Feasibility Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Approach for Inhalation Exposure Assessment: Case Study for Biocide Spray
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Zero-Dimensional Spray Model
2.2. Measurement of the Sprayed Biocide Concentration
2.3. Numerical Simulatiom
2.3.1. Modeling the Flow Field
2.3.2. Modeling the Aerosol Motion
2.3.3. Modeling the Aerosol Concentration
2.3.4. Numerical Setting and Domain
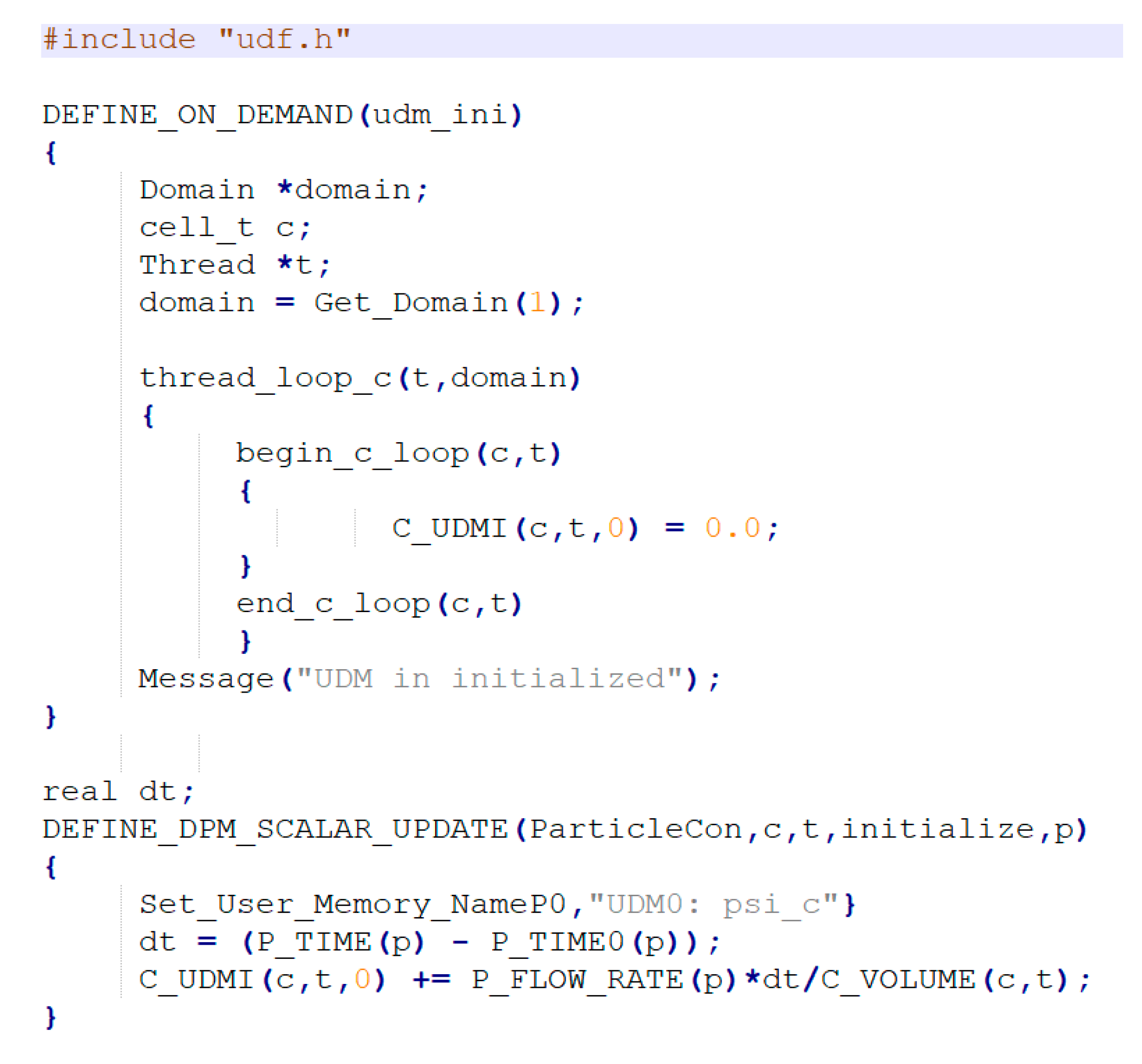
2.3.5. Numerical Method for Exposure Assessment of Aerosol Concentration by Biocide Spray
3. Results
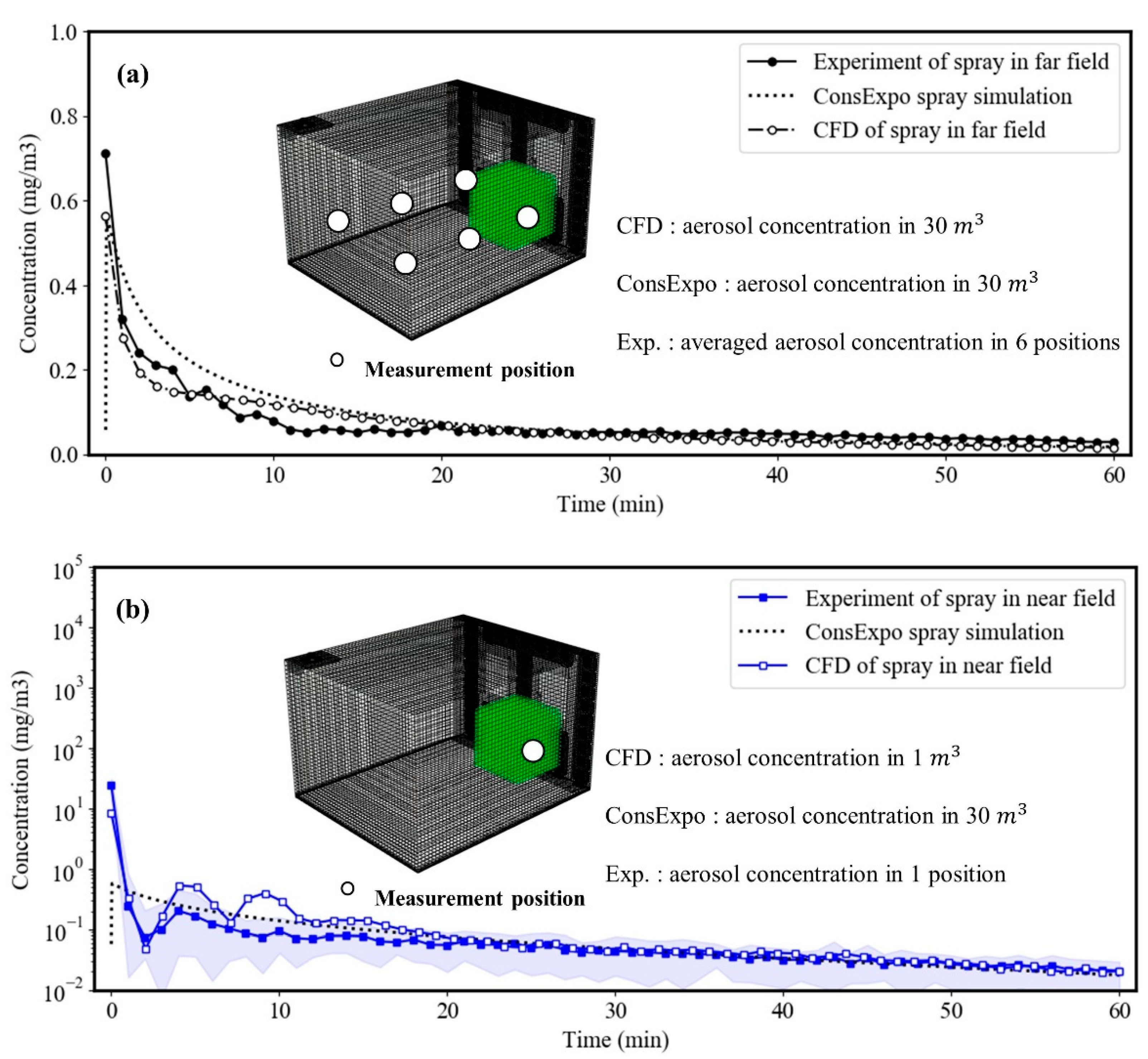
3.1. Evaluation on the Underestimation Possiblity of Inhalation Exposure by Zero-Dimensional Spray Model Based on CFD and Experiment Results
3.2. Evaluation on the Feasibility of CFD for Inhalation Exposure Assessment Based on Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- RIVM. ConsExpo Nano Tool. Available online: www.consexponano.nl.www.consexpoweb.nl (accessed on 30 October 2007).
- RIVM. Consexpo Web. Available online: www.consexpoweb.nl (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- US EPA. Consumer Exposure Model (CEM) User Guide. Available online: www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-06/documents/cem_2.1_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Delmaar, J.E.; Bremmer, H.J. Modeling and Experimental Validation of the Inhalation Exposure of Consumers to Aerosols from Spray Cans and Trigger Sprays; RIVM: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Young, B.M.; Tulve, N.S.; Egeghy, P.P.; Driver, J.H.; Zartarian, V.G.; Johnston, J.E.; Barnekow, D.E. Comparison of four probabilistic models (CARES®, CalendexTM, Zero-dimensional, and SHEDS) to estimate aggregate residential exposures to pesticides. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.F.; Ramachandran, G. Influence of parameter values and variances and algorithm architecture in ConsExpo model on modeled exposures. J Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2014, 11, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmaar, C.; Meesters, J. Modeling consumer exposure to spray products: An evaluation of the ConsexpoWeb and Consexponano models with experimental data. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Yoon, C.; Lee, K. Comparison of modeled estimates of inhalation exposure to aerosols during use of consumer spray products. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.S.; Lee, I.B.; Han, H.T.; Shin, C.Y.; Hwang, H.S.; Hong, S.W.; Bitog, J.P.; Seo, I.H.; Han, C.P. Analysing ventilation efficiency in a test chamber using age-of-air concept and CFD technology. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrie, J.W.; MacCalman, L.; Fransman, W.; Tielemans, E.; Tischer, M.; Van Tongeren, M. Revisiting the effect of room size and general ventilation on the relationship between near- and far-field air concentrations. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2011, 55, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, D.; Cha, J.; Kim, M.; Go, J.S. Multi-objective optimization and comparison of surrogate models for separation performances of cyclone separator based on CFD, RSM, GMDH-neural network, back propagation-ANN and genetic algorithm. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2020, 14, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.; Kim, M.; Park, D.; Go, J.S. Experimental determination of the viscoelastic parameters of K-BKZ model and the influence of temperature field on the thickness distribution of ABS thermoforming. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Xu, X.; Gao, R. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of airflow patterns and particle deposition characteristics in children upper respiratory tracts. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2012, 6, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Yu, S.C.M.; Lai, A.C.K. Modeling particle distribution and deposition in indoor environments with a new drift-flux model. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xu, H.; Li, W.; Sheng, D. An improved VOF-DEM model for soil-water interaction with particle size scaling. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 128, 103818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Qi, H.; Wen, W.; Du, K.; Ma, Y.; Yu, Y. Numerical simulations of molten breakup behaviors of a de laval-type nozzle, and the effects of atomization parameters on particle size distribution. Processes 2020, 8, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.F.; Campos, J.B.L.M.; Miranda, J.M.; Araújo, J.D.P. Numerical study of single taylor bubble movement through a microchannel using different CFD packages. Processes 2020, 8, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCraney, J.; Weislogel, M.; Steen, P. OpenFOAM Simulations of Late Stage Container Draining in Microgravity. Fluids 2020, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembely, M.; Alameri, W.S.; Alsumaiti, A.M.; Jouini, M.S. Pore-scale modeling of the effect of wettability on two-phase flow properties for newtonian and non-newtonian fluids. Polymers 2020, 12, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachnik, M.; Jakubowski, M. Multiphase model of flow and separation phases in a whirlpool: Advanced simulation and phenomena visualization approach. J. Food Eng. 2020, 274, 109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Xu, G.; Huang, J. Numerical study on DPM dispersion and distribution in an underground development face based on dynamic mesh. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, L.; Hastie, D.; Zigan, S. Using a coupled CFD – DPM approach to predict particle settling in a horizontal air stream. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Analysis of Flow and Wear Characteristics of Solid–Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Rotating Flow Channel. Processes 2020, 8, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wu, P.; Cao, S.J. The effects of ventilation and floor heating systems on the dispersion and deposition of fine particles in an enclosed environment. Build. Environ. 2017, 125, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS FLUENT Theory Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adedoyin, A.A.; Walters, D.K.; Bhushan, S. Investigation of turbulence model and numerical scheme combinations for practical finite-volume large eddy simulations. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2015, 9, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimzadeh, H.; Maghsoodi, R.; Sarkardeh, H.; Tavakkol, S. Simulating flow over circular spillways by using different turbulence models. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2012, 6, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Guo, B.; Ranjan, D. Numerical simulation of aerosol deposition from turbulent flows using three-dimensional RANS and les turbulence models. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2015, 9, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Go, J.S. Design of cyclone separator critical diameter model based on machine learning and cfd. Processes 2020, 8, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Kim, Y.; Ryu, S.; Gu, G.X. Prediction of composite microstructure stress-strain curves using convolutional neural networks. Mater. Des. 2020, 189, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yang, C.; Kim, Y.; Gu, G.X.; Ryu, S. Designing an Adhesive Pillar Shape with Deep Learning-Based Optimization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24458–24465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| ConsExpo Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Min/Mean/Max size | 1 × 10−7/ 11 × 10−6/ 30 × 10−6 (m) |
| Spread number | 1.5 |
| Mass generation rate | 0.0000119 (kg/s) |
| Weight fraction | |
| Density of aerosol | ) |
| Airborne fraction | 0.6 |
| Injection time | 3 s |
| Ventilation rate | 1 (1/h) |
| Room size | 30 |
| Deposition surface area | 12 |
| Boundary Condition | Values |
|---|---|
| Inlet condition (inlet velocity) | 30 |
| Outlet condition (pressure drop) | 1 (atm) |
| Time step size | 0.1 (s) |
| Number of time steps | 36,000 |
| Room size | 30 |
| Number of cells | 435.620 |
| Maximum length of grid | 0.015 m |
| DPM Condition | Values |
|---|---|
| Aerosol size range (min/max) | 0.1 to 30 () |
| Aerosol spread number | 1.5 |
| Mass generation rate | 0.0000119 (kg/s) |
| Number of aerosols | 500,000 |
| Density of aerosol | ) |
| Injection time | 3 (s) |
| Injection type | Spray solid cone |
| Aerosol injection condition | 0.5 (kPa) |
| Unit: mg/m3 | ~10 min | ~20 min | ~30 min | ~40 min | ~50 min | ~60 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental results (near field) | 2.54 | 1.3 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.46 |
| Experimental results (far field) | 0.23 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| CFD results (near field) | 1.12 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.24 |
| CFD results (far field) | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| ConsExpo model results | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, D.; Lee, J.-H. Feasibility Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Approach for Inhalation Exposure Assessment: Case Study for Biocide Spray. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020634
Park D, Lee J-H. Feasibility Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Approach for Inhalation Exposure Assessment: Case Study for Biocide Spray. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(2):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020634
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Donggeun, and Jong-Hyeon Lee. 2021. "Feasibility Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Approach for Inhalation Exposure Assessment: Case Study for Biocide Spray" Applied Sciences 11, no. 2: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020634
APA StylePark, D., & Lee, J.-H. (2021). Feasibility Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Approach for Inhalation Exposure Assessment: Case Study for Biocide Spray. Applied Sciences, 11(2), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020634





