Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes with Different Types of Superplasticizer as a Dispersing Agent for Self-Sensing Cementitious Materials
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Materials Characterization
2.2. CNT Dispersion in Water Using SPs and Ultrassound
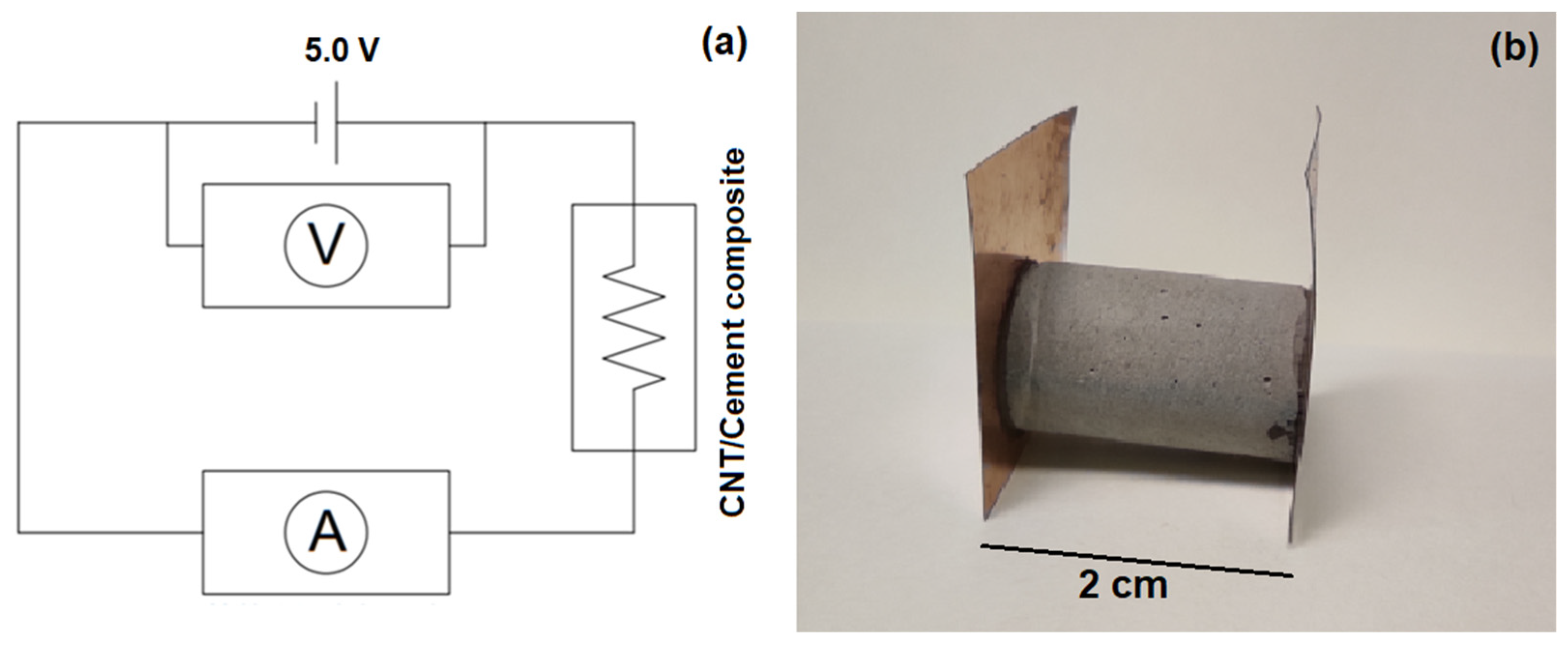
2.3. CNT–Cement Composites Preparation and Electrical Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Materials Characterization
3.2. CNT Dispersion in Water Using SP and Ultrassound
3.2.1. CNT:SP Variations for SPs B and D
3.2.2. CNT–SP Variations for SPs A and C
3.3. Electrical Resistivity of the CNT–Cement Composites
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, M.F.; Lourie, O.; Dyer, M.J.; Moloni, K.; Kelly, T.F.; Ruoff, R.S. Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load. Science 2000, 287, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwirzen, A.; Habermehl-Cwirzen, K.; Penttala, V. Surface decoration of carbon nanotubes and mechanical properties of cement/carbon nanotube composites. Adv. Cem. Res. 2008, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunashyal, A.M.; Tippa, S.V.; Quadri, S.S.; Banapurmath, N.R. Experimental Investigation on Effect of Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Fibres on the Behavior of Plain Cement Mortar Composite Round Bars under Direct Tension. ISRN Nanotechnol. 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawreen, A.; Bogas, J.A.; Dias, A.P.S. On the mechanical and shrinkage behavior of cement mortars reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, S.S.-H.; Khitab, A.; Ahmad, S.; Khushnood, R.A.; Ferro, G.A.; Saleem Kazmi, S.M.; Qureshi, L.A.; Restuccia, L. Improving the mechanical performance of cement composites by carbon nanotubes addition. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2017, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, K.M.; Kai, M.F.; Zhang, L.W. Carbon nanotube reinforced cementitious composites: An overview. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 91, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Multifunctional and Smart Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Cement-Based Materials. Nanotechnol. Civ. Infrastruct. 2011, 1, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S. Smart concretes and structures: A review. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1303–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Sahmaran, M.; Mesbah, H.A.; Anwar, K. Advanced engineered cementitious composites with combined self-sensing and self-healing functionalities. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, S.; Tulliani, J.-M.; Ferro, G.; Tagliaferro, A. Influence of carbon nanotubes structure on the mechanical behavior of cement composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, F.; Zheng, L. Dispersion of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) by ionic liquid-based Gemini pyrrolidinium surfactants in aqueous solution. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gao, L.; Sun, J. Production of aqueous colloidal dispersions of carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, O.; Toledo, R. Nanotube–Cement Composites. In Carbon Nanomaterials Sourcebook: Nanoparticles, Nanocapsules, Nanofibers, Nanoporous Structures, and Nanocomposites; Sattler, K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume II, pp. 573–596. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, B.; Jian, S.; Korayem, A.H.; Collins, F.; Wang, C.M. Effect of ultrasonication energy on engineering properties of carbon nanotube reinforced cement pastes. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 85, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Mende, M.; Pötschke, P.; Petzold, G. Dispersability and particle size distribution of CNTs in an aqueous surfactant dispersion as a function of ultrasonic treatment time. Carbon N. Y. 2010, 48, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochaiya, T.; Chaipanich, A. Behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the porosity and microstructure of cement-based materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 1941–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Grasley, Z.; Tyson, B.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. Distribution of Carbon Nanofibers and Nanotubes in Cementitious Composites. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2142, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Ouyang, D.; Xu, W. Mechanical properties and durability of ultra high strength concrete incorporating multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Materials 2016, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szeląg, M. Mechano-physical properties and microstructure of carbon nanotube reinforced cement paste after thermal load. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gay, C.; Sanchez, F. Performance of Carbon Nanofiber–Cement Composites with a High-Range Water Reducer. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2142, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, O.; Sierra, G.; Tobón, J.I. Influence of super plasticizer and Ca(OH)2 on the stability of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes dispersions for cement composites applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Reales, O.A.; Ocampo, C.; Arias Jaramillo, Y.P.; Ochoa Botero, J.C.; Quintero, J.H.; Silva, E.C.C.M.; Toledo, R.D. Reinforcing Effect of Carbon Nanotubes/Surfactant Dispersions in Portland Cement Pastes. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Zhang, K.; Yu, X.; Kwon, E.; Ou, J. Fabrication of Piezoresistive CNT/CNF Cementitious Composites with Superplasticizer as Dispersant. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Reales, O.A.; Dias Toledo Filho, R. A review on the chemical, mechanical and microstructural characterization of carbon nanotubes-cement based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, J.; Vanli, O.A.; Liang, R. A Review of Spectral Methods for Dispersion Characterization of Carbon Nanotubes in Aqueous Suspensions. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Yu, A.; Kim, E.; Zhao, B.; Itkis, M.E.; Bekyarova, E.; Haddon, R.C. Influence of the zeta potential on the dispersability and purification of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 11520–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Ubertini, F.; García-Macías, E.; Castro-Triguero, R.; Downey, A.; Laflamme, S.; Meoni, A.; Materazzi, A.L. Static and Dynamic Strain Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Components through Embedded Carbon Nanotube Cement-Based Sensors. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowska-Renkas, E. The effect of superplasticizers’ chemical structure on their efficiency in cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, S.; Havel, M.; Gogotsi, Y. Monitoring oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Reales, O.A.; Duda, P.; Dias Toledo Filho, R. Effect of a Carbon Nanotube/Surfactant Aqueous Dispersion on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Portland Cement Pastes. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, O.; Pearl, W.; Paiva, M.D.M.; Miranda, C.; Toledo Filho, R. Effect of a commercial dispersion of multi walled carbon nanotubes on the hydration of an oil well cementing paste. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2016, 10, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.; Chang, T.; Hsiao, T. Effect of nanosilica on characterization of Portland cement composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 424, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Barbhuiya, S.A.; Charan, D.; Pandey, S.P. Characterising cement-superplasticiser interaction using zeta potential measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Tiecco, M.; Meoni, A.; Ubertini, F. Improved strain sensing properties of cement-based sensors through enhanced carbon nanotube dispersion. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chung, D.D. Electric polarization and depolarization in cement-based materials, studied by apparent electrical resistance measurement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; Zinno, R. Electrical conductivity of self-monitoring CFRC. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wansom, S.; Kidner, N.; Woo, L.; Mason, T. AC-impedance response of multi-walled carbon nanotube/cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Kawashima, S.; Yin, H. Influence of carbon nanotube clustering on mechanical and electrical properties of cement pastes. Materials 2016, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, S.; Zhu, Z.H.; Meguid, S.A. Carbon nanotube agglomeration effect on piezoresistivity of polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2014, 55, 5488–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-rekabi, S.; Cundy, A.B.; Lampropoulos, A.; Savina, I.N. Experimental investigation of the effect of superplasticizer/surfactant aided aqueous dispersion of multi-walled Carbon nanotubes on workability and mechanical properties of cementitious composites. In Proceedings of the 25th Workshop and Colloquium, Regensburg, Germany, 2 March 2016. [Google Scholar]









| Code | Superplasticizer Name | Solids Content * | Superplasticizer Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Glenium 51 | 33% | Ether polycarboxylate |
| B | ADI-SUPER H40 | 40% | Ether polycarboxylate |
| C | MC-PowerFlow 1180 | 35% | Ether polycarboxylate |
| D | Hormitec SP430 | 40% | Naphtalene |
| Dispersion | SP Type | CNT (%) | SP (%) | Water (%) | CNT:SP | Sonication Energy (J/gdispersion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25%CNT/1.00%SP A | A | 0.25 | 1.00 | 98.75 | 1:4 | 900 |
| 0.25%CNT/1.00%SP B | B | 1000 | ||||
| 0.25%CNT/1.00%SP C | C | 1000 | ||||
| 0.25%CNT/1.00%SP D | D | 1000 |
| Composite | CNT (% *) | Cement (%) | VMA (% *) | w/c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF | - | 100.0 | 0.60 | 0.50 |
| 0.10% CNT–cement/SP A | 0.10 | |||
| 0.10% CNT–cement/SP B | ||||
| 0.10% CNT–cement/SP C | ||||
| 0.10% CNT–cement/SP D | ||||
| 0.40% CNT–cement/SP A | 0.40 | |||
| 0.40% CNT–cement/SP B | ||||
| 0.40% CNT–cement/SP C | ||||
| 0.40% CNT–cement/SP D |
| Dispersion | SP Type | CNT (%) | SP (%) | Water (%) | CNT:SP | Sonication Energy (J/gdispersion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.40%CNT/1.60%SP B | B | 0.40 | 1.60 | 98.00 | 1:4 | 1100 |
| 0.80%CNT/1.60%SP B | B | 0.80 | 1.60 | 97.60 | 1:2 | 1000 |
| 0.40%CNT/1.60%SP D | D | 0.40 | 1.60 | 98.00 | 1:4 | 900 |
| 0.80%CNT/1.60%SP D | D | 0.80 | 1.60 | 97.60 | 1:2 | 1000 |
| Dispersion | SP Type | CNT (%) | SP (%) | Water (%) | CNT:SP | Sonication Energy (J/gdispersion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25%CNT/0.25%SP A | A | 0.25 | 0.25 | 99.50 | 1:1 | 600 |
| 0.25%CNT/3.00%SP A | A | 0.25 | 3.00 | 96.75 | 1:12 | 900 |
| 0.80%CNT/1.60%SP A | A | 0.80 | 1.60 | 97.60 | 1:2 | 1000 |
| 0.25%CNT/0.25%SP C | C | 0.25 | 0.25 | 99.50 | 1:1 | 600 |
| 0.25%CNT/3.00%SP C | C | 0.25 | 3.00 | 96.75 | 1:12 | 800 |
| 0.80%CNT/1.60%SP C | C | 0.80 | 1.60 | 97.60 | 1:2 | 1000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Almeida Carísio, P.; dos Santos Mendonça, Y.G.; Soares, C.F.T.; Reales, O.A.M.; de Moraes Rego Fairbairn, E.; Filho, R.D.T. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes with Different Types of Superplasticizer as a Dispersing Agent for Self-Sensing Cementitious Materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188452
de Almeida Carísio P, dos Santos Mendonça YG, Soares CFT, Reales OAM, de Moraes Rego Fairbairn E, Filho RDT. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes with Different Types of Superplasticizer as a Dispersing Agent for Self-Sensing Cementitious Materials. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188452
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Almeida Carísio, Pedro, Yasmim Gabriela dos Santos Mendonça, Carlos Fernando Teodósio Soares, Oscar Aurelio Mendoza Reales, Eduardo de Moraes Rego Fairbairn, and Romildo Dias Toledo Filho. 2021. "Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes with Different Types of Superplasticizer as a Dispersing Agent for Self-Sensing Cementitious Materials" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188452
APA Stylede Almeida Carísio, P., dos Santos Mendonça, Y. G., Soares, C. F. T., Reales, O. A. M., de Moraes Rego Fairbairn, E., & Filho, R. D. T. (2021). Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes with Different Types of Superplasticizer as a Dispersing Agent for Self-Sensing Cementitious Materials. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8452. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188452







