Abstract
The aim of this prospective study was to compare a fixed lingual orthodontic appliance with a commonly used aligner system, focusing on oral impacts and speech disturbances, during the first 3 months of orthodontic treatment. Two groups of adults were evaluated: 21 treated with Invisalign® and 26 with In-Ovation L® lingual brackets. Health-related quality of life questionnaires were used to assess the oral impacts, and speech samples were collected for speech evaluation by professionals. The levels of pain and painkiller intake were similar, increasing on the first day, and decreasing at 3 months. Subtle injuries on the lip and cheeks were initially reported in the aligner group. Lingual patients experienced more discomfort in swallowing and opening the mouth, tongue injuries and food residues, even at 3 months. The consonants “s” and “z” were mainly affected in both groups immediately after appliance insertion, but more often in the aligner group. These speech disturbances recovered in the following 3 months. In conclusion, both groups reported disturbances in quality-of-life measures; however, patients wearing lingual appliances experienced more disturbances, which persisted after three months. Speech disturbances were slightly more pronounced in the aligner group and recovered after three months.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the demand for and the provision of aesthetic orthodontic treatment appliances have increased among patients. This trend reflects an acceptance that invisible orthodontic appliances, namely, clear aligners and lingual brackets, are preferable for adults, in terms of appearance, to more traditional orthodontic appliances [1,2,3]. The aesthetic advantages of these appliances over conventional buccal appliances have contributed to a shift in the demographic of the orthodontic patient population to increase the percentage of adults [1].
Nevertheless, adaptation difficulties may affect patient perception and compliance, and thus treatment outcome. Discomfort and pain, for example, are well-documented sequelae encountered during the course of orthodontic treatment. Approximately 90–95% of patients receiving orthodontic treatments experience these symptoms during the first weeks of treatment [4,5]. Pain and the fear of pain discourage orthodontic treatment and are the main reasons for treatment discontinuation [6,7,8].
Recently, there has been growing interest in not just understanding pain and other symptoms experienced during treatment, but also the oral impacts of orthodontic treatment, such as the influence on quality of life. To this end, many oral health-related quality of life measures have been used to assess oral impacts [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. All measures assess key oral impacts: discomfort and pain, eating difficulties, speech disturbances and social activities.
Different orthodontic treatment modalities function in different ways, making it imperative to assess the oral impacts of each treatment separately. Some studies have reported conflicting results regarding pain levels between different orthodontic appliances [17,18,19]. A recent systematic review concluded that orthodontic patients treated with Invisalign® appear to experience lower levels of pain than those treated with fixed appliances during the first few days of treatment; thereafter, (up to 2 months) no differences were noted [20]. However, it was pointed out that the malocclusion complexity level among the included studies was mild and the type of malocclusion was not comprehensively described, which may lead to controversial results. Thus, the level of certainty of this evidence was moderate. Moreover, different materials may affect pain levels too: the recently developed SmartTrack material has been favorably rated by the patients in regard to pain intensity and duration as well as overall comfort [18]. Regarding the effect of aligners on overall oral health-related quality of life compared to fixed appliance treatment, a recent systematic review concluded that information was limited, and effects were inconclusive with weak evidence that aligners might cause less eating disturbance [21].
A common critique by lingual appliance users is that the adaptability of lingual appliances takes a long period of time; therefore, the oral impacts should not be evaluated only in the short-term. Moreover, differences in plaque retention and composition are anticipated during orthodontic treatment with lingual brackets [22]. A systematic review compared lingual to buccal appliances and suggested that patients wearing lingual appliances have more pain, speech difficulties, and problems in maintaining adequate oral hygiene. No differences for eating and caries risk were identified [23].
Compared to children, adults have less speech adaptability due to muscle memory, and speech alteration may lead to reduced patient compliance [24]. The smaller the profile of the lingual appliance, the less pronounced are the impairments it induces [25].
To date, there has been no study comparing the oral impacts experienced by patients wearing the most discreet appliances available, namely, aligners versus lingual orthodontic braces over a 3-month period following the insertion of the appliances.
Thus, the aim of the present study was to compare a commonly used aligner system [Invisalign®] with fixed self-ligating lingual [Innovation-L®, GAC] orthodontic appliances, focusing on the oral impacts experienced by patients, and speech disturbances, evaluated by professionals. The research hypothesis was that there are no differences in oral impacts and speech in patients treated with these two types of orthodontic appliances.
2. Materials and Methods
The study was performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines on experimentation involving human subjects. Informed consent was obtained from all participants. All patients treated with the Invisalign® appliance were supervised by an experienced Invisalign instructor, whereas all patients with lingual appliances were supervised by an experienced lingual appliance instructor. Patients were presented with the pros and cons of both appliances, and the patient’s decision regarding the desired type of appliance was respected. A total of 47 consecutively treated adult patients with either Invisalign® or lingual fixed orthodontic appliances, over the first 3 months of the treatment, were enrolled in this prospective longitudinal clinical study. Two groups of adult patients were evaluated, including 21 treated with Invisalign® (13 females, 8 males, aged 32.9 ± 2.38 years (mean ± SE)) and 26 with In-Ovation L® active self-ligating 0.018-inch lingual brackets (18 females, 8 males, aged 38.5 ± 2.12 years (mean ± SE)).
Calculation of the required sample size was based on an assumed minimum clinically significant difference of 10 units in the 0–100 HRQoL scale between the two groups at Day 1. Standard deviations were assumed to be common in the two groups and equal to 11 units, according to initial results from the first 10 patients. Setting the desired level of power to 0.80 at an alpha level of 0.05, the resulting sample size was 21 patients per group.
Patients who met the following inclusion criteria were eligible to participate in the study:
(a) Caucasian origin; (b) treatment need for both dental arches with required lateral cephalometric radiograph; (c) no inherited or acquired craniofacial deformities; (d) no neurologic disorders or tongue thrust habits; (e) no hearing deficits or history of speech/hearing therapy; and (f) no previous orthodontic treatment.
The cephalometric radiographs were obtained with the aid of a cephalostat that ensures reproducible and stable patient positioning. The initial wire inserted in the lingual fixed orthodontic appliances was 0.012-inch NiTi wire and was maintained for the first three months. In the Invisalign group (SmartTrack: multi-layer aromatic thermoplastic polyurethane 0.75 mm), bite ramps that may influence speech were not used and the aligners were changed every 7 days. Patients were instructed to wear the aligners for 22 h per day, excluding eating and brushing. Patients with aligners were instructed to only drink water and to abstain from coffee, tea or red wine. Patients were asked to track their cooperation with this timetable daily, and their adherence was reinforced at each appointment. If the edge of the aligner was rubbing against the lips, tongue or gums, it was smoothed off or trimmed without compromising the way it fitted.
Assessments of the treatment need with the IOTN and the cephalometric evaluation were performed for each patient by two examiners, who were not involved in the treatment of the patients and were blinded to the treatment group assignment [26]. Cephalometric evaluation included skeletal classification (ANB), vertical position of the mandible (GoGn-SN), upper and lower incisor inclination (U1/PP and L1/MP), and facial divergency (Z-angle). Questionnaires and speech samples were gathered at the following intervals: T0, immediately prior to appliance insertion; T1, immediately following appliance insertion for the speech samples and the first day following appliance insertion for the questionnaires; T3, 3 months post-insertion.
Ratings of oral impacts and satisfaction were performed using the HRQoL instrument, filled out by the patients (Appendix A). This questionnaire has been used and validated in previous studies [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Speech samples were collected for evaluation by professionals. These samples were obtained in a video imaging room with a reduced-noise environment. The patient was seated in an upright position with a mounted video camera recorder positioned 30–45 cm away from the patient’s face. At each time point, the subjects were asked to perform three repetitions of five characteristic Indo-European words (reading them from paper) common in most languages: “Mississippi”, “Suzuki”, “Patala”, “Emma”, and “Diesel”. Two samples were obtained from each patient (frontal and 3/4). Each sample was assigned a number at random, and a spreadsheet was generated by one author with information about each speech sample, only available to him. A speech pathologist and two orthodontists performed the semi-objective assessments independently and blindly. Auditory evaluations were performed on each audio file by indicating alterations in speech production in every letter according to the following 5-point Likert scale: 1, not at all affected; 2, slightly affected; 3, moderately affected; 4, very affected; and 5, extremely affected. Each rater re-evaluated 20 speech samples, with a 1-month interval between the two evaluations, in order to assess intra- and inter-examiner reliability.
In order to summarize the questionnaire results, a total score was created by adding the numerical responses to questions 3–16 (i.e., all questions except for the first, which was a 1–10 pain score, and the second one, which was a yes–no question regarding analgesics). In question 7, which addresses a positive aspect—opposite to all other questions—the values were reversed in all calculations. The questionnaire results, as well as the results of consonant speech articulation, were transformed to a 0–100 scale (0, best; 100, worst score).
Statistical Analysis
Intra- and inter-examiner agreement was assessed using Lin’s concordance coefficient (speech assessments and cephalometric measurements) and a weighted version of Cohen’s kappa coefficient of agreement (ΙOΤΝ). Cephalometric measurement errors were assessed using Dahlberg’s formula and reported as relative (%) values. Exploratory comparisons between the two groups at different time-points were based on t-tests and Fisher’s exact tests for quantitative variables and categorical variables, respectively. The main analysis of the complete data set (all measurements from both groups in all 3 time points) was based on linear mixed models, taking into account the potential correlation of repeated measurements of the same individual. p-values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using Stata version 14.2 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
Intra- and inter-examiner agreement were high, regarding the cephalometric measurements (Lin’s concordance coefficients 0.923–0.993) and the Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need (IOTN) scores (weighted Cohen’s kappa coefficient of agreement 0.950–1.000). Relative Dahlberg’s errors for cephalometric measurements were very low (0.80–2.1%).
The baseline demographic characteristics did not present significant differences between the two groups (Table 1).

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics by group.
No significant statistical difference was found between the two groups in the initial cephalometric measurements, after adjustment for age and gender (Table 2). However, male patients presented statistically significant higher values of Z-angle.

Table 2.
Cephalometric measurements by group (mean, SD).
Furthermore, the aesthetic and dental component of IOTN was evaluated by group, and no significant correlation was detected between the two groups after adjusting for age and gender (Table 3).

Table 3.
Aesthetic and dental component of IOTN index by group.
3.2. HRQoL Questionnaires
3.2.1. Baseline (T0)
The results of the HRQoL questionnaire were analyzed at baseline (T0), day 1 (T1) and 3 months (T3) (Supplementary Table S1). At baseline (T0), the HRQoL results did not present statistically significant differences between the groups. However, in Q9 (“Was it difficult to sleep last night?”), six patients reported “a few times” (four patients from the Invisalign group and two patients from the lingual group, p = 0.386).
3.2.2. Day 1 (T1)
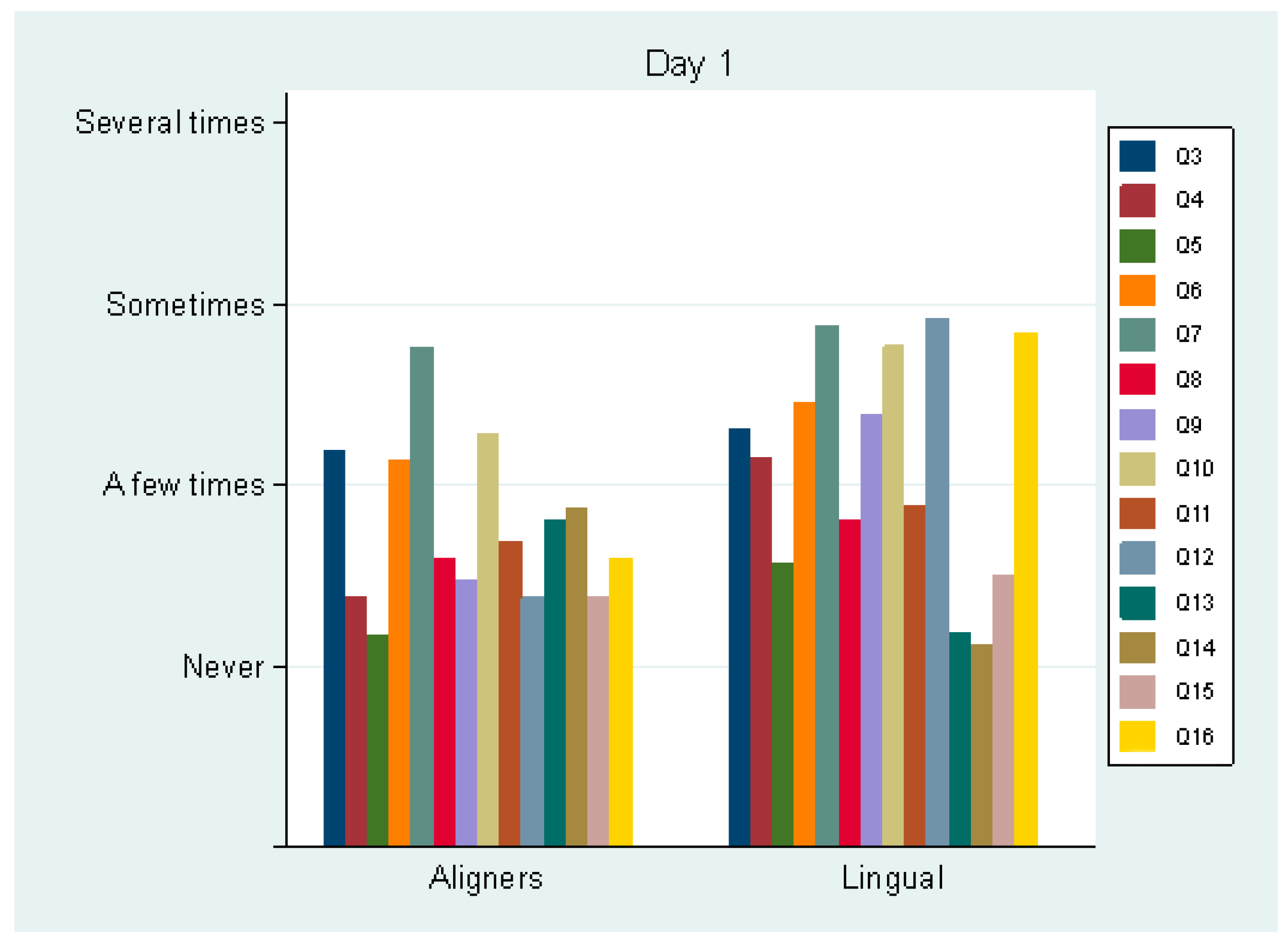
On day 1 (T1), pain perception was not statistically significant (p = 0.331) between the aligner (mean score 4.2 ± 2.0) and the lingual group (3.7 ± 1.8). Analgesic consumption was also not statistically significant (p = 0.999). Only 10% of each group took analgesics on day 1. Regarding Q3–16, statistically significant differences between the groups were detected in Q4 (swallowing difficulty, p = 0.031), Q5 (mouth opening difficulty, p = 0.024), Q6 (not being able to eat certain foods, p = 0.030), Q9 (sleeping difficulty, p = 0.048), Q12 (tongue sores, p = 0.001), Q14 (lip sores, p = 0.025) and Q16 (food debris under the appliance, p = 0.001). The aligner group exhibited better scores in all these questions apart from one (Q14: “Do you have sores on your lip?”) (Figure 1). The two groups differed in the total Q3–16 score (transformed to a 0–100 scale, 0, best score; 100, worst score): 19.2 (±10.5) for the aligner group and 28.2 (±7.9) for the lingual group (p = 0.046).
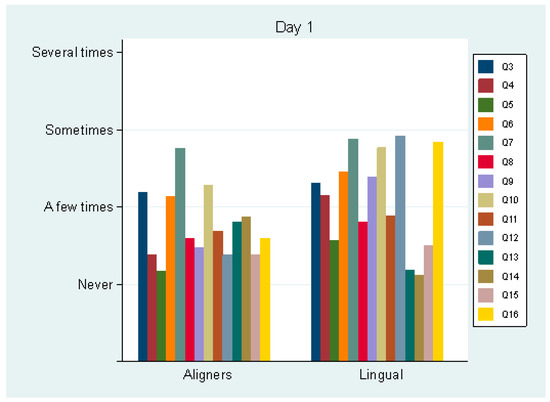
Figure 1.
Average values of questions 3–16 by group, the first day following appliance insertion.
3.2.3. Month 3 (T3)
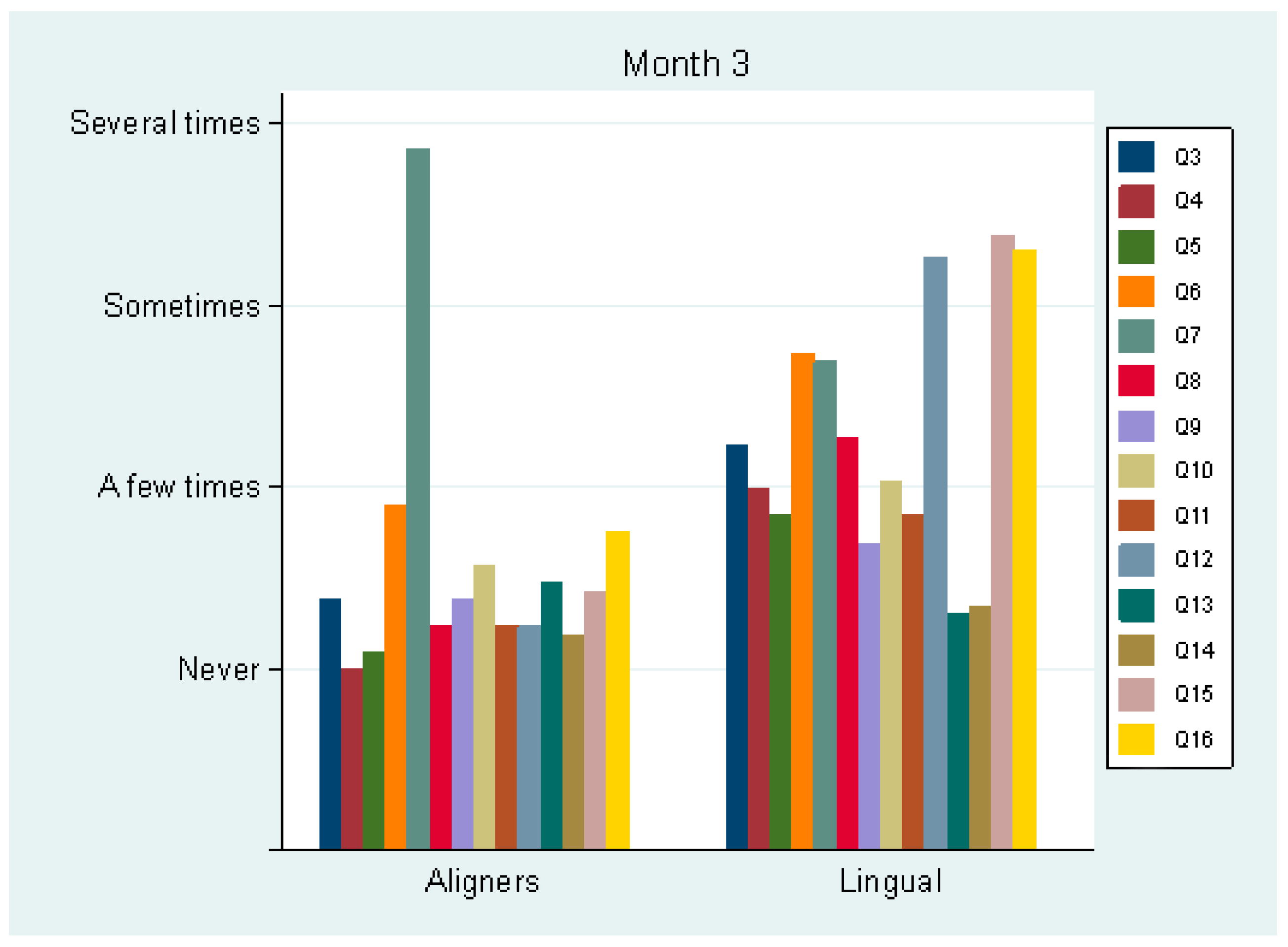
At month 3 (T3), pain perception was not statistically significant (p = 0.240) between the aligner (mean score 2.5 ± 2.1) and the lingual group (3.0 ± 0.7). Only one patient took analgesics in each group (in the aligner group, this was the patient with the least adherence to wearing the appliances). The use of analgesics was more frequent at the beginning of the treatment compared to the third month. Regarding Q3–16, statistically significant differences between the groups were detected in all questions (p < 0.005), except Q13 and Q14, i.e., sores on cheeks/lips were equal between the groups (“a few times”, 25% and 27%, respectively) (Figure 2). All but one statistically significant difference favored the aligner group. The two groups differed in total Q3–16 score (transformed to a 0–100 scale, 0, best score; 100, worst score): 13.9 (±8.6) for the aligner group and 32.1 (±8.7) for the lingual group (p < 0.001). Therefore, it was considered more difficult to speak, swallow, open the mouth and sleep in the lingual group. Additionally, these patients reported higher scores in avoiding foods, change in the sense of taste, sore tongue and food debris under the appliance.
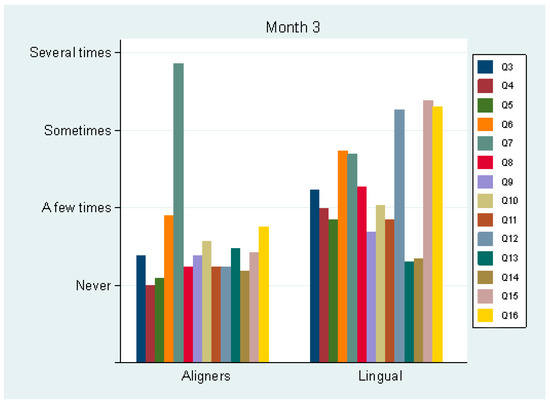
Figure 2.
Average values of answers to questions 3–16 by group, after 3 months.
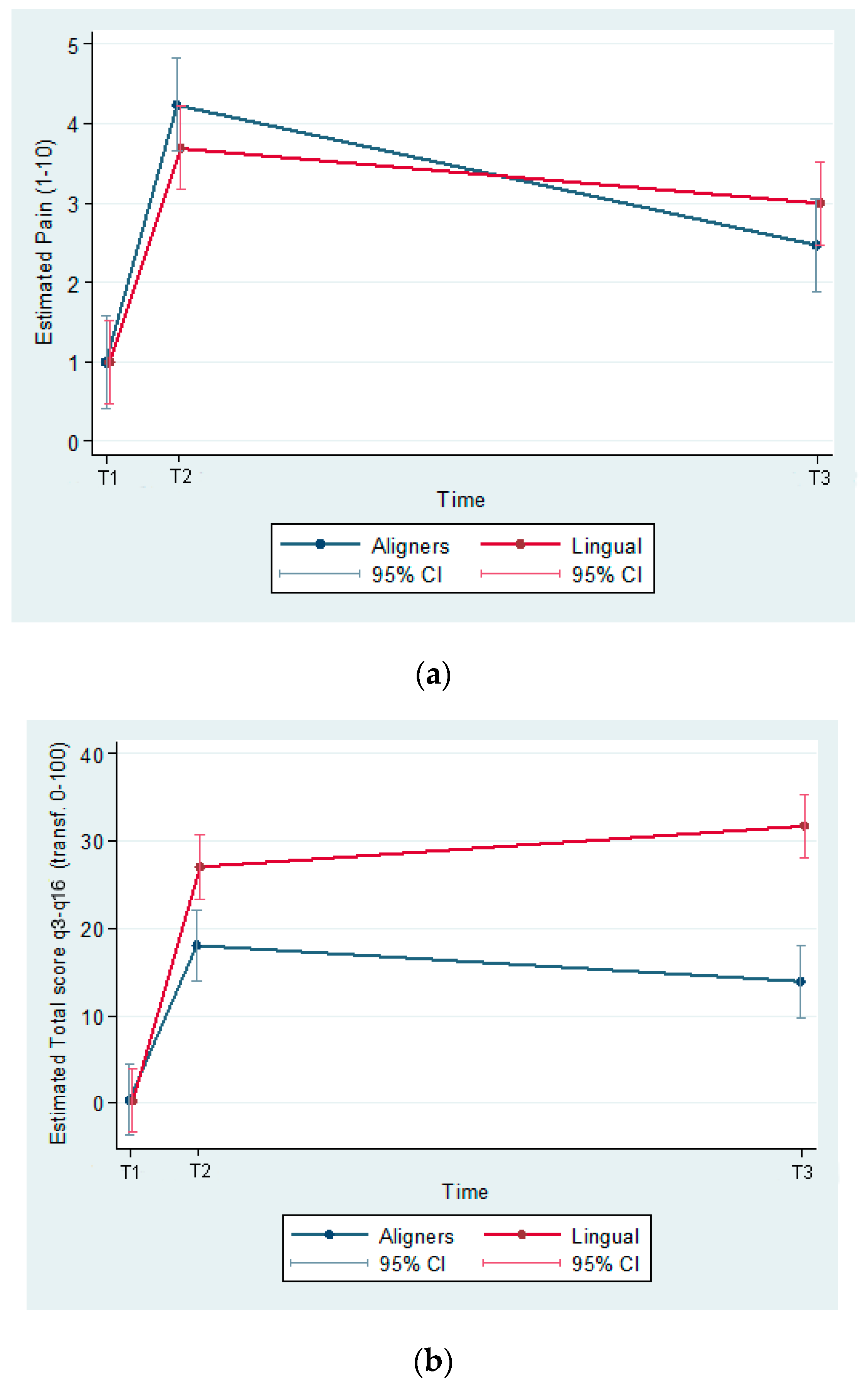
The predicted values of pain perception and total score for Q3–16 (transformed to a 0–100 scale, 0, best score; 100, worst score) were estimated from a model including group effects, time effects and their interaction.
The estimated differences (95% C.I.) between groups (Aligners–Lingual) at T1 was 9.1 (3.4, 14.7); p = 0.002 and at T3 18.2 (12.6, 23.9) (p ≤ 0.001). Between T2 and T3, the HRQoL score increased non-significantly in the lingual group (p = 0.152) and decreased non-significantly (p = 0.075) in the aligners group (Figure 3a,b).
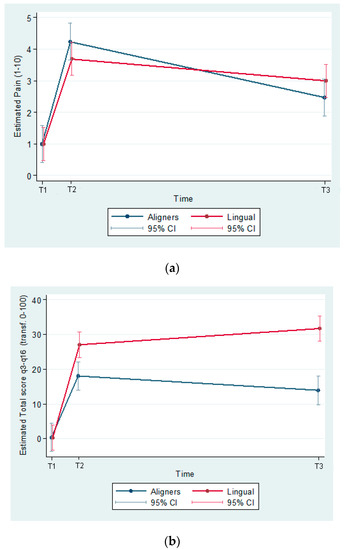
Figure 3.
(a) Predicted pain (1–10) by group and time (T1, baseline; T2, the first day following appliance insertion; T3, after 3 months). (b) Predicted total score Q3–16 (transf. 0–100) by group and time.
3.3. Speech Evaluation
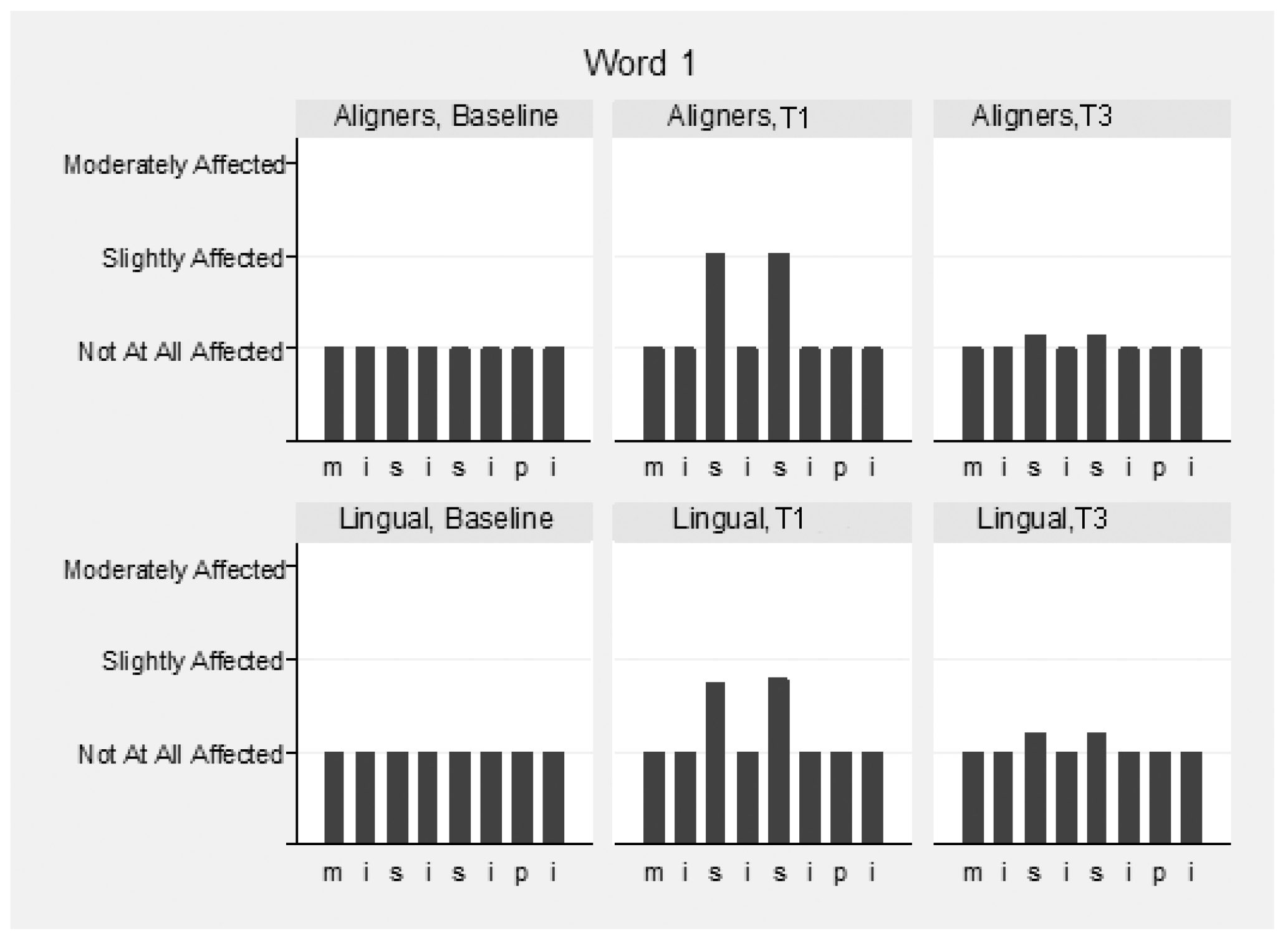
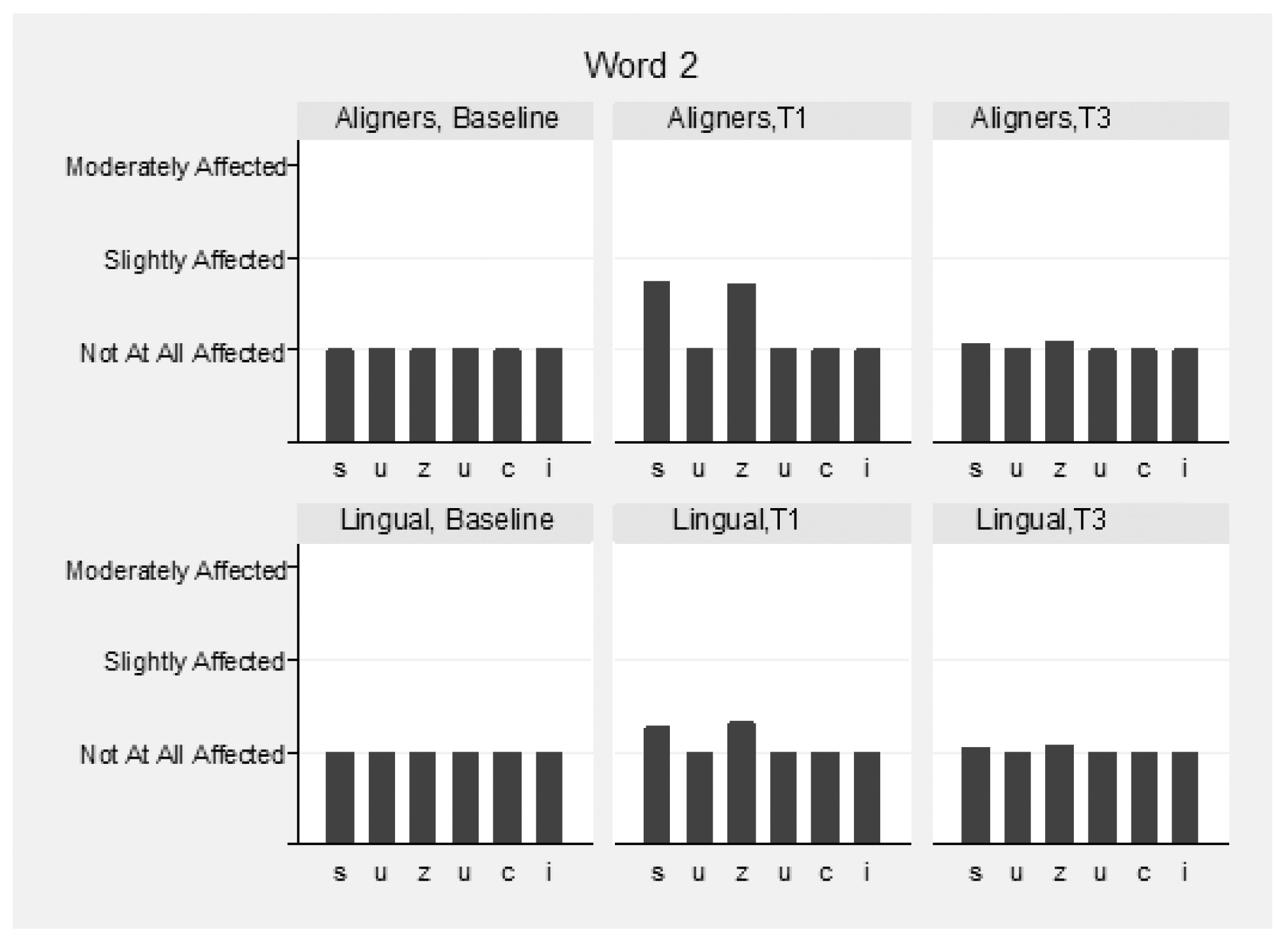
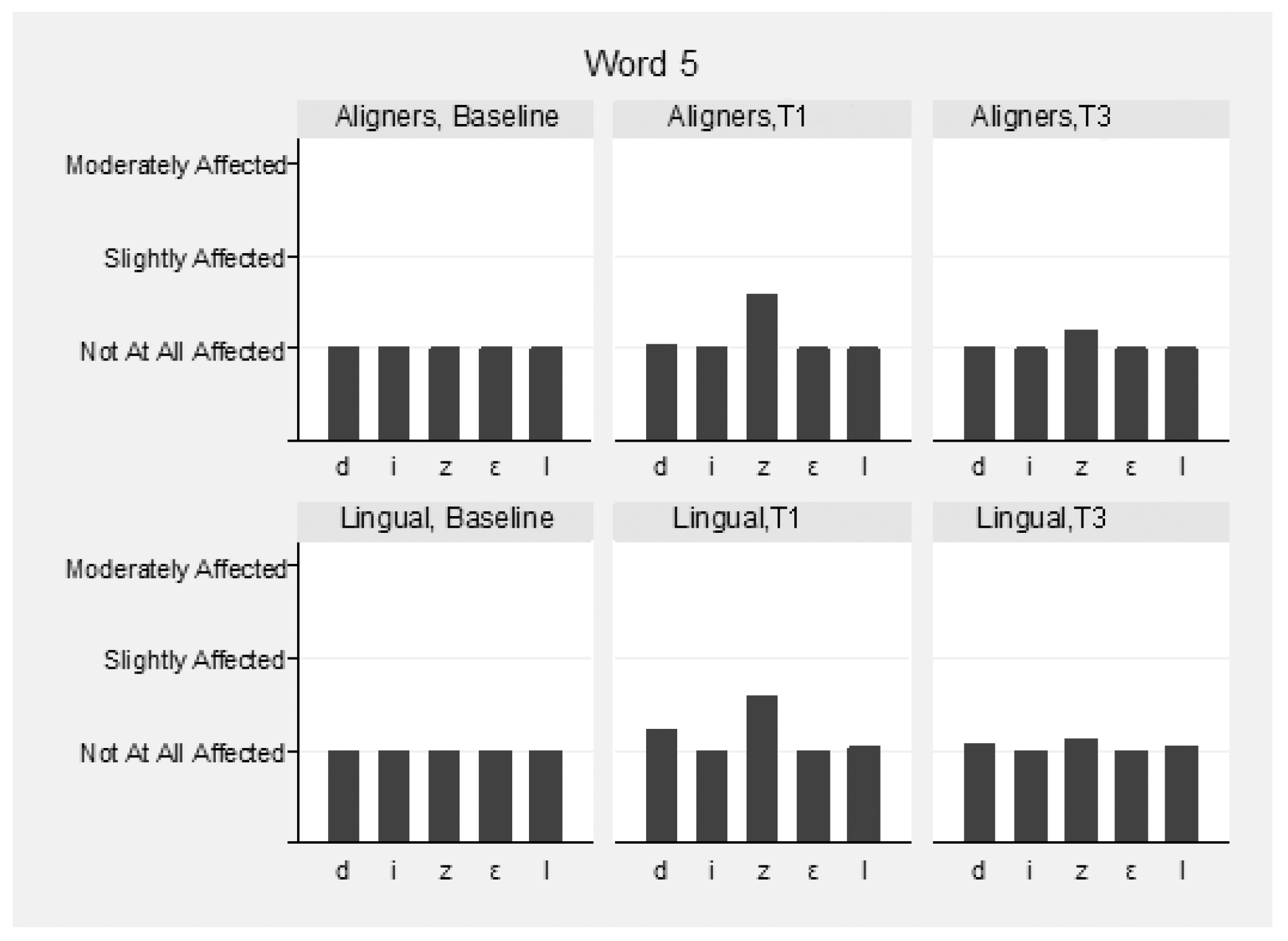
The speech samples were analyzed before (T0) and immediately following appliance insertion (T1), as well as after 3 months (T3) (Supplementary Table S2). Intra- and inter-examiner reliability for the speech evaluation were high and ranged between 0.976 and 0.983 and 0.911 and 0.932 between the three raters, respectively. Mean values of the three raters were used for the overall assessment of speech. Slight speech disturbances were detected in both groups immediately following appliance insertion, but this recovered in the following 3 months. The pronunciation of vowels was not hampered, although the consonants “s” and “z” were mostly affected in both groups (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). These two consonants were more affected in the aligner group at T1, to a statistically significant degree. The remaining consonants were not affected.
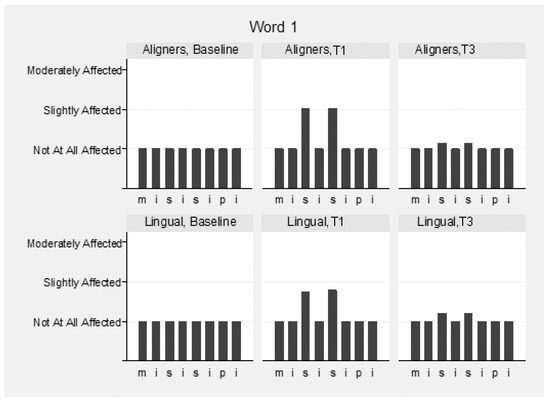
Figure 4.
Speech articulation (1st word: “Mississippi”) by group and time (T1, baseline; T2, immediately following appliance insertion; and T3, after 3 months).
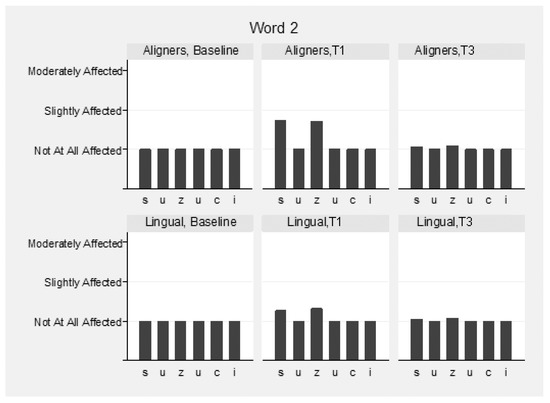
Figure 5.
Speech articulation (2nd word: “Suzuki”) by group and time.
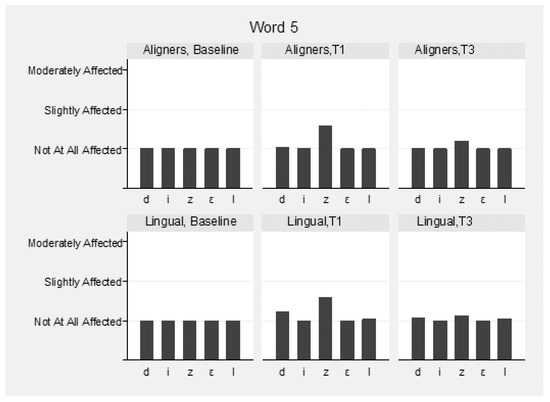
Figure 6.
Speech articulation (5th word: “Diesel”) by group and time.
More specifically, for the word “Mississippi”, the differences at T1 in the first “s” were marginally not statistically significant (p = 0.056), and in the second, “s” were marginally statistically significant (p = 0.043) between the groups, favoring lingual appliances. In the word “Suzuki”, the differences at T1 in “s” and “z” were statistically significant (p = 0.004 and p = 0.015, respectively), favoring lingual appliances. In the word “Diesel”, the differences in “z” were not statistically significant between the groups at all times (p = 0.790). The pronunciation of words “Patala” and “Emma” was not altered.
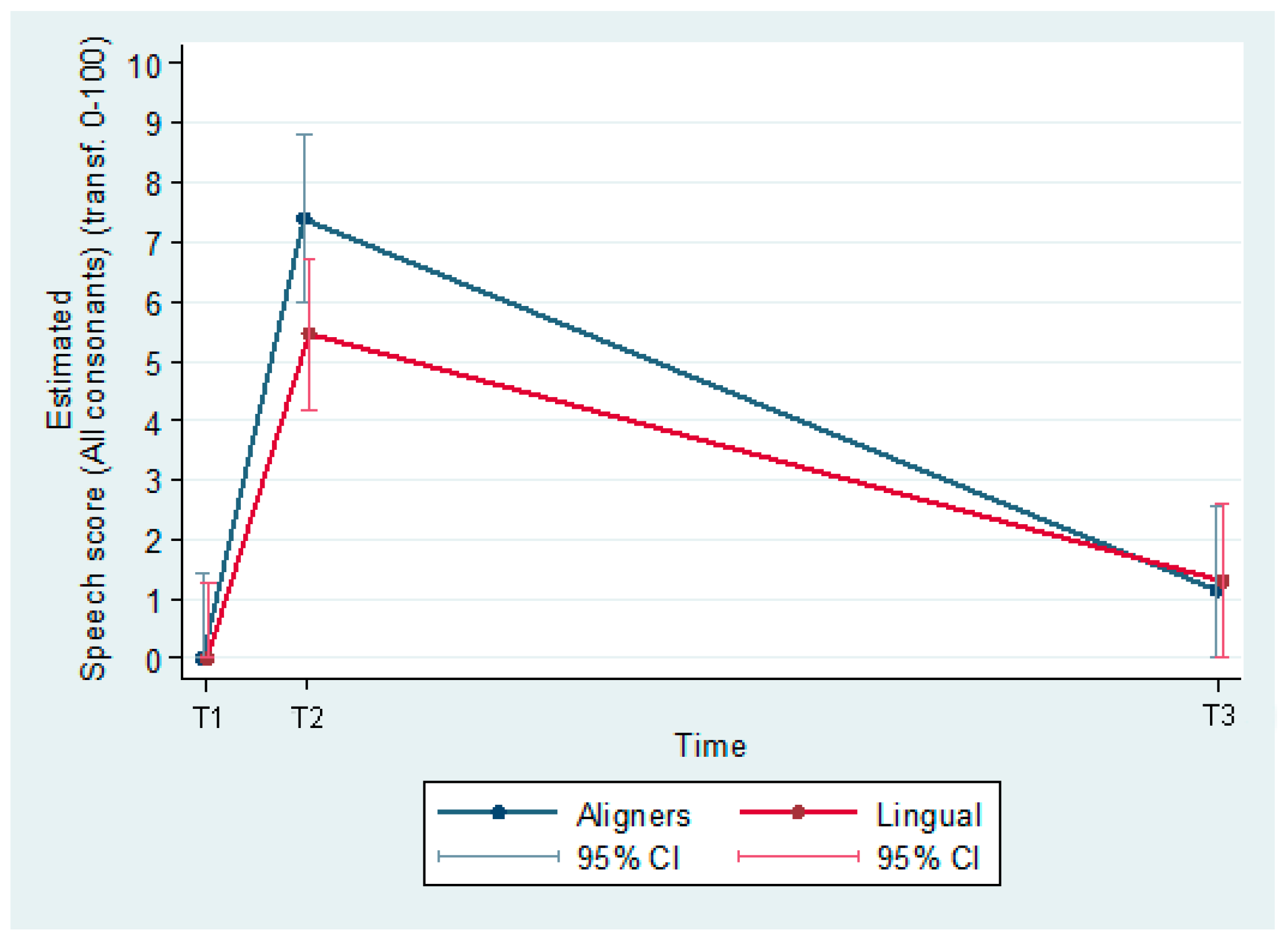
The predicted values of speech (transformed to a 0–100 scale, 0, best score; 100, worst score) were estimated from a model including group effects, time effects and their interaction. The estimated difference (95% C.I.) between groups (Aligners–Lingual) at T1 was −1.9 (−3.9, −0.0; p = 0.047), and at T3, 0.2 (−1.8, 2.1; p ≤ 0.872) (Figure 7).
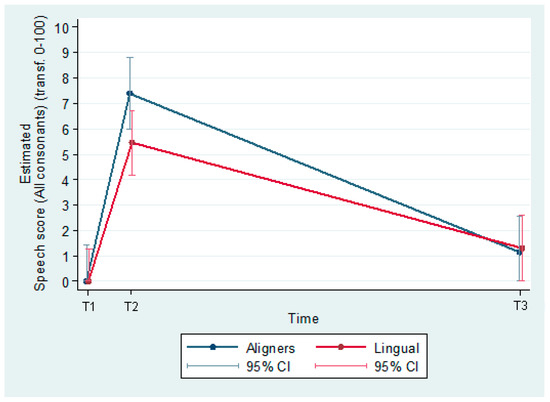
Figure 7.
Speech articulation.
4. Discussion
This prospective study investigated the oral impacts of aligners vs. SLLA, as experienced by the patients, as well as the speech disturbances, evaluated by professionals, during the first 3 months of orthodontic treatment. The present study may assist patients and clinicians in choosing the most appropriate treatment modality in relation to HRQoL and speech parameters.
The sample was homogenous, with similar demographic and cephalometric data, as well as orthodontic treatment needs. Thus, the possible tongue restrictions from the lingual appliances due to differences in SNA and SNB angles could be excluded [27]. Most publications evaluating aligners report on mild/moderate cases; however, most patients of the present sample were in moderate/great need of orthodontic treatment (Table 3). Minor differences between sexes were evident in the initial cephalometric measurements, i.e., male patients had higher Z-angle values, as expected due to chin prominence (sexual dimorphism). Non-growing patients were chosen for the study because they represent the majority of patients currently receiving aligner or lingual treatment worldwide [28]. In addition, they may provide better compliance in appliance wear, further reducing possible bias due to incompliance. Six patients reported sleep disorders at T0; however, it is already known that anxious individuals prefer “invisible” orthodontic appliances [29].
Pain levels and the consumption of analgesics were similar between the two groups. The use of analgesics was more frequent at the beginning of the treatment (10% of each group took analgesics at day 1). At T3, only one patient took analgesics in each group (in the aligner group, this was the patient with the least adherence to wearing the aligners). A more pronounced decrease in pain perception was evident in the aligner group between T1 and T3, i.e., in the aligner group, the reduction in pain was faster compared to the group with lingual appliances, in which the pain remained at moderate levels, even 3 months later. However, this finding did not reach statistical significance (Figure 3a). Wu et al. did not find any significant differences in pain levels or the intake of analgesics among patients treated with lingual or labial appliances for a period of three months [30]. However, a recent prospective study with a shorter observation period (2 weeks) demonstrated that lingual appliances were associated with more severe pain, greater analgesic consumption, and the most difficult and longest recovery, in comparison with labial appliances or aligners [17]. Furthermore, a recent systematic review concluded that the level of pain was significantly higher, during the first two weeks of treatment, in patients treated with lingual braces compared to patients with buccal brackets [31]. This difference may be explained by the fact that the archwire–bracket type combination in this study was 0.014-inch NiTi in Incognito brackets [17], whereas in our study, a 0.012-inch NiTi wire was used in a self-ligating bracket throughout the observation period. Additionally, patients treated with labial self-ligating appliances exhibited lower visual analog scale scores than subjects treated using conventional labial appliances [32,33]. It should also be considered that pain during orthodontic treatment is associated with several factors such as the patient’s age, individual psychological susceptibility, personal expectation of treatment outcome and the duration of orthodontic treatment, with subjects under orthodontic treatment for a longer time being more intolerant and with higher expectations of completing the treatment [17,34]. Patients well-informed about the discomfort that may occur during orthodontic treatment and patients who have more positive attitudes present lower levels of pain during treatment [24,35].
The present study demonstrated significantly worse scores in the patients wearing SLLA for discomfort in swallowing, mouth opening, food remaining in the oral cavity and tongue injuries, even three months after the beginning of treatment. The above results are similar to the findings of two other prospective studies which demonstrated that lingual appliances were associated with the greatest oral and general dysfunction [17,36]. However, after the initial discomfort period, these hindrances persisted only in a small percentage of lingual orthodontic patients [36]. In the above-mentioned studies, the groups and the observation periods were not the same, nor were the types of lingual appliances; thus, the results are not directly comparable. According to a systematic review, eating difficulties were more commonly reported in patients with lingual appliances than in patients with buccal appliances, and mainly during the first month of insertion [31].
An interesting finding, not present in the orthodontic literature, was that aligner patients presented with subtle injuries on the lip and cheeks immediately after the initiation of treatment, although these disturbances ceased at the 3-month re-evaluation. This finding may be associated with the use of power ridges for torque (power ridges were used in 57% of the present aligner sample) or precision cuts for elastics (in 9.5% of aligner patients, precision cuts were used), or in some cases, with sharp or rough edges of the aligners that were not noted at the insertion of the appliances. To date, most studies on aligners have rarely provided data on the presence of power ridges, precision cuts and attachments used; therefore, the comparability between such studies is rendered difficult [37]. Furthermore, sleeping disturbances were more common in the present group of lingual appliances at T0, a finding in agreement with the prospective study of Shalish et al. [17]. Sleeping disturbances persisted for up to 3 months in our study; however, results did not differ between the two groups. Similar sleep patterns were reported between patients treated with lingual and buccal appliances [30].
This is the first study to compare speech disturbances between self-ligating lingual appliances and aligners for a medium-term time period. Both groups presented minor speech impairment, which recovered after three months.
It has been reported that both aligners and lingual appliances induce alterations in speech, because the contact area of the tongue shifts based on the presence of an unfamiliar appliance on the lingual surface [36,38,39]. In the aligner group of the present study, the impairment in some consonants (“s” and “z”) was slightly more pronounced; however, this difference was clinically non-significant. The “s” sound was most affected, probably because the alveolar fricative is sensitive to morphological changes in the maxillary incisors [40]. The less pronounced impairments of “s” and “z” with self-ligating lingual appliances used in this study may be associated with the smooth spring clips. The possible effect of different clips/designs of lingual appliances on speech should be further investigated.
The questionnaire used in the present study included a subjective question regarding self-speech assessment. Interestingly, the patients felt that their speech was more strongly affected, compared to the alterations identified by the professionals. Even at T3, 32% of the present sample reported subjective speech difficulties, more often in the lingual appliance group. A recent study reported speech impairment of different degrees of severity in half of a patient sample treated with aligners [39]. Moreover, one-quarter of the lingual patients presented speech difficulties even after three months [36], and they faced more speech difficulties compared to patients treated with buccal appliances [33].
The present study presents certain limitations. A randomized clinical trial may have provided stronger evidence; however, it was not feasible, because most patients had already developed a strong opinion regarding which aesthetic appliance they preferred, and the patient’s decision should be respected.
The questionnaire used in the present study was validated and used extensively in previous studies; however, the questions about eating/swallowing/food debris under the appliance are relevant only for the patients with fixed appliances. The aligners can be removed, and the patients are not supposed to wear them during eating.
Even though most aligner patients reported wearing the appliances for 22 h, two of them exhibited reduced appliance wear, and were advised to increase the period to 2 weeks.
Results regarding speech disturbances may differ between trials, because of the altered pronunciation among different languages [36]. This study utilized subjective and semi-subjective analyses. It would be interesting to perform objective acoustic analyses via digital sonography, which may be the scope of a follow-up study [24,41].
Finally, a continuous speech sample represents a valid alternative for determining speech intelligibility. However, the results of such a study would have been of national interest only. Single Indo-European words said with three repetitions were chosen in the present study in order not to exclude patients due to ethnicity.
5. Conclusions
Different kinds of disturbances in the oral cavity were detected in both groups. These disturbances were more prominent in the patients with lingual appliances, even three months after the initiation of treatment.
No differences in pain intensity were found between the two groups the day after or three months after treatment initiation; however, in the group of self-ligating lingual appliances, the level of pain decreased at a slower rate during this three-month period.
Most patients did not take analgesics the day after or three months after treatment initiation.
Speech disturbances were reported immediately after appliance insertion in both groups, although slightly more pronounced in the aligner group. These disturbances improved after three months.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/10.3390/app112110074/s1, Table S1: Estimated differences by group and time for the HRQoL questionnaires, Table S2: Estimated differences by group and time for the speech samples.
Author Contributions
G.G.A.: formal analysis, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, review and editing. P.K.: investigation and writing—review and editing. G.V.: formal analysis, investigation, and writing—original draft, review and editing. A.Z.: formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing. I.S.: conceptualization, methodology, project administration, formal analysis, methodology, investigation, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received the Align Technology Global Funding Awarded Towards Advancing Orthodontic and Dental Research (2017). The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Dentistry, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece (339/15.5.2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all the subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available (General Data Protection Regulation, EU), but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Health-Related Quality of Life Questionnaire
It’s important for us to know how the orthodontic appliance has affected your daily life in order to improve the quality of care. Please choose the number that corresponds to your assessment over the past 24 h.
- Rate the worst pain you have felt during the past 24 h on a scale of 1 to 10 (1—not at all, 10—very much).
- Have you taken any medication to relieve pain today? (0 = no, 1 = yes).
For the following questions, please use this rating:
1 = no instances, 2 = few instances, 3 = some instances, 4 = several instances, 5 = numerous instances.
- 3.
- Has it been difficult to speak today?
- 4.
- Has it been difficult to swallow today?
- 5.
- Has it been difficult to open your mouth today?
- 6.
- Were there any foods you could not eat today?
- 7.
- Have you enjoyed your food today?
- 8.
- Have you noticed a change in your sense of taste today?
- 9.
- Was it difficult to sleep last night?
- 10.
- Does the appliance disturb you at work or when studying today?
- 11.
- Has it been difficult to continue your daily activities today?
- 12.
- Do you have sores on your tongue?
- 13.
- Do you have sores on your cheeks?
- 14.
- Do you have sores on your lip?
- 15.
- Have you had a bad taste or bad smell in your mouth today?
- 16.
- Has there been any food debris under the appliance today?
Please report any complaints you may have.
References
- Rosvall, M.D.; Fields, H.W.; Ziuchkovski, J.; Rosenstiel, S.F.; Johnston, W.M. Attractiveness, acceptability, and value of orthodontic appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, e1–e12; discussion 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuchkovski, J.P.; Fields, H.W.; Johnston, W.M.; Lindsey, D.T. Assessment of perceived orthodontic appliance attractiveness. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, S68–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alansari, R.A. Youth perception of different orthodontic appliances. Patient Prefer. Adher. 2020, 14, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachêco-Pereira, C.; Pereira, J.R.; Dick, B.D.; Perez, A.; Flores-Mir, C. Factors associated with patient and parent satisfaction after orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 148, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoting, L.I.; Yin, T.; Yangxi, C. Interventions for pain during fixed orthodontic appliance therapy. A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, R.G.; Knapman, Y.M. Attitudes to orthodontic treatment. Br. J. Orthod. 1985, 12, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V. Non-Completion of Orthodontic Treatment: A Study of Patient and Parental Factors Contributing to Discontinuation in the Hospital Service and Specialist Practice. Master’s Thesis, University of Wales, Wales, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lew, K.K. Attitudes and perceptions of adults towards orthodontic treatment in an Asian community. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1993, 21, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, D.; Jokovic, A. Using subjective oral health status indicators to screen for dental care needs in older adults. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1996, 24, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Kay, L.; Fox, D.; Mandall, N. Assessing oral health outcomes for orthodontics--measuring health status and quality of life. Community Dent. Health 1998, 15, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, S.J.; Hunt, N.P. Quality of life and its importance in orthodontics. J. Orthod. 2001, 28, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokovic, A.; Locker, D.; Stephens, M.; Kenny, D.; Tompson, B.; Guyatt, G. Validity and reliability of a questionnaire for measuring child oral-health-related quality of life. J. Dent. Res. 2002, 81, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaushu, G.; Becker, A.; Zeltser, R.; Branski, S.; Chaushu, S. Patients’ perceptions of recovery after exposure of impacted teeth with a closed-eruption technique. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 125, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaushu, S.; Becker, A.; Zeltser, R.; Vasker, N.; Chaushu, G. Patients’ perceptions of recovery after surgical exposure of impacted maxillary teeth treated with an open-eruption surgical-orthodontic technique. Eur. J. Orthod. 2004, 26, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaushu, S.; Becker, A.; Zeltser, R.; Branski, S.; Vasker, N.; Chaushu, G. Patients perception of recovery after exposure of impacted teeth: A comparison of closed- versus open-eruption techniques. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaushu, G.; Becker, A.; Zeltser, R.; Vasker, N.; Branski, S.; Chaushu, S. Patients’ perceptions of recovery after routine extraction of healthy premolars. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2007, 131, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalish, M.; Cooper-Kazaz, R.; Ivgi, I.; Canetti, L.; Tsur, B.; Bachar, E.; Chaushu, S. Adult patients’ adjustability to orthodontic appliances. Part I: A comparison between Labial, Lingual, and Invisalign™. Eur. J. Orthod. 2012, 34, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bräscher, A.K.; Zuran, D.; Feldmann, R.E., Jr.; Benrath, J. Patient survey on Invisalign® treatment comparing the SmartTrack® material to the previously used aligner material. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2016, 77, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyama, K.; Honjo, T.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuoka, S.; Deguchi, T. Analysis of pain level in cases treated with Invisalign aligner: Comparison with fixed edgewise appliance therapy. Prog. Orthod. 2014, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, P.C.; Espinosa, D.G.; Mecenas, P.; Flores-Mir, C.; Normando, D. Pain level between clear aligners and fixed appliances: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, X.; Huo, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Z. Effect of clear aligners on oral health-related quality of life: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2017, 20, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Ortan, Y.Ö.; Gorgun, Ö.; Panza, C.; Scuzzo, G.; Siciliani, G. Changes in the oral environment after placement of lingual and labial orthodontic appliances. Prog. Orthod. 2013, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ata-Ali, F.; Ata-Ali, J.; Ferrer-Molina, M.; Cobo, T.; De Carlos, F.; Cobo, J. Adverse effects of lingual and buccal orthodontic techniques: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, G.M.; Zentner, A.; Klages, U.; Sergl, H.G. Relationship between patient discomfort, appliance acceptance and compliance in orthodontic therapy. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2000, 61, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohoff, A.; Stamm, T.; Goder, G.; Sauerland, C.; Ehmer, U.; Seifert, E. Comparison of 3 bonded lingual appliances by auditive analysis and subjective assessment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 124, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, P.H.; Shaw, W.C. The development of an index of orthodontic treatment priority. Eur. J. Orthod. 1989, 11, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiechmann, D.; Gerß, J.; Stamm, T.; Hohoff, A. Prediction of oral discomfort and dysfunction in lingual orthodontics: A preliminary report. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Mousoulea, S.; Gkantidis, N.; Kloukos, D. Clinical effectiveness of Invisalign® orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper-Kazaz, R.; Ivgi, I.; Canetti, L.; Bachar, E.; Tsur, B.; Chaushu, S.; Shalish, M. The impact of personality on adult patients’ adjustability to orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.K.; McGrath, C.; Wong, R.W.; Wiechmann, D.; Rabie, A.B. A comparison of pain experienced by patients treated with labial and lingual orthodontic appliances. Eur. J. Orthod. 2010, 32, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diddige, R.; Negi, G.; Sai Kiran, K.V.; Chitra, P. Comparison of pain levels in patients treated with 3 different orthodontic appliances—A randomized trial. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, A.M.; Petrie, A.; Cunningham, S.J.; McKnight, M. Prospective randomized clinical trial to compare pain levels associated with 2 orthodontic fixed bracket systems. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 136, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Gölz, L.; Jäger, A.; Eliades, T.; Bourauel, C. Lingual vs. labial fixed orthodontic appliances: Systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment effects. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 124, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergl, H.G.; Klages, U.; Zentner, A. Pain and discomfort during orthodontic treatment: Causative factors and effects on compliance. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1998, 114, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, A.; Hoogstraten, J.; Prahl-Andersen, B. The theory of reasoned action and patient compliance during orthodontic treatment. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 2005, 33, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caniklioglu, C.; Oztürk, Y. Patient discomfort: A comparison between lingual and labial fixed appliances. Angle Orthod. 2005, 75, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, T.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Ireland, A.J. The use of attachments in aligner treatment: Analyzing the “innovation” of expanding the use of acid etching-mediated bonding of composites to enamel and its consequences. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 158, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, P.M.; Cannito, M.F.; Goates, L.J.; Solomos, L.F.; Alexander, C.M. Patient responses to lingual appliances. J. Clin. Orthod. 1986, 20, 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- Nedwed, V.; Miethke, R.R. Motivation, acceptance and problems of Invisalign patients. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2005, 66, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runte, C.; Lawerino, M.; Dirksen, D.; Bollmann, F.; Lamprecht-Dinnesen, A.; Seifert, E. The influence of maxillary central incisor position in complete dentures on/s/sound production. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohoff, A.; Seifert, E.; Fillion, D.; Stamm, T.; Heinecke, A.; Ehmer, U. Speech performance in lingual orthodontic patients measured by sonagraphy and auditive analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 123, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).