Energy Saving Strategies and On-Site Power Generation in a University Building from a Tropical Climate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
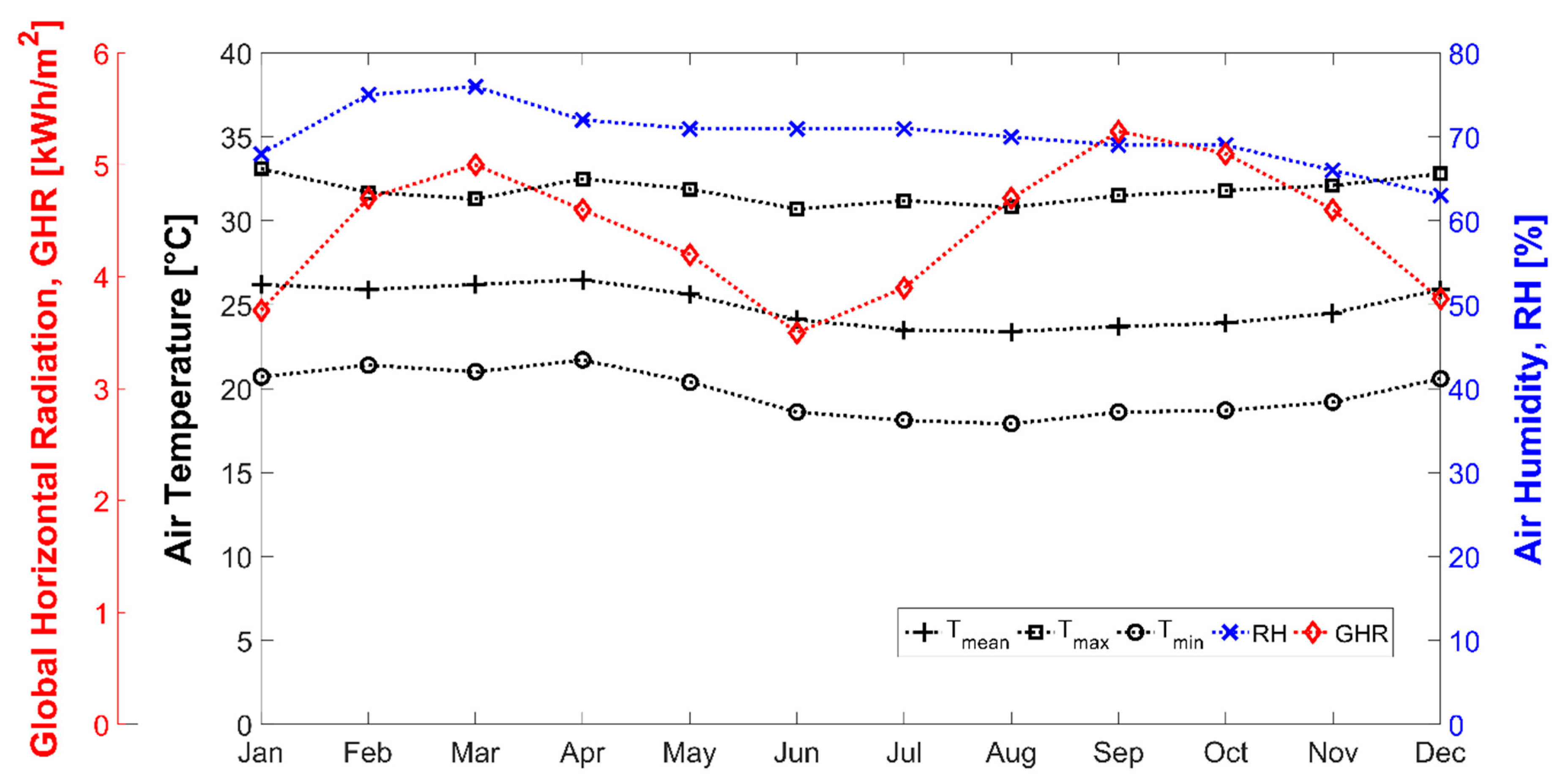
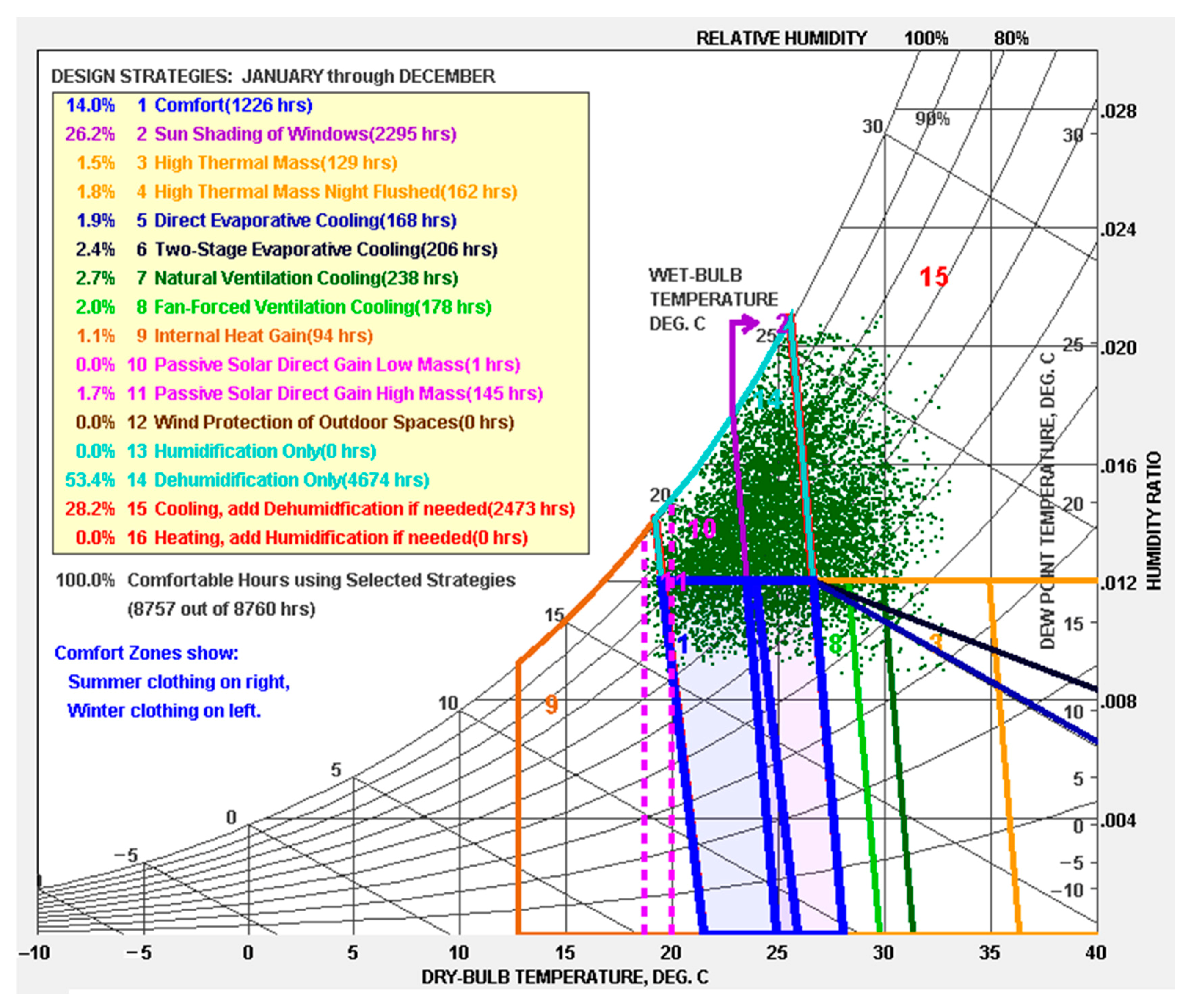
3.1. Location and Climate Conditions
3.2. Building Description
3.3. Building Energy Model in EnergyPlus
3.4. Energy Saving Scenarios
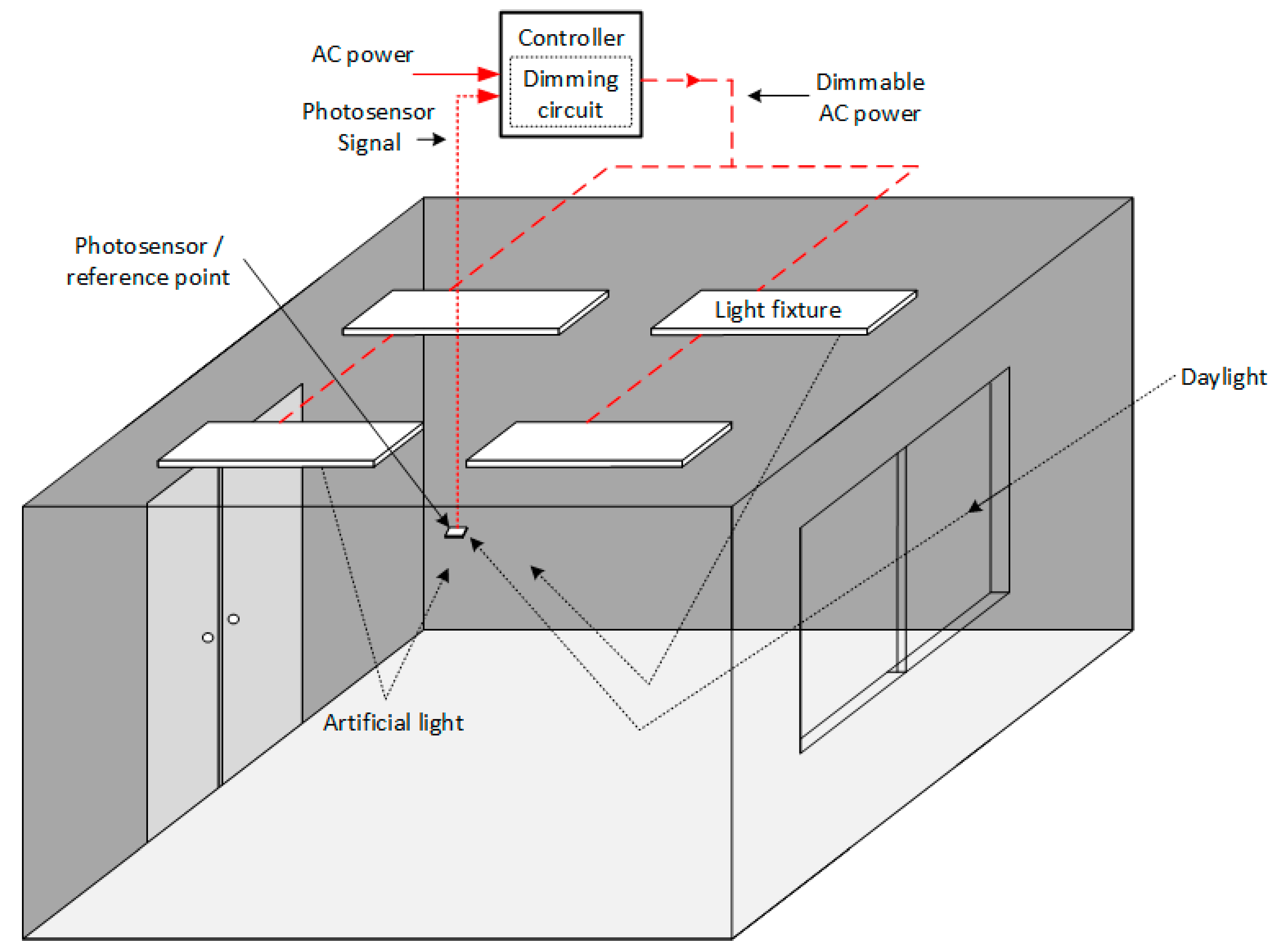
3.4.1. Integration of Daylight with Artificial Lighting
3.4.2. Window to Wall Ratio (WWR-20%)
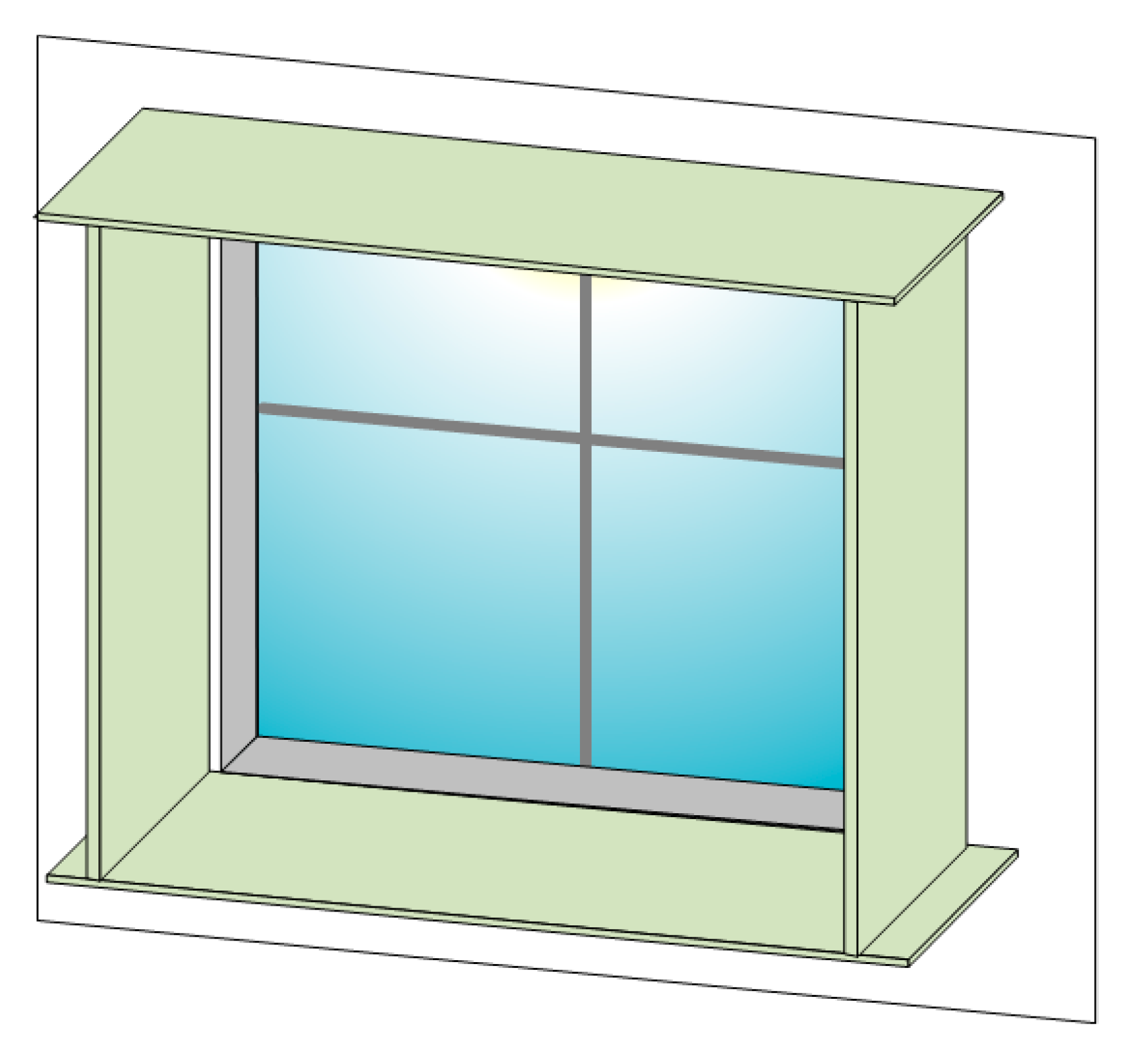
3.4.3. Static Solar Shading
3.4.4. High Performance Windows (TrpLoE)
3.4.5. Active Measures for Energy Saving
3.4.6. Combined Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Daylighting control + TrpLoE + Active measures
- Scenario 2: Shading + TrpLoE + Actives measures
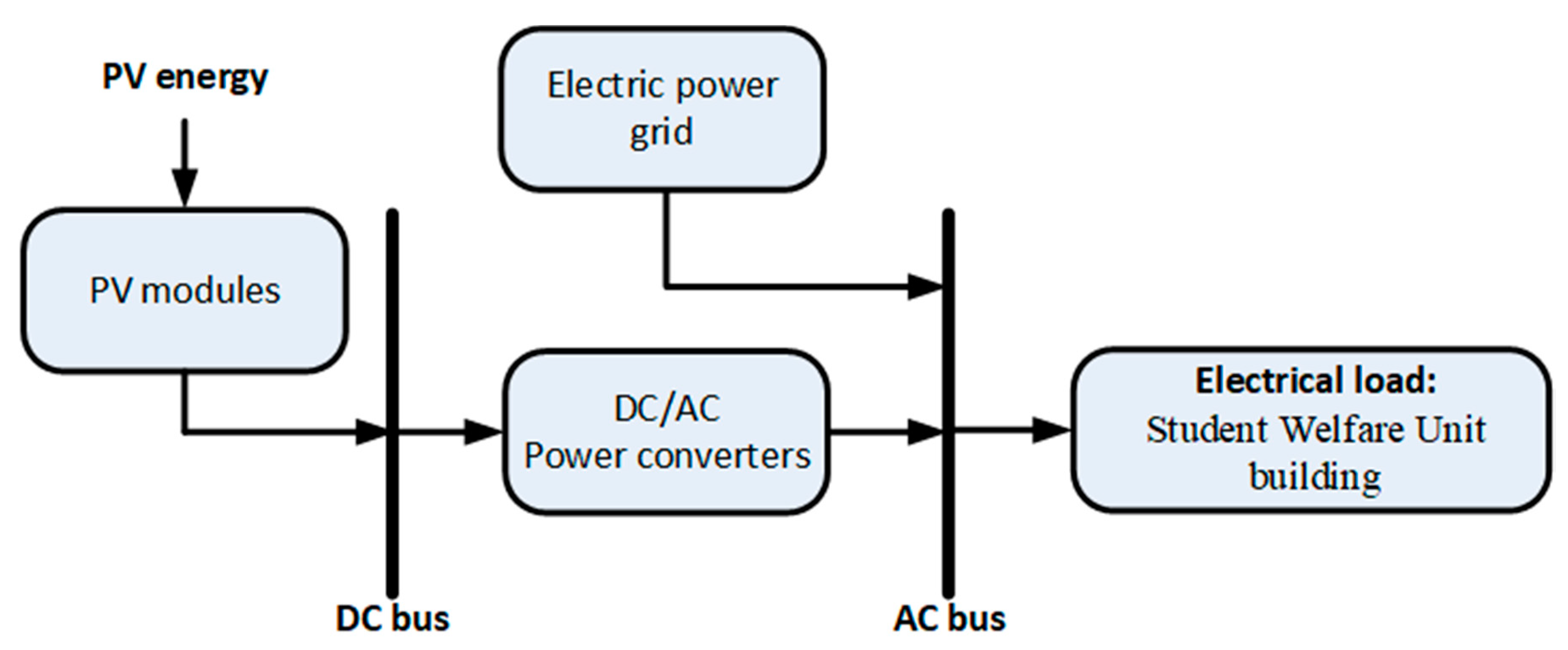
3.5. On-Site Energy Generation
4. Results
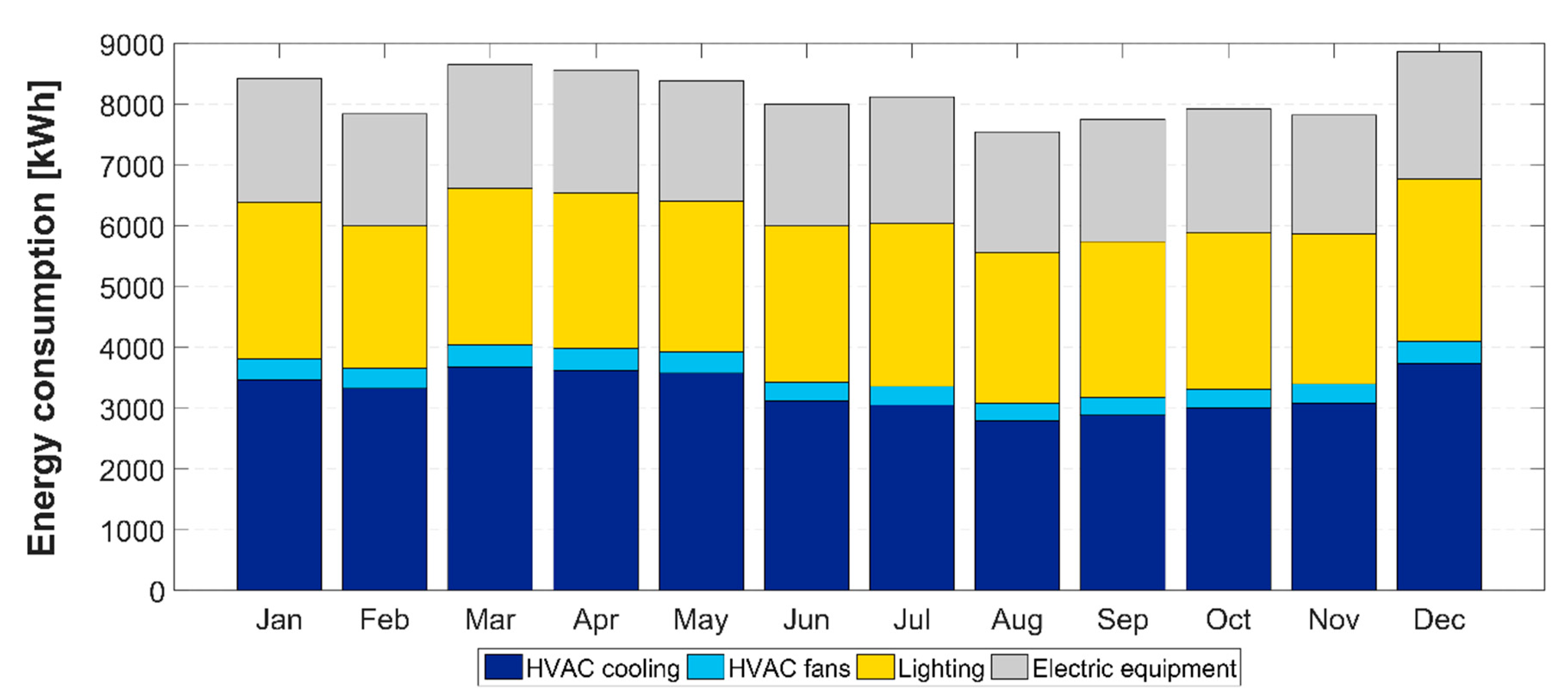
4.1. Baseline
4.2. Energy Saving Scenarios
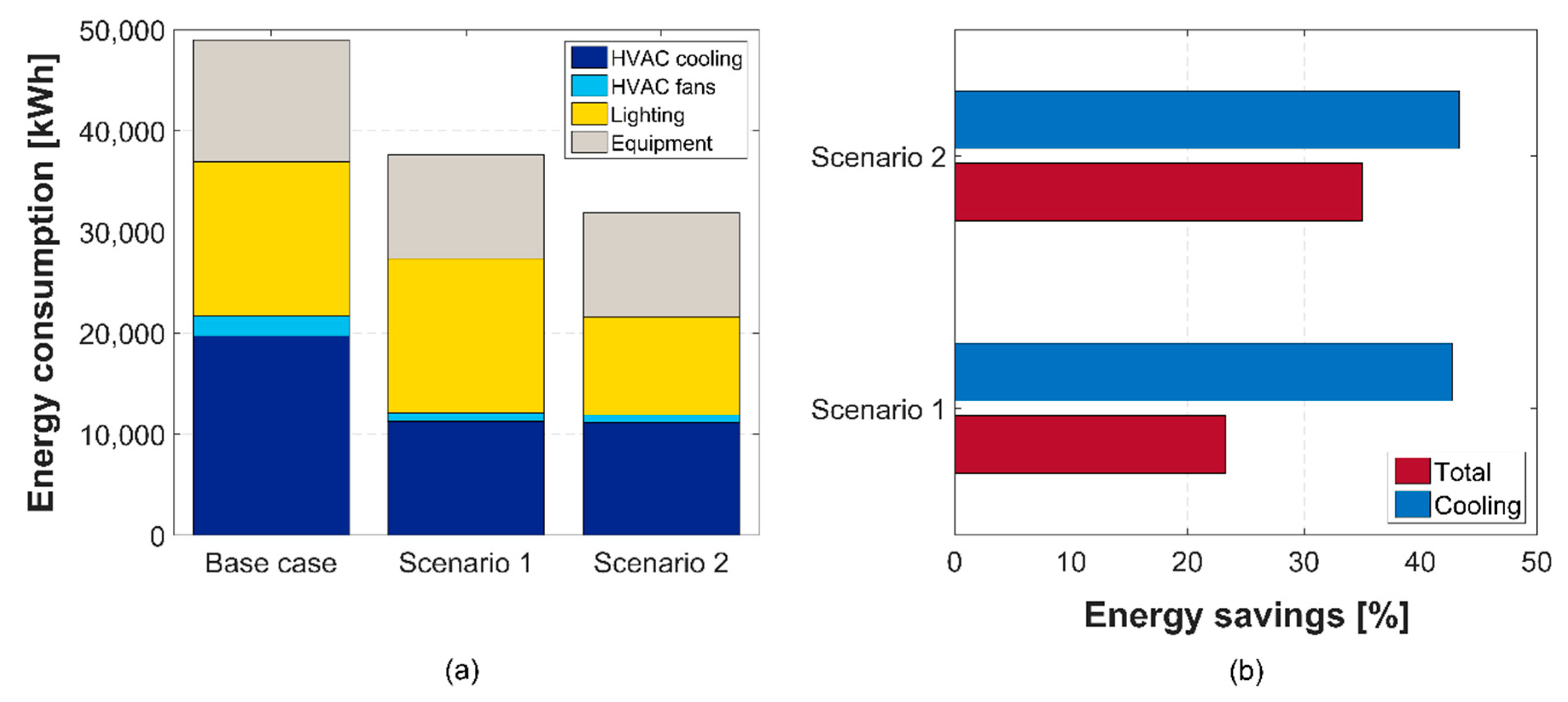
4.3. Combined Scenarios
4.4. Investment Cost of the Proposed Energy Saving Scenarios
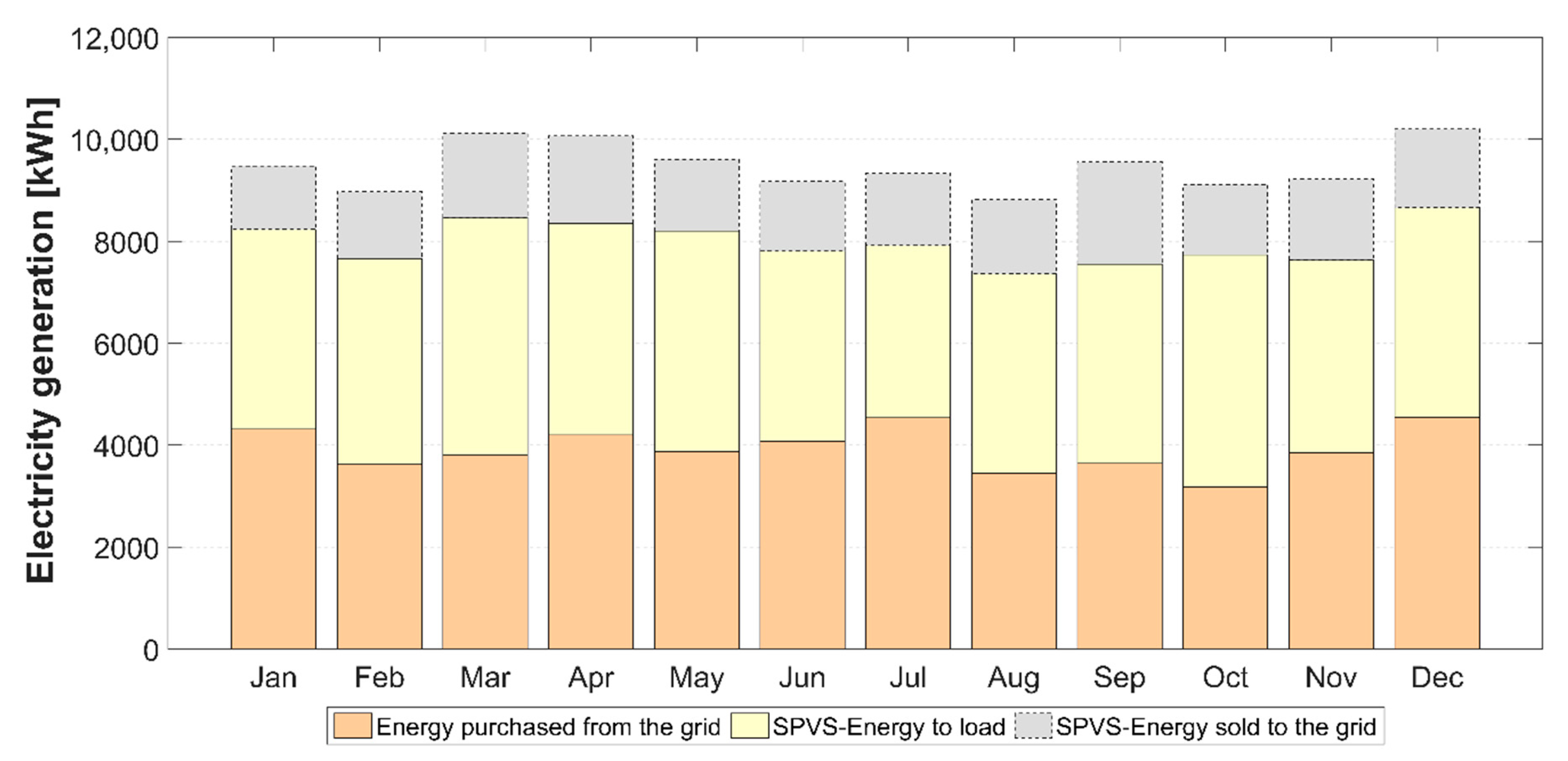
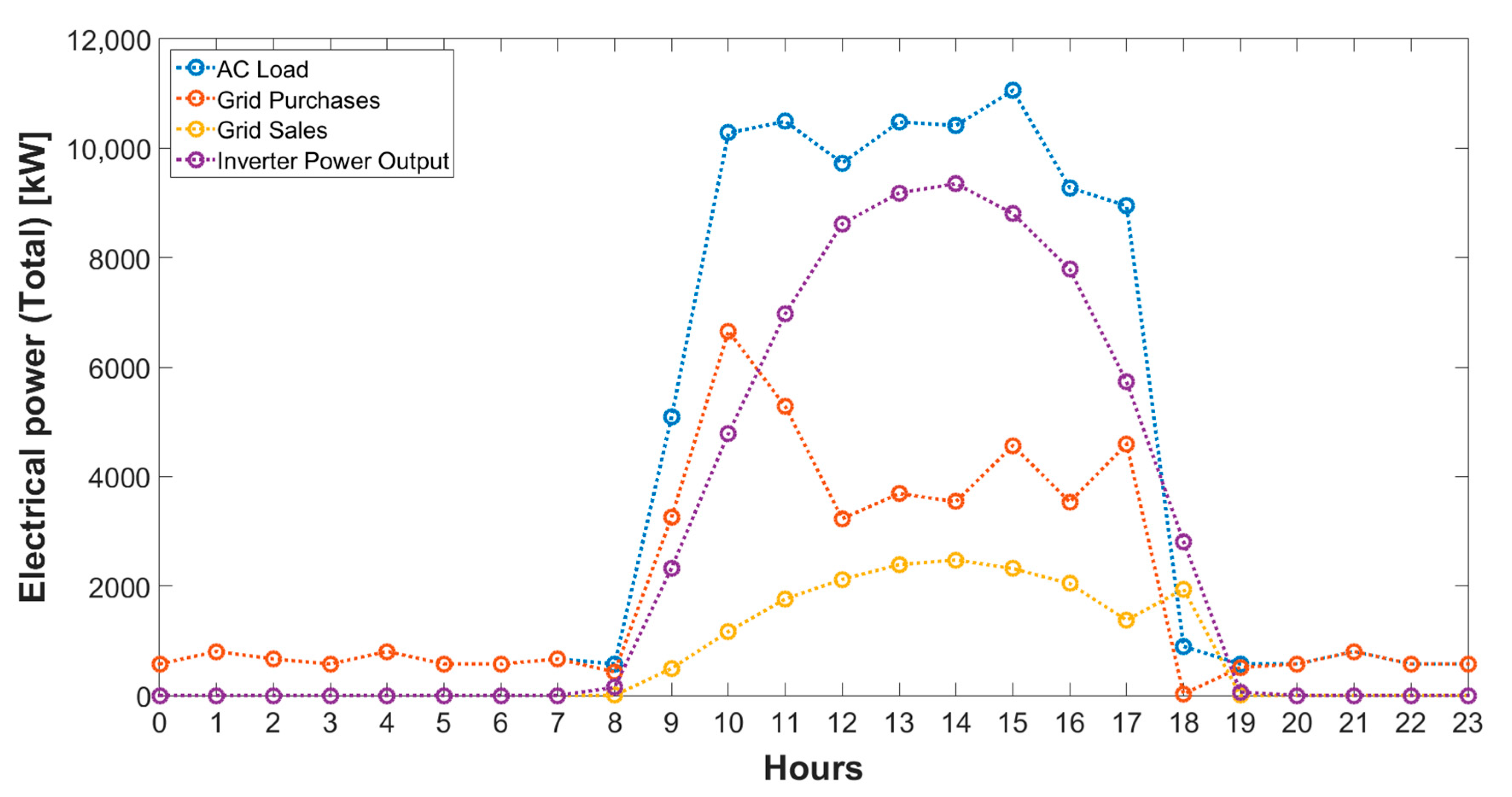
4.5. On-Site Power Generation
5. Discussion
- What could be the best shading configurations to be applied in Guayaquil taking into account the incident solar radiation in each façade?
- What could be the best cooling set point to save energy considering the thermal comfort of the occupants in these type of buildings?
- ○
- Should this cooling set point change depending on the season (wet/dry)?
- What could be the best cooling strategy to provide energy savings and reduce the building’s carbon footprint without compromising indoor thermal comfort in this climate?
- Apart from the implementation of daylighting controls, what could be another low-payback alternative to reduce energy in this climate?
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Electricity Consumption, World 1990–2018; IEA: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- GlobalABC; UNE; IEA. Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Towards a Zero Emissions, Efficient and Resilient Buildings and Construction Sector; UN Environment and IEA: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. International Energy Outlook 2019 with Projections to 2050; IEA: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Leon, R.; Urquizo, J.; Macias, J.; Siguenza, D.; Singh, P.; Wu, J.; Soriano, G. Energy Harvesting Technologies: Analysis of Their Potential for Supplying Power to Sensors in Buildings. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 3rd Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting, Cuenca, Ecuador, 15–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Lü, X.; Viljanen, M. A Novel and Dynamic Demand-Controlled Ventilation Strategy for CO2 Control and Energy Saving in Buildings. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Jia, G.; Li, H.; Li, W. Urban Heat Island Impacts on Building Energy Consumption: A Review of Approaches and Findings. Energy 2019, 174, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinejad, T.; Erfani, A.; Fathi, A.; Shafii, M.B. Bi-Level Energy-Efficient Occupancy Profile Optimization Integrated with Demand-Driven Control Strategy: University Building Energy Saving. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalaki, E.G.; Balaras, C.A.; Kontoyiannidis, S.; Droutsa, K.G. Modeling Energy Refurbishment Scenarios for the Hellenic Residential Building Stock towards the 2020 & 2030 Targets. Energy Build. 2016, 132, 74–90. [Google Scholar]
- Manic, M.; Wijayasekara, D.; Amarasinghe, K.; Rodriguez-Andina, J.J. Building Energy Management Systems: The Age of Intelligent and Adaptive Buildings. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2016, 10, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Chong, A. Building Occupancy and Energy Consumption: Case Studies across Building Types. Energy Built Environ. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.D.; Boero, A.; Rivela, B.; Melendres, A.M.; Espinoza, S.; Salas, D.A. Life Cycle Methods to Analyze the Environmental Sustainability of Electricity Generation in Ecuador: Is Decarbonization the Right Path? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-León, R.; Litardo, J.; Urquizo, J.; Moreira, D.; Singh, P.; Soriano, G. Some Factors Involved in the Improvement of Building Energy Consumption: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fourth Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), Guayaquil, Ecuador, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- DeForest, N.; Shehabi, A.; Selkowitz, S.; Milliron, D.J. A Comparative Energy Analysis of Three Electrochromic Glazing Technologies in Commercial and Residential Buildings. Appl. Energy 2017, 192, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litardo, J.; Macías, J.; Hidalgo-León, R.; Cando, M.G.; Soriano, G. Measuring the Effect of Local Commercial Roofing Samples on the Thermal Behavior of Social Interest Dwelling Located in Different Climates in Ecuador. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exhibition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–14 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Doulos, L.T.; Kontadakis, A.; Madias, E.N.; Sinou, M.; Tsangrassoulis, A. Minimizing Energy Consumption for Artificial Lighting in a Typical Classroom of a Hellenic Public School Aiming for near Zero Energy Building Using LED DC Luminaires and Daylight Harvesting Systems. Energy Build. 2019, 194, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagiman, K.R.; Abdullah, M.N.; Hassan, M.Y.; Radzi, N.H.M.; Kwang, T.C. Lighting System Control Techniques in Commercial Buildings: Current Trends and Future Directions. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouhi, A.; El Fouih, Y.; Kousksou, T.; Jamil, A.; Zeraouli, Y.; Mourad, Y. Energy Consumption and Efficiency in Buildings: Current Status and Future Trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 109, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, J.; Iturburu, L.; Rodriguez, C.; Agdas, D.; Boero, A.; Soriano, G. Embodied and Operational Energy Assessment of Different Construction Methods Employed on Social Interest Dwellings in Ecuador. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litardo, J.; Palme, M.; Borbor-Cordova, M.; Caiza, R.; Macias, J.; Hidalgo-Leon, R.; Soriano, G. Urban Heat Island Intensity and Buildings’ Energy Needs in Duran, Ecuador: Simulation Studies and Proposal of Mitigation Strategies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, C.; Fraisse, G.; Achard, G. Influence of the Coupling between Daylight and Artificial Lighting on Thermal Loads in Office Buildings. Energy Build. 2004, 36, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, A. Experimental Study on Modelling and Control of Lighting Components in a Test-Cell Building. Sol. Energy 2018, 166, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Mehmood, M.U.; Ahmed, R.; Kim, Y.; Dutton, S.; Lim, S.H.; Chun, W. An Advanced Lighting System Combining Solar and an Artificial Light Source for Constant Illumination and Energy Saving in Buildings. Energy Build. 2019, 203, 109404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruisselbrink, T.W.; Dangol, R.; van Loenen, E.J. A Comparative Study between Two Algorithms for Luminance-Based Lighting Control. Energy Build. 2020, 228, 110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvaeye, R.; Ryckaert, W.; Stroobant, L.; Hanselaer, P.; Klein, R.; Breesch, H. Analysis of Energy Savings of Three Daylight Control Systems in a School Building by Means of Monitoring. Energy Build. 2016, 127, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, N.; Cetin, K.S.; Passe, U.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y. Energy Savings and Daylighting Evaluation of Dynamic Venetian Blinds and Lighting through Full-Scale Experimental Testing. Energy 2020, 197, 117190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.; Chong, A.; Wei, Z.; Thangavelu, S.R. Energy Saving Potential of Low-e Coating Based Retrofit Double Glazing for Tropical Climate. Energy Build. 2020, 206, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, C.; Nucara, A.; Pietrafesa, M. Does Window-to-Wall Ratio Have a Significant Effect on the Energy Consumption of Buildings? A Parametric Analysis in Italian Climate Conditions. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 13, 169–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Peng, C. An Investigation of Optimal Window-to-Wall Ratio Based on Changes in Building Orientations for Traditional Dwellings. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 64–81. [Google Scholar]
- Troup, L.; Phillips, R.; Eckelman, M.J.; Fannon, D. Effect of Window-to-Wall Ratio on Measured Energy Consumption in US Office Buildings. Energy Build. 2019, 203, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoul, S.K.; Rijabo, H.G.; Mashena, M.E. Energy Consumption in Buildings: A Correlation for the Influence of Window to Wall Ratio and Window Orientation in Tripoli, Libya. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 11, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Li, Q.; Xie, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J. Optimization of Window-to-Wall Ratio with Sunshades in China Low Latitude Region Considering Daylighting and Energy Saving Requirements. Appl. Energy 2019, 233, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praprost, M.; Fleming, K.A.; Dahlhausen, M. ENERGY STAR for Tenants: An Online Energy Estimation Tool for Commercial Office Building Tenants; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Luddeni, G.; Krarti, M.; Pernigotto, G.; Gasparella, A. An Analysis Methodology for Large-Scale Deep Energy Retrofits of Existing Building Stocks: Case Study of the Italian Office Building. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Joo, H.; Kwak, H. Experimental Identification of Effects of Using Dual Airflow Path on the Performance of Roof-Type BAPV System. Energy Build. 2020, 226, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.M.; Chokwitthaya, C.; Poche, R. Retrofitting Building Roofs with Aerodynamic Features and Solar Panels to Reduce Hurricane Damage and Enhance Eco-Friendly Energy Production. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y. Study on Comprehensive Energy-Saving of Shading and Photovoltaics of Roof Added PV Module. Energy Procedia 2017, 132, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Gonzalez, E.; Domingo-Irigoyen, S.; Sánchez-Ostiz, A. Rooftop Extension as a Solution to Reach NZEB in Building Renovation. Application through Typology Classification at a Neighborhood Level. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 57, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrini, A.; Lentini, G.; Cuman, S.; Bodrato, A.; Marenco, L. From Nearly Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) to Positive Energy Buildings (PEB): The next Challenge-The Most Recent European Trends with Some Notes on the Energy Analysis of a Forerunner PEB Example. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; Baggio, P.; Prada, A.; Grazieschi, G.; Guattari, C. Dynamic Life Cycle Assessment Modelling of a NZEB Building. Energy 2020, 191, 116489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, H.; Wang, R.; Zhou, N.; Ye, Q.; Hao, B.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.; Lau, S.S.Y. A Review of Net Zero Energy Buildings in Hot and Humid Climates: Experience Learned from 34 Case Study Buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, K.; Winderl, M.; Priya, S.S. Net-Zero Building Designs in Hot and Humid Climates: A State-of-Art. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 13, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghenai, C.; Bettayeb, M. Modelling and Performance Analysis of a Stand-Alone Hybrid Solar PV/Fuel Cell/Diesel Generator Power System for University Building. Energy 2019, 171, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, S.; Yang, H. Overview on Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic-Electrical Energy Storage Technologies for Power Supply to Buildings. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 187, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated World Map of the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification. In Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions; European Geosciences Union: Munich, Germany, 2007; Volume 4, pp. 439–473. [Google Scholar]
- Guevara, G.; Soriano, G.; Mino-Rodriguez, I. Thermal Comfort in University Classrooms: An Experimental Study in the Tropics. Build. Environ. 2020, 187, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEC. Proyección de La Población Ecuatoriana, Por Años Calendario, Según Cantones 2010–2020; INEC: Quito, Ecuador, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Meteotest. Meteonorm 7.3; Meteotest: Bern, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Energy Design Tools UCLA. Climate Consultant 6.0 Sofware; UCLA: Los Ángeles, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ESPOL. Escuela Superior Politécnica Del Litoral (ESPOL). Available online: http://www.espol.edu.ec/ (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Agencia de Regulación y Control de Electricidad (ARCONEL). Pliego Tarifario Para Las Empresas Eléctricas de Distribución Codificado; ARCONEL: Quito, Ecuador, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, K.; Long, N.; Swindler, A. Building Component Library: An Online Repository to Facilitate Building Energy Model Creation; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ANSI; ASHRAE; IES. Standard 90.1-2019 Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings; ASHRAE: Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Cho, H.; Koh, J.; Im, P. Net-Zero Energy Building Design and Life-Cycle Cost Analysis with Air-Source Variable Refrigerant Flow and Distributed Photovoltaic Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 118, 109508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer Energy. Homer PRO; Homer Energy: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maxeon Solar Technologies. Sun Power Maxeon 2—360W; Maxeon Solar Technologies: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ProViento, Paneles Solares. Available online: https://proviento.com.ec/10-paneles-solares (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Jamil, W.J.; Rahman, H.A.; Shaari, S.; Desa, M.K.M. Modeling of Soiling Derating Factor in Determining Photovoltaic Outputs. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2020, 10, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, C.; Villacreses, G.; Vásquez, F.; Godoy, F. Evaluación Comparativa de Los Consumos Energéticos de Edificaciones Públicas En La Región Costa y Galápagos; Instituto Nacional de Eficiencia Energértica y Energías Renovables (INER): Quito, Ecuador, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Litardo, J.; Hidalgo-León, R.; Macías, J.; Delgado, K.; Soriano, G. Estimating Energy Consumption and Conservation Measures for ESPOL Campus Main Building Model Using EnergyPlus; IEEE CONCAPAN: Ciudad de Guatemala, Guatemala, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cámara de la Construcción de Guayaquil. Available online: http://www.cconstruccion.net/precios.html (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Compras Públicas Ecuador, Sistema Oficial de Contratación Pública. Available online: https://www.compraspublicas.gob.ec/ProcesoContratacion/compras/ (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Syahputra, R.; Soesanti, I. Planning of Hybrid Micro-Hydro and Solar Photovoltaic Systems for Rural Areas of Central Java, Indonesia. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5972342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, W.J.; Alghoul, M.A.; Bakhtyar, B.; Elayeb, O.; Shameri, M.A.; Alrubaih, M.S.; Sopian, K. The Role of Window Glazing on Daylighting and Energy Saving in Buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishegar, N.; Boubekri, M. Quantifying Electrical Energy Savings in Offices through Installing Daylight Responsive Control Systems in Hot Climates. Energy Build. 2017, 153, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, A.J.-W.; Yang, T.-H.; Deng, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Tseng, W.-C.; Chou, C.-H. A Review of Daylighting System: For Prototype Systems Performance and Development. Energies 2019, 12, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, H. Daylighting Controls, Performance, and Global Impacts. Sustain. Built Environ. 2020, 383–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, C.H.; Chae, M.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, S.S. Analysis of Energy Saving Effect and Cost Efficiency of ECMs to Upgrade the Building Energy Code. Energies 2020, 13, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, S.; Kontokosta, C.E.; Vlachokostas, A.; Azar, E. Rethinking HVAC Temperature Setpoints in Commercial Buildings: The Potential for Zero-Cost Energy Savings and Comfort Improvement in Different Climates. Build. Environ. 2019, 155, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienvenido-Huertas, D.; Sánchez-García, D.; Pérez-Fargallo, A.; Rubio-Bellido, C. Optimization of Energy Saving with Adaptive Setpoint Temperatures by Calculating the Prevailing Mean Outdoor Air Temperature. Build. Environ. 2020, 170, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, J. Energy Efficiency Optimization Strategies for University Research Buildings with Hot Summer and Cold Winter Climate of China Based on the Adaptive Thermal Comfort. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 18, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masrani, S.M.; Al-Obaidi, K.M.; Zalin, N.A.; Isma, M.A. Design Optimisation of Solar Shading Systems for Tropical Office Buildings: Challenges and Future Trends. Sol. Energy 2018, 170, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuwayil, W.K.; Mujeebu, M.A.; Algarny, A.M.M. Impact of External Shading Strategy on Energy Performance of Multi-Story Hotel Building in Hot-Humid Climate. Energy 2019, 169, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Touma, A.; Ouahrani, D. Shading and Day-Lighting Controls Energy Savings in Offices with Fully-Glazed Façades in Hot Climates. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wati, E.; Meukam, P.; Nematchoua, M.K. Influence of External Shading on Optimum Insulation Thickness of Building Walls in a Tropical Region. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 90, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARCONEL. Resolucion Nro. ARCONEL-042/18; Agencia de Regulacion y Control de Electricidad: Quito, Ecuador, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vaca-Revelo, D.; Ordóñez, F. Mapa Solar del Ecuador 2019; Escuela Politécnica Nacional (EPN): Quito, Ecaudor, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Korsavi, S.S.; Zomorodian, Z.S.; Tahsildoost, M. Energy and Economic Performance of Rooftop PV Panels in the Hot and Dry Climate of Iran. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhower, B.; O’Neill, Z.; Fonoberov, V.A.; Mezić, I. Uncertainty and Sensitivity Decomposition of Building Energy Models. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2012, 5, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumo, N.; Mago, P.; Luck, R. Methodology to Estimate Building Energy Consumption Using EnergyPlus Benchmark Models. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. Guideline 14-2002, Measurement of Energy and Demand Savings; Technical Report; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Judkoff, R.; Neymark, J. Model Validation and Testing: The Methodological Foundation of ASHRAE Standard 140; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]





| Construction | Density [kg/m3] | Thermal Conductivity [W/m-K] | Specific Heat [J/kg-K] | U-Value [W/m2-K] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roof | ||||
| Steel sheet (1 mm) | 7800 | 50 | 450 | |
| Heavy weight concrete (30 cm) | 2240 | 1.31 | 837 | |
| Wall | ||||
| Hollow concrete block (9 cm) | 1600 | 0.47 | 1000 | |
| Plaster (1 cm) | 800 | 0.37 | 340 | |
| Floor | ||||
| Heavy weight concrete (10 cm) | 2240 | 1.31 | 837 | |
| Acoustic tile (2 cm) | 368 | 0.06 | 59 | |
| Windows | ||||
| Clear glass (6 mm) | 5.78 | |||
| Metal frame |
| System | Description | Installed Power [W] |
|---|---|---|
| Lighting | LED and saving lighting | 11,974 |
| Electric equipment | Appliances | 25,716 |
| Air-conditioning | Direct expansion mini and floor/ceiling splits | 170,567 (581,999 BTU/h) |
| Cooling Capacity [BTU/h] | COP |
|---|---|
| <65,000 | 3.45 (SEER 14) |
| ≥65,000 and <135,000 | 3.55 (SEER 14.6) |
| Energy Saving Scenario | Investment Cost | Unit | Total | Payback |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daylighting controls | ||||
| Dimming controller Photosensor | From $100.00/unit From $60.00/unit | 20 20 | From $3200.00 | 2.34 years |
| Window to wall ratio reduction | ||||
| WWR-20% Windows desmounting Cement filling New windows installation | From $4.25/m2 From $10.00/m2 From $31.00/m2 | 310 m2 181 m2 129 m2 | From $7126.50 | 18.7 years |
| Static shading devices | ||||
| Overhangs and vertical fins from aluminium | From $118.76/m2 | 211 m2 | From $25,058.36 | 47.16 years |
| TrpLoE | ||||
| Triple glazing (6 mm) with double low emissivity films and aluminum profile | From $174.80/m2 | 310 m2 | From $54,188.00 | 103.8 years |
| Active measures | ||||
| Changing the cooling setpoint temperature | - | - | - | 63.7 years |
| Replacement of obsolete air-conditioners with their higher efficiency equivalent | Mini split 12,000 BTU/h: from $500.00/unit Mini split 18,000 BTU/h: from $700.00/unit Floor/ceiling split 36,000 BTU/h: from $950.00/unit Floor/ceiling split 60,000 BTU/h: from $1200.00/unit | 10 7 6 2 | From $18,000.00 | |
| Replacemet of obsolete electric equipment with their equivalent ENERGY STAR | Computer: from $1100.00/unit Copy machine: from $1200.00/unit Printer: from $200.00/unit | 31 9 1 | From $45,100.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Litardo, J.; Palme, M.; Hidalgo-León, R.; Amoroso, F.; Soriano, G. Energy Saving Strategies and On-Site Power Generation in a University Building from a Tropical Climate. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020542
Litardo J, Palme M, Hidalgo-León R, Amoroso F, Soriano G. Energy Saving Strategies and On-Site Power Generation in a University Building from a Tropical Climate. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(2):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020542
Chicago/Turabian StyleLitardo, Jaqueline, Massimo Palme, Rubén Hidalgo-León, Fernando Amoroso, and Guillermo Soriano. 2021. "Energy Saving Strategies and On-Site Power Generation in a University Building from a Tropical Climate" Applied Sciences 11, no. 2: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020542
APA StyleLitardo, J., Palme, M., Hidalgo-León, R., Amoroso, F., & Soriano, G. (2021). Energy Saving Strategies and On-Site Power Generation in a University Building from a Tropical Climate. Applied Sciences, 11(2), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020542









