Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis Using TOPSIS: Sustainable Approach to Technical and Economic Evaluation of Rocks for Lining Canals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. TOPSIS: Relevance and State of the Art
3. Site Investigation and Data Collection
4. Mechanical and Physical Properties of Studied Samples
5. Material Uses
5.1. Limestone
5.2. Dolomite
5.3. Basalt
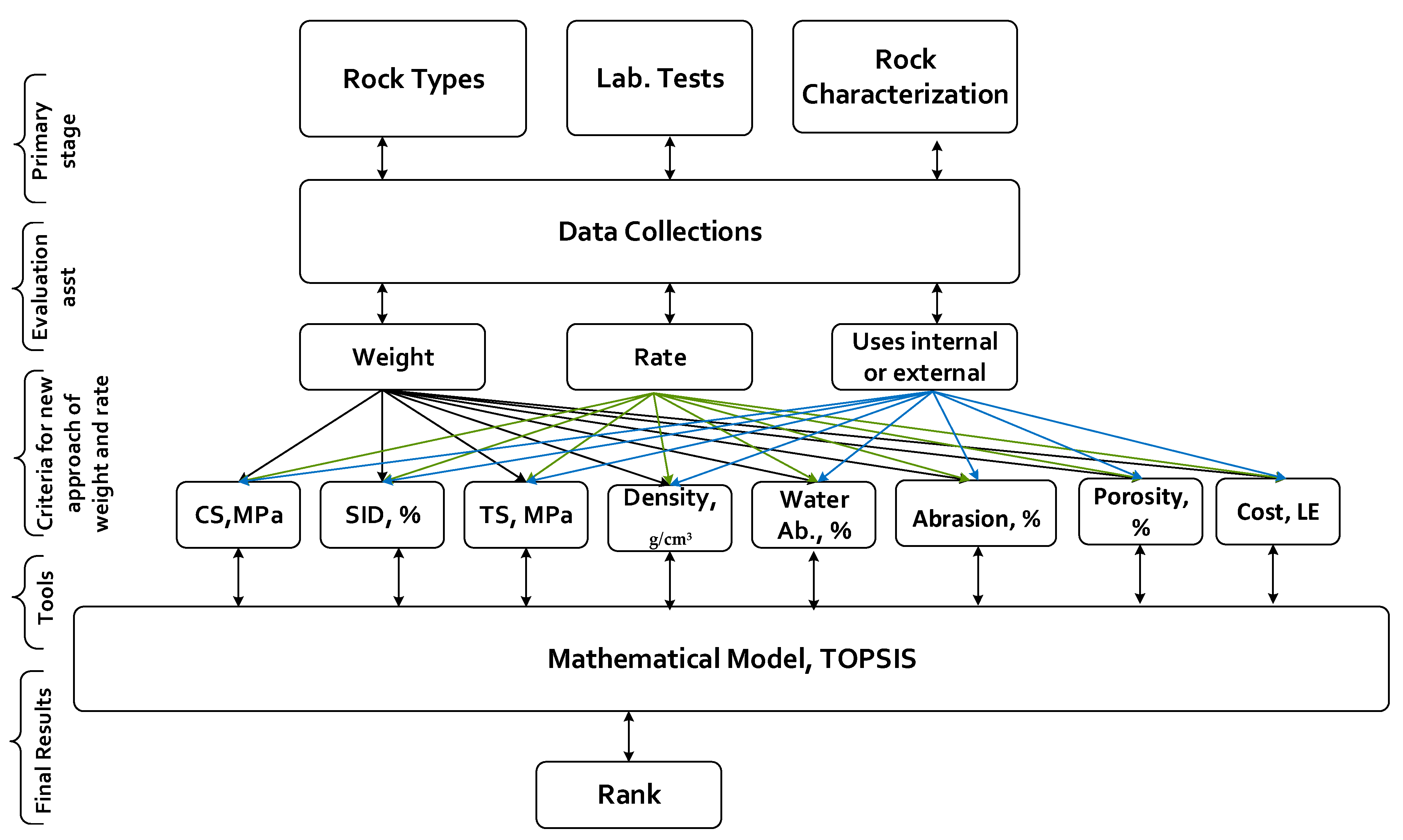
6. Methodology
- Normalize the decision matrix. This can be calculated byrij = xij__mk = 1 × 2kj, i = 1, …, m; j = 1, …, n, where rij denotes the normalized value of the jth criterion for the ith alternative Ai.
- Calculate the weighted normalized decision matrix. can be calculated asvij = wj rij, i = 1, …, m; j = 1, …, n (2), where wj is the weight of the jth criterion or attribute.
- Determine the ideal positive and negative solutions which can be calculated by
- Calculate the Euclidean distance from the ideal worst condition. can be described aswhere Vij = weighted and normalized decision matrix (Vij),S+ = the Euclidean distance from the ideal best,S− = the Euclidean distance from the ideal worst.
- Calculate the performance score and ranking This can be calculated by
7. Results and Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, S. The use of improved TOPSIS method based on experimental design and Chebyshev regression in solving MCDM problems. J. Intell. Manuf. 2017, 28, 229.e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, K.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.T. Decision optimization for power grid operating conditions with high and low-voltage parallel loops. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, Z.; Marija, D.; Edita, K. Application of vikor method in ranking the investment projects. Int. J. Econ. 2018, 8, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Kaveh, K.D.; Madjid, T.; Soheil, S.N. An integrated multi-objective framework for solving multi-period project selection problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 219, 3122–3138. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Singhal, S. Implementation of fuzzy TOPSIS methodology in selection of procedural approach for facility layout planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.F.; Mohd, A.; Javed, M. Siliceous concrete materials management for sustainability using fuzzy-TOPSIS approach. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3457. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, F.; Li, Y. An extended TOPSIS model based on the possibility theory under fuzzy environment. Knowl. Based Syst. 2014, 67, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykasglu, A.; Golcuk, I. Development of a novel multiple-attribute decision making model via fuzzy cognitive maps and hierarchical fuzzy TOPSIS. Inf. Sci. 2015, 301, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Macias, A.; Alvarado, A.; Garcia, J.L.; Balderrama, C.O. Intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS for ergonomic compatibility evaluation of advanced manufacturing technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 70, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, P.D.; David, L.C.; Delia, V.R.; Jesus, I.H.H.; Manual, I.R.B. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term and TOPSIS to access lean performance. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 873. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.; Yangyan, Z.; Yixiong, F.; Zhenyu, L.; Jianrong, T. Structural Optimization of a High-Speed Press Considering Multi-Source Uncertainties Based on a New Heterogeneous TOPSIS. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Chia-Nan, W.; Van, T.N.; Duy, H.D.; Hoang, T.N.T. A Hybrid fuzzy analysis network process (FNAP) and the technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS) approaches for solid waste to energy plant location selection in Vietnam. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1100. [Google Scholar]
- Youhua, J.; Mingshuo, F.; Ziqi, L.; Wenji, W. Comprehensive evaluation of power quality based on an improved TOPSIS method considering the correlation between indices. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3603. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El-Anwar, E.A.; Mekky, H.S.; Abd El Rahim, S.H. Mineralogy, geochemistry, petrography, and depositional environment of Gebel El-Qurn, Early Eocene, West Luxor, South Egypt. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2018, 42, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.I.S.; Abdel-wahab, A.A. Geotechnical properties of some middle Eocene limestone along the Nile valley. Egypt J. Geol. 1983, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mojtaba, K.; Rassoul, A. Evaluation of the mechanical degradation of carbonate aggregate by rock strength tests. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 11, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cultrone, G. Mineralogy and physical behavior of solid bricks with additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, C.; Zenaide, S.; Joaquim, S. Evaluation of Portuguese limestones’ susceptibility to salt mist through laboratory testing. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 523. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.I.S.; Abuel-Anwar, E.A. Petrophysical properties of some carbonate rocks at Abu-Roush area. Sedimentol. Egypt 2002, 10, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tahlawi, M.R. Geological and Geotechnical evaluation of the Eocene limestone of the Nile valley Egypt. Bull. Fac. Eng. 1973, 1, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, S.V.A.N.K.; Yilmaz, M.; Armaghani, D.J.; Tugrul, A. Prediction of the durability of limestone aggregates using computational techniques. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 29, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, S.A. Limestone deposits and small scale production of lime in Nigeria. Eng. Geol. 1977, 11, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, P.; Alonso, F.J.; Carrizo, L.; Molina, E.; Cultrone, G.; Blanco, M.; Zamora, I. Evaluation of the petrophysical properties of sedimentary building stones in order to establish quality criteria. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Rıza, S.; Ersel, G. Evaluation of limestone quarries for concrete and asphalt production: A case study from Ankara, Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 613. [Google Scholar]
- Machel, H.G. Dolomites and Dolomitization. 1978. Available online: https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F3-540-31079-7_72 (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Machel, H.G.; Lonnee, J. Hydrothermal dolomite—A product of poor definition and imagination. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 152, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, J.J.; Al-Aasm, I. Dolomite Discrimination in the D-1: Round up the Usual Suspects; Diamond Jubilee Convention of the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, R. Dolomite from Western Canada: Some thoughts on the Origin; Diamond Jubilee Convention of the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, S. Investigation of Physical Properties of Basalt Stones in The Southeast Anatolian Region of Turkey. In e-Journal of New World Sciences Academy; Goodman, R.E., Ed.; Number: 4. Rock in Engineering Construction, Engineering Geology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 3, p. 412. [Google Scholar]
- Mahrous, A.M.; Ahmed, H.M. Engineering characteristics of Egyptian limestone. J. Min. Miner. Depos. 2019, 13, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Mostaf, M.M.A.; El-Beblwi; Mohamed, A.Y.; Hassan, A.A.; El Sageer, M.T.; Mahrous, A.M. Quality Index to determine the Optimum Utility of some Egyptian Limestones as Building, Road Construction and Cement Industry. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Mining, Petroleum and Metallurgical Engineering; Mining and Metallurgical Deportment, Faculty of Engineering, Suez University: Suez, Egypt, 2009; pp. 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Klein, C.M. An efficient approach to solving fuzzy MADM problems. Fuzzy Set Syst. 1997, 88, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, A. Physical properties and indirect estimation of microfractures using Nigerian carbonate rocks examples. Eng. Geol. 1992, 33, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Biblawi, M.M.; Mohamed, A.Y.; Hassan, A.A.; El-Sageer; Mostafa, T.; Mahrous, A.M. Quality Index as a mean to determine the optimum utility of Limestone for different purposes. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Mining, Petroleum and Metallurgical Engineering, Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt, 15–19 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Teme, S.C. An evaluation of the engineering properties of some Nigerian limestone as construction materials for highway pavements. Eng. Geol. 1991, 31, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.Y.; El-Biblawy, M.M.A.; El-Sageer, H.A.A. The possibility of using some Egyptian limestone as building materials, in road construction and in cement manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference for Building and Construction, Interbuilding, Cairo, Egypt, 26–30 June 1997; Volume 1, pp. 1003–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.M.; Mostafa Tantawi, M.; El-Sageer, H. Evaluation of the engineering properties of some Egyptian limestones as construction materials for highway pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar]
- Shohda, A.M.; Draz, W.M.; Ali, F.A.; Yassien, M.A. Quality Index to Determine the Optimum Utility of Some Egyptian Stones as Ornamental Stones. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2016, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Teme, S.C.; Esu, E.O.; Edet, A.E.; Okereke, C.S. A study of some Nigerian carbonate rocks for the building construction industry. Eng. Geol. 1994, 37, 271–283. [Google Scholar]
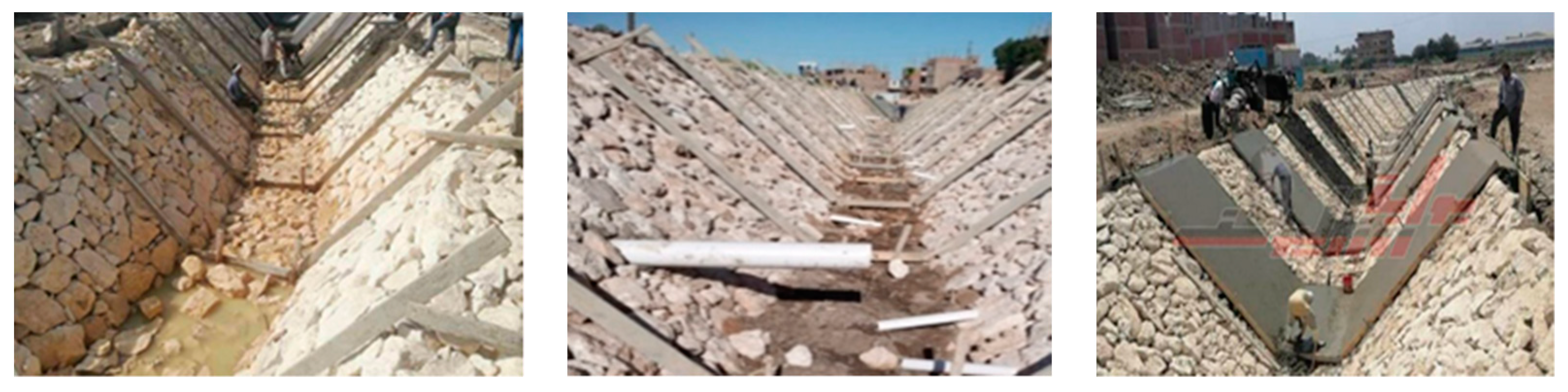


| Canal Capacity, m3/s | Thickness of Lining, mm | Average Dimension along the Longest Axis, mm | Minimum Dimensions at Any Section, mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 < 50 | 150 | 150 | 75 |
| 50 < 100 | 225 | 225 | 110 |
| >100 | 300 | 300 | 150 |
| Rock Type | Rock Class | Abbreviation | CS, MPa | TS, MPa | DIS, % | Water Absorption, % | Density, g/cm3 | Abrasion, % | P Wave Velocity, m/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limestone 1 | Sedimentary | L1 | 69.5 | 18.7 | 95.8 | 3.5 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 3655.6 |
| Limestone 2 | L2 | 72.8 | 19.3 | 98.2 | 4.04 | 2.2 | 2.22 | 3462.3 | |
| Limestone 3 | L3 | 81.5 | 20.8 | 98.5 | 3.2 | 2.7 | 1.85 | 3125.4 | |
| Limestone 4 | L4 | 78.6 | 18.9 | 98.1 | 3.6 | 2.6 | 0.98 | 3425.6 | |
| Dolomite 1 | Metamorphic | D1 | 111.5 | 28.2 | 98.9 | 2.55 | 2.6 | 0.035 | 4560.5 |
| Dolomite 2 | D2 | 125.4 | 29.6 | 98.5 | 2.04 | 2.7 | 0.031 | 4897.6 | |
| Dolomite 3 | D3 | 130.3 | 31.5 | 99.1 | 1.89 | 2.8 | 0.029 | 5001.2 | |
| Basalt 1 | Igneous | B1 | 135.3 | 35.2 | 99.5 | 0.38 | 2.8 | 0.082 | 5050.8 |
| Basalt 2 | B2 | 145.5 | 34.6 | 99.6 | 0.39 | 2.9 | 0.078 | 4985.7 | |
| Basalt 3 | B3 | 165.7 | 36.2 | 97.1 | 0.28 | 2.9 | 0.087 | 5010.4 |
| Properties | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | D1 | D2 | D3 | B1 | B2 | B3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS, MPa | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| TS, MPa | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| DIS, % | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Water absorption, % | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Abrasion, % | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| P wave velocity, m/s | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Cost, LE | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Cost, LE | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Parameter | Rating | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | |
| Uniaxial compressive strength (MPa) | <250 | 250–500 | 500–750 | 750–1000 | >1000 |
| Very low | low | Medium | High | Very high | |
| TS, MPa | <25 | 25–50 | 50–100 | 100–150 | >150 |
| Very low | low | Medium | High | Very high | |
| DIS, % | <50 | 50–60 | 60–75 | 75–100 | >100 |
| Very low | low | Medium | High | Very high | |
| Water absorption, % | >0.75 | 0.75–0.5 | 0.5–0.25 | 0.25–0.1 | <0.1 |
| Very high | high | Medium | low | Very low | |
| Density, g/cm3 | <2 | 2–2.3 | 2.3–2.6 | 2.6–2.9 | >3 |
| Very low | low | Medium | High | Very high | |
| Abrasion, % | >0.5 | 0.5–0.3 | 0.3–0.1 | 0.1–0.05 | <0.05 |
| Very high | High | Medium | low | Very low | |
| P wave velocity, m/s | <2750 | 2750–3500 | 3500–4250 | 4250–5000 | >5000 |
| Very weak | Weak | Moderate | strong | Very strong | |
| Cost, LE | <50 | 50–60 | 60–70 | 70–80 | >80 |
| Very cheep | cheep | Moderate | Expansive | Extremely Expensive | |
| Weights/Rates | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | TS | DIS | W. ab. | D. | Abr. | PWV | Cost | |
| L1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| L2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| L3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| L4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| D1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| D2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| D3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 |
| B1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.6 |
| B2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| B3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.6 |
| CS | TS | DIS | W. ab. | D. | Abr. | PWV | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.3162 | 0.1890 | 0.3162 | 0.1715 | 0.1715 | 0.0887 | 0.2500 | 0.1525 |
| L2 | 0.3162 | 0.1890 | 0.3162 | 0.1715 | 0.1715 | 0.0887 | 0.1667 | 0.1525 |
| L3 | 0.3162 | 0.1890 | 0.3162 | 0.1715 | 0.3430 | 0.0887 | 0.1667 | 0.1525 |
| L4 | 0.3162 | 0.1890 | 0.3162 | 0.1715 | 0.3430 | 0.0887 | 0.1667 | 0.1525 |
| D1 | 0.3162 | 0.3780 | 0.3162 | 0.1715 | 0.3430 | 0.4437 | 0.3333 | 0.305 |
| D2 | 0.3162 | 0.3780 | 0.3162 | 0.1715 | 0.3430 | 0.4437 | 0.3333 | 0.305 |
| D3 | 0.3536 | 0.3922 | 0.3536 | 0.1768 | 0.3536 | 0.4472 | 0.4369 | 0.305 |
| B1 | 0.3162 | 0.3780 | 0.3162 | 0.5145 | 0.3430 | 0.3549 | 0.4167 | 0.463 |
| B2 | 0.3162 | 0.3780 | 0.3162 | 0.5145 | 0.3430 | 0.3549 | 0.3333 | 0.458 |
| B3 | 0.3162 | 0.3780 | 0.3162 | 0.5145 | 0.3430 | 0.3549 | 0.4167 | 0.458 |
| CS | TS | DIS | W. ab. | D. | Abr. | PWV | Cost, LE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1.2649 | 0.0756 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.1029 | 0.0710 | 0.2000 | 0.0915 |
| L2 | 1.2649 | 0.0756 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.1029 | 0.0710 | 0.1333 | 0.0915 |
| L3 | 1.2649 | 0.0756 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.2058 | 0.0710 | 0.1333 | 0.0915 |
| L4 | 1.2649 | 0.0756 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.2058 | 0.0710 | 0.1333 | 0.0915 |
| D1 | 1.2649 | 0.1512 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.2058 | 0.3549 | 0.2667 | 0.183 |
| D2 | 1.2649 | 0.1512 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.2058 | 0.3549 | 0.2667 | 0.183 |
| D3 | 1.4142 | 0.1569 | 0.2121 | 0.1414 | 0.2121 | 0.3578 | 0.3495 | 0.183 |
| B1 | 1.2649 | 0.1512 | 0.1897 | 0.4116 | 0.2058 | 0.2840 | 0.3333 | 0.2777 |
| B2 | 1.2649 | 0.1512 | 0.1897 | 0.4116 | 0.2058 | 0.2840 | 0.2667 | 0.2745 |
| B3 | 1.2649 | 0.1512 | 0.1897 | 0.4116 | 0.2058 | 0.2840 | 0.3333 | 0.2745 |
| V+ | 1.2649 | 0.0756 | 0.1897 | 0.1372 | 0.1029 | 0.0710 | 0.1333 |
| V− | 1.4142 | 0.1569 | 0.2121 | 0.4116 | 0.2121 | 0.3578 | 0.3495 |
| Si+ | Si− | Pi | Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0667 | 0.5059 | 0.88 | 1 | L1 |
| 0.5294 | 0.5294 | 0.50 | 6 | L2 |
| 0.5181 | 0.5181 | 0.50 | 6 | L3 |
| 0.5181 | 0.5181 | 0.50 | 6 | L4 |
| 0.3376 | 0.3241 | 0.49 | 7 | D1 |
| 0.3376 | 0.3738 | 0.53 | 5 | D2 |
| 0.2863 | 0.3282 | 0.53 | 5 | D3 |
| 0.1690 | 0.4824 | 0.74 | 2 | B1 |
| 0.1876 | 0.2643 | 0.58 | 4 | B2 |
| 0.1691 | 0.2515 | 0.60 | 3 | B3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, M.A.M.; Kim, J.-G.; Awadallah, Z.H.; Abdo, A.M.; Hassan, A.M. Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis Using TOPSIS: Sustainable Approach to Technical and Economic Evaluation of Rocks for Lining Canals. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209692
Ali MAM, Kim J-G, Awadallah ZH, Abdo AM, Hassan AM. Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis Using TOPSIS: Sustainable Approach to Technical and Economic Evaluation of Rocks for Lining Canals. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(20):9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209692
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Mahrous A. M., Jong-Gwan Kim, Zakaria H. Awadallah, Ahmed M. Abdo, and Abbas M. Hassan. 2021. "Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis Using TOPSIS: Sustainable Approach to Technical and Economic Evaluation of Rocks for Lining Canals" Applied Sciences 11, no. 20: 9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209692
APA StyleAli, M. A. M., Kim, J.-G., Awadallah, Z. H., Abdo, A. M., & Hassan, A. M. (2021). Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis Using TOPSIS: Sustainable Approach to Technical and Economic Evaluation of Rocks for Lining Canals. Applied Sciences, 11(20), 9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209692






