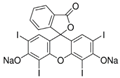
Abstract
Various synthetic dyes are artificially added to herbal medicines for the purpose of visual attraction. In order to monitor the illegal usage of synthetic dyes in herbal medication, a rapid and straightforward analysis method to determine synthetic dyes is required. The study aimed to develop and validate a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis to determine ten synthetic dyes in Hawthorn fruit, Cornus fruit, and Schisandra fruit. Ten synthetic dyes such as Tartrazine, Sunset yellow, Metanil yellow, Auramine O, Amaranth, Orange II, Acid red 73, Amaranth, New Coccine, Azorubine, and Erythrosine B, were extracted using 50 mM ammonium acetate in 70% MeOH; then separated by gradient elution with a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and 50 mM ammonium acetate in distilled water using a photodiode array detector (PDA) at 428 nm or 500 nm. In addition, this study established the LC-MS/MS method to confirm the existence of synthetic dyes in the positive sample solution. The HPLC analysis had good linearity (r2 > 0.999). The recoveries of this method ranged from 74.6~132.1%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) values were less than 6.9%. Most of the samples fulfilled the acceptance criteria of the AOAC guideline. This study demonstrates that the HPLC analysis can be applied to determine ten synthetic dyes in herbal medication.
Keywords:
herbal medicine; HPLC; LC-MS/MS; synthetic dye; Hawthorn fruit; Cornus fruit; Schisandra fruit 1. Introduction
Synthetic dyes are often used in various products, including food, dietary supplements, cosmetics, and drugs because they not only improve the products’ physical appearance and visual attractiveness but are also relatively facile and cheap to produce [1]. Since synthetic dyes are frequently used in food and drug formulations, concerns regarding the safety of synthetic dyes have increased for decades. Although the evaluation for their toxicological potential has been continuously updated based on new findings [2], the following agenda is still an ongoing debate. Fortunately, several research works have demonstrated the risk of synthetic dyes provoking behavior disorders in children, including Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), allergies, and hyperactivity [3].
According to the Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) portal, risk information related to the adulteration of synthetic colorants in herbal medicines has reported that turmeric powders are adulterated by Orange II (2019. 9, Belgium) or Sudan I and Sudan II (2017.5, Finland). In another case, Orange II was artificially added to Safflowers (2019, 4, Germany and the United Kingdom). According to a survey of adulterated traditional Chinese medicines in China between 2003 and 2017, the adulteration of synthetic dyes in herbal medicines showed a trend toward gradual increase [4]. Guo et al. [5] claimed that synthetic dyes, such as Azorubine, Auramine O, and Acid Orange 7, were found in Schisandra chinensis (Schisandra fruit), Carthamus tinctorius (Safflower), and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Salvia Miltiorrhiza root). The following risk information in foreign countries led us to establish a rapid and straightforward method urgently and essentially. By developing this method, we aimed to examine whether synthetic colorants adulterate herbal medicines because most herbal medicines consumed in Korea are mainly imported from other countries, including China. The Chinese government designated a list of synthetic dyes in herbal medicines that must be assessed to inhibit illegal usage. They also provided HPLC analyses to determine the existence of synthetic dyes in herbal drugs [6]. Since the addition of any synthetic dyes in herbal medicines is not allowed in Korea, there is an urgency to establish an appropriate analysis method to determine synthetic dyes in herbal medicines and distinguish whether these illegal synthetic dyes are adulterated or not in herbal medicines. Most of the herbal medicines used in Korea are imported from various countries, including China.
Various analysis methods have been developed and studied for a long time to identify illegal dyes in food products, including techniques based on spectrophotometry [7], thin layer chromatography (TLC) [8], capillary liquid chromatography [9], enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) [10], electrochemical sensing devices [11], HPLC [1,12], and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) [13]. Unlike reports related to analysis techniques for detecting illegal dyes in foods, some analytical methods have been reported to contain high-performance thin layer chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPTLC-MS) [14], high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [15,16,17], and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) [5,18,19]. Additionally, several challengeable methods have been declared, including a computer vision system to determine synthetic colorants in dyed Safflower [20], Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for detection of Sudan dyes in herbal medicine [21], and Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) method to quantify chemical dyes in safflowers [22]. In general, the HPLC technique is considered to be a more economical and easily accessible procedure than LC-MS/MS. Most of the herbal medicine markets in our country are comparatively small, and usually, the herbal medicine companies prefer to use economic analysis procedures with low analysis expense when certain examinations of hazardous materials in their products are required. Therefore, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) in Korea publicly recommended more economic HPLC analysis to identify illegal synthetic dyes in herbal medicines instead of LC-MS/MS. The objective of this study was to develop a simple and economic HPLC analysis to identify illegal synthetic colorants in herbal medicines by improving the HPLC analysis provided by the Chinese government.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Herbal Medicines and Synthetic Dyes
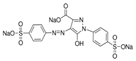
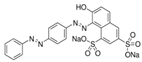
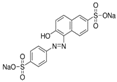
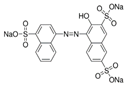
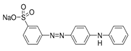
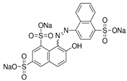
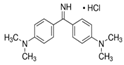
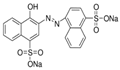
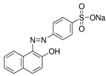
The Chinese government suggests a list of synthetic pigments and herbal medicines to investigate color adulteration [6]. This study chose three herbal medicines with the color red for developing the HPLC method because of their potential to be adulterated with synthetic dyes due to their color. Even though Cornus fruit and Hawthorn fruit are not listed as target herbal medicines by the Chinese government, a large amount of Cornus fruit and Hawthorn fruit consumed as dietary supplements in our country have been mainly imported from China. This study included them as target herbal medicines for developing an HPLC analysis. The Chinese government has monitored several herbal medicines to discern the adulteration of synthetic pigments such as Tartrazine, Sunset yellow, Azorubin, Metanil yellow, Acid red 73, New Coccine, Erythrosine, Auramine O, and Orange II using HPLC-UV analysis. The target synthetic colorants depend on which herbal medicines are examined. The HPLC-UV analysis can quantify six synthetic colorants at once. However, this study selected ten synthetic colorants (Table 1) for establishing an HPLC-PDA analysis to determine illegal synthetic colorants in three herbal medicines by adding Amaranth, which is known as a hazardous material.

Table 1.
Chemical structures, molecule weights, and formulas of ten synthetic pigment compounds.
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
The present study used three herbal medicinal products, including Hawthorn fruit (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge), Cornus fruit (Cornus officinalis Siebold et Zuccarini), and Schisandra fruit (Schisandra chinensis Baillon), which are variants of the color red, to develop a method to determine synthetic colorants. The standardized herbal medicines were purchased from a herbal medicinal store located in Daejeon, Korea, where the majority of samples were imported from China. Before conducting the experiments, the identities of the herbal medicines were confirmed through sensory tests performed by a specialist. Voucher specimens were deposited at the National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation in Osong, Chungbuk, Korea.
The ten synthetic colorants, including Tartrazine (≥99.0%, 1934-21-0), Sunset yellow (≥95.0%, 2783-94-0), Metanil yellow (≥98.0%, 587-98-4), Auramine O (≥85.0%, 2465-27-2), Orange II (≥98.0%, 633-96-5), Acid red 73 (≥97.0%, 5413-75-2), Amaranth (≥98.0%, 915-67-3), New Coccine (≥99.0%, 2611-82-7), Azorubine (≥98.0%, 3567-69-9), and Erythrosine B (≥98.0%, 16423-68-0) were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich, Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA) (Table 1). HPLC-graded acetonitrile, methanol, and ammonium acetate were purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). Distilled water was prepared using a CascadaTM AN water purification system (Pall Corporation, New York, NY, USA) with specific resistivity of 18.0 ΜΩ.
2.3. Preparation of the Standard Solution
Synthetic colorants, such as Tartrazine, Amaranth Sunset yellow, Azorubin, Acid red 73, and Orange II were individually dissolved in 70% methanol at a concentration of ~2500 µg/mL. Meanwhile, the other colorants, such as Orange II, Metanil yellow, and Erythrosine B, were individually dissolved in 100% methanol at a concentration of ~2500 µg/mL. For manufacturing the stock solutions of each synthetic dye, the solvents were decided based on the solubility of synthetic dyes. The mixed color standard solution was prepared at a concentration of 250 µg/mL by mixing each synthetic dye solution and diluting it with 70% methanol. The mixed standard solution was filtered through a 0.45 μm syringe filter (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) before being injected into the HPLC system. The calibration standard was designed in the concentration of 1, 5, 10, 20, 40 µg/mL.
2.4. Sample Preparations
After each herbal medicinal product was homogeneously ground using a stainless grinder (KSP-35, Koreamedi, Korea), 2 g of sample was mixed with 100 mM ammonium acetate in 70% methanol (MeOH) solution (20 mL) in a centrifuge tube. After vortexing, the sample solution was sonicated in a bath (Sonicator, 8510, Branson) for 30 min to extract the dyes from the samples and subjected to centrifugation at 3220× g for 10 min. After repeating the extraction under the same conditions, the first and second supernatants were combined. They were filtered through a 0.45 μm PTFE syringe filter (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) before being injected into the HPLC system.
2.5. HPLC-PDA Analysis Conditions
The employed HPLC instrument consisted of a Waters e2695 separation module and PDA detector (Waters 2998) running Empower3 (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). A YMC-Pack ODS-A column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm, Tokyo, Japan) was used for the HPLC analysis. The HPLC system was coupled with a PDA detector. The detection wavelengths for Tartrazine, Auramine O, and Metanil yellow were set to 428 nm, whereas those for Orange II, Amaranth, New Coccine, Sunset yellow, Azorubine, Erythrosine B, and Acid red 73 were set to 500 nm. The mobile phase comprised acetonitrile (solvent A) and 50 mM ammonium acetate in distilled water (solvent B). A linear gradient was employed as follows: 0 min, 5% solvent A; 15 min, 45% solvent A; 40~45 min, 45% solvent A; 46 min, 5% solvent A. The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min, and the injection volume was 10 µL.
2.6. Method Validation
The proposed test method was validated based on the Association of Official Analytical Chemists [23]. Specificity is the ability of the analytical method to distinguish between the analyte(s) and other components in the sample matrix. For assuring the specificity of a analysis method, it should be confirmed that the peaks of analytes are completely separated from other peaks originated from the sample matrix. Specificity evaluation was performed by separately injecting 10 µL solution of standard, blank sample, and spiked samples into the chromatographic system. The linearity of the proposed method was established in five calibration concentrations of 1, 5, 10, 20, and 40 µg/mL for each colorant in the mixed standard solutions, and the measurements were conducted in triplicate.
The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were measured after the injection of the standard solution with a concentration range between 1~40 µg/mL and calculated based on 3.3 or 10 × standard deviations of the response and the slope of the calibration curve, respectively (n = 3). The method’s precision and accuracy were tested by using samples spiked with the mixed standard solution. The mixed standard solution was spiked into the blank samples to become 5, 10, and 25 µg/mL of the final test solution. The spiked samples were treated with the proposed extraction, and then HPLC-PDA analysis was performed. The intra-day precision (repeatability) and accuracy (recovery rates) were assessed following the analysis of samples spiked at three levels in triplicate on the same day (n = 3). The inter-day precision and accuracy were measured following the triplicate analysis of samples at three concentration levels over three consecutive days.
2.7. LC-MS/MS Analysis
A LC-MS/MS analysis was conducted for qualitative analysis. The LC-MS/MS system was coupled to a Shimadzu NexeraX2 system equipped with a DGU-20A degasser, CTO-20AC column oven, LC-30AD pump, SIL-20AC autosampler, and LCMS-8060 triple quadrupole LC-MS/MS spectrometer (Shimadzu Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The ESI ionization was executed in either negative or positive mode. Data acquisition and processing were accomplished using LC-MS lab solutions software version 5.82 (Shimadzu). The Ultra-Fast Liquid Chromatography (UFLC) analysis used a UK-C18 column (C18, 100 mm × 2.0 mm i.d., 3 μm) and mobile phases composed of 5 mM ammonium acetate in acetonitrile containing 0.1% acetic acid (solvent A) and 5 mM ammonium acetate in water containing 0.1% acetic acid (solvent B). A linear gradient was employed as follows: 0–1 min, 0% solvent A; 1–3 min, 0~30% solvent A; 3–7 min, 30~80% solvent A; 7–9 min, 80% solvent A; 9.1 min, 0% solvent A. Chromatographic separation of the synthetic dyes was achieved at a constant flow of 0.3 mL/min and the use of injection at a volume of 5 µL. The final standard solution was prepared by diluting mixed color standard solution (250 µg/mL) described above with 70% MeOH, including 100 mM ammonium acetate. After the positive HPLC samples were properly diluted and filtered using a 0.2 μm PTFE membrane, the LC-MS/MS analysis was conducted to identify the analytes.
2.8. Cross-Validation
Cross-validation was also conducted by the same procedure described above with three samples to discern the reliability of the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis at the Chungbuk National University laboratory in Korea. The cross-validation evaluated selectivity, linearity, LOD, LOQ, recovery, and precision of the HPLC-PDA analysis.
2.9. Application of the Proposed Method to Real Samples
This study attempted to determine ten illegal synthetic dyes in three herbal medicinal samples: Hawthorn fruit, Cornus fruit, and Schisandra fruit. For monitoring study before the experiment, fifteen samples of each herbal medicine were selected by specialist evaluation through a sensory test. The quantitative analysis was conducted using the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis and was determined with triplicate samples (n = 3).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Extraction
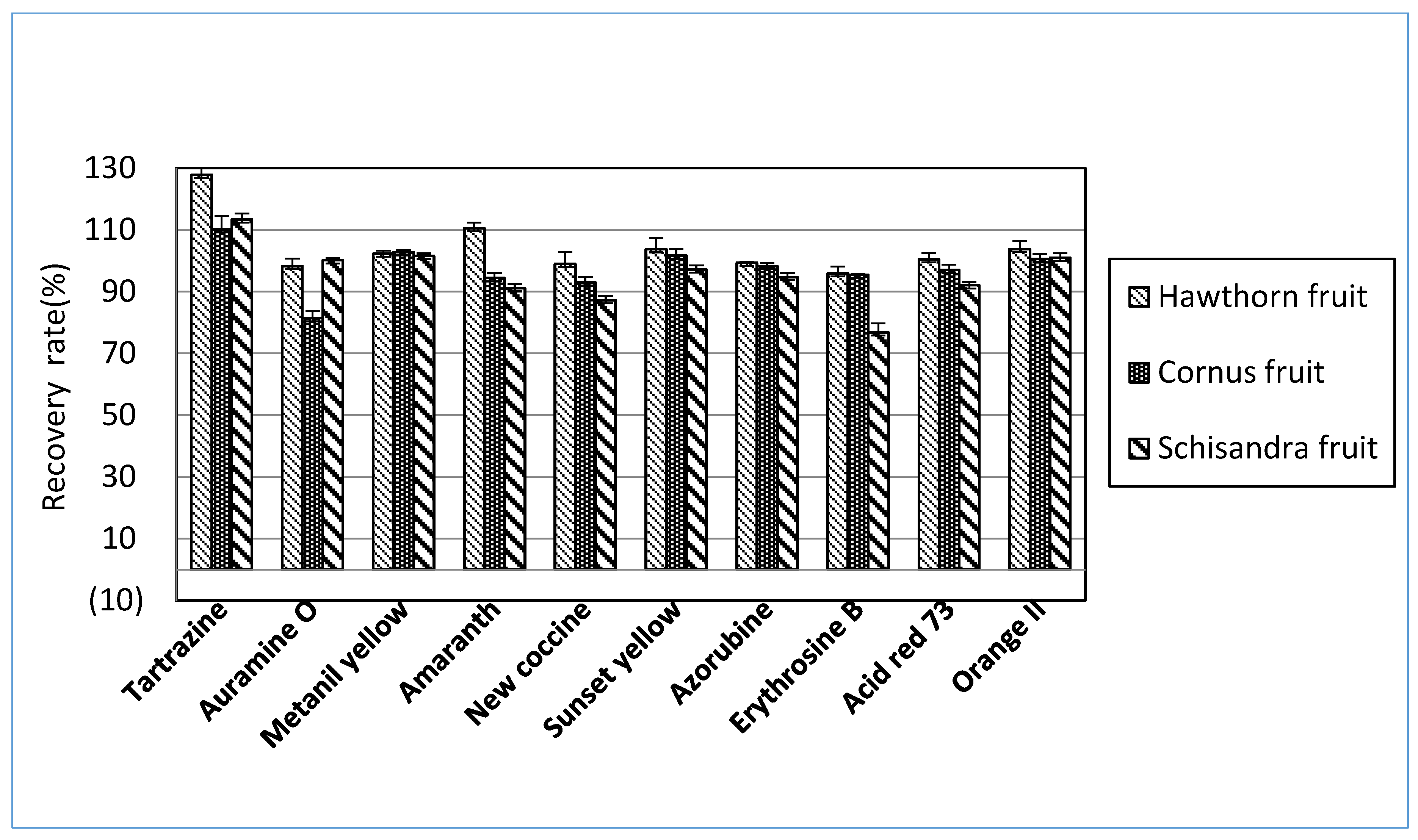
Extraction was needed before the detection stage to remove all impurities that may interrupt the results. The most common extraction methods were liquid-liquid extraction, solid-phase extraction, membrane filtration, and cloud point extraction [24]. The extraction procedures significantly influenced the recovery of most dyes, and the selection of suitable extraction methods depended on the target samples [25]. For a rapid and straightforward HPLC-PDA analysis to determine ten synthetic dyes in herbal medicines, this study referred to the Chinese government’s HPLC-UV methods [15] to distinguish synthetic colorants in herbal medicines. The HPLC-UV analysis uses 70% ETOH as an extraction solvent. This study investigated the recoveries of ten synthetic dyes in herbal medicines among several candidate solvents to search for an optimal extract solvent. As shown in Figure 1, the recoveries of several synthetic dyes were far below the acceptance criteria when 70% ETOH or 70% MeOH was used for the extraction solutions. The solvent combination consisted of 50 mM ammonium in 70% MeOH and 100 mM HCl in 70% MeOH, resulting in higher recoveries than 70% ETOH. Among candidate solvents, however, 100 mM ammonium acetate in 70% MeOH was considered an optimal solvent to extract the synthetic dyes from herbal medicines (Figure 1). When the selected extraction solvent was applied for three herbal medicines, most of the analytes indicated satisfactory recoveries greater than 80% (Figure 2). When considering these results, ten synthetic dye adulterants in herbal medicines can be successfully released through double extraction using 100 mM ammonium acetate in 70% MeOH without an additive purification process. Guo et al. [6] demonstrated that 50% MeOH as an extraction solvent in developing the LC-MS/MS method can determine synthetic dyes in herbal medicines, and the recoveries obtained from the test method were in the range between 83.4~92.7%. Brazeau [26] argued that the mixed solution comprising MeOH and 100mM ammonium acetate can result in an excellent extraction of synthetic colors in foods.
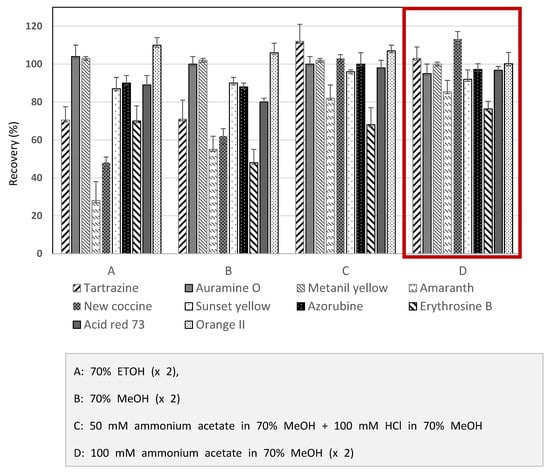
Figure 1.
Recoveries of ten synthetic colorants obtained from extraction using various solvents from Hawthorn fruit spiked with the color mixture solution.
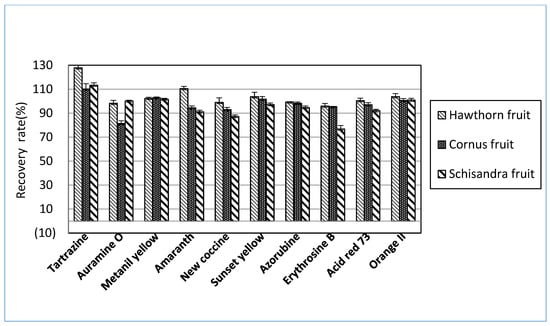
Figure 2.
Mean recoveries of each synthetic dye obtained from each herbal medicine spiked in low, medium, or high concentrations of the mixed ten standard solutions using the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis.
3.2. Selectivity of the Proposed Method
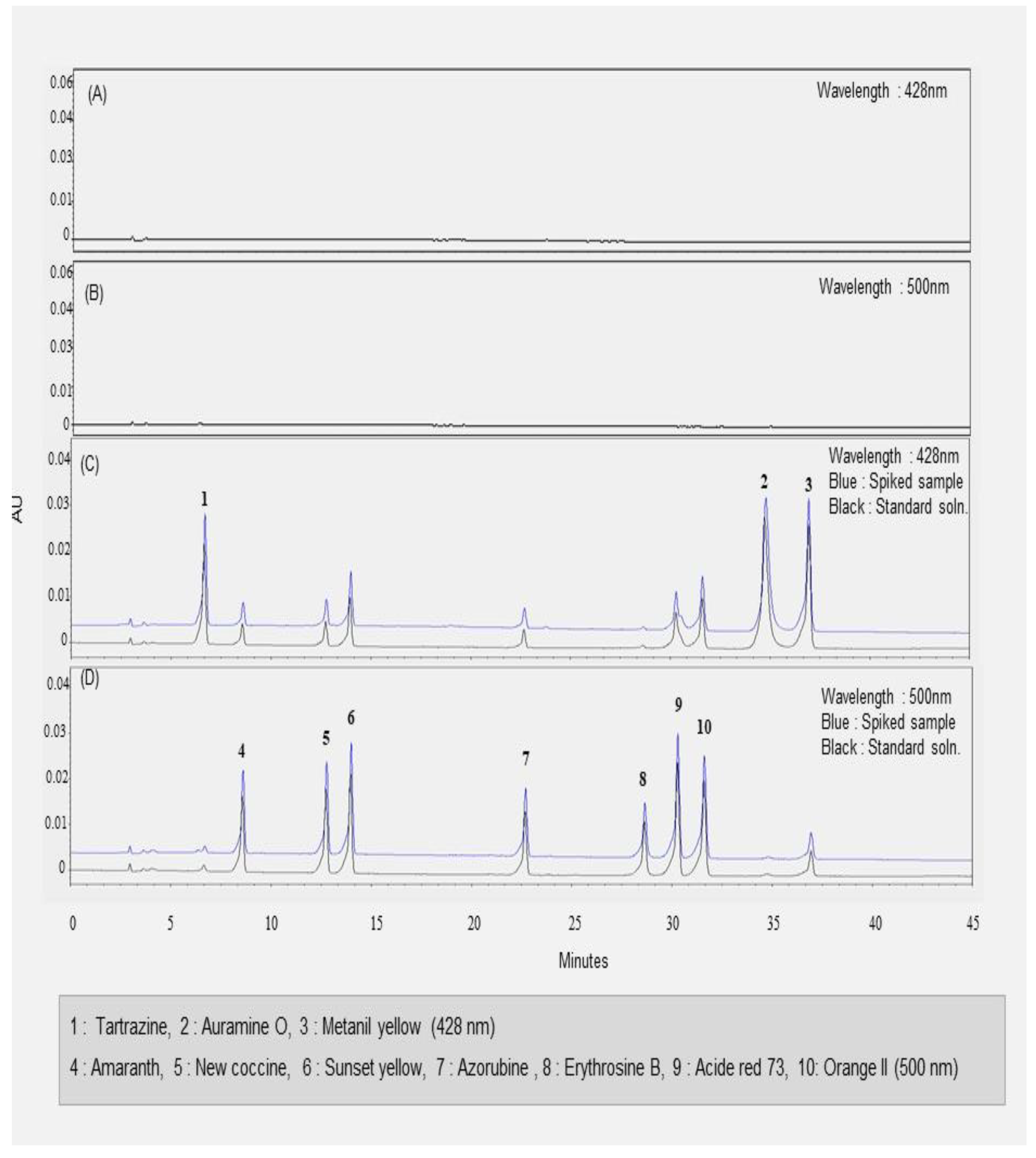
The HPLC-UV analysis provided by the Chinese government used two measurement wavelengths: 428 nm for Tartrazine, Auramine O, and Metanil yellow; 500 nm for Sunset yellow, Orange II, Amaranth, Erythrosine, Acid red 73, and Azorubine [6]. The developed HPLC method also employed identical wavelengths as the Chinese method for quantitative analysis of illegal synthetic dyes. Specificity was evaluated by comparing the chromatograms of the blank solution, standard solution, and sample solution under selected chromatographic conditions. The chromatogram results are shown in Figure 3A–D. The ten synthetic colorants were well-separated within the range of retention times between 6.5 and 37.5 min. Three synthetic dyes, such as Tartrazine, Auramine O, and Metanil yellow, were separated and detected at 428 nm, and their retention time was 6.5, 34.6, and, 37.5 min, respectively. In contrast, seven synthetic colorants were analyzed at 500 nm and were well-separated within 32 min. Hawthorn fruit, Cornus fruit, and Schisandra fruit did not express any peaks in the blank samples at either 428 or 500 nm. There were no coeluting peaks to interfere with peaks of analytes at the retention time of ten synthetic dyes in three herbal medicines. In other words, their matrices did not influence ten analytes in HPLC quantitative analysis. This result indicated that the analyte peaks were pure and successfully separated under these HPLC analysis conditions. That is, the specificity of the proposed HPLC method was achieved.
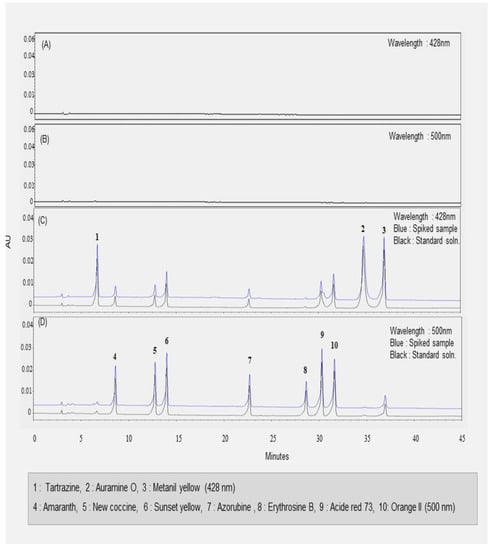
Figure 3.
The HPLC chromatograms of synthetic dyes in Hawthorn fruit. (A) The blank sample solution at 428 nm; (B) the blank sample solution at 500 nm; (C) the mixed standard solution and spiked sample at 428 nm; (D) the mixed standard solution and spiked sample at 500 nm.
3.3. Linearity and Sensitivity
In terms of linearity, the calibration functions were calculated by linear regression. Determination coefficients indicated outstanding linearity (0.999) in the ten synthetic colorants, showing a good relationship between peak areas and concentrations in the studied range (Table 2). The LOD and LOQ were acquired by calculating based on 3.3 or 10 × standard deviations of the response and slope of the calibration curve in the linear portion at 1–40 µg/mL. As shown in Table 2, the LOD and LOQ values were in the ranges of 0.8~8.4 µg/g and 2.2~25.4 µg/g, respectively.

Table 2.
The values of LOD, LOQ, and linearity obtained from the HPLC-PDA analysis method.
LOD/LOQ values of each synthetic dye indicated little difference among the three herbal medicines. The Schisandra fruits showed comparatively higher LOQ values, whereas most of the analytes in Hawthorn fruit and Cornus fruit revealed LOQ values of less than 10 µg/g, except for two samples. Such difference was presumably ascribed to physicochemical characteristics of the herbal medicines. For sensitivity of the synthetic dyes, Tartrazine, Amaranth, and Erythrosine B indicated higher LOQ values (approximately 20~25 µg/g) than other dyes in Schisandra fruits, whereas Tartrazine and Amaranth fruit showed comparatively high LOQ values of 17 µg/g and 15 µg/g, respectively in Hawthorn.
It is important to be aware of about herbal medicines adulterated with illegal synthetic dyes because their usage is not allowed in herbal medicines for most countries. By considering these results, this study suggests that the proposed HPLC method can determine if some herbal medicines are adulterated with synthetic dyes.
3.4. Accuracy and Precision
The accuracy of the HPLC-PDA method was evaluated as recoveries of the analytes after spiking the mixed color standard solution covering three different concentrations of herbal medicine blank samples. Furthermore, precision was demonstrated based on the intra- and inter-day relative standard deviations values. The recoveries of ten synthetic colorants obtained from each herbal medicine are summarized in Table 3. The intra-day recoveries of ten synthetic colorants ranged from 94.3~132.1% for Hawthorn fruits, 78.3~111.2% for Cornus fruits and 74.6~115.0% for Schisandra fruits (Table 3). On the other hand, inter-day recoveries were found in the range of 86.0~105.2% for Safflower, 94.0~116.0% for Hawthorn fruits, 78.4~112.2% for Cornus fruits, and 74.9~115.0% for Schisandra fruits (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials). The acceptable limits of AOAC were 80~115% for 10 µg/g of the analysis concentration in dietary supplements and botanicals [23]. When recoveries obtained from samples spiked with low, medium, and high concentrations were calculated as average values, most samples had satisfactory recoveries by indicating the acceptable range of AOAC guidelines, even if a few samples showed either a slightly lower or higher recoveries than the acceptable criteria.

Table 3.
Intra-day recoveries and precisions obtained from the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis method in three herbal medicines.
The values of intra-day relative standard deviation (RSD, repeatability) and inter-day RSD (reproducibility, RSDr) are represented in Table 3 and Table S1, respectively. The ranges of RSD and RSDr indicated 0.2~6.9% for Hawthorn fruit, 0.1~3.4% for Cornus fruit, and 0.2~2.5% for Schisandra fruit. The AOAC guideline requires an acceptable repeatability value of 6% and reproducibility of 11% at 10 µg/g of the analysis concentration in validated dietary supplements and botanicals. The proposed analysis method was found to accomplish satisfactory precision. Therefore, the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis appears to be a useful procedure that can quantify ten synthetic dyes regardless of the type of herbal medicine.
3.5. Confirmation by LC-MS/MS Analysis
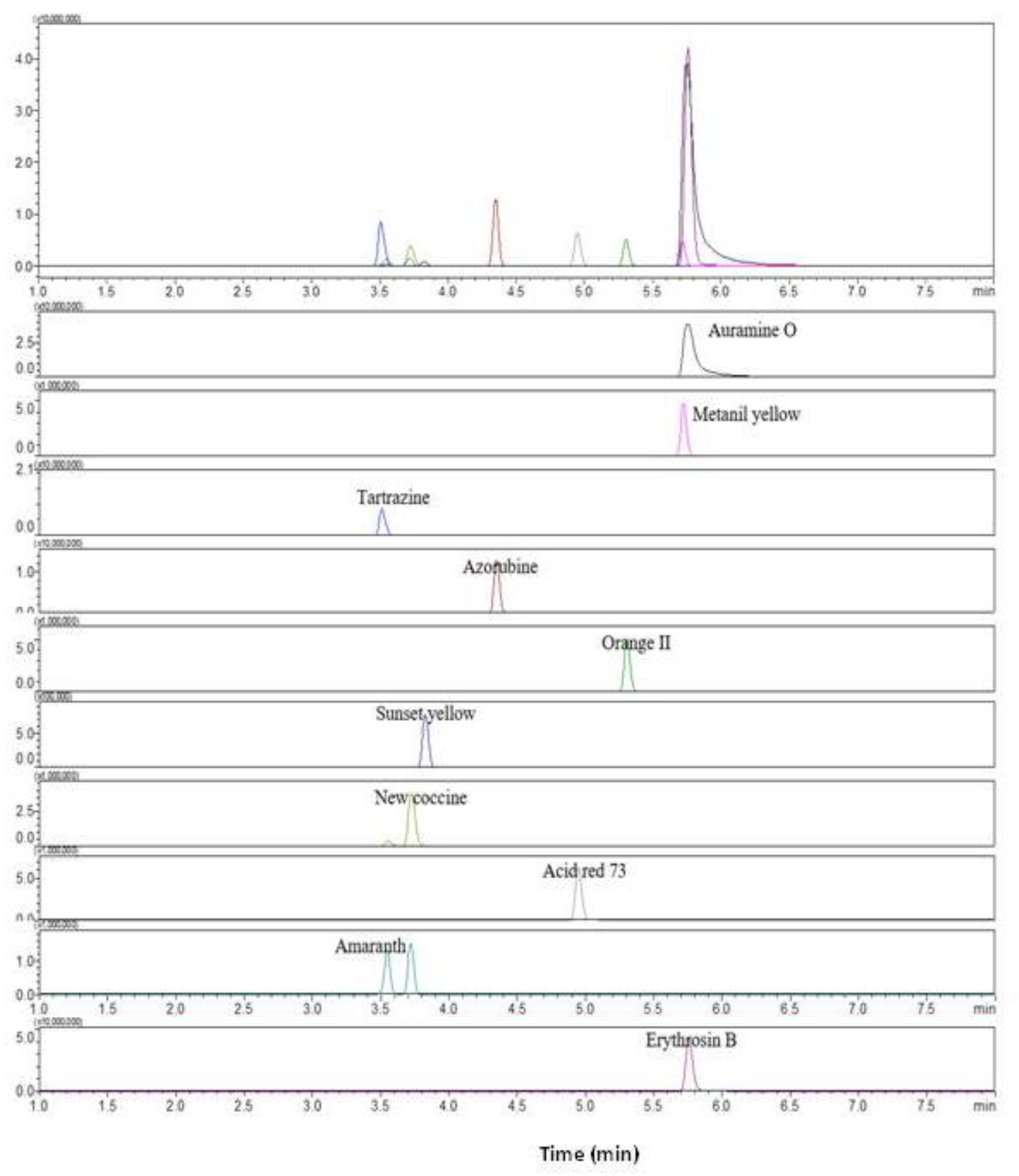
The LC-MS/MS analysis was conducted to identify analytes from positive samples of synthetic dyes with suspected adulteration after HPLC analysis. This study established the precursor and production of each synthetic pigment by referring to the LC-MS/MS analysis of detecting synthetic dyes in foodstuffs or herbal medicines (Table 4). Most dyes were ionized under negative ESI modes, while only Auramine O was analyzed under positive ESI modes. These findings confirmed that ten synthetic pigments in the mixed standard solution can be identified through the LC-MS/MS analysis using the MRM conditions shown in Figure 4. The sample solution obtained after pretreating samples spiked with the mixed color solution was assumed to be a positive sample solution in the present study. In order to evaluate the reliability of the developed LC-MS/MS analysis, the positive sample solution was analyzed using the MRM conditions suggested in Table 4. The results revealed that ten synthetic dyes in the sample solution were successfully identified through LC-MS/MS analysis by indicating target ions and reference ions identical to those of the mixed standard solution in each synthetic dye.

Table 4.
MRM conditions of the LC-MS/MS to identify ten synthetic dyes in herbal medicines.
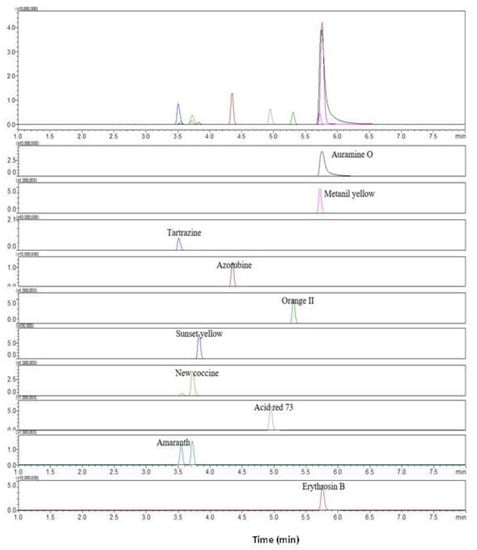
Figure 4.
Total ion chromatography of LC-MS/MS for ten synthetic dyes extracted by the MRM conditions in the mixed standard synthetic dye solution: Tartrazine, m/z 467.1 > 198.0; Auramine O, m/z 268.0 > 147.1; Metanil yellow, m/z 352.2 > 1560; Amaranth, m/z 537 > 3120; New Coccine, m/z 398 > 120; Sunset yellow, m/z 398 > 120; Erythrosine, m/z 398 > 120; Azorubin, m/z 398 > 120; Acid red 73, m/z 398 > 120, and Orange II. m/z 398 > 120.
Guo et al. [5] developed a hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS) method to detect 21 synthetic dyes in herbal medicines. They emphasized that, when they investigated 54 herbal medicine batch samples, herbal medicine samples such as Schisandra fruit (Schisandra chinensis), Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius), Rhubarb (Rheum officinale Baillon), and Salvia Miltiorrhiza root (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) contained Azorubine, Auramine O, and Acid orange 7. In general, LC-MS/MS techniques are considered more sensitive and selective analysis procedures than HPLC analysis. Considering the economic situation of the herbal medicine industry in Korea, this study focused on developing an HPLC analysis as a more economical and accessible analysis procedure for quantifying ten synthetic dyes in herbal medicines.
3.6. Cross-Validation
In the cross-validation results, any interfering peaks were not presented in the chromatograms obtained from Cornus fruit, Hawthorn fruit, and Schisandra fruit. The linearity was >0.999 in all cases, and the LOQs were in the range between 1.4~3.6 µg/g in ten synthetic dyes. The recoveries and RSDs were found to be in the ranges of 80.6~114.8% and 0.4~7.8%, respectively (Tables S2 and S3 in Supplementary Materials). The recoveries and intermediate precision obtained from cross-validation satisfied the AOAC acceptance criteria. Based on these results, the proposed HPLC method is reliable for discerning color adulteration in herbal medicines.
3.7. Application of the Proposed Method to Real Samples
The proposed HPLC-PDA analysis method was applied to determine ten illegal synthetic dyes in forty-five herbal medicine samples purchased from Korean herbal medicine markets. Fifteen herbal medicine samples per matrix were used for the monitoring study. Five Hawthorn fruit samples were imported from China and manufactured in Korea, whereas the other ten Hawthorn samples were produced and manufactured domestically. All Cornus fruit samples were produced and manufactured in Korea. Thirteen Schisandra fruit samples were produced and manufactured domestically, whereas two other samples were produced from China and manufactured in Korea. Among the forty-five samples used in the monitoring study, only seven samples were herbal medicine products imported from China. As a result, most samples did not indicate any analytes, and a few analytes had contents of less than LOQ values suggested in this study. Although the herbal medicines used in this study did not appear to be adulterated by illegal synthetic dyes, steady and regular monitoring activity to control the adulteration of synthetic dyes, especially in imported herbal medicines, is required for public health using HPLC-PDA analysis.
4. Conclusions
The main purpose of this study was to develop a straightforward HPLC analysis that can determine synthetic dye adulterants in herbal medicines. The proposed HPLC analysis used 100 mM ammonium acetate in 70% MeOH to extract ten synthetic dyes from herbal medicines. In the HPLC analysis coupled with a PDA detector, two detection wavelengths of 428 nm or 500 nm were employed. An ODS-A C18 column and mobile phase solution comprising acetonitrile and 50 mM ammonium acetate in distilled water were used to separate ten synthetic dyes from the herbal medicine sample solution. This study also established the LC-MS/MS analysis method to endorse positive samples suspected by the HPLC results. When comparing the HPLC analysis with 70% ETOH provided by the Chinese government, the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis indicated a higher recovery for quantitative analysis of synthetic dyes in herbal medicine samples. Most of the samples were within recovery (80~115%) and great precision (≤ 7%) criteria recommended by AOAC. Therefore, the HPLC-PDA analysis is considered a reliable analysis procedure capable of determining synthetic dyes in herbal medicines. This study also claims to successfully apply in real fields to quantify ten synthetic dyes in herbal medicines.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11146641/s1; Table S1: Inter-day recoveries obtained from the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis in three herbal medicines; Table S2: LOD, LOQ, and linearity values of the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis in cross validation.; Table S3: Recoveries and RSD values of the proposed HPLC-PDA analysis in the cross-validation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-Y.K.; methodology, K.-Y.K. and S.-H.J.; formal analysis, E.-Y.C. and S.K.; data curation, S.-H.J. and E.-Y.C.; investigation, S.K., C.-K.L.; funding acquisition, C.L.; project administration, S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, K.-Y.K.; writing—review and editing, S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [MFDS, Korea], grant number [Project No. 19171MFDS193] in 2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the first author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all companies who contributed to accomplish this study in herbal medicine research division, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with this study.
References
- Esen, B.; Oymak, T.; Dural, E. Determination of food colorings in pharmaceutical preparations and food additives by a validated HPLC method. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2018, 9, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ibarbia, L.; Majdanski, T.; Schubert, S.; Windhab, N.; Schubert, U.S. Safety and regulatory review of dyes commonly used as excipients in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 10, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, D.; Barrett, A.; Cooper, A.; Crumpler, D.; Dalen, L.; Grimshaw, K.; Kitchin, E.; Lok, K.; Porteous, L.; Prince, E.; et al. Food additives and hyperactive behavior in 3-year-old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Huang, B.; Gao, F.; Zhai, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Shi, L. Assessment of adulterated traditional Chinese medicines in China:2003–2017. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Li, K.; Xing, S.; Sun, H.; Shi, F.; Zhang, G.; Sun, H. Application of quadrupole-Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry in rapid screening and identification of synthetic dyes in herbal medicines. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 25, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YunNan Institute for Food and Drug Control (IFDC); SiChuan IFDC; JiLin IFDC. Supplementary Inspection Method for Lemon Yellow, Acid Yellow 36 and Goldamine O Test Items in Typhae Pollen of Chinese Herbal Medicine and Beverage Tablets. 2018. 03. National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (NIFDC), China. Available online: https://www.nifdc.org.cn/nifdc/bzhchx/ypjyfaxm/index.html (accessed on 27 June 2021).
- Tikhomirova, T.I.; Ramazanova, G.R.; Apyari, V.V. A hybrid sorption–spectrometric method for determination of synthetic anionic dyes in foodstuffs. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, F.I.; Guedes, M.I.F.; Vieira, Í.G.P.; Mendes, F.N.P.; Rodrigues, P.A.S.; Maia, C.S.C.; Ávila, M.M.M.; de Matos Ribeiro, L. Determination of synthetic food dyes in commercial soft drinks by TLC and ion-pair HPLC. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmassaoud, Y.; Villaseñor, M.J.; Salghi, R.; Jodeh, S.; Algarra, M.; Zougagh, M.; Ríos, Á. Magnetic/Non-Magnetic Argan Press Cake Nanocellulose for the Selective Extraction of Sudan Dyes in Food Samples before the Determination by Capillary Liquid Chromatograpy. Talanta 2017, 166, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oplatowska, M.; Elliott, C.T. Development and validation of rapid disequilibrium enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of Methyl Yellow and Rhodamine B dyes in foods. Analyst 2011, 136, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipskikh, O.; Korotkova, E.; Khristunova, Y.P.; Barek, J.; Kratochvil, B. Sensors for voltammetric determination of food azo dyes-a critical review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanikolopoulos, G.; Gerakis, A.; Papadopoulou, K.; Mastrantoni, I. Determination of synthetic food colorants in fish products by an HPLC-DAD method. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Oberson, J.M.; Meschiari, M.; Munari, C. Determination of 18 water-soluble artificial dyes by LC-MS in selected matrices. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; He, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, R.; Lu, J.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S. Screening of Chemical Dyes in Traditional Chinese Medicine by HPTLC-MS. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.; Wei, F.; Ma, S. Study on Major Problems Affecting the Quality of Typhae Pollen and Quality Standard. Chin. Pharm. Affairs. 2018, 32, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Yang, S.; Zhao, H.; Tan, Y.; Feng, J.; Xia, M.; Li, T. Analysis of traditional Chinese medicine components by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection based on double qualitative principles. Se Pu 2018, 36, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.-Y.; Liu, Z.-P.; Yu, X.; Su, Z.-H.; Wen, F.-R. Simultaneous determination of five kinds of unallowable yellow industrial dyes in traditional Chinese medicine by HPLC. Chem. Res. Appl. 2014, 26, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Yong, W.; Sun, L.; Jiang, G.; Chu, X. Highly sensitive and accurate screening of 40 dyes in soft drinks by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B. 2011, 879, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, J.L.; Li, J.H.; Li, X.L.; Li, J.; Lu, X.Y.; Shen, J.Z.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, Z.H. Analysis of water-soluble azo dyes in soft drinks by high-resolution UPLC-MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Exp. Risk Assess. 2011, 28, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Dai, S.; Wu, Z.; Shi, X.; Qiao, Y. Rapid analysis of dyed safflowers by color objectification and pattern recognition methods. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2016, 3, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, P.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, M.; Li, H.; Lu, F. Functional paper-based SERS substrate for rapid and sensitive detection of Sudan dyes in herbal medicine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mole Biomol. Spectrochim. 2018, 196, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Y.; Chen, B.Q.; Yuan, S.S.; Yang, B.B.; Yang, T.; Shi, M.H.; Lyu, G.-H. Determination of common dyes in dyed safflower by near-infrared spectroscopy. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 44, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Guidelines for Single-Laboratory Validation of Chemical Methods for Dietary Supplements and Botanicals. In Official Methods of Analysis, 19th ed.; Appendix K; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rovina, K.; Siddiquee, S.; Shaarani, S.M. A review of extraction and analytical methods for the determination of Tartrazine(E102) in foodstuffs. Crit. Rev. Analy. Chem. 2017, 47, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamjala, K.; Nainar, M.S.; Ramisetti, N.R. Methods for the analysis of azo dyes employed in the food industry—A review. Food Chem. 2015, 192, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazeau, J. Identification and Quantitation of Water-Soluble Synthetic Colors in Foods by Liquid Chromatography/Ultraviolet–Visible Method Development and Validation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6577–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.G.; Gong, W.J.; Zhao, Y.G. Rapid method for quantification of seven synthetic pigments in colored Chinese steamed buns using UFLC-MS/MS without SPE. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Che, F.; Lu, Y.; Xi, X.; Lan, T.; Wei, Y. Identification of the impurity in auramine O by high-performance liquid chromatography-ion trap-time of flight mass spectrometry and preparation of the auramine O reference standard by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2019, 37, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).