Effects of Piper sarmentosum on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Related Complications: A Review of Preclinical Evidence
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
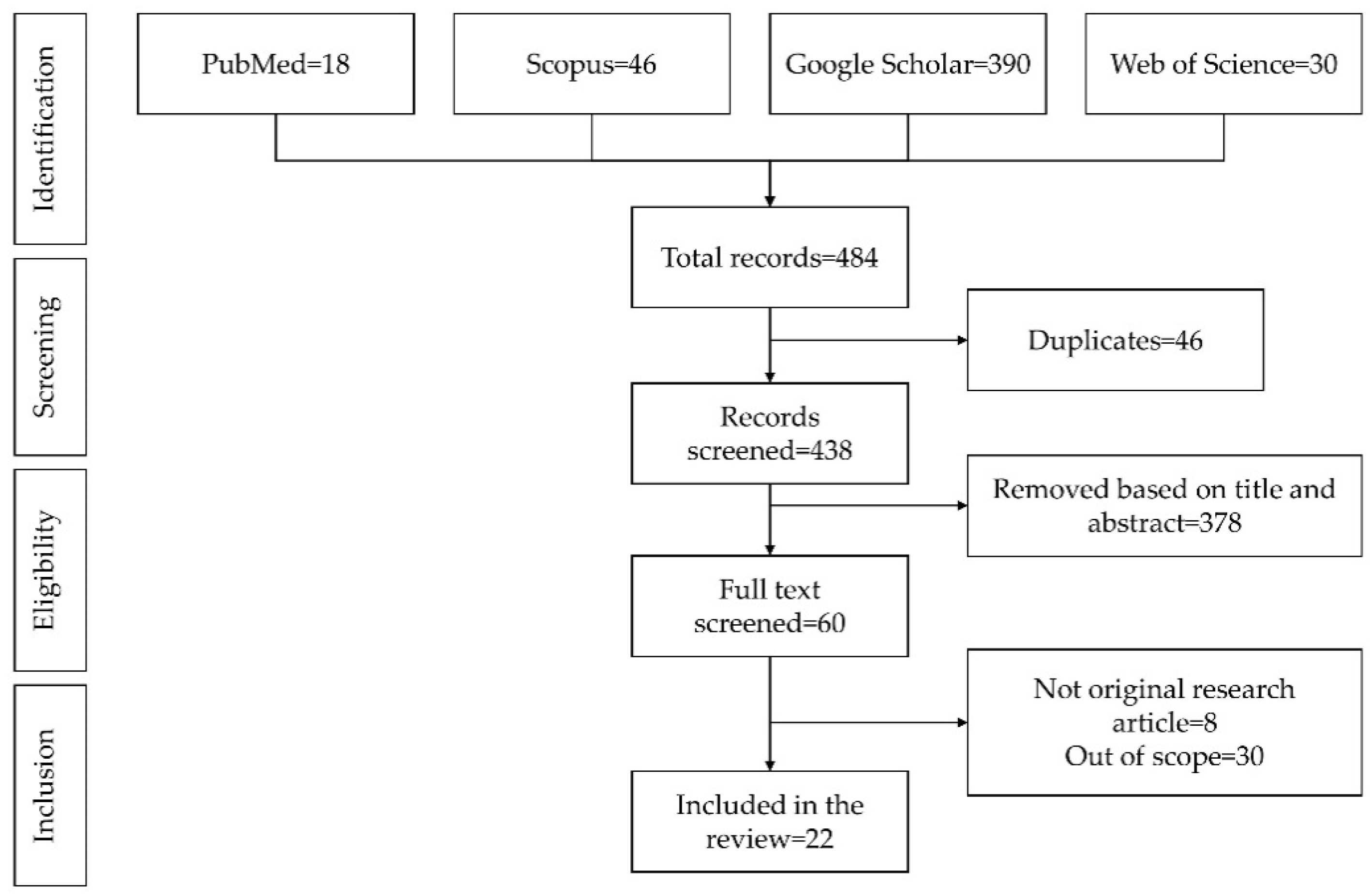
2. Literature Search
3. Effect of PS on Components of MetS
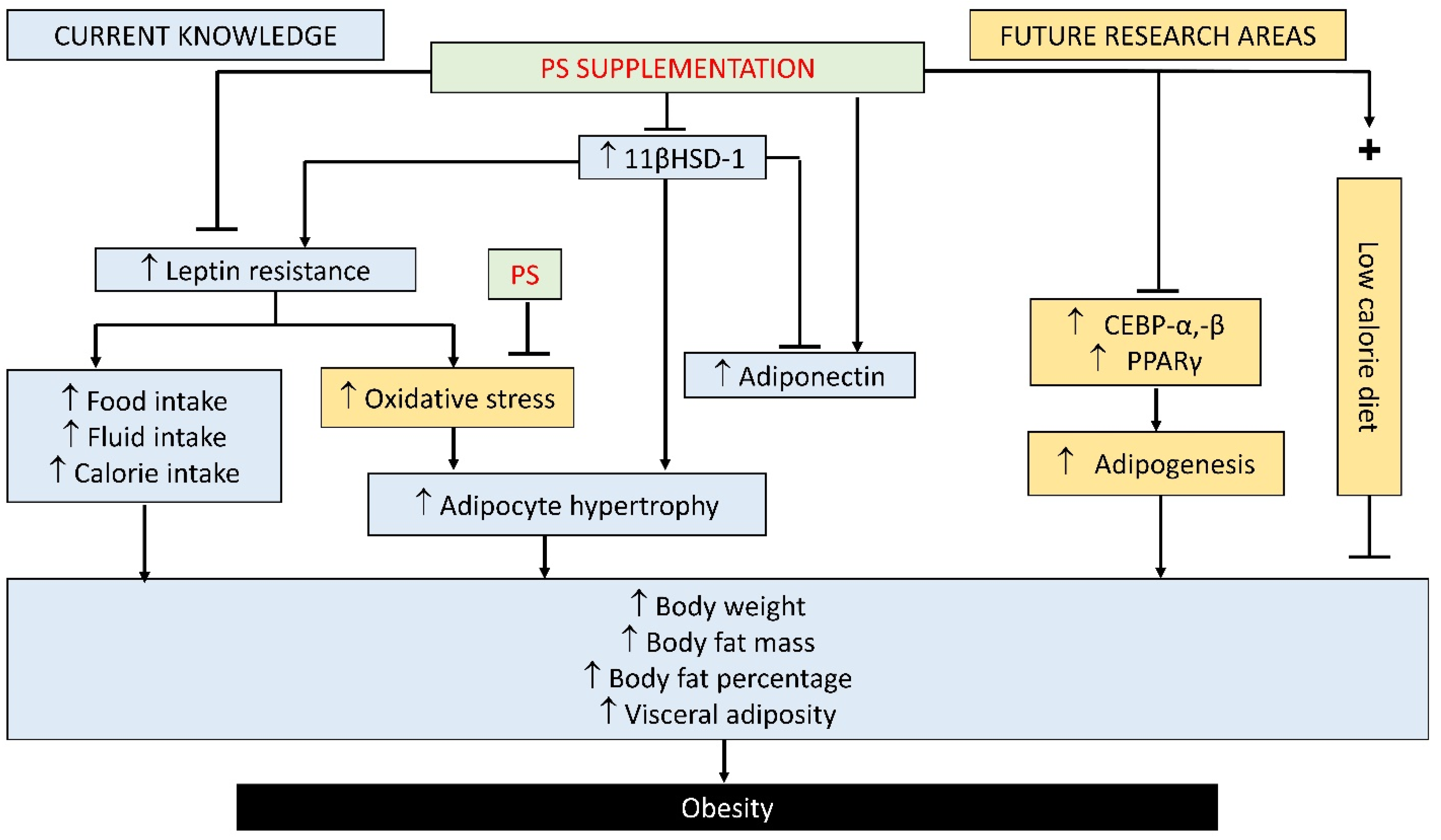
3.1. Effect of PS on Obesity
3.2. Effect of PS on Hyperglycaemia or Diabetes
3.3. Effect of PS on Hypertension
3.4. Effect of PS on Dyslipidaemia and Its Complications
4. Effect of PS on Cardiovascular Diseases Linked to MetS
5. Safety and Bioavailability of PS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez-Baixauli, J.; Quesada-Vázquez, S.; Mariné-Casadó, R.; Cardoso, K.G.; Caimari, A.; Del Bas, J.M.; Escoté, X.; Baselga-Escudero, L. Detection of early disease risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome: A new era with the NMR metabolomics assessment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCracken, E.; Monaghan, M.; Sreenivasan, S. Pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Metabolic syndrome: A closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.-A.; Lee, J.-H.; Lim, S.-Y.; Ha, H.-S.; Kwon, H.-S.; Park, Y.-M.; Lee, W.-C.; Kang, M.-I.; Yim, H.-W.; Yoon, K.-H.; et al. Metabolic syndrome as a predictor of type 2 diabetes, and its clinical and usefulness. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 4, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Mathangasinghe, Y.; Jayawardena, R.; Hills, A.P.; Misra, A. Prevalence and trends of metabolic syndrome among adults in the asia-pacific region: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.J.; Yen, C.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Lee, B.J.; Hsia, S.; Lin, P.T. Relationships between Inflammation, Adiponectin, and Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, J.M.; Reeves, G.; Billman, G.E.; Sturmberg, J.P. Inflammation-nature’s way to efficiently respond to all types of challenges: Implications for understanding and managing “the epidemic” of chronic diseases. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vona, R.; Gambardella, L.; Cittadini, C.; Straface, E.; Pietraforte, D. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8267234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezzani, R.; Franco, C. Liver, oxidative stress and metabolic syndromes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyaprom, K.; Kaewprasert, S.; Putpadungwipon, P.; Namjuntra, P.; Klongthalay, S. Association of antioxidant status and inflammatory markers with metabolic syndrome in Thais. J. Health. Popul. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, E.S.; Mokdad, A.H.; Giles, W.H.; Brown, D.W. The metabolic syndrome and antioxidant concentrations: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2346–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic syndrome: Pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, A.; Pula, G. The Role of NADPH Oxidases and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sena, C.M.; Leandro, A.; Azul, L.; Seiça, R.; Perry, G. Vascular Oxidative Stress: Impact and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dikalov, S.I.; Nazarewicz, R.R. Angiotensin II-induced production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: Potential mechanisms and relevance for cardiovascular disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, S.; Uliana, M.; Virdis, A. Angiotensin II and vascular damage in hypertension: Role of oxidative stress and sympathetic activation. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2019, 115, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.T.; Tian, X.Y.; Huang, Y. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes and hypertension: Cross talk in RAS, BMP4, and ROS-dependent COX-2-derived prostanoids. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakudya, T.T.; Tshabalala, T.; Dangarembizi, R.; Erlwanger, K.H.; Ndhlala, A.R. The potential therapeutic value of medicinal plants in the management of metabolic disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, Isolation, and Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Casado, A. The Health Potential of Fruits and Vegetables Phytochemicals: Notable Examples. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Gyawali, R.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Rajkovic, J.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Khan, T.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ozleyen, A.; Turkdonmez, E.; et al. Piper species: A comprehensive review on their phytochemistry, biological activities and applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amran, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Othman, F.; Das, S.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Raj, S.; Nordin, N.A.M.M. Effect of methanolic extract of Piper sarmentosum leaves on neointimal foam cell infiltration in rabbits fed with high cholesterol diet. EXCLI J. 2012, 11, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisanapun, C.; Wongkrajang, Y.; Temsiririrkkul, R.; Phornchirasilp, S.; Peungvicha, P. In vitro evaluation of anti-diabetic potential of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. extract. FASEB J. 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zainudin, M.; Zakaria, Z.; Megat Mohd Nordin, N.A. The use of Piper sarmentosum leaves aqueous extract (KadukmyTM) as antihypertensive agent in spontaneous hypertensive rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.H.; Padzil, A.M.; Syahida, A.; Abdullah, N.; Zuhainis, S.W.; Maziah, M.; Sulaiman, M.R.; Israf, D.A.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N.H. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antinociceptive activities of six Malaysian medicinal plants. J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 5555–5563. [Google Scholar]
- Sireeratawong, S.; Vannasiri, S.; Sritiwong, S.; Itharat, A.; Jaijoy, K. Anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive and antipyretic effects of the ethanol extract from root of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2010, 93 (Suppl. 7), S1–S6. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, E.T.Y.; Wong, K.W.L.; See, M.L.; Wong, K.Y.; Gan, S.Y.; Chan, E.W.L. Piper sarmentosum Roxb. confers neuroprotection on beta-amyloid (Aβ)-induced microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 217, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameshkumar, K.B.; Nandu, T.G.; Anu Aravind, A.P.; Mathew, S.P.; Shiburaj, S. Chemical composition and FtsZ GTPase inhibiting activity of the essential oil of Piper sarmentosum from Andaman Islands, India. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2017, 29, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, W. Anti-inflammatory effect of myristicin on RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Molecules 2011, 16, 7132–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, K.; Mou, X.; Huang, J.; Xiong, N.; Li, H. Trans-Caryophyllene Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Neuroinflammatory Responses by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation in Microglia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 54, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainol Abidin, I.Z.; Fazry, S.; Jamar, N.H.; Ediwar Dyari, H.R.; Zainal Ariffin, Z.; Johari, A.N.; Ashaari, N.S.; Johari, N.A.; Megat Abdul Wahab, R.; Zainal Ariffin, S.H. The effects of Piper sarmentosum aqueous extracts on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos and caudal fin tissue regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Asri, N.A.A.M. The Study of Antioxidant Activities of Piper sarmentosum and Piper Nigrum. TRAB 2020, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlina, M.F.N.; Qodriyah, H.M.S.; Akmal, M.N.; Ibrahim, I.A.A.; Kamisah, Y. In vivo effect of Piper sarmentosum methanolic extract on stress-induced gastric ulcers in rats. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hafizah, A.H.; Zaiton, Z.; Zulkhairi, A.; Mohd Ilham, A.; Nor Anita, M.M.N.; Zaleha, A.M. Piper sarmentosum as an antioxidant on oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by hydrogen peroxide. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, N.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Wang, F. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effect of Naringenin in different nociceptive and inflammatory mice models. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Y.; Liou, S.S.; Hong, T.Y.; Liu, I.M. Protective effects of hesperidin (Citrus flavonone) on high glucose induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in a cellular model for diabetic retinopathy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand David, A.V.; Arulmoli, R.; Parasuraman, S. Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Klöting, N.; Blüher, M. Adipocyte dysfunction, inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotillard, A.; Poitou, C.; Torcivia, A.; Bouillot, J.L.; Dietrich, A.; Klöting, N.; Grégoire, C.; Lolmede, K.; Blüher, M.; Clément, K. Adipocyte size threshold matters: Link with risk of type 2 diabetes and improved insulin resistance after gastric bypass. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1466–E1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurk, T.; Alberti-Huber, C.; Herder, C.; Hauner, H. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I.; Domínguez, A.P.; Drägert, K.; Humar, R.; Haas, E.; Battegay, E.J. Hypoxia potentiates tumor necrosis factor-α induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in white and brown adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosacka, J.; Kern, M.; Klöting, N.; Paeschke, S.; Rudich, A.; Haim, Y.; Gericke, M.; Serke, H.; Stumvoll, M.; Bechmann, I.; et al. Autophagy in adipose tissue of patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 409, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, N.; Gatterer, H.; Faulhaber, M.; Burtscher, M.; Pramsohler, S.; Pesta, D. Hypoxia, Oxidative Stress and Fat. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldini, G.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Facino, R.M.; Milzani, A.; Carini, M. Intervention strategies to inhibit protein carbonylation by lipoxidation-derived reactive carbonyls. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 817–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Ghanim, H.; Chaudhuri, A.; Dhindsa, S.; Kim, S.S. Macronutrient intake induces oxidative and inflammatory stress: Potential relevance to atherosclerosis and insulin resistance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.M.; Tuomilehto, J.; Rydén, L. The metabolic syndrome–What is it and how should it be managed? Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairus, A.; Ima Nirwana, S.; Elvy Suhana, M.R.; Tan, M.H.; Santhana, R.; Farihah, H.S. Piper sarmentosum is comparable to glycyrrhizic acid in reducing visceral fat deposition in adrenalectomised rats given dexamethasone. Clin. Ter. 2013, 164, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuster, A.; Patlas, M.; Pinthus, J.H.; Mourtzakis, M. The clinical importance of visceral adiposity: A critical review of methods for visceral adipose tissue analysis. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akalestou, E.; Genser, L.; Rutter, G.A. Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Obesity and Following Weight Loss. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, K.; Marino, J.S.; Sanchez, E.R.; Hinds, T.D. The glucocorticoid receptor: Cause of or cure for obesity? Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2015, 310, E249–E257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aslan, H.; Altunkaynak, B.Z.; Altunkaynak, M.E.; Vuraler, O.; Kaplan, S.; Unal, B. Effect of a high fat diet on quantitative features of adipocytes in the omentum: An experimental, stereological and ultrastructural study. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundbom, M.; Kaiser, C.; Björkstrand, E.; Castro, V.M.; Larsson, C.; Selén, G.; Nyhem, C.S.; James, S.R. Inhibition of 11βHSD1 with the S-phenylethylaminothiazolone BVT116429 increases adiponectin concentrations and improves glucose homeostasis in diabetic KKAy mice. BMC Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azlina, A.A.; Farihah, H.S.S.; Qodriyah, H.M.S.M.S.; Azlina, M.F.N.; Aida Azlina, A.; Farihah, H.S.S.; Qodriyah, H.M.S.M.S.; Nur Azlina, M.F. Effects of Piper sarmentosum Water Extract on 11-β Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Bioactivity in Ovariectomy-Induced Obese Rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 5, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryo, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kihara, S.; Kumada, M.; Shibazaki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nagai, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T. Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hotta, K.; Funahashi, T.; Arita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsuda, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Iwahashi, H.; Kuriyama, H.; Ouchi, N.; Maeda, K.; et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, M.; Kihara, S.; Sumitsuji, S.; Kawamoto, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Ouchi, N.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Hiraoka, H.; et al. Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery disease in men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kern, P.A.; Di Gregorio, G.B.; Lu, T.; Rassouli, N.; Ranganathan, G. Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: Relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cnop, M.; Havel, P.J.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; Brunzell, J.D.; Kahn, S.E. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: Evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomlinson, J.W.; Moore, J.; Cooper, M.S.; Bujalska, I.; Shahmanesh, M.; Burt, C.; Strain, A.; Hewison, M.; Stewart, P.M. Regulation of expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in adipose tissue: Tissue-specific induction by cytokines. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, D.J.; Rask, E.; Livingstone, D.E.W.; Söderberg, S.; Olsson, T.; Walker, B.R. Local and systemic impact of transcriptional up-regulation of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in adipose tissue in human obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Maskari, M.Y.; Alnaqdy, A.A. Correlation between serum leptin levels, body mass index and obesity in Omanis. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2006, 6, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Society for Endocrinology. Leptin. Available online: https://www.yourhormones.info/hormones/leptin/ (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, Z.A.; Hannan, K.S.; Greenberg, M.L.; Friedman, J.M. Hyperleptinemia Is Required for the Development of Leptin Resistance. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azlina, A.A.; Farihah, S.; Qodriyah, M.S.; Azlina, M.F.N. Effects of Piper sarmentosum (Kaduk) Water Extract on Adiponectin and Blood Glucose Levels in Ovariectomy-Induced Obese Rats. Res. J. Med. Plant 2009, 3, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Ramli, E.S.M.; Nasir, N.A.A.; Ismail, N.M.; Fahami, N.A.M. Methanolic extract of Piper sarmentosum attenuates obesity and hyperlipidemia in fructose-induced metabolic syndrome rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Polotsky, V.Y. Leptin and leptin resistance in the pathogenesis of obstructive sleep apnea: A possible link to oxidative stress and cardiovascular complications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5137947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Dusting, G.J.; Peshavariya, H.; Jiang, F.; Hsiao, S.T.F.; Chan, E.C.; Liu, G.S. Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into fat involves reactive oxygen species and forkhead box o1 mediated upregulation of antioxidant enzymes. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, H.; Ko, E.H.; Kim, J.W. Reactive oxygen species facilitate adipocyte differentiation by accelerating mitotic clonal expansion. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 10601–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, B.C.; Kanters, S.; Bandayrel, K.; Wu, P.; Naji, F.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Ball, G.D.C.; Busse, J.W.; Thorlund, K.; Guyatt, G.; et al. Comparison of weight loss among named diet programs in overweight and obese adults: A meta-analysis. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2014, 312, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garvey, W.T.; Ryan, D.H.; Henry, R.; Bohannon, N.J.V.; Toplak, H.; Schwiers, M.; Troupin, B.; Day, W.W. Prevention of type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes and metabolic syndrome treated with phentermine and topiramate extended release. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falkner, B.; Cossrow, N.D.F.H. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and obesity-associated hypertension in the racial ethnic minorities of the United States. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Woollard, J.R.; Jordan, K.L.; Lerman, A.; Lerman, L.O.; Eirin, A. Mitochondrial targeted peptides preserve mitochondrial organization and decrease reversible myocardial changes in early swine metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luc, K.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 809–824. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, S.; Shabeer, M.; Parvaresh Rizi, E.; Agarwal, M.; Lee, M.H.; Ooi, D.S.Q.; Chia, C.; Aung, N.; Ng, G.; Teo, Y.; et al. Heredity of type 2 diabetes confers increased susceptibility to oxidative stress and inflammation. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e000945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szkudelski, T. The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol. Res. 2001, 50, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Deeds, M.C.; Anderson, J.M.; Armstrong, A.S.; Gastineau, D.A.; Hiddinga, H.J.; Jahangir, A.; Eberhardt, N.L.; Kudva, Y.C. Single dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Considerations for study design in islet transplantation models. Lab. Anim. 2011, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prentki, M.; Nolan, C.J. Islet β cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabák, A.G.; Jokela, M.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimäki, M.; Witte, D.R. Trajectories of glycaemia, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: An analysis from the Whitehall II study. Lancet 2009, 373, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thent, Z.C.; Seong Lin, T.; Das, S.; Zakaria, Z. Effect of Piper sarmentosum extract on the cardiovascular system of diabetic sprague-dawley rats: Electron microscopic study. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 628750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peungvicha, P.; Thirawarapan, S.S.; Temsiririrkkul, R.; Watanabe, H.; Kumar Prasain, J.; Kadota, S. Hypoglycemic effect of the water extract of Piper sarmentosum in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 60, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussan, F.; Zin, M.; Choon, Y.S.; Lin, T.S. Piper sarmentosum Water Extract Attenuates Diabetic Complications in Streptozotocin induced Sprague-Dawley Rats (Ekstrak Air Piper sarmentosum Mengurangkan Komplikasi Diabetes dalam Tikus Sprague-Dawley Teraruh Streptozotocin). Sains Malaysiana 2013, 42, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T.Z.; Stephens, M.W.; Kumar, P.; Chudleigh, R.A. Renal complications of diabetes. Br. Med. Bull. 2012, 104, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bur, A.; Herkner, H.; Woisetschläger, C.; Vlcek, M.; Derhaschnig, U.; Hirschl, M.M. Is fasting blood glucose a reliable parameter for screening for diabetes in hypertension? Am. J. Hypertens. 2003, 16, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skovsø, S. Modeling type 2 diabetes in rats using high fat diet and streptozotocin. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Chin, K.Y.; Soelaiman, I.N. Leptin, adiponectin and insulin as regulators for energy metabolism in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Sains Malaysiana 2019, 48, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, K.N.; Cruzat, V.F.; Carlessi, R.; de Bittencourt, P.I.H.; Newsholme, P. Molecular Events Linking Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Insulin Resistance and β-Cell Dysfunction. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 181643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, S.S.; Barboza, M.G.; Pio, J.R.; Wong, N.D. Blood pressure categories, hypertensive subtypes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, F.S.; Choi, H.; Miller, M.R.; Stark, R.J. TNFα and Reactive Oxygen Signaling in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Hypertension and Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 33, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybalkin, S.D.; Rybalkina, I.G.; Feil, R.; Hofmann, F.; Beavo, J.A. Regulation of cGMP-specific Phosphodiesterase (PDE5) Phosphorylation in Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3310–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Förstermann, U. Oxidative stress in vascular disease: Causes, defense mechanisms and potential therapies. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 5, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M. Reactive Oxygen Species as Mediators of Calcium Signaling by Angiotensin II: Implications in Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwi, N.A.N.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Karim, A.A.H.; Nordin, N.A.M.M.; Ugusman, A.; Nik Mohd Alwi, N.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Karim, A.A.H.; Megat Mohd Nordin, N.A.; Ugusman, A. Antihypertensive Effect of Piper sarmentosum in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Sains Malaysiana 2018, 47, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugusman, A.; Md Fadze, N.; Hamid, A.A.; Asmawi, Z.; Aminuddin, A. Piper sarmentosum attenuates dexamethasone-induced hypertension by stimulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J. Res. Pharm. 2020, 24, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firdaus Azmi, M.; Aminuddin, A.; Azdina Jamal, J.; Hamid, A.A.; Ugusman, A. Quantified Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Leaves Aqueous Leaf Extract and Its Antihypertensive Effect in Dexamethasone-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Sains Malaysiana 2021, 50, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim Fauzy, F.; Mohd Zainudin, M.; Ismawi, H.R.; Elshami, T.F.T. Piper sarmentosum Leaves Aqueous Extract Attenuates Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zainudin, M.; Elshami, T.F.T.; Ismawi, H.R.; Hashim Fauzy, F.; Abdul Razak, T. Factors Regulating Nitric Oxide Production in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Treated with Piper sarmentosum Aqueous Extract. IIUM Med. J. Malaysia 2020, 18, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, J.P.; Spradley, F.T. The kidneys, volume and blood pressure regulation, and hypertension. In Disorders of Blood Pressure Regulation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rautureau, Y.; Schiffrin, E.L. Endothelin in hypertension: An update. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Park, W.J. Endothelial dysfunction: Clinical implications in cardiovascular disease and therapeutic approaches. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sibal, L.; C Agarwal, S.; D Home, P.; H Boger, R. The Role of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) in Endothelial Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2010, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamanishi, K.; Yamashita, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Okuzaki, D.; Shimada, K.; Nojima, H.; Yasunaga, T.; Okamura, H.; et al. Analysis of genes causing hypertension and stroke in spontaneously hypertensive rats: Gene expression profiles in the brain. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerman, L.O.; Kurtz, T.W.; Touyz, R.M.; Ellison, D.H.; Chade, A.R.; Crowley, S.D.; Mattson, D.L.; Mullins, J.J.; Osborn, J.; Eirin, A.; et al. Animal Models of Hypertension: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2019, 73, e87–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossman, E.; Messerli, F.H. Drug-induced hypertension: An unappreciated cause of secondary hypertension. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.Q.; Silva, G.V.; Drager, L.F. What Is the Most Common Cause of Secondary Hypertension? An Interdisciplinary Discussion. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzawi, M. Assessment of Vascular Function and Contractility, Ex Vivo. In Handbook of Vascular Biology Techniques; Slevin, M., McDowell, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 65–79. ISBN 978-94-017-9715-3. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.C.; Dunn, M.J. The Role of Prostaglandins in Human Hypertension. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1985, 5, A32–A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaich, M.P.; Socratous, F.; Hennebry, S.; Eikelis, N.; Lambert, E.A.; Straznicky, N.; Esler, M.D.; Lambert, G.W. Sympathetic Activation in Chronic Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goppelt-Struebe, M.; Wolter, D.; Resch, K. Glucocorticoids inhibit prostaglandin synthesis not only at the level of phospholipase A2 but also at the level of cyclo-oxygenase/PGE isomerase. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 98, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ames, M.K.; Atkins, C.E.; Pitt, B. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its suppression. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joint committee for guideline revision 2016 Chinese guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia in adults. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Kavey, R.-E.W.; Daniels, S.R.; Lauer, R.M.; Atkins, D.L.; Hayman, L.L.; Taubert, K. American Heart Association guidelines for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease beginning in childhood. Circulation 2003, 107, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Alexander, L.; Anderson, H.R.; Bachman, V.F.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Casey, D.; Coates, M.M.; Cohen, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 2287–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruotolo, G.; Howard, B. V Dyslipidemia of the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2002, 4, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovou, G.D.; Anagnostopoulou, K.K.; Cokkinos, D. V Pathophysiology of dyslipidaemia in the metabolic syndrome. Postgrad. Med. J. 2005, 81, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minhajuddin, M.; Beg, Z.H.; Iqbal, J. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant properties of tocotrienol rich fraction isolated from rice bran oil in experimentally induced hyperlipidemic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Le, G.; Li, A.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y. Effect of antioxidant capacity on blood lipid metabolism and lipoprotein lipase activity of rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutrition 2006, 22, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Peng, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, A.; Wang, G.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Y. Association of biomarkers of inflammation with dyslipidemia and its components among Mongolians in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.N.; Choi, W.S. The association between subclinical inflammation and abnormal glucose and lipid metabolisms in normal-weight Korean individuals. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.A.; Suhaimi, F.H.; Hj, Q.; Saad, M.; Azlina, N.; Fahami, M.; Mohd Saad, Q.; Mohd Fahami, N.A. Lipid lowering effects of Piper sarmentosum extract in ovariectomy-induced obese rats. Int. J. Appl. Res. Nat. Prod. 2017, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fadze, N.F.M.; Ugusman, A.; Aminuddin, A. Protective Effect of Piper Sarmentosum against Dexamethasone-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 273, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, W.N.W.; Chin, K.Y.; Ghafar, N.A.; Soelaiman, I.N. Annatto-derived tocotrienol promotes mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells by enhancing BMP-2 protein expression via inhibiting RhoA activation and HMG-CoA reductase gene expression. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Notarnicola, M.; Messa, C.; Refolo, M.G.; Tutino, V.; Miccolis, A.; Caruso, M.G. Synergic effect of Eicosapentaenoic acid and Lovastatin on gene expression of HMGCoA reductase and LDL receptor in cultured HepG2 cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haerer, W.; Delbaere, K.; Bartlett, H.; Lord, S.R.; Rowland, J. Relationships between HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statin) use and strength, balance and falls in older people. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.C.; Hodgson, J.M.; Puddey, I.B.; Mori, T.A.; Beilin, L.J.; Croft, K.D. Oxidative stress in human hypertension: Association with antihypertensive treatment, gender, nutrition, and lifestyle. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboonabi, A.; Meyer, R.R.; Singh, I. The association between metabolic syndrome components and the development of atherosclerosis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, I. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Atherosclerosis; Gianturco, B.H.E.-L., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; Chapter 3; ISBN 978-1-78923-561-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, S.M.; Sundar, U.M.; Hui, C.K.; Aminuddin, A.; Ugusman, A. Piper sarmentosum attenuates TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2018, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O. Molecular mechanisms regulating monocyte recruitment in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundar, U.M.; Ugusman, A.; Chua, H.K.; Latip, J.; Aminuddin, A. Piper sarmentosum promotes endothelial nitric oxide production by reducing asymmetric dimethylarginine in tumor necrosis factor-α-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugusman, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Hui, C.K.; Nordin, N.A.M.M. Piper sarmentosum increases nitric oxide production in oxidative stress: A study on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Clinics 2010, 65, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Hou, L.; Xu, D.; Chen, A.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fassett, J.T.; Chen, Y. Effect of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) on heart failure development. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2016, 54, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czarnecka, A.; Milewski, K.; Zielińska, M. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Hepatic Encephalopathy: Cause, Effect or Association? Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitroulas, T.; Sandoo, A.; Kitas, G.D. Asymmetric dimethylarginine as a surrogate marker of endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk in patients with systemic rheumatic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12315–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amran, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Othman, F.; Das, S.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Nordin, N.A.M. Changes in the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and c-reactive protein following administration of aqueous extract of Piper sarmentosum on experimental rabbits fed with cholesterol diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasceri, V.; Willerson, J.T.; Yeh, E.T. Direct proinflammatory effect of C-reactive protein on human endothelial cells. Circulation 2000, 102, 2165–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amran, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Othman, F.; Das, S.; Raj, S.; Nordin, N.-A.M.M.N. Aquaeous extract of Piper sarmentosum decreases atherosclerotic lesions in high cholesterolemic experimental rabbits. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolphin, P.J. Serum and hepatic nascent lipoproteins in normal and hypercholesterolemic rats. J. Lipid Res. 1981, 22, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangdong, L.; Yuanwu, L.; Hua, Z.; Liming, R.; Qiuyan, L.; Ning, L. Animal models for the atherosclerosis research: A review. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, J.; Xu, Q.; Xu, X.; Yin, H.; Xu, R.; Guo, S.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.-M. Hexarelin suppresses high lipid diet and vitamin D3-induced atherosclerosis in the rat. Peptides 2010, 31, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, X.F.; Ng, C.Y.; Jaarin, K. Animal Models in Cardiovascular Research: Hypertension and Atherosclerosis. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 528757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lock, A.L.; Horne, C.A.M.; Bauman, D.E.; Salter, A.M. Butter naturally enriched in conjugated linoleic acid and vaccenic acid alters tissue fatty acids and improves the plasma lipoprotein profile in cholesterol-fed hamsters. Proc. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorfman, S.E.; Wang, S.; Vega-López, S.; Jauhiainen, M.; Lichtenstein, A.H. Dietary fatty acids and cholesterol differentially modulate HDL cholesterol metabolism in Golden-Syrian hamsters. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thent, Z.C.; Lin, T.S.; Das, S.; Zakaria, Z. Histological changes in the heart and the proximal aorta in experimental diabetic rats fed with Piper sarmentsoum. African J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridtitid, W.; Ruangsang, P.; Reanmongkol, W.; Wongnawa, M. Studies of the anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activities of the methanolic extract of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. leaves in rats. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2007, 29, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Zainudin, M.; Zakaria, Z.; Megat Mohd Nordin, N.A.; Othman, F. Does oral ingestion of Piper sarmentosum cause toxicity in experimental animals? Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, K.; Ismail, Z.; Sadikun, A.; Ibrahim, P. Standardization and in vivo antioxidant activity of ethanol extracts of fruit and leaf of Piper sarmentosum. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, K.; Ismail, Z.; Sadikun, A.; Ibrahim, P. Bioactive Markers Based Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Extracts of a Traditional Medicinal Plant, Piper sarmentosum. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Researcher | Study Design | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity | ||
| Azlina et al. [53] | Animals: 42 female Sprague Dawley rats (180–200 g) Mode of disease induction: ovariectomy-induced obesity Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 5 months Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 120 mg/kg/day of GCA for 5 months | ↓ 11βHSD-1 activity in liver and adipose tissue compared to negative control ↔ 11βHSD-1 activity in heart compared to negative control ↔ blood pressure at 3 and 5 months compared to negative control ↔ body weight compared to negative control |
| Azlina et al. [67] | Animals: 28 female Sprague Dawley rats (180–200 g) Mode of disease induction: ovariectomy-induced obesity Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 5 months Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 120 mg/kg/day of GCA for 5 months | ↓ blood glucose level at 3 and 5 months compared to negative control ↑ plasma adiponectin level at 3 and 5 months compared to negative control ↔ body weight compared to negative and positive control |
| Kumar et al. [68] | Animals: 40 male Wistar rats (180–200 g) Mode of disease induction: fructose-induced MetS Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of MEPS for 4 weeks Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 100 mg/kg/day of naringin for 4 weeks | ↓ food, fluid, and calorie intake compared to negative control ↓ body weight compared to negative control at week 2; negative and positive control at week 4 ↓ fat mass and fat percentage compared to negative and positive control ↓ serum leptin and adiponectin compared to negative and positive control ↓ adipocyte surface area compared to negative control |
| Fairus et al. [47] | Animals: 21 male Sprague Dawley rats (200–250 g) Mode of disease induction: adrenalectomy + dexamethasone-induced visceral obesity Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of PS extract for 48 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 240 mg/kg/day of GCA for 48 days | ↓ visceral fat deposition compared to negative control ↓ diameter of adipocyte membrane compared to positive and negative control ↔ area, perimeter, and width of individual perirenal adipocytes compared to positive and negative control |
| Diabetes | ||
| Thent et al. [84] | Animals: 24 male Sprague Dawley rats (200 ± 50 g) Mode of disease induction: STZ-induced diabetes Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↑ body weight and ↓ fasting blood glucose and urine glucose level compared to negative control |
| Hussan et al. [86] | Animals: 18 male Sprague Dawley rats (150 ± 50 g) Mode of disease induction: STZ-induced diabetes Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↔ body weight, fasting blood glucose, kidney weight index, and percent glomerular area in a renal corpuscle compared to negative control ↓ inflammatory cells infiltration, size of urinary space, and glomerular membrane thickening in kidney compared to negative control. |
| Peungvicha et al. [85] | Animals: 18 male Wistar rats (5 weeks old; 140–220 g) Mode of disease induction: STZ-induced diabetes Treatment: 125 and 250 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 7 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: glibenclamide (5 mg/kg/day) for 7 days | ↔ fasting plasma glucose level compared to positive and negative control |
| Hypertension | ||
| Alwi et al. [97] | Animals: 36 adult male Wistar rats (6–8 weeks old; 170–220 g) Mode of disease induction: L-NAME-induced hypertension Treatment: 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 4 weeks Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↓ SBP and MABP at week 2 and 4 compared to negative control ↓ DBP in 250 and 500 mg/kg at week 2 and all concentrations at week 4 compared to the negative control. ↓ serum MDA compared to negative control ↑ serum NO compared to negative control |
| Azmi et al. [99] | Animals: 30 adult male Sprague Dawley rats (8–12 weeks old; 250–300 g) Mode of disease induction: dexamethasone-induced hypertension Treatment: 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: captopril (40 mg/kg/day) for 28 days | ↓ SBP, DBP, and MABP at day 14 and 28 compared to negative control |
| Fadze et al. [98] | Animals: 30 male Sprague Dawley rats (8–12 weeks old) Mode of disease induction: dexamethasone-induced hypertension Treatment: 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: captopril (40 mg/kg/day) for 28 days | ↓ SBP, DBP, and MABP at day 14 and 28 compared to negative control ↑ eNOS expression in thoracic aorta compared to negative control ↑ eNOS protein level in thoracic aorta tissues compared to negative control ↑ eNOS activity in thoracic aorta compared to negative control. ↑ serum eNOS compared to negative control |
| Fauzy et al. [100] | Animals: 24 male spontaneously hypertensive rats (8–12 weeks old; 250–300 g) Mode of disease induction: spontaneous hypertension Treatment: 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: perindopril (3 mg/kg/day) for 28 days | ↓ SBP, DBP, and MABP compared to negative control ↔ HR compared to negative and positive control ↓ ET-1 and ↑ NO in mesenteric artery compared to negative control |
| Mohd Zainudin et al. [101] | Animals: 24 male spontaneously hypertensive rats (8–12 weeks old; 250–300 g) Mode of disease induction: spontaneous hypertension Treatment: 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: perindopril (3 mg/kg/day) for 28 days | ↓ SBP and DBP compared to negative control ↑ serum NO levels compared to negative control ↓ plasma ADMA levels compared to negative control ↔ plasma arginine levels compared to negative control |
| Zainudin et al. [24] | Animals: 32 male spontaneously hypertensive rats (10 weeks old) Mode of disease induction: spontaneous hypertension Treatment: 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: Normotensive male Wistar rats (250 ± 10 g) Positive: no treatment | ↓ SBP, DBP, and MABP from week 2–5 compared to positive control ↔ HR, CPK, and LDH compared to positive control ↑ NO and ↓ MDA in serum compared to positive control ↓ serum cholesterol at 1 mg/kg compared to positive control |
| Dyslipidaemia | ||
| Kumar et al. [68] | Animals: 40 male Wistar rats (180–200 g) Mode of disease induction: fructose-induced MetS Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of MEPS for 4 weeks Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 100 mg/kg/day of naringin for 4 weeks | ↓ Plasma LDL, TC, TG, and HMGCR compared to positive and negative control ↓ HMGCR enzyme bioactivity compared to positive and negative control ↑ Plasma HDL compared to positive and negative control |
| Ali et al. [124] | Animals: 40 female Sprague Dawley rats (180–200 g) Mode of disease induction: ovariectomy-induced obesity Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 3 and 5 months Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 120 mg/kg/day of GCA for 3 and 5 months | ↓ Plasma LDL, TC, TG, and HMGCR at 3 and 5 months compared to negative control ↓ HMGCR enzyme bioactivity at 3 and 5 months compared to negative control ↑ Plasma HDL at 3 and 5 months compared to negative control |
| Fadze et al. [125] | Animals: 30 male Sprague Dawley rats (180–200 g) Mode of disease induction: dexamethasone-induced hyperlipidaemia Treatment: 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: 40 mg/kg/day of captopril for 28 days | ↓ LDL, TC, and TG compared to negative control ↔ HDL compared to negative control |
| Researcher | Study Design | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Culture Studies | ||
| Ismail et al. [133] | Cell line: HUVECs Mode of disease induction: TNF-α-induced atherosclerosis Treatment: 100, 150, 250, and 300 μg/mL AEPS for 24 h Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↓ ICAM-1 and NF-κB p65 protein expression at 150, 250, and 300 μg/mL compared to negative control ↓ VCAM-1 protein expression compared to negative control |
| Ugusman et al. [136] | Cell line: HUVECs Mode of disease induction: H2O2-induced atherosclerosis Treatment: 150 μg/mL AEPS for 24 h Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↑ expression of eNOS mRNA compared to negative control ↑ eNOS protein levels compared to negative control ↑ eNOS enzyme activity compared to negative control ↑ NO production compared to negative control |
| Sundar et al. [135] | Cell line: HUVECs Mode of disease induction: TNF-α-induced atherosclerosis Treatment: 150, 250, and 300 μg/mL AEPS for 24 h Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↑ NO levels compared to negative control ↑ DDAH1 mRNA expression, protein level, and enzyme activity compared to negative control ↓ ADMA level compared to negative control |
| Animal Studies | ||
| Amran et al. [140] | Animals: 42 male New Zealand White rabbits (1.8 ± 2 kg) Mode of disease induction: HCD-induced atherosclerosis Treatment: 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 10 weeks Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: simvastatin (1.2 mg/kg) for 10 weeks | ↓ ICAM, VCAM, and CRP at 500 mg/kg compared to negative control |
| Amran et al. [142] | Animals: 42 male New Zealand White rabbits (1.8 ± 2 kg) Mode of disease induction: HCD-induced atherosclerosis Treatment: 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 10 weeks Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: simvastatin (1.2 mg/kg) for 10 weeks | ↓ atherosclerotic lesions and fat deposit in the intimal surface of the aorta at 500 mg/kg compared to negative control ↓ thickening of intimal ratio in the abdominal aorta at 250 and 500 mg/kg compared to negative control ↓ foam cells in intima layer of the abdominal aorta at 250 and 500 mg/kg compared to negative control |
| Amran et al. [22] | Animals: 36 male New Zealand White rabbits (1.8 ± 2 kg) Mode of disease induction: HCD-induced atherosclerosis Treatment: 62.5, 125, and 250 mg/kg/day of MEPS for 10 weeks Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: simvastatin (1.2 mg/kg) for 10 weeks | ↓ fatty streak in abdominal aorta compared to negative control ↓ neointimal area and intima ratio of abdominal aorta compared to negative control ↓ foam cells covering intima layer of abdominal aorta compared to negative control |
| Thent et al. [149] | Animals: 24 male Sprague Dawley rats (200–250 g) Mode of disease induction: STZ-induced diabetes Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↓ deformation in sizes and shapes of the cardiomyocytes nuclei of cardiac tissue compared to negative control ↓ thickness of the tunica media of aortic wall compared to negative control ↓ disruption in the arrangement of the elastic fibres in aortic tissue compared to negative control |
| Thent et al. [84] | Animals: 24 male Sprague Dawley rats (200 ± 50 g) Mode of disease induction: STZ-induced diabetes Treatment: 125 mg/kg/day of AEPS for 28 days Control: Negative: no treatment Positive: no | ↓ disturbance and irregular arrays of myofibrils within sarcomere of cardiac tissues compared to negative control ↓ size, disruption, and patchy areas of cytoplasmic space in mitochondria of cardiac tissue compared to negative control ↓ invagination and disruption of nuclei in cardiac tissue compared to negative control ↓ disruption of the elastic lamina, proliferation of smooth muscle cells and ↑ endothelial cells in proximal aorta compared to negative control |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ekeuku, S.O.; Nur Azlina, M.F.; Chin, K.-Y. Effects of Piper sarmentosum on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Related Complications: A Review of Preclinical Evidence. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219860
Ekeuku SO, Nur Azlina MF, Chin K-Y. Effects of Piper sarmentosum on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Related Complications: A Review of Preclinical Evidence. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):9860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219860
Chicago/Turabian StyleEkeuku, Sophia Ogechi, Mohd Fahami Nur Azlina, and Kok-Yong Chin. 2021. "Effects of Piper sarmentosum on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Related Complications: A Review of Preclinical Evidence" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 9860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219860
APA StyleEkeuku, S. O., Nur Azlina, M. F., & Chin, K.-Y. (2021). Effects of Piper sarmentosum on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Related Complications: A Review of Preclinical Evidence. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 9860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219860







