The Design and FPGA-Based Implementation of a Stream Cipher Based on a Secure Chaotic Generator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
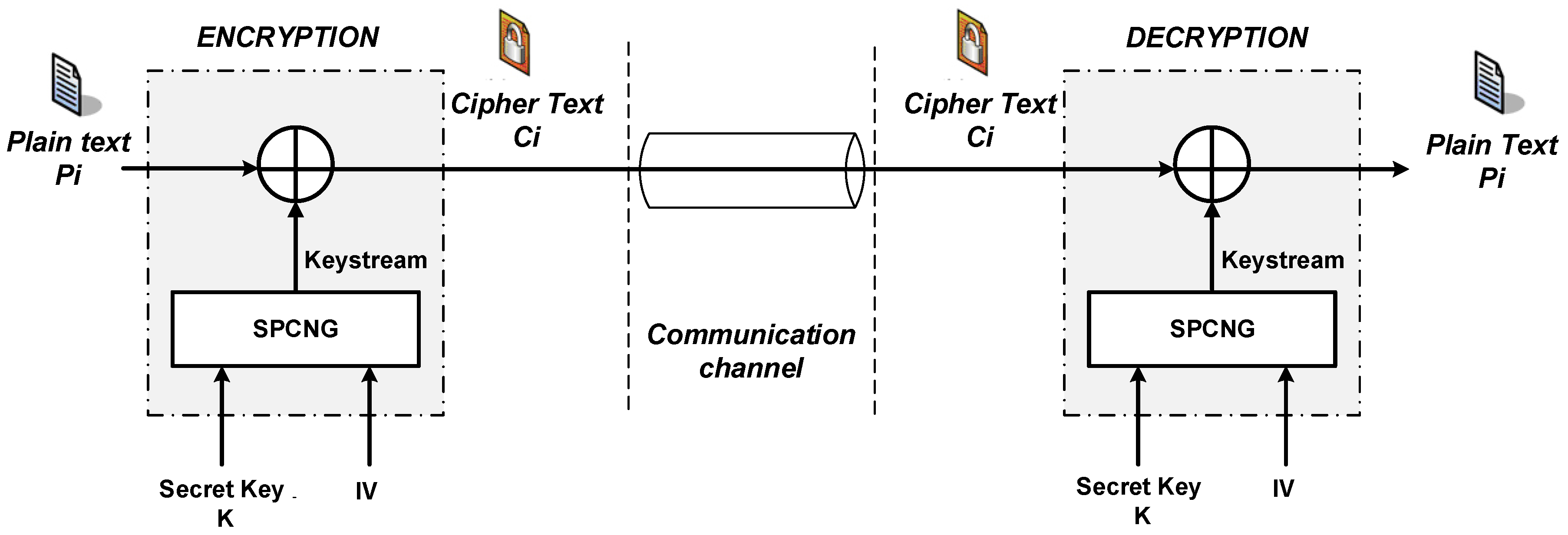
2. The Proposed SCbSC-Based Architecture
Description of the Architecture of the Proposed SPCNG
- The discrete logistic map [25]:This is the discretized equation of the standard logistic map:with here and .
- The discrete skew-tent map [26]:This is the discretized equation of the standard skew-tent map:with .
- The discrete 3D Chebyshev map [27]:This is the discretized equation of the standrd 3D Chebyshev map:with .
| Algorithm 1: Generation of the pseudo-chaotic sequence X(n). |
 |
3. Hardware Implementation of the Proposed SCbSC and Evaluation of Its Performance
3.1. Hardware Cost of the Proposed Secure PCNG
3.2. SPCNG Resilience against Statistical Attacks
3.2.1. Phase Space Test
3.2.2. Histogram and Chi-Square Tests
- : number of classes.
- : number of calculated samples in the ith class .
- : expected number of samples of a uniform distribution.
- Ns: the number of samples produced—here, Ns = 3,125,000
3.2.3. NIST Test
4. Performance Analysis of the Proposed SCbSC
4.1. SCbSC Hardware Metrics
4.2. Cryptanalytic Analysis
4.2.1. Key Size and Sensitivity Analysis
4.2.2. Statistical Analysis
Histogram and Chi-Square Analysis
Entropy Analysis
Correlation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorenz, E.N.; Haman, K. The essence of chaos. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1996, 147, 598–599. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zhang, F.-C.; Cao, G.-H. New chaotical image encryption algorithm based on Fisher–Yatess scrambling and DNA coding. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 040504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belazi, A.; Abd El-Latif, A.A.; Belghith, S. A novel image encryption scheme based on substitution-permutation network and chaos. Signal Process. 2016, 128, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo, J.; Kocarev, L.; Szczepanski, J. Theory and practice of chaotic cryptography. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 366, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocarev, L. Chaos-based cryptography: A brief overview. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2001, 1, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acho, L. A chaotic secure communication system design based on iterative learning control theory. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datcu, O.; Macovei, C.; Hobincu, R. Chaos Based Cryptographic Pseudo-Random Number Generator Template with Dynamic State Change. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdoun, N.; El Assad, S.; Manh Hoang, T.; Deforges, O.; Assaf, R.; Khalil, M. Designing Two Secure Keyed Hash Functions Based on Sponge Construction and the Chaotic Neural Network. Entropy 2020, 22, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battikh, D.; El Assad, S.; Hoang, T.M.; Bakhache, B.; Deforges, O.; Khalil, M. Comparative Study of Three Steganographic Methods Using a Chaotic System and Their Universal Steganalysis Based on Three Feature Vectors. Entropy 2019, 21, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, T.-L.; Wan, P.-Y.; Yan, J.-J. Design of synchronized large-scale chaos random number generators and its application to secure communication. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pareek, N.K.; Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K. Image encryption using chaotic logistic map. Image Vis. Comput. 2006, 24, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocarev, L.; Jakimoski, G. Logistic map as a block encryption algorithm. Phys. Lett. A 2001, 289, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, M.; Grosges, T.; Barchiesi, D.; Erra, R. Pseudo-random number generator based on mixing of three chaotic maps. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2014, 19, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Qin, X. A new pseudo-random number generator based on CML and chaotic iteration. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 70, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.A.; Assad, S.E.; Queudet, A.; Deforges, O. Design and efficient implementation of a chaos-based stream cipher. Int. J. Internet Technol. Secur. Trans. 2017, 7, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallouli, O.; El Assad, S.; Chetto, M.; Lozi, R. Design and analysis of two stream ciphers based on chaotic coupling and multiplexing techniques. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 13391–13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozi, R. Emergence of randomness from chaos. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2012, 22, 1250021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Q. A new lightweight stream cipher based on chaos. Symmetry 2019, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelfatah, R.I.; Nasr, M.E.; Alsharqawy, M.A. Encryption for multimedia based on chaotic map: Several scenarios. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, G.; Le Glatin, M.; El Assad, S.; Hamidouche, W.; Déforges, O.; Guilley, S.; Facon, A. Hardware Implementation of Lightweight Chaos-Based Stream Cipher. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cyber-Technologies and Cyber-Systems, Porto, Portugal, 22 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tanougast, C. Hardware implementation of chaos based cipher: Design of embedded systems for security applications. In Chaos-Based Cryptography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 297–330. [Google Scholar]
- Koyuncu, İ.; Tuna, M.; Pehlivan, İ.; Fidan, C.B.; Alçın, M. Design, FPGA implementation and statistical analysis of chaos-ring based dual entropy core true random number generator. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2020, 102, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, R. Penetration Testing on a C-Software Implementation aff1709rns006-c; Internal Report; Secure-IC SAS: Cesson-Sévigné, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, R.; Facon, A.; Guilley, S.; Gautier, G.; El Assad, S. Speed-up of SCA Attacks on 32-bit Multiplications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Codes, Cryptology, and Information Security, Rabat, Morocco, 22–24 April 2019; pp. 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; You, M.; Yang, Z.; Jin, S. Research on a block encryption cipher based on chaotic dynamical system. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC 2007), Haikou, China, 24–27 August 2007; pp. 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, N.; Jakimoski, G.; Aihara, K.; Kocarev, L. Chaotic block ciphers: From theory to practical algorithms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2006, 53, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Assad, S. Chaos-Based Cryptography, Internal Report; University of Nantes: Nantes, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jallouli, O. Chaos-Based Security under Real-Time and Eenergy Constraints for the Internet of Things. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nantes, Nantes, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, D.; Vigna, S. Scrambled linear pseudorandom number generators. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.01407. [Google Scholar]
- Vigna, S. Further scramblings of Marsaglia’s xorshift generators. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2017, 315, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coron, J.-S.; Rondepierre, F.; Zeitoun, R. High order masking of look-up tables with common shares. IACR Trans. Cryptogr. Hardw. Embed. Syst. 2018, 40–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coron, J.-S.; Roy, A.; Vivek, S. Fast evaluation of polynomials over binary finite fields and application to side-channel countermeasures. In International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 170–187. [Google Scholar]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Booz-allen and Hamilton Inc.: McLean, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Manifavas, C.; Hatzivasilis, G.; Fysarakis, K.; Papaefstathiou, Y. A survey of lightweight stream ciphers for embedded systems. Secur. Commun. Networks 2016, 9, 1226–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maximov, A.; Biryukov, A. Two trivial attacks on Trivium. In International Workshop on Selected Areas in Cryptography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 36–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gaj, K.; Southern, G.; Bachimanchi, R. Comparison of hardware performance of selected Phase II eSTREAM candidates. In Proceedings of the State of the Art of Stream Ciphers Workshop (SASC 2007), eSTREAM, ECRYPT Stream Cipher Project, Report. Lausanne, Switzerland, 31 January–1 February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bulens, P.; Kalach, K.; Standaert, F.-X.; Quisquater, J.-J. FPGA implementations of eSTREAM phase-2 focus candidates with hardware profile. In Proceedings of the State of the Art of Stream Ciphers Workshop (SASC 2007), eSTREAM, ECRYPT Stream Cipher Project, Report. Lausanne, Switzerland, 31 January–1 February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schneier, B. Applied Cryptography: Protocols, Algorithms, and Source Code in C; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Noonan, J.P.; Agaian, S. NPCR and UACI randomness tests for image encryption. Cyber J. Multidiscip. J. Sci. Technol. Sel. Areas Telecommun. 2011, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Saveriades, G.; Agaian, S.; Noonan, J.P.; Natarajan, P. Local Shannon entropy measure with statistical tests for image randomness. Inf. Sci. 2013, 222, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| XL0 and XT0 | The initial conditions of the chaotic maps: logistic and 3D Chebyshev respectively, ranging from 1 to . |
| XLC1, XSC1, and XTIC1 | The initial conditions of the delayed values in recursive cells: logistic, skew-tent, and 3D Chebyshev respectively, in the range . |
| Q0 | The initial value Q0 of the Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) defined by: |
| KL, KS, and KT | The coefficients of the recursive cells: logistic, skew-tent, and 3D Chebyshev respectively, ranging from 1 to . |
| The control parameter of the skew-tent map, in the range . | |
| The parameters of the coupling matrix M, in the interval with . | |
| The transient phase of 10 bits. |
| Versions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chaotic Multiplexing | XOR Operation | |||||
| Without LFSR | With LFSR | Without LFSR | With LFSR | |||
| Resources used | Area | LUTs | 3744/7.04% | 3763/7.07% | 3586/6.74% | 3599/6.77% |
| FFS | 1066/1% | 1130/1.06% | 1064/1% | 1128/1.06% | ||
| Slices * | 1079/8.11% | 1087/8.17% | 1031/7.75% | 1029/7.74% | ||
| DSPs | 25/11.36% | 25/11.36% | 22/10% | 22/10% | ||
| Speed | WNS [ns] | −18.968 | −19.062 | −19.632 | −18.018 | |
| Max. Freq. [Mhz] | 37.08 | 36.95 | 36.18 | 38.43 | ||
| Throughput [Mbps] | 1186.59 | 1182.46 | 1158.07 | 1229.91 | ||
| Efficiency [Mbps/Slices] | 1.09 | 1.08 | 1.12 | 1.19 | ||
| NIST | Successful | Successful | Successful | Successful | ||
| Test | p-Value | Proportion % |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency test | 0.616 | 100 |
| Block-frequency test | 0.182 | 97 |
| Cumulative-sums test (2) | 0.825 | 99.5 |
| Runs test | 0.956 | 100 |
| Longest-run test | 0.868 | 100 |
| Rank test | 0.182 | 99 |
| FFT test | 0.868 | 99 |
| Nonperiodic-templates (148) | 0.507 | 98.912 |
| Overlapping-templates | 0.956 | 99 |
| Universal | 0.575 | 98 |
| Approximate Entropie | 0.658 | 99 |
| Random-excursions (8) | 0.511 | 99.432 |
| Random-excursion-variant(18) | 0.376 | 99.832 |
| Serial test (2) | 0.290 | 98 |
| Linear-complexity | 0.834 | 100 |
| Resources used | Area | LUTs | 3631/6.83% |
| FFS | 1225/1.15% | ||
| Slices | 1081/8.13% | ||
| DSPs | 22/10% | ||
| Speed | WNS [ns] | −18.845 | |
| Max. Freq. [Mhz] | 37.25 | ||
| Throughput [Mbps] | 1192.02 | ||
| Efficiency [Mbps/Slices] | 1.1 | ||
| Cipher | Device | Frequency [Mhz] | Slices | Throughput | Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clock Frequency | Max. Freq. | [Mbps] | [Mbps/slices] | |||
| SCbSC | Pynq Z2 | 125 | 37.25 | 1081 | 1119.02 | 1.1 |
| LWCB SC [20] | Zynq7000 | - | 18.5 | 2363 LUTs | 565 | - |
| Lorenz’s chaotic System [21] | Virtex-II | 50 | 15.598 | 1926 | 124 | 0.06 |
| Chaos-ring [22] | Virtex-6 | 125 | 464.688 | 1050 | 464.688 | 0.44 |
| Trivium [36] | Spartan 3 | 50 | 190 | 388 | 12,160 | 31.34 |
| Grain-128 [37] | Virtex- II | 50 | 181 | 48 | 181 | 3.77 |
| Mickey-128 [37] | Virtex- II | 50 | 200 | 190 | 200 | 1.05 |
| Test | Lena | Pepper | Baboon | Barbara | Boats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPCR % | 99.5483 | 99.5452 | 99.5788 | 99.5513 | 99.5529 |
| UACI % | 33.7768 | 33.6530 | 33.5595 | 33.7723 | 33.6886 |
| 0.5015 | 0.4991 | 0.4996 | 0.5009 | 0.4996 |
| Chi-Square Test | Lena | Pepper | Baboon | Barbara | Boats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 216.10 | 231.84 | 244.05 | 233.62 | 265.47 | |
| (255, 0.05) | 293.24 | 293.24 | 293.24 | 293.24 | 293.24 |
| Entropy | Lena | Pepper | Baboon | Barbara | Boats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain image | 7.4504 | 7.5939 | 7.3102 | 7.5199 | 7.2392 |
| Cipher image | 7.9571 | 7.9550 | 7.9545 | 7.9570 | 7.9567 |
| Image | Horizontal | Vertical | Diagonal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lena | 0.939403 | 0.971060 | 0.931085 |
| Lena encrypted | −0.003684 | −0.009015 | 0.002278 |
| Peppers | 0.959869 | 0.967869 | 0.940375 |
| Peppers encrypted | −0.005938 | −0.004665 | −0.001154 |
| Baboon | 0.877794 | 0.834230 | 0.788141 |
| Baboon encrypted | −0.006750 | −0.005998 | −0.002088 |
| Barbara | 0.907829 | 0.946119 | 0.883508 |
| Barbara encrypted | −0.008293 | −0.010526 | 0.004815 |
| Boats | 0.940837 | 0.953357 | 0.904555 |
| Boats encrypted | −0.002802 | −0.009909 | 0.002302 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dridi, F.; El Assad, S.; El Hadj Youssef, W.; Machhout, M.; Lozi, R. The Design and FPGA-Based Implementation of a Stream Cipher Based on a Secure Chaotic Generator. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020625
Dridi F, El Assad S, El Hadj Youssef W, Machhout M, Lozi R. The Design and FPGA-Based Implementation of a Stream Cipher Based on a Secure Chaotic Generator. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(2):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020625
Chicago/Turabian StyleDridi, Fethi, Safwan El Assad, Wajih El Hadj Youssef, Mohsen Machhout, and René Lozi. 2021. "The Design and FPGA-Based Implementation of a Stream Cipher Based on a Secure Chaotic Generator" Applied Sciences 11, no. 2: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020625
APA StyleDridi, F., El Assad, S., El Hadj Youssef, W., Machhout, M., & Lozi, R. (2021). The Design and FPGA-Based Implementation of a Stream Cipher Based on a Secure Chaotic Generator. Applied Sciences, 11(2), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020625








