Effects of Palm Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Alone or in Combination with Glucosamine Sulphate on Grip Strength, Cartilage Structure and Joint Remodelling Markers in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Treatment Solution
2.2. Animal Treatment
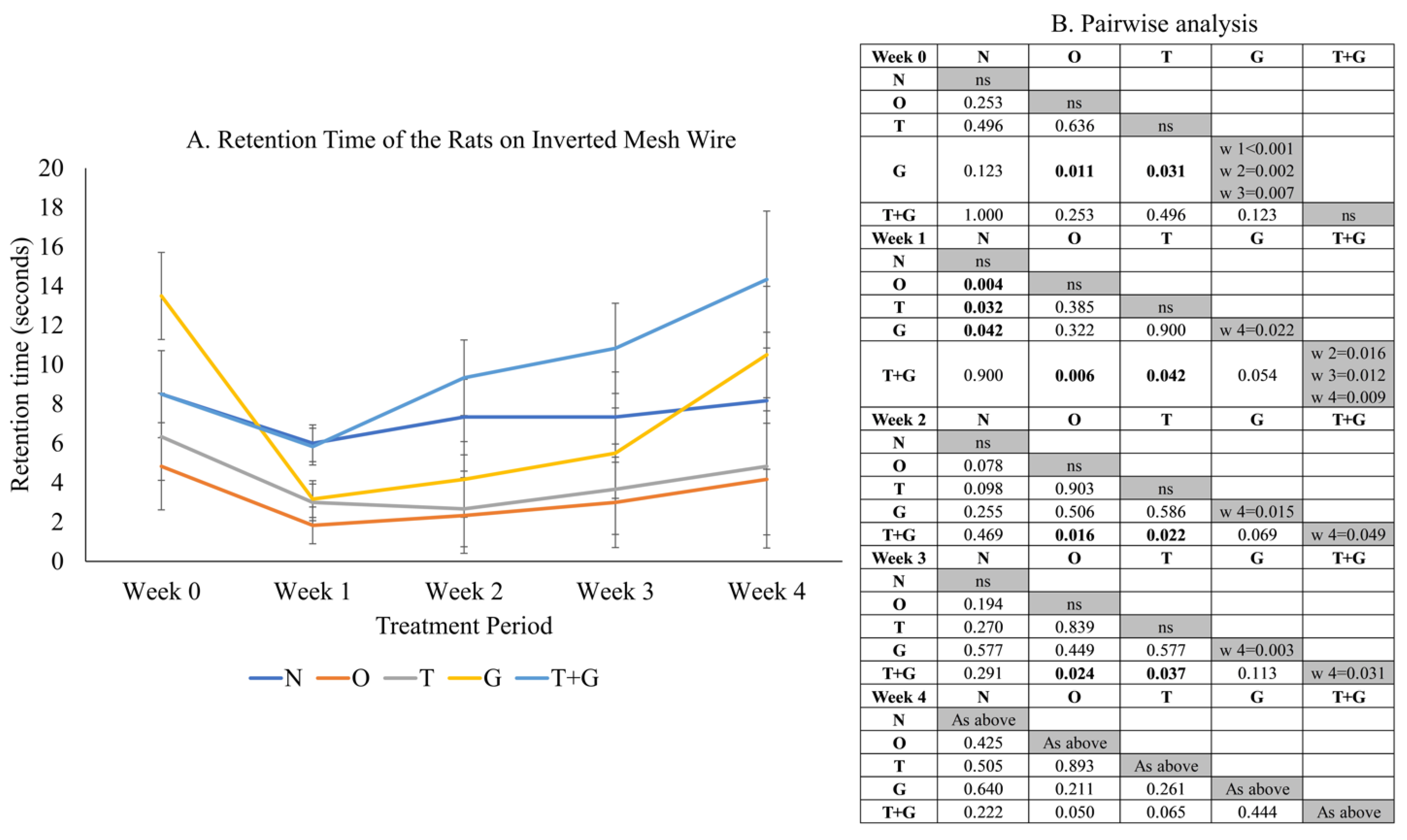
2.3. Grip Strength Assessment
2.4. Histological Assessment
2.5. Biochemical Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patent
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belluzzi, E.; Macchi, V.; Fontanella, C.G.; Carniel, E.L.; Olivotto, E.; Filardo, G.; Sarasin, G.; Porzionato, A.; Granzotto, M.; Pozzuoli, A.; et al. Infrapatellar Fat Pad Gene Expression and Protein Production in Patients with and without Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, A.R. Osteoarthritis as a whole joint disease. HSS J. 2012, 8, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dell’Isola, A.; Steultjens, M. Classification of patients with knee osteoarthritis in clinical phenotypes: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lespasio, M.J.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Husni, M.E.; Muschler, G.F.; Guarino, A.; Mont, M.A. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Primer. Perm. J. 2017, 21, 16–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results. Osteoarthritis—Level 3 Cause. Available online: http://www.healthdata.org/results/gbd_summaries/2019/osteoarthritis-level-3-cause (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Courtney, P.M.; Boniello, A.J.; Berger, R.A. Complications Following Outpatient Total Joint Arthroplasty: An Analysis of a National Database. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramoff, B.; Caldera, F.E. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, H.; Sevdalina, L.; Ulf, M.-L. Current Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2018, 14, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saadi, H.M.; Pang, K.-L.; Ima-Nirwana, S.; Chin, K.-Y. Multifaceted Protective Role of Glucosamine against Osteoarthritis: Review of Its Molecular Mechanisms. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, T.; Ideno, Y.; Akai, M.; Seichi, A.; Hagino, H.; Iwaya, T.; Doi, T.; Yamada, K.; Chen, A.Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of glucosamine in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Sánchez-García, A.; Vilchez-Cavazos, F.; Acosta-Olivo, C.A.; Peña-Martínez, V.M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E. Effect of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1413–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Souich, P. Absorption, distribution and mechanism of action of SYSADOAS. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 142, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S. The Role of Tocotrienol in Preventing Male Osteoporosis-A Review of Current Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.K.; Kamisah, Y.; Mohamed, N.; Muhammad, N.; Masbah, N.; Fahami, N.A.M.; Mohamed, I.N.; Shuid, A.N.; Saad, Q.M.; Abdullah, A.; et al. Potential Role of Tocotrienols on Non-Communicable Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence. Nutrients 2020, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chin, K.Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S. The Role of Vitamin E in Preventing and Treating Osteoarthritis—A Review of the Current Evidence. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Tudawe, D.; Chakravarthi, S.; Chiew, G.S.; Haleagrahara, N. Effect of γ-tocotrienol in counteracting oxidative stress and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleagrahara, N.; Swaminathan, M.; Chakravarthi, S.; Radhakrishnan, A. Therapeutic Efficacy of Vitamin E Tocotrienol in Collagen-Induced Rat Model of Arthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 539540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zainal, Z.; Rahim, A.A.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Chang, S.K.; Khaza’ai, H. Investigation of the curative effects of palm vitamin E tocotrienols on autoimmune arthritis disease in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.-Y.; Wong, S.K.; Japar Sidik, F.Z.; Abdul Hamid, J.; Abas, N.H.; Mohd Ramli, E.S.; Afian Mokhtar, S.; Rajalingham, S.; Ima Nirwana, S. The Effects of Annatto Tocotrienol Supplementation on Cartilage and Subchondral Bone in an Animal Model of Osteoarthritis Induced by Monosodium Iodoacetate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haflah, N.H.; Jaarin, K.; Abdullah, S.; Omar, M. Palm vitamin E and glucosamine sulphate in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Saudi Med. J. 2009, 30, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Aresta, A.; Zambonin, C. Determination of α-Tocopherol in Olive Oil by Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1580–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.H.; Tang, C.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Hsieh, S.P.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, G.S.; Ng, H.F.; Neoh, C.A.; Hsieh, C.S.; et al. Glucosamine sulfate reduces experimental osteoarthritis and nociception in rats: Association with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase in chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khotib, J.; Pratiwi, A.P.; Ardianto, C.; Rahmadi, M. Attenuation of IL-1ß on the use of glucosamine as an adjuvant in meloxicam treatment in rat models with osteoarthritis. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharm. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M.J. Measuring the strength of mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 76, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.H.; Lv, Q.; Yu, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Niu, K.R.; Yi, C.Q. Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor-α blockade by adalimumab on articular cartilage and subchondral bone in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.W.; Huang, T.C.; Hu, Y.C.; Hsieh, B.S.; Chiu, P.R.; Cheng, H.L.; Chang, K.L. Zinc protects chondrocytes from monosodium iodoacetate-induced damage by enhancing ATP and mitophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, L.; Geng, C.; Gong, D.; Jiang, L.; Ishikawa, N.; Kajima, K.; Zhong, L. Monosodium iodoacetate induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway involving ROS production and caspase activation in rat chondrocytes in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.-L.; Chow, Y.Y.; Leong, L.M.; Law, J.X.; Ghafar, N.A.; Soelaiman, I.N.; Chin, K.-Y. Establishing SW1353 Chondrocytes as a Cellular Model of Chondrolysis. Life 2021, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Park, S.J.; Yun, J.M.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, J. Antarctic Krill Oil Ameliorates Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Irregularities in Articular Cartilage and Inflammatory Response in the Rat Models of Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyan, H.M.; Terzi, M.Y.; Karaboğa, İ.; Doğan, S.; Kalacı, A. In vivo protective effects of upper zone of growth plate and cartilage matrix associated protein against cartilage degeneration in a monosodium iodoacetate induced osteoarthritis model. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2020, 98, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.R.; Lee, J.A.; Kim, M.J.; Park, H.J.; Park, B.W.; Seo, S.B.; Roh, S.S. Protective Effects of Phellinus linteus Mycelium on the Development of Osteoarthritis after Monosodium Iodoacetate Injection. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 7240858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, K.; Kucuk, O.; Orhan, C.; Tuzcu, M.; Durmus, A.S.; Ozercan, I.H.; Sahin, N.; Juturu, V. Niacinamide and undenatured type II collagen modulates the inflammatory response in rats with monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, K.L.; Coustry, F.; Hecht, J.T. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: COMPopathies and beyond. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjal, A.; Bapat, S.; Hubbard, D.; Hunter, M.; Kolhe, R.; Fulzele, S. Advances in Molecular biomarker for early diagnosis of Osteoarthritis. Biomol. Concepts 2019, 10, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, E.F.; Salgueiro, A.F.; Goulart, A.D.S.; Mendes, V.P.; Anjos, B.L.; Folmer, V.; da Silva, M.D. Evaluation of monosodium iodoacetate dosage to induce knee osteoarthritis: Relation with oxidative stress and pain. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batallé, G.; Cabarga, L.; Pol, O. The Inhibitory Effects of Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donors in the Mechanical Allodynia, Grip Strength Deficits, and Depressive-Like Behaviors Associated with Chronic Osteoarthritis Pain. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segatto, M.; Szokoll, R.; Fittipaldi, R.; Bottino, C.; Nevi, L.; Mamchaoui, K.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Caretti, G. BETs inhibition attenuates oxidative stress and preserves muscle integrity in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englander, Z.K.; Wei, H.-J.; Pouliopoulos, A.N.; Bendau, E.; Upadhyayula, P.; Jan, C.-I.; Spinazzi, E.F.; Yoh, N.; Tazhibi, M.; McQuillan, N.M.; et al. Focused ultrasound mediated blood-brain barrier opening is safe and feasible in a murine pontine glioma model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, M.F.; Loh, Y.C.; Tan, C.S.; Khadijah Adam, S.; Abdul Manan, N.; Basir, R. General Pathways of Pain Sensation and the Major Neurotransmitters Involved in Pain Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Ma, K.; Liu, J.R.; Wang, H.X.; Tian, W.X.; Tu, Y.H.; Sun, W.G. γ-tocotrienol inhibits the invasion and migration of human gastric cancer cells through downregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K. Tocotrienol attenuates oxidative-nitrosative stress and inflammatory cascade in experimental model of diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik, J.J.; Pope, R.; Hoedebecke, S.S.; Schram, B.; Orr, R.; Lieberman, H.R. Effects of Oral Glucosamine Sulfate on Osteoarthritis-Related Pain and Joint-Space Changes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Spec. Oper. Med. 2018, 18, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H.; Kumakura, S.; Shimada, K. Establishment of a novel objective and quantitative method to assess pain-related behavior in monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rat knee. J. Pharm. Toxicol. Methods 2012, 65, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalem, M.; Haddad, M.; Altarifi, A.; Aldossary, S.A.; Kalbouneh, H.; Abojaradeh, A.M.; El-Salem, K. Impairment in locomotor activity as an objective measure of pain and analgesia in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Score | Structure | Cell | Safranin O Staining |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| 1 | Surface irregularity | Diffuse hypercellularity | Slight reduction |
| 2 | Pannus and surface irregularity | Cloning | Moderate reduction |
| 3 | Clefts to the transitional zone | Hypocellularity | Severe reduction |
| 4 | Clefts to the radial zone | n/a | No dye noted |
| 5 | Clefts to the calcified zone | n/a | n/a |
| 6 | Complete disorganisation | n/a | n/a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Saadi, H.M.; Chin, K.-Y.; Ahmad, F.; Mohd Ramli, E.S.; Arlamsyah, A.M.; Japar Sidik, F.Z.; Abdul Hamid, J.; Soelaiman, I.N. Effects of Palm Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Alone or in Combination with Glucosamine Sulphate on Grip Strength, Cartilage Structure and Joint Remodelling Markers in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188577
Al-Saadi HM, Chin K-Y, Ahmad F, Mohd Ramli ES, Arlamsyah AM, Japar Sidik FZ, Abdul Hamid J, Soelaiman IN. Effects of Palm Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Alone or in Combination with Glucosamine Sulphate on Grip Strength, Cartilage Structure and Joint Remodelling Markers in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188577
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Saadi, Hiba Murtadha, Kok-Yong Chin, Fairus Ahmad, Elvy Suhana Mohd Ramli, Azlan Mohd Arlamsyah, Fadhlullah Zuhair Japar Sidik, Juliana Abdul Hamid, and Ima Nirwana Soelaiman. 2021. "Effects of Palm Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Alone or in Combination with Glucosamine Sulphate on Grip Strength, Cartilage Structure and Joint Remodelling Markers in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188577
APA StyleAl-Saadi, H. M., Chin, K.-Y., Ahmad, F., Mohd Ramli, E. S., Arlamsyah, A. M., Japar Sidik, F. Z., Abdul Hamid, J., & Soelaiman, I. N. (2021). Effects of Palm Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Alone or in Combination with Glucosamine Sulphate on Grip Strength, Cartilage Structure and Joint Remodelling Markers in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188577







