Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma Sterilizer Combined with Dielectric Barrier Discharge and Corona Discharge Inactivates Prions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Brain Homogenates Derived from Mice Infected with Prion
2.2. Hydrogen Gas Plasma Instrument RENO-S130
2.3. DBD Plasma Generation
2.4. Corona Discharge Plasma Generation
2.5. Measurement of Voltage and Current Waveforms
2.6. Treatment of Prions with the RENO-S130 Device
2.7. Prion Inoculation
2.8. Western Blot Analyses
2.9. PMCA
2.10. Statistical Analyses
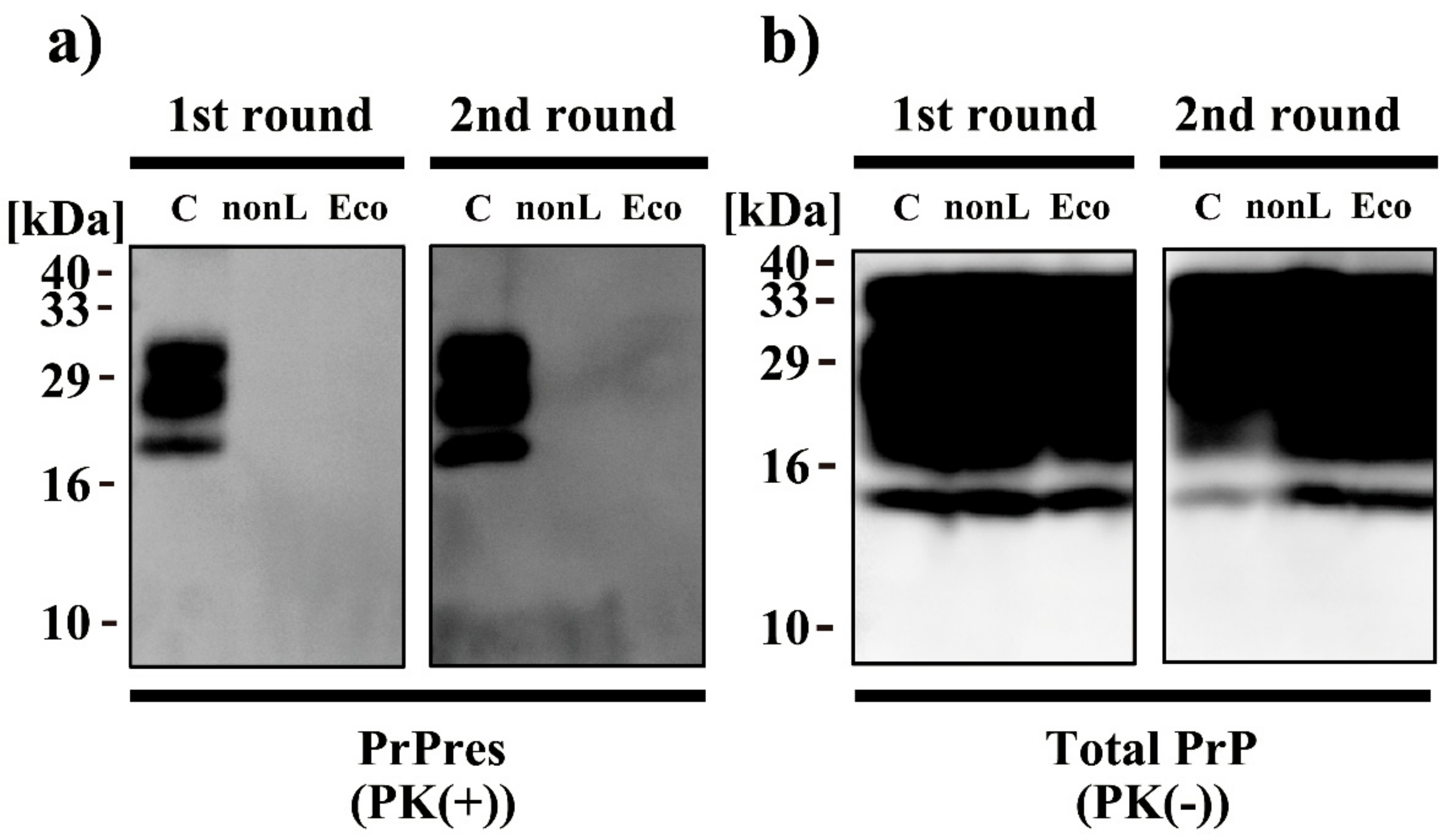
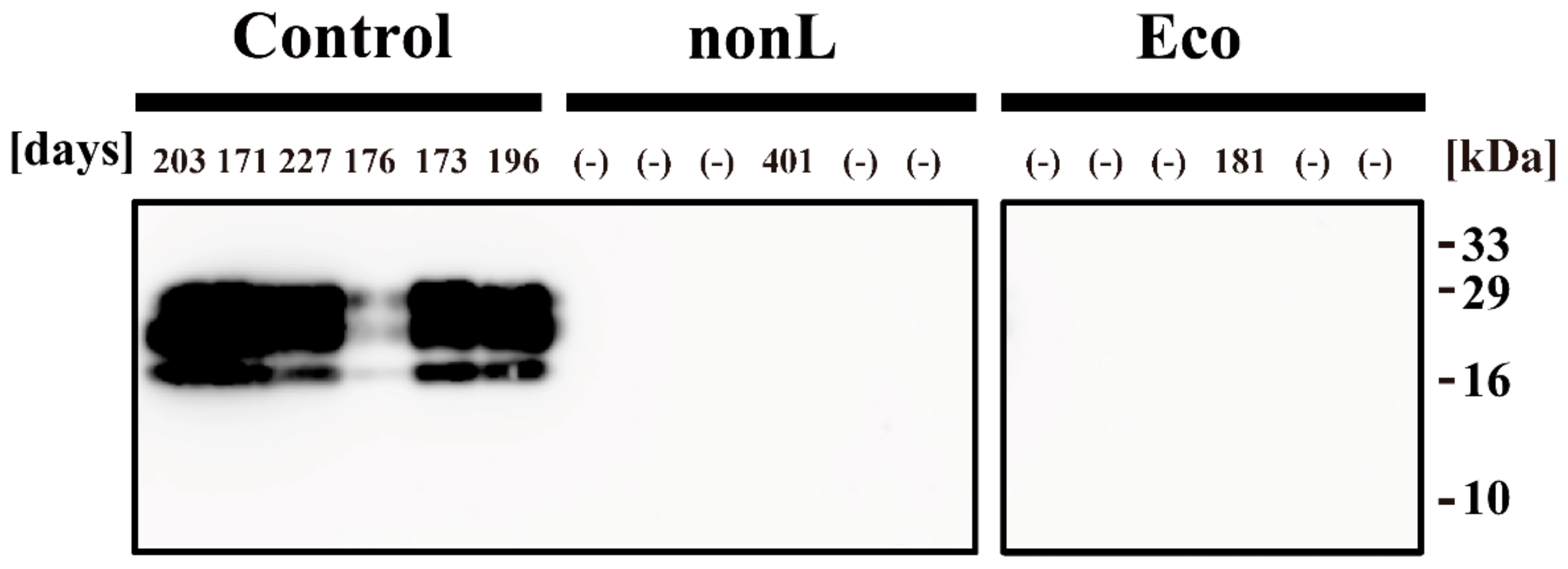
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakudo, A.; Ikuta, K. Fundamentals of prion diseases and their involvement in the loss of function of cellular prion protein. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Ikuta, K. Prion protein functions and dysfunction in prion diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.M.; Baldwin, M.; Nguyen, J.; Gasset, M.; Serban, A.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Huang, Z.; Fletterick, R.J.; Cohen, F.E.; et al. Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Pathologic conformations of prion proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 793–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castilla, J.; Saa, P.; Morales, R.; Abid, K.; Maundrell, K.; Soto, C. Protein misfolding cyclic amplification for diagnosis and prion propagation studies. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 412, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Saborio, G.P.; Anderes, L. Cyclic amplification of protein misfolding: Application to prion-related disorders and beyond. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzkow, S.; Wagenfuhr, K.; Daus, M.L.; Boerner, S.; Lemmer, K.; Thomzig, A.; Mielke, M.; Beekes, M. Quantitative detection and biological propagation of scrapie seeding activity in vitro facilitate use of prions as model pathogens for disinfection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belondrade, M.; Nicot, S.; Beringue, V.; Coste, J.; Lehmann, S.; Bougard, D. Rapid and highly sensitive detection of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease abnormal prion protein on steel surfaces by protein misfolding cyclic amplification: Application to prion decontamination studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belondrade, M.; Jas-Duval, C.; Nicot, S.; Bruyere-Ostells, L.; Mayran, C.; Herzog, L.; Reine, F.; Torres, J.M.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Beringue, V.; et al. Correlation between bioassay and protein misfolding cyclic amplification for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease decontamination studies. mSphere 2020, 5, e00649-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakudo, A. Inactivation methods for prions. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 36, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakudo, A.; Ano, Y.; Onodera, T.; Nitta, K.; Shintani, H.; Ikuta, K.; Tanaka, Y. Fundamentals of prions and their inactivation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Guideline for disinfection and sterilization of prion-contaminated medical instruments. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erana, H.; Perez-Castro, M.A.; Garcia-Martinez, S.; Charco, J.M.; Lopez-Moreno, R.; Diaz-Dominguez, C.M.; Barrio, T.; Gonzalez-Miranda, E.; Castilla, J. A Novel, Reliable and Highly Versatile Method to Evaluate Different Prion Decontamination Procedures. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 589182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.T.; Lin, S.M. Hydrogen Peroxide Plasma Sterilization System. U.S. Patent 4,756,882, 27 January 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, M.C.; Bécasse, P.; Verjat, D.; Darbord, J.C. Gas plasma sterilization: Relative efficacy of the hydrogen peroxide phase compared with that of the plasma phase. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 160, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Shintani, H. Nova Medical: Sterilization and Disinfection by Plasma: Sterilization Mechanisms, Biological and Medical Applications (Medical Devices and Equipment); Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shintani, H. Is SteradR from J&J is truly plasma gas sterilizer? Pharmaceut. Reg. Aff. 2013, 3, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eveland, R.W. Disinfection and Sterilization with Hydrogen Peroxide. In Block’s Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation, 6th ed.; McDonnell, G., Hansen, J., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 671–683. [Google Scholar]
- Domonkos, M.; Tichá, P.; Trejbal, J.; Demo, P. Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Technology in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjasteh, A.; Dehghani, Z.; Lamichhane, P.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H.; Kaushik, N.K. Recent Progress in Applications of Non-Thermal Plasma for Water Purification, Bio-Sterilization, and Decontamination. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, K.; Dove, B.K.; Parks, S.R.; Walker, J.T.; Bennett, A.M. Hydrogen peroxide vapour decontamination of surfaces artificially contaminated with norovirus surrogate feline calicivirus. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 80, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckert, R.A.; Best, M.; Jordan, L.T.; Dulac, G.C.; Eddington, D.L.; Sterritt, W.G. Efficacy of vaporized hydrogen peroxide against exotic animal viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3916–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berrie, E.; Andrews, L.; Yezli, S.; Otter, J.A. Hydrogen peroxide vapour (HPV) inactivation of adenovirus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, J.A.; Budde-Niekiel, A. Hydrogen peroxide vapor: A novel method for the environmental control of lactococcal bacteriophages. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottage, T.; Richardson, C.; Parks, S.; Walker, J.T.; Bennett, A.M. Evaluation of hydrogen peroxide gaseous disinfection systems to decontaminate viruses. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 74, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.M.; Chander, Y.; Yezli, S.; Otter, J.A. Evaluating the virucidal efficacy of hydrogen peroxide vapour. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 86, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet, G.; Antloga, K.; Comoy, E.; Deslys, J.P.; McDonnell, G. Prion inactivation using a new gaseous hydrogen peroxide sterilisation process. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 67, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet, G.; Comoy, E.; Duval, C.; Antloga, K.; Dehen, C.; Charbonnier, A.; McDonnell, G.; Brown, P.; Lasmezas, C.I.; Deslys, J.P. Novel methods for disinfection of prion-contaminated medical devices. Lancet 2004, 364, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Yamashiro, R.; Harata, C. Effect of non-concentrated and concentrated vaporized hydrogen peroxide on scrapie prions. Pathogens 2020, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasma Sterilizer RENO-S130. Available online: http://renosem.com/portfolio/plasma-sterilizer-reno-s130/ (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Occupational Safety & Health Administration. Sampling and Analytical Methods. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/dts/sltc/methods/partial/t-id126sg-pv-01-0201-m/t-id126sg-pv-01-0201-m.html (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Sakudo, A.; Iwamaru, Y.; Furusaki, K.; Haritani, M.; Onishi, R.; Imamura, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Onodera, T. Inactivation of scrapie prions by the electrically charged disinfectant CAC-717. Pathogens 2020, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Imanishi, Y.; Hirata, A.; Koga, Y.; Shintani, H. Effect of nitrogen gas plasma generated by a fast-pulsed power supply using a static induction thyristor on scrapie prion. Pathogens 2020, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RENO-S130. Available online: https://www.media-inc.co.jp/icbu/product/reno/products_s130.html (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Sakudo, A.; Yagyu, Y.; Onodera, T. Disinfection and sterilization using plasma technology: Fundamentals and future perspectives for biological applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Julák, J.; Janoušková, O.; Scholtz, V.; Holada, K. Inactivation of prions using electrical DC discharges at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, H.C.; Campbell, G.A.; Whittaker, A.G.; Jones, A.C.; Aitken, A.; Simpson, A.H.; Casey, M.; Bountiff, L.; Gibbard, L.; Baxter, R.L. Elimination of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy infectivity and decontamination of surgical instruments by using radio-frequency gas-plasma treatment. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86 Pt 8, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Keudell, A.; Awakowicz, P.; Benedikt, J.; Raballand, V.; Yanguas-Gil, A.; Opretzka, J.; Flötgen, C.; Reuter, R.; Byelykh, L.; Halfmann, H.; et al. Inactivation of bacteria and biomolecules by low-pressure plasma discharges. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.T.; Lin, S.M. Hydrogen Peroxide Plasma Sterilization System. U.S. Patent 4,643,876, 17 February 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rogez-Kreuz, C.; Yousfi, R.; Soufflet, C.; Quadrio, I.; Yan, Z.X.; Huyot, V.; Aubenque, C.; Destrez, P.; Roth, K.; Roberts, C.; et al. Inactivation of animal and human prions by hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pattison, I.H. The relative susceptibility of sheep, goats and mice to two types of the goat scrapie agent. Res. Vet. Sci. 1966, 7, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Cochran, S.P.; Groth, D.F.; Downey, D.E.; Bowman, K.A.; Martinez, H.M. Measurement of the scrapie agent using an incubation time interval assay. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, H.; Taylor, D.; Dickinson, J.; Walker, J.T.; Perrett, D.; Raven, N.D.; Sutton, J.M. Surface decontamination of surgical instruments: An ongoing dilemma. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 63, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, K.; Hitchins, V.M.; Brown, S.A. Safety and cleaning of medical materials and devices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 53, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Toyokawa, Y.; Imanishi, Y. Nitrogen gas plasma generated by a static induction thyristor as a pulsed power supply inactivates adenovirus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Toyokawa, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Yagyu, Y.; Imanishi, Y. Nitrogen gas plasma treatment of bacterial spores induces oxidative stress that damages the genomic DNA. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Chida, J.; Pasiana, A.D.; Uchiyama, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Naito, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamamura, J.; Kuromatsu, H.; Sakaguchi, S. Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide and Ozone Gas Synergistically Reduce Prion Infectivity on Stainless Steel Wire. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Moreno, A.; Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Moudjou, M.; Espinosa, J.C.; Beringue, V.; Torres, J.M. Thermostability as a highly dependent prion strain feature. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakudo, A.; Tsuji, Y. Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma Sterilizer Combined with Dielectric Barrier Discharge and Corona Discharge Inactivates Prions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9777. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209777
Sakudo A, Tsuji Y. Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma Sterilizer Combined with Dielectric Barrier Discharge and Corona Discharge Inactivates Prions. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(20):9777. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209777
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakudo, Akikazu, and Yosuke Tsuji. 2021. "Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma Sterilizer Combined with Dielectric Barrier Discharge and Corona Discharge Inactivates Prions" Applied Sciences 11, no. 20: 9777. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209777
APA StyleSakudo, A., & Tsuji, Y. (2021). Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma Sterilizer Combined with Dielectric Barrier Discharge and Corona Discharge Inactivates Prions. Applied Sciences, 11(20), 9777. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11209777





