Removal of Nitrate Ions Using Thermally and Chemically Modified Bioadsorbents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Adsorbents
2.2.2. Adsorption Tests
2.2.3. Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bioadsorbent Characterization
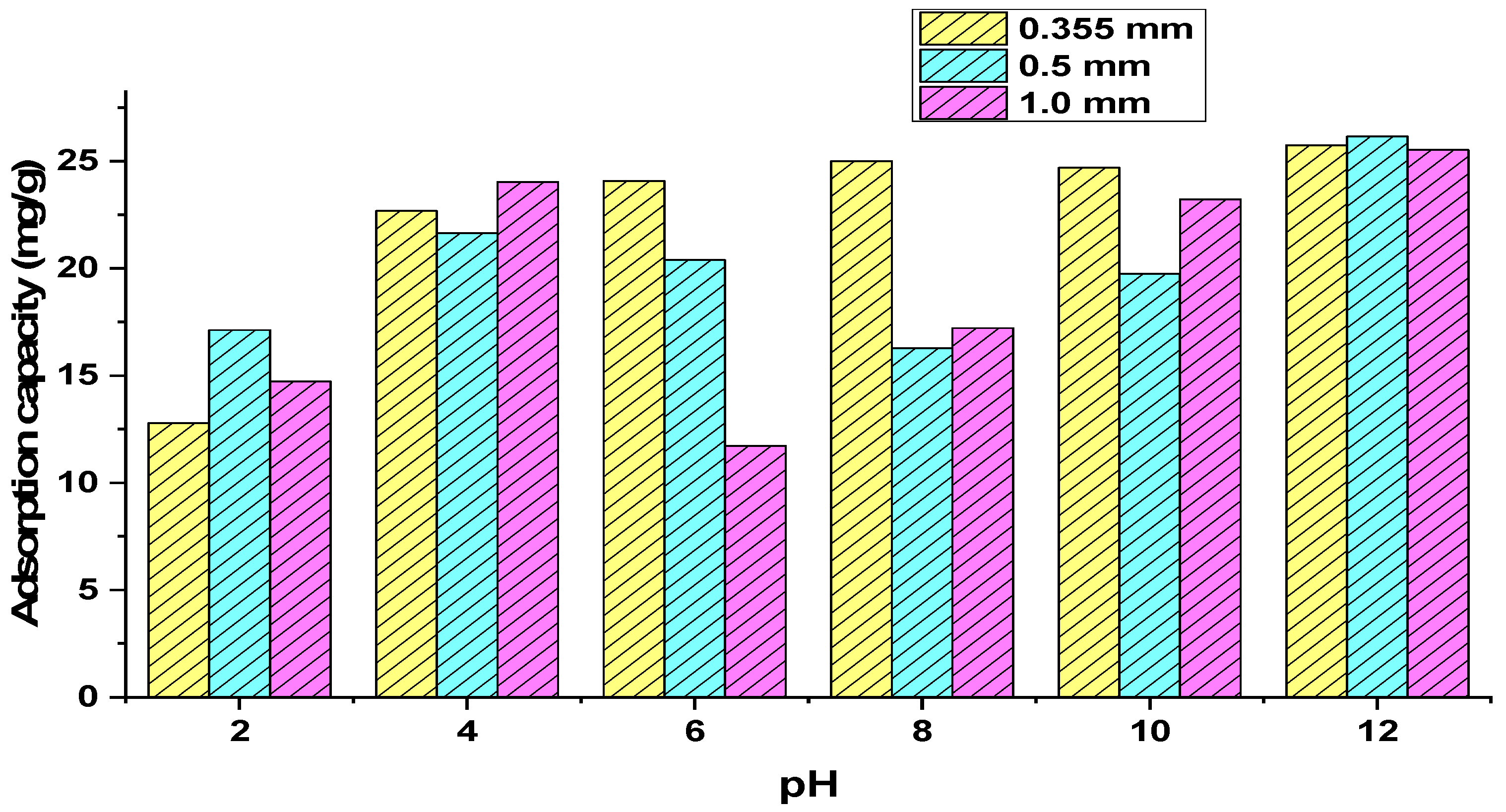
3.2. Adsorption Tests
3.3. Adsorption Equilibrium
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
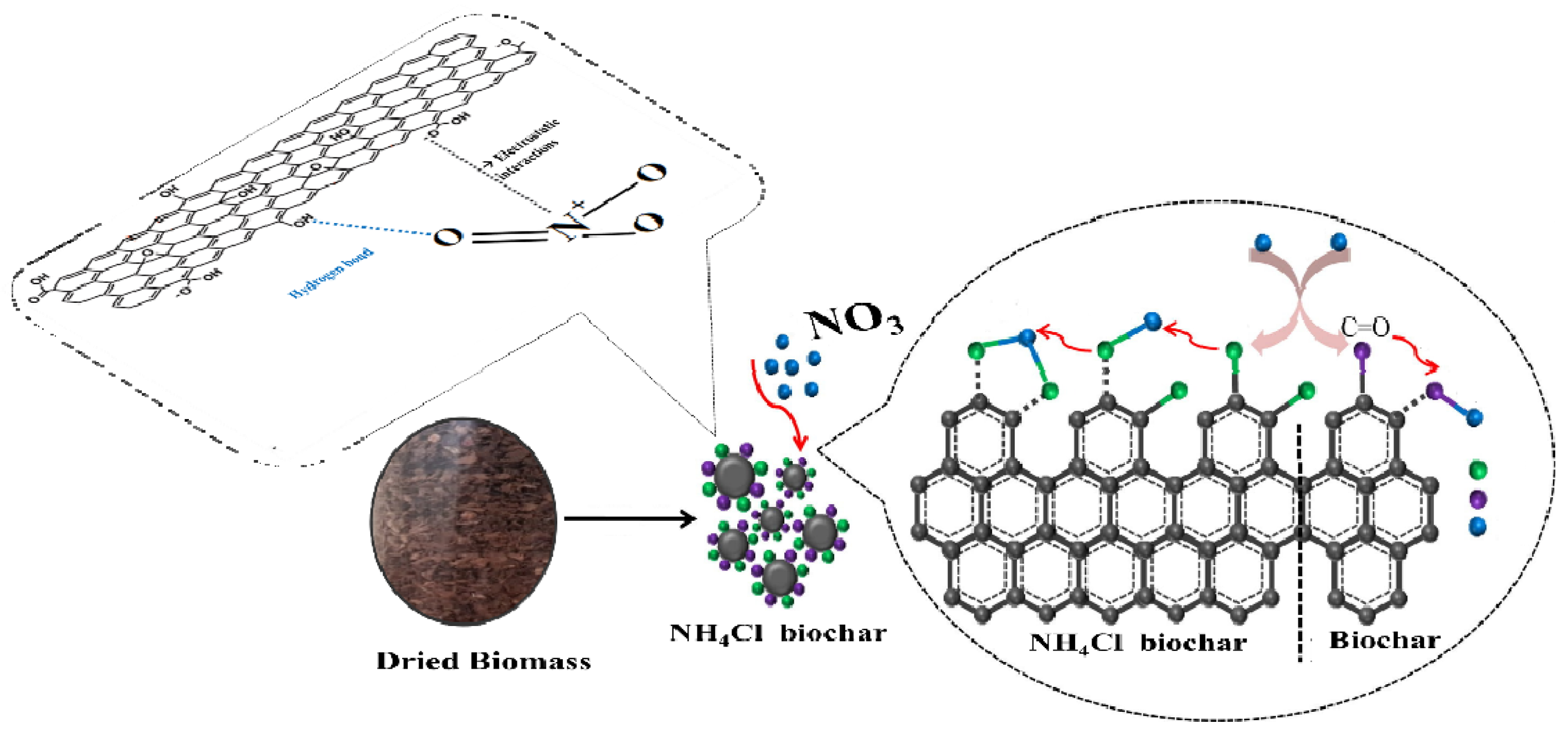
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Drinking-Water. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; De Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; Van Breda, S.G. Drinking Water Nitrate and Human Health: An Updated Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Solares, S.; Merillas, B.; Cimavilla-Román, P.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.; Pinto, J. Enhanced nitrates-polluted water remediation by polyurethane/sepiolite cellular nanocomposites. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Feng, T. Application of modified chitosan microspheres for nitrate and phosphate adsorption from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 90878–90886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.T.; Ali, S.; Idris, A.; Haroon, R. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of nitrate adsorption from aqueous solution by lignocellulose-based anion resins. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 62, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, X.; Huang, H.; Mei, K.; Xia, F.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Ji, X. Riverine nitrate source apportionment using dual stable isotopes in a drinking water source watershed of southeast China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 724, 137975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N. Spatial distribution, exposure, and potential health risk assessment from nitrate in drinking water from semi-arid region of South India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 310–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Parveen, S.; Bhat, B.N.; Ahmad, U. Seasonal Variations in Water Quality Parameters of River Yamuna, India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 694–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.M.; Shoaib, M.; Agwanda, P.; Lee, J.L. Modeling Approach for Water-Quality Management to Control Pollution Concentration: A Case Study of Ravi River, Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2018, 10, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, C.P.; Yamada, K. Impact of Population Growth on the Water Quality of Natural Water Bodies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de la Proteccion Social. Decreto 1575 de 2007 del Ministerio de ambiente, Vivienda y desarrollo territorial; Ministerio de la Proteccion Social: Bogotá, Colombia, 2007; pp. 1–14.
- Ministerio de la Protección Social; Ministerio de ambiente, vivienda y desarrollo sostenible. Resolución 2115 de 2007; Ministerio de la Protección Social: Ministerio de ambiente, vivienda y desarrollo sostenible: Bogotá, Colombia, 2007; pp. 1–23.
- Castrillón-Jaimes, Y.C.; Acevedo-Peñaloza, C.H.; Rojas-Suárez, J.P. Evaluation of the drinking water treatment system (STAP) San Fernando –Los Patios urbanization, Colombia. Efficiency and quality. UIS Ing. 2020, 19, 149–156. Available online: https://revistas.uis.edu.co/index.php/revistauisingenierias/article/view/10743/10969 (accessed on 28 July 2021). [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Jaramillo, L.; Mendoza-Atencio, M.A.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.E. Water quality in the municipalities of Sincerín and Gambote, Bolívar, Colombia (2017–2018. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioq. 2021, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.M.; De Cartagena, U.; Maestre, R.F. Matute creek, Cartagena, Colombia: Deterioration of water quality by human impact Arroyo. Rev. UDCA Actual. Divulg. Científica 2017, 20, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanvase, B.A.; Ugwekar, R.P.; Mankar, R.B. Novel Water Treatment and Separation Methods: Simulation of Chemical Processes; Apple Academic Press, INC: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z. Biochar as an adsorbent for inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus removal from water: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26297–26309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, M.; Pan, B. Limited role of biochars in nitrogen fixation through nitrate adsorption. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 592, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaney, N.; Ukpong, E.; Lin, C. Low-molecular-weight organic acids enable biochar to immobilize nitrate. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bakshi, S.; Li, C.; Parikh, S.J.; Hsieh, H.-S.; Pignatello, J.J. Modification of pyrogenic carbons for phosphate sorption through binding of a cationic polymer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 579, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Parikh, S.J.; Du, J.; Qi, F.; Willett, I.R. Influences of feedstock sources and pyrolysis temperature on the properties of biochar and functionality as adsorbents: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 744, 140714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z. Application of Mg–Al-modified biochar for simultaneous removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate from eutrophic water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Sahoo, D.; Remya, N. Biochar from microwave pyrolysis of rice husk for tertiary wastewater treatment and soil nourishment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xue, Y.; Long, L.; Hu, X. Adsorption of nitrate onto biochar derived from agricultural residuals. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Crespo, H.; Ortiz-Velásquez, M. Importance and determinants of the agricultural productive association: Yam cultivation in the Colombian Caribbean. Soc. Econ. 2020, 41, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, C.G.; Correa, M.J.; Ferrero, C. Resistant starches: A smart alternative for the development of functional bread and other starch-based foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.-N.; Liao, A.-M.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Huang, J.-H.; Wei, Z.-J. Microstructural, Textural, Sensory Properties and Quality of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles. Foods 2019, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, P.S.; Ávila, S.; Masisi, K.; Malunga, L.N.; Lazzarotto, M.; Schnitzler, E.; Ribani, R.H.; Beta, T. Green Development of Biodegradable Films Based on Native Yam (Dioscoreaceae) Starch Mixtures. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.D.; Rawat, K.; Bhadauria, V.; Singh, H. Recent trends in the application of modified starch in the adsorption of heavy metals from water: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 117763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimón-Bolívar, W.; Tejeda-Benítez, L.; Herrera, A.P. Removal of mercury (II) from water using magnetic nanoparticles coated with amino organic ligands and yam peel biomass. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villabona-Ortíz, A.; Tejada-Tovar, C.; Ruiz-Paternina, E.; Frías-González, J.D.; Blanco-García, G.D. Optimization of the Effect of Temperature and Bed Height on Cr (VI) Bioadsorption in Continuous System. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2019, 29, e10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Comparative adsorption performance of ibuprofen and tetracycline from aqueous solution by carbonaceous materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunell, G.V.; Fernandez, M.E.; Bonelli, P.R.; Cukierman, A.L. Desarrollo de un adsorbente específico en base a biomasa forestal para el tratamiento terciario de aguas contaminadas con iones nitrato., in CAIQ2013—VII Congreso Argentino de Ingeniería Química- 2das. Jorn. Argent. Segur. Procesos 2013, 7, 2. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM D7781—14 Standard Test Method for Nitrite-Nitrate in Water by Nitrate Reductase; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Boeykens, S.; Piol, M.N.; Legal, L.E.S.; Saralegui, A.B.; Vázquez, C. Eutrophication decrease: Phosphate adsorption processes in presence of nitrates. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Orta, M.D.M.; Medina-Carrasco, S.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Evaluation of a modified mica and montmorillonite for the adsorption of ibuprofen from aqueous media. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 171, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.K.M.P.; Mandlimath, T.R.; Sangeetha, P.; Revathi, S.K.; Kumar, S.K.A. Nanoscale materials as sorbents for nitrate and phosphate removal from water. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, R.; Tan, Z. Comparative analysis on adsorption properties and mechanisms of nitrate and phosphate by modified corn stalks. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 36468–36476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Tovar, C.; Gonzalez-Delgado, A.D.; Villabona-Ortiz, A. Characterization of Residual Biomasses and Its Application for the Removal of Lead Ions from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of nitrate and phosphate in binary systems on a novel adsorbent derived from corn stalks. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 188, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotsing, P.N.; Bouazizi, N.; Woumfo, E.D.; Mofaddel, N.; Le Derf, F.; Vieillard, J. Investigation of chromate and nitrate removal by adsorption at the surface of an amine-modified cocoa shell adsorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.P.; Selvakumar, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Extraction and modification of cellulose nanofibers derived from biomass for environmental application. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 42750–42773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, C.; Nayanathara, O.; Navarathna, C.M.; Jayawardhana, Y.; Nawalage, S.; Burk, G.; Karunanayake, A.G.; Madduri, S.B.; Vithanage, M.; Kaumal, M.N.; et al. The influence of three acid modifications on the physicochemical characteristics of tea-waste biochar pyrolyzed at different temperatures: A comparative study. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 17612–17622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Shibuya, R.; Akiba, C.; Saji, S.; Kondo, T.; Nakamura, J. Active sites of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for oxygen reduction reaction clarified using model catalysts. Science 2016, 351, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaruban, M.; Loganathan, P.; Shim, W.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, G.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S. Removing nitrate from water using iron-modified Dowex 21K XLT ion exchange resin: Batch and fluidised-bed adsorption studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zheng, H.; Gao, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Shao, M.; et al. Reaction intermediate-mediated electrocatalyst synthesis favors specified facet and defect exposure for efficient nitrate–ammonia conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.I.; Lou, K.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Ok, Y.S.; Anyia, A.O.; Chang, S.X. Adsorption of ammonium in aqueous solutions by pine sawdust and wheat straw biochars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25638–25647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Zarur, J.; Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona-Ortíz, A.; Acevedo, D.; Tejada-Tovar, R. Thermodynamics, Kinetics and Equilibrium Adsorption of Cr (VI) and Hg (II) in Aqueous Solution on corn cob (Zea mays). Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2018, 11, 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tejada-Tovar, C.N.; Villabona-Ortiz, Á.; Alvarez-Bajaire, G.; Attin-Torres, L.; Granados-Conde, C. Influencia de la altura del lecho sobre el comportamiento dinámico de columna de lecho fijo en la biosorción de mercurio. TecnoLógicas 2017, 20, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona, A.; Cabarcas, A.; Benitez, C.; Acevedo, D. Optimization of variables in fixed-bed column using the response surface methodology. Contemp. Eng. Sci. 2018, 11, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garba, Z.N.; Ugbaga, N.I.; Abdullahi, A.K. Evaluation of optimum adsorption conditions for Ni (II) and Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution by modified plantain peels (MPP). Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Baglou, M.A.S. Surface modified montmorillonite with cationic surfactants: Preparation, characterization, and dye adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battas, A.; EL Gaidoumi, A.; Ksakas, A.; Kherbeche, A. Adsorption Study for the Removal of Nitrate from Water Using Local Clay. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafshejani, L.D.; Hooshmand, A.; Naseri, A.A.; Mohammadi, A.S.; Abbasi, F.; Bhatnagar, A. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution by modified sugarcane bagasse biochar. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, A.; Meenakshi, S. A novel quaternized resin with acrylonitrile/divinylbenzene/vinylbenzyl chloride skeleton for the removal of nitrate and phosphate. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 257, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodeh, H.R.; Sereshti, H.; Afsharian, E.Z.; Nouri, N. Enhanced removal of phosphate and nitrate ions from aqueous media using nanosized lanthanum hydrous doped on magnetic graphene nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Hu, W. Nitrate adsorption from aqueous solution using granular chitosan-Fe3+ complex. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.; Rauf, T.A. Adsorption performance of amine functionalized cellulose grafted epichlorohydrin for the removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, S.K.; Nasseri, S.; Nabizadeh, R.; Khoobi, M.; Nazmara, S.; Mahvi, A.H. Adsorption of nitrate onto anionic bio-graphene nanosheet from aqueous solutions: Isotherm and kinetic study. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, B.-Y.; Yue, W.-W.; Yue, Q.-Y. Preparation and utilization of wheat straw anionic sorbent for the removal of nitrate from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, M.W.; Woo, S.H. Nitrate removal from aqueous solutions by cross-linked chitosan beads conditioned with sodium bisulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Wang, F.; Xue, N.; Sun, S.; Song, W.; Jia, R. Adsorption of nitrate from aqueous solution by magnetic amine-crosslinked biopolymer based corn stalk and its chemical regeneration property. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, U.; Baes, A.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Preparation of agricultural residue anion exchangers and its nitrate maximum adsorption capacity. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Nitrate adsorption by multiple biomaterial based resins: Application of pilot-scale and lab-scale products. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Tan, X.; Yue, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y. Nitrate removal from aqueous solution by Arundo donax L. reed based anion exchange resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203–204, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Ren, Y.; Shi, D.; Chai, H.; Ai, H.; He, Q.; Gu, L. Enhanced nitrate adsorption by using cetyltrimethylammonium chloride pre-loaded activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 3562–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Liu, H. Kinetic and isotherm studies of nitrate adsorption on granular Fe-Zr-chitosan complex and electrochemical reduction of nitrate from the spent regenerant solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61944–61954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhu, Z. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution using cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) modified zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliem, M.K.; Komarneni, S.; Byrne, T.; Cannon, F.; Shahien, M.; Khalil, A.; El-Gaid, I.A. Removal of nitrate by synthetic organosilicas and organoclay: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 110, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifam, S.; Komarneni, S.; Lakzian, A.; Fotovat, A.; Khorassani, R.; Huang, W.; Ma, J.; Hong, S.; Cannon, F.S.; Wang, Y. Highly selective removal of nitrate and perchlorate by organoclay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.K.; Ghosh, P.; Sen, K.; Mondal, A.; Debnath, P. Efficacy of onion peel towards removal of nitrate from aqueous solution and field samples. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 11, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golie, W.M.; Upadhyayula, S. An investigation on biosorption of nitrate from water by chitosan based organic-inorganic hybrid biocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
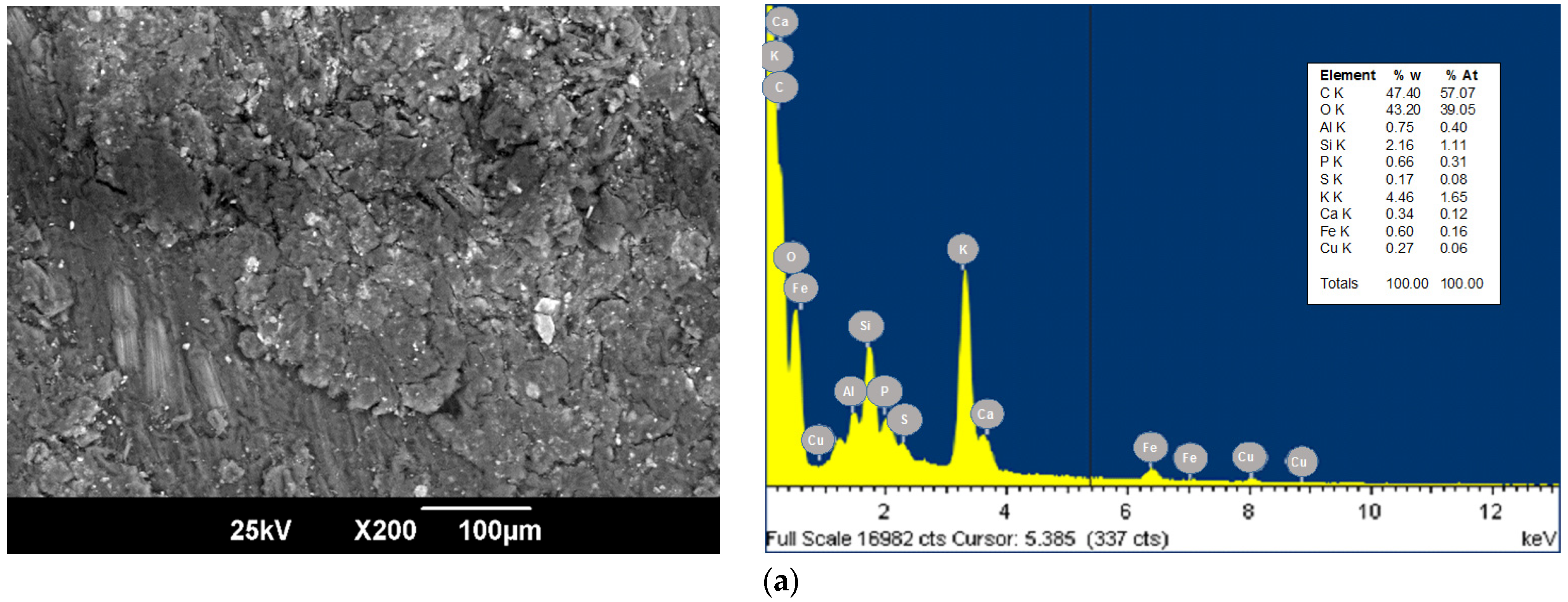
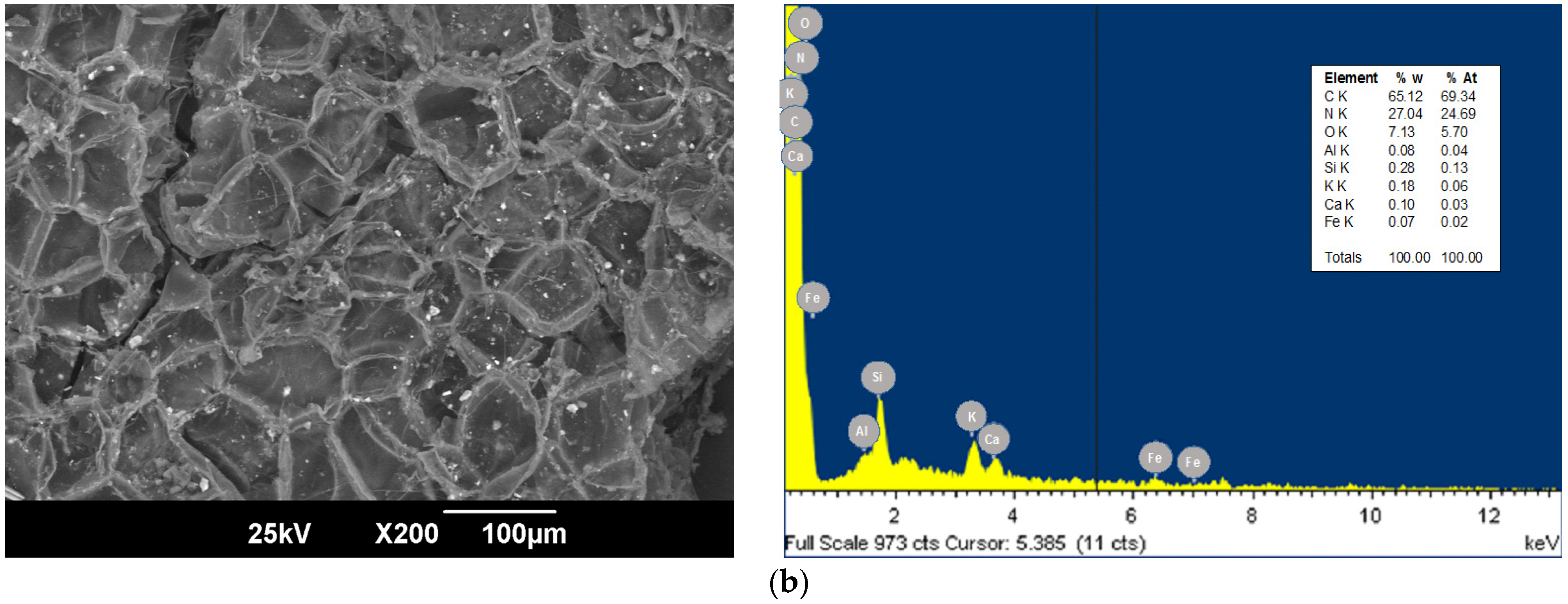
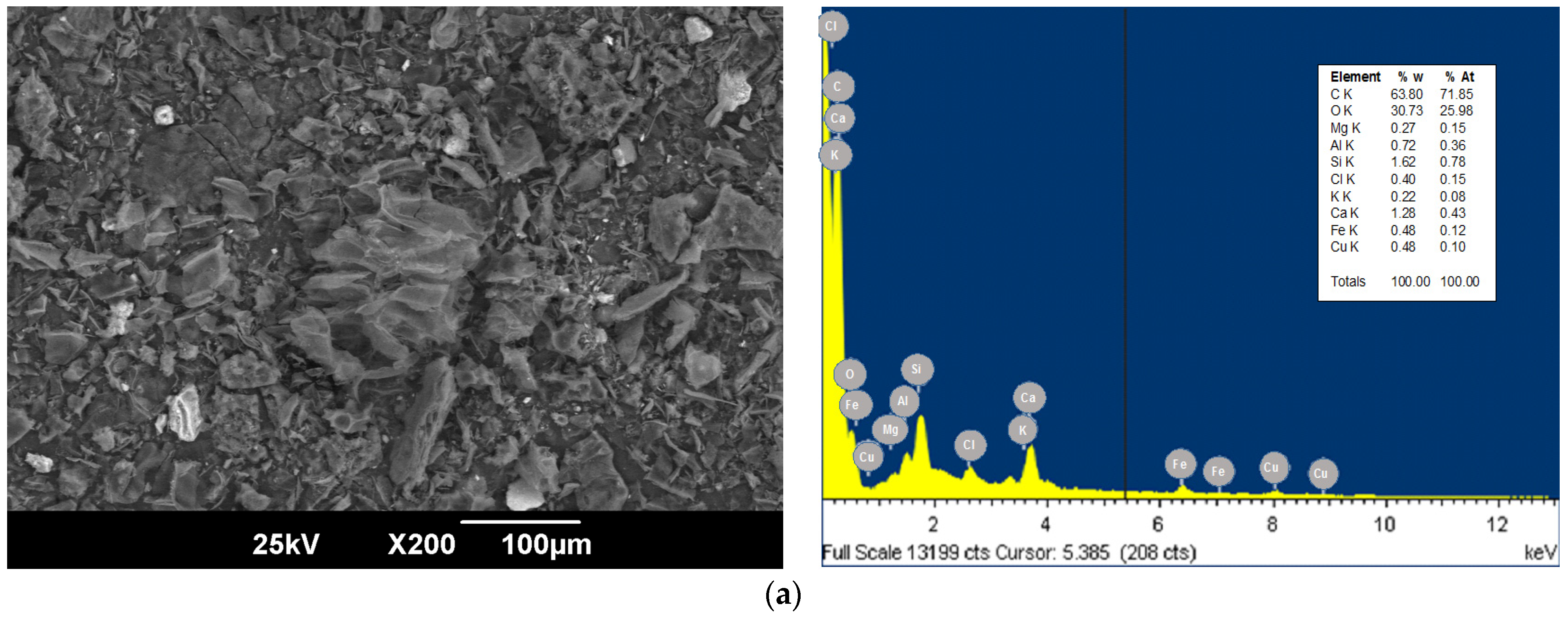



| Source | Sum of Squares | F-Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: pH | 128.0 | 7.36 | 0.0188 |
| B: Particle size | 28.6 | 1.64 | 0.2243 |
| AA | 0.959 | 0.05 | 0.8186 |
| AB | 1.54 | 0.09 | 0.7712 |
| BB | 2.13 | 0.12 | 0.7328 |
| Total error | 209.0 | ||
| Total (corr.) | 371.0 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | F-Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: Adsorbent type | 31.9 | 4.11 | 0.0821 |
| B: pH | 253.0 | 32.55 | 0.0007 |
| AB | 15.7 | 2.03 | 0.1975 |
| BB | 0.0199 | 0.00 | 0.9610 |
| Total error | 54.3 | ||
| Total (corr.) | 355.0 | ||
| A: Adsorbent type | 31.9 |
| Model | Parameters | MYP | CYP | CC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | KL (L/mg) | 3.698 × 10−05 | 0.0163 | 0.019 |
| qmax (mg/g) | 7.675 | 10.834 | 8.612 | |
| R2 | 0.773 | 0.971 | 0.996 | |
| Freundlich | KF (L/g) | 1.012 | 0.696 | 0.738 |
| n | 0.615 | 2.058 | 2.304 | |
| R2 | 0.955 | 0.991 | 0.966 | |
| Dubinin–Radushkevich | KDR (mol2/kJ2) | 3.275 × 10−06 | 5.789 | 7.266 × 10−05 |
| qDR (mg/g) | 33.999 | 6.747 | 5.975 | |
| E (KJ/mol) | 390.737 | 92.936 | 82.954 | |
| R2 | 0.875 | 0.629 | 0.808 |
| Adsorbent | qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Functionalized cellulose grafted epichlorohydrin | 232.56 | [59] |
| Anionic biographene nanosheet | 182.506 | [60] |
| Cheat straw crosslinked with epichlorohydrin and dimethylamine | 128.97 | [61] |
| Crosslinked chitosan beads | 104.0 | [62] |
| Magnetic amine-crosslinked biopolymer based on corn stalk | 102.04 | [63] |
| Rice hull | 74.41 | [64] |
| Amberlite IRA-900 | 74.41 | |
| Pine bark | 65.73 | |
| Moringa husk | 63.25 | |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 63.25 | |
| Coconut shell | 55.18 | [64] |
| Wheat stalk resin | 50.24 | [65] |
| Persimmon tealeaf | 48.36 | [64] |
| Lauan sawdust | 47.74 | |
| Arundo donax L. reed-based anion exchange resin | 44.61 | [66] |
| Cotton stalk resin | 39.15 | [65] |
| Chitosan microspheres | 32.15 | [4] |
| Polyurethane/sepiolite cellular nanocomposites | 23.30 | [3] |
| Carbon from yam peel modified with NH4Cl | 10.834 | Present study |
| Activated carbon modified with cetyl trimethyl ammonium chloride | 10.80 | [67] |
| Granular Fe–Zr–chitosan complex | 10.60 | [68] |
| Zeolite modified with cetylpyridinium bromide | 9.68 | [69] |
| Commercial carbon | 8.612 | Present study |
| Organosilica | 7.75 | [70] |
| Yam peel modified with NH4Cl | 7.675 | Present study |
| Chitosan doped with Fe3+ | 5.00 | [58] |
| Model | Parameter | MYP | CYP | CC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first order | qe (mg/g) | 21.389 | 26.669 | 24.621 |
| k1 (min−1) | 26.955 | 1.175 | 1.357 | |
| R2 | 0.984 | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| Pseudo-second order | qe (mg/g) | 21.389 | 24.701 | 24.636 |
| k2 (g/mg·min) | 1.483 × 1016 | 1.329 | 2.957 | |
| R2 | 0.984 | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| Elovich | α (mg/g·min) | 5.005 | 4.403 | 4.400 |
| β (g/mg) | 1.242 × 1044 | 7.015 × 1044 | 5.374 × 1044 | |
| R2 | 0.971 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona-Ortíz, Á.; Gonzalez-Delgado, Á.D. Removal of Nitrate Ions Using Thermally and Chemically Modified Bioadsorbents. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188455
Tejada-Tovar C, Villabona-Ortíz Á, Gonzalez-Delgado ÁD. Removal of Nitrate Ions Using Thermally and Chemically Modified Bioadsorbents. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188455
Chicago/Turabian StyleTejada-Tovar, Candelaria, Ángel Villabona-Ortíz, and Ángel Darío Gonzalez-Delgado. 2021. "Removal of Nitrate Ions Using Thermally and Chemically Modified Bioadsorbents" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188455
APA StyleTejada-Tovar, C., Villabona-Ortíz, Á., & Gonzalez-Delgado, Á. D. (2021). Removal of Nitrate Ions Using Thermally and Chemically Modified Bioadsorbents. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8455. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188455








