Abstract
Pain is a common distress in chronic inflammatory diseases, and etoricoxib (ETB) is frequently used in its management. It possesses fewer adverse effects when compared with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In the present study, ETB-loaded nanoemulsion (ETB-NE) was formulated and optimized. Eucalyptus oil, Tween 20, and PEG 200 were chosen as the oil, surfactant, and co-surfactant, respectively. The formulation was optimized using the Box–Behnken design. The optimized ETB-NE contained oil, Smix, and water in concentrations of 11.5, 38, and 50% respectively. It had droplet size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential values of 179.6 ± 4.21 nm, 0.373 ± 0.02, and −10.9 ± 1.01 mV, respectively. The optimized ETB-NE sample passed the thermodynamic stability and dispersibility tests. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed the spherical morphology of the NE droplets. The ETB-NE showed a biphasic drug release pattern and released 85.3 ± 1.8% of ETB at 12 h. The ETB-NE was formulated into nanoemulsion gel (NEG) by using 1% carbopol 934. ETB-NEG was characterized for pH, viscosity, drug content, and percentage entrapment efficiency. During in vitro permeation studies, the apparent permeability coefficient value was 0.072 cm−2 h−1 for ETB-NEG, while it was only 0.047 cm−2 h−1 for the ETB gel. The skin histopathology study results confirmed that the ETB-NEG formulation was non-irritant and safe for topical use. The maximum possible analgesia observed for ETB-NEG was significantly high (p < 0.05) with a value of 47.09% after 60 min. Similarly, a formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain study in rats also demonstrated higher analgesia for the ETB-NEG, with % inhibition values of 37.37 ± 5.9 and 51.95 ± 4.4 in the acute and late phases, respectively. Further, ETB-NEG showed 78.4 ± 3.5% inhibition at 8 h in the in vivo anti-inflammatory testing by rat paw edema method. The ETB-NEG was found to enhance the in vivo analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of ETB. The study results could stimulate further studies in this area for establishing a clinically successful NEG formulation of ETB.
1. Introduction
Pain is a common distress in chronic inflammatory diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are examples of such diseases. The therapy of such diseases depends on the efficacy, safety, and potency of the drug [1]. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are recommended for such diseases. Further, it has been observed that cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-selective NSAIDs are better tolerated than and nonselective NSAIDs and have lower side effects [2]. Etoricoxib (ETB) is a highly selective COX-2 inhibitor and has been found to possess fewer adverse effects than other popular NSAIDs, such as indomethacin and diclofenac [3]. Meanwhile, ETB has higher analgesic activity than celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Further, it has about 40% lower gastrointestinal adverse effects compared to other NSAIDs [4]. ETB does not inhibit the production of prostaglandin in the stomach and hence causes the fewer side effects [5]. Importantly, ETB has both anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, and is very useful in chronic inflammatory diseases. Thus, it is useful against rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and acute gouty arthritis [6]. Further, ETB is well tolerated in chronic inflammatory diseases. The therapeutic efficacy of ETB in clinical trials also favors its use in such diseases [7].
The gastrointestinal ulcers caused by ETB pose a major concern in its oral delivery. Therefore, topical delivery of ETB could be a good choice for the enhancement of its analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities, while decreasing the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse effects [8]. Further, topical delivery can avoid gastrointestinal adverse effects of drugs by directly delivering the drugs to the systemic circulation. Interestingly, the utility of nanoemulsions (NEs) and nanoemulsion gels (NEGs) is well established for the topical delivery of drugs [9,10]. The small particle size and reduced interfacial tension are some of the advantages of NE in promoting skin permeation. The oil phase helps to solubilize poorly water-soluble drugs. Natural terpene-containing volatile oils have good skin permeability enhancement potential [11]. Eucalyptus oil has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties and it is a good choice for topical delivery of ETB [12]. Eucalyptus oil mainly contains α-pinene, p-cymene, aphellandrene, 1,8-cineole, c-terpinene, and limonene [13]. It is reported that 1,8-cineole enhances skin permeability of both lipophilic and hydrophilic compounds [14].
Formulation of NE to NEG is needed to render it suitable for application to the skin surface. The thixotropic effects of NEG, due to the presence of the thickening agents, provides product attributes that are appropriate for a topical drug delivery vehicle [15]. Further, modulation of the skin permeation effects of NE is possible by its conversion to NEG. Carbopol polymers are useful for such a purpose. By selecting the appropriate concentration of carbopol 934, it is possible to get a desired topical delivery system [16].
Commercially available topical gels and creams of ETB are useful in the management of pain and inflammation. Thus, it was anticipated that a NEG formulation would further enhance the therapeutic effect of ETB. Interestingly, a reported study had made such an effort to develop a NEG formulation for ETB [17]. Nevertheless, this reported study used Triacetin as the oil phase and did not explore the possibility of using oils, such as eucalyptus oil. Thus, in the present study, we aimed to develop a NEG formulation of ETB for enhanced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects by using eucalyptus oil as the oil phase. Moreover, the present study also aimed to evaluate the effects of formulation factors on ETB-loaded nanoemulsion (ETB-NE), which were not explored in the reported study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
ETB was received from Jamjoom Pharmaceuticals, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Eucalyptus oil was purchased from Allin Exporters, Noida, India. Tween 20, polyethylene glycol 200 (PEG 200), and carbopol 934 were from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA. All other chemicals used in the study were of analytical reagent grade.
2.2. Solubility of ETB in Formulation Components
The solubility of ETB in eucalyptus oil (oil phase), Tween 20 (surfactant), and PEG 200 (co-surfactant) was determined in triplicate by shaking excess of ETB in these NE formulation components at 37 ± 1.0 °C for 72 h. Then, they were centrifuged, filtered, and 5000 times diluted with methanol. The diluted samples were analyzed at 283 nm by UV–Vis spectrophotometry (UV 1700, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan).
2.3. Formulation and Optimization of Etoricoxib-Loaded NE (ETB-NE)
In the present study, a three-factor three-level BBD was selected. Percent concentrations of eucalyptus oil, Tween 20, and PEG 200 were the independent factors, and the particle size (PS) and polydispersity index (PDI) were chosen as the dependent factors. Sixteen experiments with five center points suggested by the software were performed (Table 1).

Table 1.
Nanoemulsion trials and the independent factors.
NEs were prepared by the spontaneous emulsification technique. In brief, ETB (10 mg) was added to the eucalyptus oil. To this drug solution, the addition of Smix (prepared by mixing Tween 20 and PEG 200) was carried out. The resultant mix was subjected to vortexing (300 rpm) for 0.5 h. This mixture was then added to the aqueous phase (distilled water) in small portions under stirring to form the NE. Vortexing was continued for another 0.5 h.
The NE formulations were analyzed for mean PS and PDI after 250 times dilution with distilled water using a Malvern zetasizer (NanoZS4700, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK). Numerical optimization was carried out for the optimization of ETB-NE formulation and the minimum values of PS and PDI were set as the goal.
2.4. Thermodynamic Stability and Dispersibility Studies of the Optimized ETB-NE
The thermodynamic stability of ETB-NE was tested by a reported method (Table 2) [18]. In addition, the dispersibility test was also conducted with the optimized ETB-NE according to a reported procedure [19]. Briefly, 1 mL of ETB-NE was added to 500 mL of water at 37 ± 0.5 °C in a rotating paddle apparatus at 50 rpm and checked for clarity.

Table 2.
Thermodynamic stability and dispersibility testing of ETB-NE and evaluation criteria.
2.5. Characterization of Optimized ETB-NE
2.5.1. Particle Size Analysis and Zeta Potential Determination
The optimized ETB-NE was analyzed in triplicate for mean PS and PDI, after 250 times dilution with distilled water, using a Malvern zetasizer (NanoZSP, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK).
2.5.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Briefly, one drop of the ETB-NE sample was 100 times diluted with distilled water and stained with 1% phosphotungstic acid and imaged (TEM; H 7500, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
2.5.3. Refractive Index and Percentage Transmittance of ETB-NE
The refractive index of the ETB-NE sample was estimated in triplicate at 25 °C using an Abbes type refractometer. One mL of ETB-NE was mixed with methanol and analyzed at 283 nm for the determination of percentage transmission.
2.6. Preparation of ETB-NEG Using Optimized ETB-NE
ETB-NEG was prepared using carbopol 934. A 1% w/w dispersion of carbopol 934 was prepared in distilled water. Then, optimized ETB-NE was added in small portions to the carbopol 934 dispersion during stirring. The pH of the dispersion was adjusted to 5.5 with triethanolamine to obtain the ETB-NEG. The blank NEG (without drug) was prepared using same composition (eucalyptus oil (11.5%), Tween 20, PEG 200 (Smix 38%), water (50%) and 1% carbopol 934) and procedure. The ETB gel was prepared by dispersing ETB in 1% carbopol 934.
2.7. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
A dialysis membrane was cut and tied onto a Franz diffusion apparatus with phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.4) in the receptor compartment. The experiment was carried out at 37 ± 0.5 °C and 100 rpm. The upper surface of the dialysis membrane was considered as the donor compartment. The ETB-NE sample (0.5 mL) was applied on the membrane and the samples were taken at time intervals of 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 12 h, and the samples were analyzed using UV at 283 nm. The comparison of in vitro release profiles of ETB and ETB-NE was evaluated by determining the similarity factor (f2) recommended for such a purpose [20].
2.8. pH, Viscosity, Drug Content, and Percentage Entrapment Efficiency of ETB-NEG
The pH of the ETB-NEG sample was determined in triplicates at 25 °C. The viscosity of the ETB-NEG sample was estimated using a Brookfield viscometer with a spindle no. 00 at 25 ± 0.5 °C. The drug content and percent entrapment were determined following a reported procedure with slight modification [21]. Briefly, after 2-times dilution with methanol, the sample was subjected to centrifugation (3500 rpm) for 15 min and analyzed by UV method.
2.9. In Vitro Skin Permeation Studies with ETB-NEG
A weighed quantity of ETB-NEG and the ETB gel (containing 10 mg of ETB) were spread on the pre-treated abdominal skin of a Wistar rat placed on the donor compartment of the Franz diffusion cell. The diffusion area was 1.13 cm2 and the volume of receptor chamber was 10 mL. The study samples (0.5 mL) were taken at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 h. The samples were then filtered (0.45 μm filter) and analyzed for ETB content at 245 nm. The steady-state flux was calculated from the slope of plot obtained between a cumulative amount of drug permeated/unit area (mg/cm2) of across skin surfaces versus time (h). The apparent permeability (Papp) was determined as the ratio of the flux and the amount of ETB taken in the donor chamber. The enhancement ratio was also determined as the ratio of flux observed for ETB-NEG and ETB gel [22].
2.10. In Vivo Studies with ETB-NEG
The animal protocol was approved by the animal ethical committee of the Faculty of Pharmacy, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia (PH-1442-38).
2.10.1. Analgesic Activity
Hot plate and formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain methods were employed for the evaluation of the analgesic activity. Wistar rats were used in the studies to test the efficacy of the ETB-NEG.
Hot Plate Method
ETB-NEG, blank NEG, and ETB gel were tested for analgesic activity using the hot plate method [23]. Animals were divided into four groups with four rats in each animal group (n = 4). The reaction time by rats towards thermal pain was tested here. Paw-licking or jumping responses are noted after placing the rats at 55 °C (hot plate). The reaction time after 0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of treatment was recorded. The maximum reaction time was set at 0.45 min. The maximum possible analgesia (MPA) was estimated using Equation (1).
Formalin-Induced Paw Licking Test
Animals were divided into four groups with four rats in each animal group (n = 4). Group I was control group, group II was treated with ETB gel, group III was treated with ETB-NEG, and group IV was treated with blank NEG. After 30 min of applying the samples on the dorsal surface of the right hind paw, formalin (20 μL of 5%) was administered by subcutaneous route. The rats were observed for 5 min immediately after formalin injection (acute phase) and after 20 min after formalin injection (late phase) [24]. The percentage of inhibition of licking was calculated using Equation (2).
2.10.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
The study was done by the carrageenan-induced rat paw edema method. The groups (with four Wistar rats each) I, II, and III were treated with ETB gel, ETB-NEG, and blank NEG. Group IV was administered 1% w/w carrageenan suspension and considered as the positive control. After 30 min of administration of formulations, paw edema was caused by the injection of carrageenan (0.1 mL,1% w/w) in distilled water to the right hind paws of rats. Changes in paw volume were calculated at 1, 2, 4, and 8 h. Percentage inhibition of paw edema was then estimated [25].
2.10.3. Histopathology of Treated Rat Skin
To negate topical toxicity and skin irritation of all treated formulations, histopathology studies were carried out on Wistar albino rats (200–300 g). The dorsal surface of the rat after removal of hair was used in the study. The rats were grouped into four, with three rats in each group. Group I was the control without any treatment, Group II was administered with 0.8% v/v aqueous solution of formalin and was considered as the positive control, Group III was administered with a blank NEG, and Group IV was subjected to treatment with the ETB-NEG. Then, 200 mg of formulations were topically applied to the hairless skin area (1 cm2) and were observed after 24 h for dermal reactions such as erythema and edema [26]. Afterward, the skin was removed and washed with phosphate buffer and stored in formalin solution at 4°C. The preserved skin tissues were sectioned using a microtome and further stained with an eosin and hematoxylin dye for visualization under microscopy.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was done by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test; a p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility of ETB in Formulation Components
The solubility of ETB in eucalyptus oil, Tween 20, and PEG 200 was found to be 78.9 ± 3.20, 62.10 ± 3.5, and 58.5 ± 2.0 mg/mL, respectively. The solubility of ETB in eucalyptus was much higher compared to its solubility reported in the arachis, castor, mustard, olive, sesame, and sunflower oils [27]. Thus, eucalyptus oil was chosen as the oil phase for the formulation of ETB-loaded nanoemulsion. In the case of Tween 20, it was already successfully used as a surfactant for nanoemulsification of eucalyptus oil [28]. Further, the solubility of ETB in Tween 20 was good. The solubility of ETB in PEG 400 was around 2.2 mg/mL in a previous report; however, the study was carried out at 25 ± 1.0 °C for 24 h. In addition, this reported study suggested that hydrophobic interactions were responsible for higher solubility in PEG [29]. The higher solubility of ETB in PEG in the present study could be attributed to the higher temperature (37 ± 1.0 °C) and time (72 h) employed for the solubility determination. Further, the present study used PEG 200 instead of the reported PEG 400. It is established that PEGs with higher molecular weights have higher hydrophilicity and vice versa [30]. Conversely, low molecular weight PEGs have more hydrophobicity. Thus, PEG 200 with a lower molecular weight than PEG 400 has better hydrophobic interactions with ETB, resulting in higher solubility. Interestingly, this argument can be easily justified by the reported higher solubility of ETB in PEG 400 than in PEG 600 [31].
3.2. Formulation and Optimization of Etoricoxib-Loaded NE (ETB-NE)
The formulation and optimization of ETB-NE were carried out using a three-factor, three-level BBD. The responses obtained for various NE formulation trials are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The responses obtained (observed and predicted values) for various NE formulation trials.
A two-factor interaction (2FI) model was suggested for PS by the software based on the data of the trials performed. The 2FI model was significant with a p-value < 0.0001. The lack of fit was not significant, and thus the model was acceptable. The predicted and adjusted R-squared values of 0.9058 and 0.9664, respectively, were comparable. Further, the observed and fitted values for the PS were in good agreement with each other (Table 3).
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) data of the model is provided in Table 4. From the data, it was seen that only two independent factors had a significant influence on the particle size of NE droplets. The oil percent and Smix percent had a highly significant (p-value < 0.0001) effect on the particle size.

Table 4.
ANOVA data for PS of ETB-NE formulations.
The polynomial equation suggested by the software for PS is provided in Equation (3). From the polynomial equation for PS, we can conclude that an increase in oil percent increases the particle size of NE. Meanwhile, an increase in Smix percentage will decrease the PS of NE. Among these, the higher magnitude for the regression coefficient for the factor B (Smix percent) indicated that the effect of Smix percentage is more on the PS of NE.
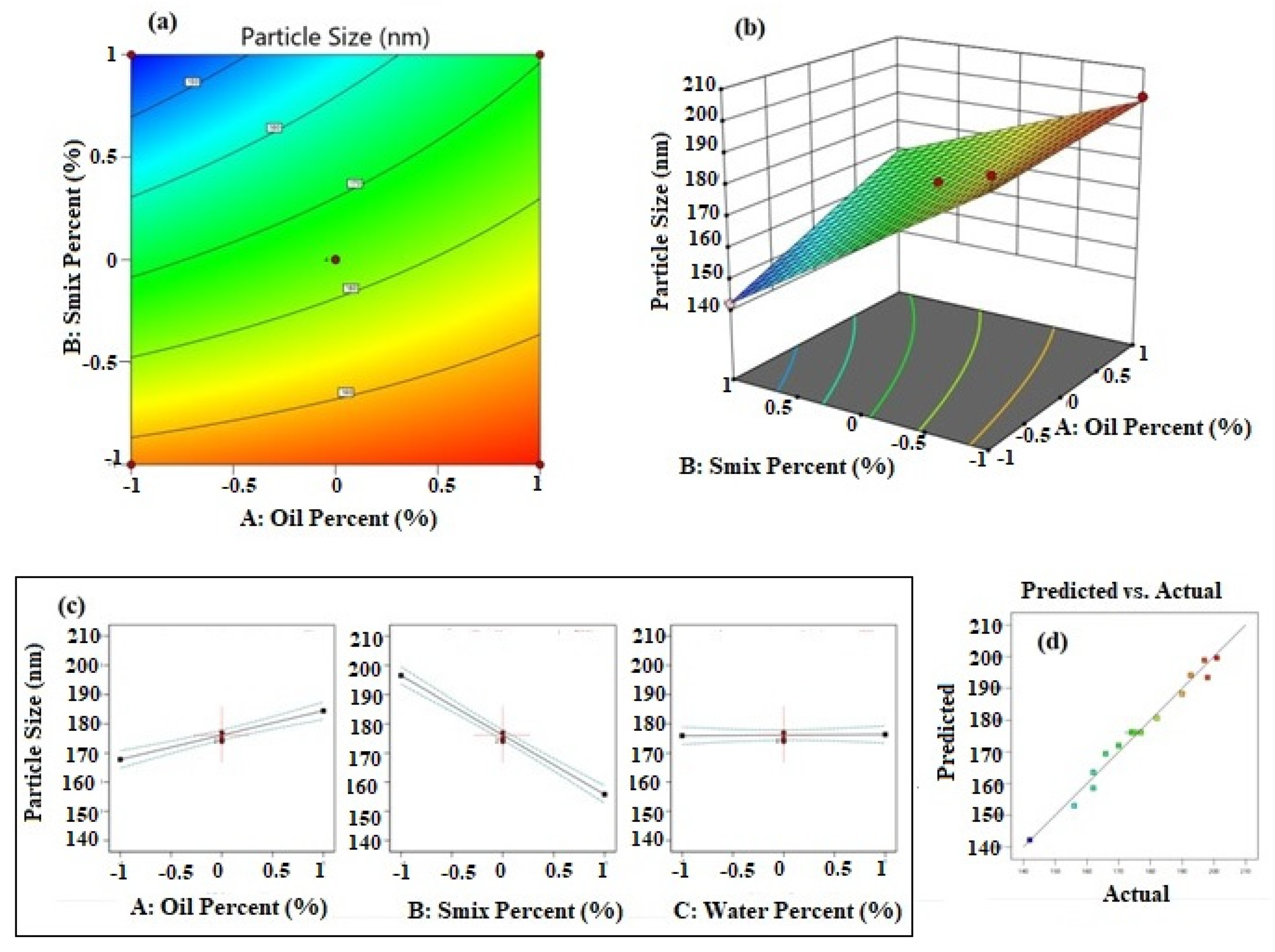
PS = +176.16 + 8.35A − 20.34B + 0.2125C + 5.25AB − 4.00AC + 2.58BC
Figure 1a shows the contour plot for data of particle size. It was observed that the iso-value curves of the contour plot show more changes on increasing the Smix percentage. This result was in concurrence with the inference from the polynomial equation. Further, the elevation of the response surface was more towards the axis of oil percentage and less towards the axis of Smix percentage (Figure 1b). The individual effects of the factors (Figure 1c) also confirmed that higher values for oil percentage increase PS and higher values for Smix percentage decrease PS. It was also observed that the water percentage did not influence the PS of NE. The predicted versus actual plot shown in Figure 1d shows a good prediction power of the design model.
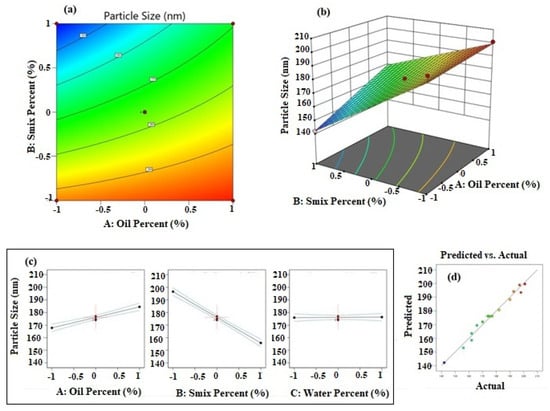
Figure 1.
Results of analysis of data of particle size; (a) contour plot, (b) response surface plot, (c) individual factor effects, and (d) predicted versus actual plot.
In the case of PDI, a quadratic response surface model was suggested by the software and the model was significant with a p-value < 0.0001. The lack of fit was not significant, and thus the model was acceptable for further use in optimization. The predicted and adjusted R-squared values of 0.9453 and 0.9700, respectively, were in reasonable agreement. Further, the observed and fitted values for the PDI were in good agreement with each other (Table 3).
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) data of the model for PDI is provided in Table 5. From the data, it was seen that oil percentage, Smix percentage, water percentage, A2, B2, and C2 were significant terms influencing the PDI value.

Table 5.
ANOVA data for PDI of ETB-NE formulations.
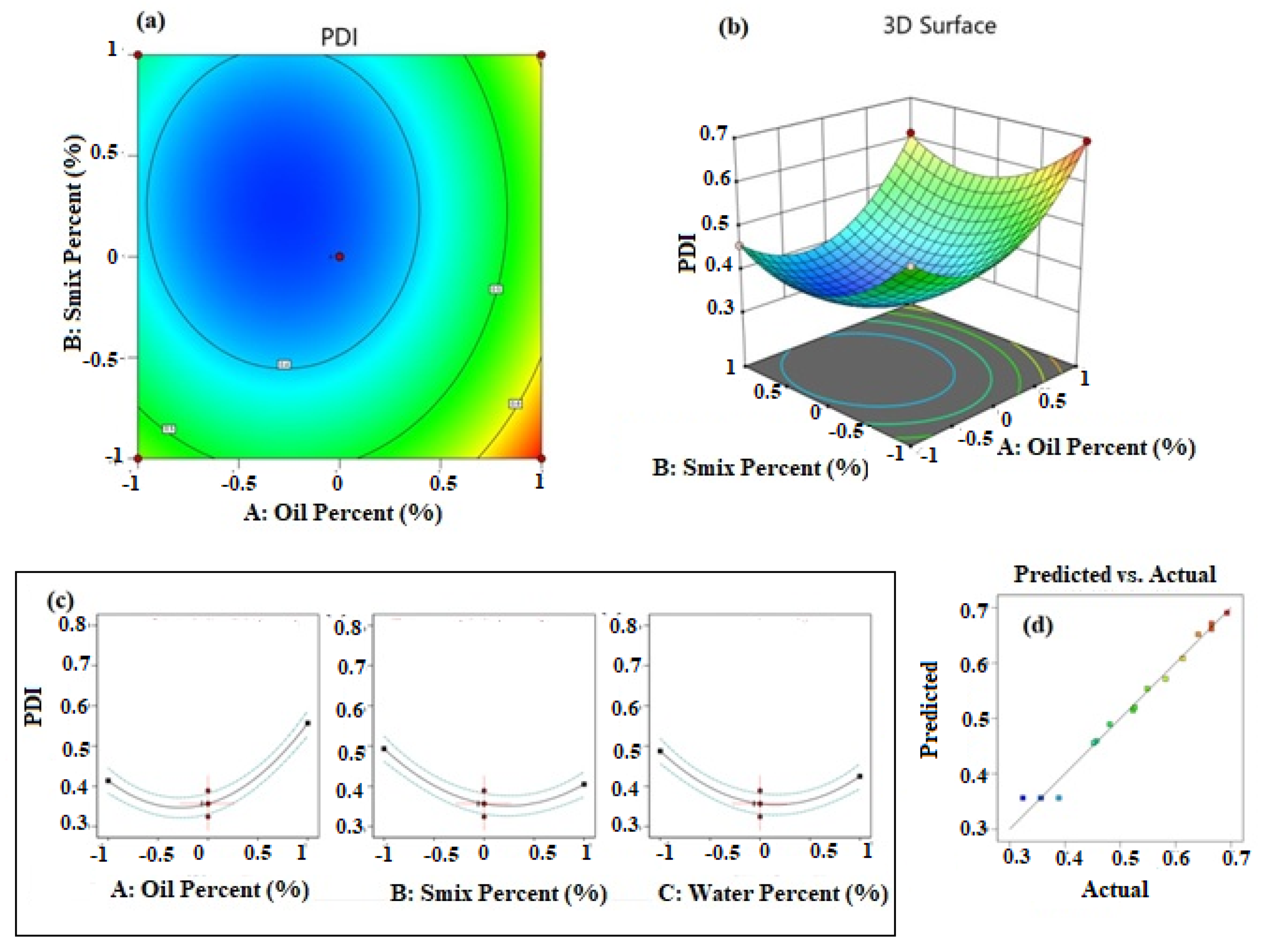
The polynomial equation suggested by the software for PDI is provided in Equation (4). The equation revealed that the influence of independent factors on the PDI was in the order oil percentage > Smix percentage >water percentage. The significant effects of A2, B2, and C2 have contributed towards the fitting of the PDI data to a quadratic polynomial equation.
PDI = +0.3565 + 0.0715A − 0.0441B − 0.0314C + 0.0030AB + 0.0265AC + 0.0468BC + 0.1289A2 + 0.0926B2 + 0.0996C2
The influence of the independent factors is presented in Figure 2. The contour (Figure 2a) and response surface (Figure 2b) plots demonstrate data fitting a quadratic polynomial equation. The iso-value curves are circular in the contour plot and the response surface has a depression towards the middle of the plot. These results indicated that the PDI value decreases towards the mid-value of the selected range of percentage of oil, Smix, and water. This was further confirmed by the individual effect plots for the independent factors and is shown in Figure 2c. Further, the predicted and actual values were in a good linear relationship as observed in the plot shown in Figure 2d, and confirmed a high degree of prediction ability of the selected quadratic response surface model.
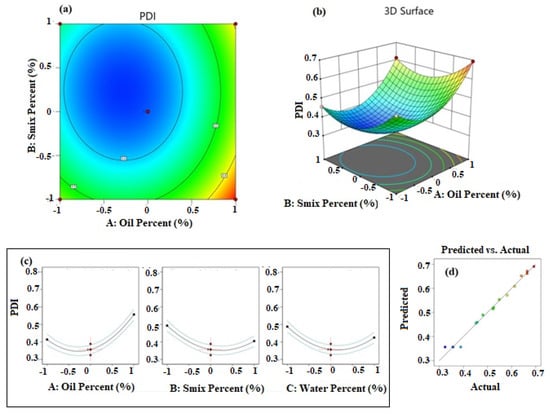
Figure 2.
Results of analysis of data of PDI; (a) contour plot, (b) response surface plot, (c) individual factor effects, and (d) predicted versus actual plot.
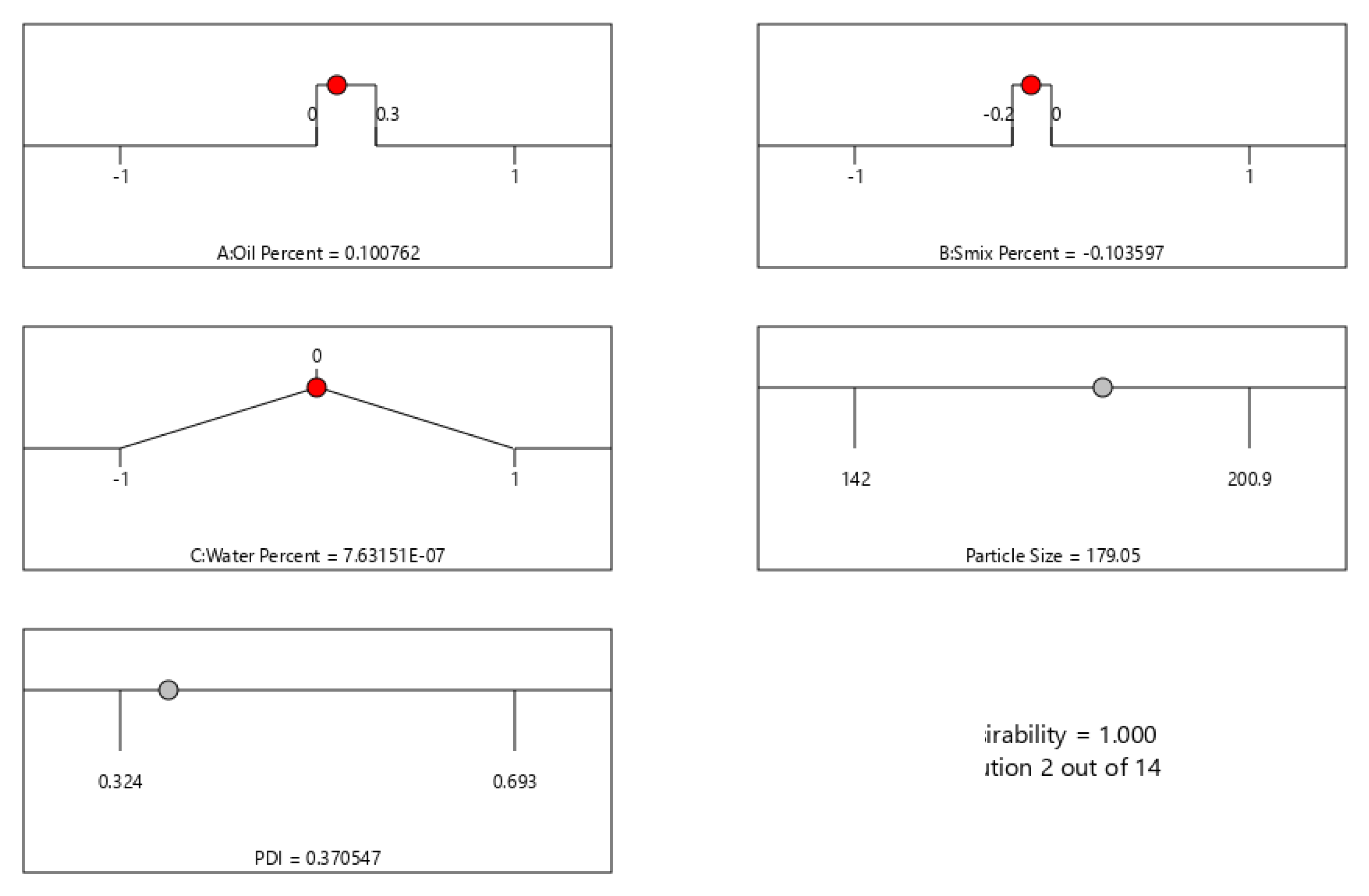
The optimized formula and the predicted responses are shown in Figure 3. Minimum values for PS and PDI were set as the goal for numerical optimization. The desirability was 1 for the suggested formula with 11.5% oil, 38% Smix, and 50% water. The predicted PS and PDI for the suggested optimum formula were 179.05 nm and 0.371, respectively.
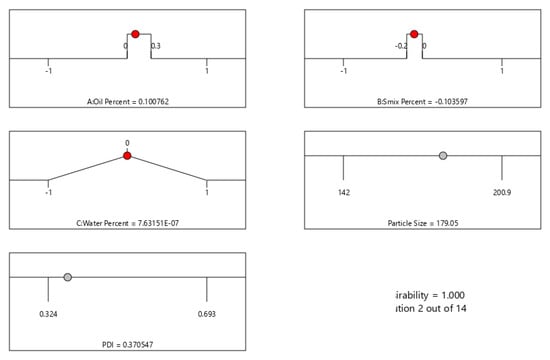
Figure 3.
Numerical optimization data for ETB-NE by Box–Behnken design, showing the optimized values for independent factors and predicted values for the PS and PDI.
3.3. Thermodynamic Stability and Dispersibility Studies of the Optimized ETB-NE
Thermodynamic stability and good physical stability are specific advantages of nanoemulsions [32,33]. The thermodynamic stability of the ETB-NE was confirmed as it passed the heating–cooling cycle, centrifugation, and freeze–thaw cycle test. No phase separation, creaming, or cracking was observed with ETB-NE. Further, ETB-NE was clear after dispersibility testing, and thus it passed the dispersibility test too.
3.4. Characterization of Optimized ETB-NE
3.4.1. Particle Size Analysis and Zeta Potential Determination
The droplet size of ETB-NE was found to be 179.6 ± 4.21 nm with a PDI value of 0.373 ± 0.02. It has been demonstrated that eucalyptus oil nanoemulsion with polysorbate as a surfactant can yield droplet size of 2.27–2771.00 nm, and with a PDI value range of 0.256–1.000, depending on the eucalyptus oil concentration and the ratio of eucalyptus oil with polysorbate [34]. Further, the PDI value of the prepared ETB-NE was low enough for considering it as a monodisperse system. Thus, the observations in the present study were in concurrence with previous studies [35]. Further, the values of both droplet size and PDI were very close to their predicted values during numerical optimization. The zeta potential value was −10.9 ± 1.01 mV for the ETB-NE and was in good agreement with a reported value of −9 mV for eucalyptus oil nanoemulsion [35].
3.4.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
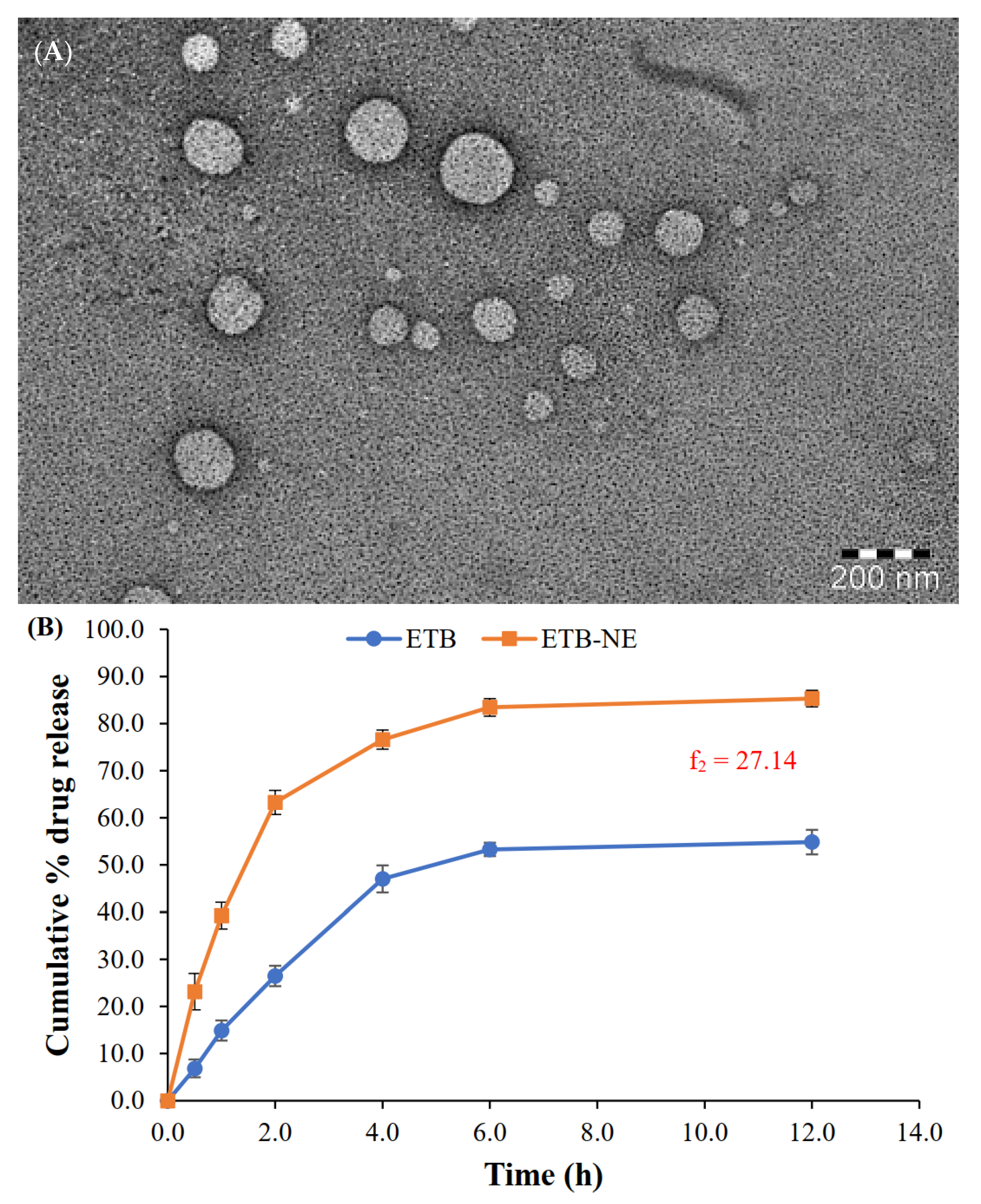
The TEM image of the optimized ETB-NE (Figure 4A) shows spherical morphology with a droplet size of less than 200 nm. The droplet size analysis also provided similar results. The morphology of a reported eucalyptus oil NE was comparable to that observed in the present study [35]; however, the ETB-NE has a smaller droplet size compared to that observed in this reported work.
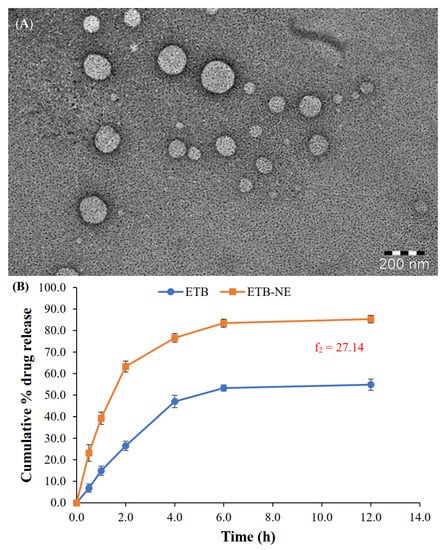
Figure 4.
(A) TEM image of ETB-NE. (B) In vitro drug release profiles from the aqueous dispersion of ETB and ETB-NE (f2 = 27.14).
3.4.3. Refractive Index and Percentage Transmittance of ETB-NE
The refractive index of value provides a measure of the easiness with which light can pass through it. Thus, any refractive index value near to water (the dispersion medium), indicates the transparent nature of the NE [36]. In the present study, the refractive index of the ETB-NE was found to be 1.39 ± 0.02 at 25 °C. This value is very close to the refractive index of water at 25 °C, i.e., 1.3329 [37]. Considering the observed transparency of the prepared ETB-NE, this value was in line with expectations. Meanwhile, the refractive index value near that of water indicated the possibility of a high percentage transmittance for the ETB-NE. As expected, the percentage transmittance observed of ETB-NE was 98.16 ± 0.22%. Further, this high percentage transmittance value was in agreement with reported values for NEs [38].
3.5. In Vitro Drug Release from ETB-NE
The in vitro release study results (Figure 4B) showed a significant enhancement of ETB release upon formulation to ETB-NE. The ETB-NE showed a biphasic ETB release pattern. At the end of 2 h, 63.3 ± 2.6% ETB release occurred from ETB-NE. Meanwhile, only 26.5 ± 2.2% ETB was released from free ETB. Thus, initially, the ETB release from the aqueous dispersion was significantly lower. The ETB release from ETB-NE reached 85.3 ± 1.8% at the end of 12 h. However, the ETB could release only a maximum of 54.8 ± 2.6% at the end of 12 h. This type of substantial enhancement of release or dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs from NE is widely reported and explained [38]. The small droplet size of NE and the presence of a surfactant/co-surfactant system are some of the accepted reasons for this drug release enhancement. The recommended method of comparison of in vitro drug release profiles by USFDA is the use of similarity factor (f2). An f2 value below 50 indicates dissimilar release profiles. Thus, the f2 value of 27.14 observed in the present study indicated a significant difference between the in vitro release profiles of ETB and ETB-NE.
3.6. pH, Viscosity, Drug Content, and Percentage Entrapment Efficiency of ETB-NEG
ETB-NEG was prepared and evaluated for pH, viscosity, drug content, and percentage entrapment efficiency. The pH of the prepared ETB-NEG was 5.53 ± 0.32 and was in good match with that of the skin acid mantle [38]. Thus, any pH-related skin irritation may be precluded from the prepared ETB-NEG. Meanwhile, the viscosity of the ETB-NEG was 572.9 ± 3.45 cps. This value was in good agreement with the viscosity (504 ± 21.4 cps) of a reported curcumin-loaded NEG for wound healing application [39].
The drug content was determined to be 96.54 ± 1.26%, whereas the entrapment efficiency was 93.18 ± 1.69%. The drug content is a measure of drug loading and can influence the amount reaching the systemic circulation. It can also influence the drug release pattern from the NEG. The drug content near to 100% can be expected in the formulations such as NE and NEG. Low chances of drug loss are responsible for such high drug loading behavior. The entrapment efficiency is also influenced by the drug loading and drug content. Therefore, the high entrapment efficiency observed for ETB-NEG is justified. Most of the reported NEG formulations provide such high values for drug content and entrapment efficiency [38,39].
3.7. In Vitro Skin Permeation Studies with ETB-NEG
Comparative studies are widely reported for establishing the efficiency of NEG formulations over conventional ETB gel formulations [22,38]. Therefore, it was imperative in the present study to show that the developed ETB-NEG was superior to ETB gel in terms of in vitro permeation. The in vitro skin permeation study evaluated the permeation of ETB through rat skin when presented as ETB-NEG in comparison to ETB gel formulation. The permeation was evaluated in terms of flux, Papp, and enhancement ratio [40,41]. The flux of ETB was found to be 0.72 ± 0.03 and 0.47 ±0.04 µg cm−2 h−1 for ETB-NEG and ETB gel, respectively. Thus, the ETB flux from ETB-NEG was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that from ETB gel. This highlighted the importance of the developed ETB-NEG formulation. In consensus with the flux, the Papp value was higher for ETB-NEG compared to ETB gel. The Papp value was 0.072 cm−2 h−1 for ETB-NEG, while it was only 0.047 cm−2 h−1 for ETB gel. Thus, the enhancement ratio of 1.53 was obtained for ETB-NEG. Overall, the permeation studies confirmed the effectiveness of the ETB-NEG formulation over the ETB gel in the ability to deliver the drug across the skin.
3.8. In Vivo Studies with ETB-NEG
3.8.1. Analgesic Activity
The analgesic effect of the ETB-NEG was studied using the hot plate and formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain methods.
Hot Plate Method
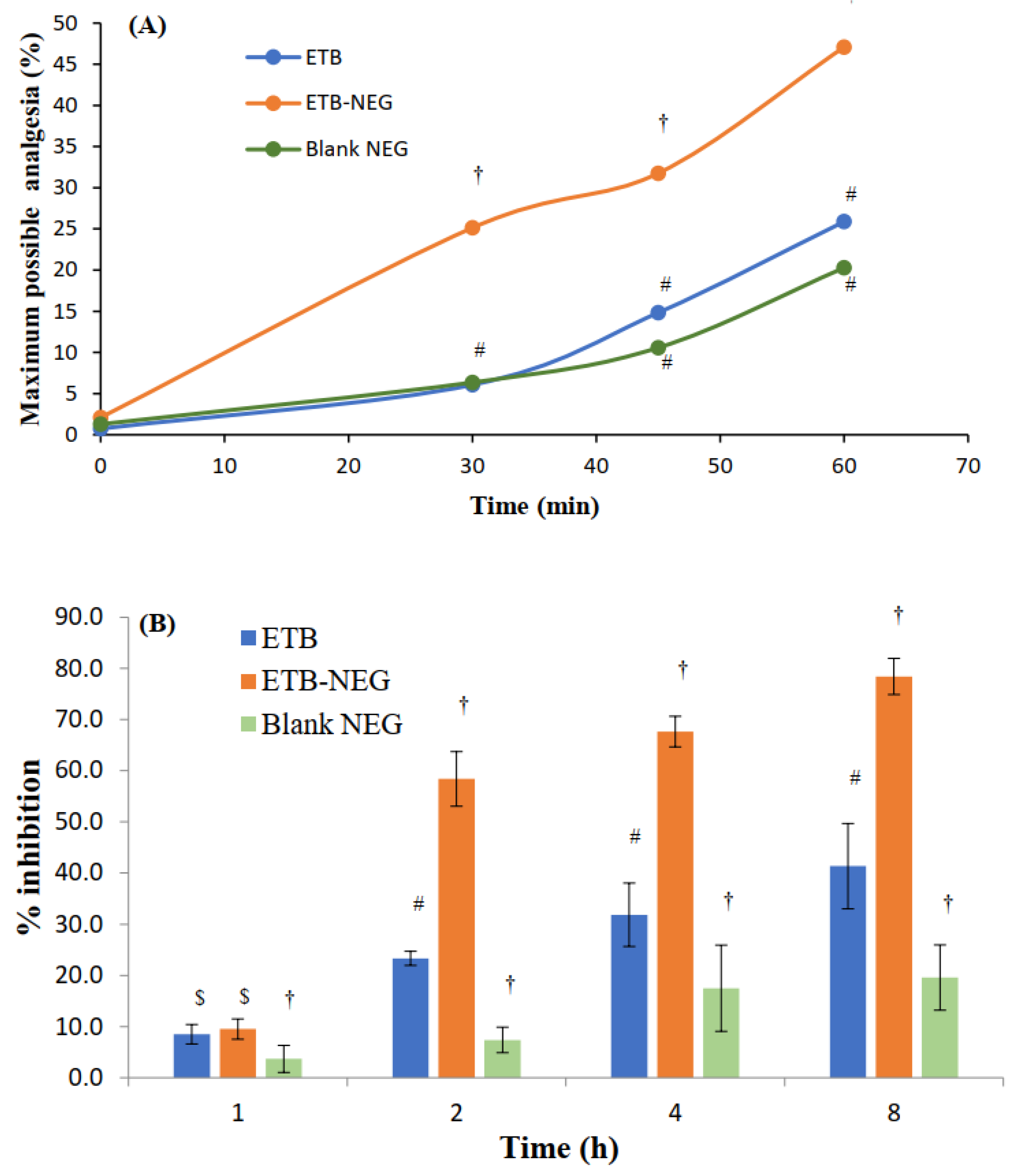
The hot plate method is suitable for the evaluation of centrally-acting analgesics [23]. The maximum possible analgesia (MPA) was determined to evaluate the analgesic effect in the hot plate method. The results showed a significant enhancement of MPA by the ETB-NEG compared to blank NEG and ETB gel (p-value < 0.05) (Figure 5A). Higher skin permeation of the drug when delivered using NEG formulation can be attributed to the high value of MPA for the ETB-NEG sample. The MPA for the ETB-NEG sample reached a value of 47.09% after 1.0 h. Meanwhile, it was noted that the ETB gel showed a low MPA value of 25.89% after 1.0 h. Surprisingly, the effect of ETB gel and blank NEG was similar at all time points (p-value > 0.05). The MPA values for blank NEG were very close to those for ETB gel at 45 and 60 min, and were without any statistically significant difference (p-value > 0.05). The use of eucalyptus oil as the oil phase could have produced such a result. It is established that eucalyptus oil nanoemulsion stabilized by surfactant micelles can produce an analgesic effect [42]. Thus, the analgesic effect of blank NEG is justified.
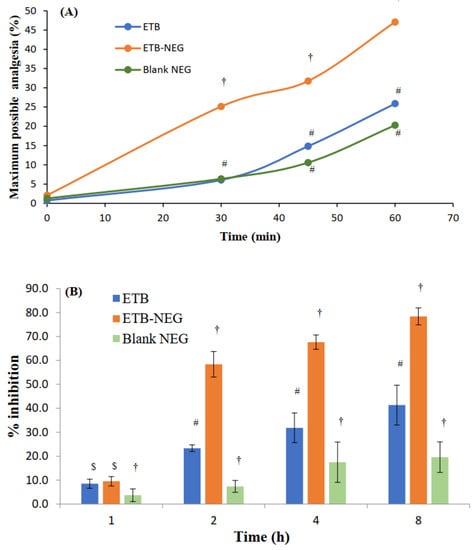
Figure 5.
(A) Maximum possible analgesia (MPA) at time intervals of 0, 30, 45, and 60 min after treatment with ETB gel, ETB-NEG, and blank NEG. (B) Anti-inflammatory effects of ETB, ETB-NEG, and blank NEG samples in carrageenan-induced paw edema rats (Statistical inferences: †, p < 0.05, compared to ETB; #, p < 0.05, compared to ETB-NEG; $, p < 0.05, compared to blank NEG; ns, p > 0.05, not significant with any group).
Formalin-Induced Paw Licking Test
The evaluation of response in acute and late phases provides the effect on neurogenic and peripheral pains, respectively [43]. The formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain method of evaluating the analgesic activity also confirmed the enhanced analgesic activity of ETB-NEG (Table 6). Both in the acute and late phases, the % inhibition was highest for ETB-NEG with significant differences from the effects of ETB gel and blank NEG (p-value < 0.05). Similar to the observation in the results of the hot plate method, in the formalin-induced paw licking test, blank NEG also produced some analgesic effect to some extent due to the presence of eucalyptus oil in the NEG [42].

Table 6.
Effects of ETB gel, ETB-NEG, and blank NEG in the formalin-induced paw licking test.
The analgesic activities studied by hot plate and formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain methods proved that the formulation of ETB gel to ETB-NEG significantly enhanced the analgesic activity. Thus, the formulation of ETB-NEG is a promising approach for the enhancement of analgesic activity. Similar results of enhancement of the analgesic activity of diclofenac sodium by the formulation of its NEG are reported [44]. Enhanced skin permeation of the drug, when applied as its NEG formulation, contributes significantly to the effect. Further, the use of eucalyptus oil in the nanoemulsion formulation synergized the analgesic activity of the ETB-NEG.
3.8.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Nanoemulsion gels provide better anti-inflammatory effects than the pure drug [45]. Small droplet size and high skin penetrability can be expected from NE-based systems and thus, it was expected that the ETB-NEG formulation could demonstrate better anti-inflammatory activity. The results of the study also confirmed the higher anti-inflammatory activity of ETB-NEG (Figure 5B). It was noted that the ETB-NEG had substantially high percent inhibition at all time points (p-value < 0.05), except at 1 h (p-value > 0.05). A delay in the effect may be caused by the lag time in drug permeation through the skin. This result was comparable to that observed in a reported study with NEG formulation of ETB [17]. There was also no significant anti-inflammatory effect observed at 1 h post-treatment (p-value > 0.05). As in the case of analgesic activity, an anti-inflammatory effect was also demonstrated by the blank NEG. This effect was found to increase with time; however, the effect was significantly less than both ETB and ETB-NEG samples (p-value <0.05). The ETB-NEG sample produced paw edema inhibition of 78.4 ± 3.5% at 8 h. Meanwhile, the inhibition was only 41.3 ± 8.3 and 19.6 ± 6.4% at 8 h for ETB gel and blank NEG, respectively. In addition to analgesic activity, eucalyptus oil also has anti-inflammatory activity [12]; this contributed towards the reduction of paw volume in rats. Thus, the ETB-NEG with eucalyptus oil and ETB was found to be superior for its anti-inflammatory activity.
3.8.3. Histopathology Studies
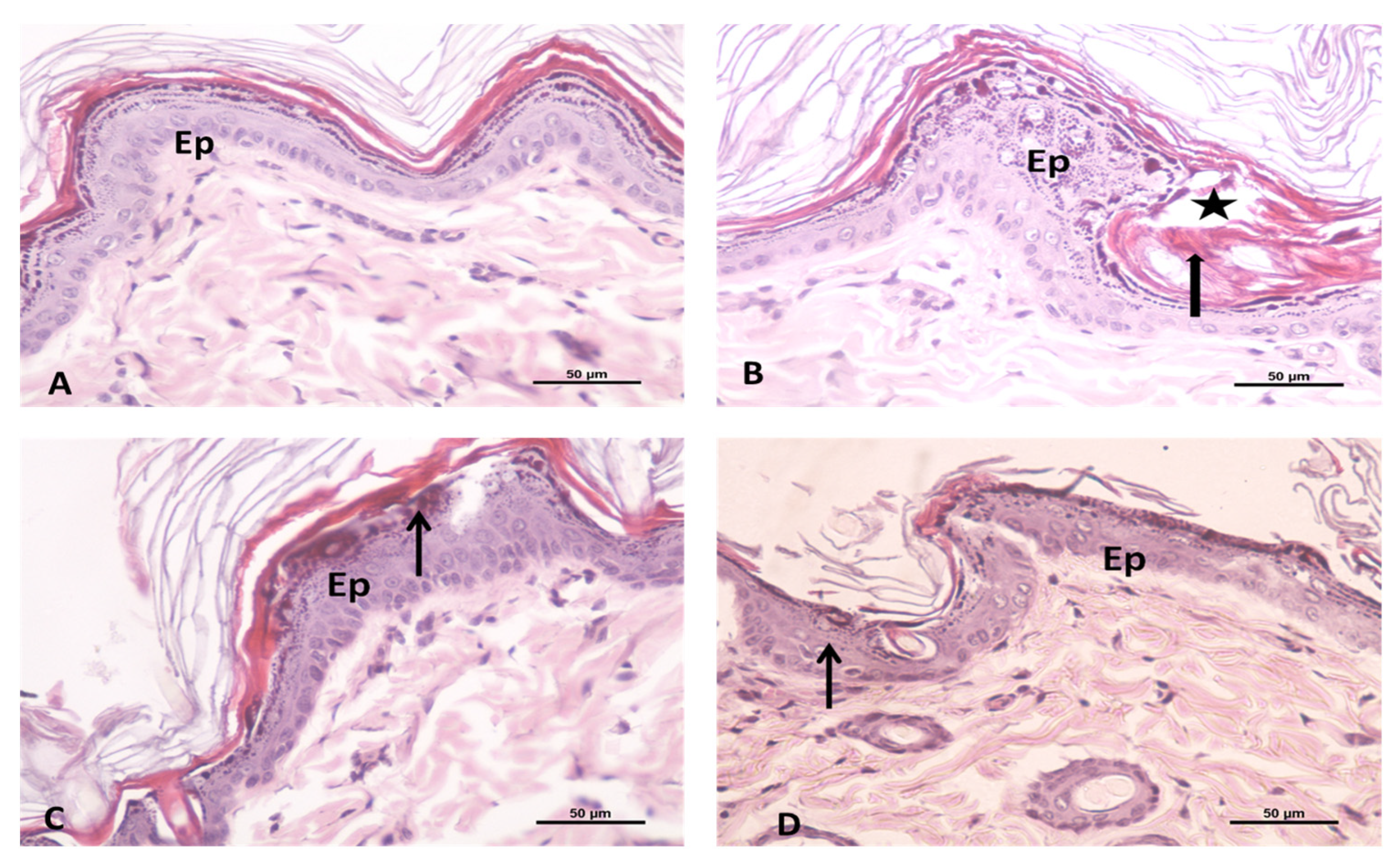
In order to ascertain that the formulated ETB-NEG is non-toxic and non-irritant for topical delivery application, a histopathology studies test was conducted. This study is important to confirm its utility for clinical applications. The irritation potential of ETB-NEG was tested in comparison to different samples and controls. The results showed that no severe irritation symptoms such as erythema (redness) and edema (swelling) occurred during 24 h, except for in the reference positive control group II (formalin solution). The anatomy of the ETB-NEG treated rat skin was compared with the untreated groups I, positive control, and blank NEG as shown in Figure 6A–D. The untreated control group I showed an intact and normal structure of skin with two layers; the epidermis and dermis. The epidermal–dermal junction shows many dermal papillae (Figure 6A). The formalin-treated rat skin showed the thickened epidermis (Ep), invaginated keratin layer into the epidermis, and intercellular edema (Figure 6B). The images of the blank NEG group and ETB-NEG groups showed moderately thickened epidermis, and no abnormal changes in the treated rat skin as compared to the control group (Figure 6C,D). Thus, the study results confirmed that the ETB-NEG formulation was non-irritant and safe for topical application. The non-irritancy of NEGs is proved also in previous studies [26].
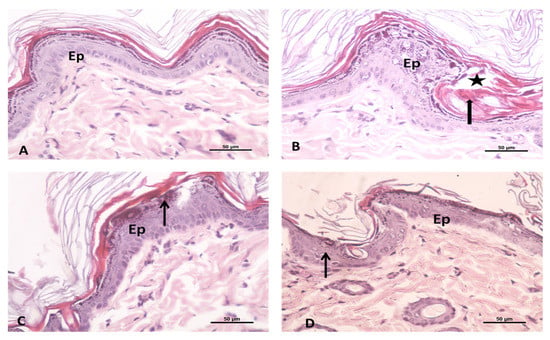
Figure 6.
Photomicrograph showing the (A) untreated control group of rat skin: this is formed of two layers; epidermis (Ep) and dermis. The epidermal–dermal junction shows many dermal papillae; (B) formalin treated rat skin as a positive control group showing the thickened epidermis (Ep), invaginated keratin layer into the epidermis (thick arrow) and intercellular edema (star); (C) Blank NEG treated rat skin; and (D) ETB-NEG treated rat skin showing the moderately thickened epidermis (Ep) and the presence of little reaction (↑). H&E 400×.
4. Conclusions
ETB-NE was formulated and optimized using percentages of oil, Smix, and water as the independent factors, and PS and PDI as responses. The optimized ETB-NE contained oil, Smix, and water in concentrations of 11.5, 38, and 50%, respectively. The optimized ETB-NE had satisfactory droplet size and PDI close to the predicted values. Meanwhile, the zeta potential value was −10.9 ± 1.01 mV for the ETB-NE. The in vitro drug release was significantly higher from the ETB-NE than from the aqueous dispersion of the drug. The nanoemulsion gel prepared from the ETB-NE was characterized for pH, viscosity, drug content, and percentage entrapment efficiency. Further, significantly higher in vitro skin permeation was observed from the ETB-NEG. The non-irritant and non-toxicity of ETB-NEG formulation in rat skin were confirmed by the histopathology study. In the in vivo evaluation of analgesic activity, MPA was significantly higher for ETB-NEG (47.09% after 60 min), demonstrating its enhanced analgesic activity compared to pure drug. The formalin-induced acute inflammatory pain study in rats also demonstrated higher analgesia for the ETB-NEG sample, and in both in acute and late phases. Similarly, the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity was more for ETB-NEG and the percentage inhibition was 78.4 ± 3.5% at 8 h. Thus, the results of the studies proved ETB-NEG to be superior to the pure drug for topical delivery. The study encourages future research in this area for further development of ETB-NEG to a clinically successful formulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A.A., J.A. and S.M.; Data curation, N.A.A., S.K., J.A., M.S.A., K.M.H., R.A.S., B.G.E., Y.R., H.Z.A., N.A. and S.M.; Formal analysis, N.A.A., S.K., M.S.A., K.M.H., R.A.S., B.G.E., H.Z.A. and S.M.; Investigation, J.A., R.A.S., Y.R. and H.Z.A.; Methodology, N.A.A., S.K., M.S.A., K.M.H., R.A.S., B.G.E., Y.R. and N.A.; Software, K.M.H.; Writing—original draft, S.K., M.S.A., Y.R. and S.M.; Writing—review & editing, J.A., B.G.E., H.Z.A. and N.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant no. (RG-11-166-38).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kwiatkowska, B.; Majdan, M.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Niewada, M.; Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Mamcarz, A. Status of etoricoxib in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Expert panel opinion. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 290–297. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29491537 (accessed on 10 February 2019). [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.Y.; Gwee, K.A.; Cheng, Y.K.; Yoon, K.H.; Hee, H.T.; Omar, A.R. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in chronic pain: Implications of new data for clinical practice. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 1937–1948. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30288088 (accessed on 10 February 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.-L.; Wang, J. Efficacy and safety of etoricoxib compared with NSAIDs in acute gout: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 35, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmingham, B.; Buvanendran, A. 40—Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen, and COX-2 inhibitors. In Practical Management of Pain, 5th ed.; Benzon, H.T., Rathmell, J.P., Hurley, W., Eds.; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MI, USA, 2014; pp. 553–568.e5. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323083409000402 (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Williams, B.S.; Buvanendran, A. Nonopioid analgesics: NSAIDs, COX-2 inhibitors, and acetaminophen. In Essentials of Pain Medicine, 3rd ed.; Benzon, H.T., Raja, S.N., Liu, S.S., Fishman, S.M., Cohen, S.P., Hurley, R.W., Natouze, S., Malik, K.M., Candido, K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Chapter 17; pp. 641–668. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781437722420000262 (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Capone, M.L.; Tacconelli, S.; Patrignani, P. Clinical pharmacology of etoricoxib. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2005, 1, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, K.F.; Siddiqui, M.A.A. Etoricoxib. Drugs 2009, 69, 1513–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhande, P.P.; Gupta, A.O.; Jain, S.; Dawane, J.S. Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of Topical Formulations of Pterocarpus Santalinus Powder in Rat Model of Chronic Inflammation. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, FF01–FF04. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28892928 (accessed on 25 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Pramod, K.; Shanavas, S.; Ansari, S.H.; Ali, J. Eugenol Nanodroplet Gel as Novel Biomaterial in Nanomedicine. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastiti, C.M.R.R.; Ponto, T.; Abd, E.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.E.; Roberts, M.S. Topical Nano and Microemulsions for Skin Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 37. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28934172 (accessed on 22 March 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, L.T.; Gerber, M.; Du Plessis, J.; Hamman, J.H. Transdermal Drug Delivery Enhancement by Compounds of Natural Origin. Molecules 2011, 16, 10507–10540. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6264261/ (accessed on 11 February 2019). [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Abebe, W.; Sousa, S.; Duarte, V.; Machado, M.; Matos, F. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of essential oils of Eucalyptus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebei, K.; Sakouhi, F.; Herchi, W.; Khouja, M.L.; Boukhchina, S. Chemical composition and antibacterial activities of seven Euca-lyptus species essential oils leaves. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 7. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25654423 (accessed on 15 February 2019). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, D.T.; Rajan, R. Effect of permeation enhancers on the penetration mechanism of transfersomal gel of ketoconazole. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2012, 3, 112–116. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22837959 (accessed on 18 February 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Moturi, V.; Lee, Y. Thixotropic property in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 88–98. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365909001254 (accessed on 19 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ouyang, W.-Q.; Wei, Y.-P.; Syed, S.F.; Hao, C.-S.; Wang, B.-Z.; Shang, Y.-H. Effects of Carbopol® 934 proportion on nanoemulsion gel for topical and transdermal drug delivery: A skin permeation study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5971–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lala, R.R.; Awari, N.G. Nanoemulsion-based gel formulations of COX-2 inhibitors for enhanced efficacy in inflammatory conditions. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotta, S.; Khan, A.W.; Ansari, S.H.; Sharma, R.K.; Ali, J. Formulation of nanoemulsion: A comparison between phase inversion composition method and high-pressure homogenization method. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, R.; Younis, M.K.; Hassan, D.H.; El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.-G.; Hassanein, E.; El-Batouty, K.; Elfaham, A. Formulation and characterization of chlorhexidine HCl nanoemulsion as a promising antibacterial root canal irrigant: In-vitro and ex-vivo studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4697–4708. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31303754 (accessed on 24 March 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotta, S.; Mubarak Aldawsari, H.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Shadab. Coconut oil-based resveratrol nanoemulsion: Opti-mization using response surface methodology, stability assessment and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129721. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814621007275 (accessed on 7 May 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarheed, O.; Shouqair, D.; Ramesh, K.V.R.N.S.; Khaleel, T.; Amin, M.; Boateng, J.; Drechsler, M. Formation of stable nanoemulsions by ultra-sound-assisted two-step emulsification process for topical drug delivery: Effect of oil phase composition and surfactant concentration and loratadine as ripening inhibitor. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118952. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517319309974 (accessed on 15 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Aggarwal, G.; Harikumar, S.L.; Kaur, K. Nanoemulsion Based Hydrogel for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Ketoprofen. Adv. Pharm. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.-H.; Ali, N.A.; Basri, D.F. Evaluation of Analgesic Activity of the Methanol Extract from the Galls of Quercus infectoria(Olivier) in Rats. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desai, S.; Ahmad, A.; Gite, M.; Gavitre, B.; More, Y.; Kundnani, K. Comparative evaluation of polyherbal formulations for an-ti-inflammatory and analgesic activity in rats and mice. Der Pharm Lett. 2010, 2, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, V.; Singh, I.; Gauttam, V.; Kalia, A.N. Anti-inflammatory activity of aqueous extract of Mirabilis jalapa Linn. leaves. Pharmacogn. Res. 2010, 2, 364–367. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21713140 (accessed on 13 June 2019). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, A.; Samad, A.; Singh, S.K.; Ahsan, M.N.; Haque, M.W.; Faruk, A.; Ahmed, F.J. Nanoemulsion gel-based topical delivery of an antifungal drug in vitro activity and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K.; Mishra, G.; Mohanty, B. In vitro corneal permeation of etoricoxib from oil drops. Asian J. Pharm. 2018, 12, S1208–S1214. Available online: https://www.asiapharmaceutics.info/index.php/ajp/article/view/2912 (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Kaur, N.; Kocher, D.; Sidhu, A. Synthesis and Testing of Eucalyptus globulus Oil-Based Nanoemulsion for Its Larvicidal Potential against Aedes aegypti. Afr. Èntomol. 2019, 27, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Panigrahi, P.P. Solubility Enhancement of Etoricoxib by Cosolvency Approach. ISRN Phys. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolourchian, N.; Mahboobian, M.M.; Dadashzadeh, S. The Effect of PEG Molecular Weights on Dissolution Behavior of Simvastatin in Solid Dispersions. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2013, 12, 9–18. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24250667 (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Fonseca, V.R.; Bhide, P.J.; Joshi, M.P. Formulation, Development and Evaluation of Etoricoxib Nanosize Microemulsion Based Gel for Topical Drug Delivery. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2019, 53, s571–s579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laxmi, M.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mehta, S.; Mehta, A. Development and characterization of nanoemulsion as carrier for the enhancement of bioavailability of artemether. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2013, 43, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboofazeli, R. Nanometric-Scaled Emulsions (Nanoemulsions). Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2010, 9, 325–326. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24381596 (accessed on 17 March 2020).
- Adak, T.; Barik, N.; Patil, N.B.; Govindharaj, G.-P.-P.; Gadratagi, B.G.; Annamalai, M.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Rath, P.C. Nanoemulsion of eucalyptus oil: An al-ternative to synthetic pesticides against two major storage insects (Sitophilus oryzae (L.) and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst)) of rice. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111849. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926669019308593 (accessed on 6 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- De Godoi, S.N.; Quatrin, P.M.; Sagrillo, M.R.; Nascimento, K.; Wagner, R.; Klein, B.; Santos, R.C.V.; Ourique, A.F. Evaluation of stability and in vitro security of nanoemulsions containing eucalyptus globulus oil. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xin, C.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Z. Antitumor activity of nanoemulsion based on essential oil of Pinus koraiensis pinecones in MGC-803 tumor-bearing nude mice. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8226–8238. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878535220303920 (accessed on 4 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- Waxler, R.M.; Weir, C.E. Effect of pressure and temperature on the refractive indices of benzene, carbon tetrachloride, and water. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. Sect. A: Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 163–171. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31580621 (accessed on 4 March 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlGahtani, M.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Ahmad, J. Nanoemulgel for improved topical delivery of retinyl palmitate: Formulation design and stability evaluation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Zakir, F.; Mirza, M.A.; Anwer, K.; Ahmad, F.; Iqbal, Z. Development of Curcumin loaded chitosan polymer based nanoemulsion gel: In vitro, ex vivo evaluation and in vivo wound healing studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 569–579. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141813016328495 (accessed on 4 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F.; Ramadan, W.; Ahmed, M.A. Investigation of true nanoemulsions for transdermal potential of indomethacin: Characterization, rheological characteristics, and ex vivo skin permeation studies. J. Drug Target. 2009, 17, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, R.; Boddu, S.H.; Renukuntla, J.; Babu, R.J.; Tiwari, A.K. Alternatives to Biological Skin in Permeation Studies: Current Trends and Possibilities. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aziz, Z.A.A.; Nasir, H.M.; Ahmad, A.; Setapar, S.H.M.; Ahmad, H.; Noor, M.H.M.; Rafatullah, M.; Khatoon, A.; Kausar, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; et al. Enrichment of Eucalyptus oil nanoemulsion by micellar nanotechnology: Transdermal analgesic activity using hot plate test in rats’ assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, Y.D.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Pathak, U. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of amifostine, DRDE-07, and their analogs, in mice. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2010, 42, 17–20. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20606831 (accessed on 5 April 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadab; Alhakamy, N.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Kotta, S.; Ahmad, J.; Akhter, S.; Alam, S.; Khan, M.A.; Awan, Z.; Sivakumar, P.M. Improved Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Diclofenac Sodium by Topical Nanoemulgel: Formulation Development—In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 4071818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baboota, S.; Shakeel, F.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J.; Shafiq, S. Design, development and evaluation of novel nanoemulsion formulations for transdermal potential of celecoxib. Acta Pharm. 2007, 57, 315–332. Available online: https://content.sciendo.com/view/journals/acph/57/3/article-p315.xml (accessed on 3 February 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).