Abstract
Deep drawing is characterized by extremely complex deformation that is influenced by process characteristics such as die and punch shapes, blank shape, blank holding force, material properties, and lubrication. The optimization of the deep drawing process is a challenging issue due to the complicated functions that define and relate the process parameters. However, the optimization is essential to enhance the productivity and the product cost in the deep drawing process. In this paper, a MATLAB toolbox (Pattern Search) was employed to minimize the maximum deep drawing force (Fd-min) at different values of the operating and the geometrical parameters. As a result, a minimum deep drawing force chart (carpet plot) was generated to show the best combination of friction coefficients at the blank contact interfaces. The extracted friction coefficients guided the selection of proper lubricants while minimizing the deep drawing force. A finite element analysis (FEA) was applied through 3D model to simulate the deep drawing process. The material modeling was implemented utilizing the ABAQUS/EXPLICIT program with plastic anisotropy. The optimization results showed that the deep drawing force and the wrinkling decrease when compared with experimental and numerical results from the literature.
1. Introduction
In terms of production capacity, energy consumption, and process improvement potential, the deep drawing process is one of the most significant technologies in current manufacturing [1,2]. During the deep drawing process, a variety of factors might contribute to product failure [3,4]. This failure typically manifests as wrinkling, tearing, earing, and rupture. These studies contained descriptions of material properties, die design, and operating factors such as blank holder load, friction coefficients, deep drawing ratio, and maximum drawing force; careful control of these parameters helps lower the likelihood of failure for drawing parts [5]. Singh et al. [6] discovered the effectiveness of deep drawing variables, including die shoulder radii, punch nose radii, friction coefficients, and deep drawing ratios for cylinder-shaped parts. Using a genetic algorithm, this research created an evolutionary neural system, i.e., error back transmission. The evolutionary algorithm uses the results of the system to find factors that are preferable to maintaining a consistent thickness in the final cup. A complex blank stamping procedure may be examined under particular assumptions, allowing the use of the multi-objective optimization approach to be used [7]. After multi-objective optimization methods are created for a sheet metal forming problem, special considerations are given to conflicting objectives [8]. The maximal punch load (Fd) to perform the process is a main factor in the deep drawing process. This load is utilized in the choice of the instrument press and equipment, and it controls the creation of wrinkling on the lip of the drawn product. There exists no special mathematical calculation to compute the necessary deep drawing force in the drawing process [9]. Generally, the drawing load for the first draw of circular components can be achieved using two methods, one from theoretical analysis taking into account the plasticity principle, and the other by utilizing well-established practical equations. The generalized function or expression takes the following form:
where σ1 is the principal stress value, FBH is the blank holder load, μ is the friction coefficient, h is the drawing cup height, t is the initial thickness of the sheet metal, n is the exponent of the strain hardening, K is the coefficient of the strain hardening, and r is the coefficient of normal anisotropy. Suitable records of σ1 and t can be achieved by differentiating Fd with regard to effective stress, such that
Fd = f (σ1, FBH, μ, h, t, n, K, r),
dF/dσ = 0.
In the optimization of the operation of deep drawing, Gharib et al. [10] developed an optimization system to be used in determining the optimum blank holder force (BHF) scheme that minimizes punch force without running into any of the two operation restrictions: wrinkling and tearing. The design factors of the deep drawing machine included the geometrical factors for the punch and the die, in addition to the blank holder load. Hsiao-Chu et al. [11] described the forecast of the drawing load and forming rise in perspective of optimizing the operating parameters included in the deep drawing operation. A model was employed to discover that friction has substantial effects on the punch force, and the low friction between the die and blank holder can significantly decrease the failure probability and increase the quality of the deep drawing process. The lubrication system and the type of lubricant used can significantly affect the process output and the amount of energy consumed [12]. Plevy [13] studied the minimization of drawing power used in the deep drawing operation by reducing the effect of friction and proposed the utilization of a solid lubricating polymer film barrier rather than oil lubrication. This lubricating barrier significantly decreases the drawing energy of precoated sheet metal at small tolerances. The polymer film contributed successfully in saving surface reliability of the sheet metal [14]. An optimized lubricant application method through a Taguchi and regression model during deep drawing was proposed [15]. The optimum combination of lubricant and sheet surface microstructure was investigated experimentally. The experimental results were analyzed statistically to select the optimum combination of the two factors. Minimum work done while avoiding tearing, wrinkling, and spring back was achieved [16,17,18]. Zhang et al. [19] mentioned that variability in the deep drawing operation may result in effects which the deterministic models are not able to expect. A common method was applied to determine the doubts and combine them through the response surface method (RSM) in order to direct probabilistic established optimization [20]. The probabilistic design model was used to discover the optimum arrangement of blank holder load and friction coefficient through the existence of a variety of material characteristics. The outcome demonstrated that, by utilizing the probabilistic model, the wrinkling and failure decreased by 42% compared with the conventional design [19]. The uncertainness and unreliability of the deterministic optimization models utilized in deep drawing encouraged further researchers to implement quality enhancement applications, e.g., six sigma [21]. Atrian and Fereshteh [22] examined the influence of diverse factors on the deep drawing operation of steel/brass blanks. Finite element and experimental investigations of the deep drawing process of steel/brass blanks were conducted to display the positions of tearing for the cup. In this research, a straight-line relationship was obtained between the maximum punch load and the initial blank diameter. Manoochehri and Kolahan [23] developed a combined finite element (FE), artificial neural network (ANN), and simulated annealing (SA) algorithm as a method to model and optimize the deep drawing operation for stainless steel 304 (SUS304). In this method, the parameters (die radius, punch radius, blank holder load, and frictional coefficients) were considered as input factors. Kakandikar and Nandedkar [24] suggested a new procedure combining two methods for optimizing and decreasing sheet metal thickness for the cover of automotive sealing. Mathematical equations were generated to join input operation factors and thinning. The optimum process was expressed for thinning using a genetic algorithm. Volk et al. [25] generated a new optimizing method for optimizing the deep drawing operation utilizing the finite element technique incorporated with the response surface method (RSM). This optimizing method was a procedure for obtaining the optimal values of blank holder loads and then the desirable final product. Dienemann et al. [26] presented an innovative method for optimizing shell structures taking into consideration their middle surface areas, such as undercuts. The authors presented a production restriction to the 3D topology optimization depending on the stiffness technique to be able to get an optimum structure with no undercuts, along with consistent thickness. Then, these shell structures could be produced by deep drawing within one stage. Lastly, the thickness of the shell enhanced the efficiency of the shell structure using this technique. Kottayam et al. [27] suggested a procedure to simultaneously identify the ideal blank shape to minimize the earing and the ideal value of the blank holder load in the deep drawing operation for the circular cup. The total production cost was decreased by utilizing this procedure.
In the present work, the optimization MATLAB toolbox (Pattern Search) was utilized to minimize the maximum deep drawing force. The deep drawing force and the value of the dimensionless ratio of die shoulder radius to sheet thickness (rd/t) were optimized to minimize the forming work. The other operating parameters and geometrical parameters were constrained according to logical and practical limits documented in the literature [28]. A carpet plot chart for a given value of the best interfacial frictional combinations at different values of the sheet metal thickness was extracted, showing that the proper selection of equivalent conditions led to the minimum deep drawing force (Fdmin). Furthermore, in this research, a finite element analysis (FEA) 3D model was created to simulate the deep drawing operation by utilizing the ABAQUS/EXPLICIT FEA program with proper boundary conditions. As a final point, the optimization results using the finite element analysis (FEA) model were compared with the results of the recommended values from the literature by using the experimental work for validation of the optimization results.
2. Simulation of Deep Drawing Process
2.1. The Simulation Model
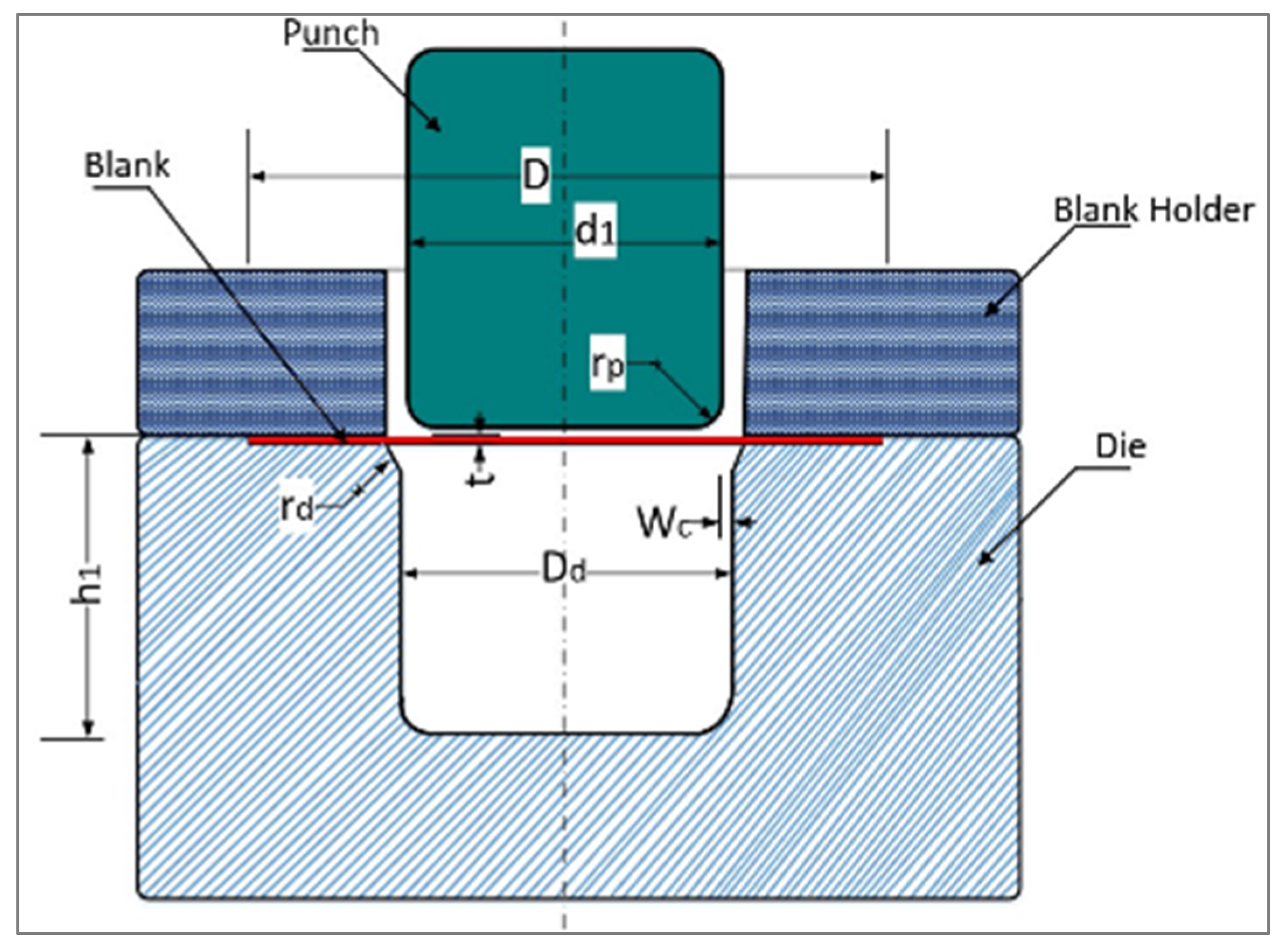
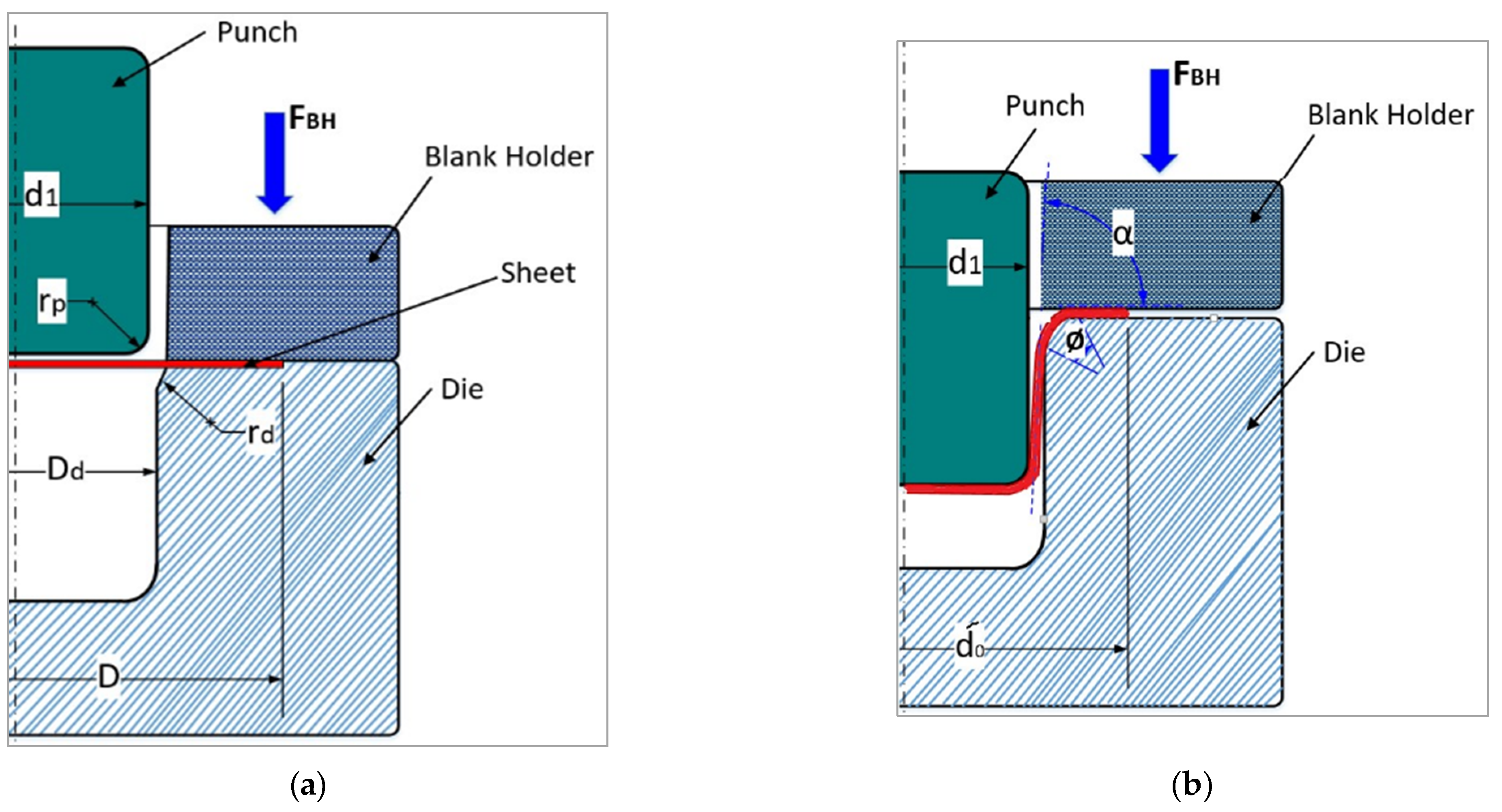
The deep drawing operation is displayed in several stages: the round blank was placed between the blank holder and the die; the punch traveled downward; the blank diameter reduced with the blank was drawn into the die hole. Figure 1 shows the main dimensions of the blank, die, punch, and the blank holder. Furthermore, the main dimensions with the recommended values of friction coefficients are displayed in Table 1, according to an FEA simulation from an earlier study [28].
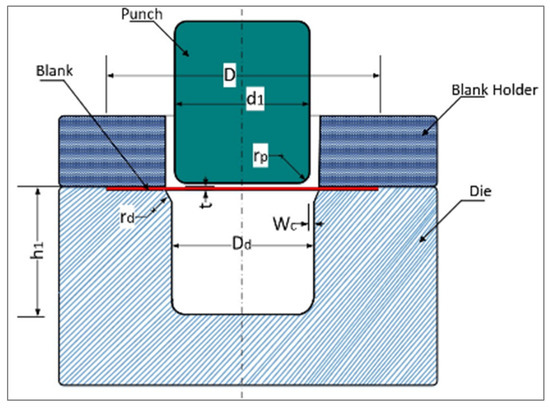
Figure 1.
Assembly and dimensions of the deep drawing die.

Table 1.
Geometrical and the operating parameters.
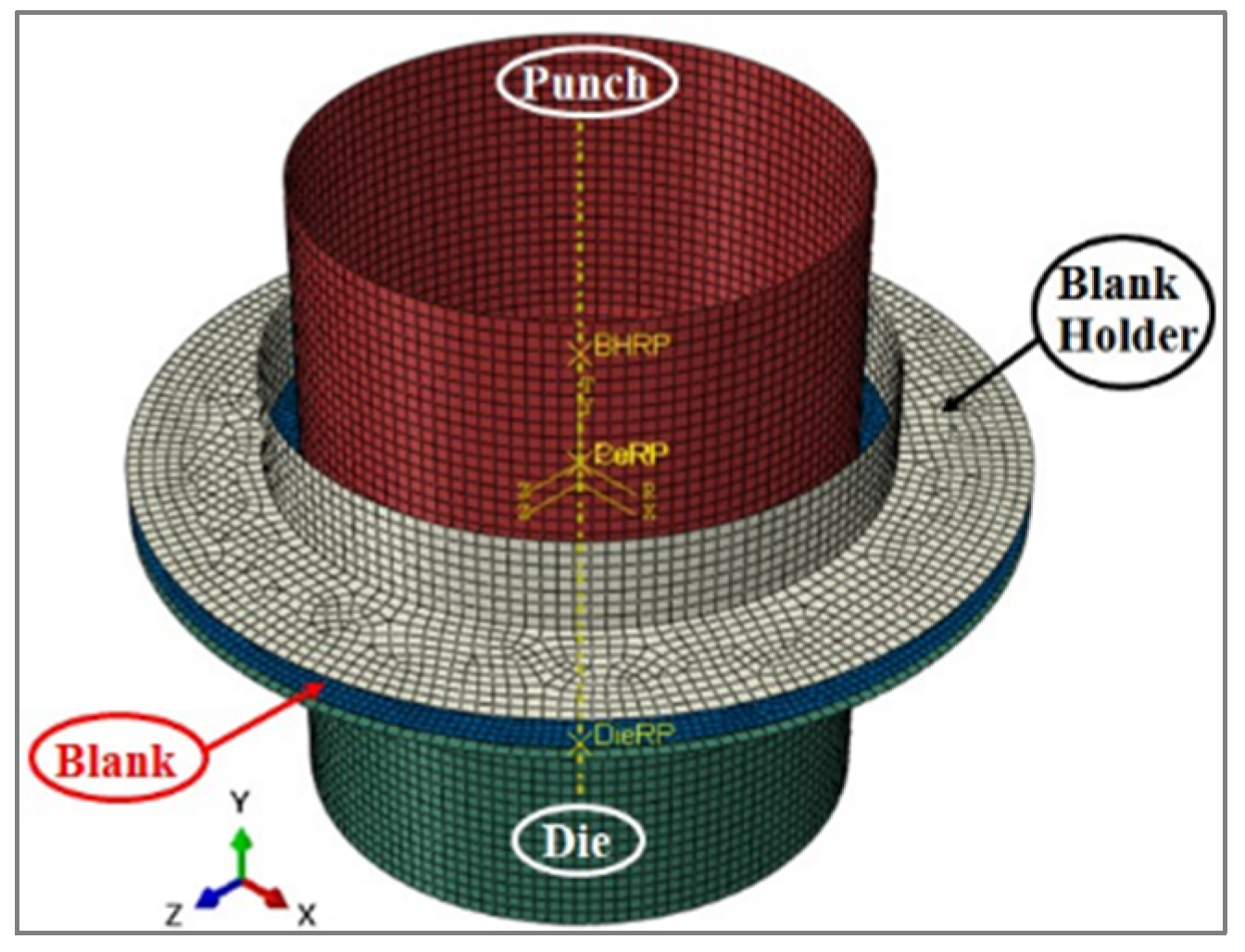
The 3D FE model is shown in Figure 2. The discrete rigid form was utilized to model the punch, the blank holder, and the die, whose movements were represented by the movement of a single node, identified as the rigid body reference node. The punch, the blank holder, and the die were meshed with R3D4 elements. On the other hand, the round blank sheet metal (45 mm radius × 0.8 mm thickness) was modeled as a deformable planar shell base and meshed with shell-type elements of reduced integration S4R elements [29].
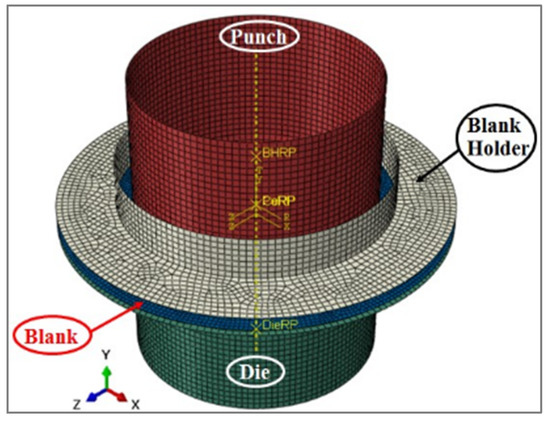
Figure 2.
Assembly of the 3D finite element model (FEM) by ABAQUS.
2.2. Material Properties
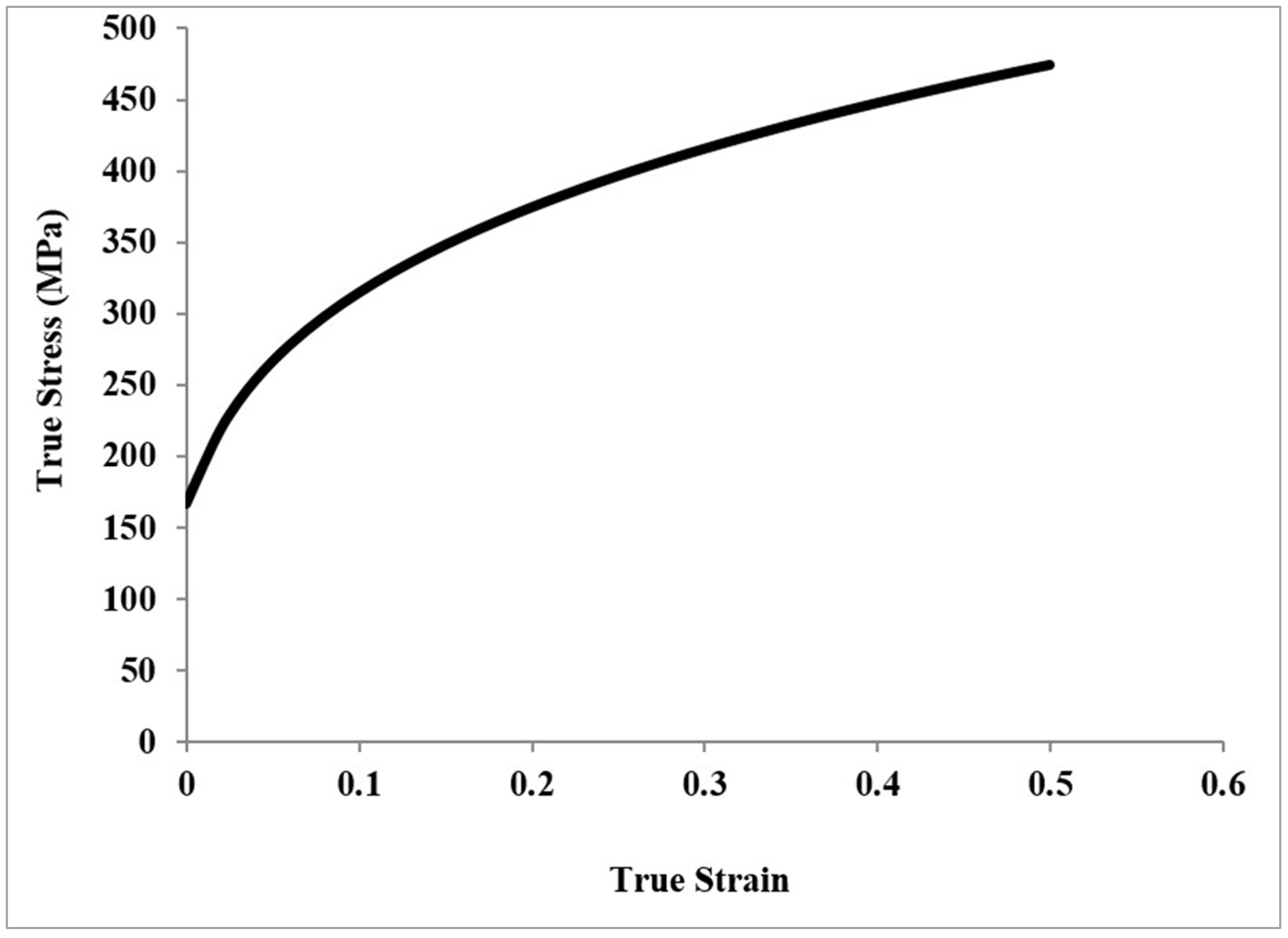
The sheet metal blank was created from mild steel, and modeling was implemented as an elastic–plastic material with isotropic elasticity [30]. The Hill anisotropic yield theory was employed for the plasticity to depict the anisotropic properties of the sheet metal blank in the interior of the FEA simulation program (ABAQUS/EXPLICIT) [31]. The true stress–true strain curve of the material is shown in Figure 3, and Table 2 presents the material properties [32].
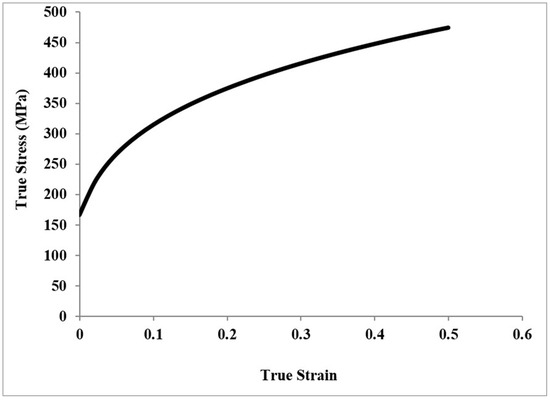
Figure 3.
Plastic true stress–true strain curve of mild steel [30].

Table 2.
The material properties of sheet metal blank [1].
2.3. Forming Limit Stress Diagram (FLSD)
The failure at different values of the geometrical and operating parameters was investigated by using the damage initiation criteria in ABAQUS for the forming limit stress diagram (FLSD) to determine the mechanical properties of the sheet metal. The material was assumed to be anisotropic with three perpendicular similarity planes. The yield theory is presented as the following quadratic function [33,34,35]:
where f is the yield function, F, G, H, L, M, and N are factors particular to the anisotropic condition of the material, and x, y, and z are the principal anisotropic axes. For the plane stress condition (σz = τxz = τyz = 0; σx ≠ 0; σy ≠ 0; τxy ≠ 0), the yield criterion function becomes
The anisotropic constants F, G, H, and N can be formulated in terms of the r-values as follows:
The r-values r0, r45, and r90 were 1.79, 1.51, and 2.27, respectively as presented in Table 2. When the principal directions of the stress tensor correspond with the anisotropic axes (σx = σ1, σy = σ2, τxy = 0), the yield theory can be presented as the principal stress.
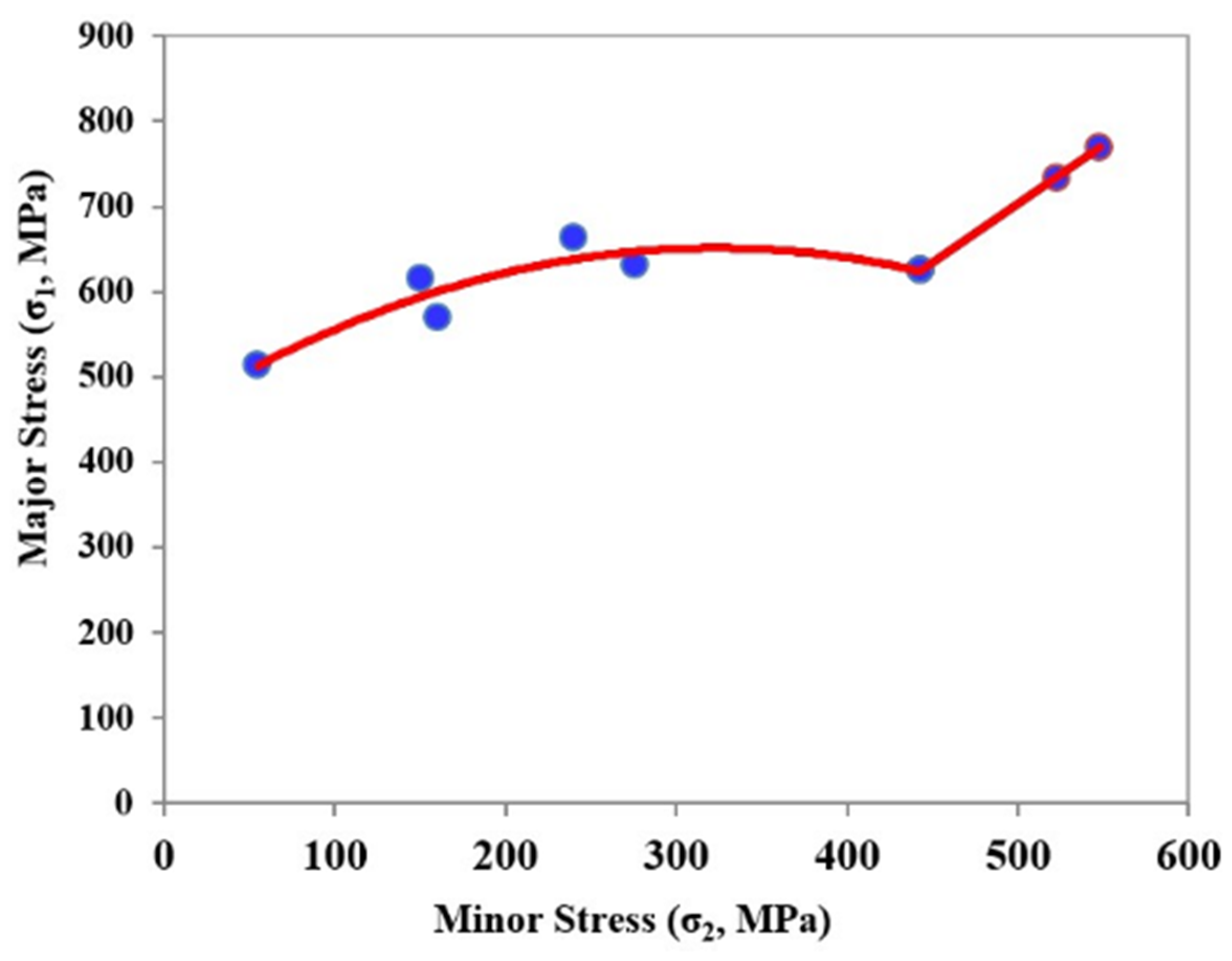
where σ1 is a major stress, σ2 is a minor stress, and σ0 is the yield stress in the rolling direction (σo) of the sheet metal. Figure 4 shows the forming limit stress diagram for the sheet metal with a thickness equal to 0.8 mm.
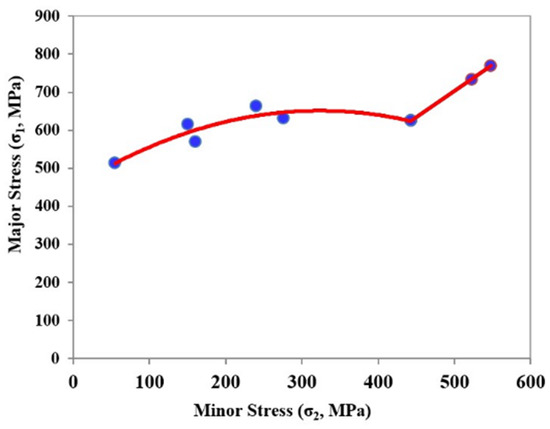
Figure 4.
Determining the forming limit stress diagram (FLSD) by yield theory [30].
3. Optimization of the Maximum Deep Drawing Force (Fdmax)
The optimization MATLAB toolbox (Pattern Search) was utilized to minimize the deep drawing load at the optimal values of the deep drawing process parameters for cylindrical cups. Figure 5 shows the basic components and configuration of the process.
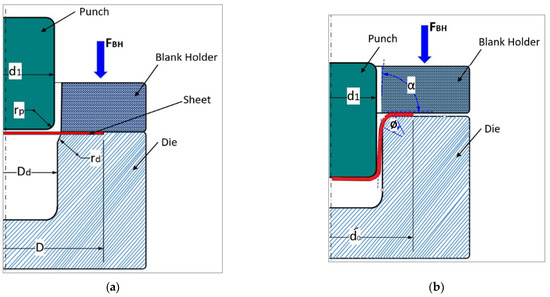
Figure 5.
Deep drawing configurations: (a) before the process; (b) during the process.
The drawing force can be obtained using the equation below [2].
where is the mean flow stress in the flange of the cup (MPa), is the instantaneous blank diameter (mm), is the mean diameter of the cup (=) (mm), d1 is the punch diameter (mm), t is the sheet metal thickness (mm), μh is the friction coefficient between holder and blank, is the blank holder force (N), is the mean flow stress in the die ring of the cup (MPa), rd is the shoulder radius (mm), and μd is the friction coefficient between die and blank. At the maximum deep drawing force (Fd-max),
where is the outside diameter of the flange when the drawing force is a maximum (mm), and D is the diameter of the developed blank (mm); at the maximum deep drawing force (Fd-max)= is the mean flow stress in the flange zone (MPa), = is the mean flow stress in the die ring zone (MPa), and α and are the angles, see Figure 5, assuming that α = = /2 at the maximum deep drawing force (Fd-max). Then,
4. Determining the Mean Flow Stresses ( and )
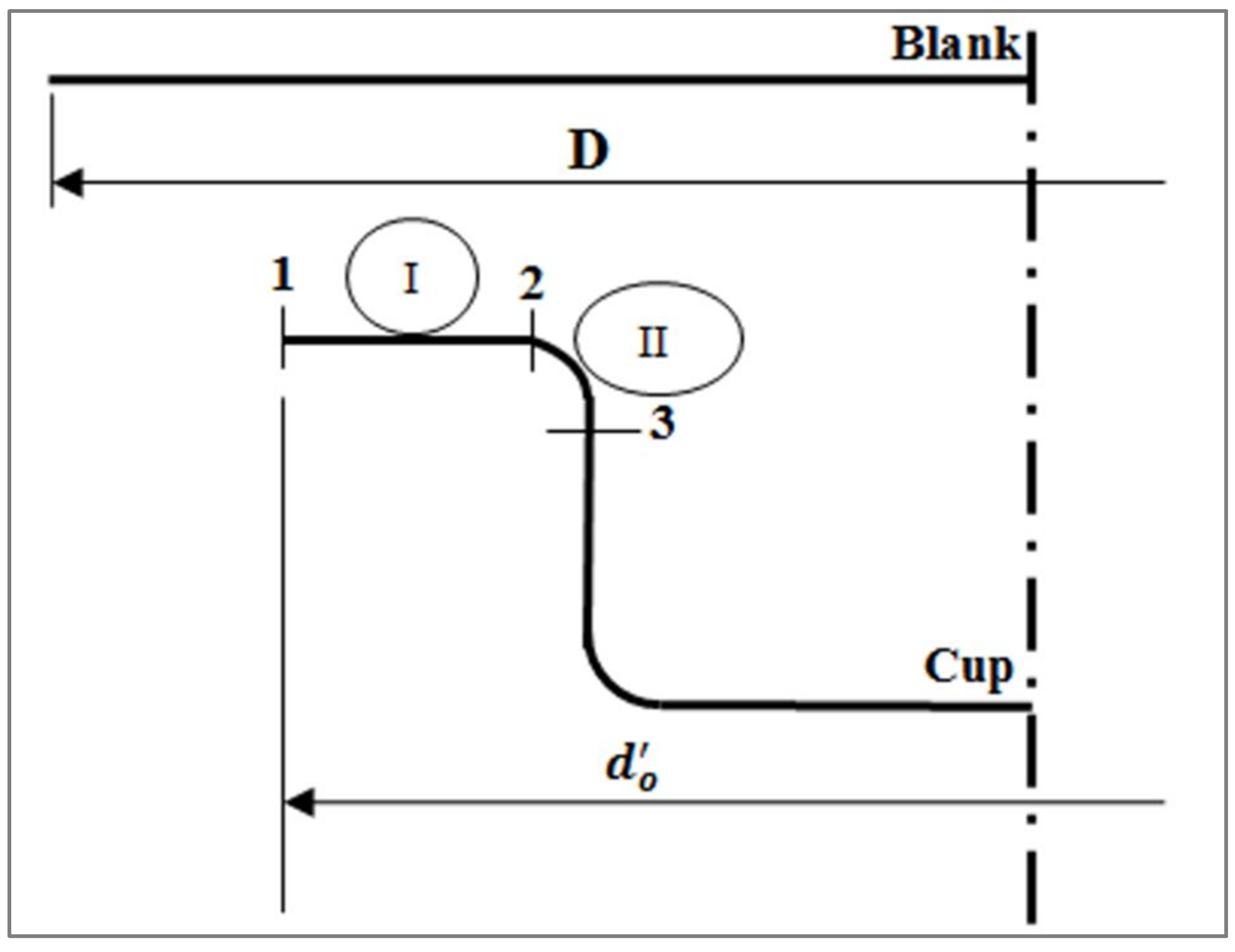
In order to calculate the maximum flow stresses, three critical controlling points 1, 2, and 3 were selected, as shown in Figure 6.
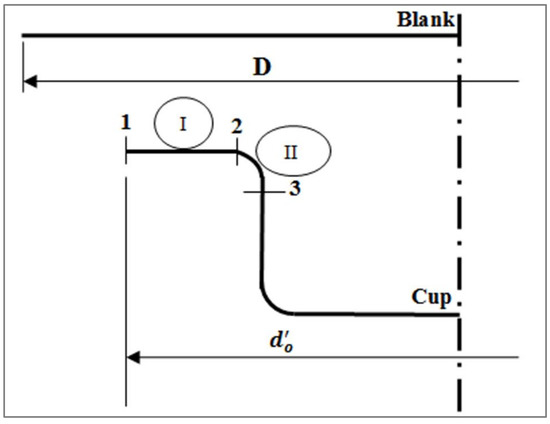
Figure 6.
Flow stress zones in deep drawing at an intermediate state.
The strain state at the rim is given as follows:
where is the instantaneous blank diameter (mm) (see Figure 6), is the diameter of the developed blank (mm), is the instantaneous sheet metal thickness (mm), and t is the sheet metal thickness (mm). Assuming that
where the volume continuity condition requires that
then the equivalent uniaxial strain () is as follows [3]:
Then, at point 1 in the cup flange,
where is the outside diameter of the flange when the drawing force is a maximum (mm), and D is the diameter of the developed blank (mm). The drawing ratio at maximum drawing force occurs according to the following relationship [4]:
The material between points 1 and 2 formed an annulus with outside diameter (D) and unknown inside diameter (di) in the blank. Assuming constant sheet thickness, the unknown diameter (di) can be calculated from the condition that the volume remains constant.
or
Then, the strain at point 2 when the load is a maximum is given as follows [5]:
where dD is the die diameter (mm),
where d1 is the punch diameter (mm), wc is the radial clearance (mm), and rd is the die shoulder radius (mm). For highly strain-hardening materials, the ratio rd/t < 10; hence, the increase in should be taken into account. In bending, the incremental strain of the outside fibers can be determined from the radius of curvature (rM) of the neutral fiber and the sheet thickness (t) [6].
dD = d1 + (2wc),
Applying this relationship to the die radius yields
Since the strain distribution is linear across the sheet thickness, the mean bending strain in the cross-section is given by
The workpiece undergoes twofold bending in the zone of the die shoulder radius such that the total mean bending strain after unbending is
The corresponding natural strain is given by
Using this result, the strain at point 3 for the maximum load can now be determined as follows, if is known:
Then, from the flow stress equation, we can calculate the maximum flow stresses at points 1, 2, and 3.
where K is the strength coefficient for the sheet metal material (MPa), and n is the exponent of the strain hardening for the sheet metal material; then, we can calculate the mean flow stresses and for (rd/t < 10).
5. Objective Function
The objective function is simply to minimize the maximum deep drawing force from Equation (9).
All values in the above equation are calculated at the position to get the maximum drawing force, where
6. Cracking Force
The biggest permissible drawing force is constrained by the force which can be transferred by the sheet metal in the zone of the punch nose radius or at the transmission from cup wall to the bottom cup radius, which is named the cracking force [7]. It should be dependably higher than the maximum value of the deep drawing force. The cracking force can be calculated from the following empirical formula [36]:
where Fcrack is the cracking force (N), t is the sheet metal thickness (mm), d1 is the punch diameter (mm), and UTS is the ultimate tensile strength of the sheet metal material (MPa).
Fcrack = π t d1UTS,
7. Constraints
The operating parameters and geometrical parameters are constrained according to logical and practical limits documented in the literature to minimize spring back and residual stresses. Die shoulder radius practical limits were based on earlier work [8,37].
4 < rd/t ≤ 10.
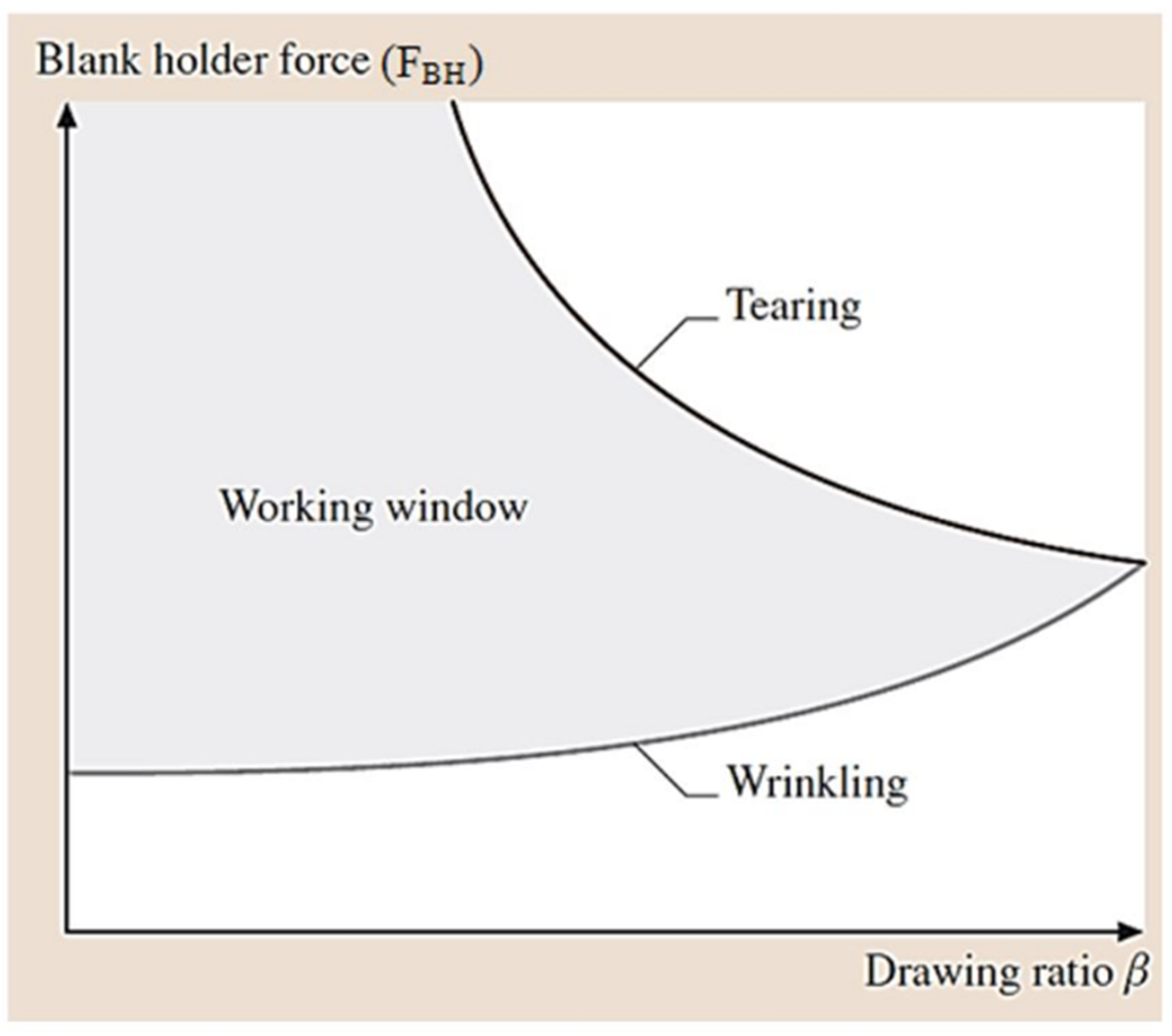
Grote and Antonsson [8] established a working domain for the deep drawing process, as shown in Figure 7, and the conditions of the drawing process are as follows:
FBH-wrinkling < FBH < FBH-tearing.
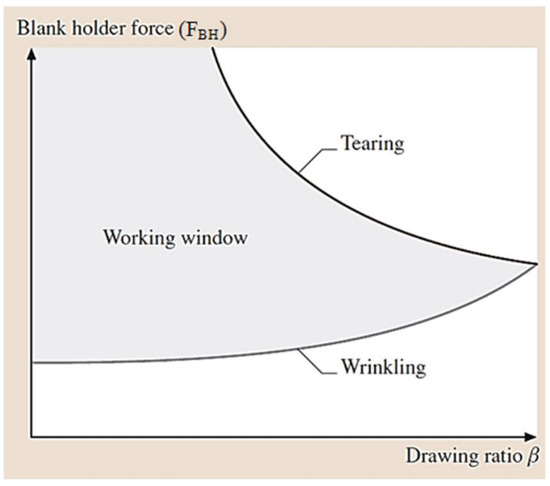
Figure 7.
The working domain in the deep drawing process [9].
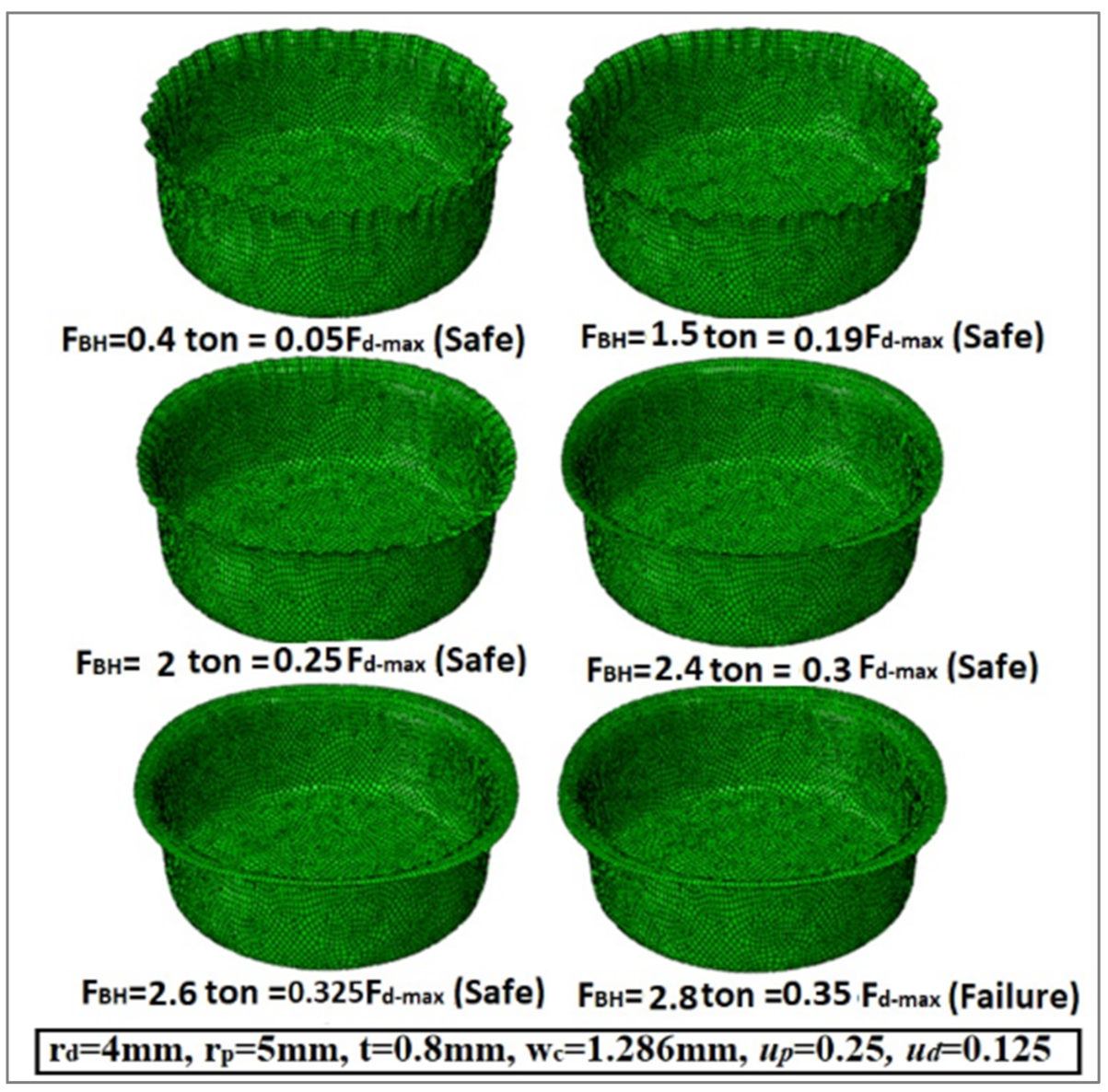
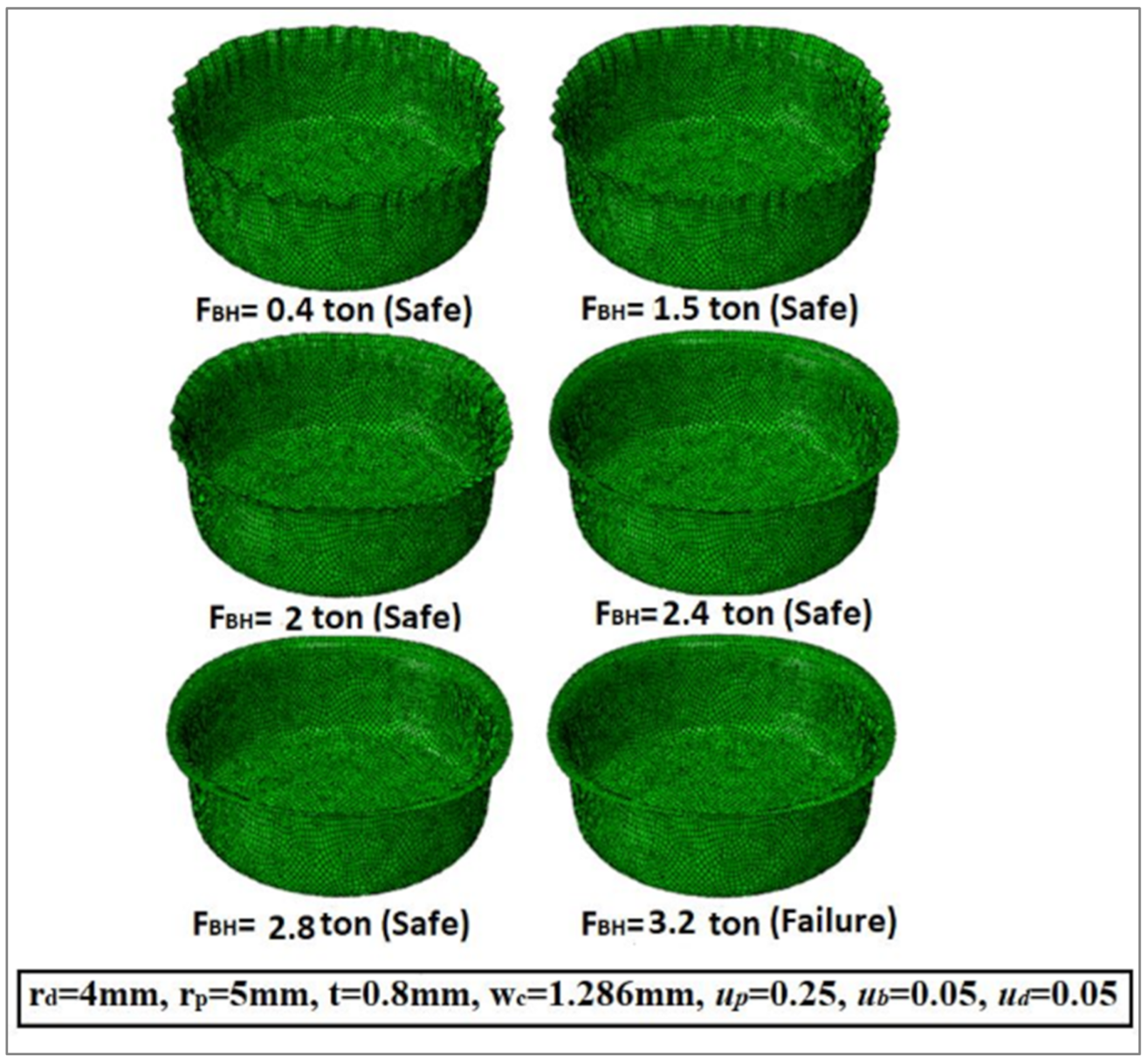
Figure 8 describes the variation in the wrinkling formations with diverse values of the blank holder force/the maximum deep drawing force (FBH/Fdmax). It is clear that the wrinkling formation is reduced with an increase in the ratio (FBH/Fd-max). A deep drawing force FBH of about 30% of the maximum deep drawing force (Fdmax) appears to be a good choice to prevent or minimize wrinkling without causing tearing of the cup wall. Figure 8 shows that the wrinkling force is 2 tons and the tearing force is 2.8 t at μd = μh = 0.125. In order to avoid wrinkling and tearing, the value of (FBH) must be between the two values of wrinkling force and tearing force. In addition, by using the finite element simulation model, Figure 9 describes the variation in the wrinkling formations with dissimilar values of the blank holder force/the maximum deep drawing force (FBH/Fdmax). Moreover, it shows that the wrinkling force is equal to 2 tons and the tearing force is equal to 3.2 t at μd = μh = 0.05. Note that the recommended values for the friction coefficients used in the finite element analysis and in the optimization were based on logical and practical limits documented in the literature [10]. Table 3 displays the values of the wrinkling force and the tearing force taken from Figure 8 and Figure 9 by utilizing the FEA simulation model.
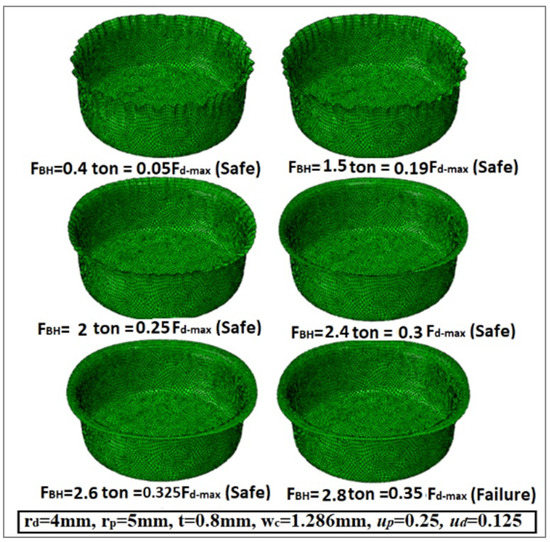

Figure 8.
Variation in wrinkling formation as a function of blank holder force (FBH) and maximum deep drawing force (Fd-max) at μh = μd = 0.125.
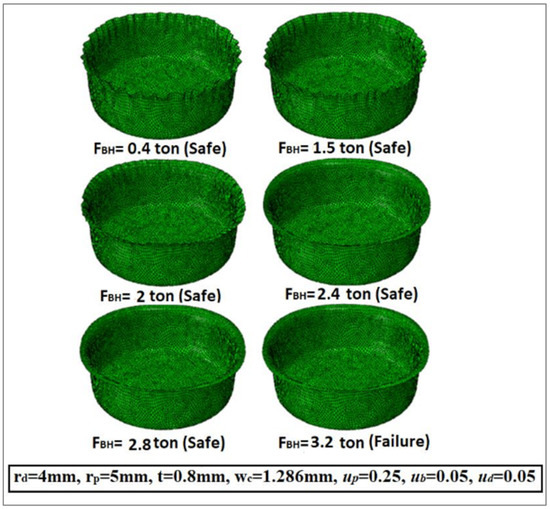

Figure 9.
Variation in wrinkling formation as a function of blank holder force (FBH) and maximum deep drawing force (Fd-max) at μh = μd = 0.05.

Table 3.
The values of the wrinkling and tearing forces at different friction coefficients.
8. Results and Discussion
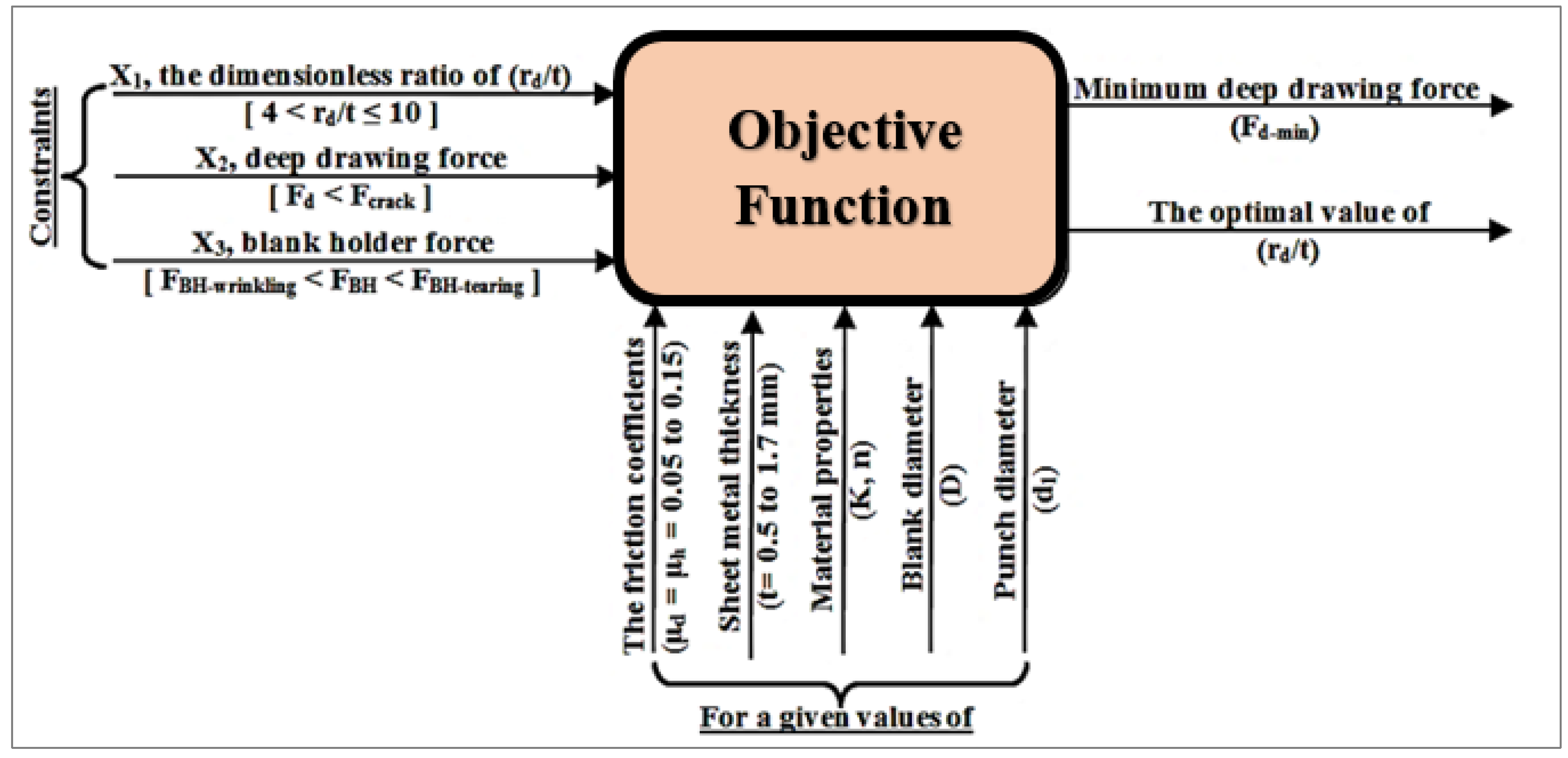
By using the optimization MATLAB toolbox (Pattern Search), the minimum deep drawing force (Fd-min) and the dimensionless ratio of (rd/t) were determined. Figure 10 shows a layout of the operating parameters and constraints of the deep drawing process considering the friction coefficients μd and μh as equal within a range of 0.05 to 0.15, and the sheet thickness was varied from t = 0.5 to 1.7 mm. The objective function (Equation (34)) and constraints were as follows:
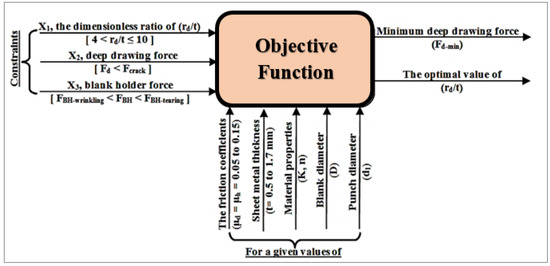
Figure 10.
Layout of the operating parameters in the objective function.
Objective function:
Constraints:
x(1) = μh (0.1 < μh ≤ 0.3) (coefficient of friction between holder/blank),
x(2) = μd (0.1 < μd ≤ 0.3) (coefficient of friction between die/blank),
x(3) = rd (4 t < rd ≤ 10 t) (die shoulder radius),
x(4) = wc (wc > t) (radial clearance),
FBH-wrinkling < FBH < FBH-tearing.
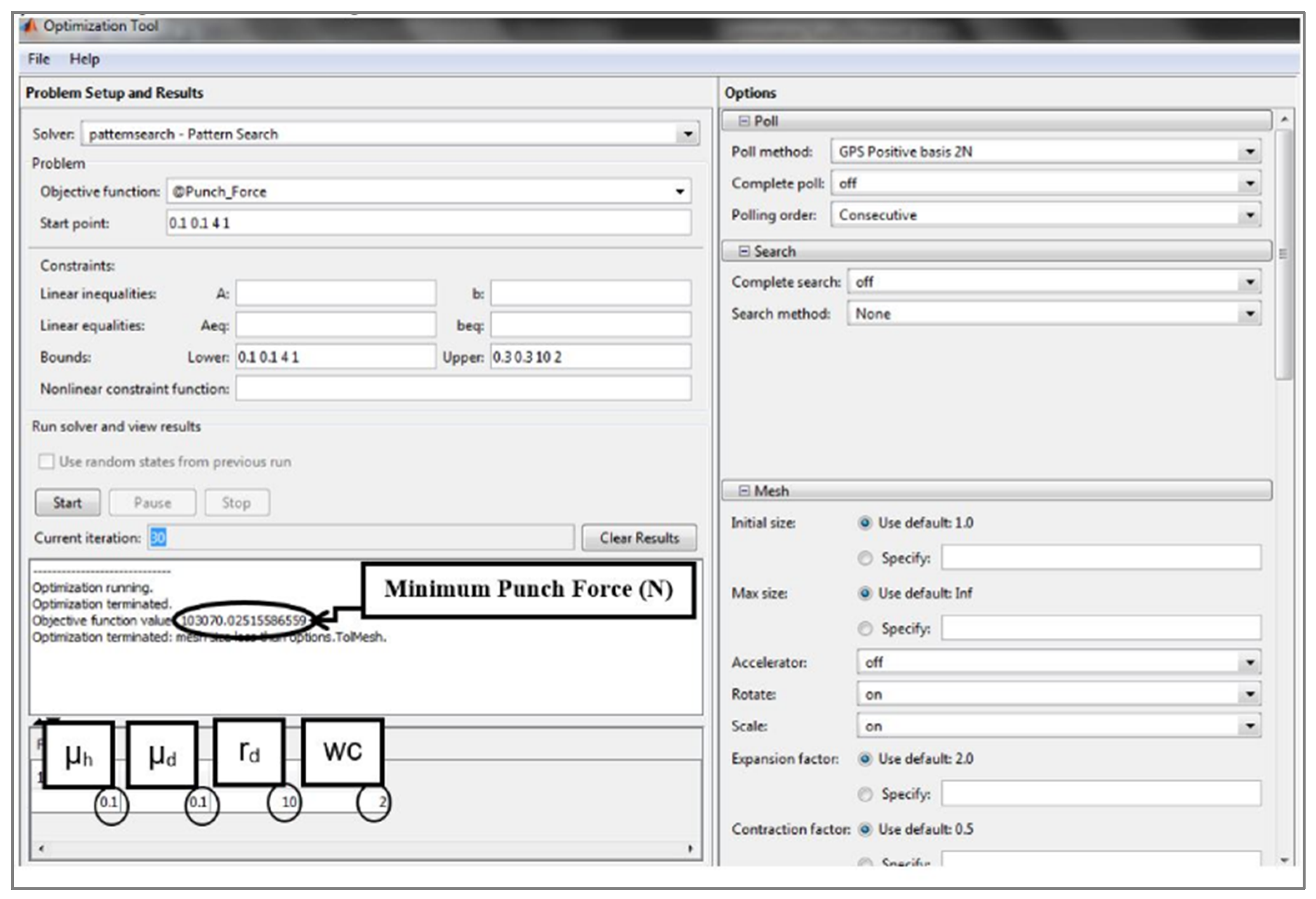
The interface of the Pattern Search optimization toolbox is shown in Figure 11.
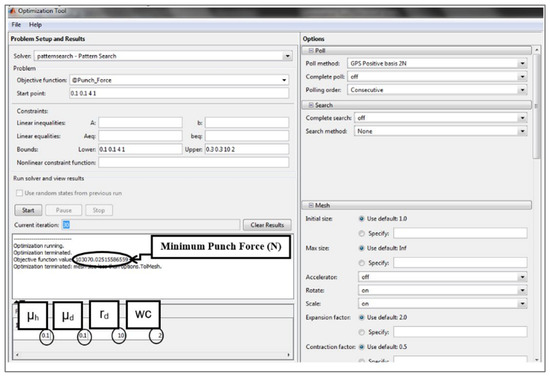
Figure 11.
Screenshot of optimization tool used in current work.
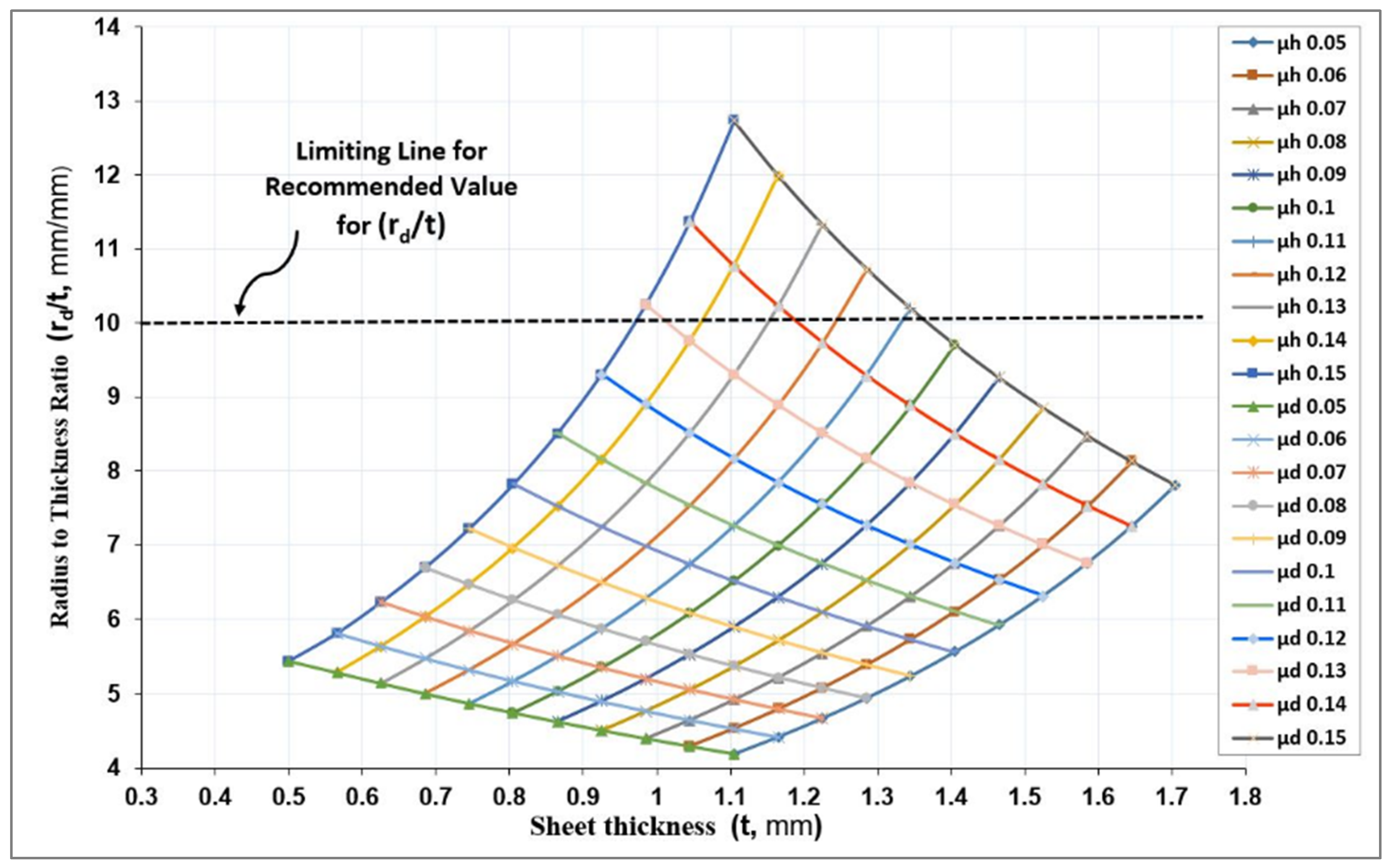
As a result of the objective function, the minimum deep drawing force Fd-min can be obtained at optimum rd/t ratios. The carpet plot shown in Figure 12 was developed to be used as a visual tool for obtaining the minimum deep drawing force considering the best combination of friction coefficients. These operating factors at a given set of design data correspond to a situation of minimum deep drawing force (Fd-min). It is obvious that the minimum deep drawing force (Fd-min) at different sheet metal thickness (t) was not constant. In addition, Figure 12 describes the different coefficient of frictions related to sheet thickness, as well as the dimensionless ratio of die shoulder radius for a wide range of geometrical and operating parameters. During the initial stage of deep drawing, the dimensionless ratio (rd/t) should not exceed 10 according to the finite element analysis results in earlier work [11]. Therefore, a limiting line was placed to limit the choices within the recommended design domain.
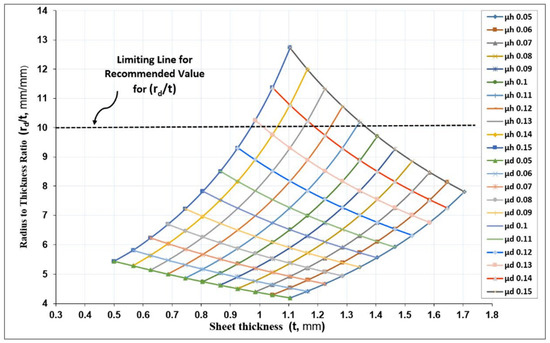
Figure 12.
Carpet plot of minimum deep drawing force at different values of radius-to-thickness ratio (rd/t), sheet metal thickness (t), and friction coefficients (μd and μh).
9. Experimental Work
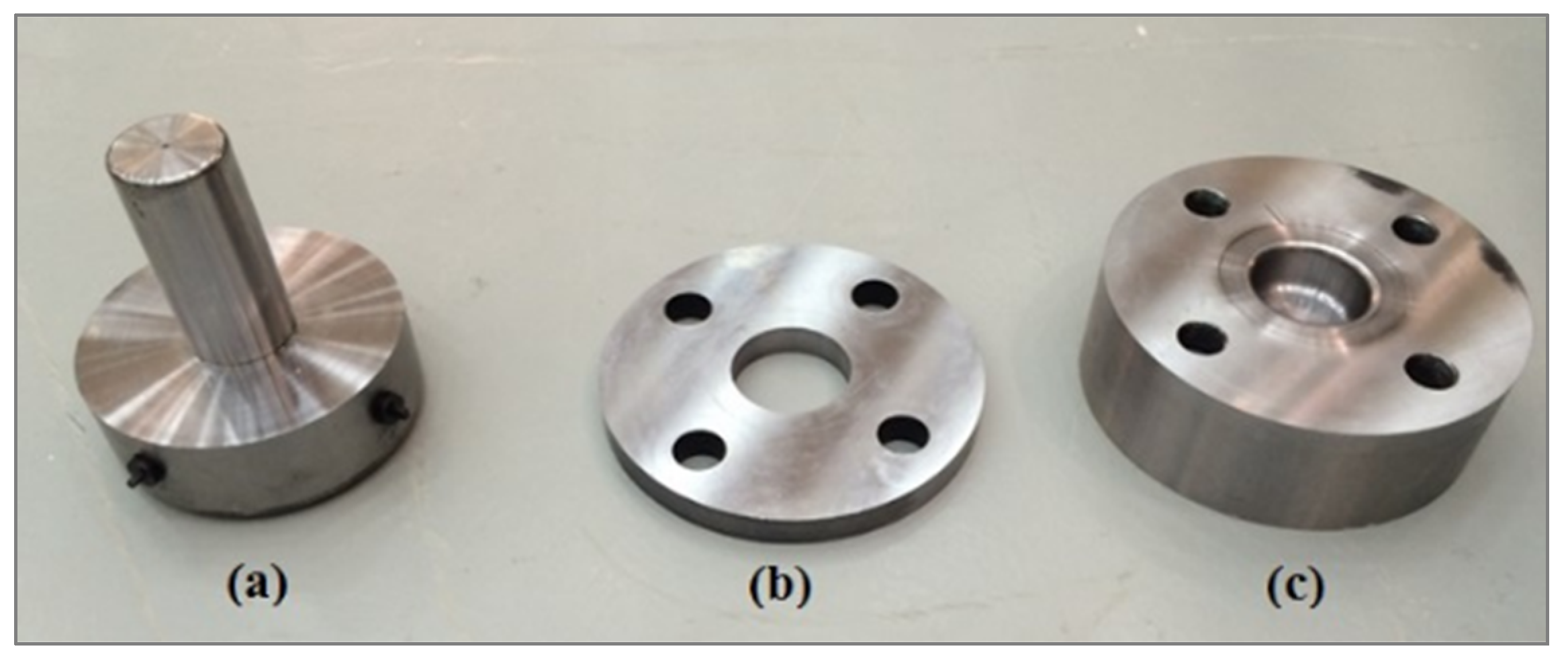
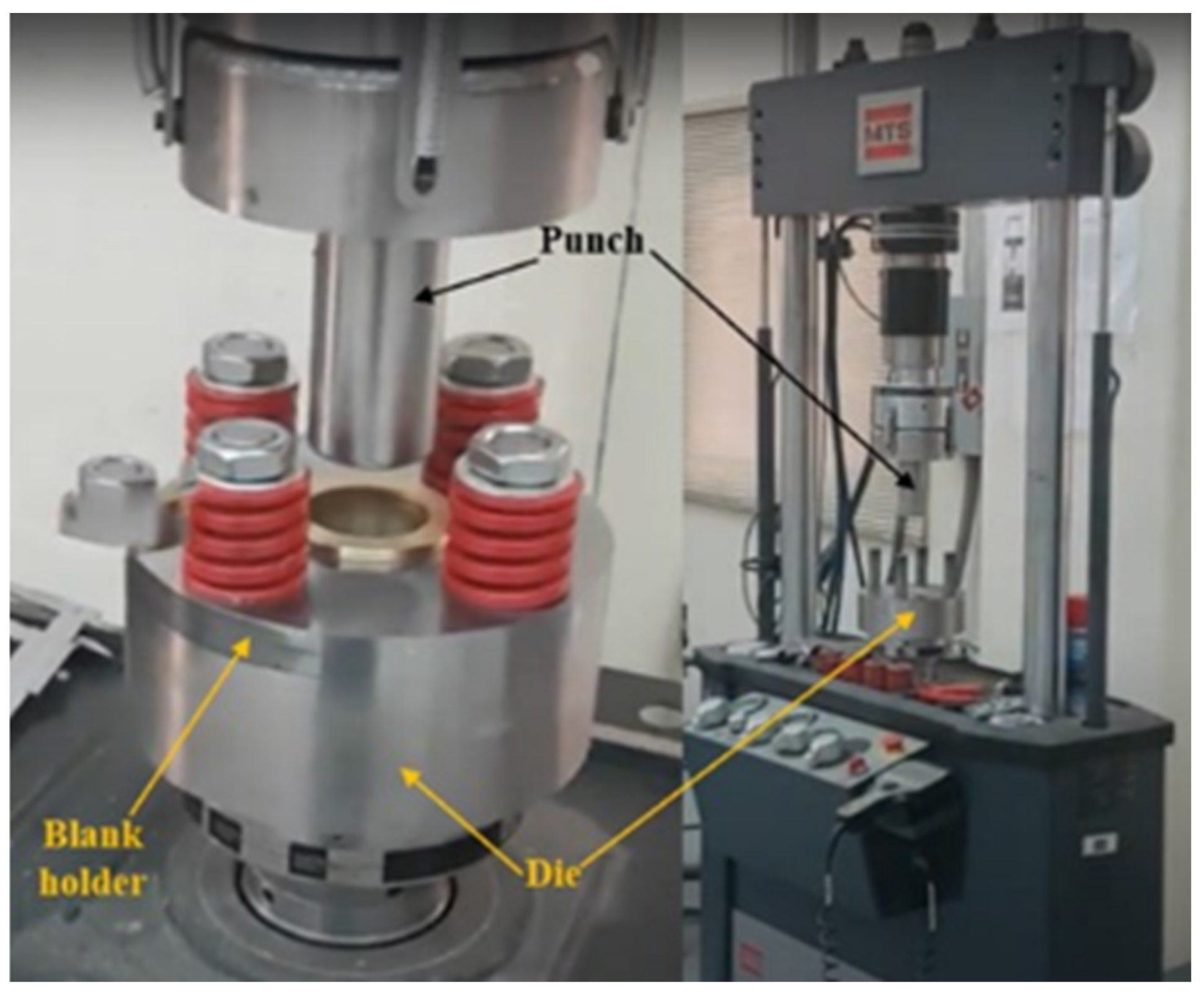
The experimental work was carried out to validate the optimization results of the carpet plot for the deep drawing operation of the cylindrical cup. The experimental work was conducted for eight samples for the recommended values from the literature of the deep drawing process. The experiments were done at room temperature by means of a 250 kN MTS testing machine with 1 mm/s as the velocity of the punch and a mild steel sheet metal of 0.8 mm thickness. Figure 13 and Figure 14 display the deep drawing die set (punch, blank holder, and die) and the setup for the deep drawing process. Table 1 displays the basic geometrical parameters utilized in the cylindrical cup deep drawing experiment.
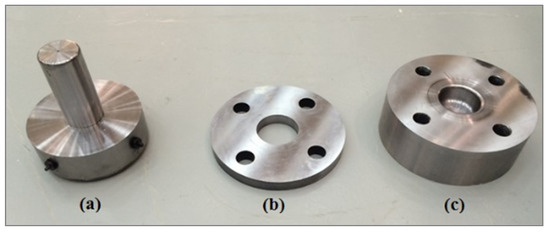
Figure 13.
The die set for the deep drawing process: (a) punch, (b) blank holder, and (c) die.
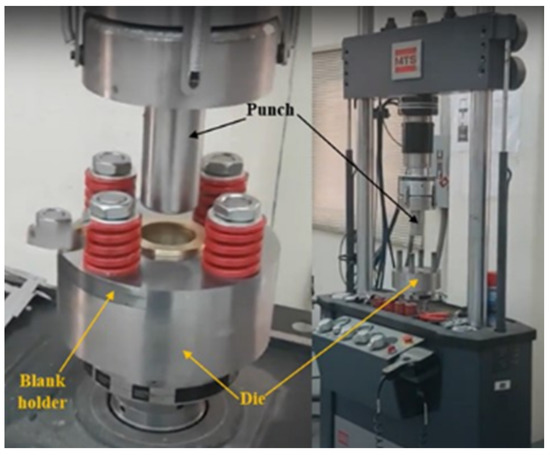
Figure 14.
The experimental work setup for the deep drawing process.
10. Validation
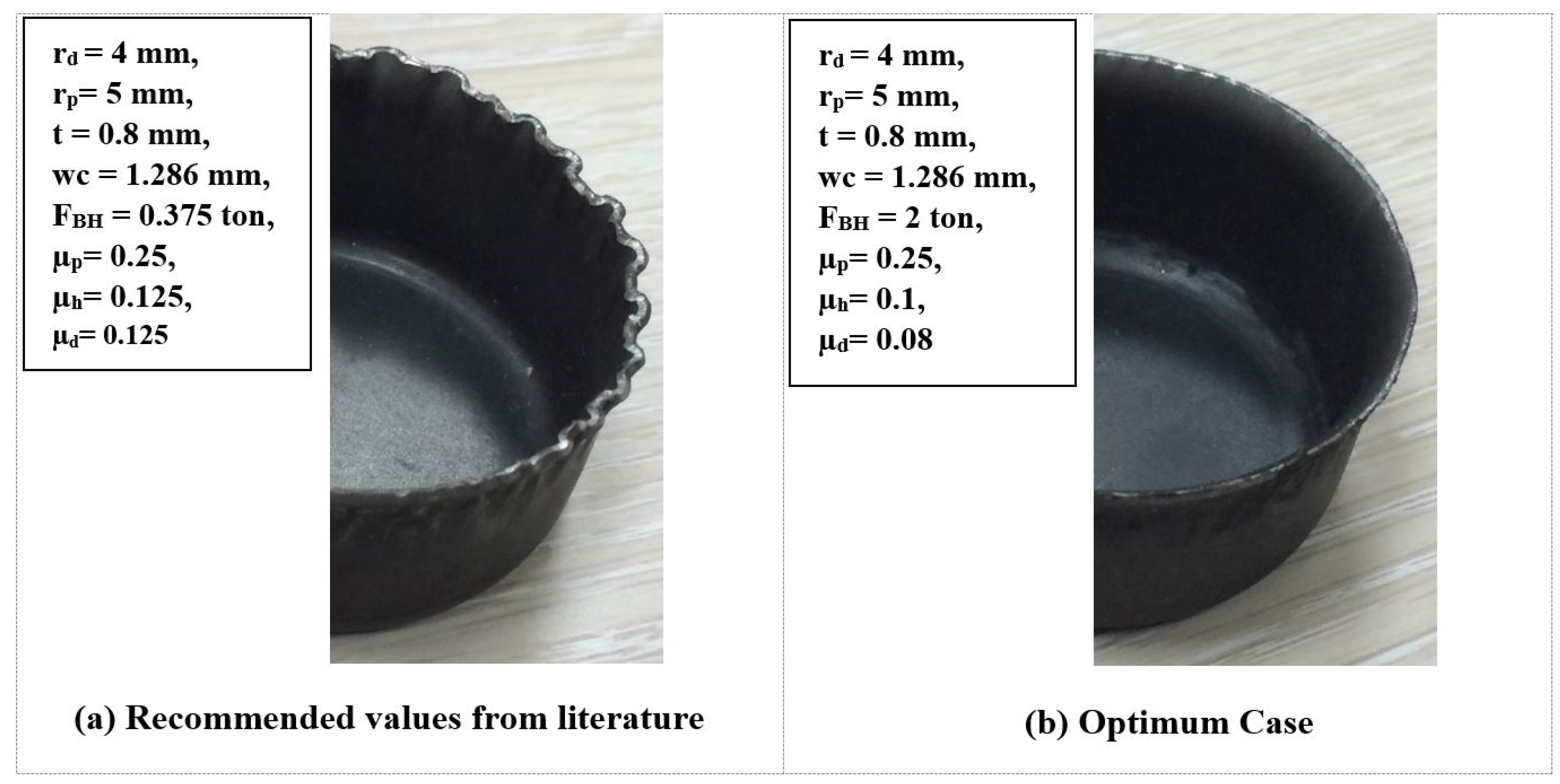
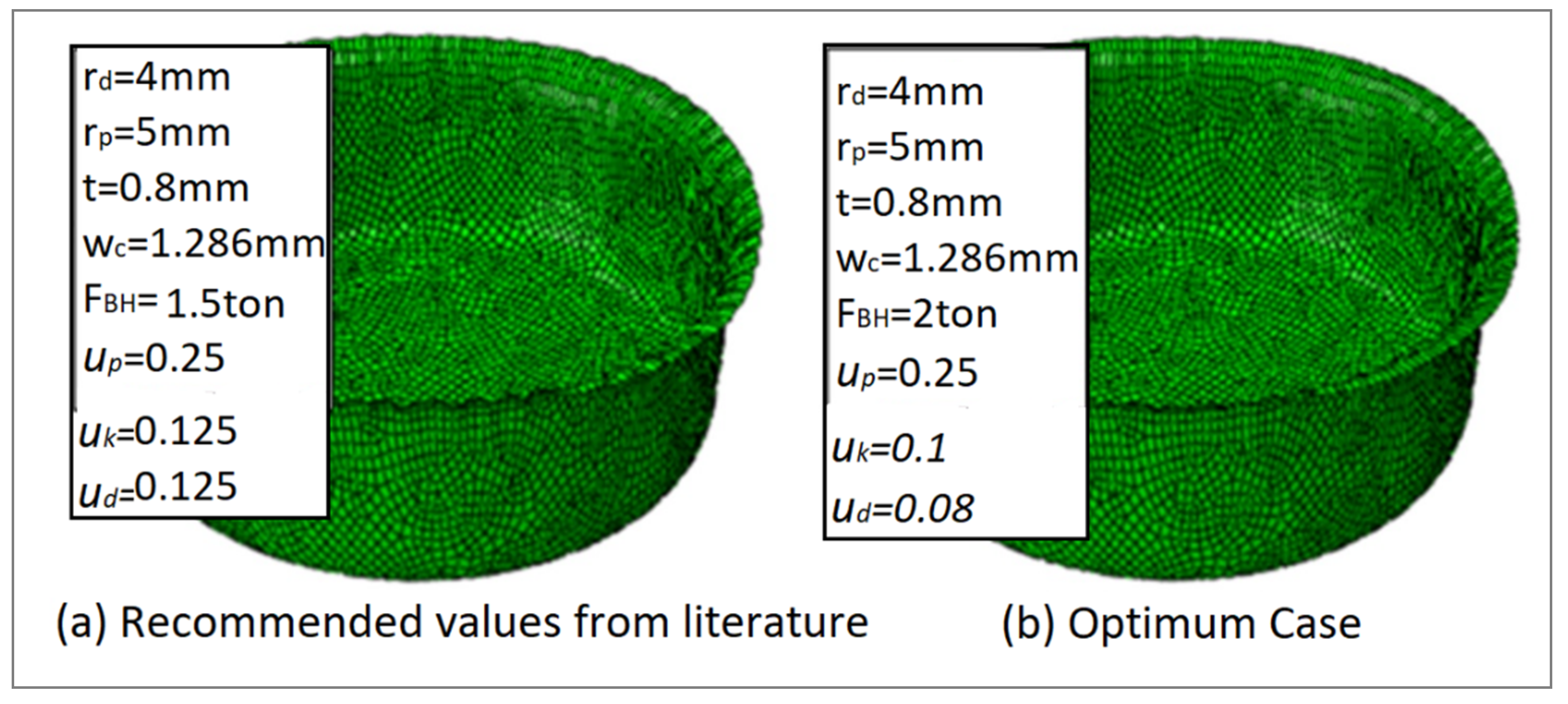
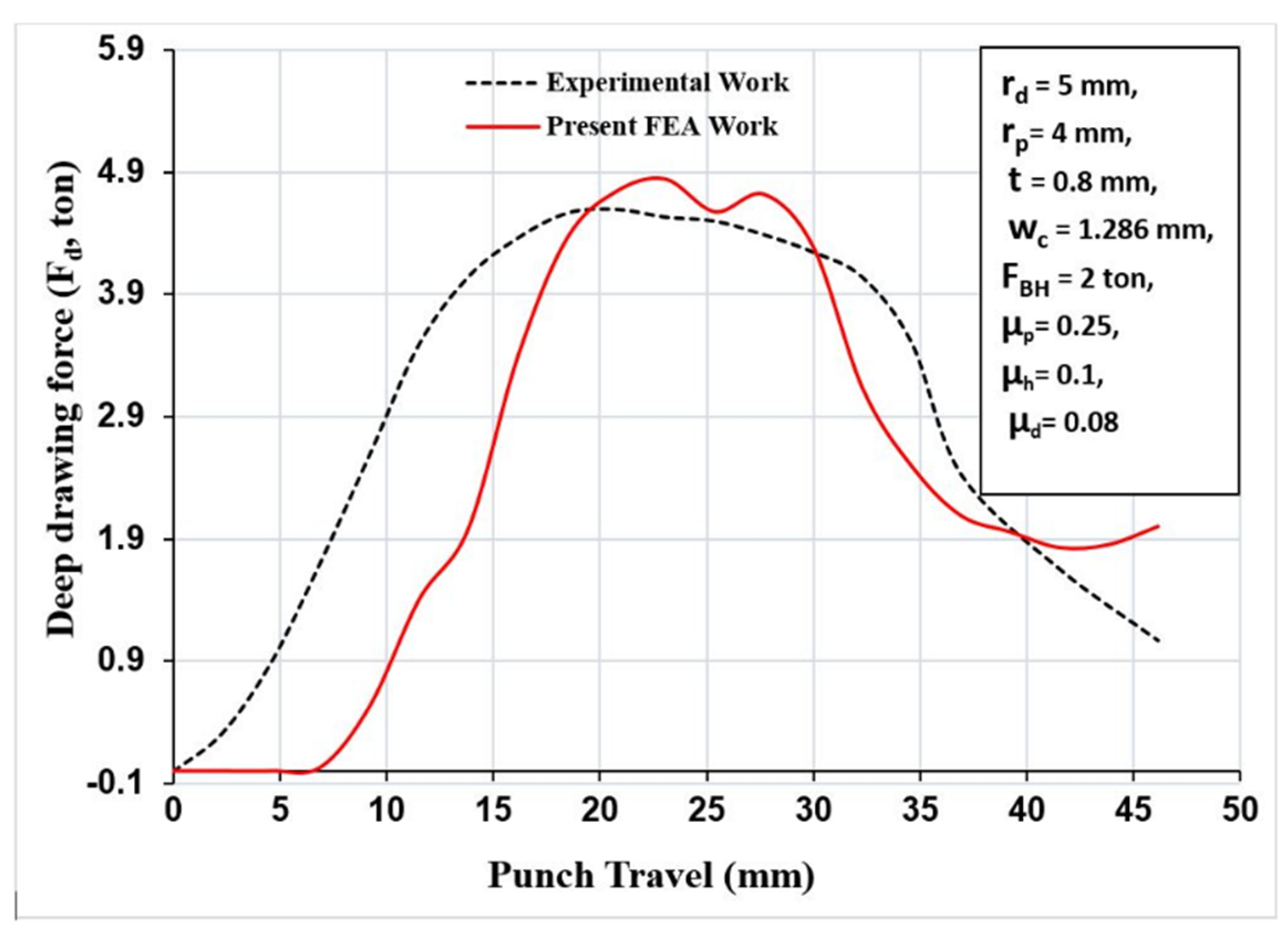
Figure 15 displays the experimental comparison of the wrinkling using the recommended values from the literature [10] and using the optimum values from minimizing the maximum deep drawing force (optimum case). It shows that wrinkling was reducing by utilizing the values extracted from the carpet plot. Furthermore, by using a parametric modeling of the FEA simulation, Figure 16 shows a comparison of the wrinkling by using the recommended values from the literature and by using the case of minimizing the maximum deep drawing force. It shows that wrinkling was reduced by using the values extracted from the carpet plot. As a final point, from Figure 15 and Figure 16, it is clear that there was a good matching between the experimental work and the FEA simulation model in the case of recommended values from the literature and in the case of optimum values. Figure 17 shows the comparison of the experimental and FE results at optimum conditions and process parameters. It can be noticed that a reasonable agreement was obtained between experimental and FE results. However, a complete matching was achieved at punch travels of 19 mm and 30 mm.
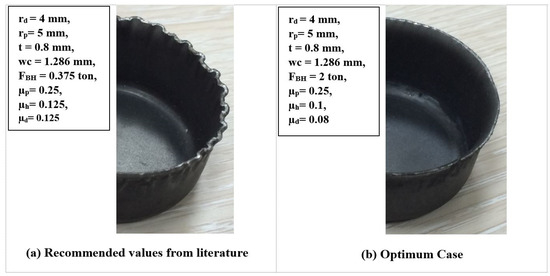
Figure 15.
Comparison of the experimental wrinkling formations: (a) recommended values from the literature; (b) optimum case.
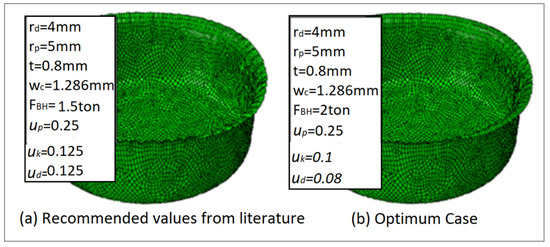
Figure 16.
FEA wrinkling formations: (a) recommended values from the literature; (b) optimum case.
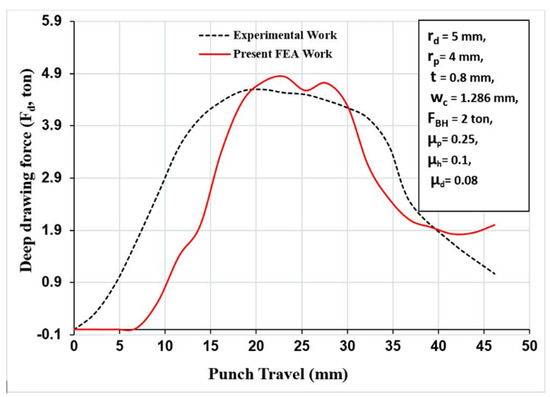
Figure 17.
Deep drawing force as a function of punch travel for validation between experimental work and the FE analysis.
11. Conclusions
The deep drawing force and value of the dimensionless ratio of (rd/t) were optimized successfully. The other geometrical and operating parameters were considered as constraints according to logical and practical limits. A carpet plot for the given value of best interfacial frictional combinations at different values of the sheet metal thickness was extracted, showing that the proper selection of equivalent conditions led to the minimum deep drawing force (Fd-min).
The optimization results showed that the minimizing of the deep drawing force was achieved satisfactorily. However, by using the friction values quoted in the carpet plot at the same geometrical parameters of the recommended values from the literature, the present work shows that the deep drawing force (Fd) was decreased by applying the values of the coefficients of friction (μd and μh) extracted from the carpet plot. In addition, wrinkling was reduced by using the values extracted from the carpet plot.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and O.M.I.; methodology, H.Z. and O.M.I.; software, H.Z.; validation, H.Z. and O.M.I.; formal analysis, H.Z.; investigation, H.Z. and O.M.I.; resources, O.M.I.; data curation, H.Z. and O.M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; and O.M.I. writing—review and editing, O.M.I.; visualization, H.Z.; supervision, O.M.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| Term | Definition |
| Fd | Punch load (deep drawing force) |
| σ1 | The principal stress (major stress) |
| FBH | Blank holder load (force) |
| μ | Friction coefficient |
| h | Drawing cup height (punch stroke) |
| t | Sheet metal thickness |
| n | The exponent of the strain hardening |
| wc | Radial clearance |
| μp | Friction coefficient between punch and blank |
| μh | Friction coefficient between holder and blank |
| μd | Friction coefficient between die and blank |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| υ | Poisson’s ratio |
| x, y, and z | The principal anisotropy axes |
| σ2 | Minor stress |
| σ0 | Yield stress in the rolling direction (0°) of the sheet metal |
| σf.m.die-ring | The mean flow stress in the die ring of the drawn cup (=σf.m.II) |
| dF.max | The outside diameter of the flange when the drawing force is a maximum |
| α and ϕ | Angles at the maximum deep drawing force |
| The instantaneous sheet metal thickness | |
| rM | The radius of curvature of the neutral fiber of the sheet metal |
| The mean bending strain of the cross-section | |
| The total mean bending strain | |
| The corresponding natural strain | |
| σf.2max | The maximum flow stress at point 2 |
| UTS | The ultimate tensile strength |
| FBH-tearing | Blank holder force which caused tearing in the wall of the cup |
| K | The coefficient of the strain hardening |
| r | The coefficient of normal anisotropy |
| D | Blank diameter |
| d1 | Punch diameter |
| rp | Punch nose radius |
| dD | Die diameter |
| rd | Die shoulder radius |
| ρ | Density |
| σy0 | Yield strength |
| r0 | The coefficient of normal anisotropy in the rolling direction (0°) of the sheet metal |
| r45 | The coefficient of normal anisotropy in (45°) to the rolling direction of the sheet metal |
| r90 | The coefficient of normal anisotropy in (90°) to the rolling direction of the sheet metal |
| F, G, H, L, M, and N | Factors particular to anisotropic condition of the material |
| σf.m.flange | The mean flow stress in the flange of the drawn cup (=σf.m.I) |
| dm | The mean diameter of the cup |
| The instantaneous blank diameter | |
| Fd-max | Maximum deep drawing force |
| εθ | Circumferential strain |
| εt | Thickness strain |
| εr | Radial strain |
| εe | The equivalent uniaxial strain |
| εs | The incremental strain of the outside fiber of the sheet metal |
| σf.1-max | The maximum flow stress at point 1 |
| σf.3-max | The maximum flow stress at point 3 |
| Fcrack | The cracking force |
| FBH-wrinkling | Blank holder force which caused wrinkling in the flange of the cup |
References
- Hattalli, V.L.; Srivatsa, S.R. Sheet metal forming processes–recent technological advances. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 2564–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalong, L.; Yanting, L.; Enlin, Y.; Yi, H.; Feng, L. Theoretical and experimental study of the drawing force under a current pulse. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nee, A.Y.C. (Ed.) Handbook of Manufacturing Engineering and Technology; Springer: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Merklein, M.; Wieland, M.; Lechner, M.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A. Hot stamping of boron steel sheets with tailored properties: A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 228, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Pöhlandt, K.; Lange, K. Improvement of the plane-strain compression test for determining flow curves. CIRP Ann. 1989, 38, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhlandt, K. Materials Testing for the Metal Forming Industry; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hingole, R. Advances in Metal Forming; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zein, H.; El Sherbiny, M.; Abd-Rabou, M. Thinning and spring back prediction of sheet metal in the deep drawing process. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, K.-H.; Antonsson, E.K. (Eds.) Springer Handbook of Mechanical Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gharib, H.H.; Wifi, A.S.; Younan, M.Y.; Nassef, A.O. Blank holder force optimization strategy in deep drawing process. Int. J. Comput. Mater. Sci. Surf. Eng. 2007, 1, 226–241. [Google Scholar]
- El Sherbiny, M.; Zein, H.; Abd-Rabou, M. Thinning and residual stresses of sheet metal in the deep drawing process. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, T.; Mousavi, A.; Stucky, T.; Böttcher, F.; Roch, T.; Schomäcker, M.; Brosius, A. Tool Optimization for Dry Forming Applications. In Proceedings of the “A” Coatings—12th International Conference in Manufacturing Engineering, Hannover, Germany, 31 March–1 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Milenija, S. Significance and limitations of variable blank holding force application in deep drawing process. Tribol. Ind. 2005, 27, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig, T.; Mousavi, S.A.; Roch, T.; Beyer, E.; Lasagni, A.F.; Brosius, A. Macro-and microstructuring of deep drawing tools for dry forming processes. Dry Met. Form. Open Access J. 2020, 81, 30–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, X. A novel hydrodynamic deep drawing utilizing a combined floating and static die cavity. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roitero, E.; Lasserre, F.; Anglada, M.; Mücklich, F.; Jiménez-Piqué, E. A parametric study of laser interference surface patterning of dental zirconia: Effects of laser parameters on topography and surface quality. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, e28–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Yousefi, R.; Boroushaki, M. Identification of optimum parameters of deep drawing of a cylindrical workpiece using neural network and genetic algorithm. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 78, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Wei, D.; Zu, G.; Jiang, Z. Influence of blank holder-die gap on micro-deep drawing of SUS304 cups. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 191, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wifi, A.; Mosallam, A. Some aspects of blank-holder force schemes in deep drawing process. J. Achiev. Mater. Manufac. Eng. 2007, 24, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.R.; Rao, B.V.S.; Reddy, G.C.M.; Prasad, P.R.; Rao, G.K.M. Parametric studies on wrinkling and fracture limits in deep drawing of cylindrical cup. Int. J. Emerg. Tech. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Gharib, H.; Wifi, A.S.; Younan, M.; Nassef, A. Optimization of the blank holder force in cup drawing. J. Optim. 2006, 1, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, T.H.; Fuh, K.H.; Yeh, W.C. Experimental optimization of deep drawing using response surface methodology. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 121, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najiha, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Yusoff, A.R. Environmental impacts and hazards associated with metal working fluids and recent advances in the sustainable systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1008–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevy, T. The role of friction in metal working with particular reference to energy saving in deep drawing. Wear 1980, 58, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shen, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, W. High-performance carbonized waste corrugated boards reinforced with epoxy coating as lightweight structured electromagnetic shields. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18718–18725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, B.; Kumar, D.R. Optimization of process parameters to enhance formability of AA 5182 alloy in deep drawing of square cups by hydroforming. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 5337–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawale, K.; Duarte, J.F.; Reis, A.; Silva, M.B. Microstructural investigation and lubrication study for single point incremental forming of copper. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 151, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.; Krebs, R. Optimization of deepdrawing presses through statistical test planning. Bander Bleche Rohre 1994, 35, 18–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, M. Micro deep drawing of T2 copper foil using proportional decreased tools. Int. J. Adv. Manufac. Tech. 2018, 95, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, H.; Al Mufadi, F. Using Forming Limit Stress Diagram (FLSD) for Investigation the Effect of the Geometrical and the Operating Parameters on the Deep Drawing Force. Minia J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 37, 152–174. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.S.; Desai, D.A.; Heyns, S.P.; Pietra, F. Literature review of numerical simulation and optimization of the shot peening process. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814018818277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakandikar, G.M.; Nandedkar, V.M. Prediction and optimization of thinning in automotive sealing cover using genetic algorithm. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2016, 3, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Atrian, A.; Fereshteh-Saniee, F. Deep drawing process of steel/brass laminated sheets. Compos. Part B 2013, 47, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoochehri, M.; Kolahan, F. Integration of artificial neural network and simulated annealing algorithm to optimize deep drawing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 73, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdarian, R. Forming limit diagram prediction of 6061 aluminum by GTN damage model. Mech. Ind. 2018, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Nardin, B.; Dolsak, B. Determining the optimal area-dependent blank holder forces in deep drawing using the response surface method. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2014, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.; Cao, J.; Karafillis, A.P.; Boyce, M.C. Numerical simulations of sheet-metal forming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1995, 50, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).