Abstract
Despite its significant effectiveness in adversarial training approaches to multidomain task-oriented dialogue systems, adversarial inverse reinforcement learning of the dialogue policy frequently fails to balance the performance of the reward estimator and policy generator. During the optimization process, the reward estimator frequently overwhelms the policy generator, resulting in excessively uninformative gradients. We propose the variational reward estimator bottleneck (VRB), which is a novel and effective regularization strategy that aims to constrain unproductive information flows between inputs and the reward estimator. The VRB focuses on capturing discriminative features by exploiting information bottleneck on mutual information. Quantitative analysis on a multidomain task-oriented dialogue dataset demonstrates that the VRB significantly outperforms previous studies.
1. Introduction
While deep reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a viable solution for complicated and high-dimensional decision-making problems [1], including games such as Go [2], chess [3], checkers [4], and poker [5,6], robotic locomotion [7,8], autonomous driving [9,10], and recommender system [11,12], the determination of an effective reward function remains a challenge, especially in multidomain task-oriented dialogue systems. Many recent studies have struggled in sparse-reward environments and employed a handcrafted reward function as a breakthrough [13,14,15,16]. However, such approaches typically are not capable of guiding the dialogue policy through user goals. For instance, as shown in Figure 1, the user cannot attain the goal because the system (S1) that exploits the handcrafted rewards completes the dialogue session too early. Moreover, as the dialog progresses, the user goal will frequently vary.
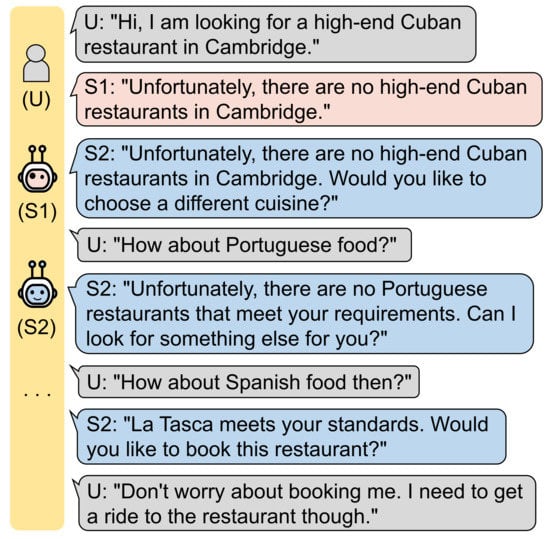
Figure 1.
The system (S2) that uses well-specified rewards can guide the user through the goal, while S1 cannot.
Due to these problems, systems that exploit the handcrafted rewards fail to assimilate user goals and guide users through user goals, achieving low performance, while humans self-judge from dialog context using well-defined reward function in their minds and generate appropriate responses despite multidomain circumstances.
MaxEnt-IRL [17] and Inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) [18,19] tackle the problem of recovering the reward function automatically and using this reward function to generate optimal behavior. Although generative adversarial imitation learning (GAIL) [20], which applies the GANs framework [21], has proven that the discriminator can be defined as a reward function, GAIL fails to generalize and recover the reward function. Adversarial inverse reinforcement learning (AIRL) [22] enables GAIL to take advantage of disentangled rewards. Guided dialogue policy learning (GDPL) [23] uses the AIRL framework to construct the reward estimator for multidomain task-oriented dialogues. However, these approaches often encounter difficulties in balancing the performance of the reward estimator and policy generator and produce excessively uninformative gradients.
In this paper, we propose the variational reward estimator bottleneck (VRB), a novel and effective regularization algorithm. The VRB uses information bottleneck [24,25,26] to constrain unproductive information flows between dialogue internal representations and state–action pairs of the reward estimator, thereby ensuring highly informative gradients and robustness. The experiments show that the VRB achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performances on a multidomain task-oriented dataset.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the brief background to set the stage for our model. Section 3 describes the proposed method in detail along with mathematical calculations. Section 4 outlines the experimental setup, whereas Section 5 presents the experiments and the results thereof. Section 6 provide discussions and the conclusions of this study.
2. Background
2.1. Dialogue State Tracker
The dialogue state tracker (DST) [27,28,29], which takes dialogue action a and dialogue history as input, updates the dialogue state x and belief state b for each slot. For example, as shown in Figure 2, DST observes the user goal where the user aims to go. At dialogue turn t, the dialogue action is represented as a slot and value pair (e.g., Attraction: (area, centre), (type, concert hall)). Given the dialogue action, DST encodes the dialogue state as .
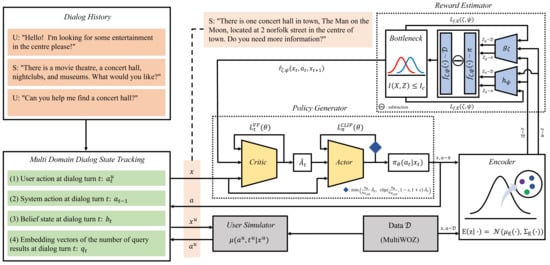
Figure 2.
Schematic depiction of the variational reward estimator.
2.2. User Simulator
Mimicking various and human-like actions is essential with respect to training task-oriented dialogue systems and evaluating these models automatically. The user simulator [30,31] in Figure 2 extracts the dialogue action corresponding to the dialogue state . stands for whether the user goal is achieved during a conversation. Note that the DST and the user simulator cannot meet the user in the absence of well-defined reward estimation.
2.3. Policy Generator
The policy generator [32,33] encourages the dialogue policy to determine the next action that maximizes the reward function :
where = , , , and is the TD residual [34]. and is the state-value function. Epsilon and are hyperparameters. The reward function can be simplified in the following manner:
where is the reward estimator, which is defined as follows [22]:
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Notations on MDP
To represent inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) as a Markov decision process (MDP), we consider a tuple = , where is state space, and is the action space. The transition probability defines the distribution of the next state given state , and at time-step t. is the reward function of the state–action pair, is the distribution of the initial state , and is the discount factor. The stochastic policy maps a state to a distribution over actions. Supposing we are given an optimal policy , the goal of IRL is to estimate the reward function from the trajectory . However, building an effective reward function is challenging, especially in a multidomain task-oriented dialogue system.
3.2. Reward Estimator
The reward estimator [23], which is an essential component of multidomain task-oriented dialogue systems, evaluates dialogue state–action pairs at dialogue turn t and estimates the reward that is used for guiding the dialogue policy through the user goal. Based on MaxEnt-IRL [17], each dialogue session in a set of human dialogue sessions can be modeled as a Boltzmann distribution that does not exhibit additional preferences for any dialogue sessions.
where , Z is a partition function, is a parameter of the reward function, and denotes a discounted cumulative reward. To imitate human behaviors, the reward estimator should learn the distributions of human dialogue sessions using the KL divergence loss:
where is the entropy of dialogue policy . The reward estimator maximizes the entropy, which indicates maximizing the likelihood of observed dialogue sessions. Therefore, the reward estimator is learned to discern between human dialogue sessions and dialogue sessions that are generated by the dialogue policy.
Note that and are not dependent on the parameters and . Thus, the reward estimator can be trained using gradient-based optimization as follows:
3.3. Variational Reward Estimator Bottleneck
The variational information bottleneck [24,25,26] is an theoretical information approach that restricts unproductive information flow between the discriminator and inputs. Inspired by this approach, we propose a regularized objective that constrains the mutual information between encoded original inputs and state–action pairs, thereby ensuring highly informative internal representations and a robust adversarial model. Our proposed method trains an encoder that is maximally informative regarding human dialogues.
To this end, we employ a stochastic encoder and an upper bound constraint on the mutual information between the dialogue states X and latent variables :
where , and D is modeled with nonlinear function. Note that is divided into the three terms , , and , based on GANs [21], GAN-GCL [35], and AIRL [22]. represents the encoded disentangled reward approximator with the parameter , and is the encoded shaping term with the parameter . Stochastic encoder can be defined as , which maps states to a latent distribution : . is standard Gaussian, and stands for an enforced upper bound on mutual information.
To optimize , VRB introduces a Lagrange multiplier as follows:
where the mutual information between dialogue states X and latent variable is
In Equation (3), the VRB minimizes the mutual information with dialogue states to focus on discriminative features. The VRB also minimizes the KL divergence with the human dialogues, while maximizing the KL divergence with the generated dialogues, thereby distinguishing effectively between samples from dialogue policy and human dialogues. Our proposed model is summarized in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Algorithm of Variational Reward Estimator Bottleneck |
 |
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Dataset Details
We evaluated our method on multidomain wizard of oz [36] (MultiWOZ), which contained approximately 10,000 large-scale, multidomain, and multiturn conversational dialogue corpora. MultiWOZ consisted of 7 distinct task-oriented domains, 24 slots, and 4510 slot values. The dialogue sessions were randomly divided into training, validation, and test set. The validation and test sets contained 1000 sessions, respectively.
4.2. Models Details
We used the agenda-based user simulator [30] and VHUS-based user simulator [31]. The policy network and value network V are MLPs with two hidden layers. and are MPLs with one hidden layer each. We used the ReLu activation function and Adam optimizer for the MLPs. We trained our model using a single NVIDIA GTX 1080ti GPU. Detailed hyperparameters are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detail description of VRB hyperparameters.
We compare the proposed method with the following previous studies: GP-MBCM [37], ACER [38], PPO [33], ALDM [39], and GDPL [23]. GP-MBCM [37] trains a number of policies on different datasets based on the Bayesian committee machine [40]. ACER [38] suggests the importance of weight truncation with bias correction for sampling efficiency. PPO [33] employs an effective algorithm that attains the data’s robust and efficient performance using only a first-order optimizer. ALDM [39] shows an adversarial learning method to learn dialogue rewards directly from dialogue samples. GDPL [23] is the current SOTA model that consists of a dialogue reward estimator based on IRL.
4.3. Evaluation Details
To evaluate the performances of these models, we introduce four metrics: (i) Turns: we record the average number of dialogue turns between the user simulator and dialogue agent. (ii) Match rate: we conduct match rate experiments to analyze whether the booked entities are matched with the corresponding constraints in the multidomain environment. For instance, in Figure 2, entertainment should be matched with concert hall in the center. The match rate ranges from 0 to 1 and scores 0 if an agent is unable to book the entity. (iii) Inform F1: we test the ability of the model to inform all of the requested slot values. For example, as shown in Figure 1, the price range, food type, and area should be informed if the user wishes to visit a high-end Cuban restaurant in Cambridge. (iv) Success rate: in the success rate experiment, a dialogue session scores 0 or 1. We obtain 1 if all required information is presented, and every entity is booked successfully.
5. Main Results
5.1. Experimental Results of Agenda-Based User Simulators
Table 2 presents the empirical results on both simulators and MultiWOZ. In the agenda-based setting, we observe that our proposed method achieves a new SOTA performance. Note that an outstanding model should obtain high scores in every metric, not just a single one, because to regard a dialogue as having ended successfully, every request should be informed precisely, thereby guiding a dialogue through the user goal. Although GDPL achieves the highest score in Inform F1, our proposed model acts more human-like with respect to Turns, which is close to the human evaluation score: 7.37, and provides more accurate slot values and matched entities than the other methods.

Table 2.
Results on agenda-based user simulators.
5.2. Experimental Results of VHUS-Based User Simulators
On the other hand, in the VHUS setting, though PPO behaves more human-like in Turns, PPO exhibits greater difficulty in providing accurate information, while our model does not because our approach constrains unproductive information flows. Results in Table 3 demonstrate that our proposed model outperforms existing models, providing more definitive information than the other methods. Similar to the agenda-based setting, the VHUS-based model also showed the best performance. It demonstrates that our methodology reflecting human-like characteristics is a very effective methodology.

Table 3.
Results on VHUS-based user simulators.
5.3. Verification of Robustness
As shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, to evaluate the robustness of the models, we conduct experiments over 30 times for each model and visualize the results using a violin plot. Experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms PPO in every metric, despite some negative outliers, and has a much lower standard deviation than PPO. An example of a dialogue session comparison between VRB and PPO is available in Table 4.
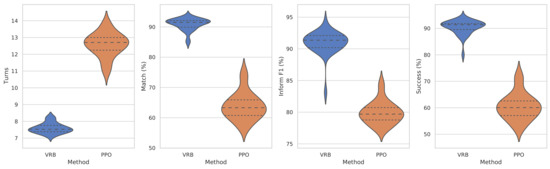
Figure 3.
Performance on the MultiWOZ and the agenda-based user simulator. Higher is better except Turns. Quartiles marked with dashed lines.
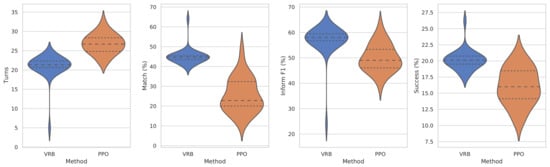
Figure 4.
Performance on the MultiWOZ and the VHUS-based user simulator. Higher is better except Turns. Quartiles marked with dashed lines.

Table 4.
A comparison between VRB and PPO with respect to the dialogue act.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we present a novel and effective regularization method known as the variational reward estimator bottleneck (VRB) for multidomain task-oriented dialogue systems. The VRB includes a stochastic encoder, which enables the reward estimator to be maximally informative, and provides information bottleneck regularization, which constrains unproductive information flows between the reward estimator and the inputs. The quantitative results show that VRB achieves new SOTA performances on two different user simulators and a multiturn and multidomain task-oriented dialogue dataset. Despite great improvements, training dialog policy via VHUS setting remains a hurdle to overcome. We leave this for future works.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P. and C.L.; data curation, J.P.; formal analysis, C.L.; funding acquisition/project administration/supervision, H.L.; investigation, J.P.; methodology/software, J.P.; visualization, J.P.; writing—review and editing, C.L., C.P. and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.P., C.L. and C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Korea, under the Information Technology Research Center (ITRC ) support program (IITP-2018-0-01405) supervised by the Institute for Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP), Institute for Information and communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP), grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2020-0-00368, A Neural-Symbolic Model for Knowledge Acquisition and Inference Techniques) and Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Korea, under the ICT Creative Consilience program (IITP-2021-2020-0-01819) supervised by the Institute for Information and communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. The data can be found here: MultiWOZ: https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.00278.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Hubert, T.; Simonyan, K.; Sifre, L.; Schmitt, S.; Guez, A.; Lockhart, E.; Hassabis, D.; Graepel, T.; et al. Mastering Atari, Go, Chess and Shogi by Planning with a Learned Model. CoRR 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; van den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M.; et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.; Hoane, A.; hsiung Hsu, F. Deep Blue. Artif. Intell. 2002, 134, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, J.; Culberson, J.; Treloar, N.; Knight, B.; Lu, P.; Szafron, D. A world championship caliber checkers program. Artif. Intell. 1992, 53, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Sandholm, T. Superhuman AI for heads-up no-limit poker: Libratus beats top professionals. Science 2018, 359, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravcík, M.; Schmid, M.; Burch, N.; Lisý, V.; Morrill, D.; Bard, N.; Davis, T.; Waugh, K.; Johanson, M.; Bowling, M.H. DeepStack: Expert-Level Artificial Intelligence in No-Limit Poker. CoRR 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.; Schaal, S. Reinforcement Learning of Motor Skills with Policy Gradients. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum Entropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic Actor. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; Dy, J., Krause, A., Eds.; Volume 80, pp. 1861–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, B.R.; Sobh, I.; Talpaert, V.; Mannion, P.; Sallab, A.A.A.; Yogamani, S.K.; Pérez, P. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving: A Survey. CoRR 2020, arXiv:2002.00444. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Huang, Z.; Lv, C. Uncertainty-Aware Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Application to Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.12194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Xia, L.; Tang, J.; Yin, D. Recommendations with Negative Feedback via Pairwise Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Sun, A.; Tay, Y. Deep Learning Based Recommender System. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Eskenazi, M. Towards End-to-End Learning for Dialog State Tracking and Management using Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue; Association for Computational Linguistics: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, B.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.N.; Ahmed, F.; Deng, L. Towards End-to-End Reinforcement Learning of Dialogue Agents for Information Access. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Vancouver, AB, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Yu, Z. Sentiment Adaptive End-to-End Dialog Systems. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, QC, Australia, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Hakkani-Tür, D.; Liu, B.; Tür, G. Bootstrapping a Neural Conversational Agent with Dialogue Self-Play, Crowdsourcing and On-Line Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 3 (Industry Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2018; pp. 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziebart, B.D.; Maas, A.L.; Bagnell, J.A.; Dey, A.K. Maximum Entropy Inverse Reinforcement Learning; AAAI: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008; Volume 8, pp. 1433–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S. Learning agents for uncertain environments. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory, Madison, WI, USA, 24–26 July 1998; pp. 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, A.; Russell, S. Algorithms for Inverse Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the ICML’00 Seventeenth International Conference on Machine Learning, Stanford, CA, USA, 29 June–2 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Ermon, S. Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29, International Barcelona Convention Center; Lee, D.D., Sugiyama, M., Luxburg, U.V., Guyon, I., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 4565–4573. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Luo, K.; Levine, S. Learning Robust Rewards with Adverserial Inverse Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2018, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Takanobu, R.; Zhu, H.; Huang, M. Guided Dialog Policy Learning: Reward Estimation for Multi-Domain Task-Oriented Dialog. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP); Association for Computational Linguistics: Hong Kong, China, 2019; pp. 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tishby, N.; Pereira, F.C.; Bialek, W. The information bottleneck method. In Proceedings of the 37-th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control and Computing, Monticello, IL, USA, 22–24 September 1999; pp. 368–377. [Google Scholar]
- Alemi, A.A.; Fischer, I.; Dillon, J.V.; Murphy, K. Deep Variational Information Bottleneck. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.00410. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.B.; Kanazawa, A.; Toyer, S.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Variational Discriminator Bottleneck: Improving Imitation Learning, Inverse RL, and GANs by Constraining Information Flow. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Raux, A.; Henderson, M. The Dialog State Tracking Challenge Series: A Review. Dialogue Discourse 2016, 7, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, F.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X. Memory-Augmented Dialogue Management for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Madotto, A.; Hosseini-Asl, E.; Xiong, C.; Socher, R.; Fung, P. Transferable Multi-Domain State Generator for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzmann, J.; Thomson, B.; Weilhammer, K.; Ye, H.; Young, S. Agenda-Based User Simulation for Bootstrapping a POMDP Dialogue System. In Human Language Technologies 2007: The Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Companion Volume, Short Papers; Association for Computational Linguistics: Rochester, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gür, I.; Hakkani-Tür, D.; Tür, G.; Shah, P. User modeling for task oriented dialogues. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Athens, Greece, 18–21 December 2018; pp. 900–906. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P.; Jordan, M.; Moritz, P. Trust Region Policy Optimization. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning; Bach, F., Blei, D., Eds.; PMLR: Lille, France, 2015; Volume 37, pp. 1889–1897. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Moritz, P.; Levine, S.; Jordan, M.; Abbeel, P. High-dimensional continuous control using generalized advantage estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, C.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P. Guided Cost Learning: Deep Inverse Optimal Control via Policy Optimization. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning—Volume 48. JMLR.org, ICML’16, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Budzianowski, P.; Wen, T.H.; Tseng, B.H.; Casanueva, I.; Ultes, S.; Ramadan, O.; Gašić, M. MultiWOZ—A Large-Scale Multi-Domain Wizard-of-Oz Dataset for Task-Oriented Dialogue Modelling. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 5016–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašić, M.; Mrkšić, N.; Su, P.; Vandyke, D.; Wen, T.; Young, S. Policy committee for adaptation in multi-domain spoken dialogue systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 13–17 December 2015; pp. 806–812. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bapst, V.; Heess, N.; Mnih, V.; Munos, R.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; de Freitas, N. Sample Efficient Actor-Critic with Experience Replay. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2017, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lane, I. Adversarial Learning of Task-Oriented Neural Dialog Models. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual SIGdial Meeting on Discourse and Dialogue; Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresp, V. A Bayesian Committee Machine. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2719–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).