Review of the Relationship between Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Elastin-Derived Peptides (EDPs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
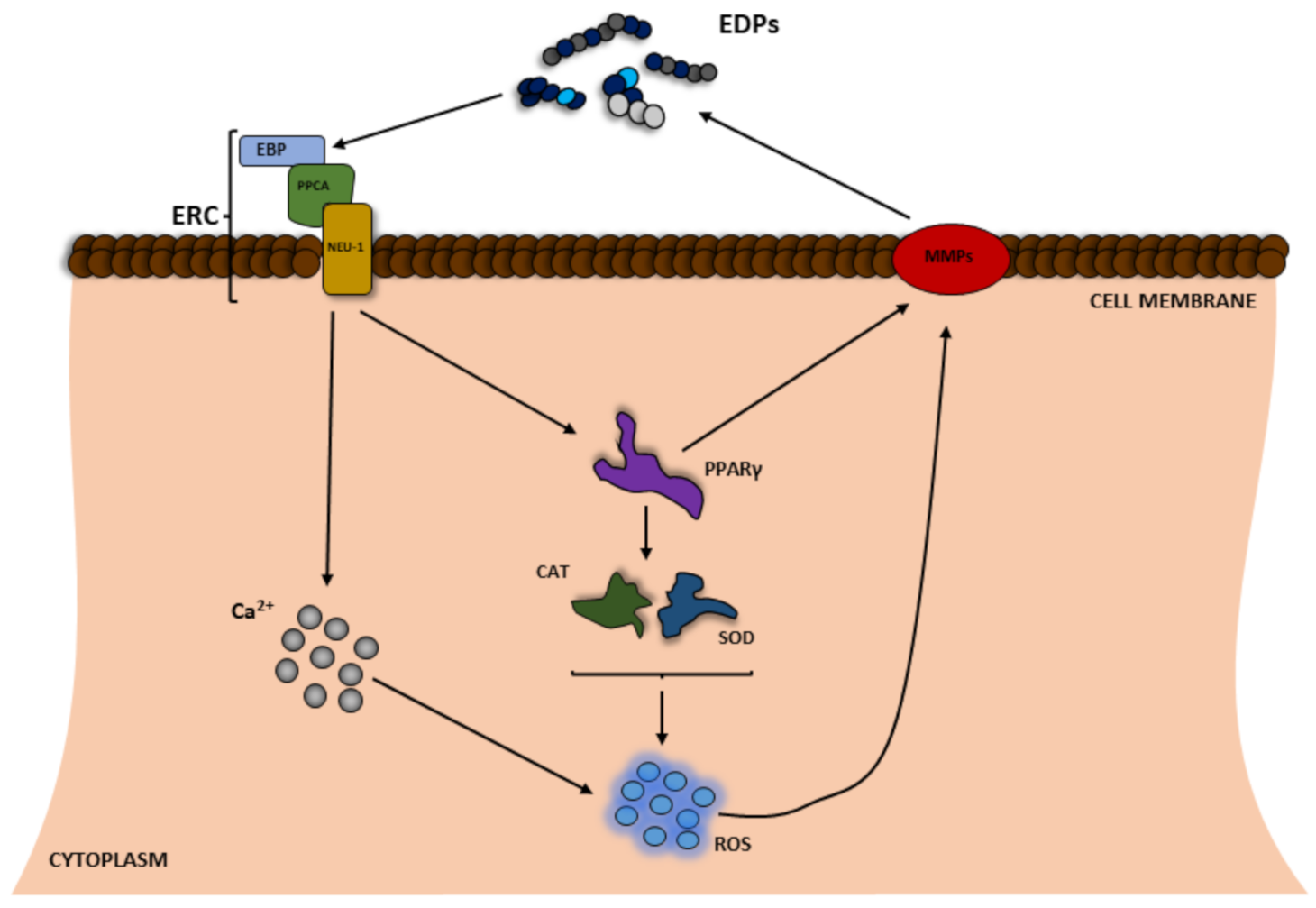
2. Role of ROS in the Origin of Elastin-Derived Peptides
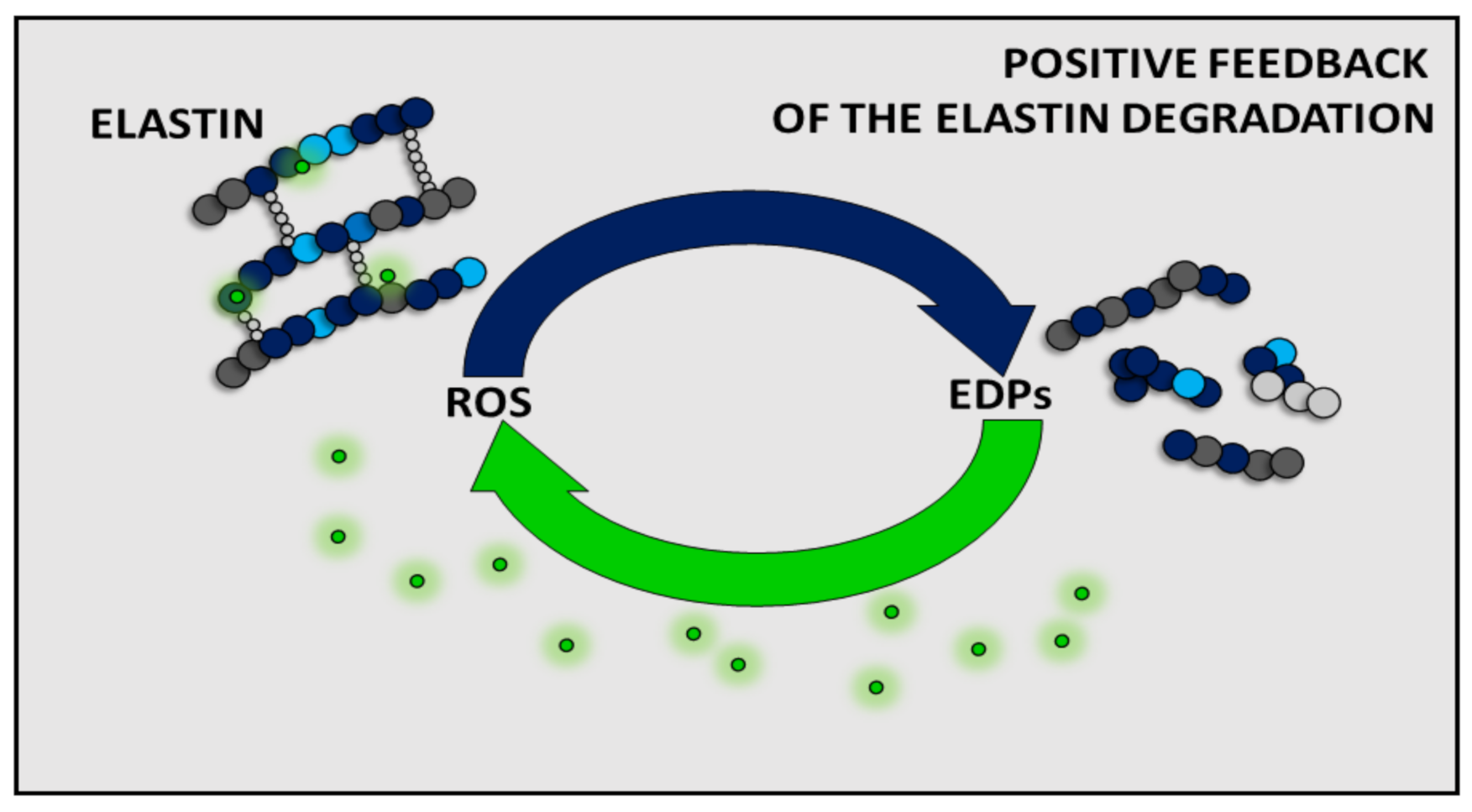
3. Impact of EDPs on ROS Production
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjala, G.W.; Onyango, A.; Onyango, C.; Makayoto, M. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, impacts on tissue oxidation and dietary management of non-communicable diseases: A review. Afr. J. Biochem. Res. 2017, 11, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. ROS in Cancer: The Burning Question. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaser, H.; Dostert, C.; Mak, T.W.; Brenner, D. TNF and ROS Crosstalk in Inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.L.; Simon, A.K.; Prescott, M.; Menendez, J.A.; Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Wolvetang, E.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Zhang, J. Autophagy in stem cells. Autophagy 2013, 9, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, P.S.; Ella, S.R.; Stupica, A.J.; Nourian, Z.; Li, M.; Martinez-Lemus, L.A.; Dora, K.A.; Yang, Y.; Davis, M.J.; Pohl, U.; et al. Spatial Distribution and Mechanical Function of Elastin in Resistance Arteries. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2889–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinek, A.; Wrenn, D.S.; Mecham, R.P.; Barondes, S.H. The elastin receptor: A galactoside-binding protein. Science 1988, 239, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, L.; Floquet, N.; Alix, A.J.P.; Haye, B.; Debelle, L. Elastin as a matrikine. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2004, 49, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Rombel-Bryzek, A.; Dołhańczuk-Śródka, A.; Gmiński, J. Antiproliferative Effect of Elastin-Derived Peptide VGVAPG on SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Neurotox. Res. 2019, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Gmiński, J. Specific role of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in elastin-derived VGVAPG peptide-dependent calcium homeostasis in mouse cortical astrocytes in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinek, A.; Kim, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Mitts, T.F. Sodium l-ascorbate enhances elastic fibers deposition by fibroblasts from normal and pathologic human skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 75, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayral, S.; Garnotel, R.; Castaing-Berthou, A.; Blaise, S.; Fougerat, A.; Berge, E.; Montheil, A.; Malet, N.; Wymann, M.P.; Maurice, P.; et al. Elastin-derived peptides potentiate atherosclerosis through the immune Neu1-PI3K pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 102, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parfrey, N.A.; Doyle, C.T. Elastosis in benign and malignant breast disease. Hum. Pathol. 1985, 16, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, L.; Blaise, S.; Romier, B.; Laffargue, M.; Gayral, S.; El Btaouri, H.; Kawecki, C.; Guillot, A.; Martiny, L.; Debelle, L.; et al. Matrix ageing and vascular impacts: Focus on elastin fragmentation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salesse, S.; Odoul, L.; Chazée, L.; Garbar, C.; Duca, L.; Martiny, L.; Mahmoudi, R.; Debelle, L. Elastin molecular aging promotes MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell invasiveness. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasaram, V.; Nosoudi, N.; Chowdhury, A.; Vyavahare, N. Pentagalloyl glucose increases elastin deposition, decreases reactive oxygen species and matrix metalloproteinase activity in pulmonary fibroblasts under inflammatory conditions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Mithieux, S.M.; Weiss, A.S. Elastin Biomaterials in Dermal Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Skóra, B.; Wójtowicz, A.K. Elastin—Derived Peptides in the Central Nervous System: Friend or Foe. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsvar, J.; Yang, C.; Cain, S.A.; Baldock, C.; Tarakanova, A.; Weiss, A.S. Tropoelastin and Elastin Assembly. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.G.; Yeo, G.C.; Hiob, M.A.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Kaplan, D.L.; Ng, M.K.C.; Weiss, A.S. Tropoelastin: A versatile, bioactive assembly module. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, S.D.; Endicott, S.K.; Province, M.A.; Pierce, J.A.; Campbell, E.J. Marked longevity of human lung parenchymal elastic fibers deduced from prevalence of D-aspartate and nuclear weapons-related radiocarbon. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.T.J.; Bolton, C.E.; Miller, B.E.; Tal-Singer, R.; Rabinovich, R.A.; Palmer, C.N.A.; Thomson, N.C.; MacNee, W. Age-dependent elastin degradation is enhanced in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adair, G.S.; Davis, H.F.; Partridge, S.M. A Soluble protein derived from elastin. Nature 1951, 167, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senior, R.M.; Griffin, G.L.; Mecham, R.P. Chemotactic activity of elastin-derived peptides. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senior, R.M.; Griffin, G.L.; Mecham, R.P.; Wrenn, D.S.; Prasad, K.U.; Urry, D.W. Val-Gly-Val-Ala-Pro-Gly, a repeating peptide in elastin, is chemotactic for fibroblasts and monocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1984, 99, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Page, A.; Khalil, A.; Vermette, P.; Frost, E.H.; Larbi, A.; Witkowski, J.M.; Fulop, T. The role of elastin-derived peptides in human physiology and diseases. Matrix Biol. 2019, 84, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmann, N.S.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Sand, J.M.B.; Diefenbach, C.; Sun, S.; Danielsen, A.; Karsdal, M.A.; Leeming, D.J. Lung tissue destruction by proteinase 3 and cathepsin G mediated elastin degradation is elevated in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novinec, M.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Turk, V.; Baici, A.; Lenarčič, B. Interaction between Human Cathepsins K, L, and S and Elastins. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7893–7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, A.; Ryu, A.; Suzuki, T.; Kawada, A.; Tajima, S. In vitro degradation of tropoelastin by reactive oxygen species. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, P.; Villain, F. Free radical scavenging properties of mannitol and its role as a constituent of hyaluronic acid fillers: A literature review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umeda, H.; Nakamura, F.; Suyama, K. Oxodesmosine and Isooxodesmosine, Candidates of Oxidative Metabolic Intermediates of Pyridinium Cross-Links in Elastin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 385, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Arunachalam, G.; Hwang, J.-W.; Chung, S.; Sundar, I.K.; Kinnula, V.L.; Crapo, J.D.; Rahman, I. Extracellular superoxide dismutase protects against pulmonary emphysema by attenuating oxidative fragmentation of ECM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15571–15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Codriansky, K.A.; Quintanilla-Dieck, M.J.; Gan, S.; Keady, M.; Bhawan, J.; Rünger, T.M. Intracellular Degradation of Elastin by Cathepsin K in Skin Fibroblasts—A Possible Role in Photoaging. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.C.; Jin, Y.S.; Mi, K.L.; Hee, C.E.; Joo, H.L.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Ultraviolet modulation of human macrophage metalloelastase in human skin in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Dhital, B.; Durlik, P.; Rathod, P.; Gul-E-Noor, F.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Chang, E.J.; Itin, B.; Boutis, G.S. Ultraviolet radiation reduces desmosine cross-links in elastin. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 10, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihermann, A.C.; Lorencini, M.; Brohem, C.A.; de Carvalho, C.M. Elastin structure and its involvement in skin photoageing. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.; Oresajo, C.; Hayward, J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: Roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro Brás, L.E.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Extracellular matrix-derived peptides in tissue remodeling and fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2020, 91–92, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, C.H.; Sasse, J.; Brodt, P.; Zetter, B.R. Identification of a tumor cell receptor for VGVAPG, an elastin-derived chemotactic peptide. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 107, 1987–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeie, J.M.; Hernandez, J.; Hinek, A.; Mullins, R.F. Molecular responses of choroidal endothelial cells to elastin derived peptides through the elastin-binding protein (GLB1). Matrix Biol. 2012, 31, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Péterszegi, G.; Robert, L. Cell death induced in lymphocytes expressing the elastin-laminin receptor by excess agonists: Necrosis and apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1998, 52, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devy, J.; Duca, L.; Cantarelli, B.; Joseph-Pietras, D.; Scandolera, A.; Rusciani, A.; Parent, L.; Thevenard, J.; Pasco, S.B.; Tarpin, M.; et al. Elastin-derived peptides enhance melanoma growth in vivo by upregulating the activation of Mcol-A (MMP-1) collagenase. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Gmiński, J. Impact of elastin-derived VGVAPG peptide on bidirectional interaction between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (Pparγ) and beta-galactosidase (β-Gal) expression in mouse cortical astrocytes in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, L.; Jacob, M.P.; Frances, C.; Godeau, G.; Hornebeck, W. Interaction between elastin and elastases and its role in the aging of the arterial wall, skin and other connective tissues. A review. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1984, 28, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandolera, A.; Rabenoelina, F.; Chaintreuil, C.; Rusciani, A.; Maurice, P.; Blaise, S.; Romier-Crouzet, B.; El Btaouri, H.; Martiny, L.; Debelle, L.; et al. Uncoupling of Elastin Complex Receptor during In Vitro Aging Is Related to Modifications in Its Intrinsic Sialidase Activity and the Subsequent Lactosylceramide Production. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.P.; Fülöp, T.; Foris, G.; Robert, L. Effect of elastin peptides on ion fluxes in mononuclear cells, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faury, G.; Usson, Y.; Robert-Nicoud, M.; Robert, L.; Verdetti, J. Nuclear and cytoplasmic free calcium level changes induced by elastin peptides in human endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2967–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faury, G.; Garnier, S.; Weiss, A.S.; Wallach, J.; Fülöp, T.; Jacob, M.P.; Mecham, R.P.; Robert, L.; Verdetti, J. Action of tropoelastin and synthetic elastin sequences on vascular tone and on free Ca2+ level in human vascular endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coquerel, B.; Poyer, F.; Torossian, F.; Dulong, V.; Bellon, G.; Dubus, I.; Reber, A.; Vannier, J.P. Elastin-derived peptides: Matrikines critical for glioblastoma cell aggressiveness in a 3-D system. Glia 2009, 57, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlach, A.; Bertram, K.; Hudecova, S.; Krizanova, O. Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupont, A.; Dury, S.; Gafa, V.; Lebargy, F.; Deslée, G.; Guenounou, M.; Antonicelli, F.; Le Naour, R. Impairment of neutrophil reactivity to elastin peptides in COPD. Thorax 2013, 68, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Gmiński, J. The VGVAPG Peptide Regulates the Production of Nitric Oxide Synthases and Reactive Oxygen Species in Mouse Astrocyte Cells In Vitro. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gmiński, J.; Wȩglarz, L.; Dróżdż, M.; Goss, M. Pharmacological modulation of the antioxidant enzymes activities and the concentration of peroxidation products in fibroblasts stimulated with elastin peptides. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1991, 22, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Zaheer, S.; Ahmed, M.E.; Raikwar, S.P.; Zahoor, H.; Saeed, D.; Natteru, P.A.; Iyer, S.; et al. Brain and peripheral atypical inflammatory mediators potentiate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, H. Role of PPAR-gamma in inflammation. Prospects for therapeutic intervention by food components. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 2010, 690, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranek, T.; Debret, R.; Antonicelli, F.; Lamkhioued, B.; Belaaouaj, A.; Hornebeck, W.; Bernard, P.; Guenounou, M.; Le Naour, R. Elastin Receptor (Spliced Galactosidase) Occupancy by Elastin Peptides Counteracts Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Human Monocytes through NF- B Down-Regulation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6184–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debret, R.; Le Naour, R.R.; Sallenave, J.-M.; Deshorgue, A.; Hornebeck, W.G.; Guenounou, M.; Bernard, P.; Antonicelli, F.D. Elastin fragments induce IL-1beta upregulation via NF-kappaB pathway in melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, Y.H.; Yang, H.S.; Sun, M.G.; Sun, J.S.; Chen, M.H. Elastin-derived peptides induce inflammatory responses through the activation of NF-κB in human ligamentum flavum cells. Connect. Tissue Res. 2012, 53, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satta, J.; Laurila, A.; Pääkkö, P.; Haukipuro, K.; Sormunen, R.; Parkkila, S.; Juvonen, T. Chronic inflammation and elastin degradation in abdominal aortic aneurysm disease: An immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1998, 15, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Jokaji, R.; Miyazawa-Hira, M.; Takatsuka, S.; Tanaka, A.; Ooi, K.; Nakamura, H.; Kawashiri, S. Elastin-derived peptides are involved in the processes of human temporomandibular disorder by inducing inflammatory responses in synovial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Gmiński, J. The Elastin-Derived Peptide VGVAPG Does Not Activate the Inflammatory Process in Mouse Cortical Astrocytes In Vitro. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, G. PPARγ activation suppresses the expression of MMP9 by downregulating NF-κB post intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 752, 135770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinet, A. Elastin-derived peptides enhance angiogenesis by promoting endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis through upregulation of MT1-MMP. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brassart, B.; Randoux, A.; Hornebeck, W.; Emonard, H. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (gelatinase A, MMP-2), membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) expression by elastin-derived peptides in human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell line. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1998, 16, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donet, M.; Brassart-Pasco, S.; Salesse, S.; Maquart, F.-X.; Brassart, B. Elastin peptides regulate HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell migration and invasion through an Hsp90-dependent mechanism. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntayi, C.; Labrousse, A.L.; Debret, R.; Birembaut, P.; Bellon, G.; Antonicelli, F.; Hornebeck, W.; Bernard, P. Elastin-Derived Peptides Upregulate Matrix Metalloproteinase-2-ediated Melanoma Cell Invasion Through Elastin-Binding Protein. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szychowski, K.A.; Skóra, B. Review of the Relationship between Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Elastin-Derived Peptides (EDPs). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188732
Szychowski KA, Skóra B. Review of the Relationship between Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Elastin-Derived Peptides (EDPs). Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188732
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzychowski, Konrad A., and Bartosz Skóra. 2021. "Review of the Relationship between Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Elastin-Derived Peptides (EDPs)" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188732
APA StyleSzychowski, K. A., & Skóra, B. (2021). Review of the Relationship between Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Elastin-Derived Peptides (EDPs). Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188732






