition. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehn, B.; Lidström, J.; Skoglund, J.; Lindström, B. Effects on leg muscular performance from whole-body vibration exercise: A systematic review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2007, 17, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Behm, D.G. Trunk muscle activity increases with unstable squat movements. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 30, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hibbs, A.E.; Thompson, K.G.; French, D.; Wrigley, A.; Spears, I. Optimizing performance by improving core stability and core strength. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkle, J.; Nesser, T.W.; Demchak, T.J.; McMannus, D.M. Effect of core strength on the measure of power in the extremities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, P.A.; Gomez, S.; Patel, M.; Johansson, L. Changes in multi-segmented body movements and EMG activity while standing on firm and foam support surfaces. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 101, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanenko, Y.P.; Solopova, I.A.; Levik, Y.S. The direction of postural instability affects postural reactions to ankle muscle vibration in humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, P.J.; Hazell, T.J. Effects of whole-body vibration with an unstable surface on muscle activation. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2014, 14, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McBride, J.M.; Cormie, P.; Deane, R. Isometric squat force output and muscle activity in stable and unstable conditions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 915. [Google Scholar]
- Ammar, A.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Effect of time-of-day on biochemical markers in response to physical exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, H.; Trabelsi, K.; Ammar, A.; Shephard, R.J.; Bragazzi, N.L. Acute effects of an “Energy drink” on short-term maximal performance, reaction times, psychological and physiological parameters: Insights from a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled, counterbalanced crossover trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saeterbakken, A.H.; Fimland, M.S. Muscle force output and electromyographic activity in squats with various unstable surfaces. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Hung, M.H.; Ho, C.S.; Lin, K.C. The acute effects of whole-body vibration on fencers’ special abilities. Percept. Mot. skills 2019, 126, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, S.S.; Lichtenstein, M.J.; Shiavi, R.G. Effect of loss of balance on biomechanics platform measures of sway: Influence of stance and a method for adjustment. J. Biomech. 1990, 23, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.E.; Miller, M.G.; Ricard, M.; Ritenour, D.; Chapman, B.L. Comparisons of static and dynamic balance following training in aquatic and land environments. J. Sport Rehabil. 2006, 15, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | Variable (Unit) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Overall performance | Shooting score (pts) | Shot score as measured in air rifle shooting: 0–10.9 |
| Stability of hold | DevX (mm) | Horizontal and vertical standard deviations of the aiming point at 10–50 ms |
| DevY (mm) | ||
| DevTotal (mm) | Total standard deviation of the aiming point at 10–50 ms | |
| Time on target | Total time (s) | Total aiming time |
| Parameter | Definition |
|---|---|
| COPxLength | Total COP displacement in the x-axis (perpendicular to line of shot) |
| COPyLength | Total COP distance in the y-axis (parallel to line of shot) |
| COP area | Area described by total COP length. |
| Pretest | 6 Week WBV+UST | Detraining | ES (Pretest–6-Week WBV+UST) | ES (Pretest—Detraining) | ES (6 Week WBV+UST—Detraining) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shooting score (pts) | 9.845 ± 0.151 | 10.051 ± 0.156 ** | 9.673 ± 0.505 | 1.34 | 0.46 | 1.01 |
| Total time (s) | 5.506 ± 0.050 | 5.390 ± 0.113 * | 5.445 ± 0.201 | 1.33 | 0.42 | 0.34 |
| 10 ms-DevTotal (mm) | 2.500 ± 0.348 | 2.058 ± 0.358 * | 2.706 ± 0.585 | 1.25 | 0.43 | 1.34 |
| 20 ms-DevTotal (mm) | 2.360 ± 0.400 | 2.015 ± 0.353 * | 2.636 ± 0.608 | 0.91 | 0.54 | 1.25 |
| 30 ms-DevTotal (mm) | 2.341 ± 0.408 | 1.912 ± 0.532 * | 2.537 ± 0.588 | 0.90 | 0.39 | 1.11 |
| 40 ms-DevTotal (mm) | 2.376 ± 0.422 | 1.893 ± 0.498 * | 2.511 ± 0.568 | 1.05 | 0.27 | 1.16 |
| 50 ms-DevTotal (mm) | 2.413 ± 0.400 | 2.050 ± 0.457 | 2.558 ± 0.612 | 0.85 | 0.28 | 0.94 |
| 10 ms-DevX (mm) | 0.626 ± 0.126 | 0.654 ± 0.177 | 0.693 ± 0.210 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.20 |
| 20 ms-DevX (mm) | 0.626 ± 0.125 | 0.655 ± 0.178 | 0.700 ± 0.213 | 0.19 | 0.42 | 0.23 |
| 30 ms-DevX (mm) | 0.631 ± 0.126 | 0.655 ± 0.178 | 0.701 ± 0.214 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.23 |
| 40 ms-DevX (mm) | 0.633 ± 0.127 | 0.656 ± 0.177 | 0.704 ± 0.212 | 0.15 | 0.41 | 0.25 |
| 50 ms-DevX (mm) | 0.659 ± 0.180 | 0.635 ± 0.129 | 0.706 ± 0.210 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.41 |
| 10 ms-DevY (mm) | 0.749 ± 0.114 | 0.549 ± 0.051 ** | 0.769 ± 0.272 | 2.26 | 0.10 | 1.12 |
| 20 ms-DevY (mm) | 0.754 ± 0.116 | 0.550 ± 0.052 ** | 0.770 ± 0.272 | 2.26 | 0.08 | 1.12 |
| 30 ms-DevY (mm) | 0.756 ± 0.116 | 0.550 ± 0.052 ** | 0.773 ± 0.273 | 2.29 | 0.08 | 1.13 |
| 40 ms-DevY (mm) | 0.756 ± 0.116 | 0.557 ± 0.051 ** | 0.775 ± 0.279 | 2.22 | 0.09 | 1.09 |
| 50 ms-DevY (mm) | 0.760 ± 0.114 | 0.556 ± 0.052 ** | 0.780 ± 0.272 | 2.30 | 0.10 | 1.14 |
| Pretest | 6 Week WBV+UST | Detraining | ES (Pretest—6-Week WBV+UST) | ES (Pretest—Detraining) | ES (6 Week WBV+UST—Detraining) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right leg | x-Length (mm) | 3.04 ± 0.57 | 2.85 ± 0.25 | 4.09 ± 1.10 | 0.43 | 1.20 | 1.55 |
| y-Length (mm) | 2.19 ± 0.38 | 2.11 ± 0.35 | 2.52 ± 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.87 | 1.12 | |
| area (mm2) | 5.29 ± 1.69 | 4.72 ± 0.88 | 6.59 ± 1.33 | 0.42 | 0.85 | 1.66 | |
| Left leg | x-Length (mm) | 3.04 ± 0.60 * | 2.85 ± 0.54 | 3.74 ± 0.86 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 1.24 |
| y-Length (mm) | 2.19 ± 0.38 | 2.10 ± 0.35 | 2.52 ± 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.83 | 1.10 | |
| area (mm2) | 5.29 ± 1.69 | 4.00 ± 0.67 | 5.41 ± 1.12 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 1.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, M.-H.; Lin, K.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Juang, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y. Effects of Complex Functional Strength Training on Balance and Shooting Performance of Rifle Shooters. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136143
Hung M-H, Lin K-C, Wu C-C, Juang J-H, Lin Y-Y, Chang C-Y. Effects of Complex Functional Strength Training on Balance and Shooting Performance of Rifle Shooters. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136143
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Min-Hao, Kuo-Chuan Lin, Chung-Cheng Wu, Jia-Hung Juang, Yen-Yu Lin, and Chi-Yao Chang. 2021. "Effects of Complex Functional Strength Training on Balance and Shooting Performance of Rifle Shooters" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136143
APA StyleHung, M.-H., Lin, K.-C., Wu, C.-C., Juang, J.-H., Lin, Y.-Y., & Chang, C.-Y. (2021). Effects of Complex Functional Strength Training on Balance and Shooting Performance of Rifle Shooters. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 6143. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136143






