Ultrafast Ultrasound-Derived Muscle Strain Measure Correlates with Carotid Local Pulse Wave Velocity in Habitual Resistance-Trained Individuals
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. One-repetition Maximum Test
2.4. Acute Bicep Curl Exercise
2.5. Muscle Stiffness
2.6. Arterial Stiffness
2.7. Carotid Function and Waveform Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
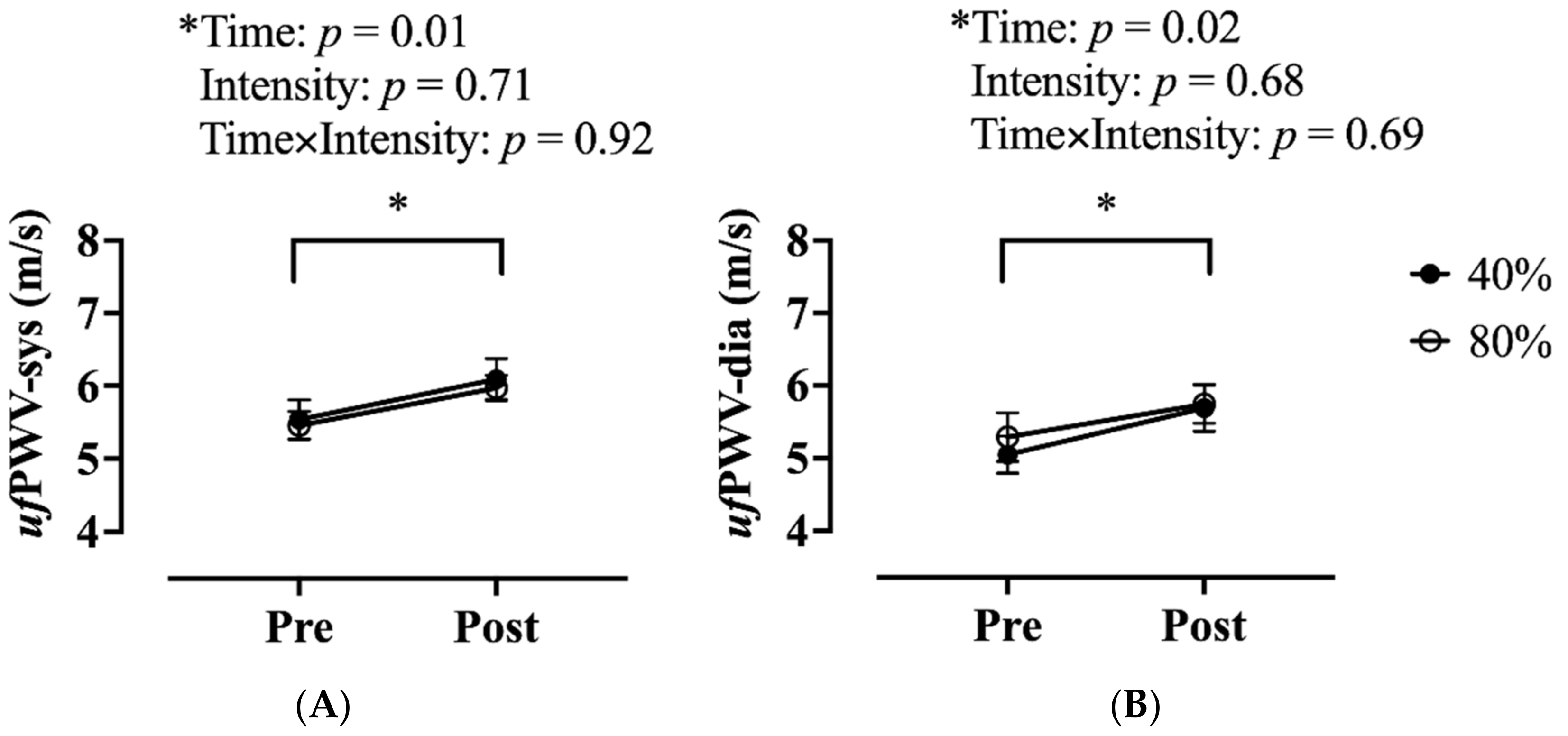
3.2. Arterial Stiffness Measures and Muscle Strain Rate Changes before and after an Acute Bout of Exercise
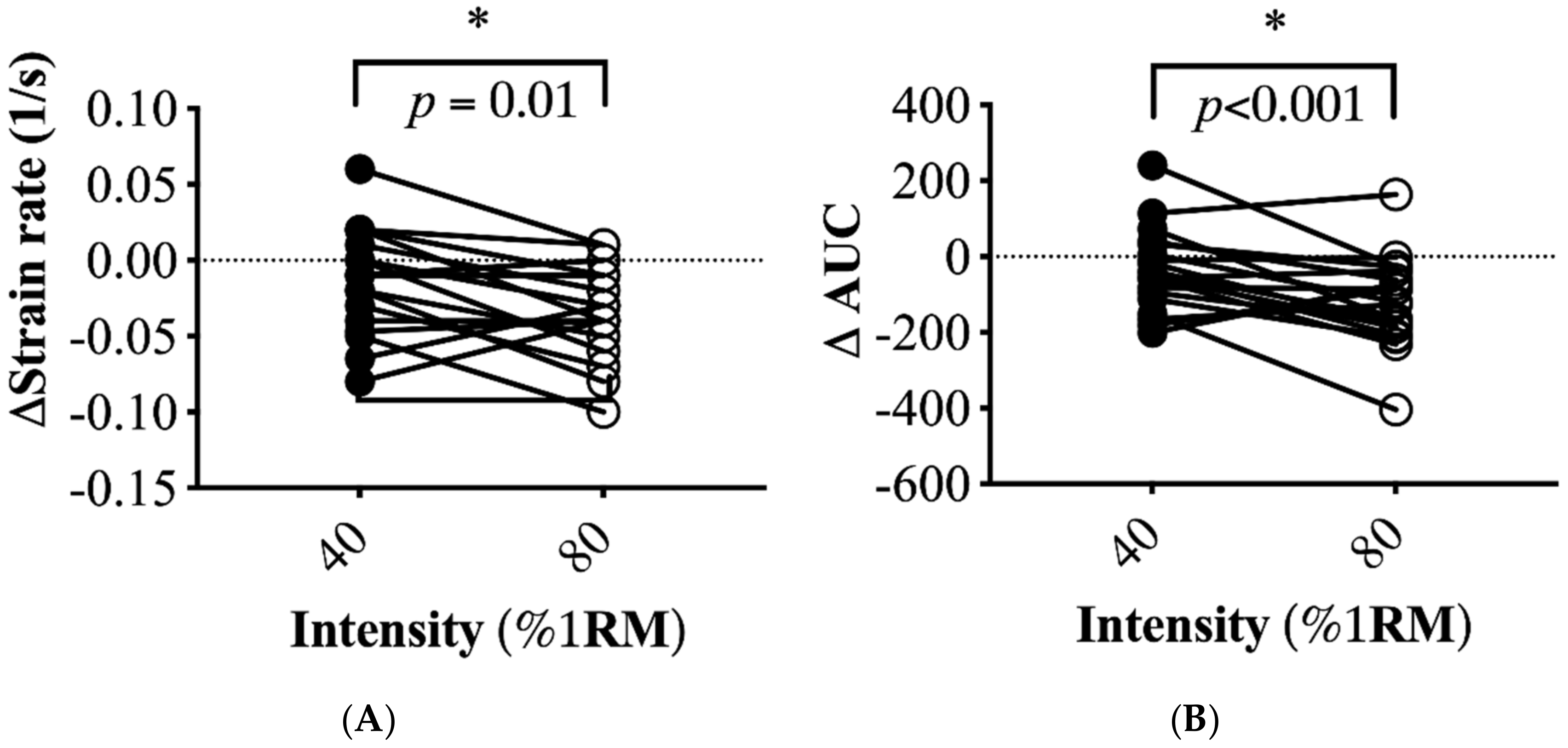
3.3. Changes in Muscle and Local Carotid Stiffness in Response to Different Exercise Intensity
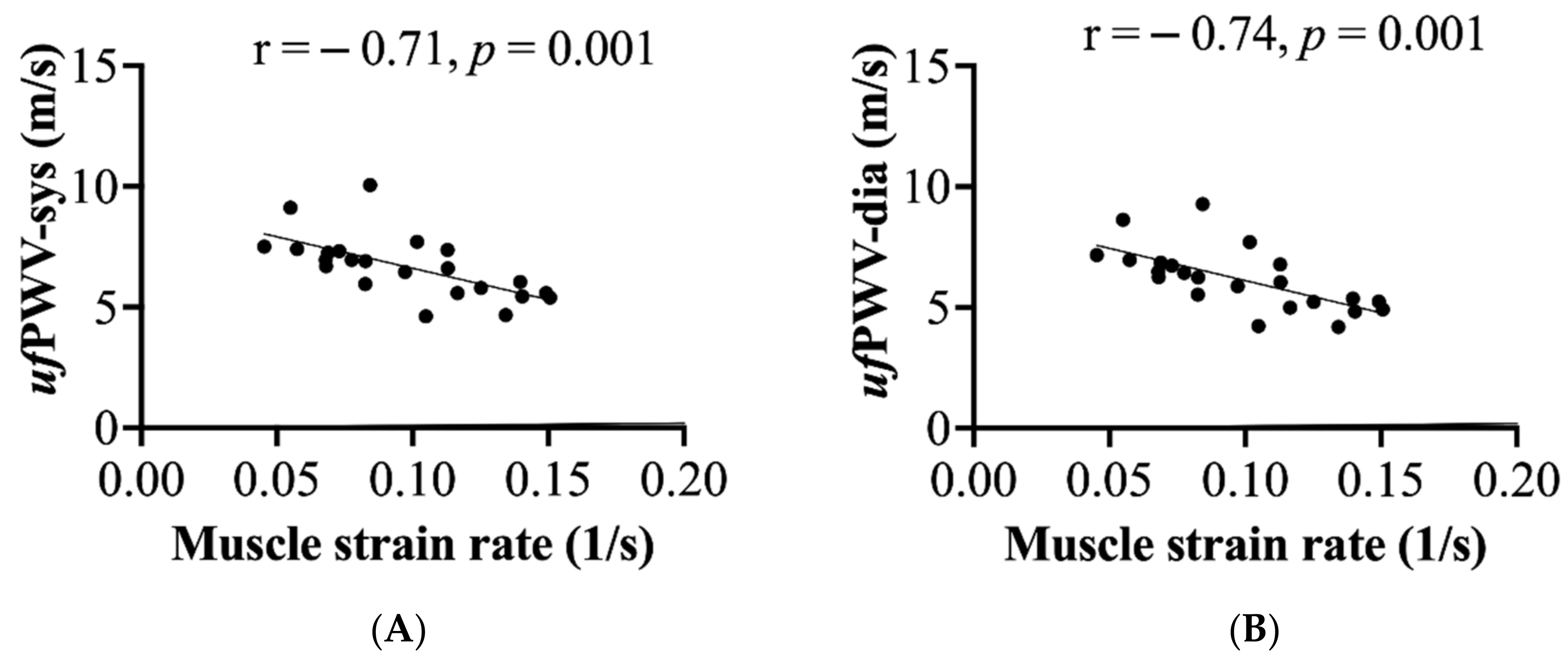
3.4. Associations of Muscle and Arterial Stiffness Measures
3.5. Contribution of ufPWV on the Increase in Central Pulse Pressure Following Exercise
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agiovlasitis, S.; Riebe, D.; Ehrman, J.K.; Liguori, G.; Magal, M. American College of Sports Medicine Wolters Kluwer Health. In ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 10th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4963-3906-5. [Google Scholar]
- DeVan, A.E.; Anton, M.M.; Cook, J.N.; Neidre, D.B.; Cortez-Cooper, M.Y.; Tanaka, H. Acute effects of resistance exercise on arterial compliance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, M.; Kawano, H.; Sugawara, J.; Takahashi, K.; Hayashi, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Tabata, I.; Tanaka, H. Unfavorable effects of resistance training on central arterial compliance: A randomized intervention study. Circulation 2004, 110, 2858–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, M. Effects of resistance training on arterial stiffness: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.N.; Trombold, J.R.; Dhindsa, M.; Lin, H.F.; Tanaka, H. Arterial stiffening following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.F.; Chou, C.C.; Cheng, H.M.; Tanaka, H. Delayed onset vascular stiffening induced by eccentric resistance exercise and downhill running. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2017, 27, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chleboun, G.S.; Howell, J.N.; Conatser, R.R.; Giesey, J.J. Relationship between muscle swelling and stiffness after eccentric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.N.; Chleboun, G.; Conatser, R. Muscle stiffness, strength loss, swelling and soreness following exercise-induced injury in humans. J. Physiol. 1993, 464, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Zhao, H.; Brault, J.S.; Chen, S.; An, K.N. Ultrasound elastography: The new frontier in direct measurement of muscle stiffness. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chino, K.; Akagi, R.; Dohi, M.; Fukashiro, S.; Takahashi, H. Reliability and validity of quantifying absolute muscle hardness using ultrasound elastography. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; He, W.; Du, L.J.; Li, S.; Cheng, L.G.; Shih, G.; Rubin, J. Ultrasound strain elastography in assessment of resting biceps brachii muscle stiffness in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A primary observation. Clin. Imaging 2016, 40, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankel, S.J.; Razzano, B.M. The impact of acute and chronic resistance exercise on muscle stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ultrasound 2020, 23, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Parker, K.H. Wave propagation in a model of the arterial circulation. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, J.; Hayashi, K.; Yokoi, T.; Tanaka, H. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity: Impact of different arterial path length measurements. Artery Res. 2010, 4, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, J.; Hayashi, K.; Tanaka, H. Distal shift of arterial pressure wave reflection sites with aging. Hypertension 2010, 56, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, J.; Tomoto, T.; Tanaka, H. Arterial path length estimation for heart-to-brachium pulse wave velocity. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messas, E.; Pernot, M.; Couade, M. Arterial wall elasticity: State of the art and future prospects. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffieux, T.; Gennisson, J.; Tanter, M.; Fink, M.; Nordez, A. Ultrafast imaging of in vivo muscle contraction using ultrasound. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 184107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Han, D.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yu, S.; Qi, Y. Measurement of carotid pulse wave velocity using ultrafast ultrasound imaging in hypertensive patients. J. Med. Ultrason. 2017, 44, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirault, T.; Pernot, M.; Frank, M.; Couade, M.; Niarra, R.; Azizi, M.; Emmerich, J.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Fink, M.; Tanter, M.; et al. Carotid stiffness change over the cardiac cycle by ultrafast ultrasound imaging in healthy volunteers and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1890–1896; discussion 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, P.C.; Chen, J.; He, W.; Du, L.J.; Min, R.; O’Dell, M. Ultrasound strain imaging in assessment of biceps muscle stiffness and dynamic motion in healthy adults. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Du, L.J.; He, W.; Li, S.; Cheng, L.G. Ultrasound strain elastography in assessment of muscle stiffness in acute Levodopa challenge test: A feasibility study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.X.; Luo, J. Comparison of different pulse waveforms for local pulse wave velocity measurement in healthy and hypertensive common carotid arteries in vivo. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Hongo, K.; Kanai, H. Measurement of regional pulse wave velocity using very high frame rate ultrasound. J. Med. Ultrason. 2013, 40, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.F.; Wang, S.C.; Cheng, H.M.; Sugawara, J. Homebased standing core exercise training improves femoral blood flow but not arterial stiffness in middle-aged to older adults. Artery Res. 2021, 27, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, R.; Tanaka, J.; Shikiba, T.; Takahashi, H. Muscle hardness of the triceps brachii before and after a resistance exercise session: A shear wave ultrasound elastography study. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agten, C.A.; Buck, F.M.; Dyer, L.; Fluck, M.; Pfirrmann, C.W.; Rosskopf, A.B. Delayed-onset muscle soreness: Temporal assessment with quantitative MRI and shear-wave ultrasound elastography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacourpaille, L.; Nordez, A.; Hug, F.; Couturier, A.; Dibie, C.; Guilhem, G. Time-course effect of exercise-induced muscle damage on localized muscle mechanical properties assessed using elastography. Acta Physiol. 2014, 211, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, O.; Niitsu, M.; Kurihara, T.; Fukubayashi, T. Evaluation of human muscle hardness after dynamic exercise with ultrasound real-time tissue elastography: A feasibility study. Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tripathy, S.; Rubin, J.M.; Stidham, R.W.; Johnson, L.A.; Higgins, P.D.; Kim, K. A new nonlinear parameter in the developed strain-to-applied strain of the soft tissues and its application in ultrasound elasticity imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.K. Tension due to interaction between the sliding filaments in resting striated muscle. The effect of stimulation. J. Physiol. 1968, 199, 637–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkjaer, T.; Toft, E.; Andreassen, S.; Hornemann, B.C. Muscle stiffness in human ankle dorsiflexors: Intrinsic and reflex components. J. Neurophysiol. 1988, 60, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Li, R.X.; Konofagou, E.E. Pulse wave imaging of the human carotid artery: An in vivo feasibility study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2012, 59, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeling, E.; Reesink, K.D.; Kornmann, L.M.; Reneman, R.S.; Hoeks, A.P. The dicrotic notch as alternative time-reference point to measure local pulse wave velocity in the carotid artery by means of ultrasonography. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 2028–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermeling, E.; Vermeersch, S.J.; Rietzschel, E.R.; de Buyzere, M.L.; Gillebert, T.C.; van de Laar, R.J.; Ferreira, I.; Hoeks, A.P.; van Bortel, L.M.; Reneman, R.S.; et al. The change in arterial stiffness over the cardiac cycle rather than diastolic stiffness is independently associated with left ventricular mass index in healthy middle-aged individuals. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Cooper, M.Y.; DeVan, A.E.; Anton, M.M.; Farrar, R.P.; Beckwith, K.A.; Todd, J.S.; Tanaka, H. Effects of high intensity resistance training on arterial stiffness and wave reflection in women. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bopp, M.; Botta, F.; Nussbaumer, M.; Schafer, J.; Roth, R.; Schmidt-Trucksass, A.; Hanssen, H. Lower body vs. upper body resistance training and arterial stiffness in young men. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Masuhara, M.; Ikuta, K. Upper but not lower limb resistance training increases arterial stiffness in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Min, S.; Sakamaki-Sunaga, M. Arterial compliance and stiffness following low-intensity resistance exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashaback, J.G.; Cluff, T.; Potvin, J.R. Muscle fatigue and contraction intensity modulates the complexity of surface electromyography. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.K.; Kayupov, E.; Gumucio, J.P.; Mendias, C.L.; Claflin, D.R.; Brooks, S.V. Intrinsic stiffness of extracellular matrix increases with age in skeletal muscles of mice. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacolley, P.; Regnault, V.; Segers, P.; Laurent, S. Vascular smooth muscle cells and arterial stiffening: Relevance in development, Aging, and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1555–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessner, B.; Liebensteiner, M.; Nachbauer, W.; Csapo, R. Age-specific response of skeletal muscle extracellular matrix to acute resistance exercise: A pilot study. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, B.E.; Carroll, C.C.; Jemiolo, B.; Trappe, S.W.; Magnusson, S.P.; Dossing, S.; Kjaer, M.; Trappe, T.A. Effect of acute resistance exercise and sex on human patellar tendon structural and regulatory mRNA expression. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gumpenberger, M.; Wessner, B.; Graf, A.; Narici, M.V.; Fink, C.; Braun, S.; Hoser, C.; Blazevich, A.J.; Csapo, R. Remodeling the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix in older age-effects of acute exercise stimuli on gene expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, M.L.; Pierce, J.R.; Alemany, J.A.; Harman, E.A.; Nindl, B.C. Effects of exercise training on the matrix metalloprotease response to acute exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
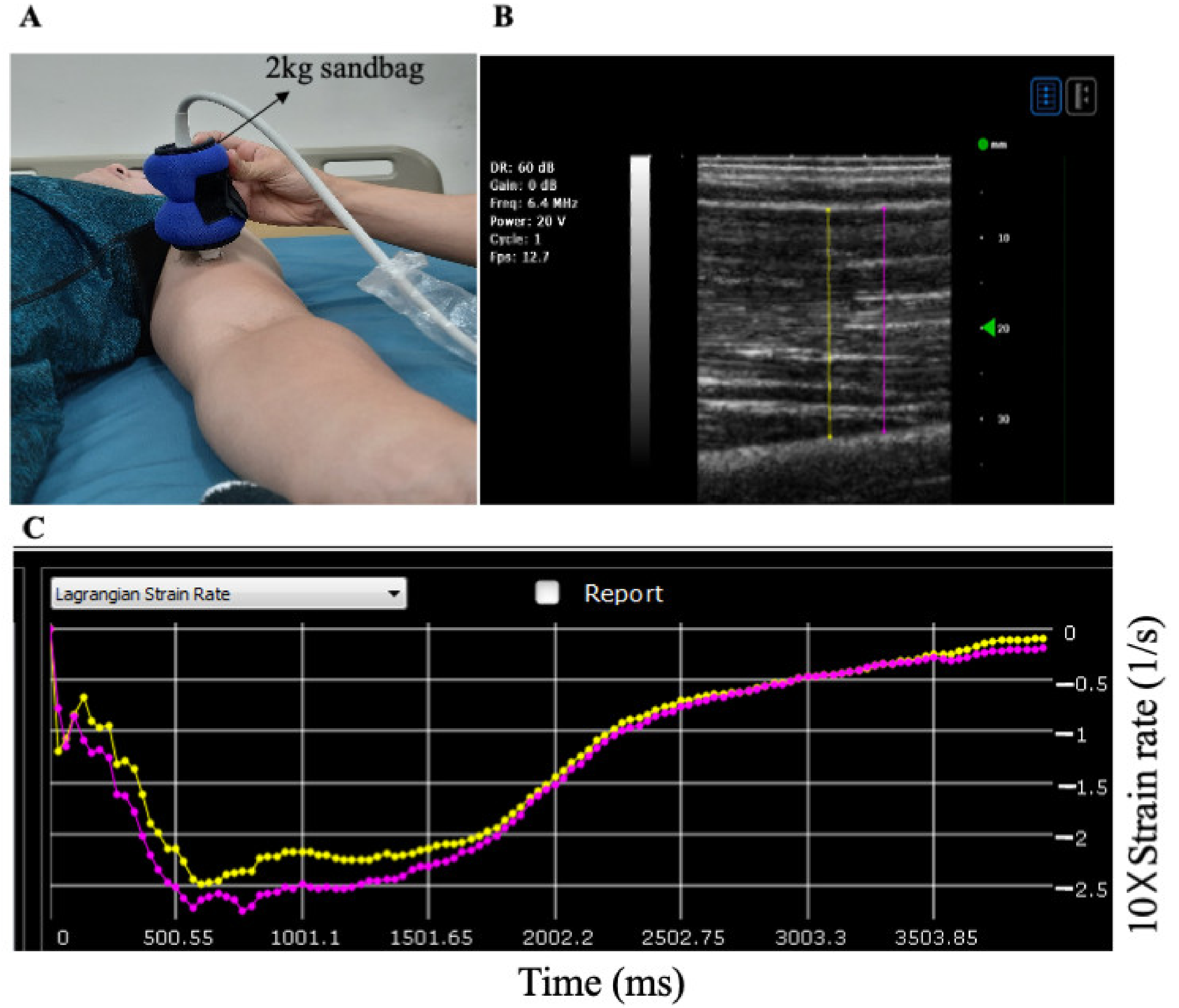
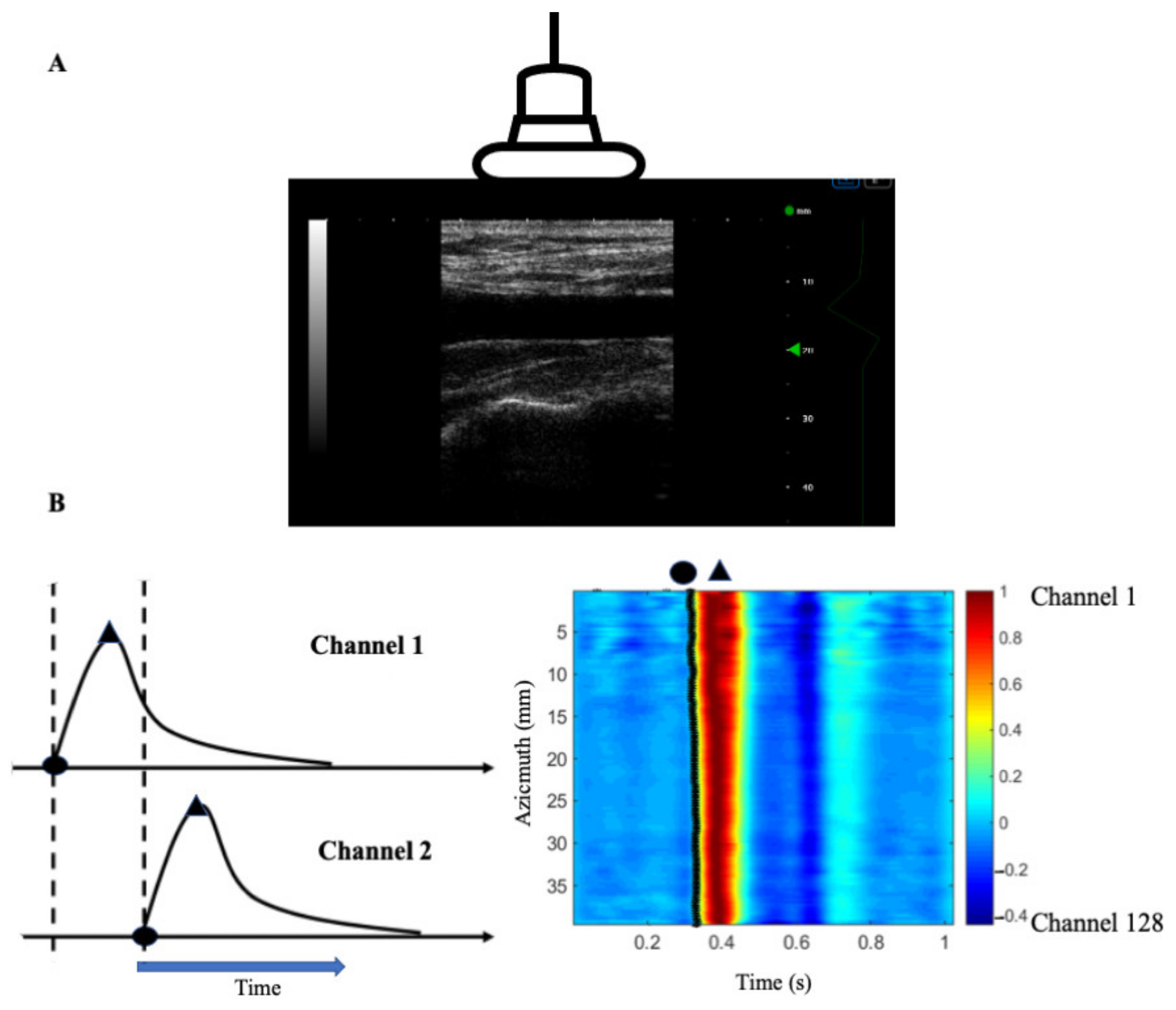
| N = 23 | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 24 ± 1 |
| Height. cm | 175 ± 2 |
| Weight, kg | 78 ± 3 |
| Waist-hip ratio | 0.81 ± 0.01 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24 ± 1 |
| 1RM of bicep curl, kg | 63 ± 3 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 58 ± 3 |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 97 ± 4 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 171 ± 5 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 83 ± 2 |
| Brachial SBP, mmHg | 127 ± 5 |
| Brachial DBP, mmHg | 68 ± 3 |
| Brachial MAP, mmHg | 91 ± 4 |
| ufPWV-sys, m/s | 6.8 ± 0.3 |
| ufPWV-dia, m/s | 6.3 ± 0.3 |
| Carotid compliance, mm2/mmHg × 10−2 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Carotid β-stiffness index, U | 6.1 ± 0.5 |
| Carotid distensibility, mm2/KPa | 8.1 ± 0.7 |
| 40%1RM | 80%1RM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |
| cSBP, mmHg | 108 ± 5 | 111 ± 4 NS | 109 ± 5 | 112 ± 4 NS |
| cDBP, mmHg | 68 ± 2 | 67 ± 1 NS | 68 ± 3 | 66 ± 2 NS |
| cPP, mmHg | 41 ± 3 | 44 ± 3 NS | 41 ± 2 | 46 ± 2 * (p = 0.04) |
| cfPWV, cm/s | 775 ± 23 | 809 ± 29 NS | 762 ± 28 | 807 ± 24 NS |
| baPWV, cm/s | 1195 ± 52 | 1247 ± 51 (p = 0.07) | 1198 ± 58 | 1302 ± 72* (p < 0.0001) |
| Muscle strain rate, 1/s | 0.128 ± 0.009 | 0.118 ± 0.010 NS | 0.128 ± 0.006 | 0.102 ± 0.009 * (p = 0.009) |
| Muscle strain rate in AUC | 327 ± 33 | 307 ± 25 NS | 357 ± 23 | 239 ± 19 * (p < 0.0001) |
| Carotid Compliance | Carotid ß-Stiffness | Carotid Distensibility | cfPWV | baPWV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle strain rate | 0.49 * (p = 0.02) | 0.84 * (p < 0.0001) | 0.54 * (p = 0.01) | −0.10 NS | −0.02 NS |
| ufPWV-sys | −0.26 NS | 0.64 * (p = 0.01) | −0.26 NS | 0.11 NS | 0.14 NS |
| ufPWV-dia | −0.27 NS | 0.67 * (p = 0.01) | −0.30 NS | 0.15 NS | 0.09 NS |
| Δ ufPWV | 0.24 NS | −0.26 NS | 0.30 NS | −0.11 NS | −0.18 NS |
| ∆ cPP | |
|---|---|
| ∆ muscle strain rate. 1/s | R2 = 0.04 |
| ∆ ufPWV-sys, m/s | R2 = 0.30 * (p = 0.003) |
| ∆ ufPWV-dia, m/s | R2 = 0.04 |
| ∆ baPWV, cm/s | R2 = 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-F.; Liao, Y.-H.; Li, P.-C. Ultrafast Ultrasound-Derived Muscle Strain Measure Correlates with Carotid Local Pulse Wave Velocity in Habitual Resistance-Trained Individuals. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188783
Lin H-F, Liao Y-H, Li P-C. Ultrafast Ultrasound-Derived Muscle Strain Measure Correlates with Carotid Local Pulse Wave Velocity in Habitual Resistance-Trained Individuals. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hsin-Fu, Yi-Hung Liao, and Pai-Chi Li. 2021. "Ultrafast Ultrasound-Derived Muscle Strain Measure Correlates with Carotid Local Pulse Wave Velocity in Habitual Resistance-Trained Individuals" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188783
APA StyleLin, H.-F., Liao, Y.-H., & Li, P.-C. (2021). Ultrafast Ultrasound-Derived Muscle Strain Measure Correlates with Carotid Local Pulse Wave Velocity in Habitual Resistance-Trained Individuals. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188783






