Routing Density Analysis of Area-Efficient Ring Oscillator Physically Unclonable Functions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Existing Works
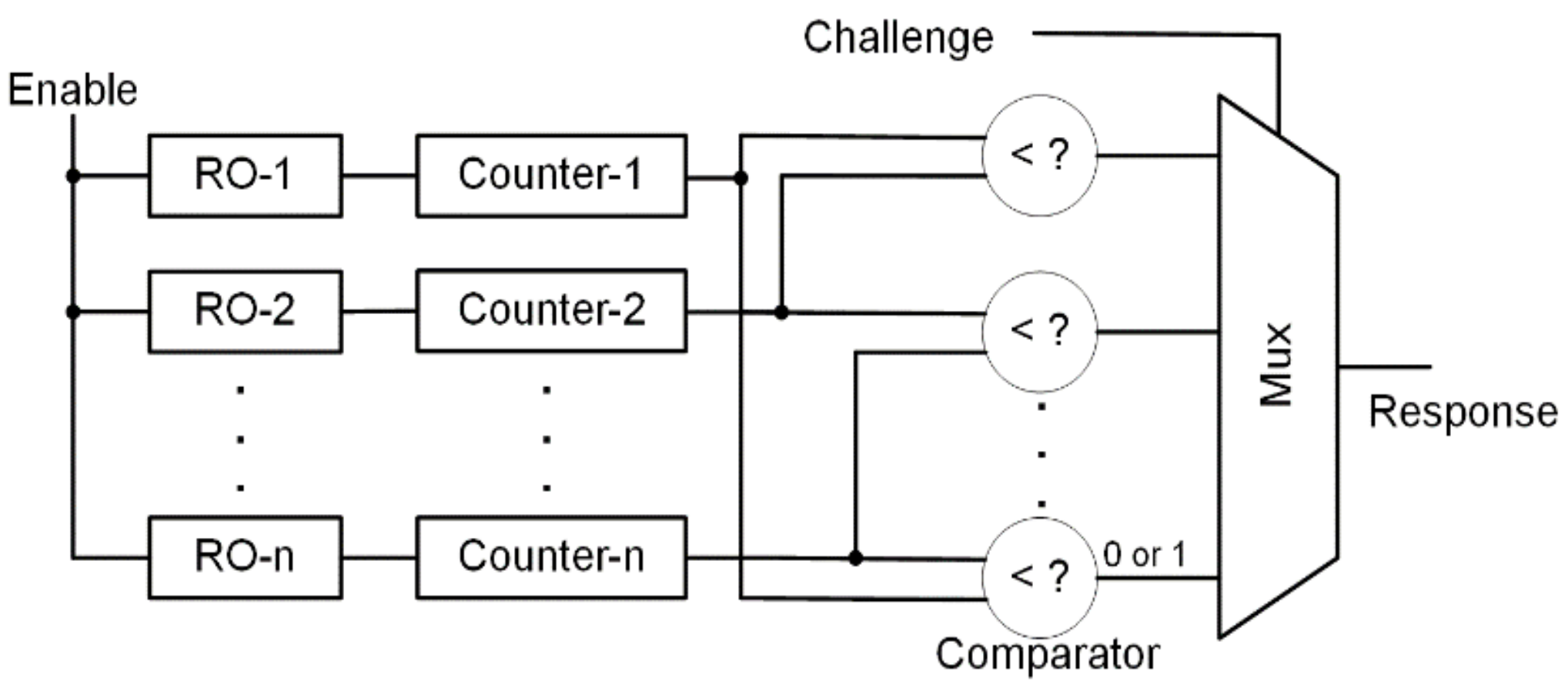
3. Proposed RO-PUF
- Routing equality—The distance between each RO to the respective counter is equal. Therefore, there will be no locking phenomena or jitter noise.
- One-time run—Each RO will only be run once. This technique would avoid the frequency difference of multiple RO run. In most conventional designs, every RO may be run more than once, leading to a slight difference in frequency. Moreover, multiple RO runs may result in less security due to a side-channel attack [29].
- Flexibility in choosing RO pairs—All CRP generation techniques proposed previously may be applied since the CRP process is independent, as shown in Figure 1.
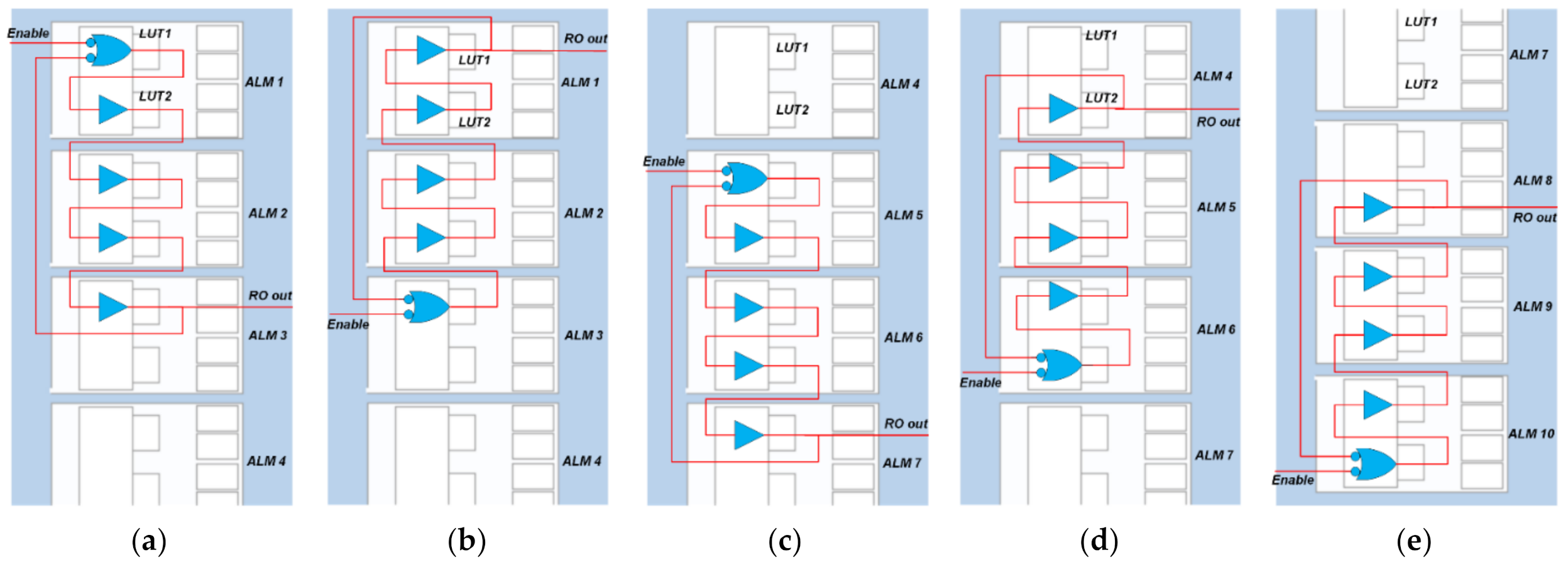
3.1. RO Implementations
3.2. RO Placement
4. Experimental Condition
4.1. Logic Arrangements
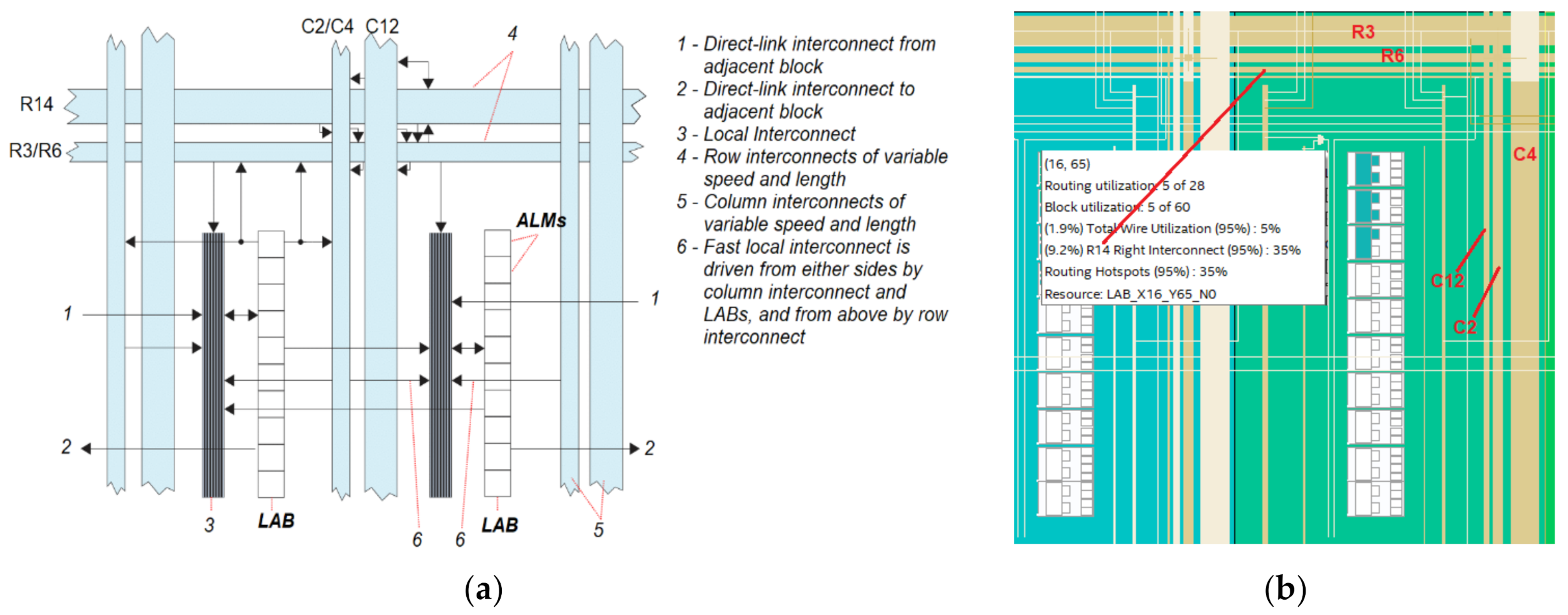
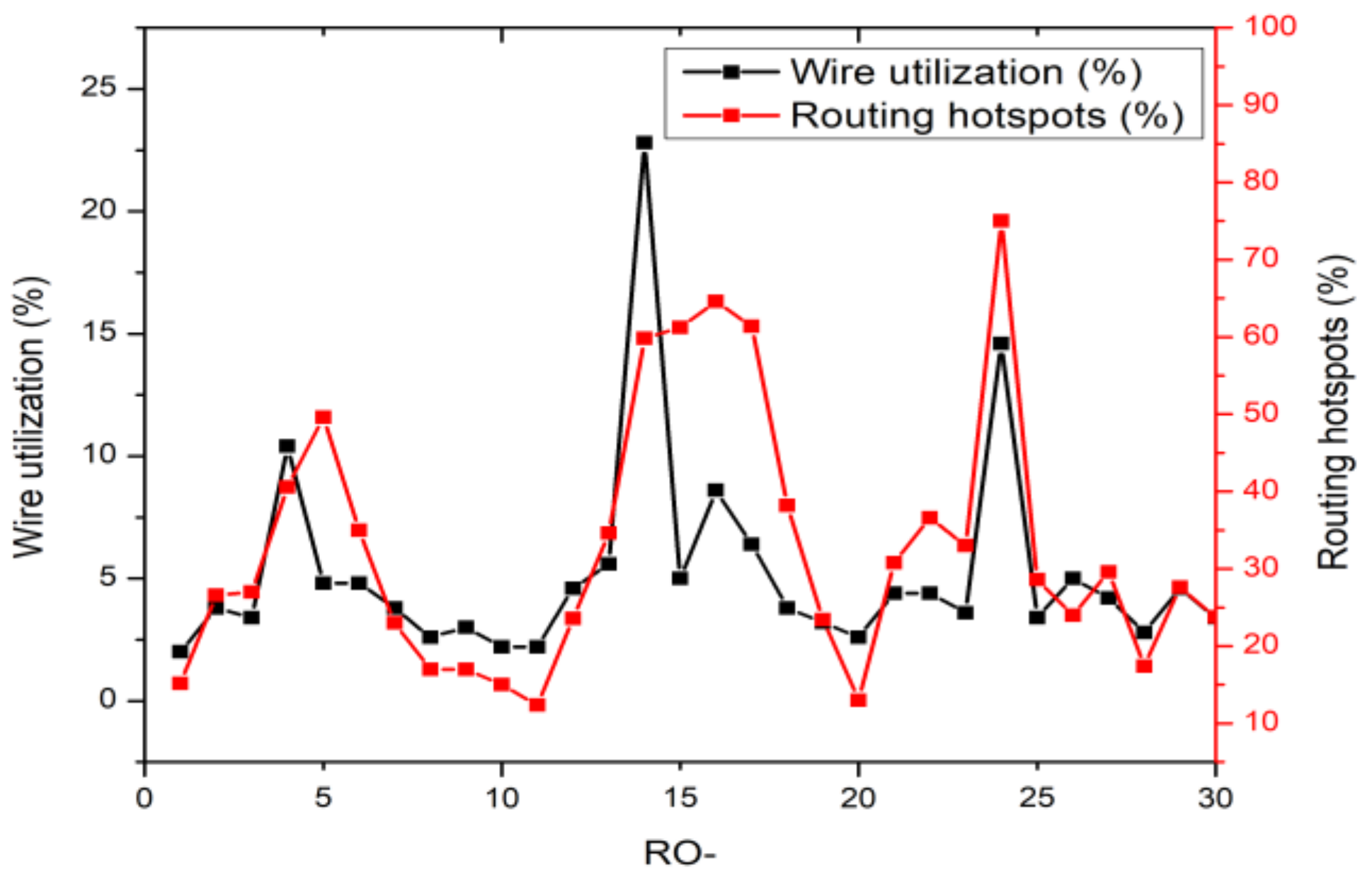
4.2. Routing Density
4.3. Metric Improvement
- The first scenario (named WR1); excludes ROs with heavy wire utilization (wh).
- The second scenario (named WR2); excludes ROs with heavy wire utilization (wh) and light wire utilization (wl).
- The third scenario (named RH1); exclude ROs with heavy routing hotspots (rh).
- The fourth scenario (named RH2); exclude ROs with heavy routing hotspots (rh) and light routing hotspots (rl).
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Statistical Properties
5.2. RO-PUF Metric
5.3. Result Comparisons
5.4. Runtimes Consideration
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maxfield, C. The Design Warrior’s Guide to FPGAs: Devices, Tools and Flows; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps, J.-P.; Bioul, G.J.; Sutter, G.D. Synthesis of Arithmetic Circuits: FPGA, ASIC and Embedded Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Roel, M. Physically Unclonable Functions: Constructions, Properties and Applications; Katholieke Universiteit: Leuven, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Cui, A.; Qu, G.; Li, H. A low-overhead PUF based on parallel scan design. In Proceedings of the 23rd Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Jeju, Korea, 22–25 January 2018; pp. 715–720. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, M.; Boehm, C. An alternative to error correction for SRAM-like PUFs. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 17–20 August 2010; pp. 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, B.; Kaps, J.-P.; Gaj, K. Implementation of efficient SR-Latch PUF on FPGA and SoC devices. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2017, 53, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Fang, X.; Ni, T.; Yi, M. A highly reliable butterfly PUF in SRAM-based FPGAs. IEICE Electron. Express 2017, 14, 20170551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, C.; Hanley, N.; O’neill, M. Improved reliability of FPGA-based PUF identification generator design. ACM Trans. Reconfig. Technol. Syst. 2017, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Shah, A.P.; Chouhan, S.S.; Gupta, N.; Pandey, J.G.; Vishvakarma, S.K. A symmetric D flip-flop based PUF with improved uniqueness. Microelectron. Reliab. 2020, 106, 113595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shah, A.P.; Chouhan, S.S.; Rani, S.; Gupta, N.; Pandey, J.G.; Vishvakarma, S.K. Utilizing manufacturing variations to design a tri-state flip-flop PUF for IoT security applications. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2020, 103, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodýtek, F.; Lórencz, R. A design of ring oscillator based PUF on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits & Systems, Belgrade, Serbia, 22–24 April 2015; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kodýtek, F.; Lórencz, R.; Buček, J. Improved ring oscillator PUF on FPGA and its properties. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2016, 47, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, T.; Yamamoto, D.; Iwamoto, M.; Sakiyama, K. Implementation of double arbiter PUF and its performance evaluation on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 20th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27–31 July 2015; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gassend, B.; Clarke, D.; Van Dijk, M.; Devadas, S. Silicon physical random functions. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Washington, DC, USA, 18–22 November 2002; pp. 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.T.; Rahman, F.; Forte, D.; Tehranipoor, M. An aging-resistant RO-PUF for reliable key generation. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2016, 4, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.R.; Kumar, S.; Mahapatra, K. A novel reliable and aging tolerant modified RO PUF for low power application. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2020, 103, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.R.; Kumar, K.S.; Mahapatra, K. A novel current controlled configurable RO PUF with improved security metrics. Integr. VLSI J. 2017, 58, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, S.; Qian, X.; Tang, B. Crossover Ring Oscillator PUF. In Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 14 February 2017; pp. 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Barbareschi, M.; Di Natale, G.; Torres, L.; Mazzeo, A. A Ring Oscillator-Based Identification Mechanism Immune to Aging and External Working Conditions. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, G.E.; Devadas, S. Physical unclonable functions for device authentication and secret key generation. In Proceedings of the 44th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, DAC’07, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 June 2007; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, A.; Schaumont, P. Improving the quality of a physical unclonable function using configurable ring oscillators. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Sydney, Australia, 9–11 December 2009; pp. 703–707. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.-E.; Qu, G. Obtaining statistically random information from silicon physical unclonable functions. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2014, 2, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Kang, H.; Iwamura, K. Direct challenge ring oscillator PUF (DC-ROPUF) with novel response selection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 6th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Nagoya, Japan, 24–27 October 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, I.; Rasmussen, K.B.; Eguro, K. Leaky Wires: Information Leakage and Covert Communication Between FPGA Long Wires. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Incheon, Korea, 4–8 June 2018; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, I.; Eguro, K.; Rasmussen, K.B. Leakier wires: Exploiting FPGA long wires for covert-and side-channel attacks. ACM Trans. Reconfig. Technol. Syst. 2019, 12, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.; Fischer, V.; Costea, C.; Fouquet, R. Implementation of ring-oscillators-based physical unclonable functions with independent bits in the response. Int. J. Reconfig. Comput. 2012, 2012, 168961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochard, N.; Bernard, F.; Fischer, V.; Valtchanov, B. True-randomness and pseudo-randomness in ring oscillator-based true random number generators. Int. J. Reconfig. Comput. 2010, 2010, 879281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feiten, L.; Spilla, A.; Sauer, M.; Schubert, T.; Becker, B. Implementation and analysis of ring oscillator PUFs on 60 nm Altera Cyclone FPGAs. Inf. Secur. J. Glob. Perspect. 2013, 22, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, D.; Schuster, D.; Stumpf, F.; Sigl, G. Semi-invasive EM attack on FPGA RO PUFs and countermeasures. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Workshop on Embedded Systems Security, Taipei, Taiwan, 9–14 October 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, A.; Kim, I.; Schaumont, P. A robust physical unclonable function with enhanced challenge-response set. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 7, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavar, M.; Mirzakuchaki, S.; Mohajeri, J. A ring oscillator-based PUF with enhanced challenge-response pairs. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2016, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapa, M. PUF Based FPGAs for Hardware Security and Trust; University of Toledo: Toledo, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfikar, Z.; Soin, N.; Hatta, S.W.M. Capacitance Effects of Ring Oscillator’s Waveform Quality in Designing Physically Unclonable Functions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Semiconductor Electronics (ICSE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mustapa, M.; Niamat, M.; Alam, M.; Killian, T. Frequency uniqueness in ring oscillator Physical Unclonable Functions on FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 56th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Columbus, Ohio, USA, 4–7 August 2013; pp. 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Feiten, L.; Oesterle, J.; Martin, T.; Sauer, M.; Becker, B. Systemic frequency biases in ring oscillator pufs on fpgas. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 2016, 2, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, C.; Bossuet, L.; Mureddu, U.; Bochard, N.; Cherkaoui, A.; Fischer, V. Implementation and characterization of a physical unclonable function for IoT: A case study with the TERO-PUF. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betz, V.; Rose, J. FPGA routing architecture: Segmentation and buffering to optimize speed and density. In Proceedings of the 1999 ACM/SIGDA Seventh International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, United States, 21–23 February 1999; pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Cyclone, V. Device Handbook Volume 1: Device Interfaces and Integration; Altera Corporation: San Jose, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Report Routing Utilization Dialog Box. Available online: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/programmable/quartushelp/17.1/index.htm#optimize/ace/acv_db_routing_congestion.htm (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Xin, X.; Kaps, J.-P.; Gaj, K. A configurable ring-oscillator-based PUF for Xilinx FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2011 14th Euromicro conference on digital system design, Oulu, Finland, 31 August–2 September 2011; pp. 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Gag, M.; Wegner, T.; Waschki, A.; Timmermann, D. Temperature and on-chip crosstalk measurement using ring oscillators in FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits & Systems (DDECS), Tallinn, Estonia, 18–20 April 2012; pp. 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Delvaux, J.; Gu, D.; Schellekens, D.; Verbauwhede, I. Helper data algorithms for PUF-based key generation: Overview and analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2014, 34, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiller, M.; Kürzinger, L.; Sigl, G. Review of error correction for PUFs and evaluation on state-of-the-art FPGAs. J. Cryptogr. Eng. 2020, 10, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-D.; Devadas, S. Secure and robust error correction for physical unclonable functions. IEEE Des. Test Comput. 2010, 27, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, X. Spartan-3 FPGA Family Data Sheet; Xilinx Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, A.; Schaumont, P. Improved ring oscillator PUF: An FPGA-friendly secure primitive. J. Cryptol. 2011, 24, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halak, B. Physically Unclonable Functions: From Basic Design Principles to Advanced Hardware Security Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Feng, S.-W.; Guo, C.-S.; Yan, X.; Feng, R.-R. All-digital thermal distribution measurement on field programmable gate array using ring oscillators. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, D.; Stumpf, F.; Eckert, C. Improving the quality of ring oscillator PUFs on FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 5th workshop on Embedded Systems Security, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 24 October 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, D.P.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chakraborty, R.S. Design of low area-overhead ring oscillator PUF with large challenge space. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Reconfigurable Computing and FPGAs (ReConFig), Cancun, Mexico, 9–11 December 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, A.S.; Sahula, V.; Mandal, A.S. Novel randomized placement for FPGA based robust ROPUF with improved uniqueness. J. Electron. Test. 2019, 35, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Hou, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Configurable ring oscillator PUF using hybrid logic gates. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161427–161437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Yew, T.-Y.; Wang, W.; Lee, Y.-H. The impact and implication of BTI/HCI decoupling on ring oscillator. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 April 2015; pp. 6–64. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, N.; Danger, J.-L.; Guilley, S. Impact of aging on the reliability of delay PUFs. J. Electron. Test. 2018, 34, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Schaumont, P. The impact of aging on a physical unclonable function. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2013, 22, 1854–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FPGA Technology | Intel Cyclone V (28 nm) |
|---|---|
| Chip No. | 5CSEMA5F31C6 and 5CSEMA4U23C6 |
| Software | Quartus Prime 17.1 |
| RO stage | Five-stage |
| Logic arrangement | Five patterns |
| RO runtimes | 100 ns–1 ms |
| Counter size | 20-bit |
| Arrangement | Input Configurations | RO Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern-1 | FB-D-C-F-F, DF-D-C-F-F, FB-A-C-F-F | F, D |
| Pattern-2 | FE-F-F-F-C | F |
| Pattern-3 | FC-F-F-F-F, FC-F-D-F-F, FC-F-C-F-F, DC-F-F-F-F, FD-F-F-F-F | F, D |
| Pattern-4 | FD-F-D-F-F, FA-F-D-F-F, DA-F-A-F-F | F, D |
| Pattern-5 | FD-F-D-F-F, FC-F-D-F-F, FD-B-A-F-F, FD-D-D-F-F | F |
| Scenarios | Pattern-1 | Pattern-2 | Pattern-3 | Pattern-4 | Pattern-5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
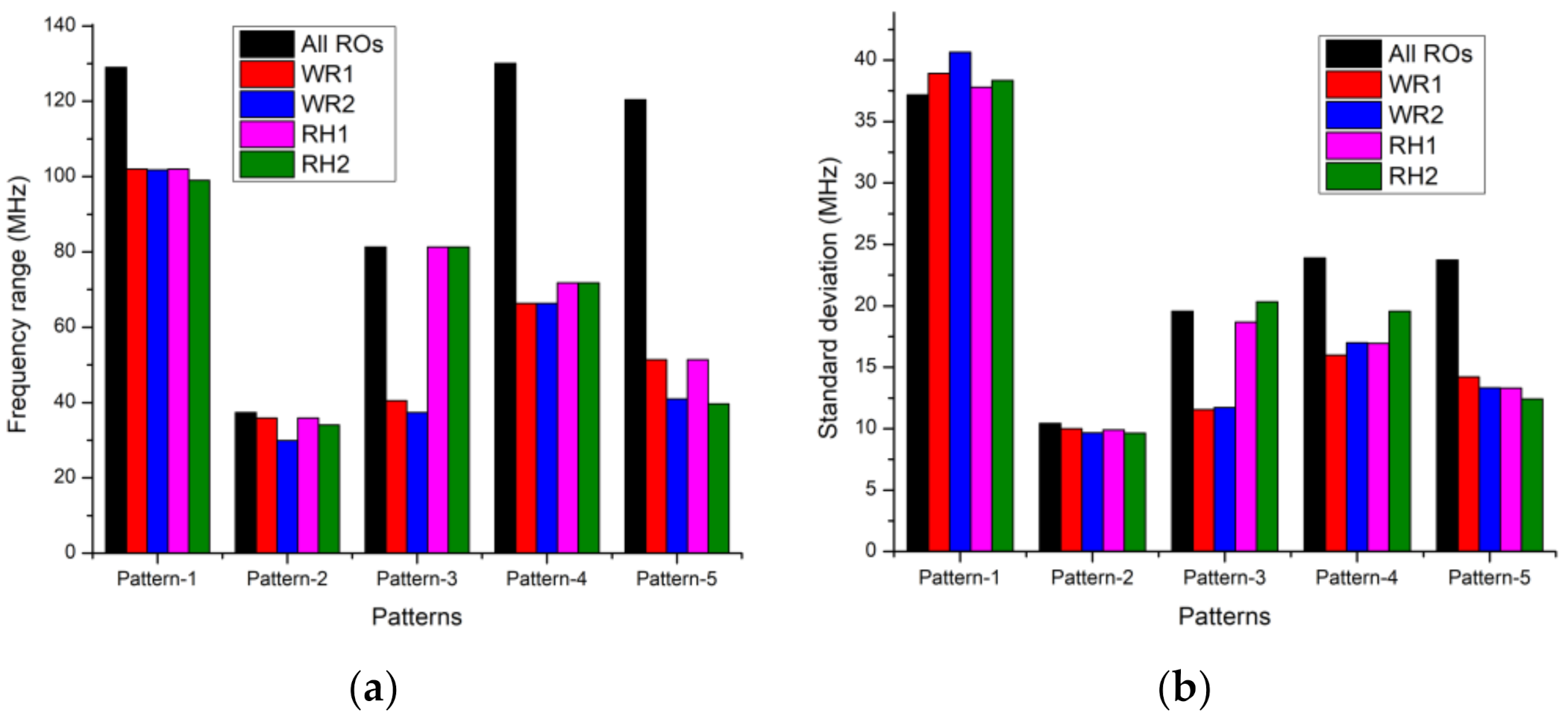
| Freq. range (MHz) | All ROs | 128.98 | 37.36 | 81.33 | 130.05 | 120.43 |
| (Smaller is better) | WR1 | 102.01 | 35.95 | 40.48 | 66.38 | 51.38 |
| WR2 | 101.75 | 29.95 | 37.36 | 66.38 | 40.99 | |
| RH1 | 102.01 | 35.95 | 81.33 | 71.83 | 51.38 | |
| RH2 | 99.06 | 34.07 | 81.33 | 71.83 | 39.70 | |
| Standard Deviation (MHz) | All ROs | 37.18 | 10.42 | 19.57 | 23.90 | 23.73 |
| WR1 | 38.92 | 10.00 | 11.55 | 15.98 | 14.22 | |
| WR2 | 40.64 | 9.66 | 11.72 | 16.99 | 13.32 | |
| RH1 | 37.80 | 9.91 | 18.67 | 16.95 | 13.31 | |
| RH2 | 38.34 | 9.64 | 20.32 | 19.56 | 12.43 | |
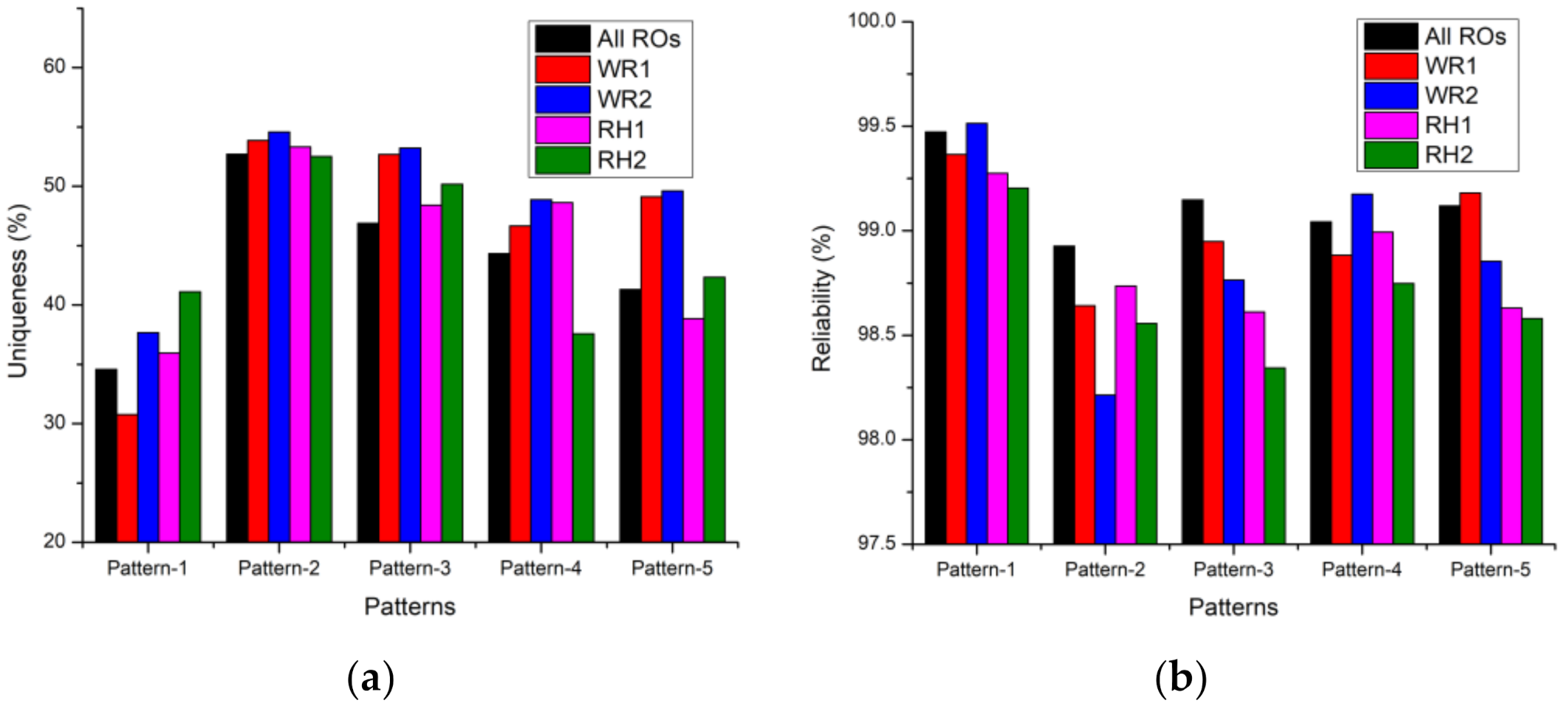
| Uniqueness (%) | All ROs | 34.58 | 52.71 | 46.90 | 44.32 | 41.31 |
| WR1 | 30.77 | 53.87 | 52.68 | 46.67 | 49.11 | |
| WR2 | 37.66 | 54.58 | 53.24 | 48.87 | 49.60 | |
| RH1 | 35.96 | 53.32 | 48.40 | 48.62 | 38.85 | |
| RH2 | 41.12 | 52.51 | 50.18 | 37.58 | 42.34 | |
| Reliability (%) | All ROs | 99.47 | 98.93 | 99.15 | 99.04 | 99.12 |
| WR1 | 99.37 | 98.64 | 98.95 | 98.88 | 99.18 | |
| WR2 | 99.51 | 98.21 | 98.76 | 99.18 | 98.85 | |
| RH1 | 99.28 | 98.74 | 98.61 | 98.99 | 98.63 | |
| RH2 | 99.20 | 98.56 | 98.34 | 98.75 | 98.58 | |
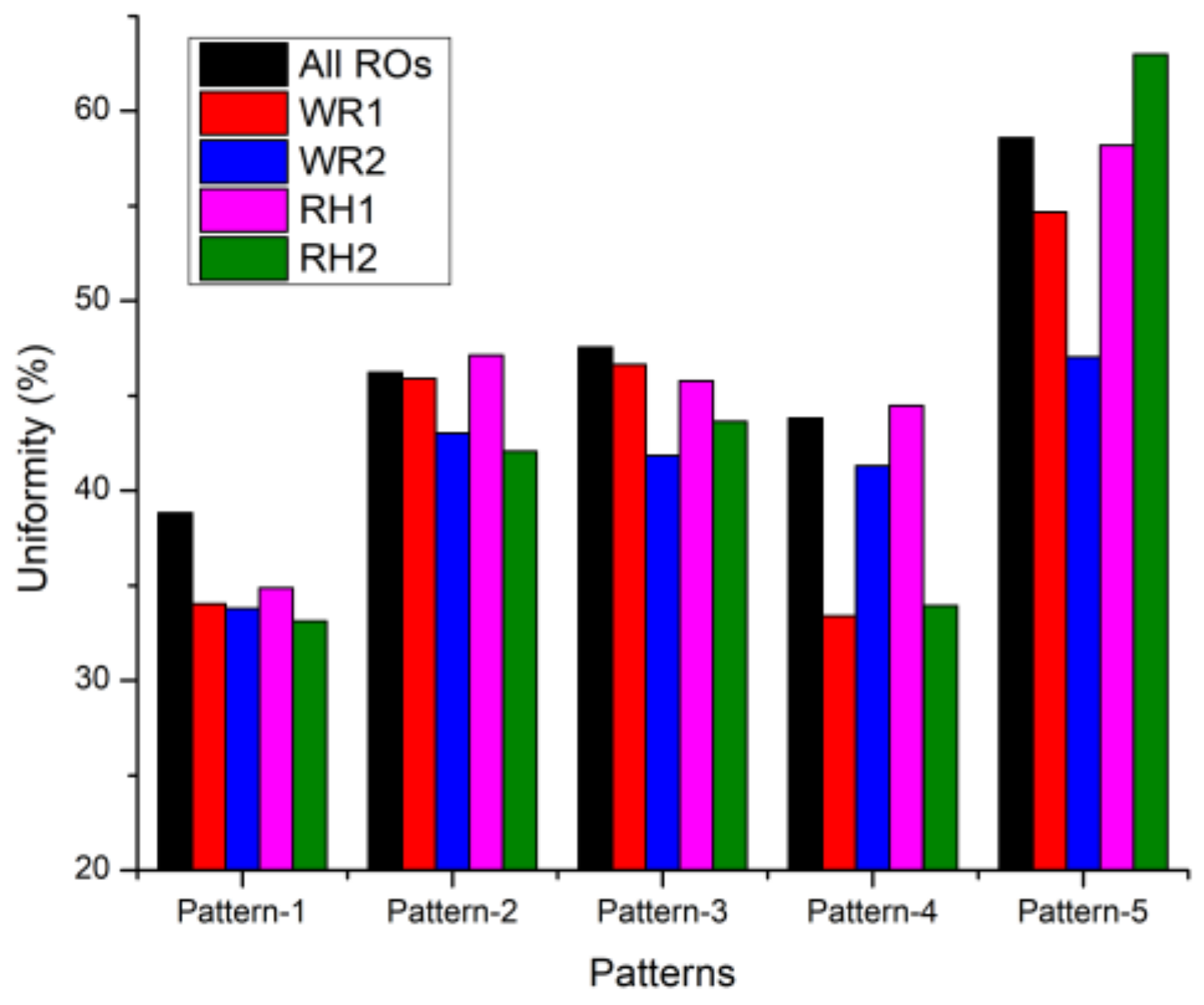
| Uniformity (%) | All ROs | 38.82 | 46.22 | 47.55 | 43.81 | 58.59 |
| WR1 | 34.05 | 45.91 | 46.65 | 33.39 | 54.66 | |
| WR2 | 33.78 | 43.04 | 41.85 | 41.32 | 47.02 | |
| RH1 | 34.86 | 47.13 | 45.77 | 44.48 | 58.19 | |
| RH2 | 33.12 | 42.08 | 43.64 | 33.93 | 62.98 |
| ROs (LUTs) | Uniqueness (%) | Reliability (%) | Uniformity (%) | Platform | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suh et al. [20], 2007 | 1024 (6144) | 46.15 | 99.52 | - | Xilinx |
| Maiti et al. [21], 2009 | 256 (1280) | 35.91–45.90 | - | - | Xilinx |
| Merli et al. [49], 2010 | 129 (-) | 43.40−48.51 | 99.20, 98.28 | - | Xilinx |
| Xin et al. [40], 2011 | 64 (3008) | 32, 41 | 99.29 | - | Xilinx |
| Maiti et al. [30], 2011 | 16 (256) | 49.99−50.07 | ±92 *, ±70 * | 50.02, 49.4 | Xilinx |
| Feiten et al. [28], 2013 | 64 (1024) | 6.68−37.03 | 99.41–82.5 | 50.00, 62.07 | Altera |
| Sahoo et al. [50], 2013 | 75 (1200) | 47.57 | 90.70 ** | 47 | Altera |
| Kodytek et al. [12], 2016 | 900 (6300) | 48.42−48.74 | 98.22, 97.55 | - | Xilinx |
| Delavar et al. [31], 2016 | 512 (775) | 49.81 | 96.07 | - | Xilinx |
| Chauhan et al. [51], 2019 | 11,264 (-) | 49.9 | 97.85–99.80 | - | Xilinx |
| Deng et al. [52], 2020 | 128 (2048) | 49.95 | 91.4–99.13 * | 49.61 | Xilinx |
| This work | 30 (150) | 50.18 # | 99.51 ## | 47.55 | Intel (Altera) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zulfikar, Z.; Soin, N.; Wan Muhamad Hatta, S.F.; Abu Talip, M.S.; Jaafar, A. Routing Density Analysis of Area-Efficient Ring Oscillator Physically Unclonable Functions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209730
Zulfikar Z, Soin N, Wan Muhamad Hatta SF, Abu Talip MS, Jaafar A. Routing Density Analysis of Area-Efficient Ring Oscillator Physically Unclonable Functions. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(20):9730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209730
Chicago/Turabian StyleZulfikar, Zulfikar, Norhayati Soin, Sharifah Fatmadiana Wan Muhamad Hatta, Mohamad Sofian Abu Talip, and Anuar Jaafar. 2021. "Routing Density Analysis of Area-Efficient Ring Oscillator Physically Unclonable Functions" Applied Sciences 11, no. 20: 9730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209730
APA StyleZulfikar, Z., Soin, N., Wan Muhamad Hatta, S. F., Abu Talip, M. S., & Jaafar, A. (2021). Routing Density Analysis of Area-Efficient Ring Oscillator Physically Unclonable Functions. Applied Sciences, 11(20), 9730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209730






