Abstract
This paper presents three methods of converting complex 3D models of STL type into solid models. For converting the STL models, specific approximation functions from CATIA and Creo Parametric software were used as well as 3D solid modeling methods that used sketches drawn for sections of the specific analyzed model. This conversion is required to get a solid 3D model that can be used for finite element analysis and to be processed using Boolean functions in specific CAD programs. This paper also presents a study of the effectiveness of FEA in respect to the time required for the analysis of each converted model. The analyzed STL files contain data obtained by computer tomography and are the 3D models of the human orthopedic system: the left zygomatic bone and upper part of the right femur. The presented conversion methods can be used by design engineers both in medical applications (where the complexity of forms is well known) for the design of implants and for industrial applications for reverse engineering.
Keywords:
STL; CT; 3D model; reverse engineering; Creo Parametric software; CATIA software; CAD; FEA 1. Introduction
Biomedical engineering combines the design and problem-solving skills of engineering with medical and biological sciences to advance health care treatment. In recent years, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has been increasingly applied and integrated in the medical technology, including among other fields computer-aided surgery, design of orthopedic devices and implants, design of tissue scaffolds, reverse engineering (RE), and 3D reconstruction. Computer tomography (CT) medical imaging is the most used tool for viewing the internal structure of the human body but is limited by its 2D image presentation. Three-dimensional (3D) solid models of medical images bring more information in the diagnosis and treatment, and the reconstructed 3D solid models can be easily converted to Rapid Prototyping physical models or in Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML) format for visualization. Usually, a 3D bio-CAD model is reconstructed through either segmentation or volumetric representation. There are several methods that can be applied to reconstruct a 3D solid model for bio-medical imaging from its 2D CT image [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Usually, the model is reconstructed through either segmentation or volumetric representation. One method involves a swept blend from the contours of each layer in point data, the second possibility is via voxel to stack and construct the model by using the marching-cube algorithm. Contour detection in each layer is also used to construct the mixed layers in the triangular stereolithography (STL) model. This format approximates 3D surfaces of a solid model with oriented triangles (facets) of different size and shape (aspect ratio) in order to get a smooth representation suitable for industrial processing of 3D parts using STL machines. However, such a representation is not suitable for the computational analysis using finite element analysis (FEA) because of inappropriate size and large aspect ratio of elements.
The FEA mesh quality is critical to the FEA results; a good mesh with high quality can lead to results with high precision. The generation of a FEA mesh from a CAD model mainly depends on the geometric shape of the CAD model: the simpler the geometric shape of a CAD model, the less time the FEA mesh generation costs, and the better the quality of the generated mesh. To shorten the mesh generation time and improve the mesh quality, the CAD mesh model is required to be simplified, which can be solved by suppressing the detailed features on the mesh without any changes to the rest before FEA mesh generation [9,10,11]. In case of human bones, the STL geometry obtained after CT scanning is very complex, with a high level of detail. Applying a geometry simplification should not alter the local topology, stress concentrators, or other important geometrical details. A hybrid method that combines significant feature points for functional structure and the ones for anatomical appearance as presented in [12] for the reconstruction of an individual three-dimensional model of fractured long bone based on feature points could be a solution.
In this paper, three methods for the conversion of 3D models of STL type into 3D solid models using different CAD systems are presented. For transformation, CATIA V5 (Computer Aided Three-dimensional Interactive Applications, Dassault Systemes, Vélizy-Villacoublay, France) and PTC Creo Parametric 2.0 (Parametric Technology Corporation, Boston, MA, USA) were used. The quality of the conversion methods is tested by comparing the results and simulation time of finite element analysis of a zygomatic bone model, which is obtained by the two methods of conversion (using the specific functions of the CATIA software and geometric modeling using sketches in Creo Parametric software). The paper underlines the methodology to use standard functionalities available in the majority of commercial or even freeware CAD software.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the working conditions and investigated bone geometries. Section 3 introduces the concepts related conversion methods and the overview of the methodology corresponding to the software packages employed. Section 4 illustrates some results and presents the advantages and disadvantages of each software and conversion method. Finally, this paper is concluded in Section 5.
2. Working Condition
In order to perform a finite element analysis, the used CAD model must be of solid type; thus, an STL model obtained through 3D or computer tomography (CT) scanning must be converted into a solid 3D model. To do this, in this article, we used two software packages: CATIA and Creo. CATIA is one of the most widely used with integrated CAD/CAM/CAE software, with applications in various fields of the industry. The integrated solutions CAD/CAM/CAE/PLM of the Creo software package offer complete functionality for all stages of product development, from conception to production.
Today, 3D modeling is the key to creating innovative products, allowing engineers to develop the idea of a concept that can be turned into a physical product [13,14,15]. These studies used CATIA Version 5 and Creo Parametric 2.0 Version. For the FEA, a Creo module and Simulate Version 2.0 were used with three-dimensional tetrahedral type elements employing high-order interpolation functions. Even though there are new releases of the above-mentioned software, the use of standard functions does not influence the capabilities of the described methodology. The workstation used for both the conversion/modeling and for FEA is an HP WorkStation xw8600, 2xCPU Intel Xeon E5420, 16GB RAM, Nvidia Quadro FX4600 video card, running the operating system Windows7 Professional.
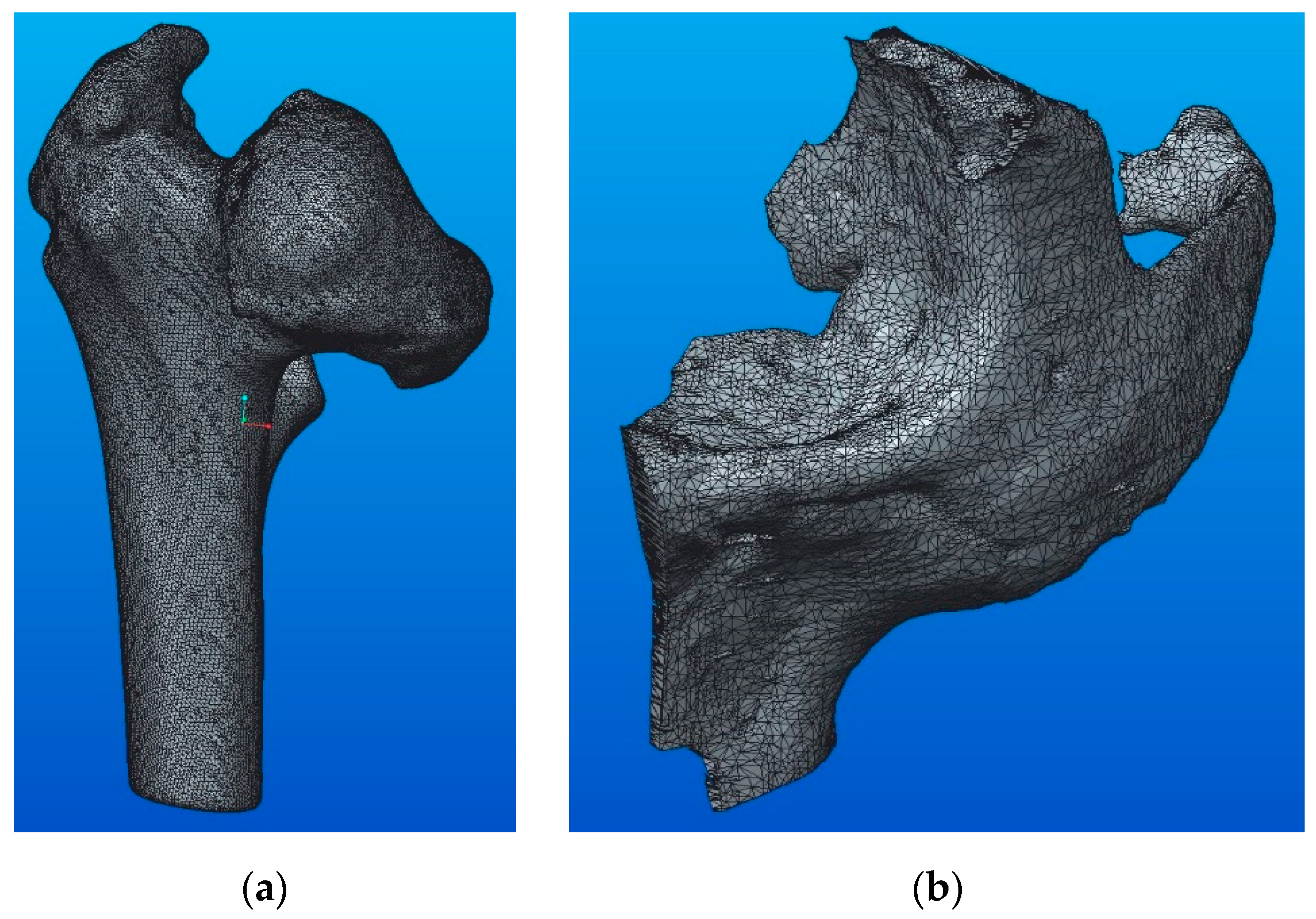
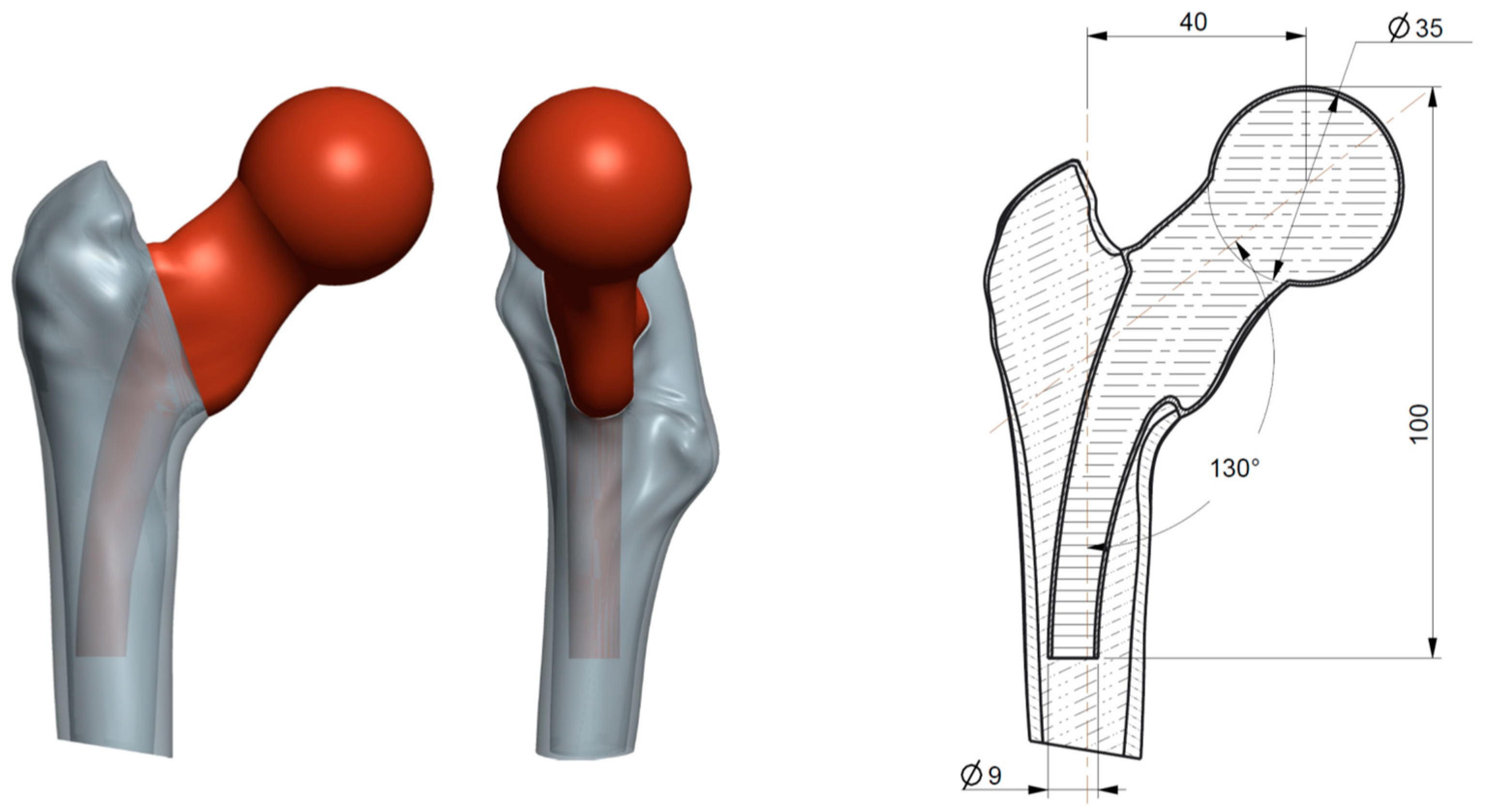
The analyzed STL files contain data obtained by computer tomography (CT), including the 3D models of the human orthopedic system, namely: the upper part of the right femur (Figure 1a) and left zygomatic bone (Figure 1b). As can be seen in Figure 1, the two models have specific anatomical shapes, with very high complexity.
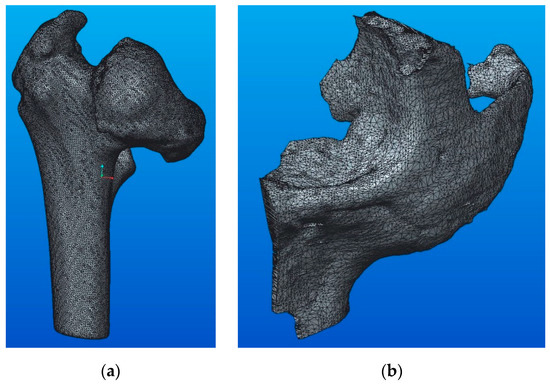
Figure 1.
Three-dimensional (3D) models: (a) femoral bone; (b) zygomatic bone.
For converting the 3D models (STL type), specific functions of CAD software (offset—CATIA and Shrinkwrap—Creo Parametric) will be used. These functions generate complex 3D solid models that are similar to the STL model. The advantages of using these functions comprise the speed at which the solid model can be obtained, and their ease of use (a high-level of modeling experience is not necessary). The major disadvantage is their sensitivity to the existence of voids (non-covered areas) in the STL model that make the conversion impossible or at a poor quality, resulting in an unusable solid. To avoid this disadvantage, this article proposes a third method that involves obtaining the solid models based on STL through geometric modeling using sketches in specific sections of the analyzed models.
3. Conversion Methods
3.1. Conversion Methods Using CATIA Functions
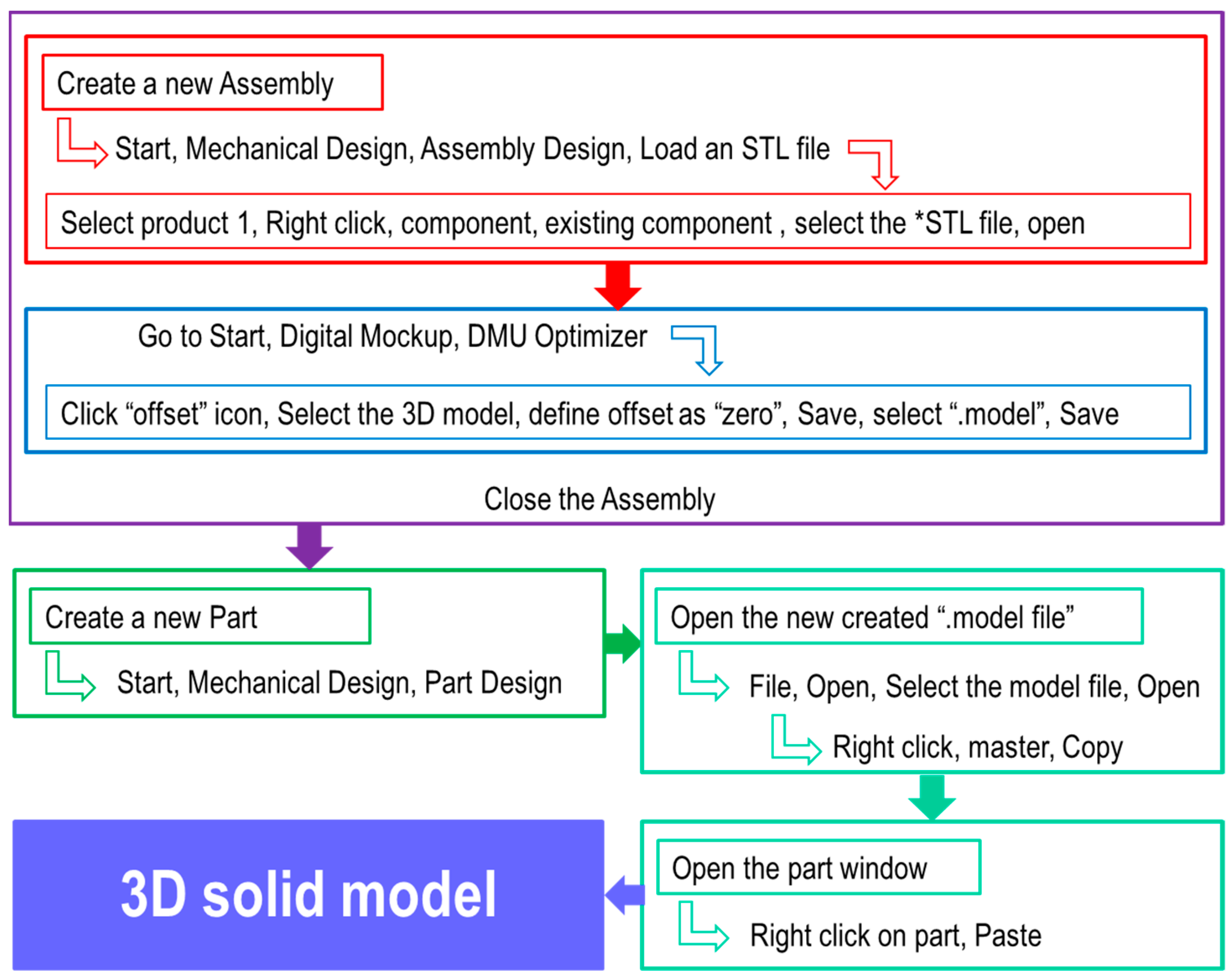
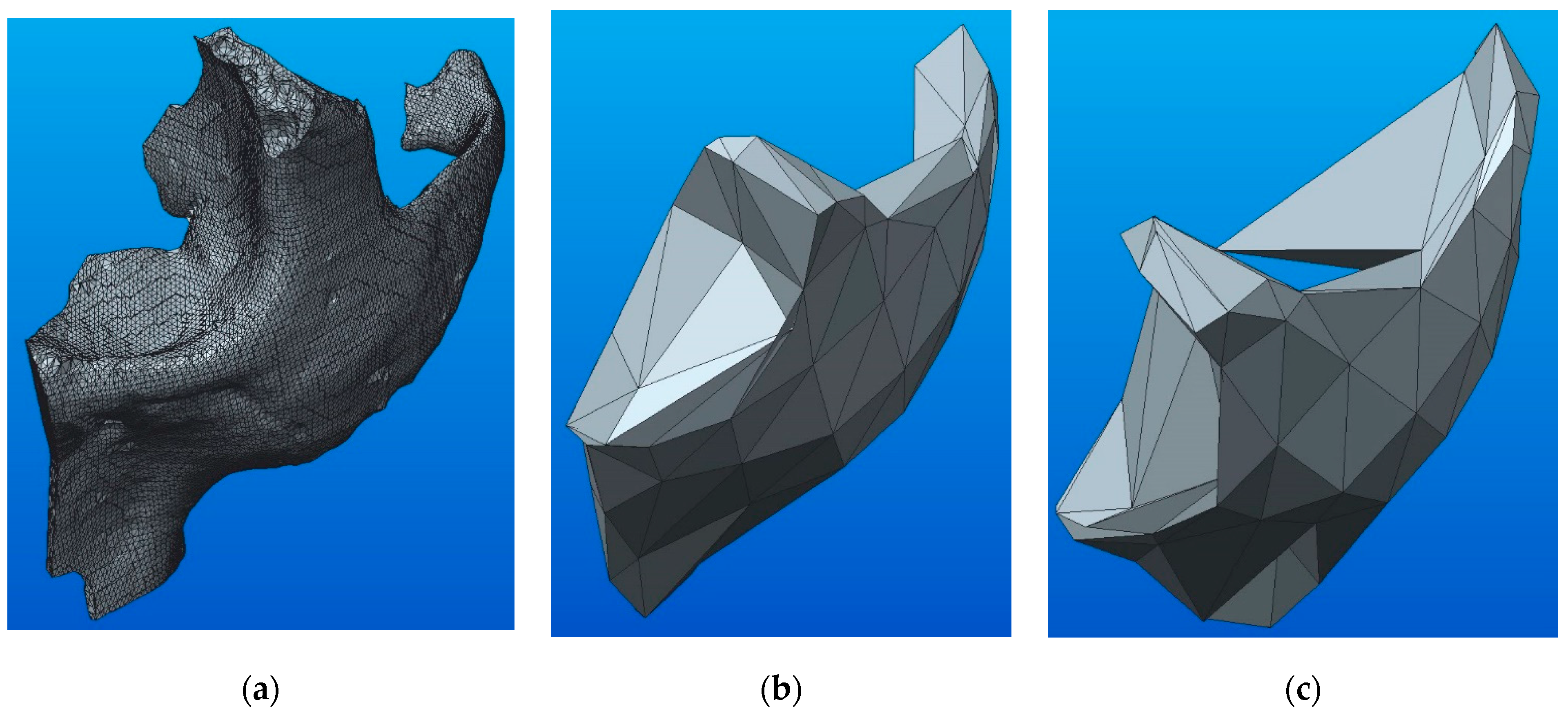
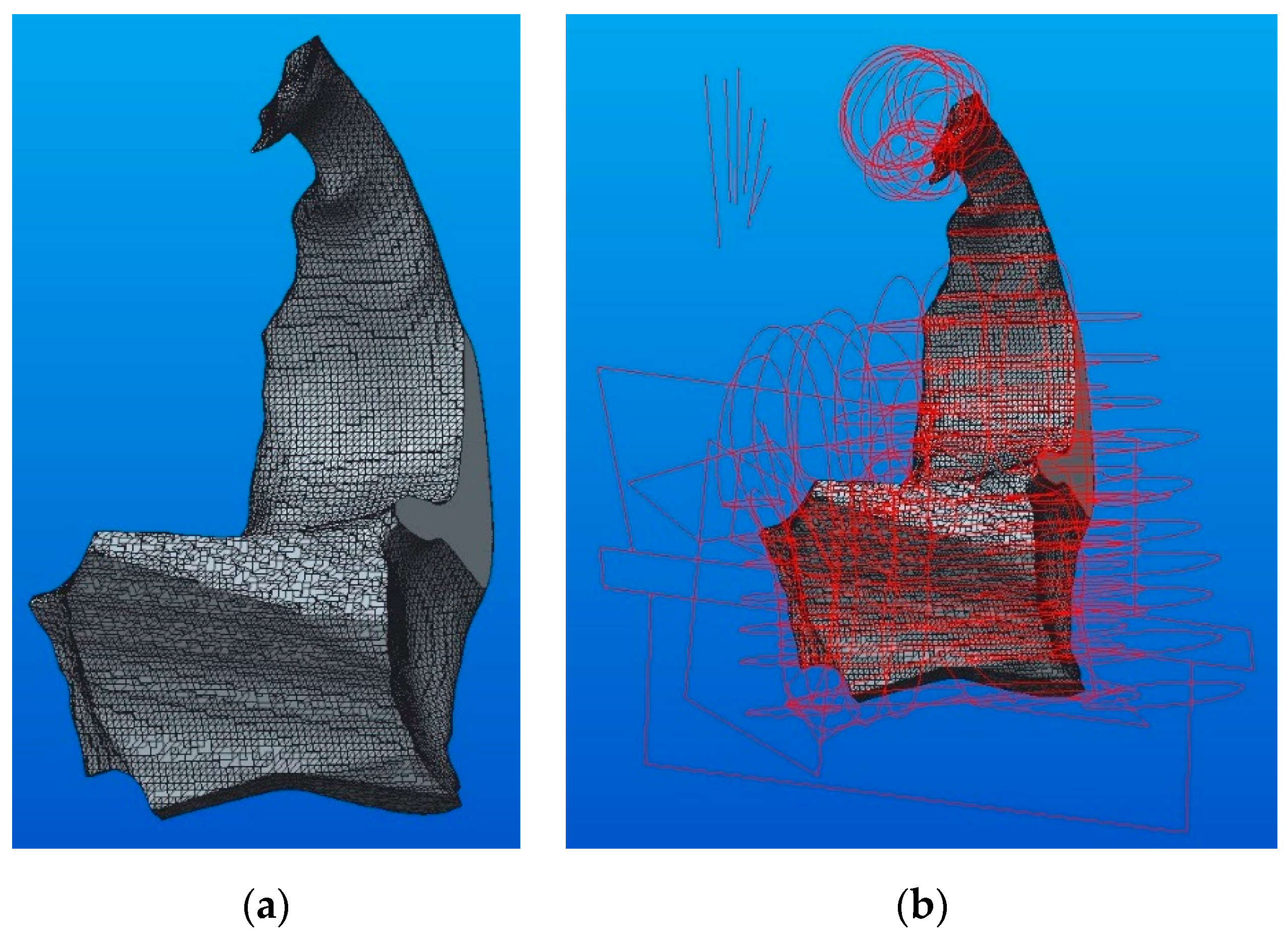
The first method of conversion of the STL files into solid files has used specific functions of the CATIA program. Figure 2 presents the steps required to obtain the 3D solid model by converting the completely closed (error-free) STL model using CATIA, and Figure 3 shows the result after conversion.
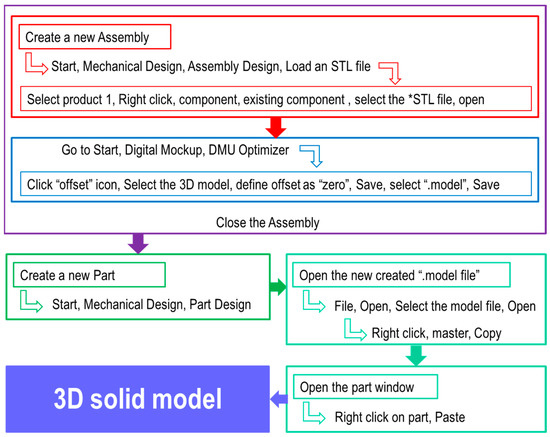
Figure 2.
Steps for converting the STL files into 3D solid models using CATIA.
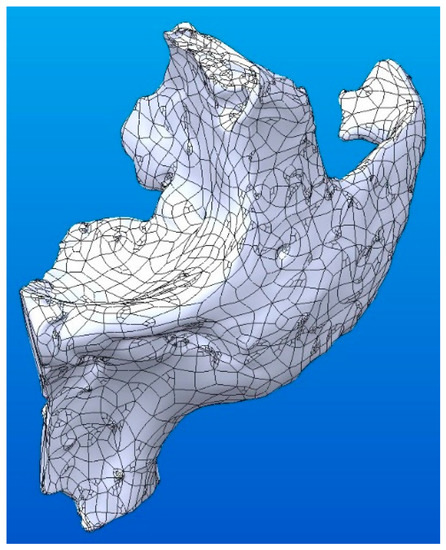
Figure 3.
The 3D solid model resulted after conversion.
After obtaining the desired solid 3D models, the FEA can be performed using the Creo Simulate program.
3.2. Conversion Methods Using Creo Parametric Functions
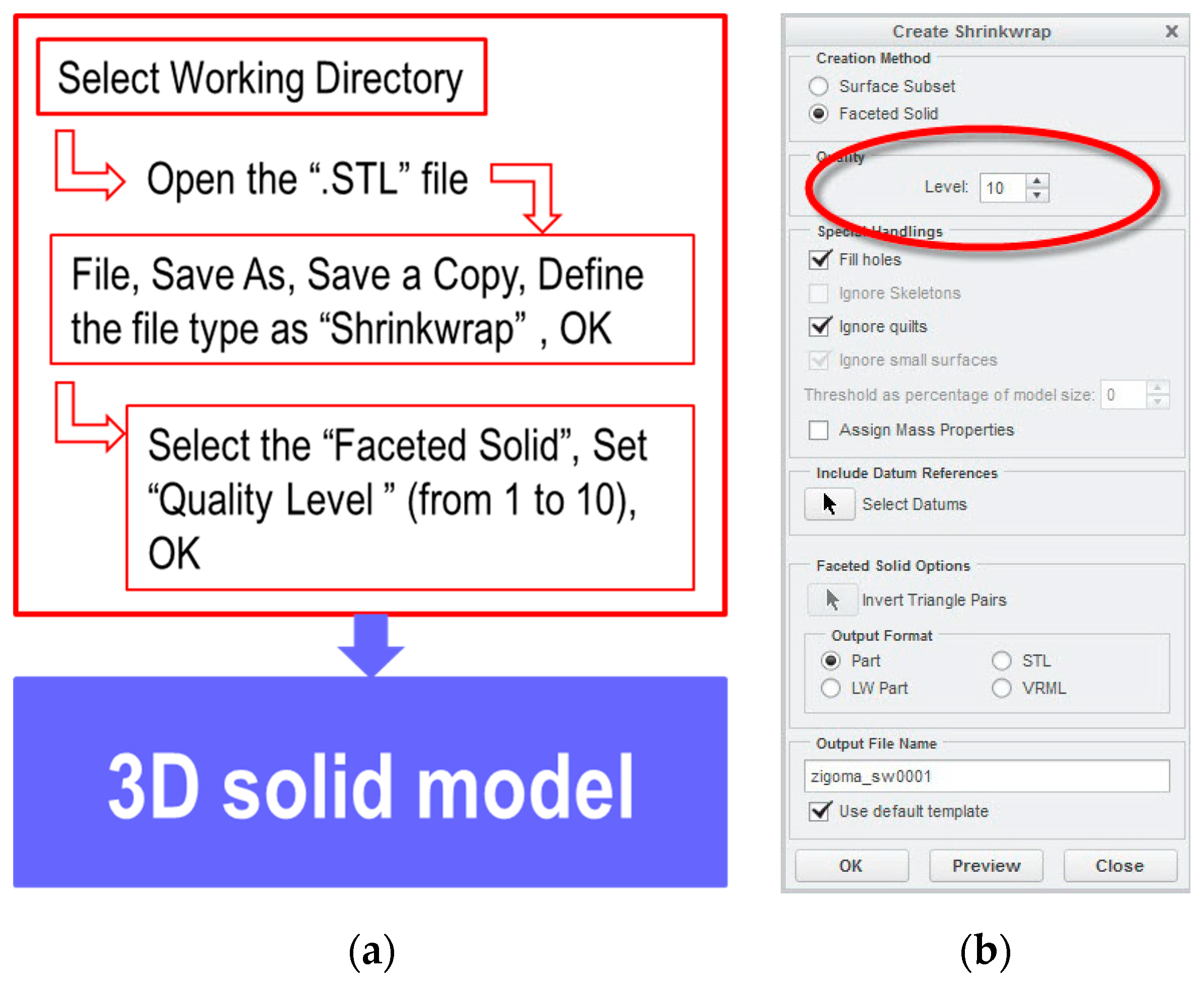
The second conversion method has used specific functions from Creo Parametric software. Figure 4 presents the conversion stages of the STL files into solid models using the Shrinkwrap function (see Figure 4b).
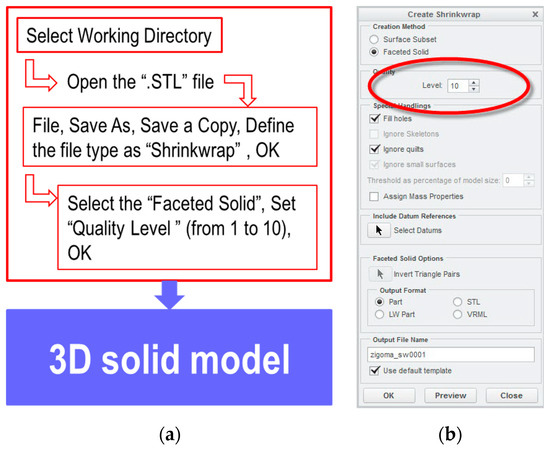
Figure 4.
Steps for converting the STL files into 3D solid models using Creo: (a) stages of conversion using the Shrinkwrap function; (b) settings to obtain a solid model.
The marked value (10) is the maximum approximation of a model, and its result is a solid model that is very close to the source model (see Figure 5a). Figure 5b presents the 3D solid model with the minimum value of approximation level, which is equal to 1. Depending on the quality of the STL model, geometry malfunction could occur in the solid models (see Figure 5c).
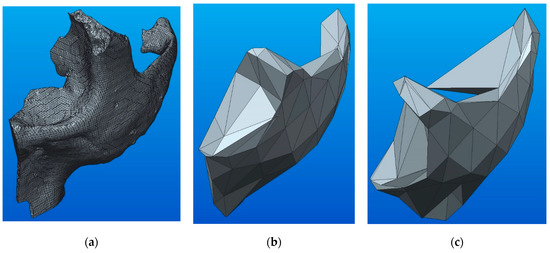
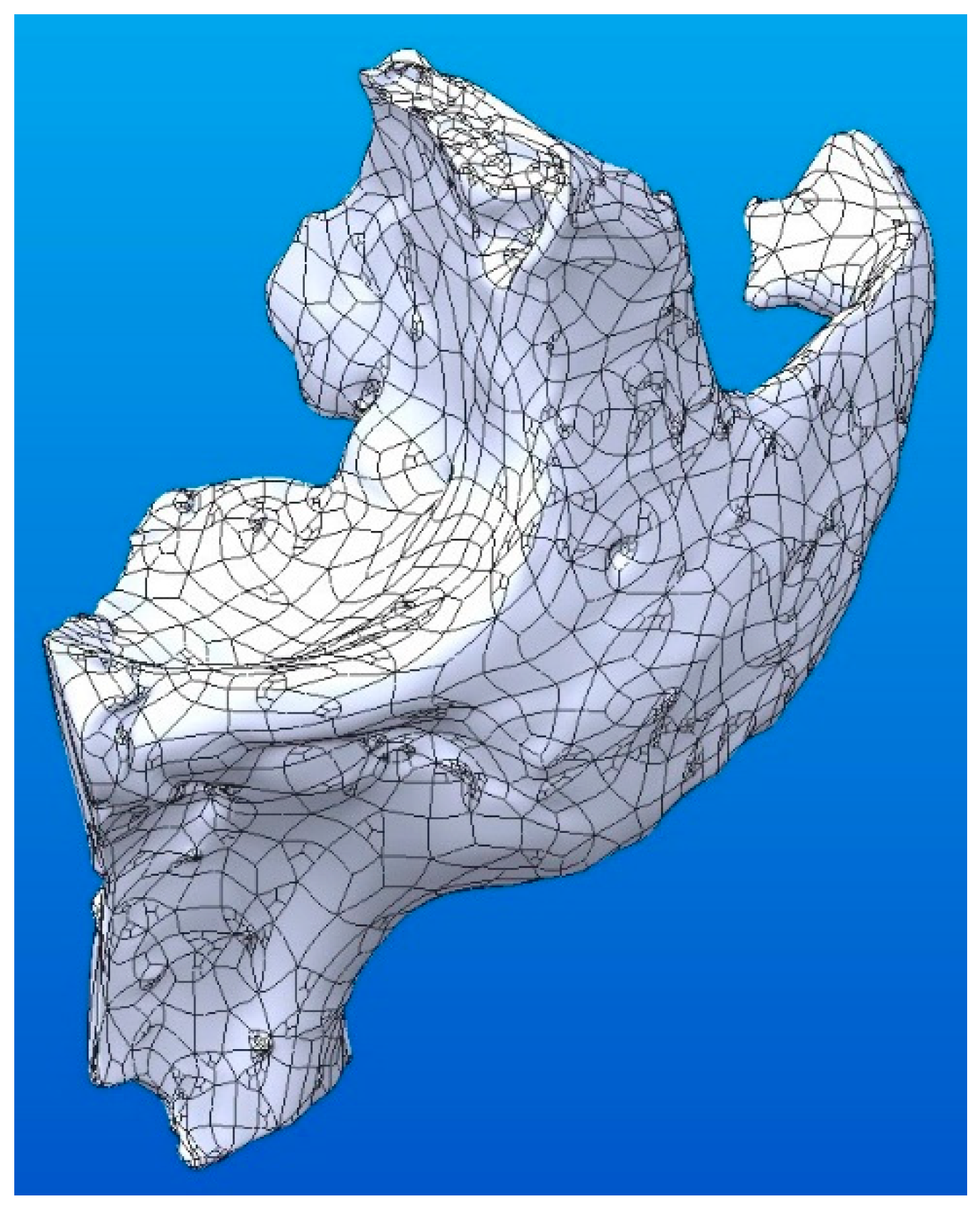
Figure 5.
Level of approximation: (a) level 10; (b) level 1; (c) malfunctioned solid.
Figure 5 shows that when converted into a solid, its surfaces are covered with flat triangular facets. A high level of approximation (level 10) results in a geometrically and mathematically complex solid, whereas a low level (1) results in a highly simplified solid. Regardless of the level of approximation, the resulting solids can be used for other CAD modeling operations or can be used as parts in building assemblies.
Unlike the previous conversion method, where the FEA could be performed, through this conversion, regardless of the level of approximation, no analysis could have been made because errors occurred in the discretization process. As a result of the large number of facets, an inappropriate size and large aspect ratio of elements is generated.
3.3. Conversion Methods Using Geometric Modeling in Creo Parametric
Given the impossibility of carrying out the FEA using the solids obtained from the Shrinkwrap function, a new method for obtaining the 3D solid models was investigated and developed, i.e., geometric modeling using sectional sketches.
One starts from the 3D model obtained by using one of the previously described methods. Cross-sections are generated through this model, these sections then being used to draw sketches that will serve for building a parametric solid model.
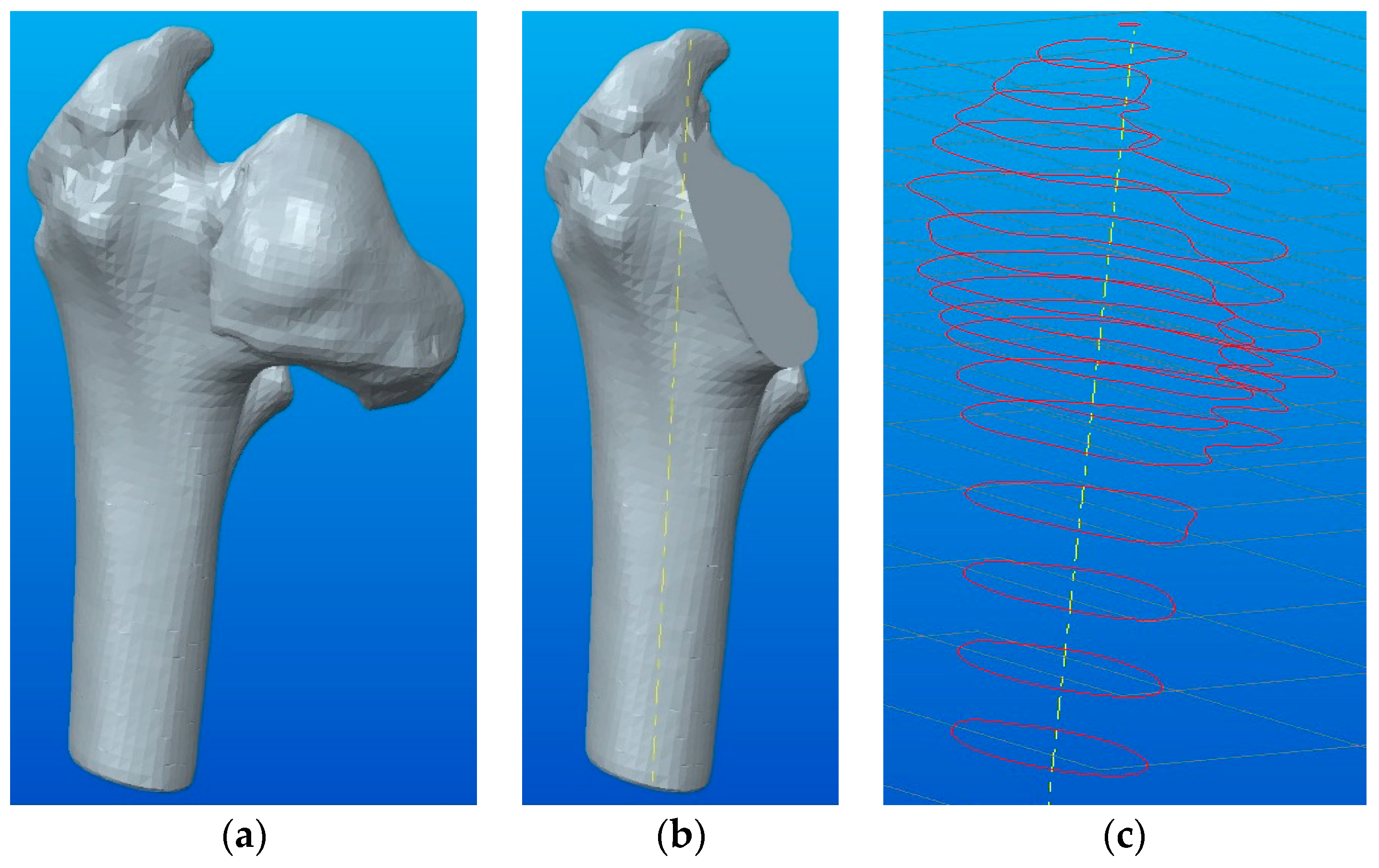
The first case study in this article presents a conversion of a 3D model (STL type) into a solid model of the human femur shown in Figure 1a. For this, only the upper part of the femur was used, and the STL model was converted into a 3D solid model, as shown in Figure 6a. Since the femur shows a malformation of the head (it requires a total prosthetic femoral head), it was not necessary to obtain a fully parameterized model (shaft, column, and femoral head). For this reason, cutting was applied with the "Extrude Cut" function in the cervix area on a well-defined direction, which facilitates its conversion (Figure 6b).
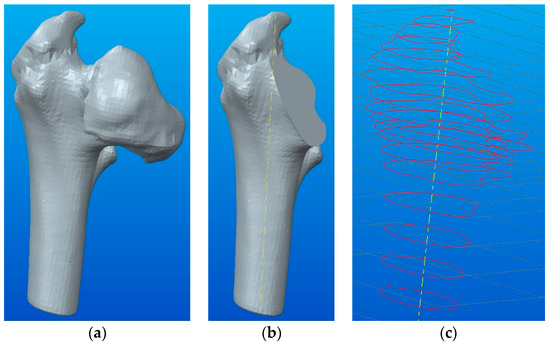
Figure 6.
Steps for converting the STL files into 3D solid models using geometric modeling in Creo Parametric: (a) 3D solid model obtained using the Shrinkwrap function; (b) tracing the femur axis (shaft); (c) achievement of the drawings in different sections.
In order to obtain the solid parameterized model, the “Swept Blend” function was used. This function involves drawing a linear path through the femur (see Figure 6b) and making sketches in intermediate sections, as shown in Figure 6c. Tracing the trajectory should consider dividing the entire model into four quadrants.
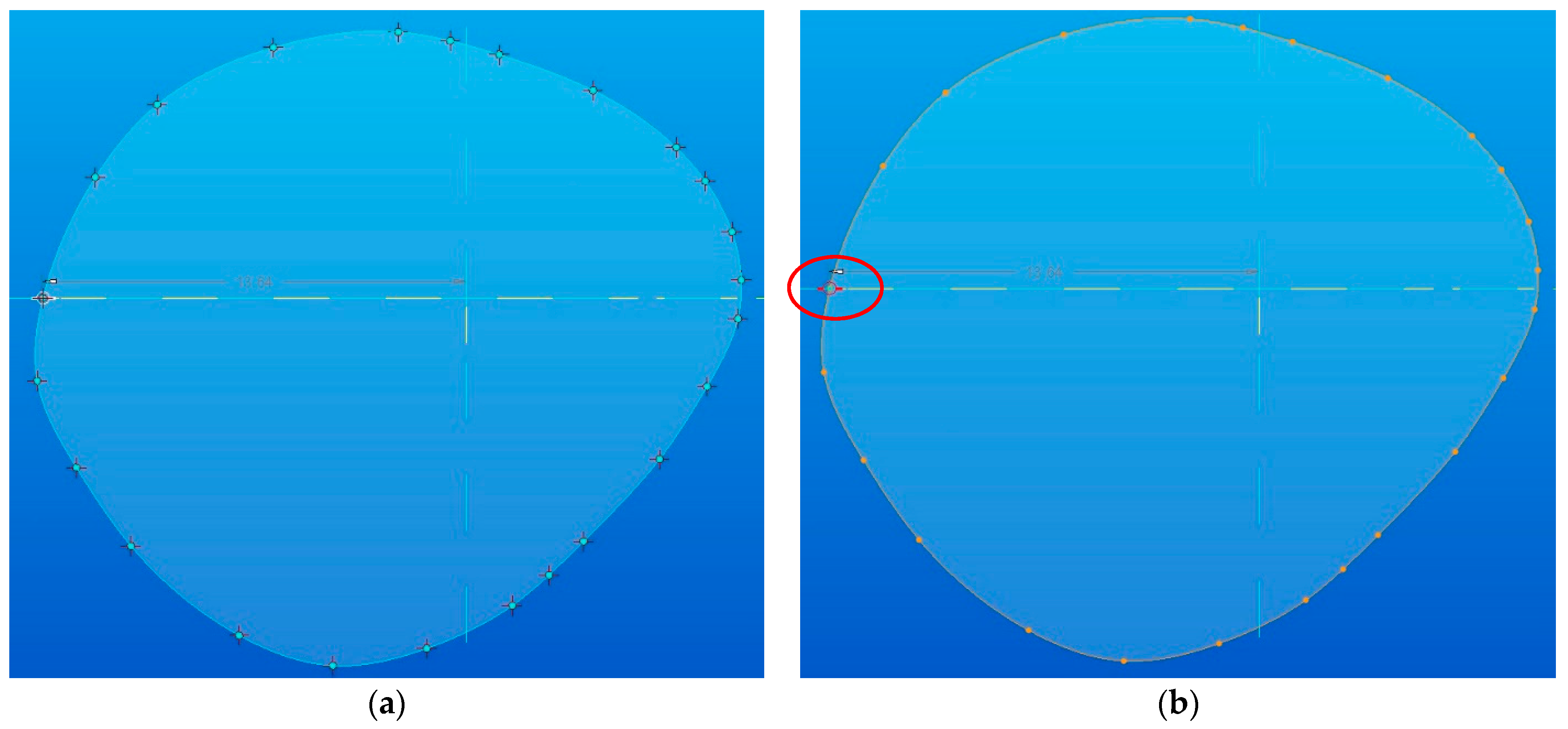
Each sketch was hand drawn using curves of Bézier type [16,17,18]; these had 24 checkpoints, as it can be seen in Figure 7a. This curve-tracing operation requires a refinement activity and attention from the operator. An important feature of each sketch is the “start/end” point (marked with red color). All of them must be in the same quadrant in order to avoid the torsion of the model (see Figure 7b).
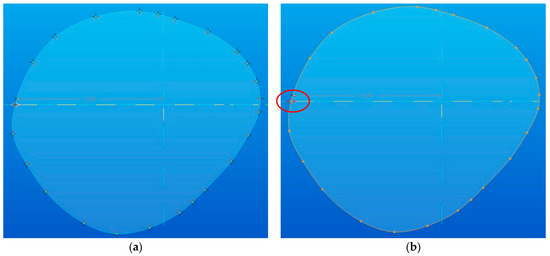
Figure 7.
Tracing start/end points in each section: (a) the checkpoints of the sketches; (b) starting point of the sketches.
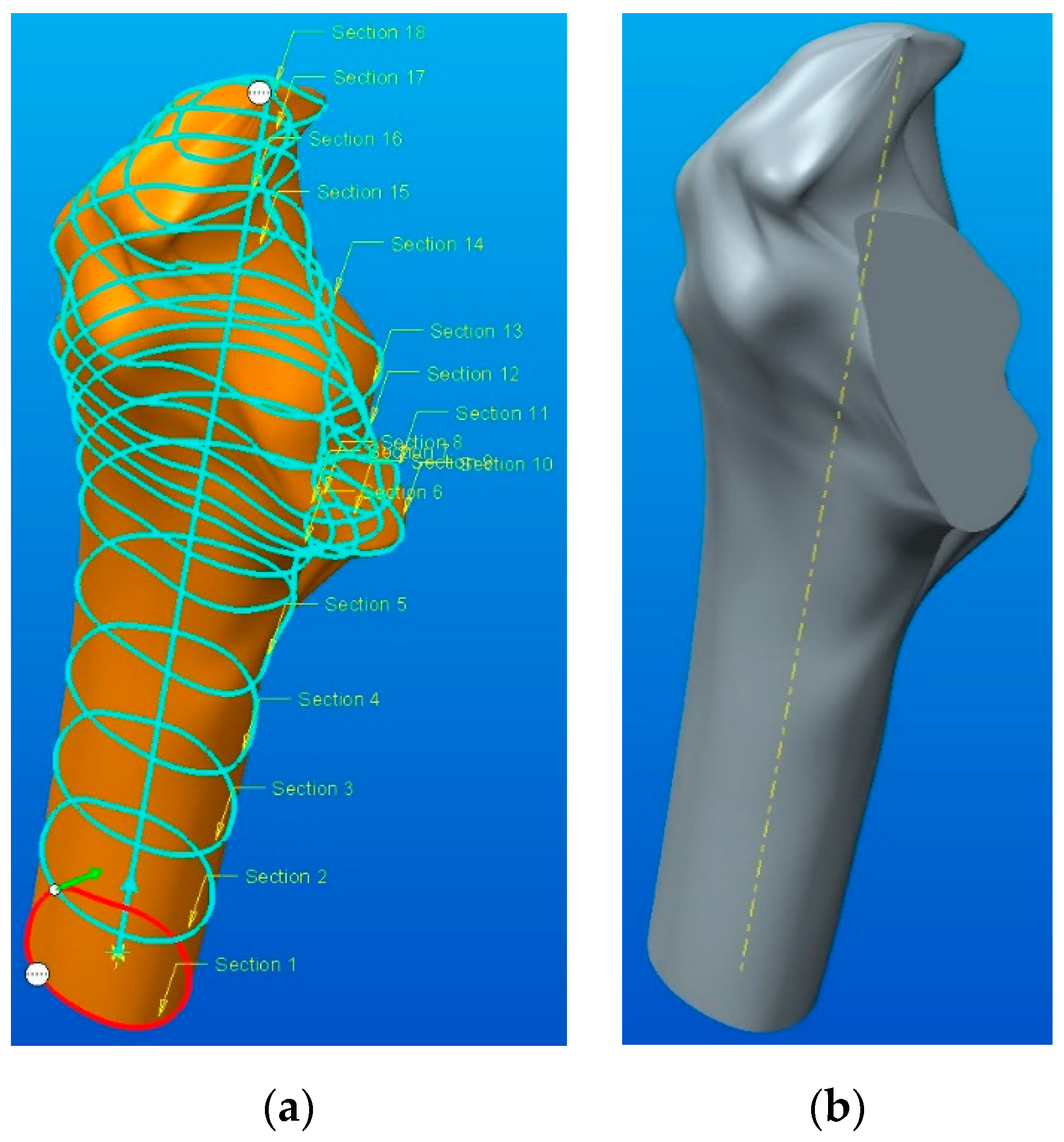
These drawings were created on planes parallel to each other and represent an outline of the model. In order to obtain the parametrized model using the Swept Blend function, it is necessary to select both the sketches in sequence order (1 to 18) and the trajectory (see Figure 8a). The number of sequences and their position relate to significant feature sections for the functional structure and the ones for anatomical appearance; a geometry simplification should not alter the local topology, stress concentrators, or other important geometrical details. After obtaining the model, the “Extrude Cut” function was used, through a previously determined direction, for achieving the parameterized model of the femur (shown in Figure 8b). It is also possible to see the similarity between the two solid models: “Shrinkwrap” model—see Figure 5b—and the parameterized model—see Figure 8b.
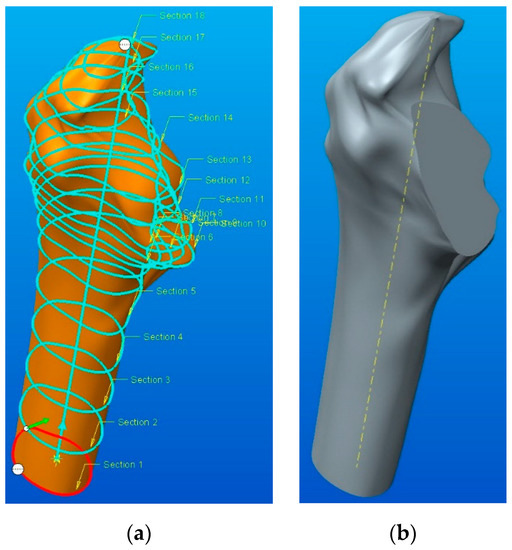
Figure 8.
Tracing the parameterized 3D model: (a) use of the Swept Blend function; (b) parametrized solid model.
This model has been used successfully in FEA; no error was reported along simulations. Based on the above-presented aspects, a study case that presents the design procedure and practical implementation of a hip prosthesis was realized [19].
The femoral head prosthesis design starts from the surface created by a cutting plane in the cervix area on a well-defined direction (see Figure 8b). To accurately reproduce the real bone structure of the femoral bone, the 3D model has been transformed in a shell structure that approximates the cortical part of the bone. Use of the “shell” function would not be possible if the model was not parameterized, for example, a geometry directly imported as an STL file. The parameterized models are also necessary to further design the hip prosthesis. Figure 9 presents the designed assembly femoral bone–hip prosthesis, and the correction of the neck-shaft angle (130°) and the arch shape of the femoral stem to facilitate the implantation can be noticed. For the fabrication of the implant, the Ti6Al7Nb alloy was the best choice because of its mechanical and biocompatibility properties; the hip prosthesis was realized by Selective Laser Sintering technology, from pure titanium, in the Rapid Prototyping Laboratory of the Technical University of Cluj-Napoca [18].
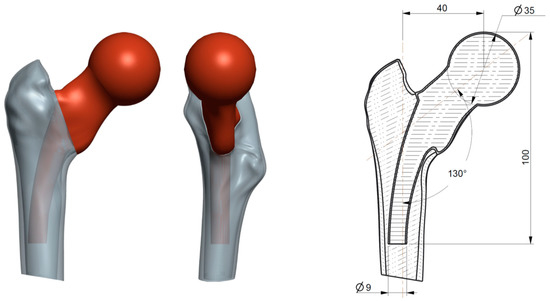
Figure 9.
Designed assembly of a femoral bone with a hip replacement.
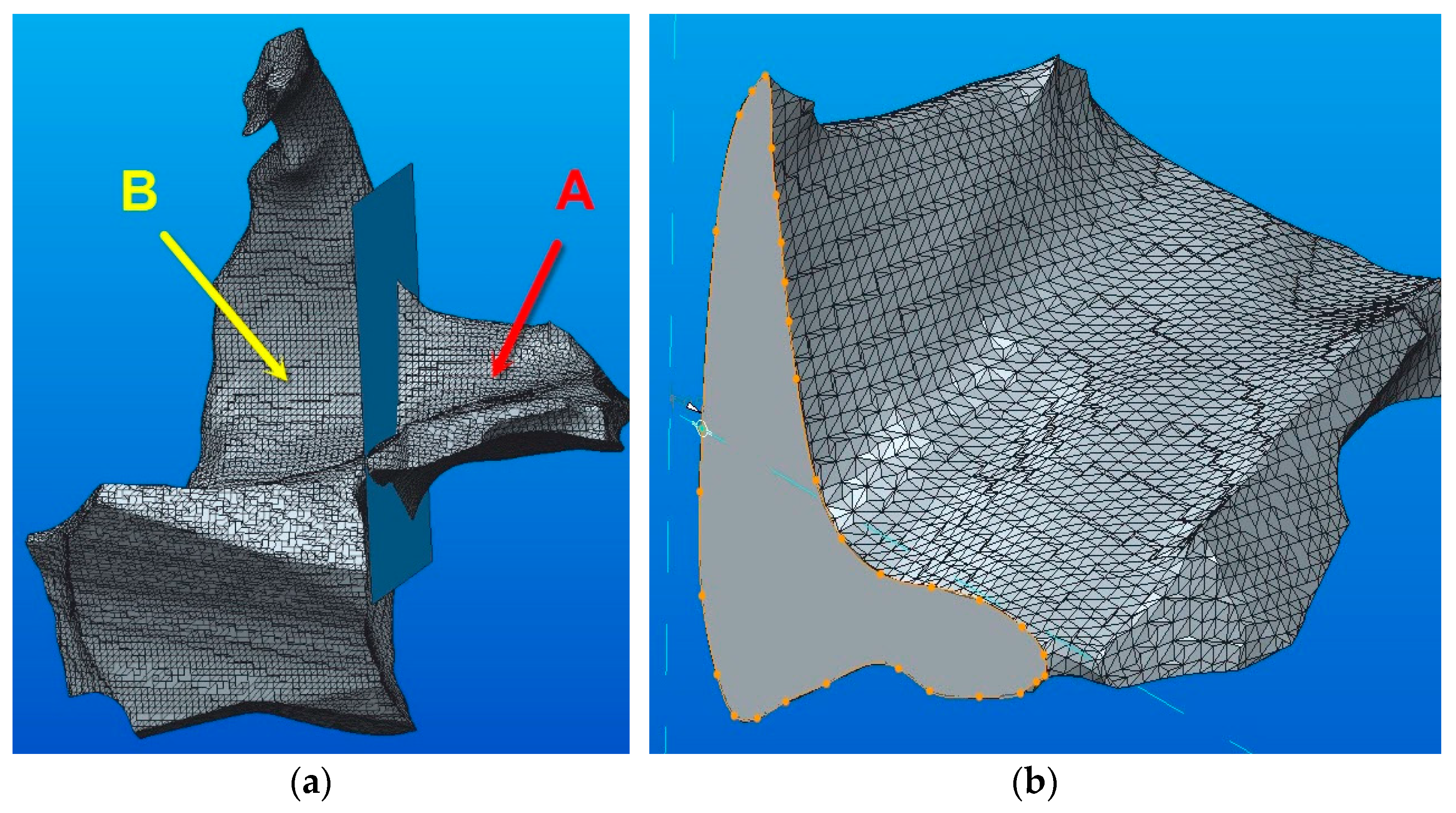
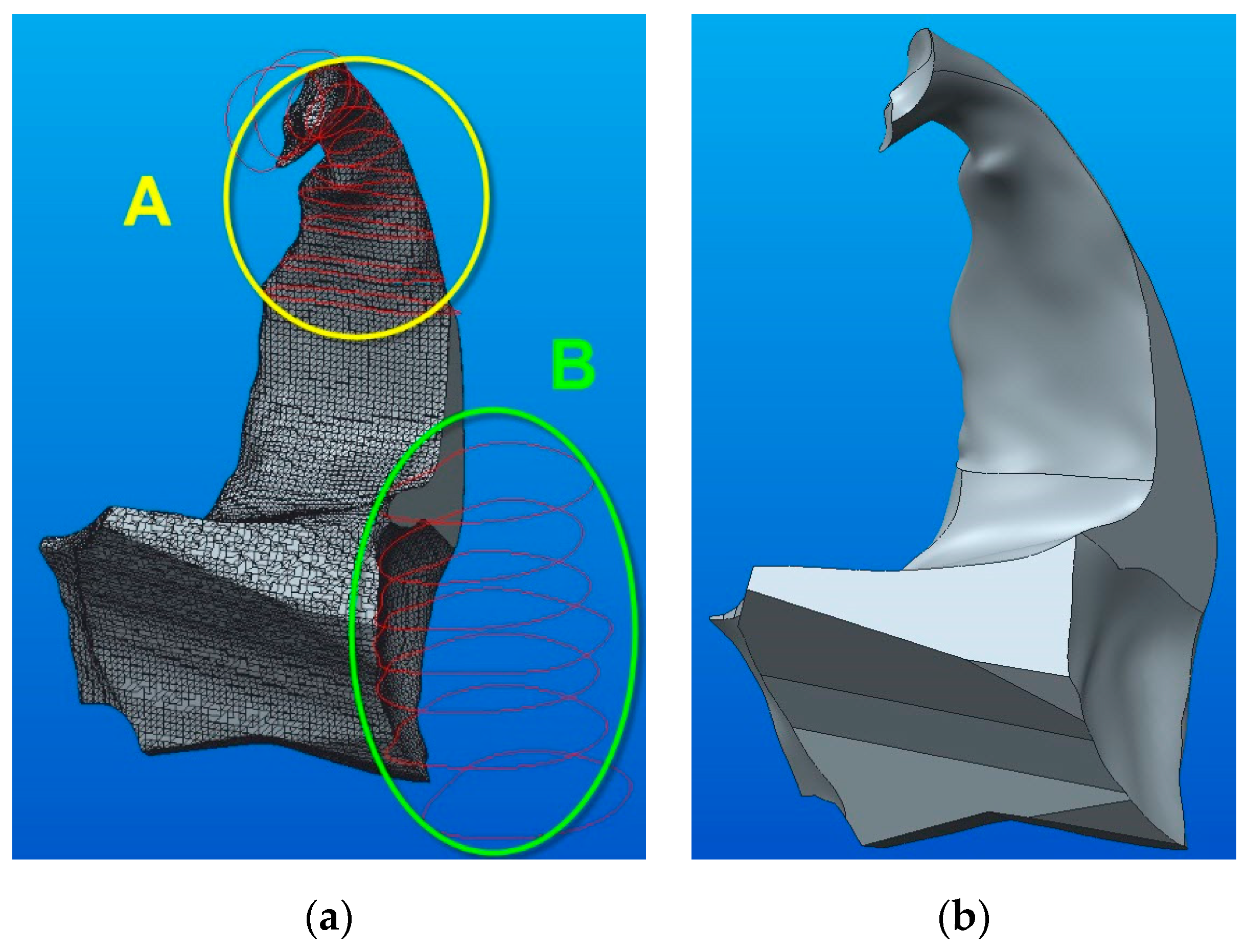
The conversion of the 3D model (STL type) of the zygomatic bone, as shown in Figure 1b, is now presented. By using the Shrinkwrap function, a complex solid is obtained where a division into two parts is required (part A and part B—see Figure 10a). After that, a sketch in the section plane was created (see Figure 10b). The sketch is required for the reunion of the two components after the conversion into parametric solids.
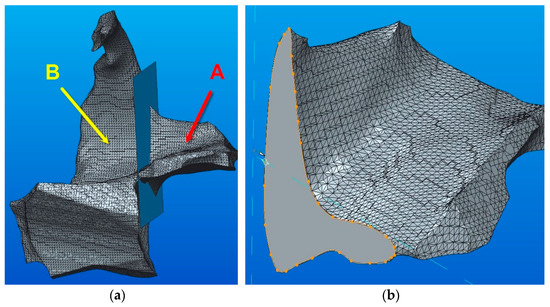
Figure 10.
The conversion of the 3D model (STL type) of the zygomatic bone: (a) 3D model components; (b) the bonding section.
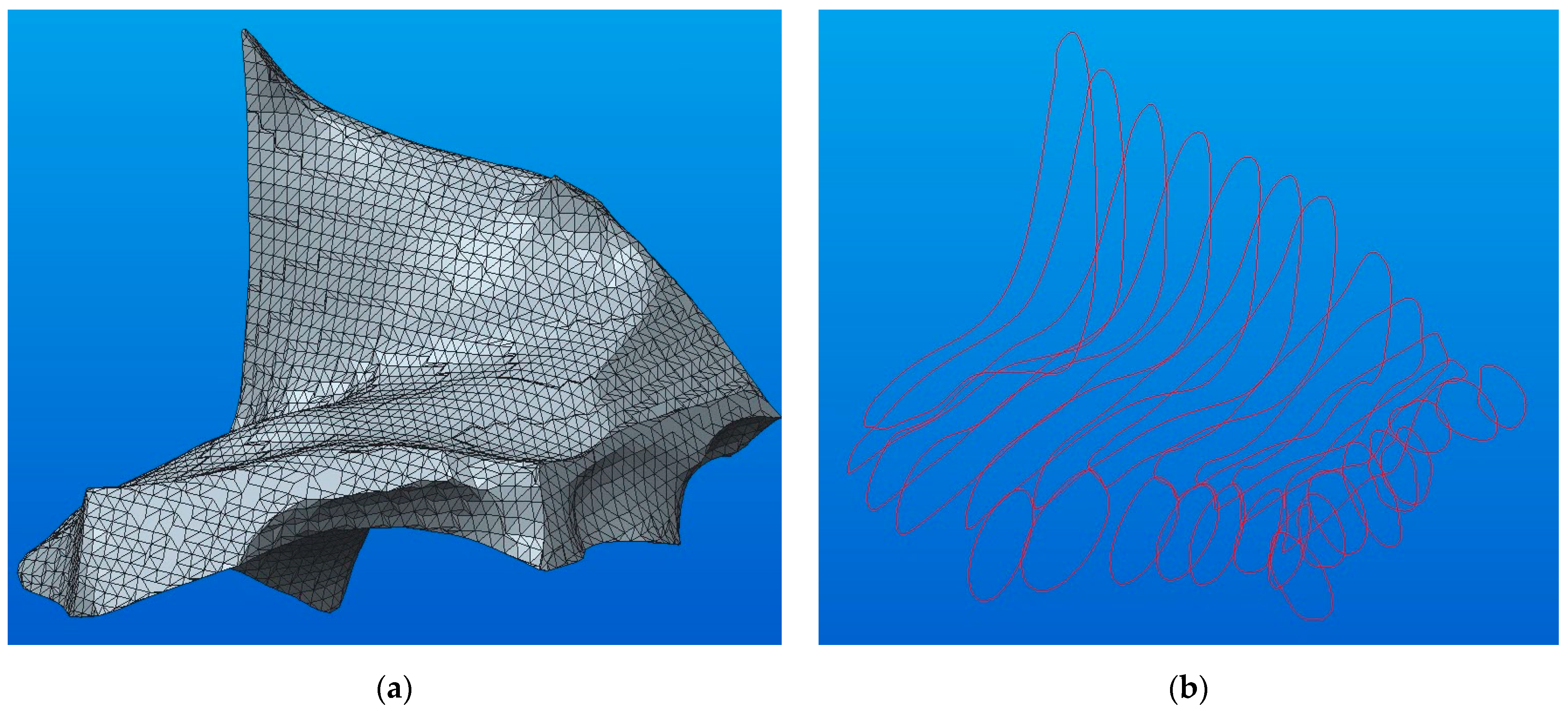
In order to obtain component A (Figure 11a), the Shrinkwrap solid was sectioned with a series of parallel planes, and these sections were sketches with Bézier curves (see Figure 11b).
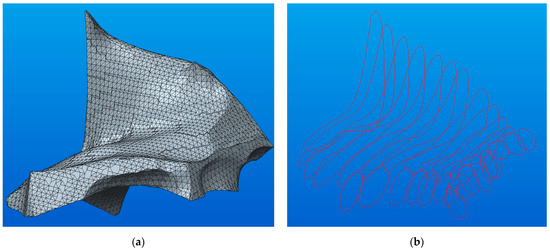
Figure 11.
The A component tracing: (a) Shrinkwrap model; (b) sketches necessary for modeling.
Since the initial model of the zygomatic bone contains both straight contours and flat and curved surfaces, after modeling them using the Blend function (Figure 12), it is necessary to adjust them via a series of operations using the Extrude Cut (Figure 12b) and Blend Cut functions (Figure 12c). These additional operations are intended to make the approximation of the initial model as accurate as possible. Figure 12c presents the final parameterized model obtained after applying all the modeling operations.
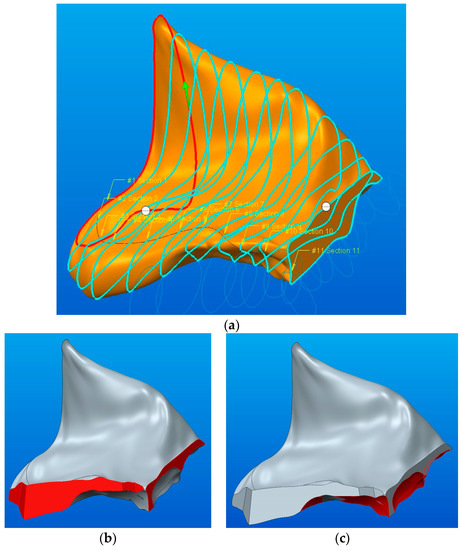
Figure 12.
The achievement of the A component—results of the following functions: (a) Blend—parameterized model; (b) Extrude Cut—obtaining straight edges and flat surfaces; (c) Blend Cut—obtaining curved surfaces.
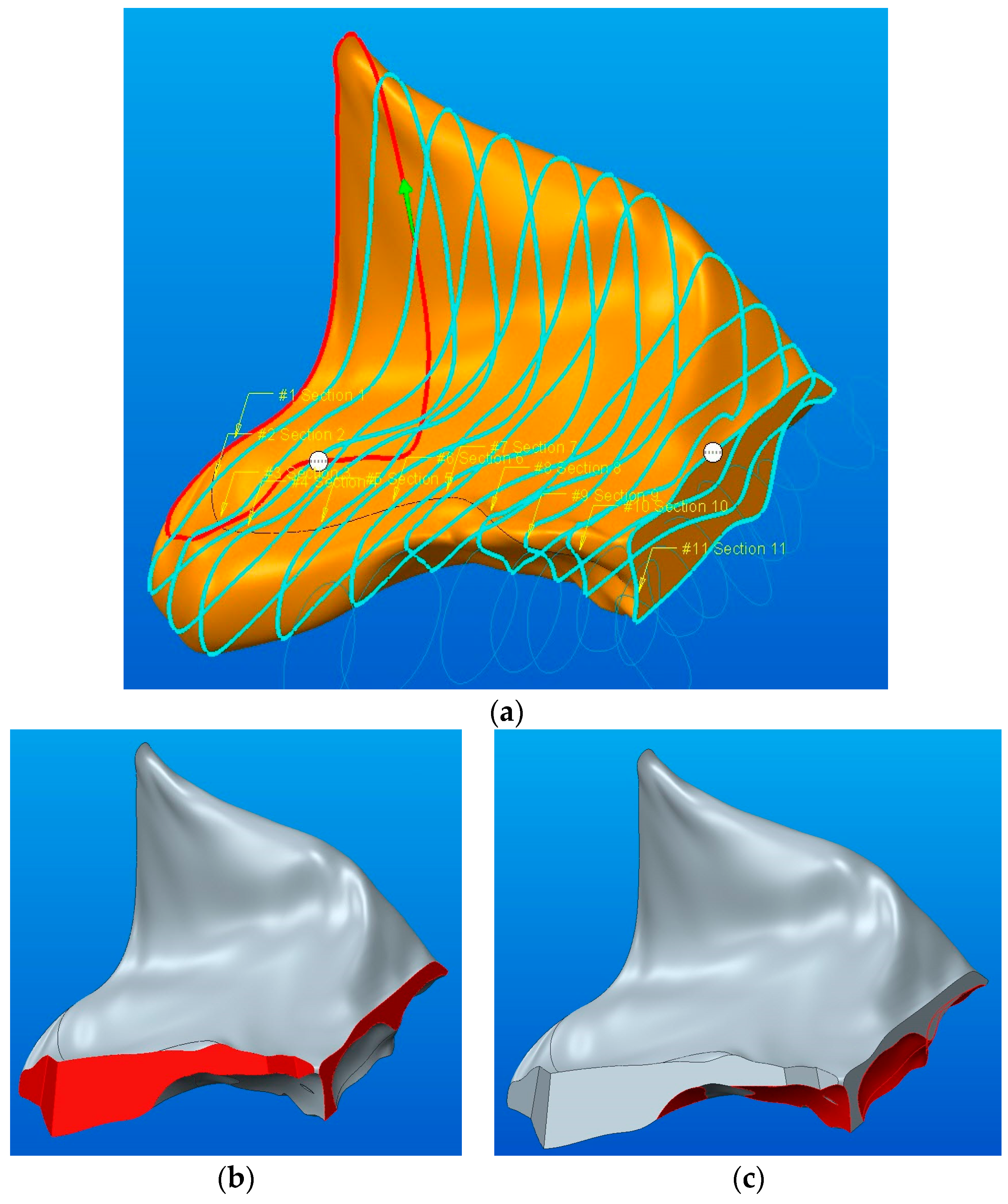
The 3D model of component B had a more complex shape, as can be seen in Figure 13a, and it required a new approach for the modeling methodology. The initial model was the basis for tracing external sketches (Figure 13b and detail B in Figure 14a). After obtaining the sketches, operations for removing the excess material from a predefined parallelepiped model were applied.
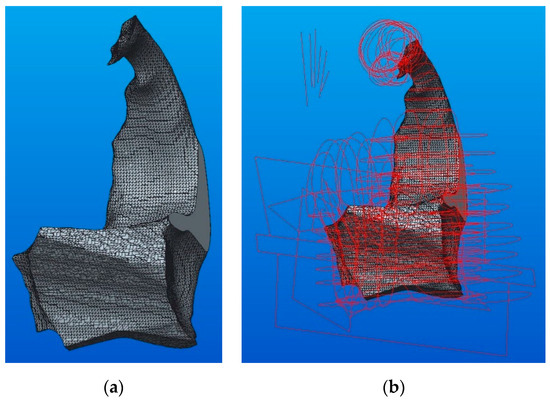
Figure 13.
The B component tracing: (a) Shrinkwrap model; (b) sketches necessary for modeling.
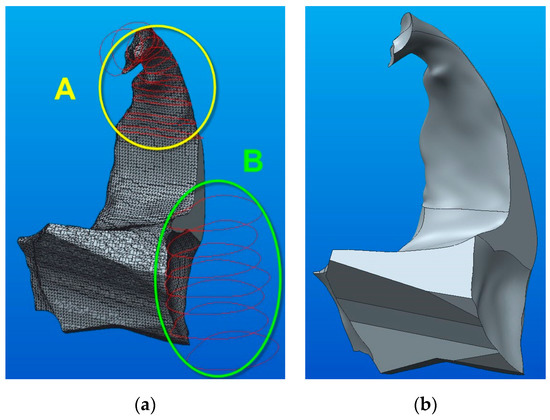
Figure 14.
Tracing of the upper and lower part of the B component: (a) details of sketches; (b) the final parameterized model of the B component.
For the upper part of the model (detail A in Figure 14), the same steps were applied as for modeling component A, with the difference that the sketches were arranged on the inclined plane normal to the axis of the zygomatic bone apophysis. Figure 14b shows the final parametrized model of the B component after applying the modeling functions: Blend—applied to the top surface, Blend Cut and Extrude Cut—applied to the exterior sketches that define the outer contour of the component.
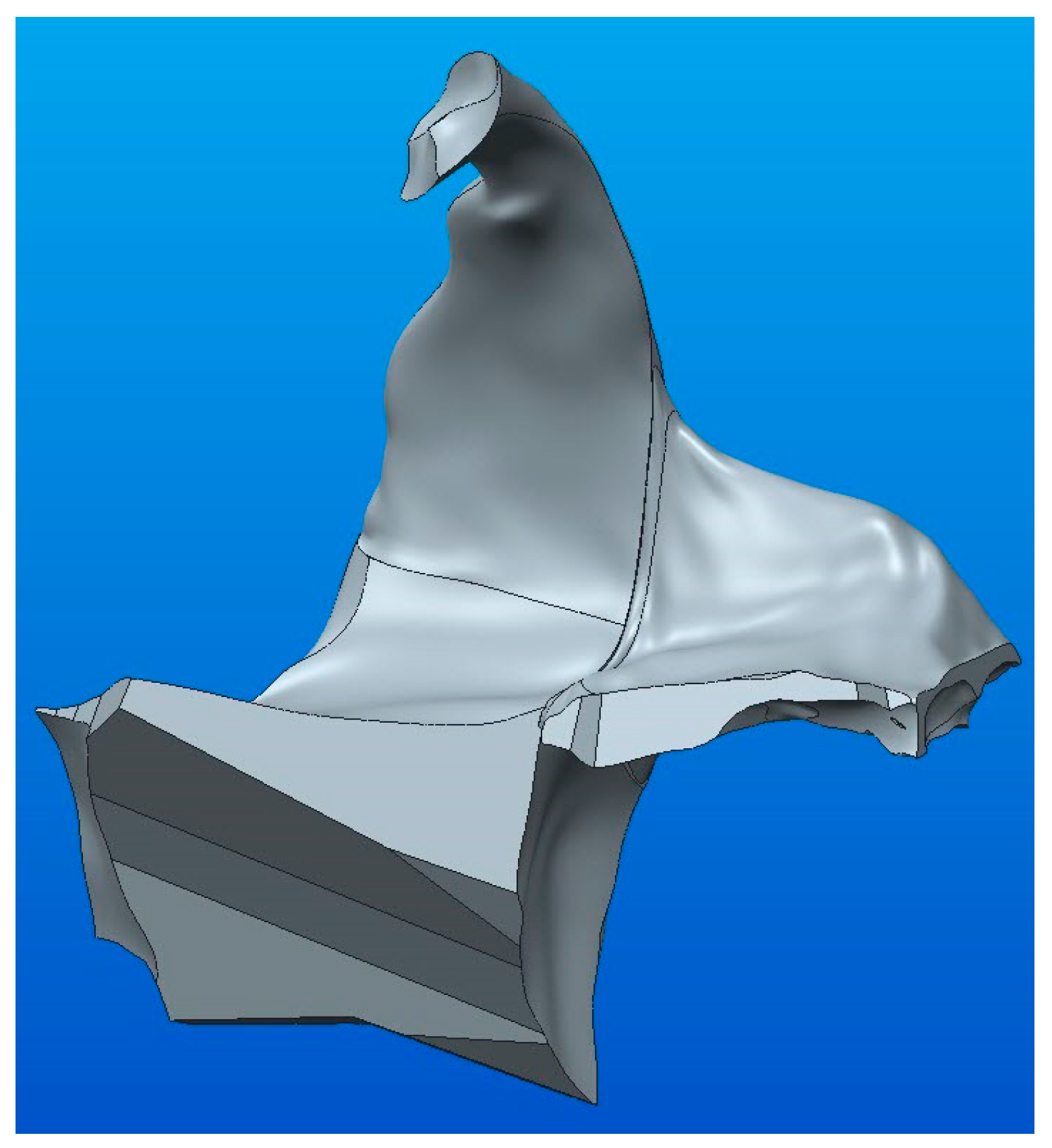
Once the two parts, marked with yellow and green (A and B), were obtained by Boolean union operation (Merge) into the bonding area (see Figure 10b), the parameterized solid model was obtained, as shown in Figure 15.
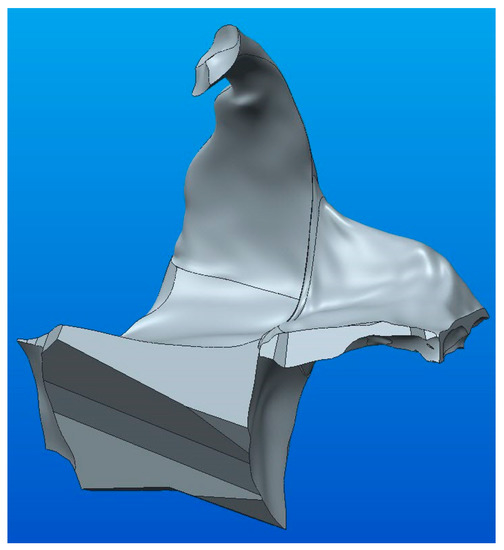
Figure 15.
The complete parametric solid model resulting from the union of components A and B.
No problems were encountered when the parametric solid models resulting from this conversion method (geometric modeling) were analyzed using FEA.
4. Results
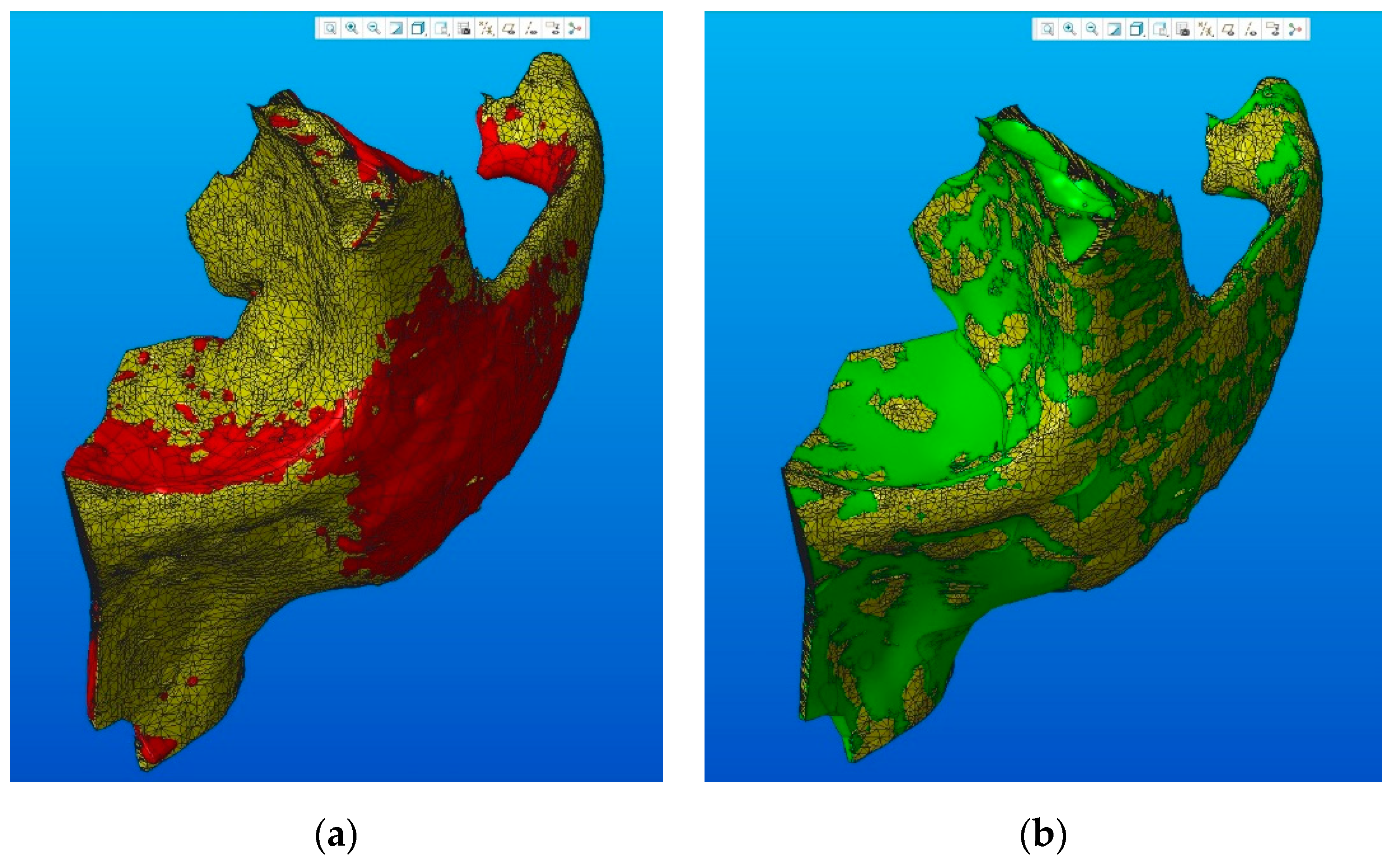
The models of the zygomatic bone obtained using the two methods of conversion (using the specific functions of the CATIA software and geometric modeling using sketches in Creo Parametric software) were subjected to FEA. Before performing the analysis, it is important to get information regarding the model accuracy with respect to the original state; a smoother model will lead to an easier mesh generation and slightly different results under the same boundary conditions. A visual comparison of the two solid models with the base STL model is presented in Figure 16. By comparing the volumes of the 3D models, we can estimate the geometry changes introduced by the conversion techniques presented above. Thus, the CATIA model (Figure 16a) has a volume of 16.35 cm3, while the Creo model (Figure 16b) has a volume of 16.66 cm3, which is comparative with the initial volume of 16.41 cm3 of the STL model. The small difference reflects the accuracy of the generated models.
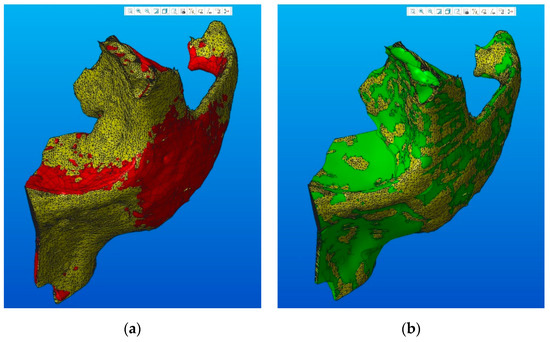
Figure 16.
Comparison between generated and initial STL models (in yellow): (a) CATIA model; (b) Creo model.
The FE analyses performed in this study were static and aimed to study the quality of the obtained models and to determine the time needed for performing the simulations.
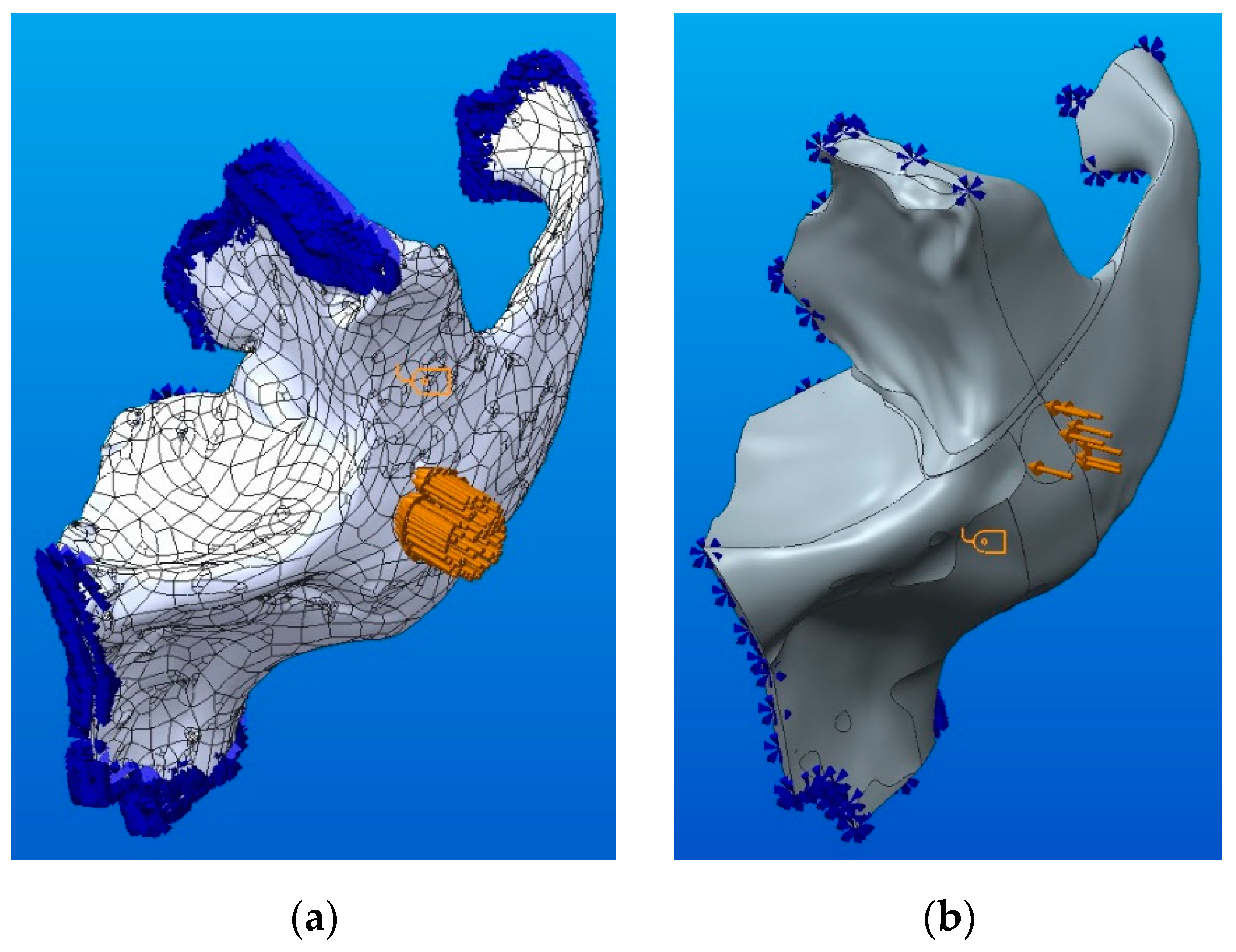
Figure 17 shows the load conditions (force uniformly distributed) and the kinematic constraints (locks on the connection areas) of two solid models obtained by conversion. The obtained model using CATIA software is shown in Figure 17a, while Figure 17b presents the parameterized model obtained by modeling using sketches in Creo Parametric software.
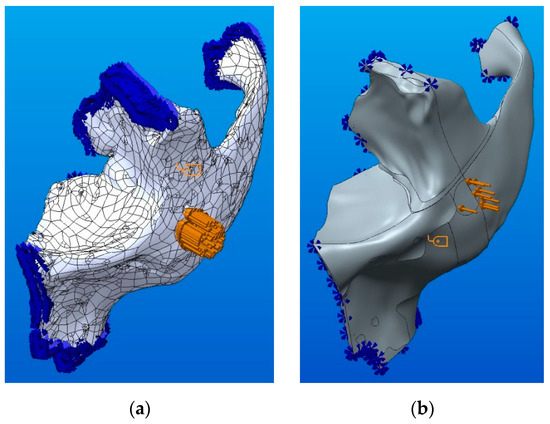
Figure 17.
Loading conditions and kinematic constraints: (a) for the CATIA model; (b) for the Creo model.
Although identical load values and constraints were applied on both models, in Figure 17, a difference of density between the force and constraints symbols can be observed due to the different number of facets that form the models. The applied load corresponds to an impact force resulting in a trauma.
Table 1 presents data referring to the mesh size of the two 3D solid models.

Table 1.
Data referring to the mesh size.
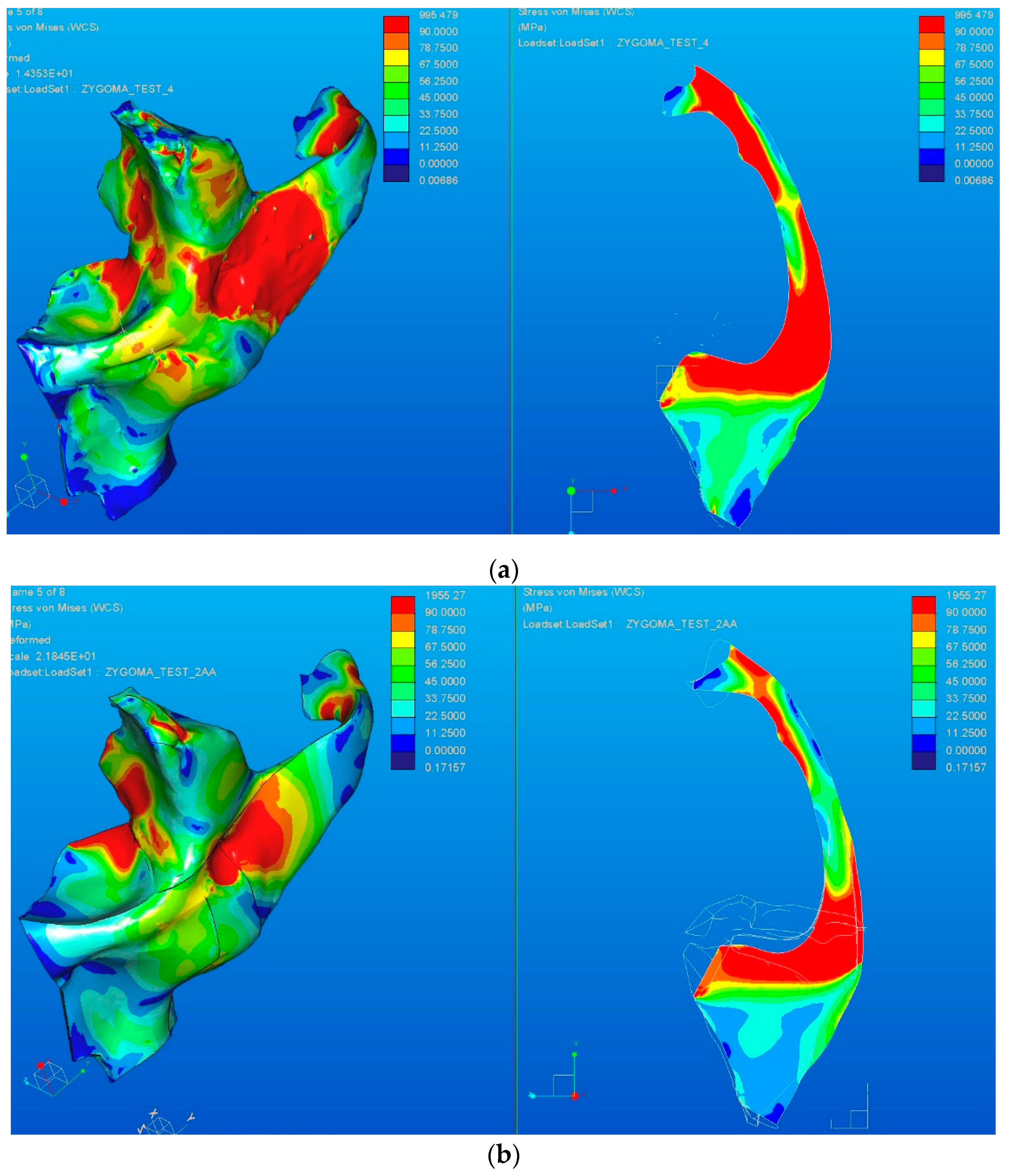
Figure 18 shows the results of the two FE analyses, respectively the equivalent von Mises stress distribution in volume (left side) and in plane (right side) located at the middle of the model that includes all the elements of the zygomatic bone. A difference in the stress distribution caused by the geometric elements that form the solid models can be observed.
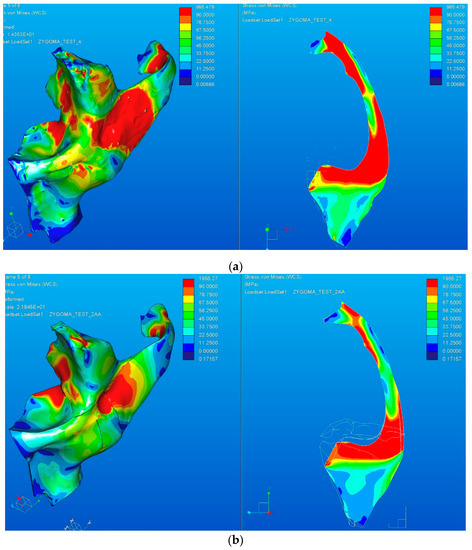
Figure 18.
Von Mises stress distribution: (a) for the CATIA model; (b) for the Creo model.
Regarding the time needed to perform the FEA, it can be seen in Table 2 that the analysis of the Creo Parametric model took only 73 s, this time being four times shorter than the time required for solving the CATIA model.

Table 2.
Computation time of the FE analyses.
It can be seen in Table 1 and Table 2 that there is a clear difference between the time requirements for the models, the parameterized model having the advantage from all points of view. The explanation consists of the fact that it can be discretized with tetrahedral elements (higher order), resulting in fewer elements: 11,324 against 254,886 (see Table 1), i.e., 22.5 times less.
5. Conclusions
This study has shown that there are several methods for converting the STL models into solid models and that these methods can be applied for complex models as a tool useful for designers that are working in reverse engineering.
By comparing the volumes of the 3D models, the geometry changes introduced can be estimated by the conversion techniques presented above. Thus, the CATIA model has a volume of 16.35 cm3, while the Creo model has a volume 16.66 cm3, which is comparative with the initial volume of 16.41 cm3 of the STL model. The differences—0.35% less for CATIA and 1.16% more for Creo software—are connected with the accuracy of the generated models and the number of generated facets.
It has been observed that for editing solid models made by conversion using CATIA software, one should consider that a feature created at the intersection of geometric elements that define the boundaries could be locked and subsequently unexecuted. On a 3D solid model created using sketches, any type of extrusion could be achieved and elimination and Boolean operations could be conducted in a shorter time and without errors. An important aspect of this technique relates to the selection of significant feature sections for functional structure and the ones for anatomical appearance; a geometry simplification should not alter the local topology, stress concentrators, or other important geometrical details.
By using Bezier curves, one may obtain parameterized solid models having a higher complexity but requiring a greater experience of the operator and longer time for modeling.
FEA has shown major differences between the two types of models; the model obtained using Creo Parametric software has advantages from all points of view (number of elements, computation time, hardware usage). This is mainly due to its parameterization being completely defined by mathematical relationships. Thus, it is recommended, especially for large parts, to make a conversion to parameterized models.
The FE results are the starting point for a patent that proposed a multi-structure medical implant obtained by optimization of the additive manufacturing process.
The above-described methodology will be applied also on dental implants and complex industrial components during the reverse engineering process.
6. Patents
These studies were an integral part of a project (AM-CIR project, PN-II-RU-TE-2014-4-1157, No. 37/01.10.2015) funded by the Romanian Government and were the basis for submitting an application patent on 17 May 2017. The patent name is “Process of manufacturing customized multi-structure medical implants by additive manufacturing technologies involves forming silicone rubber mold by vacuum casting VC, to give final shape of implant”, and the number is RO132908-A2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L. and C.V.; methodology, M.C.D.; software, C.V.; validation, D.L., C.V. and M.C.D.; investigation, D.L., C.V. and M.C.D.; resources, D.L.; data curation, D.L.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L.; writing—review and editing, D.L. and M.C.D.; visualization, C.V.; supervision, M.C.D.; project administration, D.L.; funding acquisition, D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the AM-CIR project, PN-II-RU-TE-2014-4-1157, No. 37/01.10.2015 financed from the UEFISCDI by the Romanian Government.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chung-Shing, W.; Wei-Hua, A.W.; Man-Ching, L. STL rapid prototyping bio-CAD model for CT medical image segmentation. Comput. Ind. 2010, 61, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Feature-guided shape-based image interpolation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajon, D.; Bolch, W. Marching cube algorithm: Review and trilinear interpolation adaptation for image-based dosimetric models. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2003, 27, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkhedkar, R.M.; Bhatt, A.D. Material-solid modeling of human body: A heterogeneous B-spline based approach. Comput. Des. 2009, 41, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majstorovic, V.; Trajanovic, M.; Vitkovic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Reverse engineering of human bones by using method of anatomical features. CIRP Ann. 2013, 62, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-J. Three-dimensional surface reconstruction of human bone using a B-spline based interpolation approach. Comput. Des. 2011, 43, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwen, S.; Dongming, G.; Zhenyuan, J.; Weijun, L. B-spline surface reconstruction and direct slicing from point clouds. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 27, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z. Direct generation of extended STL file from unorganized point data. Comput. Des. 2011, 43, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuming, G.; Wei, Z.; Hongwei, L.; Fanqin, Y.; Xiang, C. Feature suppression based CAD mesh model simplification. Comput. -Aided Des. 2010, 42, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Rypl, D.; Bittnar, Z. Generation of computational surface meshes of STL models. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2006, 192, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, D.V. Fundamentals of Finite Element Analysis; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. Reconstruction individual three-dimensional model of fractured long bone based on feature points. Comp. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C. Sculptured surface machining using triangular mesh slicing. Comput. -Aided Des. 2004, 36, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Reddy, N.V.; Dhande, S. Real time adaptive slicing for fused deposition modelling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2003, 43, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, N.V.; Berce, P.; Dragoi, M.V.; Oancea, G.; Ivan, M.C.; Bâlc, N.; Lancea, C.; Udroiu, R.; Vasiloni, M.; Mihail, M.; et al. CAD/CAPP/CAM Systems: Theory and Applications; Tehnică Publishing House: Bucharest, Romania, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Przemysław, G.; Paweł, W. Merging of Bézier curves with box constraints. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2016, 296, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Reyes, J. Detecting symmetries in polynomial Bézier curves. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2015, 288, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Peña, J. Accurate evaluation of Bézier curves and surfaces and the Bernstein-Fourier algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 271, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leordean, D.; Dudescu, C.; Marcu, T.; Berce, P.; Bâlc, N.; Dudescu, M.C. Customized implants with specific properties, made by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).