Abstract
Inhomogeneous structure occurring in biological membranes being rich in glycosphingolipids (GSL) has been proposed as an important phenomenon involved in the cellular endocytosis process. However, little is known about the correlation between the formation of microdomains and the GSL-dependent biogenesis for tubular endocytic pits occurred on the surface of the cellular membrane. In the present work, the interaction between the bacterial Shiga toxin from Escherichia coli (STxB) and its cellular receptor GSL globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) were studied using small unilamellar vesicle (SUV). The model membrane invagination induced by STxB was determined by the contrast variation small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and the synchrotron radiation facility based small-angle X-ray scattering (SR-SAXS). The results revealed that Gb3 molecules provided the binding sites for STxB, inducing increased membrane fluctuation. The formation of protein–lipid complex (STxB-Gb3) apparently induced the thinning of model membrane with the thickness decreased from 3.10 nm to 2.50 nm. It is the first time to successfully characterize the mesoscopic change on membrane thickness upon GSL-dependent endocytic process using a small-angle scattering technique. Overall, this paper provided a practical method to quantify the inhomogeneous biological membrane structures, which is important to understand the cellular endocytosis process.
1. Introduction
Membranes of eukaryotic cell are of well-regulated environments that can provide a dynamic platform for various cellular processes. They are also characterized by high membrane heterogeneity including discrete membrane domains formed through the protein and lipid interactions [1,2]. It is the vesicular trafficking that regulate and maintain the constant of protein and lipid contents and further keep the heterogeneous environment on eukaryotic cell membrane [3,4]. Previous studies showed that such membrane heterogeneity is important for cell viability and some pathologies [5,6,7]. Therefore, it is of great importance to understand the functional properties of membrane domains in eukaryotic cell.
Among a variety of hypothesis about the structure and function of membrane domains, one important example is GSL-enriched microdomains on membrane which may facilitate the clathrin-independent endocytic process [8,9]. Such clathrin-independent endocytosis pathways do not involve with coated pits, and account for the cargo segregation during endocytosis [10,11]. The mechanisms for cargo segregation can be broadly categorized into active or passive processes [11]. A good example for active process that depends on ATP hydrolysis is the active segregation of GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-APs), with their organizations on cell surface presenting as monomers and small fraction (20–40%) of nanoclusters (<5 nm) [12]. The passive processes are not energy-dependent and the cargo segregation depends on specific intermolecular cargo interactions [11]. Lipid structure, height of the membrane bilayer and membrane curvature may contribute to such passive clustering of membrane components [11,13,14].
Intoxication of cells by Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae requires its binding to the GSL receptor Gb3, a raft-favoring lipid. In this case, the pentavalent Shiga toxin B-subunit (STxB) can specifically bind to 15 Gb3 molecules and induce narrow tubular vesicles. The compaction of Gb3 lipids under Shiga toxin binding, which favor the negative membrane curvature formation, was thought to be the driving force [15]. A recent study on Shiga toxin argued that the toxin clustering was membrane mediated [16], and the clustering was strictly correlated with capacity of toxins to suppress membrane fluctuations. The membrane thickness was assumed to be closely related with the strength of such fluctuation-induced forces [17].
In the current work, a simple purification scheme for the isolation of STxB was set up. The purified B subunit was found to exist as a pentamer in native state, and its immunologic and biologic activities were properly characterized. Then, the surface organization of GSL with and without GSL-dependent toxin on model membrane, Gb3-DPPC mixed SUVs was determined by SR-SAXS and SANS. The invagination of GSL-DPPC membrane induced by toxin B-subunit was quantified for the first time, indicating a possibility of membrane fluctuation. The observed experimental clustering processes operating in correlation with biological membranes provide evidences to the thermal Casimir force [18] hypothesis, which is expected to apply to a wide range of membrane biological processes.
2. Materials and Methods
Plasmid construction. Plasmid pET-28S-STxB (21–89) was constructed by subcloning a portion (21–89) of the coding sequence from STxB full-length gene, which was a gift from Ludger Johannes’ research group (Curie Institute, Paris, France). To amplify this region for recombination with PET-28S vector, we designed a pair of specific primer: 21-F: CACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGAACGCCTGA TTGTGTAACTG; 89-R: TGTCGACGGAGCTCGAATTCTCAACGAAAAATAA CTTCGC. The plasmid was propagated and expressed in E. Coli BL21 (DE3). BL21 was grown aerobically at 37 °C in Luria broth supplemented with 50 μg kanamycin per ml. At an optical density at 600 nm of 0.6, isopropyl-β-d-thioacetamide (IPTG) was added to a final concentration of 0.2 mM. The culture was harvested 18–20 h at 16 °C following IPTG addition.
Purification of STxB Subunit. Bacteria were harvested by tangential flow membrane filtration. The bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation (4000 rpm, 12 min, 25 °C). The bacteria pellet was resuspended with buffer A (50 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 500 mM NaCl; 5 mM imidazole) to a final volume of 40 mL and was crushed by a high-pressure homogenizer at 4 °C. Unbroken cells were removed by centrifugation at 18,000 rpm for 12 min at 4 °C and the supernatant was added to 2 mL Ni2+-NTA agarose affinity chromatography. The Ni2+-NTA agarose beads were washed 3 times using buffer A for 30 min to remove supernatant, and then 0.1 mg Ubiquitin-like-specific protease 1 (ULP1) prepared with buffer A was added to cut SUMO tag over night at 16 °C. Purification of B subunit to homogeneity was performed by fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) gel filtration. The supernatant was first filtered with 0.22 μm membrane and further purified by chromatography of the eluted B subunit on a FPLC Superdex 75 Increase 10/300 GL gel filtration column which was equilibrated with buffer B (20 mM Tris, pH 8.0) and run at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The first peak at 280 nm UV were condensed to 10 mg/mL, giving a homogeneous preparation of STxB subunit. The physiological activity of purified STxB subunit was determined by tricine-SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using anti-STxB antibody (Sigma, Darmstadt, Germany, 1:2000, Cat# SAB4200774).
Protein Labeling. The labeled protein was prepared in reference with Zeng et al. (2018) [19] with modifications to improve the expression and purification of STxB. Purified STxB protein were exchanged into the NaHCO3 buffer containing 100 mM NaCl, 100 mM NaHCO3 (pH 8.3), 4 mM β-ME using a HiTrap desalting column and concentrated to 10 mg/mL before reaction. Cy3 NHS ester (AAT Bioquest, Sunnyvale, California) were dissolved in DMSO and incubated with the corresponding protein at room temperate for 1 h. The fluorophore was mixed with protein solution in 1:1 molar ratio. The labeling reaction was quenched by the 200 mM Tris (pH 8.2) buffer, and the labeled protein was separated with a HiTrap desalting column into buffer containing 20 mM Tris (pH 8.0). Fluorescence labeling efficiency was measured by Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
GUV Formation and Analysis. Giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) containing the fluorescent lipid β-BODIPY™ 500/510 C12-HPC (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were grown using the thin film hydration method. Briefly, the POPC (Avanti Polar Lipids, Alabaster, AL, USA) and β-BODIPY™ 500/510 C12-HPC were dissolved in chloroform and placed in a glass tube. The solvent was dried with nitrogen gas to form a thin phospholipid film and further dried under vacuum for 4 h. After adding saturated sucrose solution, the lipid film was hydrated at 37 °C under rotary shaking overnight to obtain GUVs. For GUVs containing ganglioside Gb3 (Avanti Polar Lipids, Alabaster, AL, USA), the preparation process was the same as described above, but starting with mixed lipids, POPC and Gb3. The molar ratio [Gb3]/[POPC] of the mixture was 0.1/1 with the concentration of POPC fixed at 1% w/v. The Cy3-StxB was mixed with BODIPY-GUVs in molar ratio of 1:2 and incubated at room temperature for 30 min. GUVs were examined under an inverted confocal fluorescence microscope (Leica SP8, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) equipped with a Zeiss × 63 PL APO HCX, 1.4 NA oil immersion objective.
SUV Sample Preparation. Small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs) used for SAXS and SANS measurement were prepared in reference with Hirai et al. with the following modifications [20]. Briefly, the Gb3 was selected as the glycosphingolipid candidate to constitute the SUVs. Both protiated (1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (h-DPPC), Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL, USA)) and deuterated phosphorlipids (1,2-dipalmitoyl-d62-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (d-DPPC), Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL, USA)) were used to build proper electron density contrast variations for neutron scattering, and the prepared sample solutions were extruded 21 times through 0.1μm polycarbonate Nuclepore® membranes using Avanti Mini-Extruder (Avanti Polar Lipids, Alabaster, AL, USA) before the scattering measurements.
X-ray, Neutron, and Light Scattering Experiments. Small-angle X-ray scattering measurements were performed at beamline BL19U2 of National Facility for Protein Science Shanghai (NFPS) at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) in reference to our previous work [21]. The wavelength, λ, of X-ray radiation was set as 1.033 Å. Scattered X-ray intensities were collected using a Pilatus 1 M detector (DECTRIS Ltd., Baden-Daettwil, Switzerland). The sample-to-detector distance was set such that the detecting range of momentum transfer [q = 4π sinθ/λ, where 2θ is the scattering angle] of SAXS experiments was 0.1–4.5 nm−1. SAXS data were collected in cylindrical quartz capillary with a diameter of 1.5 mm and a wall of 10 µm as 20 × 1 s exposures and scattering profiles for the 20 passes were compared at 25 °C using 60 μL sample. Small-angle neutron scattering measurement were carried out using the time of flight SANS spectrometer installed at V16 beam port at the research reactor BERII of Helmholtz-Zentrum in Berlin (HZB), Berlin, Germany [22]. In order to cover a wide q-range from 0.036 to 7.0 nm−1, each sample was measured at two samples to detector distances 2 m and 11 m, respectively. The cell unit is made of quartz and the SANS measurement was taken at 25 °C with an exposure time of 200 min. The data were corrected for the transmission and scattering background, and the absolute scattering intensity was obtained by using water scattering as a standard reference. The SANS and SAXS measurements were performed at the same temperatures. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements were carried out by using the dynamic light scattering detection device (Wyatt DynaPro NanoStar, Santa Barbara, CA, USA). The temperature of the samples was the same in the SANS and SAXS measurements.
Small-angle scattering Data Analysis. The scattering data were fitted by a bilayer vesicle model, written as
where Rc is the radius of the core, th is the thickness of the outer part of bilayer (in contact with solvent), tt is the thickness of the inner part of bilayer, ηsol, ηh and ηt are the scattering length densities of solvent, outer part of bilayer, and inter part of bilayer, respectively. The non-uniformity of the SUV structure can be accounted for by their size distribution, which gives the summary scattering intensity in an integral form. Herein, the size distribution was approximated by a log-normal function,
where Rmed is the median value and σ indicates the size distribution width. Fitting by the method of least squares to analytical model functions was performed by SASfit software [23].
For SANS data, the scattering from pure deutrated DPPC is mainly suppressed and the STxB-Gb3 binding aggregates dominate the scattering data. Therefore, model-independent Guinier law is used to fit the curves. Compared to the Guinier law for a spheroid, the Guinier law for a rod gave a better fit, expressed as
where Rg is the radius of gyration, and A is a scale factor. Equations (1) and (4) were used to fit the experimental data from the polydisperse SUV particles and determine both the bilayer thickness and size of aggregates.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of STxB Purified with a Novel Purification System
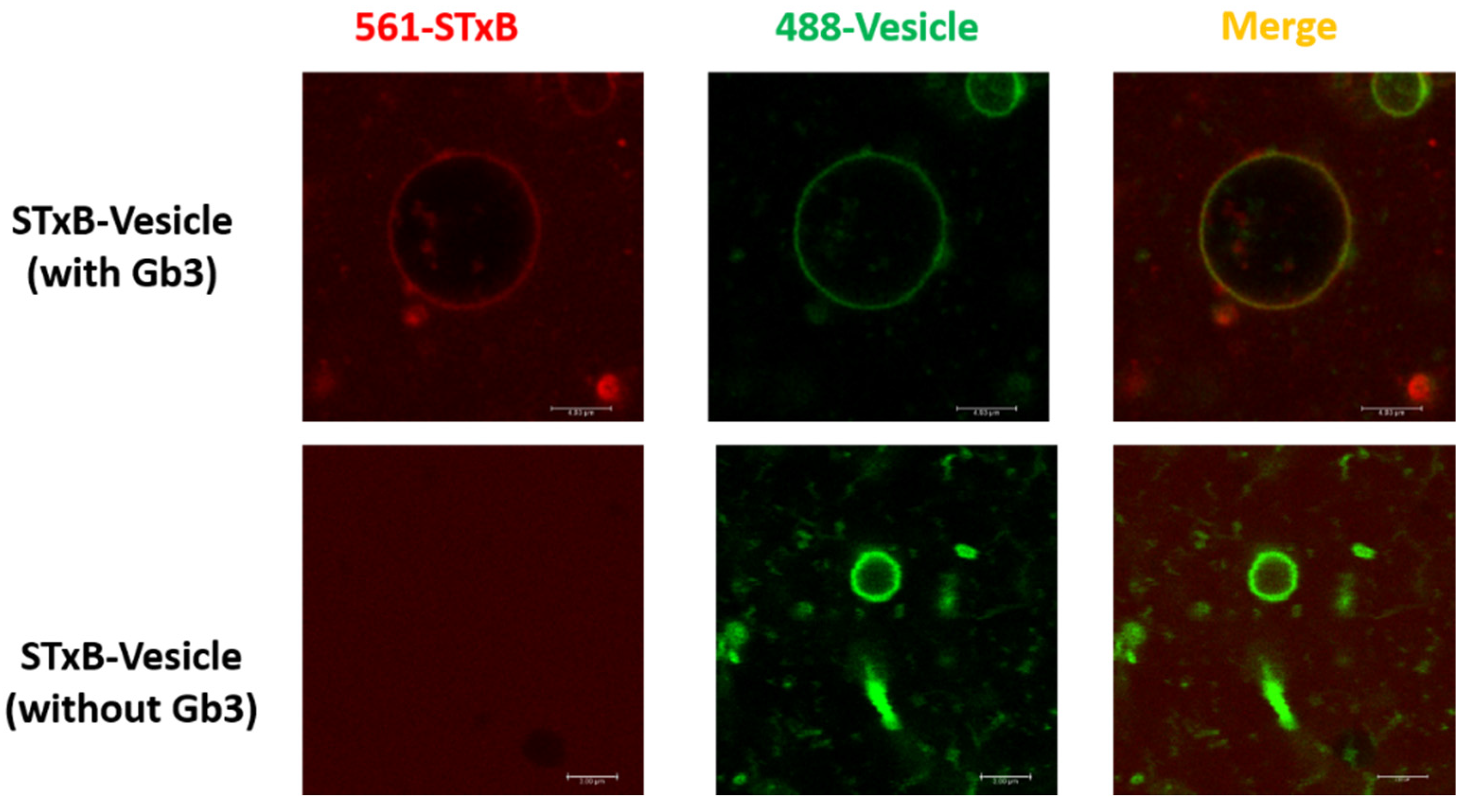
The construction of the new STxB purification system has been modified. Briefly, 6 × His-MBP tag with strong solubization capacity was combined with PET expression vectors. B subunit was expressed in E. Coli BL21 (DE3) strain and cytoplasmic extracts were purified and subjected to Tricine-SDS-PAGE (shown in Figure S1). Confirmation of STxB production was supported by Western blot analysis of the identical Tricine-SDS-PAGE gel (shown in Figure S1) with commercially available anti-STxB antibody (Sigma, Cat# SAB4200774). To test the binding specificity between STxB and Gb3, the giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) were chosen as a model membrane system, and reconstituted the surface with Gb3. Cy3-labeled STxB (red) bound to GUVs (spiked with BodipyFL-C5-HPC, green, shown in Figure 1, which proved the physiological activity of STxB purified with the novel expression system. This affinity purification strategy was practical due to the property of 6 × His-MBP tag. Such tag can be fully excised using ULP1 enzyme without any excess amino acids. The advantage of this method was cytoplasmic expression of toxin protein, which could obtain mature protein of interest without signal peptide in large amounts.
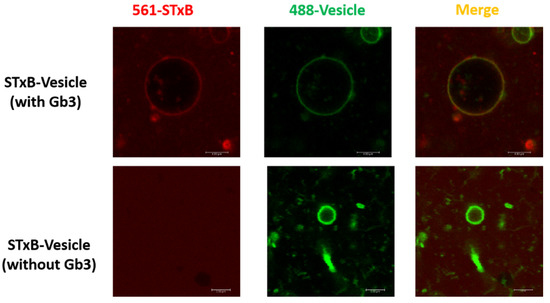
Figure 1.
Novel pentamer Shiga toxin B subunit reconstitution method. The Shiga toxin B subunit purified with novel strategy can bind with Gb3 glycosphingolipids in GUVs. GUVs were composed of DPPC (spiked with 1 mol% BodipyFL-C5-HPC, Green), containing Gb3 ganglioside. [Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1; STxB (Cy3, Red) was incubated with GUVs at 37 °C.
3.2. Contrast Dependence of the Scattering Curves
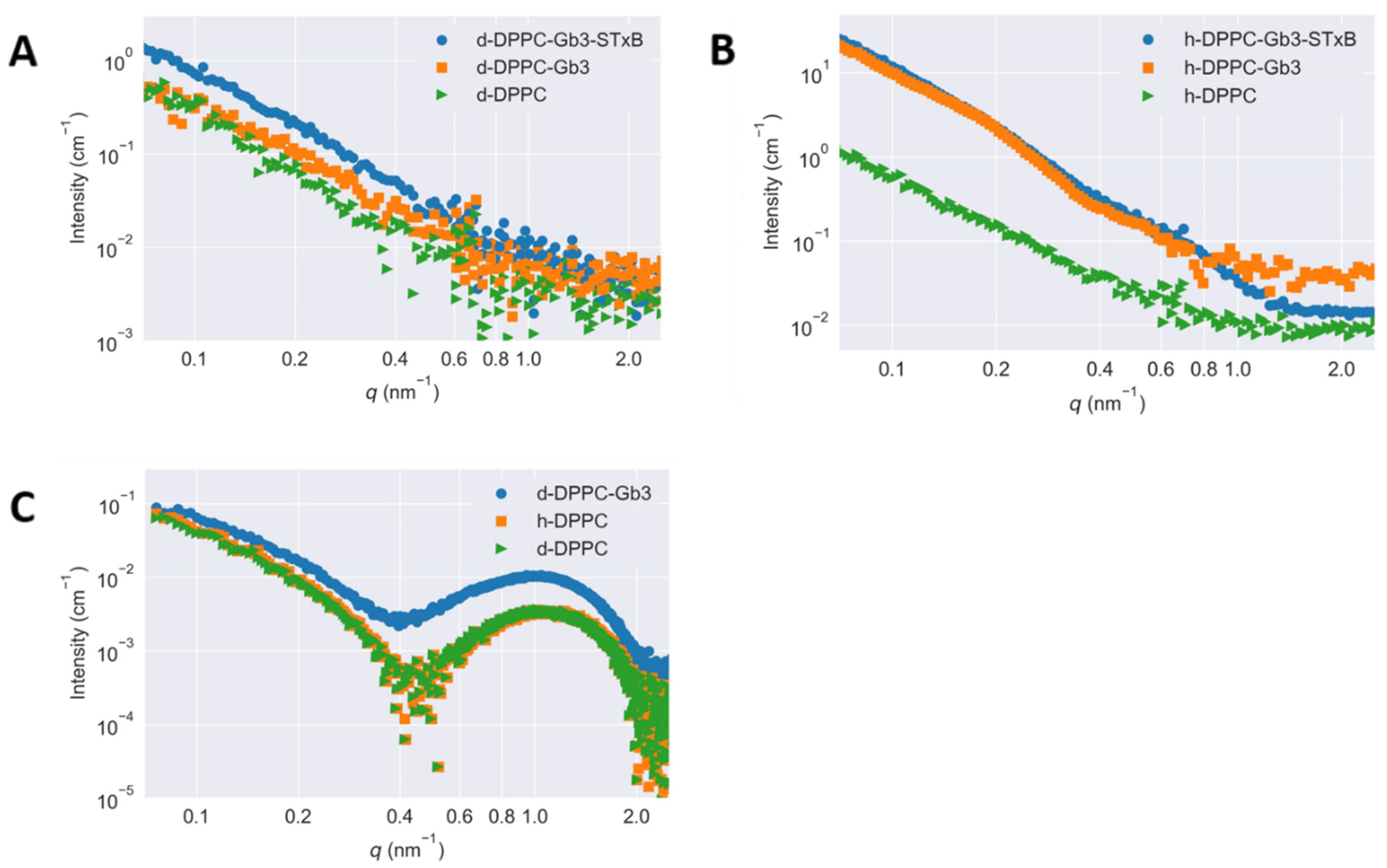
To study the lateral segregation of glycolipids on model membrane, the varied inverse contrasts of [Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1 mixture were measured using SANS, where the molar ratios of [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] were 1/0 (shown in Figure 2A) and 0/1 (shown in Figure 2B), respectively. Figure 2C shows the SAXS curves of vesicles, which are prepared in the same way as those used for SANS measurements. All X-ray scattering curves measured at the same temperature agreed well with each other, demonstrating the same contrast profiles for the measured SUVs. In considering that the head and tail portions for DPPC molecules (either h-DPPC and d-DPPC) possessed the same X-ray scattering length densities, the scattering profile of SUVs should be independent on deuteration of DPPC. More changes of SANS scattering curves have been observed in Figure 2B. The average scattering length density of the hydrophilic head portions of h-DPPC and d-DPPC molecules for neutron were identical (1.10 × 1010 cm−2). However, with the use of deuterated phospholipid, the scattering length density of the hydrophobic tail portions of DPPC molecules for neutron had high contrast (shown in Table 1) [24,25]. To minimize the scattering from hydrophobic tail portions of DPPC and hence mask the scattering from phospholipid, the molar ratio of [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 1/0 mixture was chosen. The scattering length density of Gb3 was calculated as 4.78 × 1011 cm−2, therefore, the changes of SANS curve in Figure 2B without the presence of Shiga toxin B subunit were attributed to the Gb3 inhomogeneous distribution in model membranes. The scattering length densities calculated with these parameters across the membrane are shown in Table 1. The scattering of Figure 2 illustrated with error bar was shown in Figure S2.
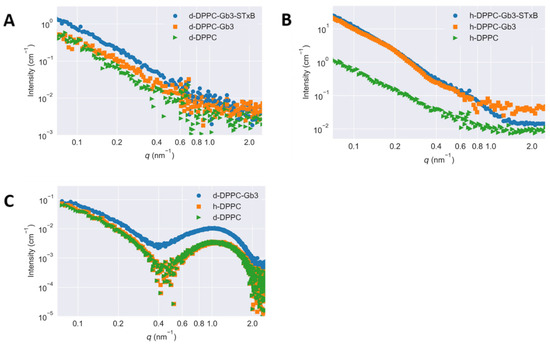
Figure 2.
Small-angle scattering curves of the SUV samples of Gb3 and DPPC mixture ([Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1. Measurements were performed at T = 25 °C. (A) Small-angle neutron scattering curves of [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 1/0; (B) small-angle neutron scattering curves of [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 0/1; (C) small-angle X-ray scattering curves for fully protiated and deuterated DPPC, and fully deuterated DPPC with Gb3.

Table 1.
The scattering length density used to determine contrast distribution profiles of the SUV bilayer structures for neutron scattering (×10−11 cm−2). The SUV samples of Gb3 and DPPC mixture was prepared with [Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1. The SLD of hydrophilic head portions of h-DPPC and d-DPPC were identical, the high contrast comes from the hydrophobic tail portions of DPPC molecules.
3.3. Model Membrane Thinning upon STxB Binding
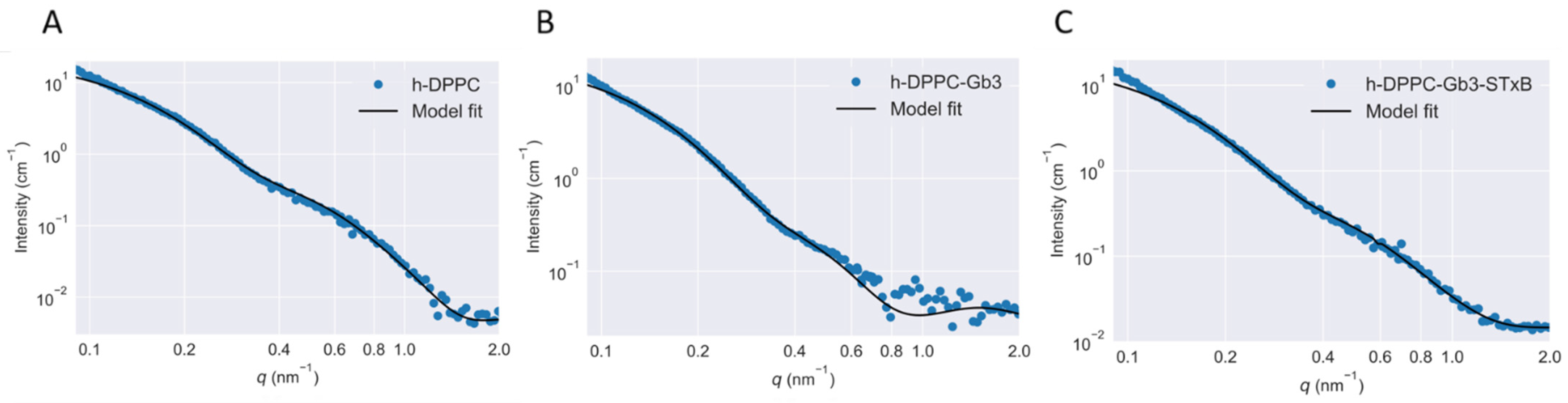
The binding of Shiga toxin to specific glycolipid receptors in the model membrane has been reported to induce membrane deformation locally [15]. This observation was further confirmed in present study using SAXS and SANS. Based on Equation (1), the experimental scattering curves were fitted with the theoretical ones therefore the vesicle bilayer related structural parameters were determined (Figure 3). The fitting residuals of scattering was shown in Figure S3. The scattering data in the small-angle region (q < 0.15 nm−1) was affected by the SUVs size distribution. However, due to the limited measurable minimum q range, it is hard to follow the scattering of the whole vesicle. Therefore, here we focused more on the internal structure of the SUVs.
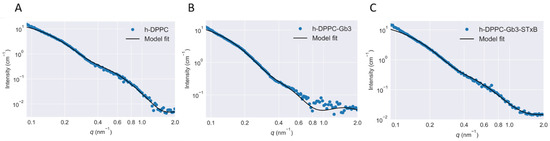
Figure 3.
Optimized theoretical scattering functions on [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 1/0 system based on polydisperse three-shell model fitting. The SUV were prepared as [Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1. Measurements were performed at T = 25 °C. (A) Empty DPPC vesicle; (B) Gb3 reconstructed DPPC vesicle; (C) Shiga toxin B subunit incubated with Gb3 reconstructed DPPC vesicle.
In previous studies, the shell-model was quite popular to be applied for fitting the scattering data. This direct analysis can determine internal structure of micellar or vesicular particles [20,26,27]. However, such shell-model fitting analysis neglected the surface structure of micellar or vesicular particles, and was not suitable for present study. Therefore, a more general three shell model was selected (shown in Figure 4). The experimental SAXS and SANS scattering curves were fitted with the integral function (Equations (1) and (3)) at the scattering vector q ranging from 0.1 to 2 nm−1 (shown in Figure 3). The value of Rc was fixed at 18 nm as in reference of previous glycosphingolipid vesicle related studies [20,26]. Overall, the data and fitting curves overlap rather well, except small deviations in the low-q region (<0.10 nm−1), which might be caused by the polydispersity or by attractive interactions between SUVs. The fitted parameters indicated the thinning of the SUV bilayers induced by STxB. Table 2 revealed the effects of Shiga toxin B subunit on the model membrane thickness, with the value of 2.50 ± 0.15 nm for STxB-Gb3-DPPC SUV bilayer, which was significantly smaller than that for pure DPPC SUV bilayer (3.33 ± 0.05 nm). It should be noted that the membrane thickness for Gb3 ganglioside reconstructed SUV remains stable, with the value of 3.10 ± 0.13 nm, which was quite comparable with the pure DPPC SUV bilayer thickness. Thus, the membrane curvature can only be induced in the presence of STxB proteins. The cellular receptor Gb3 itself had little influence on the membrane curvature changes. These results were consistent with studies on another ‘rafts’ like protein, GPI-APs. Vrljic et al. reported that there was a small fraction of species with significantly slower diffusion coefficient coexisting with larger oligomers for a GPI-anchored isoform of class II MHC molecules [28]. Sharma and his colleagues revealed the size and origin of the slowly diffusing species for GPI-APs using fluorescence photobleaching experiments [29]. Moreover, in Fujimoto’s group, they reported the nanocluster behaviors of GSL GM1 and GM3 in the membrane outer leaflet [30]; and in the inner leaflet of plasma membrane, the nanocluster segregation of Ras isoforms had been discovered [31]. Doktorova et al. showed that gramicidin increased lipid flip-flop in a complex, concentration-dependent manner [32]. Thus, it can be concluded that the cargo segregation process, which accounted for the clathrin- and caveolin-independent endocytosis, shared a common feature to begin with domains construction.
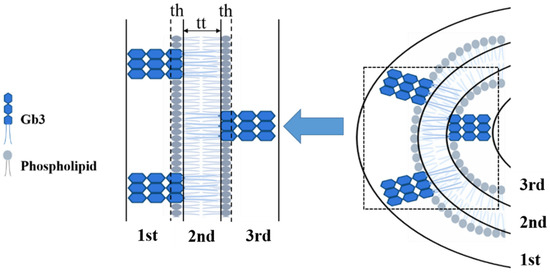
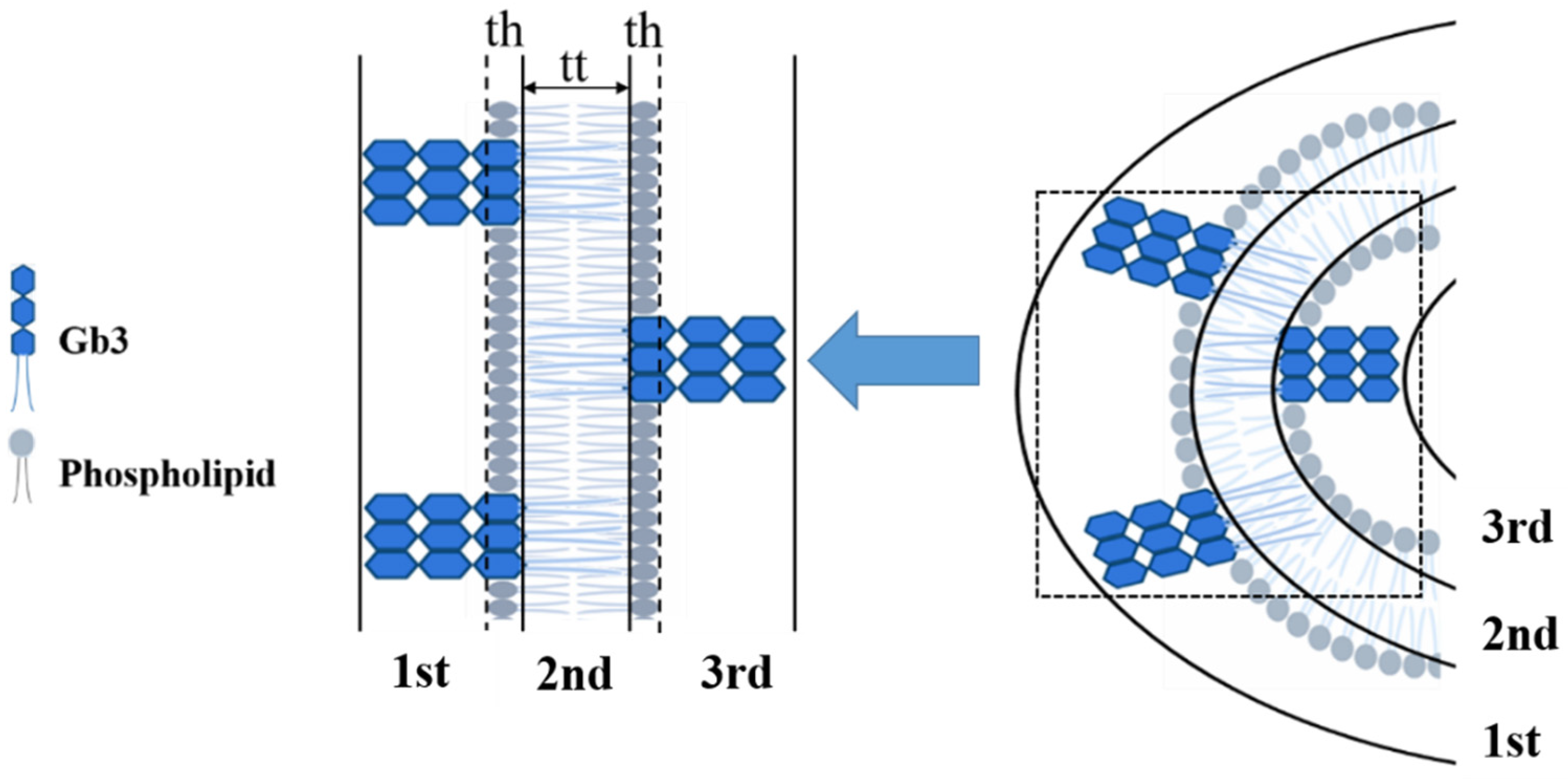
Figure 4.
Schematic picture of SUV model adopted for the three-shell model fitting. Each shell contains the following constituents. First and third shells, combination of the protruding oligosaccharide chains, the DPPC choline head, and the rest of the oligosaccharide chains; second shell, hydrocarbon chains of DPPC and Gb3. th is the thickness of hydrophilic phospholipid headgroup; tt is the thickness of the inner part of the vesicle, consisting of the hydrophobic tails of both phospholipid and Gb3.

Table 2.
The structural parameters obtained from small-angle neutron scattering.
3.4. Glycolipids Form Nanometer-Sized Clusters and Larger Scale Clusters Can Be Induced at Cell Surface
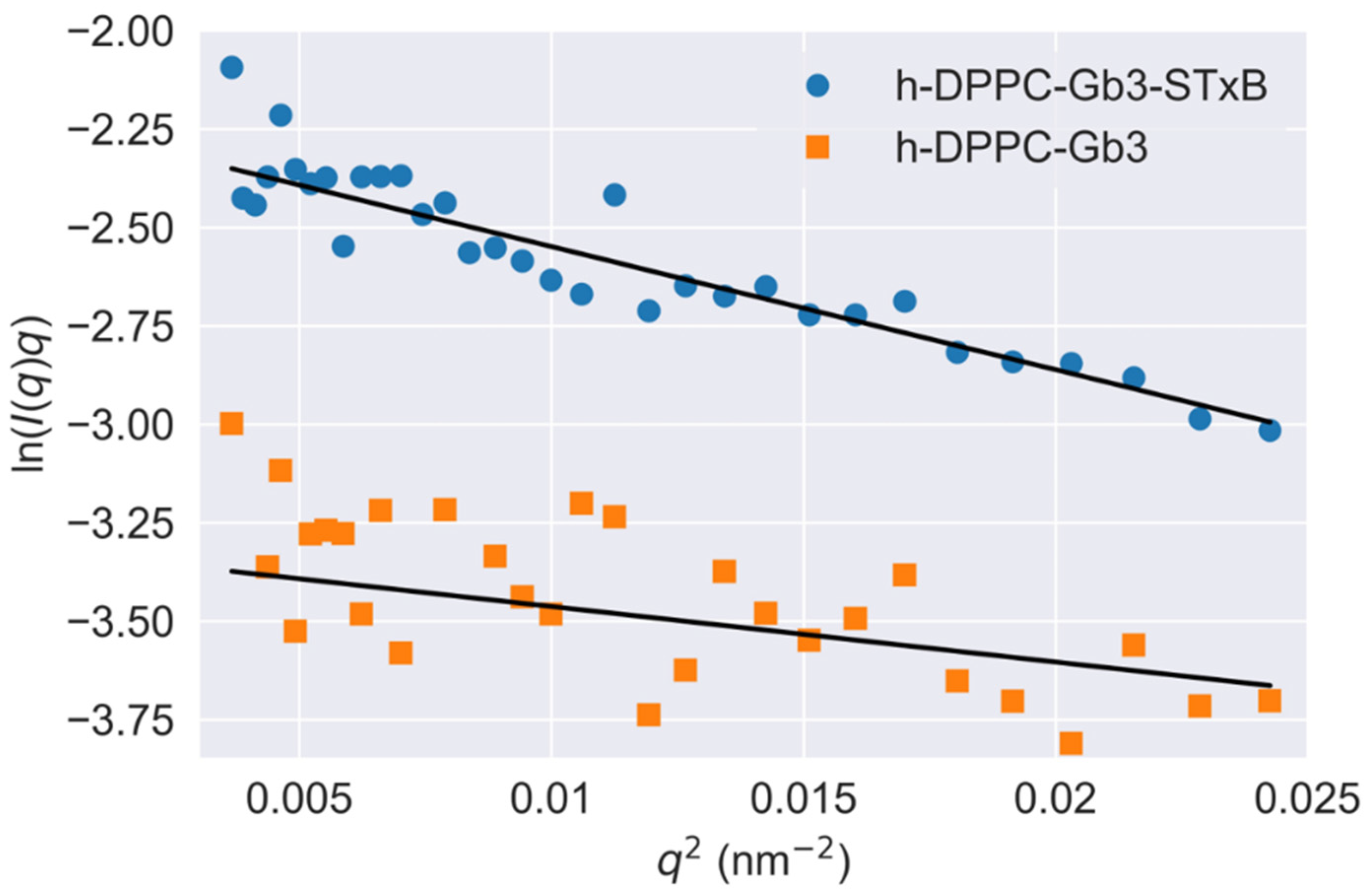
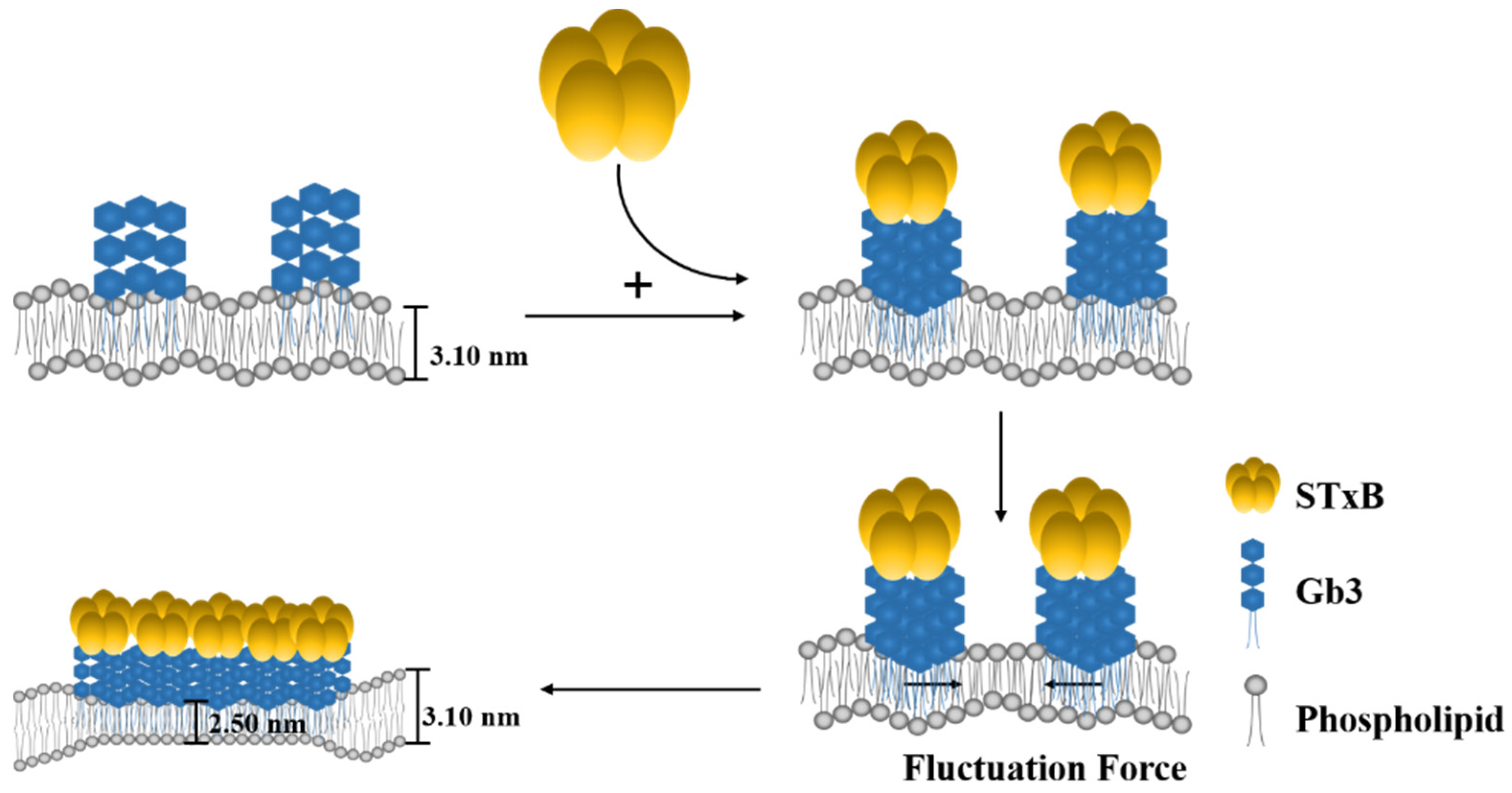
To understand the scales of glycolipid organization at cell surface, deuterated DPPC was used to prepare model vesicles, and small-angle neutron scattering was used to detect GSL microdomains. This methodology has been reasoned by Vogtt et al. to study the structure and distribution of microdomains in lipid vesicles [33]. After deuteration, the scattering from hydrophobic tail portions of DPPC were minimized. The scattering length density of Gb3 was calculated as 4.78 × 1011 cm−2; therefore, the changes of SANS curve in Figure 2B in/without the presence of Shiga toxin B subunit were attributed to the Gb3 inhomogeneous distribution in model membranes, and the scattering intensity reflected the shape and size of Gb3 on the surface of SUVs. It has been reported that the glycosphingolipids had a strong tendency to form segregated compositional domains in phospholipid bilayers [2,34,35,36]. Therefore, we hypothesized the Gb3 microdomains form elongated aggregates on the SUV surface, and fitted the scattering curves by the model-independent Guinier law for elongated objects (Equation (3)). The fitted results are shown in Figure 5. The fitting value of Gb3 radius of gyration (Rg) was 5.3 ± 0.6 nm (shown in Table S3), which gave evidence that the Gb3 itself could form nanometer-sized clusters on the model membrane. When introducing the Shiga toxin B subunits, the size of Gb3 clusters increased to 7.8 ± 0.7 nm (shown in Table S3), indicating that the toxin binding can change the corresponding lipid organization to form larger clusters. These phenomena accounted for the lipid-mediated membrane invaginations. Basically, the lipid domains formation was accompanied with the line tension occurrence between the domains and the rest of the lipid bilayer [11]. The local change in membrane shape (budding or invagination) can make a balance between the energy needed to bend the bilayer at lipid domains and the penalty paid by having a large contact surface that sets the scale of the bud [37]. This trade-off process is important for the engagement of viruses and toxins with host transmembrane proteins to enter cells. Lipid-based entry through the induction of membrane microdomains has been reported for SV40 [38], Shiga toxin [39], and Cholera toxin [40], and all these processes can subsequently induce tubular invaginations. In recent reviews, researchers claimed that it was the fluctuation force that might drive toxin clustering on model membranes and in cells [16,17]. The architecture of GSL was selected by convergent evolution to generate the membrane curvature for the clathrin-independent biogenesis of tubular endocytic pits. The schematic representation of STxB subunit induced changes of membrane invagination is shown in Figure 6. With the model membrane of Gb3-DPPC mixed SUVs, the results obtained with SAXS and SANS measurements evidenced that toxin binding could cause changes on membrane curvature, which will further induce compaction of glycolipid into larger domains and the negative curvature on the membrane through toxin-glycolipid clusters to enable changes of membrane thickness. The binding of toxins to cells alone was not sufficient to induce membrane deformation. It was the changes of membrane order, related with the protein clustering capacity, that were responsible for the membrane reorganizations.
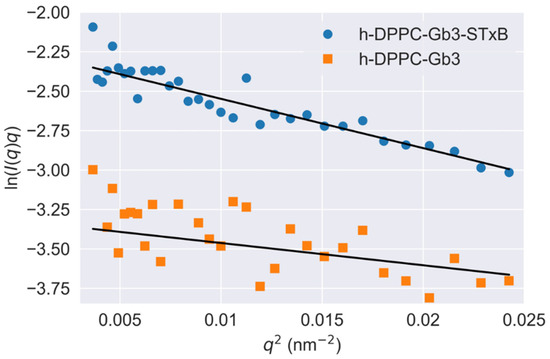
Figure 5.
Guinier plots (ln q I(q) vs. q2) on Gb3 reconstructed DPPC vesicle and Shiga toxin B subunit incubated with Gb3 reconstructed DPPC vesicle. The SUV were prepared as [Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1 for [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 0/1. Measurements were performed at T = 25 °C.
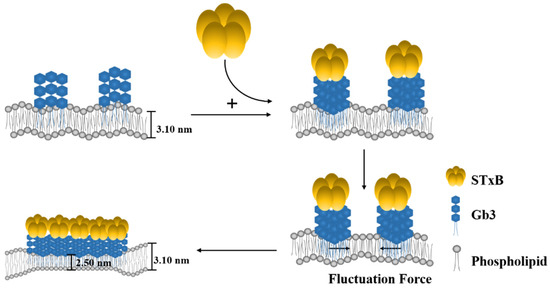
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of Shiga toxin B-subunit induced SUV membrane invagination and hypothesis on model membrane surface clustering. (1) For glycolipid Gb3 itself, it can form extremely high density clusters in nanometer size, and it only serves as connector between STxB subunit with membrane surface. (2) Toxin binding can cause inhomogeneous compaction of glycolipid into larger domains and induce the negative curvature on the membrane through toxin-glycolipid clusters to enable changes of membrane thickness.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, our results provided a practical method to quantify the connection between glycolipids lateral segregation and their involvement in toxin endocytosis process. It is the first time to reveal the mesoscopic distance change on SUV membrane thickness in the presence of proteins by SANS and SAXS. The observations presented here suggested that the tight mechanical coupling of STxB onto the membrane was required for toxin clustering, and the cluster size could regulate the extent of domain formation, which was expected to contribute to cellular, pathogenic and pharmaceutical drug delivery processes. Additionally, here in the present study, a novel reconstitution method was described to obtain purified physiological active pentamer STxB subunits. Compared with the classical Shiga toxin B subunit purification protocol proposed by Frédéric and Ludger, the method used in the present study is easier and can produce a large amount of recombinant proteins in a short time. In the future, more efforts will be focused on the improvement of this standardized small-angle scattering method to quantify mesoscopic membrane structural changes induced by protein-lipid interactions.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app11156965/s1, Figure S1: Characterization of the purified Shiga toxin B subunit. (A) Tricine-SAS-PAGE (Lanes M-1) and Western blot analysis (Lanes 2–3) of cytoplastic extracts of E. coli BL21 (DE3); (B) FPLC profile of Shiga toxin B-subunit, Figure S2: Small-angle scattering curves of the SUV samples of Gb3 and DPPC mixture ([Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1 illustrated with error bar. Measurements were performed at T = 25 °C. (A) small-angle neutron scattering curves of [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 1/0; (B) small-angle neutron scattering curves of [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 0/1, Figure S3: Fitting residuals of scattering for the [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 1/0 SUV sample using polydisperse three-shell model. The SUV were prepared as [Gb3]/[DPPC] = 0.1/1. Measurements were performed at T = 25 °C. (A) Empty DPPC vesicle; (B) Gb3 reconstructed DPPC vesicle; (C) Shiga toxin B subunit incubated with Gb3 reconstructed DPPC vesicle, Table S1: The size parameters of aggregates on SUV surface based on small-angle neutron scattering data on [h-DPPC]/[d-DPPC] = 0/1 experimental group using model-independent Guinier law fitting analysis, Table S2: The fitting parameters for scattering data used in model membranes. The reduced chi-square value is listed to prove the fitting fidelity, Table S3: The fitting parameters for scattering data used in Gb3 microdomains by the model-independent Guinier law for elongated objects with the assumption that the microdomains form elongated aggregates. The reduced chi-square value is listed to prove the fitting fidelity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.L. and R.Z.; methodology, S.T., H.Z., Y.L. and Y.Z.; Formal analysis, Q.T. and L.A.; validation, S.T. and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T., H.Z. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, N.L.; project administration, X.X.; supervision, A.Z. and N.L.; funding acquisition, Q.T., A.Z. and N.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the scientific research fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. U1832144, 21872051, 21573070), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy Science (grant No.2017319), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (21ZR1471600), Southwest University of Science and Technology (grant No. 18zx7108).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Tianfu Li (China Institute of Atomic Energy) and Vasyl M. Garamus (Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht) for assistance in small-angle neutron scattering measurements. We also thank Daniel Clemens of V16 SANS instrument at research reactor BERII of HZB and the MLZ and FRMII for allocation of neutron beamtime and for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hurley, J.H.; Boura, E.; Carlson, L.A.; Rózycki, B. Membrane budding. Cell 2010, 143, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, W.; Farris, D.; Mishra, S. Merging complexes: Properties of membrane raft assembly during lymphocyte signaling. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meer, G.; Sprong, H. Membrane lipids and vesicular traffic. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voeltz, G.K.; Prinz, W.A. Sheets, ribbons and tubules—How organelles get their shape. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furne, C.; Corset, V.; Herincs, Z.; Cahuzac, N.; Hueber, A.O.; Mehlen, P. The dependence receptor DCC requires lipid raft localization for cell death signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4128–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, A.; Russell, J.Q.; Rodgers, W.A.; Budd, R.C. Spatial differences in active caspase-8 defines its role in T-cell activation versus cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruthio, F.; Quadroni, M.; Ruegg, C.; Mariotti, A. Proteomic analysis of membrane rafts of melanoma cells identifies protein patterns characteristic of the tumor progression stage. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4733–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.; Mouritsen, O.G.; Anderson, R.G. Lipid rafts: At a crossroad between cell biology and physics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, M.T.; Mayor, S.; Parton, R.G. Molecules, mechanisms, and cellular roles of clathrin-independent endocytosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Mayor, S. Induced domain formation in endocytic invagination, lipid sorting, and scission. Cell 2010, 142, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Varma, R.; Sarasij, R.C.; Gousset, K.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Rao, M.; Mayor, S. Nanoscale organization of multiple GPI-anchored proteins in living cell membranes. Cell 2004, 166, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonny, B. Membrane deformation by protein coats. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynwar, B.J.; Illya, G.; Harmandaris, V.A.; Müller, M.M.; Kremer, K.; Deserno, M. Aggregation and vesiculation of membrane proteins by curvature-mediated interactions. Nature 2007, 447, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römer, W.; Berland, L.; Chambon, V.; Gaus, K.; Windscheigl, B.; Tenza, D.; Aly, M.R.E.; Fraisier, V.; Florent, J.C.; Perrais, D.; et al. Shiga toxin induces tubular membrane invaginations for its uptake into cells. Nature 2007, 450, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshkian, W.; Gao, H.; Arumugam, S.; Bechen, U.; Bassereau, P.; Florent, J.C.; Ipsen, J.H.; Hohannes, L.; Shillcock, J.C. Mechanism of Shiga Toxin Clustering on Membranes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassereau, P.; Jin, R.; Baumgart, T.; Deserno, M.; Dimova, R.; Frolov, V.A.; Bashkirov, P.V.; Grubmuller, H.; Jahn, R.; Risselada, H.J.; et al. The 2018 biomembrane curvature and remodeling roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casimir, H.B.G.; Polder, D. The Influence of Retardation on the London-van der Waals Forces. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Chen, X.; Guan, D.; Xu, J.; Wu, H.; Tong, P.; Zhang, M. Reconstituted Postsynaptic Density as a Molecular Platform for Understanding Synapse Formation and Plasticity. Cell 2018, 174, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.; lwase, J.; Hayakawa, T.; Koizumi, M.; Takahashi, H. Determination of asymmetric structure of ganglioside-DPPC mixed vesicle using SANS, SAXS, and DLS. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, N. Upgraded SSRF BL19U2 beamline for small-angle X-ray scattering of biological macromolecules in solution. J. Appl. Cryst. 2018, 51, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogtt, K.; Siebenburger, M.; Clemens, D.; Rabe, C.; Lindner, P.; Russina, M.; Fromme, M.; Mezei, F.; Ballauff, M. A new time-of-flight small-angle scattering instrument at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin: V16/VSANS. J. Appl. Cryst. 2014, 47, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breβler, L.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Thünemann, A.F. SASfit: A tool for small-angle scattering data analysis using a library of analytical expressions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 20, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armen, R.S.; Olivia, D.U.; Scott, E.F. Phospholipid component volumes: Determination and application to bilayer structure calculations. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, J.F.; Tristram-Nagle, S. Structure of lipid bilayers. Biochim. Bophys. Acta 2000, 1512, 159–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.; Takizawa, T. Intensive extrusion and occlusion of water in ganglioside micelles with thermal reversibility. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hayakawa, T.; Hirai, M. Hydration and thermal reversibility of glycolipids depending on sugar chains. Eur. Biophys. J. 2002, 31, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrljic, M.; Nishimura, S.Y.; Brasselet, S.; Moerner, W.E.; McConnell, H.M. Translational diffusion of individual class II MHC membrane proteins in cells. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2681–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Gowrishankar, K.; Bilgrai, S.; Ghosh, S.; Raghupath, R.; Chadda, R.; Vishwakarma, R.; Rao, M.; Mayor, S. Nanoclusters of GPI-anchored proteins are formed by cortical actin-driven activity. Cell 2008, 135, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Cheng, J.; Hirakawa, M.; Furukawa, K.; Kusunoki, S.; Fujimoto, T. Gangliosides GM1 and GM3 in the living cell membrane form clusters susceptible to cholesterol depletion and chilling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, S.J.; Muncke, C.; Parton, R.G.; Hancock, J.F. H-ras, K-ras, and inner plasma membrane raft proteins operate in nanoclusters with differential dependence on the actin cytoskeleton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15500–15505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorova, M.; Cheng, J.; Heberle, F.A.; Marquardt, D.; Rusinova, R.; Sanford, R.L.; Peyear, T.A.; Katsaras, J.; Feigenson, G.W.; Weinstein, H.; et al. Gramicidin Increases Lipid Flip-Flop in Symmetric and Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles. Biophy. J. 2019, 116, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogtt, K.; Jeworrek, C.; Garamus, V.M.; Winter, R. Microdomains in lipid vesicles: Structure and distribution assessed by small-angle neutron scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5643–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, W.; Smith, K. Properties of glycolipid-enriched membrane rafts in antigen presentation. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 25, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meer, G.V.; Vaz, W.L.C. Membrane curvature sorts lipids. Stabilized lipid rafts in membrane transport. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M. Lipid rafts take center stage in endothelial cell redox signaling by death receptors. Hypertension 2006, 47, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Julicher, F.; Lipowsky, R. Domain-induced budding of vesicles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 2964–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, H.; Romer, W.; Smith, A.E.; Bacia, K.; Dmitrieff, S.; Chai, W.; Mancini, R.; Kartenbeck, J.; Chambon, V.; Berland, L.; et al. GM1 structure determines SV40-induced membrane invagination and infection. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windschiegl, B.; Orth, A.; Romer, W.; Berland, L.; Stechmann, B.; Bassereau, P.; Johannes, L.; Steinem, C. Lipid reorganization induced by Shiga toxin clustering on planar membranes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacia, K.; Schwille, P.; Kurzchalia, T. Sterol structure determines the separation of phases and the curvature of the liquid-ordered phase in model membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3272–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).