Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystal and Inorganic Nanofillers on the Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D-Printed Photopolymer Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Pretreatment of Composites
2.2.2. Preparation of Composites
2.2.3. Mechanical Tests of Composites
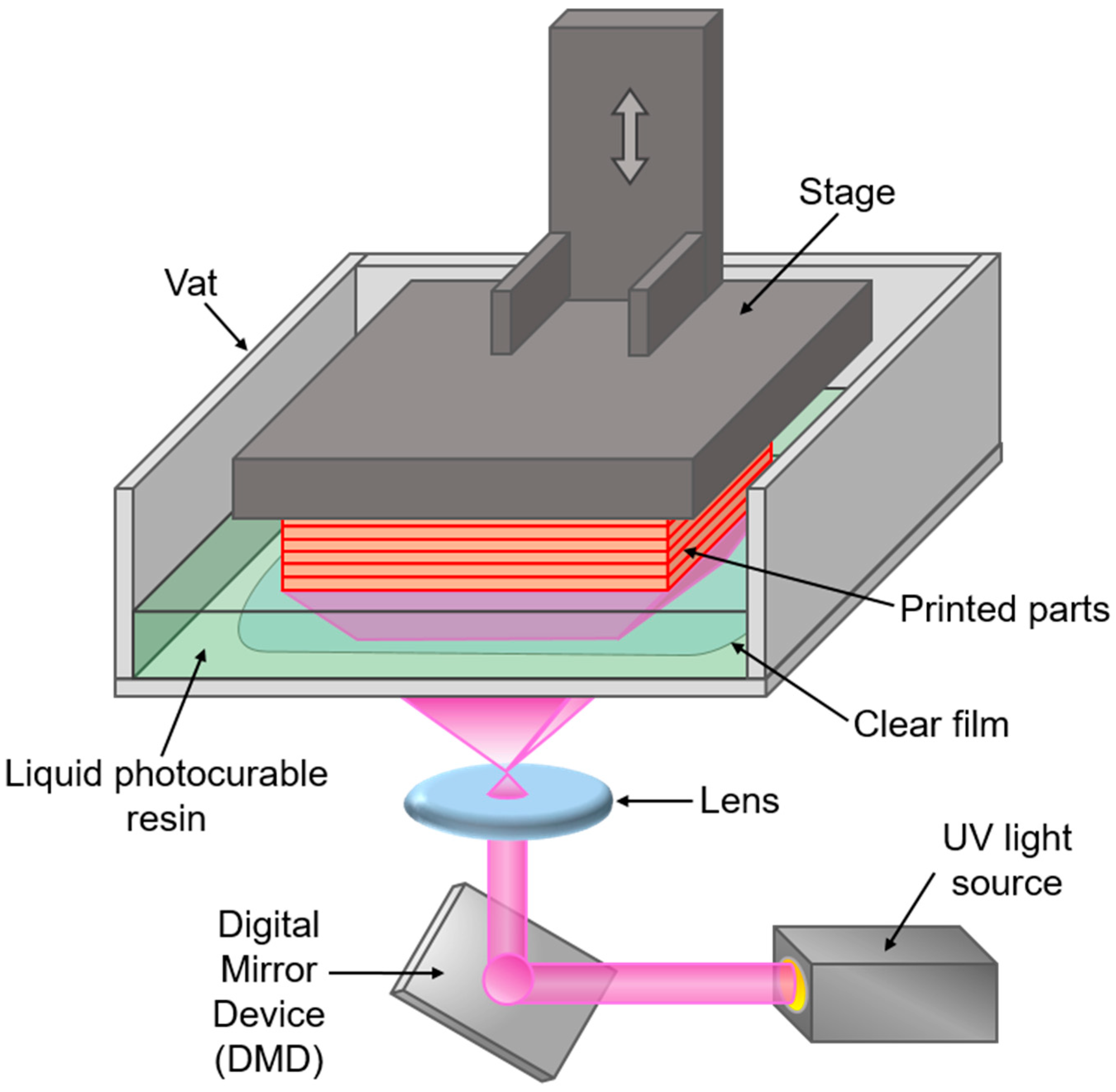
2.2.4. Morphological Analysis of Composites
3. Results and Discussion
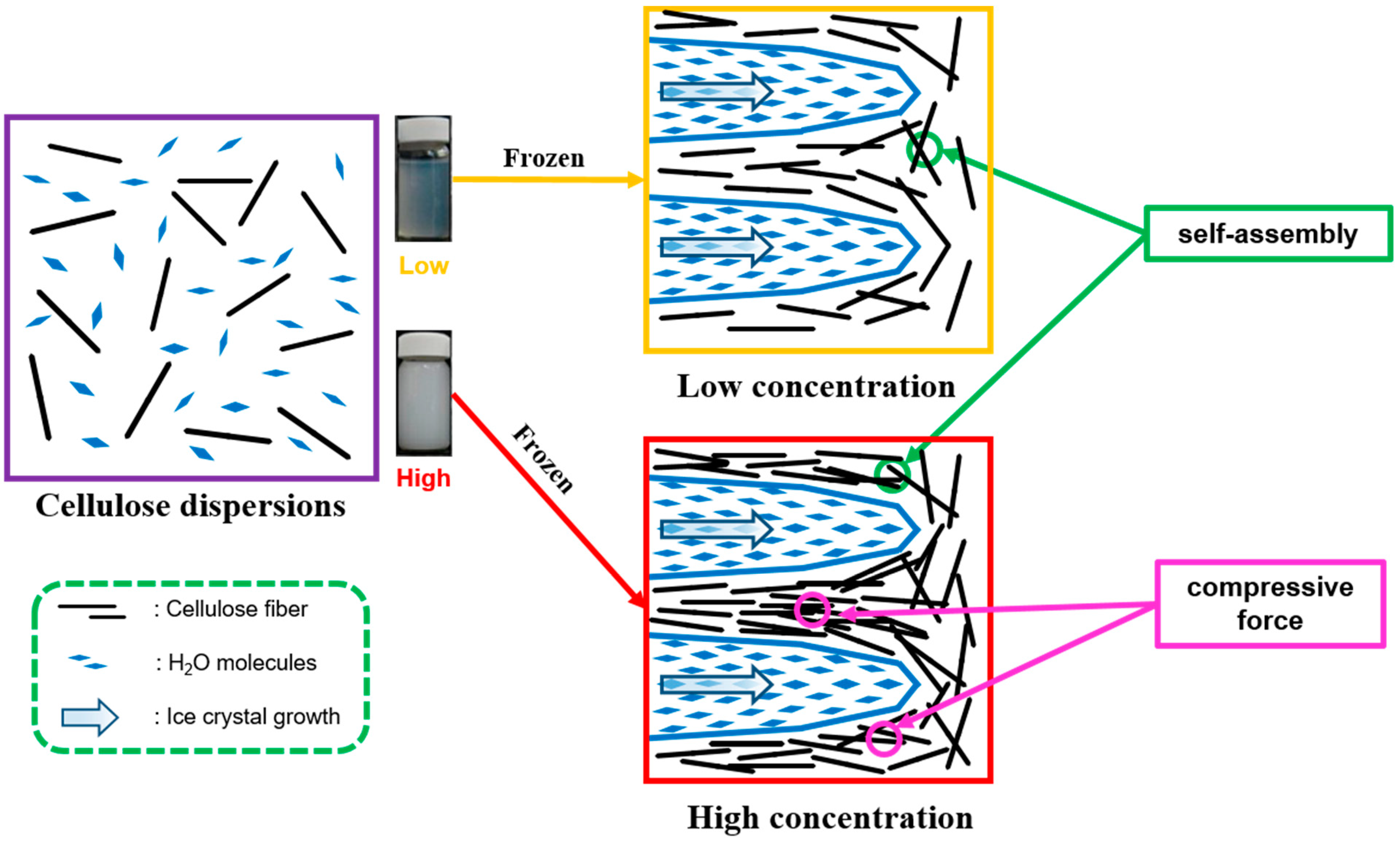
3.1. Effect of CNC Lyophilization Concentrations
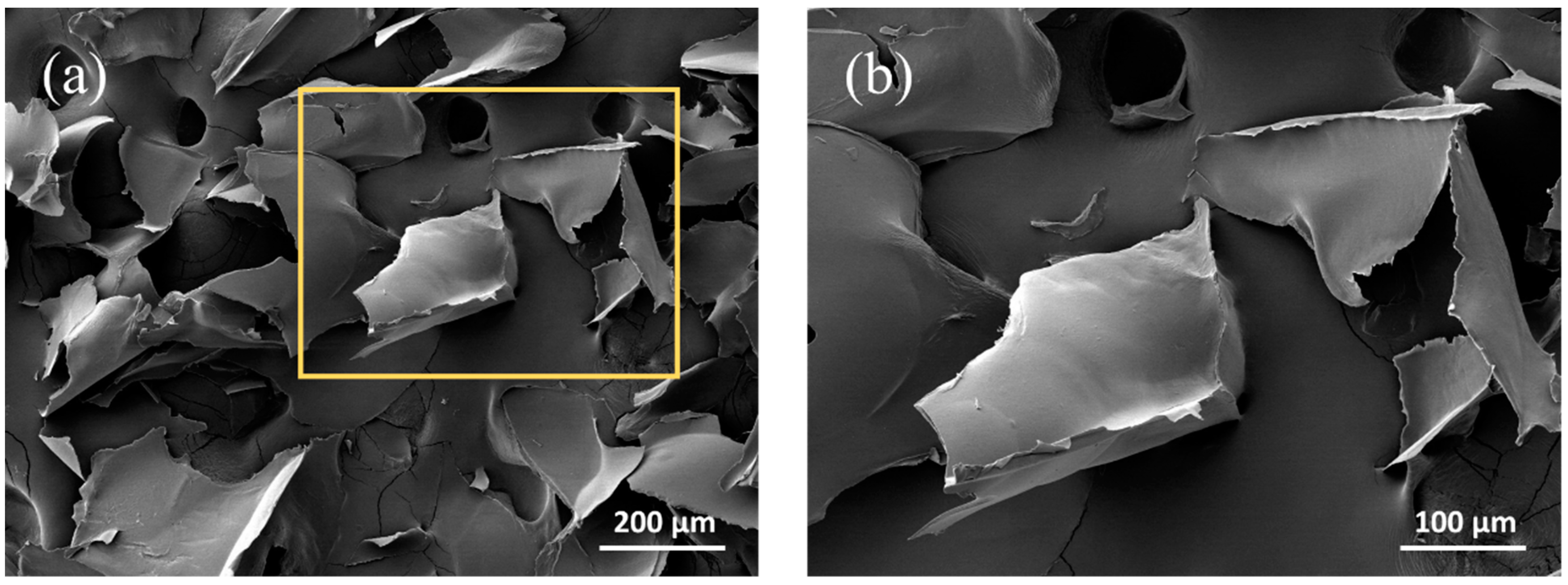
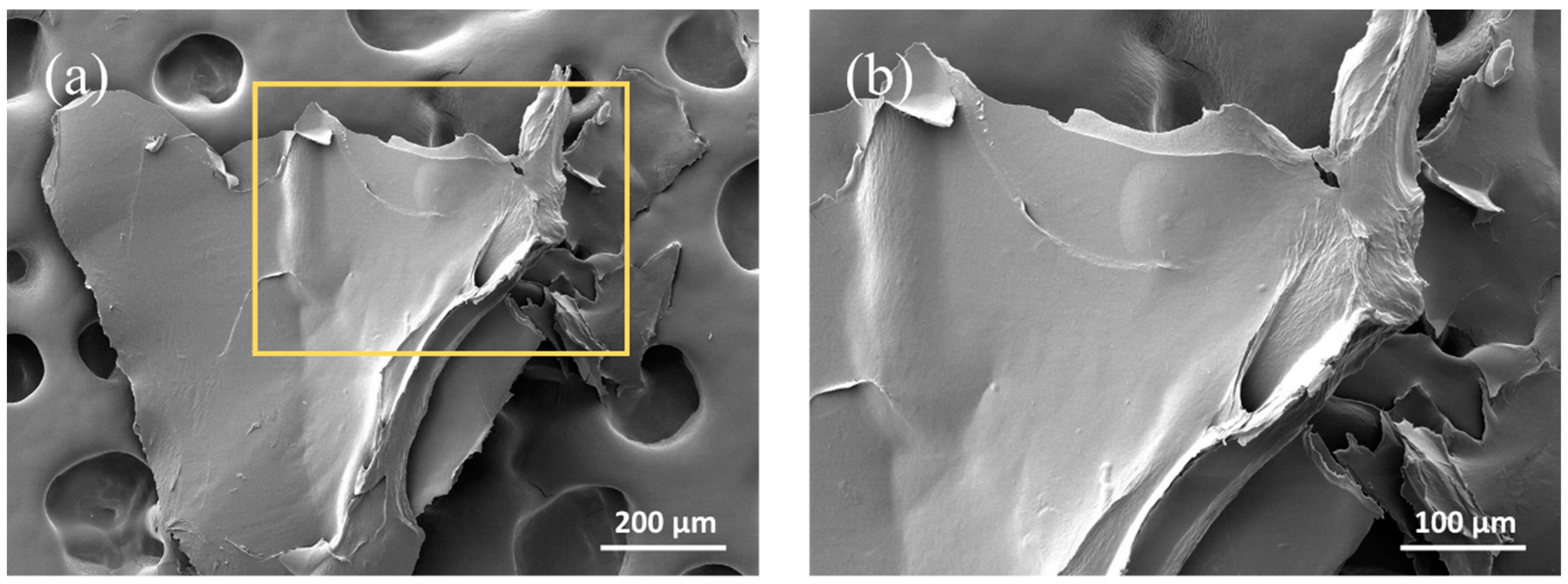
3.1.1. Morphological Properties of CNCs Processed at Different Lyophilization Concentrations
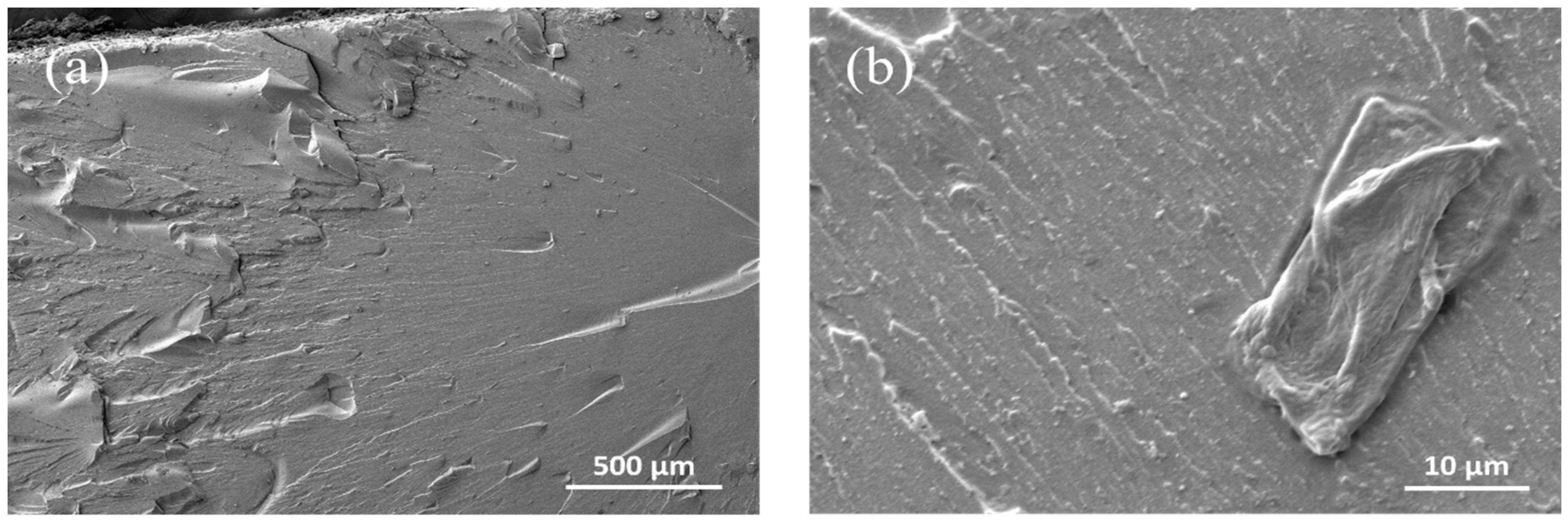
3.1.2. Morphological Properties of CNC/Photopolymer Composites Processed at Different CNC Lyophilization Concentrations
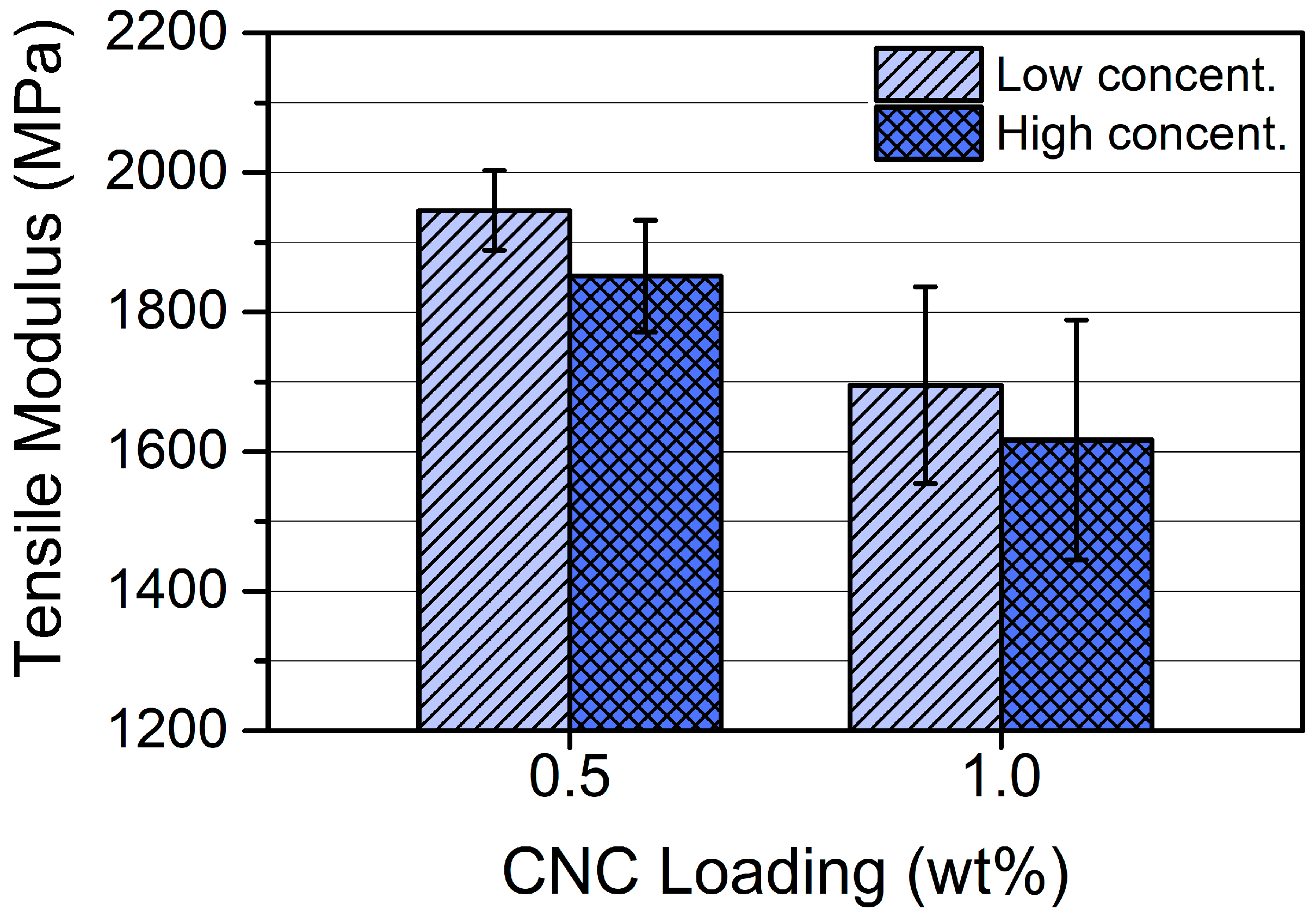
3.1.3. Mechanical Properties of CNC/Photopolymer Composites Processed at Different CNC Lyophilization Concentrations
3.2. Effect of CNC Contents on the Photopolymer Composites
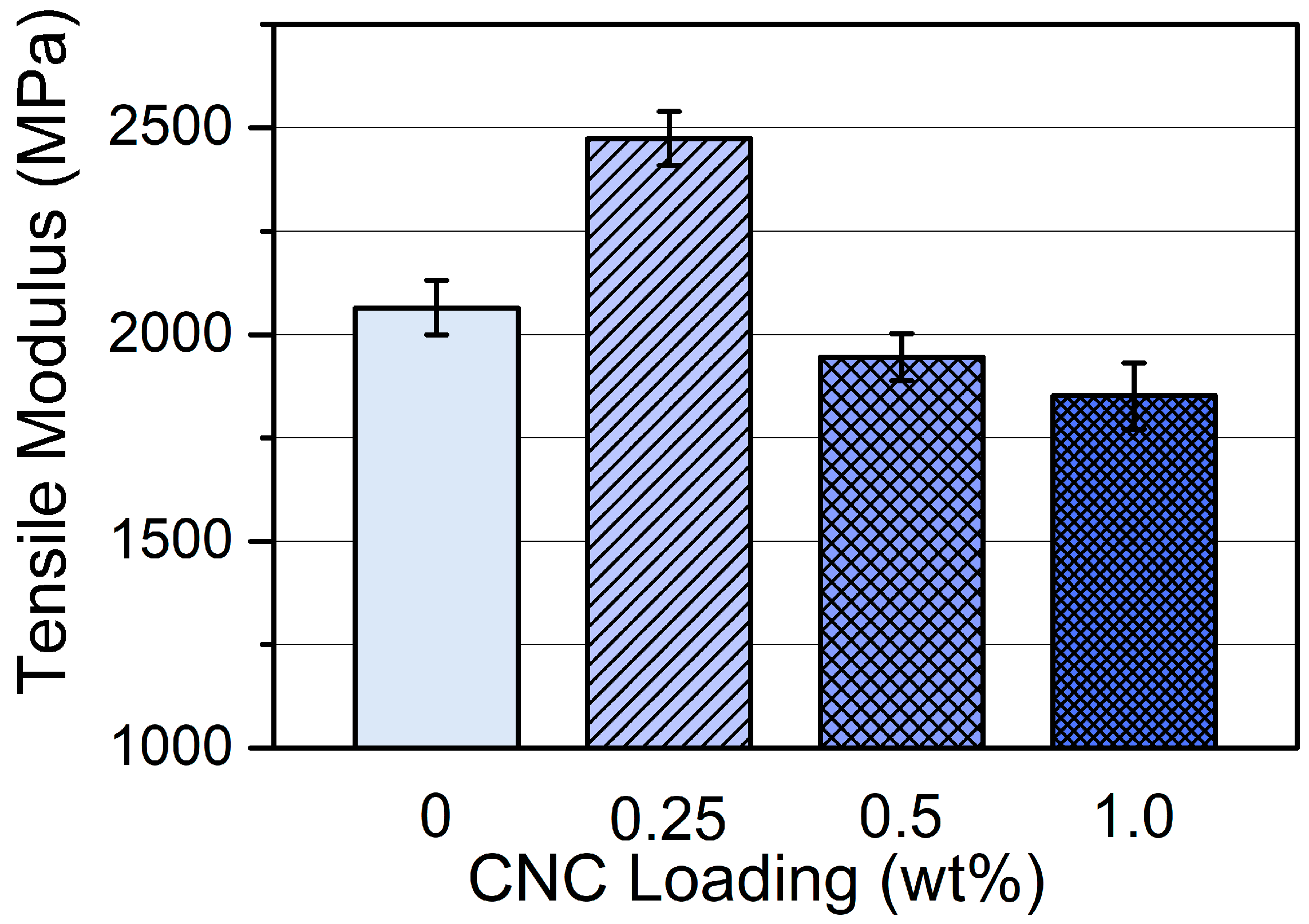
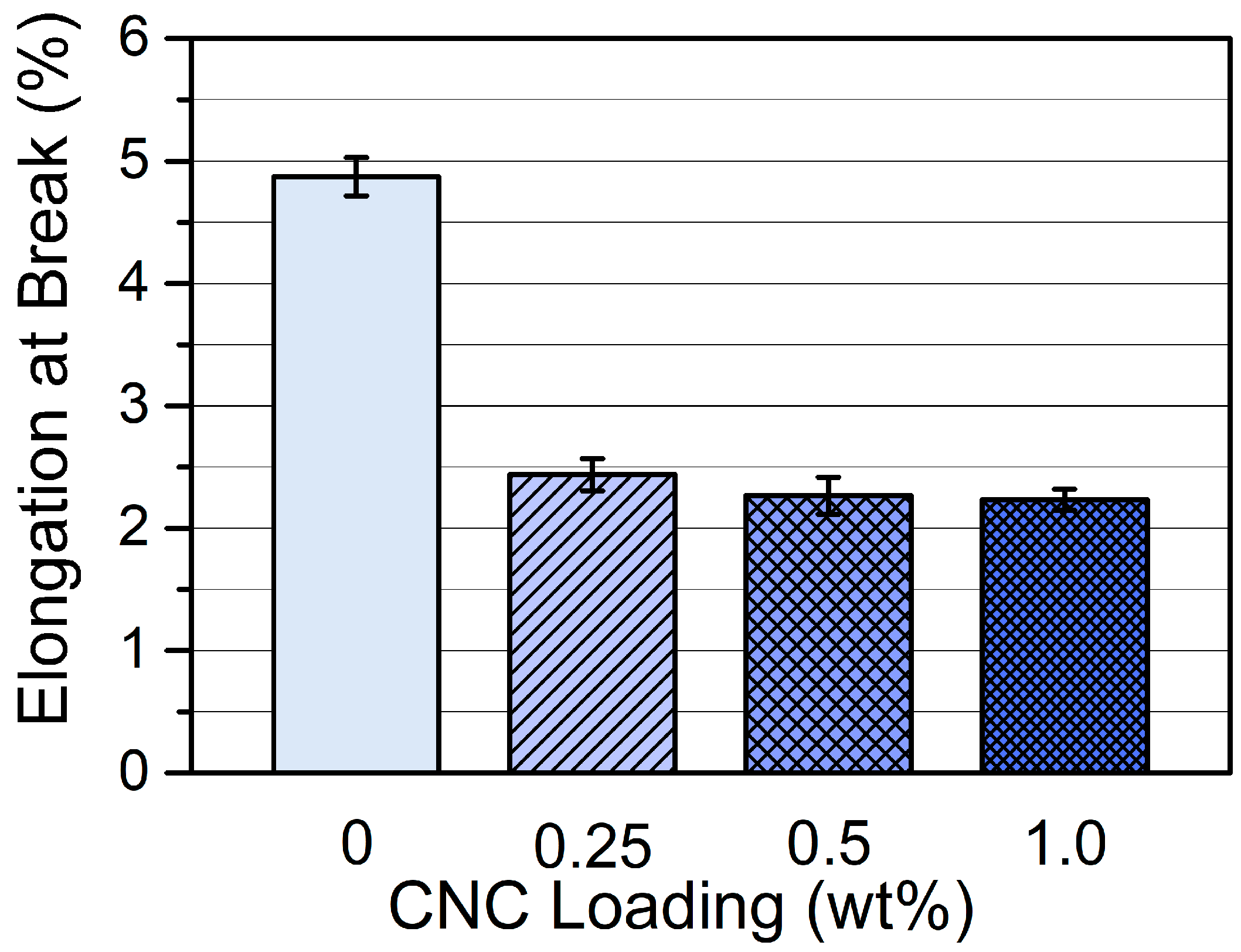
3.2.1. Mechanical Properties of CNC/Photopolymer Composites with Various CNC Loading Levels
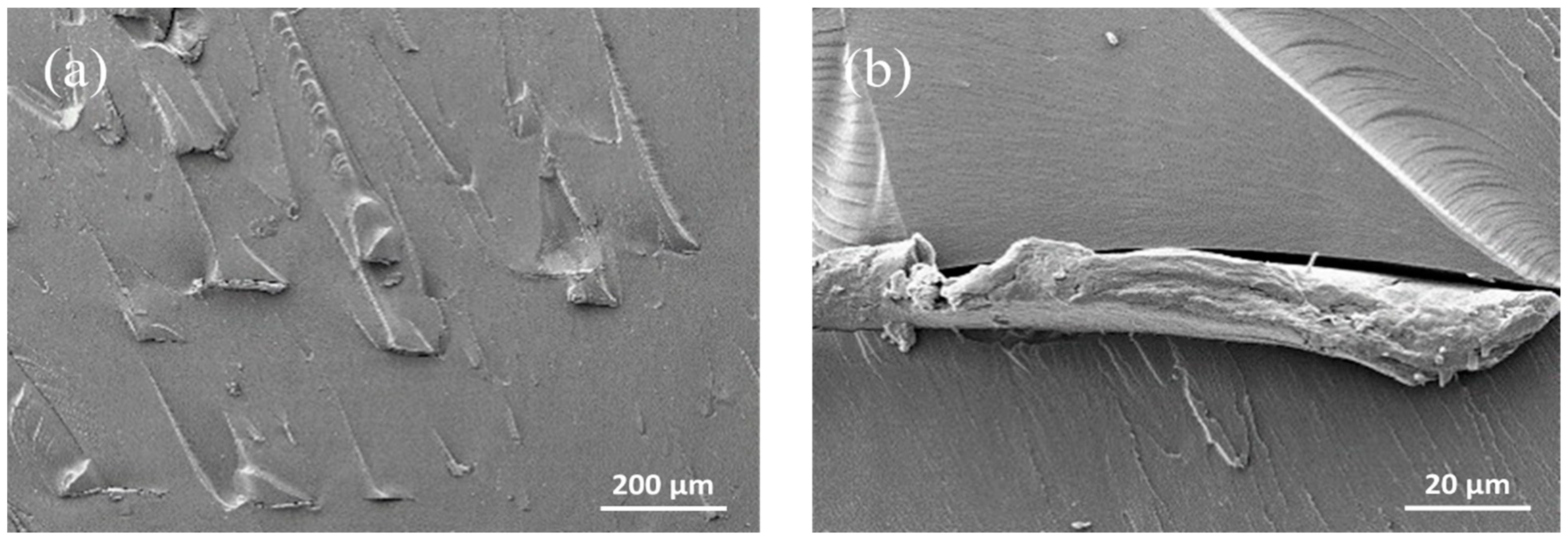
3.2.2. Morphological Properties of CNC/Photopolymer Composites with Various CNC Loading Levels
3.3. Effect of Inorganic Nanofillers on CNC/Photopolymer Composites
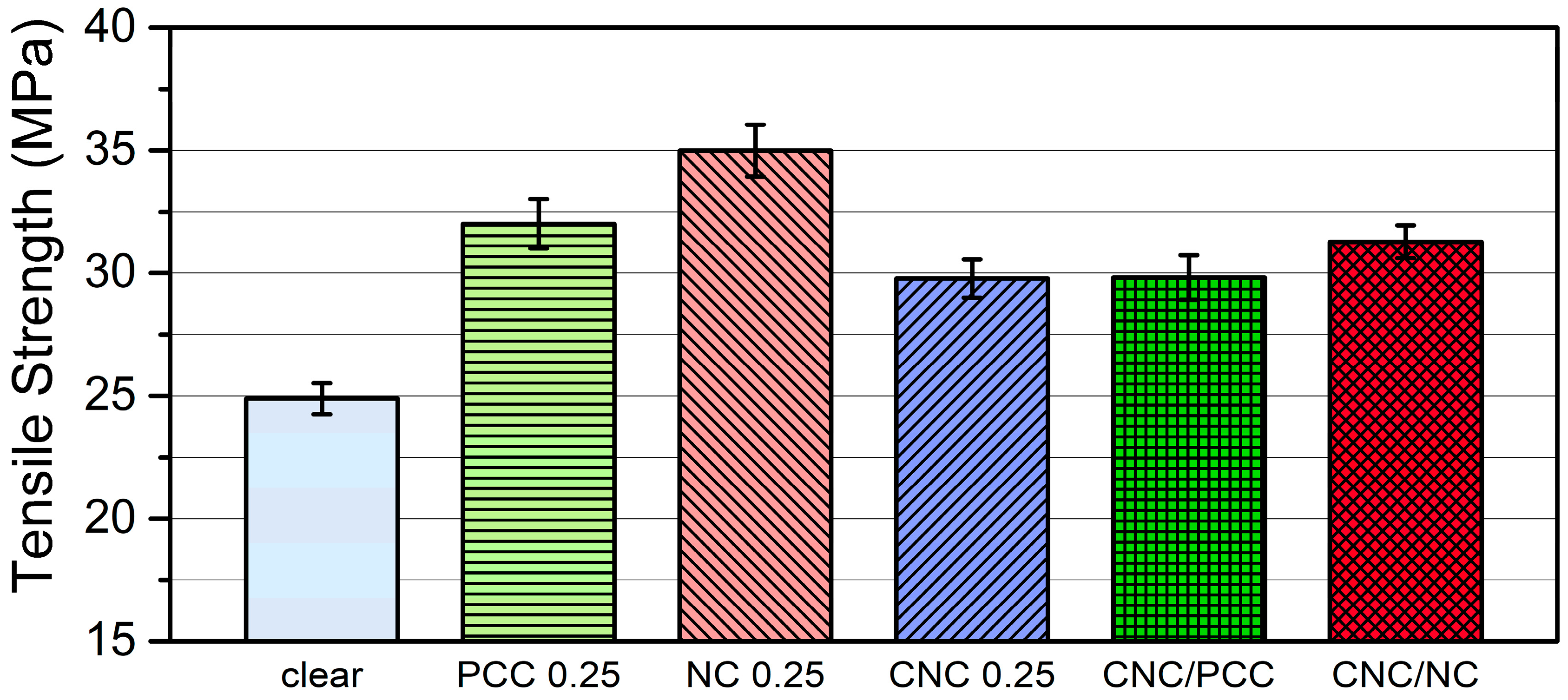
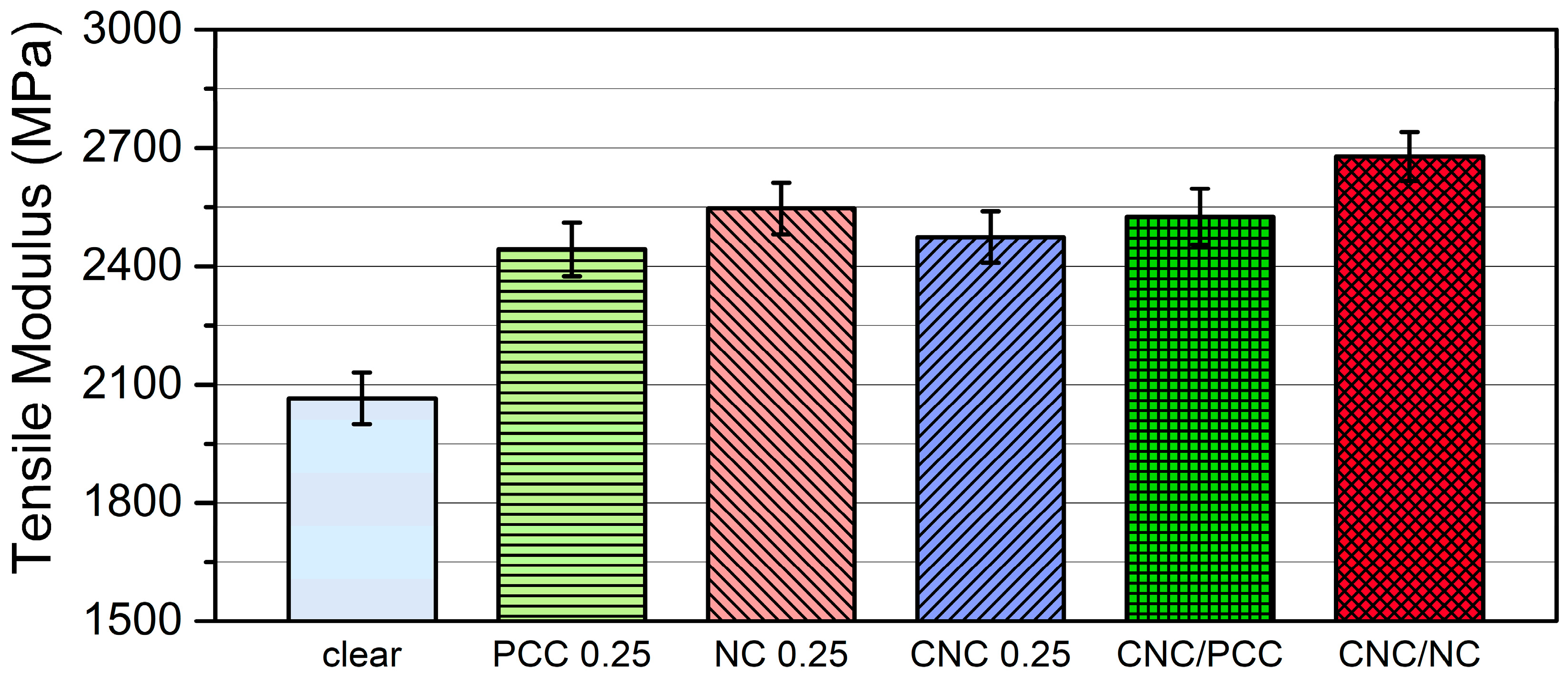
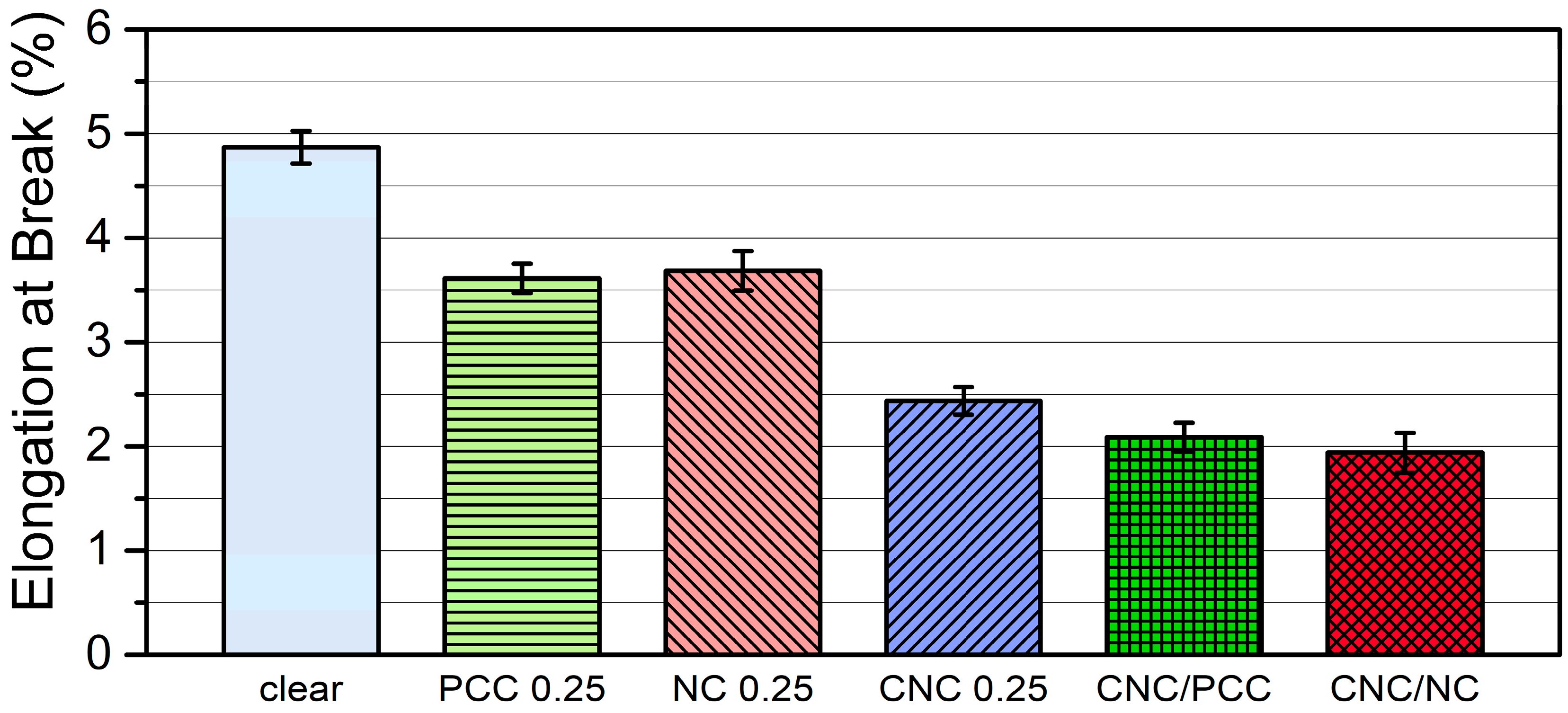
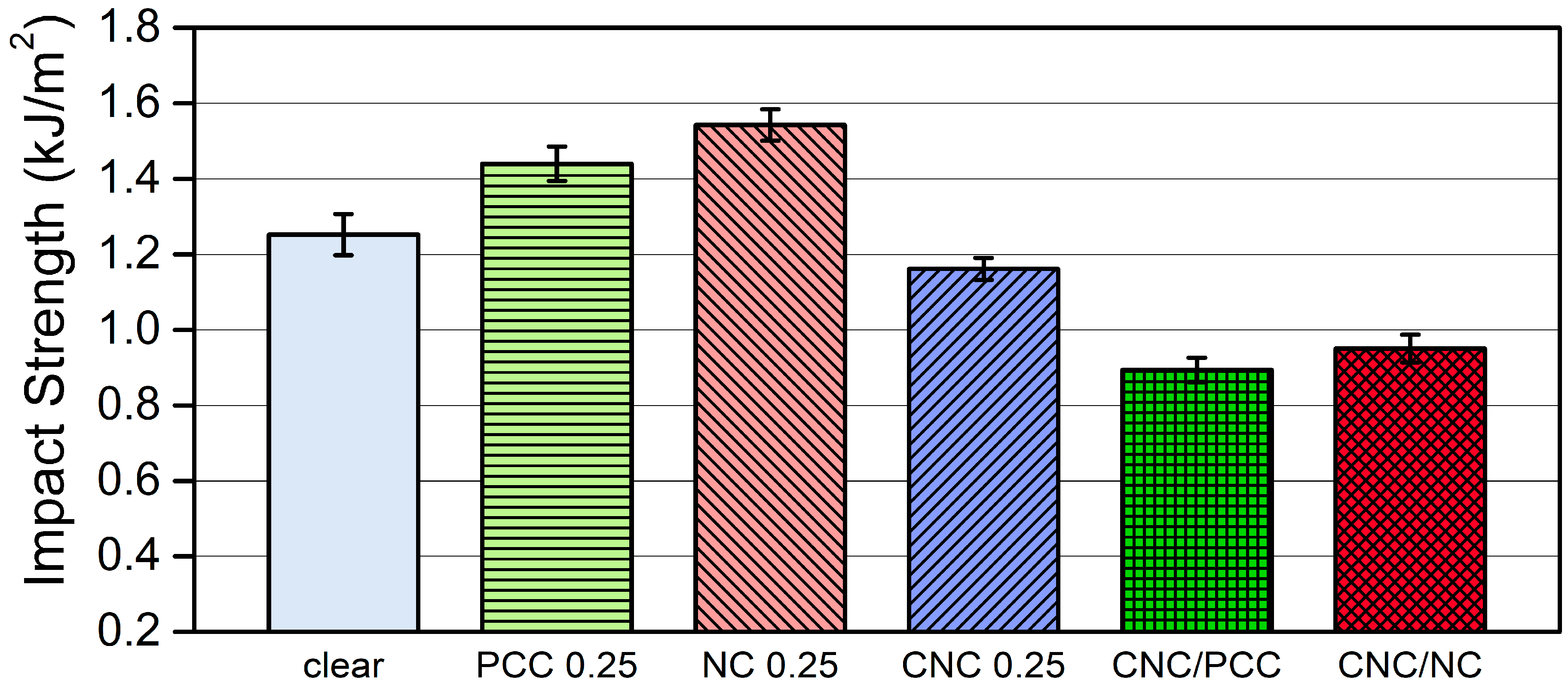
3.3.1. Mechanical Properties of Photopolymer Composites with CNC and/or Inorganic Nanofillers
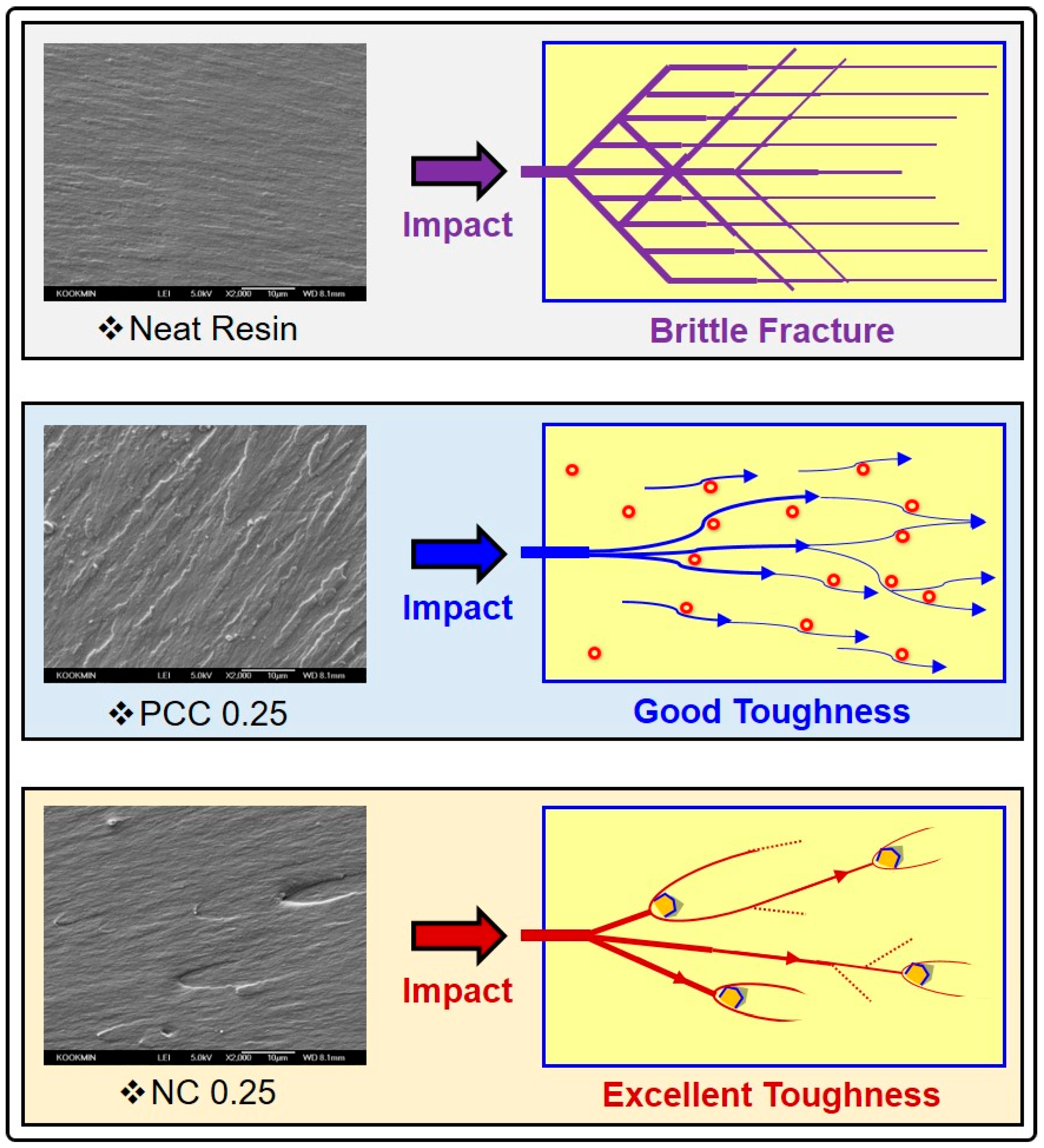
3.3.2. Morphological Properties of Photopolymer Composites with CNC and/or Inorganic Nanofillers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sames, W.J.; List, F.A.; Pannala, S.; Dehoff, R.R.; Babu, S.S. The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 315–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 148, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N. Effect of layer thickness on surface properties of 3D printed materials produced from wood flour/PLA filament. Polym. Test. 2018, 71, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntousia, M.; Fudos, I. 3D Printing Technologies & Applications: An Overview. In Proceedings of the CAD 2020 Conference, Singapore, 24–26 June 2019; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utela, B.; Storti, D.; Anderson, R.; Ganter, M. A review of process development steps for new material systems three dimensional printing (3DP). J. Manuf. Process. 2008, 10, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, M.M.; Saravanan, A.K.; Lenin, A.H.; Leno, I.J.; Mayandi’, K.; Ramalingam, P.S. A short review on 3D printing methods, process parameters and materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 6108–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Fantino, E.; Bertana, V.; Perrucci, F.; Scaltrito, L.; Pirri, F.; Sangermano, M. Development of 3D printable formulations containing CNT with enhanced electrical properties. Polymer 2017, 109, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yi, R.; Liu, Y.-J.; He, Y.; Wang, C.C. Delta DLP 3D printing with large size. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 1 December 2016; pp. 2155–2160. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.K.; Sakhaei, A.H.; Layani, M.; Zhang, B.; Ge, Q.; Magdassi, S. Highly Stretchable and UV Curable Elastomers for Digital Light Processing Based 3D Printing. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z.; An, D.; Huang, M.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Q.; Ji, X.; Wu, S.; Xie, Z. Fabrication of complex-shaped zirconia ceramic parts via a DLP-stereolithography-based 3D printing method. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A New Family of Nature-Based Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, J.-G.; Cho, H.-J.; Lee, D.; Choi, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Wu, Q.; Lee, S.-Y. Physicochemical and mechanical properties of polypropylene-cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites: Effects of manufacturing process and chemical grafting. Bioresources 2018, 13, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C.-F.; Kuang, X.; Mulyadi, A.; Hamel, C.M.; Deng, Y.; Qi, H.J. 3D printed cellulose nanocrystal composites through digital light processing. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raquez, J.M.; Murena, Y.; Goffin, A.L.; Habibi, Y.; Ruelle, B.; DeBuyl, F.; Dubois, P. Surface-modification of cellulose nanowhiskers and their use as nanoreinforcers into polylactide: A sustainably-integrated approach. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Kimura, Y. Stereocomplexed polylactides (Neo-PLA) as high-performance bio-based polymers: Their formation, properties, and application. Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, P.; Kim, S.H. Bio-based composite of stereocomplex polylactide and cellulose nanowhiskers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muiruri, J.K.; Liu, S.; Teo, W.S.; Kong, J.; He, C. Highly biodegradable and tough polylactic acid–cellulose nanocrystal composite. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3929–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chu, R.; Wu, R.; Wu, Q. Electrospun polyethylene oxide/cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibrous mats with homogeneous and heterogeneous microstructures. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zeng, H.M.; Walter, R.; Friedrich, K. Structure–property relationships of irradiation grafted nano-inorganic particle filled polypropylene composites. Polymer 2001, 42, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Errico, M.E.; Avella, M. Thermal and morphological characterization of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/calcium carbonate nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of different clay treatment on morphology and mechanical properties of PVC-clay nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, E.; Niaounakis, M. Thermo-mechanical properties of LLDPE/SiO2 nanocomposites. Polymer 2006, 47, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodjie, S.L.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Cai, W.; Li, C.Y.; Keating, M. Morphology and Crystallization Behavior of HDPE/CNT Nanocomposite. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2006, 45, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.M.; Sun, J.; Yu, D.H. Preparation and properties of nano-Al2O3 particles/polyester/epoxy resin ternary composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-W.; Park, S.-K.; Kim, D.-K. Mechanical properties of nano-MMT reinforced polymer composite and polymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnavaia, T.J.; Beall, G.W. Polymer–Clay Nanocomposites; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; 370p. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.; Sun, C. Effect of platelet dispersion on the load transfer efficiency in nanoclay composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2004, 38, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.; Bao, S. Impact fracture toughness of polyamide-6/montmorillonite nanocomposites toughened with a maleated styrene/ethylene butylene/styrene elastomer. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Paul, D.R. Nylon 6 nanocomposites by melt compounding. Polymer 2001, 42, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, A.; Chen, M.; Couillard, M.; Jakubek, Z.J.; Leng, T.; Johnston, L.J. Correlating Cellulose Nanocrystal Particle Size and Surface Area. Langmuir 2016, 32, 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.Q.; Zhou, C.J.; Wu, Y.Q.; Liu, F.Y.; Wu, Q.L. Self-Assembling Behavior of Cellulose Nanoparticles during Freeze-Drying: Effect of Suspension Concentration, Particle Size, Crystal Structure, and Surface Charge. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.J.; Dufresne, A.; Aranguren, M.; Marcovich, N.; Capadona, J.; Rowan, S.; Weder, C.; Thielemans, W.; Roman, M.; Renneckar, S. Current international research into cellulose nanofibres and nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börjesson, M.; Westman, G. Chapter 7. Crystalline nanocellulose—Preparation, modification, and properties, Cellulose—Fundamental Aspects and Current Trends; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2015; pp. 159–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, C.; Hamad, W.Y. Cellulose reinforced polymer composites and nanocomposites: A critical review. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2221–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.-K.; Lau, K.-T.; Cheung, H.-Y.; Ling, H.-Y. Effect of ultrasound sonication in nanoclay clusters of nanoclay/epoxy composites. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.-J.; Chun, S.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Wu, Q. Effect of nano-CaCO3 and Talc on property and weathering performance of PP composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.C.; Park, S.W. Fracture toughness of the nano-particle reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Struct. 2008, 86, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample Name | Composition Based on Weight (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photocurable Resin | CNC | Nano-PCC | Nanoclay | |
| Neat resin | 100 | - | - | - |
| CNC 0.25 | 99.75 | 0.25 | - | - |
| CNC 0.5 | 99.5 | 0.5 | - | - |
| CNC 1.0 | 99 | 1 | - | - |
| PCC 0.25 | 99.75 | - | 0.25 | - |
| NC 0.25 | 99.75 | - | - | 0.25 |
| CNC/PCC | 99.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | - |
| CNC/NC | 99.5 | 0.25 | - | 0.25 |
| Step | Process | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Step–1 (Magnetic stirring) | Premixing and re-dispersion of composition | 600 rpm, 40 °C, 30 min |
| Step–2 (Homogenizing) | Physical destruction of CNCs and inorganic nanofillers | 5000 rpm, 40 °C, 30 min, Gap between stator and rotator: 35 mm |
| Step–3 (Ultrasonication: bath) | Dispersion of composition | 40 kHz, 160 W, 25 °C, 20 min |
| Step–4 (Ultrasonication: probe) | Dispersion and deformation of lyophilized CNCs | 20 kHz, 750 W, Amplitude 40 %, 40 °C, 10 min |
| Step–5 (Ultrasonication: bath) | Dispersion and degassing | 40 kHz, 160 W, 25 °C, 20 min |
| Printer | MiiCraft U125 |
| XY Resolution | 65 µm |
| Wavelength | 405 nm LED |
| Base Layer | 1 Layer |
| Base Curing | 5000 ms |
| Buffer Layer | 5 Layers |
| Gap Adj. | 100 µm |
| Layer Curing | 1500 ms |
| Layer Thickness | 50 µm |
| Cleaning | Tap water & Ethyl alcohol |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, S.-U.; Kim, B.-J. Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystal and Inorganic Nanofillers on the Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D-Printed Photopolymer Composites. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156835
Bae S-U, Kim B-J. Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystal and Inorganic Nanofillers on the Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D-Printed Photopolymer Composites. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(15):6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156835
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Sang-U, and Birm-June Kim. 2021. "Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystal and Inorganic Nanofillers on the Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D-Printed Photopolymer Composites" Applied Sciences 11, no. 15: 6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156835
APA StyleBae, S.-U., & Kim, B.-J. (2021). Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystal and Inorganic Nanofillers on the Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D-Printed Photopolymer Composites. Applied Sciences, 11(15), 6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11156835






