An Intelligent Multicriteria Model for Diagnosing Dementia in People Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AIDS/HIV and Cognitive Dementia Considerations
2.2. Information Technologies Used in the Proposed Model
2.2.1. Fundamentals of the “Random Forest” Algorithm
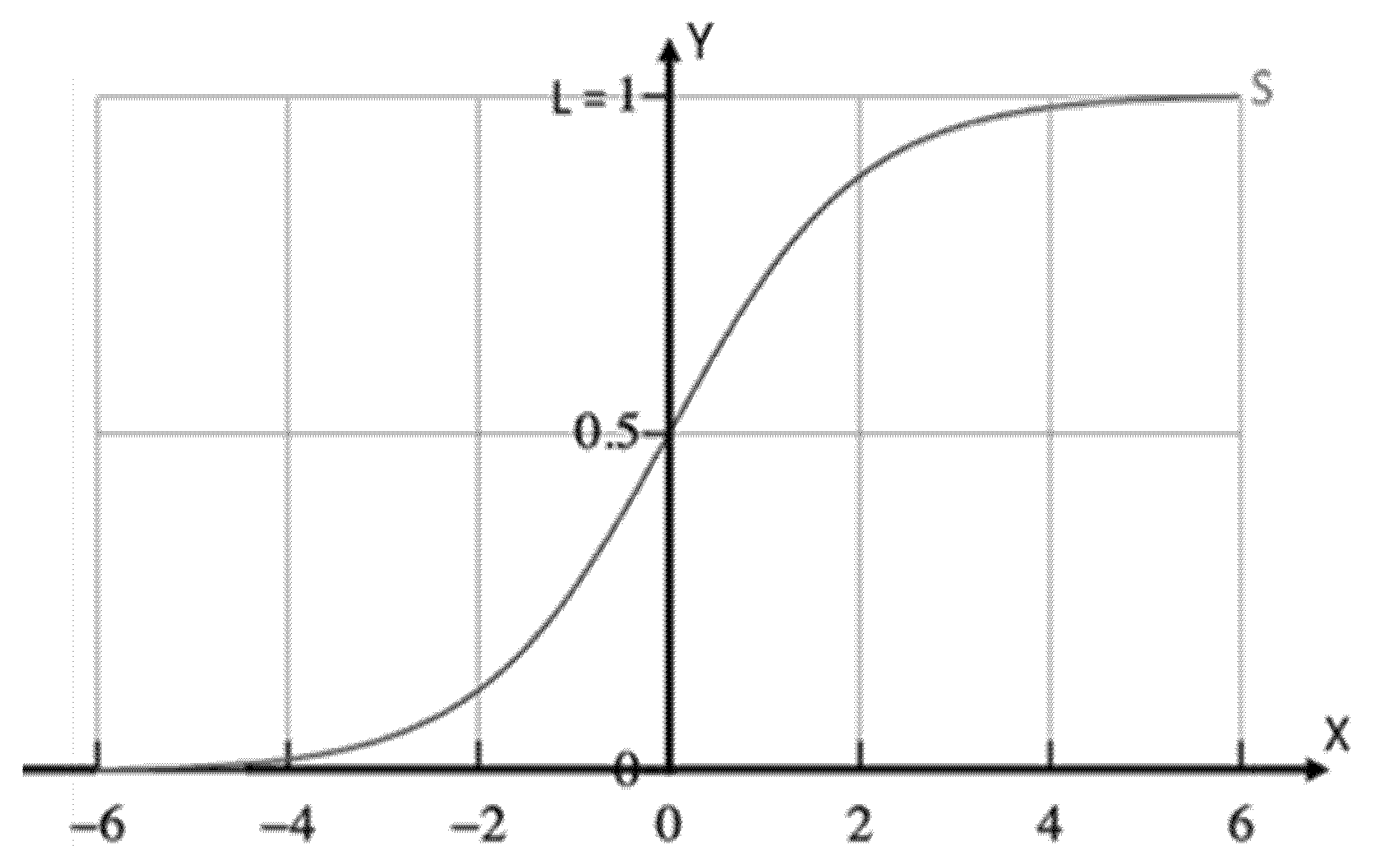
2.2.2. Fundamentals of the “Logistic Regression” Algorithm
- = value of the midpoint of the sigmoid curve,
- L = maximum value of the curve,
- k = the logistic growth rate or slope of the curve.
- if P(Y = 1) > 0.5, then Y = 1 is classified.
- if P(Y = 1) < 0.5, then Y = 0 is classified.
- Binomial or binary:
- Here, it addresses situations where the observed result for a dependent variable can have only two possible types, “0” or “1” (“sick” or “healthy”).
- They are usually referred to as “Logistic Regression”.
- Multinomial:
- This is an extension of a simple linear regression, used when we want to predict the value of a variable based on the value of two or more other variables.
- Alternatively, when we want to predict the variable called a dependent variable (or sometimes an outcome, objective, or criterion variable).
- Ordinal:
- This works with dependent and ordered variables.
- It is usually called “ordinal regression”.
- It is used to predict an ordinal dependent variable, given the independent variables [48].
2.2.3. Fundamentals of the “Naïve Bayes” Algorithm
2.2.4. Fundamentals of the Verbal Decision Analysis
- Comparison of two assessments on a verbal scale by two criteria.
- Assignment of multicriteria alternatives to decision classes.
- Comparative verbal evaluation of alternatives according to different criteria.
2.3. Proposed Hybrid Model Used in this Study
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shen, T.; Wu, P.; Zuo, C. Radiomics features as predictors to distinguish fast and slow progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Ren, H.X.; Li, H.J. Early prediction of putamen imaging features in HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment syndrome. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacktor, N. Changing clinical phenotypes of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. J. Neurovirology 2018, 24, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Villar, A.R.S.; Gutierrez, F.; Mirall, E.S.C. HIV as a chronic disease: Evaluation and management of non-AIDS defining, Management of HIV-Associated Disease in HIV. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Saylor, D.; Dickens, A.M.; Sacktor, N.; Haughey, N.; Slusher, B.; Pletnikov, M.; McArthur, J.C. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder—pathogenesis and prospects for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, S.; Gajghate, S.; Winfield, M.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Persidsky, Y. Combination of HIV-1 and Diabetes Enhances Blood Brain Barrier Injury via Effects on Brain Endothelium and Pericytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, S.A. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and cognitive computing: What do these terms mean, and how will they impact health care? J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2358–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanini, I. Hybrid Approaches of Verbal Decision Analysis Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Fortaleza, Fortaleza, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hjalmarsson, V. Machine learning and Multi-criteria decision analysis in healthcare: A comparison of machine learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Mid Sweden University, Sundsvall, Sweden, 27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro, A.K.A.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Dantas Pinheiro, M.C.; Tamanini, I. Towards the applied hybrid model in decision making: A neuropsychological diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease study case. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2011, 4, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquezl, M.Y.L.; Peñafiel, L.A.B.; Muñoz, S.X.S.; Martinez, M.A.Q. A framework for selecting machine learning models using TOPSIS. In Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Software and Systems Engineering, Proceedings of the AHFE 2020 Virtual Conferences on Software and Systems Engineering, and Artificial Intelligence and Social Computing, Florida, FL, USA, 16–20 July 2020; Springer Nature: Basingstoke, UK, 2020; Volume 1213, p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Mohdiwale, S.; Sahu, M.; Sinha, G.R.; Bajaj, V. Automated cognitive workload assessment using logical teaching learning-based optimization and promethee multi-criteria decision making approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13629–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, A.; Juneja, S.; Kaur, S.; Kumar, V. Predicting diabetes mellitus with machine learning techniques using multi-criteria decision making. Int. J. Inf. Retr. Res. 2021, 11, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.C.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Pinheiro, M.C.D.; Cavalcante, T.P. Towards the Applied Hybrid Model In Decision Making: Support the Early Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes. In International Conference on Information Computing and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7473, pp. 648–655. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, P.; Tamanini, I.; Pinheiro, M.C.D.; Albuquerque, V.H.C. Evaluation of the Alzheimer’s disease clinical stages under the optics of hybrid approaches in Verbal decision analysis. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.; Pinheiro, P.; Poggi, M. A more human-like portfolio optimization approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 256, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, S.N. Vulnerability to HIV/AIDS in the Elderly: A Comparative Study. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Paraiba, João Pessoa, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UNAIDS. Joint united nations program on HIV/AIDS. Communities at the centre: Defending rights, breaking barriers, reaching people with HIV services. Glob. AIDS 2019. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2019-global-AIDS-update_en.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the lancet commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, D.M.V.d.; Possas, C.C. Updates on cortical dementia in HIV-infected individuals. In Humanae: Controversial Issues in The Contemporary World, Recife, PE; 2018; Volume 12, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://revistas.esuda.edu.br/index.php/humanae/article/view/621/193 (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Antinori, A.; Arendt, G.; Becker, J.T.; Brew, B.J.; Byrd, D.A.; Cherner, M.; Clifford, D.B.; Cinque, P.; Epstein, L.G.; Goodkin, K.; et al. Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology 2007, 69, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, B.; Benton, T.; Cruess, D.E.; Evans, D.L. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of HIV infection and AIDS. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005, 30, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, L.M.; Paul, R.H.; Heaps-Woodruff, J.M.; Chang, J.Y.; Ortega, M.; Margolin, Z.; Usher, C.; Basco, B.; Cooley, S.; Ances, B.M. The effect of central nervous system penetration effectiveness of highly active antiretroviral therapy on neuropsychological performance and neuroimaging in HIV infected individuals. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brew, B.J.; Rosenblum, M.; Price, R.W. AIDS dementia complex and primary HIV brain infection. J. Neuroimmunol. 1988, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, B.A.; Jordan, B.D.; Price, R.W. AIDS dementia complex I: Clinical features. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, R.; Fellows, L.; Ances, B.M.; Collins, D.L. Association of brain structure changes and cognitive function with combination antiretroviral therapy in HIV-positive individuals. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, S.M. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis in the HIV infection and compartmentalization of HIV in the central nervous system. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2015, 73, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, J.; Robertson, K.R.; Winston, A. Could antiretroviral neurotoxicity play a role in the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment in treated HIV disease? AIDS 2015, 29, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simioni, S.; Cavassini, M.; Annoni, J.-M.; Abraham, A.R.; Bourquin, I.; Schiffer, V.; Calmy, A.; Chave, J.-P.; Giacobini, E.; Hirschel, B.; et al. Cognitive dysfunction in HIV patients despite long-standing suppression of viremia. AIDS 2010, 24, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Working Group of the America Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Nomenclature and research case definitions for neurologic manifestations of human immunodeficiency virus type 1(HIV-1) infection. Neurology 1991, 41, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, G.P.; Domínguez, C.I.; Rodríguez, V.G.F.; Dansilio, S.; Presentado, J.C.M. Trastornos neurocognitivos en pacientes VIH positivos Datos preliminares de una cohorte prospectiva uruguaya. Rev. Médica Del Urug. 2019, 35, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.; Stone, C. Classification and regression trees. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2011, 1, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Scornet, E.; Biau, G.; Vert, J. Consistency of random forests. Ann. Stat. Inst. Math. Stat. 2015, 43, 1716–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beğenilmiş, E.; Uskudarli, S. Classification of organized behavior of sets of tweets using supervised learning methods. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics (WIMS ’18), Association for Computing Machinery, Novi Sad, Serbia, 25–27 June 2018; Volume 36, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A. Introduction to Logistic Regression. Average. Towards Data Science. 2019. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-logistic-regression-66248243c148 (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Andrade, E.; Portela, S.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Nunes, L.C.; Simão Filho, M.; Costa, W.S.; Pinheiro, M.C.D. A Protocol for the Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder Structured in Machine Learning and Verbal Decision Analysis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Ma, L.; Yu, C. Financial prediction: Application of logistic regression with factor analysis. In Proceedings of the 2008 4th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networks and Mobile Computing, Dalian, China, 12–14 October 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecka, A.; Kurdyś-Kujawska, A.; Zawadzka, D. Applying logistic regression models to assess household financial decisions regarding debt. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 176, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVT—Vidhya Analytics Team. Simple Guide to Logistic Regression in R and Python. 2015. Available online: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2015/11/beginners-guide-on-logistic-regression-in-r/ (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Andrew, N.G. CS229 Lecture Notes. Stanford University, 2012. Available online: http://cs229.stanford.edu/syllabus.html. (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Bacaer, N. Verhulst and the logistic equation. In A Short History of Mathematical Population Dynamics, 2011th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, G. To explain or predict? Stat. Sci. 2010, 25, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference, and prediction. Math. Intell. 2005, 27, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Introduction to the logistic regression model. Appl. Logist. Regression. 2000, 2, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motrenko, A.; Strijov, V.; Weber, G.W. Sample size determination for logistic regression. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2014, 255, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Özsu, M.T. Bayes classifier. In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund’s Research Binomial. Binomial Logistic Regression Using SPSS Statistics. 2018. Available online: https://statistics.laerd.com/spss-tutorials/binomial-logistic-regression-using-spss-statistics.php (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Krause, P.J. Learning Probabilistic Networks, Philips research laboratories. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 1999, 13, 321–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larichev, O.I.; Moshkovich, H.M. Verbal Decision Analysis for Unstructured Problems; Kluwer Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tamanini, I.; De Castro, A.K.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Pinheiro, M.C.D. Verbal decision analysis applied on the optimization of alzheimer’s disease diagnosis: A case study based on neuroimaging. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 696, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanini, I.; Pinheiro, P.R. Reducing incomparability in multicriteria decision analysis: An extension of the zapros methods. Pesqui. Oper. 2011, 31, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanini, I.; Pinheiro, P.R. Challenging the incomparability problem: An approach methodology based on zapros. In International Conference on Modelling, Computation and Optimization in Information Systems and Management Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Larichev, O. Ranking multicriteria alternatives: The method ZAPROS III. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 131, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkovich, H.; Mechitov, A.; Olson, D. Ordinal judgments in multiattribute decision analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 137, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanini, I.; Pinheiro, P.R.; dos Santos, C.N. A hybrid approach to verbal decision analysis and machine learning. In International Conference on Rough Sets and Current Trends in Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, A.K.A.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Pinheiro, M.C.D. A hybrid model for aiding in decision making for the neuropsychological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, RSCTC ’08. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Rough Sets and Current Trends in Computing, Akron, OH, USA, 23–25 October 2008; pp. 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabtah, F.; Peebles, D. A new machine learning model based on induction of rules for autism detection. Health Inform. J. 2019, 26, 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, L.I.C.C.; Pereira, M.L.D.; Fernandez, M.P.; Filho, F.M.V.; de Abreu, W.J.C.P.; Pinheiro, P.G.C.D. Application of data mining algorithms for dementia in people with HIV/AIDS. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couronné, R.; Probst, P.; Boulesteix, A.-L. Random forest versus logistic regression: A large-scale benchmark experiment. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demšar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, Č.; Hočevar, T.; Milutinovič, M.; Zupan, B. Orange: Data mining toolbox in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- CIF, 2001. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Available online: https://psychiatr.ru/download/1313?view=name=CF_18.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Tamanini, I.; Pinheiro, P.R.; Carvalho, A.L. Aranaú Software: A New Tool of the Verbal Decision Analysis; Technical Report; University of Fortaleza: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Angelim, R.C.D.M.; Brandão, B.M.G.D.M.; Marques, S.C.; de Oliveira, D.C.; Abrão, F.M.D.S. Representações e práticas de cuidado de profissionais de saúde às pessoas com HIV. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2019, 53, e03478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, R.; Alteri, C.; Perno, C.F.; Svicher, V.; Aquaro, S. The role of HIV infection in neurologic injury. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, B.A.; Amogne, W.; Gemechu, L. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder and HIV-associated myelopathy in a patient with a preserved CD4, but high viral load-a rarely reported phenomenon: A case report and literature review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Borrazzo, C.; Lazzaro, A.; Innocenti, G.P.; Celani, L.; Cavallari, E.M.; Pinacchio, C.; Santinelli, L.; Mastroianni, C.M.; dÉttorre, G. Problems in diagnosing asymptomatic neurosyphilis in HIV-positive patients: A retrospective study. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.S.; Leite-Aguiar, R.; da Silva, J.P.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; Savio, L.E.B. Purinergic signaling in infectious diseases of the central nervous system. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A. Neuroinfectious diseases. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, K.; Vera, J.H. Cognitive impairment in people living with HIV in the ART era: A review. Br. Med. Bull. 2018, 127, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masquillier, C.; Wouters, E.; Mortelmans, D.; Wyk, B.V. On the road to HIV/AIDS competence in the home: Building a health-friendly environment for people living with HIV/AIDS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3264–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyidogan, P.; Anderson, K.S. Current perspectives on HIV-1 antiretroviral drug resistance. Viruses 2014, 6, 4095–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, C.C.; Pieper, A.A.; Treisman, G.J. Safety considerations in drug treatment of depression in HIV-positive patients: An updated review. Drug Saf. 2011, 34, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, D. Cognitive function and depression in HIV-positive individuals and matched controls. In Proceedings of the Presented at the National AIDS Treatment Advocacy Project Conference, Glasgow, Scotland, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Waltl, I.; Kaufer, C.; Gerhauser, I.; Chhatbar, C.; Ghita, L.; Kalinke, U.; Loscher, W. Microglia have a protective role in the development of viral encephalitis-induced seizures and hippocampal damage. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Mukadam, N. Prevention, intervention and care for dementia: 2020 Lancet Commission report. Lancet 2020, 396, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipolito, R.L.; De Oliveira, D.C.; Da Costa, T.L.; Marques, S.C.; Pereira, E.R.; Gomes, A.M.T. Quality of life of people living with HIV/AIDS: Temporal, socio-demographic and perceived health relationship 1. Rev. Latino-Am. Enferm. 2017, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Question | Criteria | Alternatives | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild/Moderate | Severe | Complete | ||
| 1. Functions that allow volitional control of thought such as rumination, affection, sadness, fear, tension for a positive diagnosis for high risk of dementia. | A | 5 | 17 | 18 |
| B | 16 | 20 | 4 | |
| C | 15 | 16 | 9 | |
| 2. Difficulty in relating voluntarily with other people (functions of auditory and visual perception and hallucinations or illusions) for a high risk of developing dementia. | A | 5 | 16 | 19 |
| B | 18 | 19 | 3 | |
| C | 21 | 14 | 5 | |
| 3. I do not like to walk alone. | A | 3 | 18 | 19 |
| B | 7 | 17 | 16 | |
| C | 19 | 15 | 6 | |
| 4. Difficulty in reproducing an event or symbol (imitating or copying a drawing). | A | 7 | 16 | 17 |
| B | 3 | 15 | 22 | |
| C | 19 | 16 | 5 | |
| 5. Body functions related to protection against foreign substances, including infections, through specific immune responses (immune deficiencies, lymphadenitis). | A | 6 | 16 | 18 |
| B | 11 | 19 | 10 | |
| C | 4 | 9 | 27 | |
| 6. Specific memory functions for recording and storing information and retrieving it, when necessary, in the short and long term, recent and remote. | A | 6 | 14 | 20 |
| B | 14 | 18 | 8 | |
| C | 12 | 14 | 14 | |
| 7. General mental functions of the physiological and psychological mechanisms that encourage the individual to act persistently to satisfy needs. | A | 3 | 16 | 21 |
| B | 7 | 17 | 16 | |
| C | 17 | 17 | 6 | |
| 8. Difficulties in self-care (taking care of the body and body parts, such as skin, face, teeth, scalp and genitals). | A | 6 | 17 | 17 |
| B | 3 | 16 | 21 | |
| C | 13 | 19 | 8 | |
| 9. Difficulties in producing a safe and assertive temperament for a positive diagnosis for dementia. | A | 1 | 18 | 21 |
| B | 5 | 17 | 18 | |
| C | 24 | 9 | 7 | |
| 10. Difficulty concentrating on an external stimulus or an internal experience for the necessary period (functions of maintenance, change and division of attention, distraction). | A | 6 | 14 | 20 |
| B | 5 | 13 | 22 | |
| C | 12 | 20 | 8 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinheiro, L.I.C.C.; Pereira, M.L.D.; Andrade, E.C.d.; Nunes, L.C.; Abreu, W.C.d.; Pinheiro, P.G.C.D.; Holanda Filho, R.; Pinheiro, P.R. An Intelligent Multicriteria Model for Diagnosing Dementia in People Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110457
Pinheiro LICC, Pereira MLD, Andrade ECd, Nunes LC, Abreu WCd, Pinheiro PGCD, Holanda Filho R, Pinheiro PR. An Intelligent Multicriteria Model for Diagnosing Dementia in People Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):10457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110457
Chicago/Turabian StylePinheiro, Luana I. C. C., Maria Lúcia D. Pereira, Evandro C. de Andrade, Luciano C. Nunes, Wilson C. de Abreu, Pedro Gabriel Calíope D. Pinheiro, Raimir Holanda Filho, and Plácido Rogerio Pinheiro. 2021. "An Intelligent Multicriteria Model for Diagnosing Dementia in People Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 10457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110457
APA StylePinheiro, L. I. C. C., Pereira, M. L. D., Andrade, E. C. d., Nunes, L. C., Abreu, W. C. d., Pinheiro, P. G. C. D., Holanda Filho, R., & Pinheiro, P. R. (2021). An Intelligent Multicriteria Model for Diagnosing Dementia in People Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 10457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110457








