Abstract
Celiac disease (CD) is an autoimmune disease characterized by gluten-induced intestinal inflammation. Dietary restrictions and symptoms may have a significant impact on the patient’s quality of life, body composition (BC), and strength. This study was designed to assess the impact of an isocaloric gluten free diet and resistance exercise in women. A total of 28 Spanish women, aged 40 years old or more, took part in a randomized controlled trial. Each group received a different intervention: group 1, gluten-free nutrition plan + exercise (GFD + E); group 2, gluten-free nutrition plan (GFD); group 3, celiac controls (NO-GFD); and group 4, non-celiac controls (CONTROL). The variables studied were quality of life, BC and isometric hand strength. After 12 weeks of intervention, celiac women that followed a gluten-free diet and exercise showed higher scores on the psychological health scale than celiac women without intervention. The women in group 1 were the only ones who presented improvements in BC variables; fat mass, BMI, and fat-free mass. Negative correlations were found between the perception of quality of life and age, however a positive correlation between quality of life and isometric strength test results was found. In addition to a gluten-free diet, resistance training is essential to improve BC, strength, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
1. Introduction
Celiac disease (CD) affects approximately 1% of the worldwide population [1,2]. It is an autoimmune enteropathy that occurs in genetically susceptible individuals to gluten consumption in the diet, being more frequent in women than men in a proportion of 2:1. Specifically in Spain, the prevalence of celiac disease is 0.26%, higher among women than among men (2.31:1), a statistically significant difference [3]. Currently, new cases of CD are being diagnosed between the third and fourth decades of life. The average age at CD diagnosis in adults is 52 and 44 years in men and women, respectively [4]. However, in Spain there are about 45,000 diagnosed while there may actually be up to 450,000 celiac patients [5]. This makes it difficult to obtain large samples for study.
Despite significant progress in the understanding of the pathophysiology and treatment of CD, the only actual available treatment remains a strict lifelong gluten-free diet (GFD) [6]. The disorder is usually characterized by a combination of gluten-dependent symptoms; diarrhea, malabsorption, abdominal pain, or weight loss; however, there are also asymptomatic patients. Extraintestinal manifestations may occur, such as arthralgia, osteoporosis, chronic fatigue, iron deficiency anemia, or depression [7]. Dietary restrictions and symptoms can have a significant impact on the quality of life (QoL) of the patient.
Some authors have reported a positive effect of a GFD in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients [8], while others have described an increase in QoL only in symptomatic patients [9,10]. In contrast, other authors even found no significant differences in QoL between the healthy and celiac population in the short and long term GFD [11].
Furthermore, QoL is one of the key outcomes in exercise interventions, as improved physical and psychological well-being suggests effective disease management [12]. Participation in regular physical activity is associated with several physical and psychological benefits among chronically ill populations [12]. According to the International Physical Activity Questionnaire, preliminary research reveals that physical activity rates among women living with CD are very low, over 50% of them engaging in only a low level of physical activity [13,14].
In addition to gluten control, the GFD must be nutritionally adequate to satisfy the nutritional needs of everyone. Excessive restriction of cereal consumption as a solution to avoid gluten intake may result in a low carbohydrate (CHO) intake, with an excess of fat and protein intake [2]. These patients often presented an underconsumption of dietary fiber, iron, unsaturated fatty acids, calcium, and certain vitamins (B12, A, D, E, K) [15]. This lack in intake of some essential nutrients is often related to a higher potential for obesity [16].
In studies conducted more than 10 years ago, most celiac patients were found to have a normal or elevated body mass index (BMI) at the time of diagnosis [17,18]; however, more recent studies [2,19] conducted with celiac women indicate that only less than 6.5% are overweight and that there were no cases of obesity. In accordance with these results, Bardella et al. [20] found a lower BMI index in celiac patients than in the general population.
In the study by Bode et al. [21], patients with CD with good adherence to a GFD, with a mean age of 42 years, compared to healthy subjects, had a lower BMI, lower body fat percentage, and lower bone mineral content in the spine and forearms. González et al. [22], analyzed women with CD, aged 20–60 years, with or without GFD, and compared them with a control group of women of the same age. In both groups, women with CD had a lower BMI and height compared to the control group, and women with CD without GFD had a lower BMI than those on a GFD, as well as lower body fat and fat-free mass than women in the control group.
In celiac disease, there is a problem of nutrient absorption, which can lead to a nutritional deficit. The consequences can be different, less vitality, worse nutritional status, less physical exercise, less strength, and psychological problems due to the factors that affect the quality of life of patients daily. In this context, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the QoL, body composition (BC), and upper limb strength of a sample of menopausal or post-menopausal women, after undergoing different treatments: (1) gluten-free diet + exercise in celiac women, (2) gluten-free diet in celiac women, (3) celiac controls without a balanced and personalized GFD and exercise, and (4) healthy controls, establishing intra-group differences. Another aim was to establish differences between groups, depending on the intervention.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
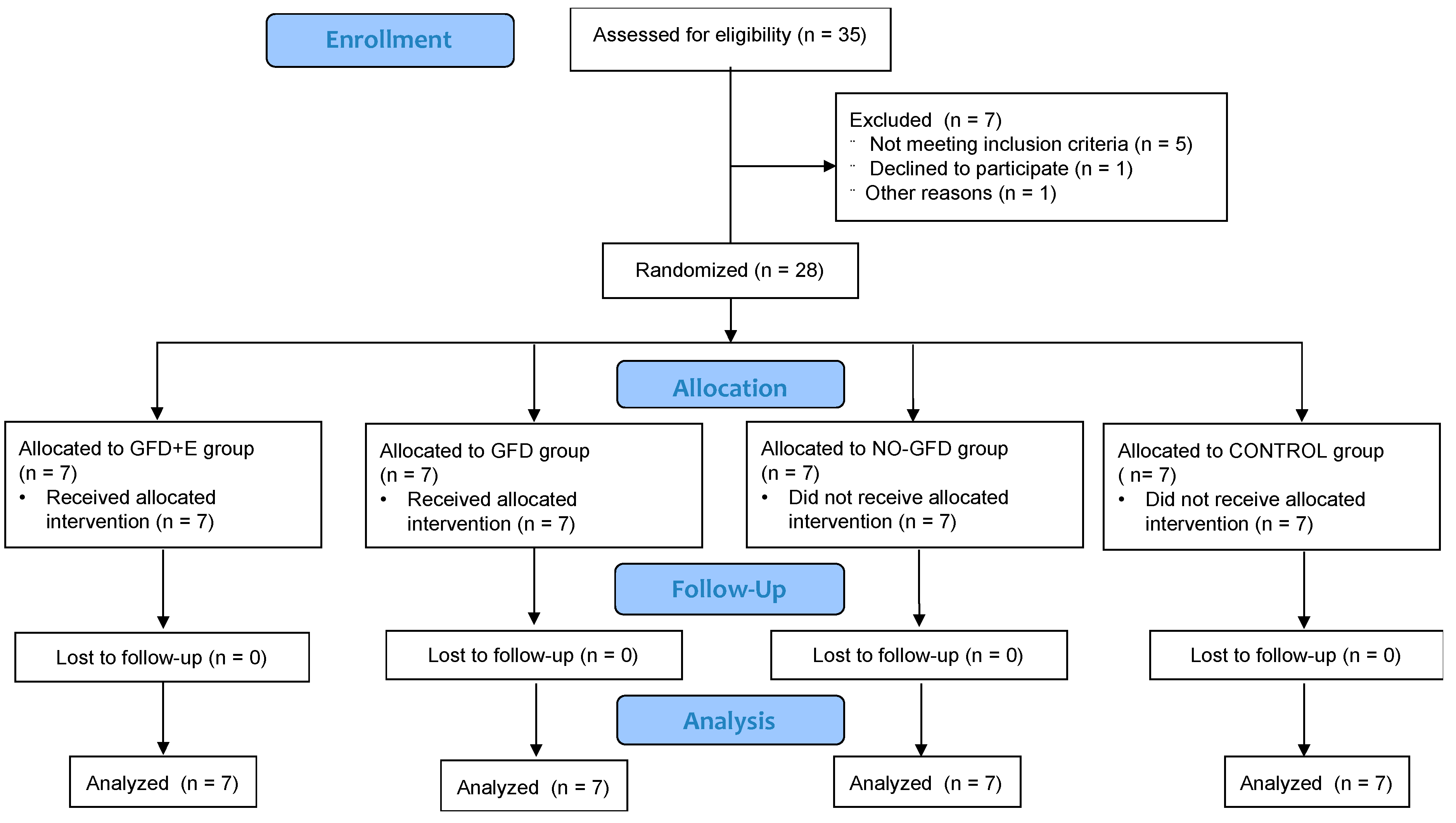
In this study, the subjects were divided into four randomized groups: group 1, gluten-free nutrition plan + exercise (GFD + E); group 2, gluten-free nutrition plan (GFD); group 3, celiac controls (NO-GFD); and group 4, non-celiac controls (CONTROL). Following published recommendations [23], subjects were randomized electronically by block design into four groups (experimental group 1, experimental group 2, celiac controls, and healthy controls) using online computer software, as shown in Figure 1. A researcher who was not involved in the assessments or interventions in this study prepared these envelopes.
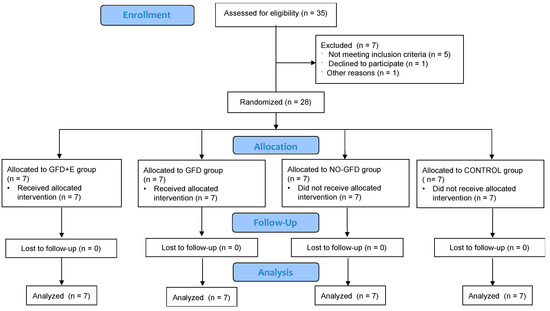
Figure 1.
Consort 2010 flow diagram.
2.2. Participants
Twenty-eight women from the Comunidad Valenciana, Spain, participated in the research. A total of 7 women participated in each group. The selection of the woman was done among women who met the requirements of the study: menopausal or post-menopausal celiac women. Among them, an informative talk was done informing them of the aim and asking for their collaboration. All women who were engaged in physical exercise or were consulting a nutritionist at the time of the study could not participate in the study.
This research was conducted according to the standards of the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the University Human Research Ethics Committee of Alicante University (Spain), code UA-2018-10-22. All participants signed an informed consent form after being informed of the benefits, risk, and detailed description of this research. All data were coded to maintain the confidentiality of the study participants. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 27 October 2021) as NCT05052164.
2.3. Intervention
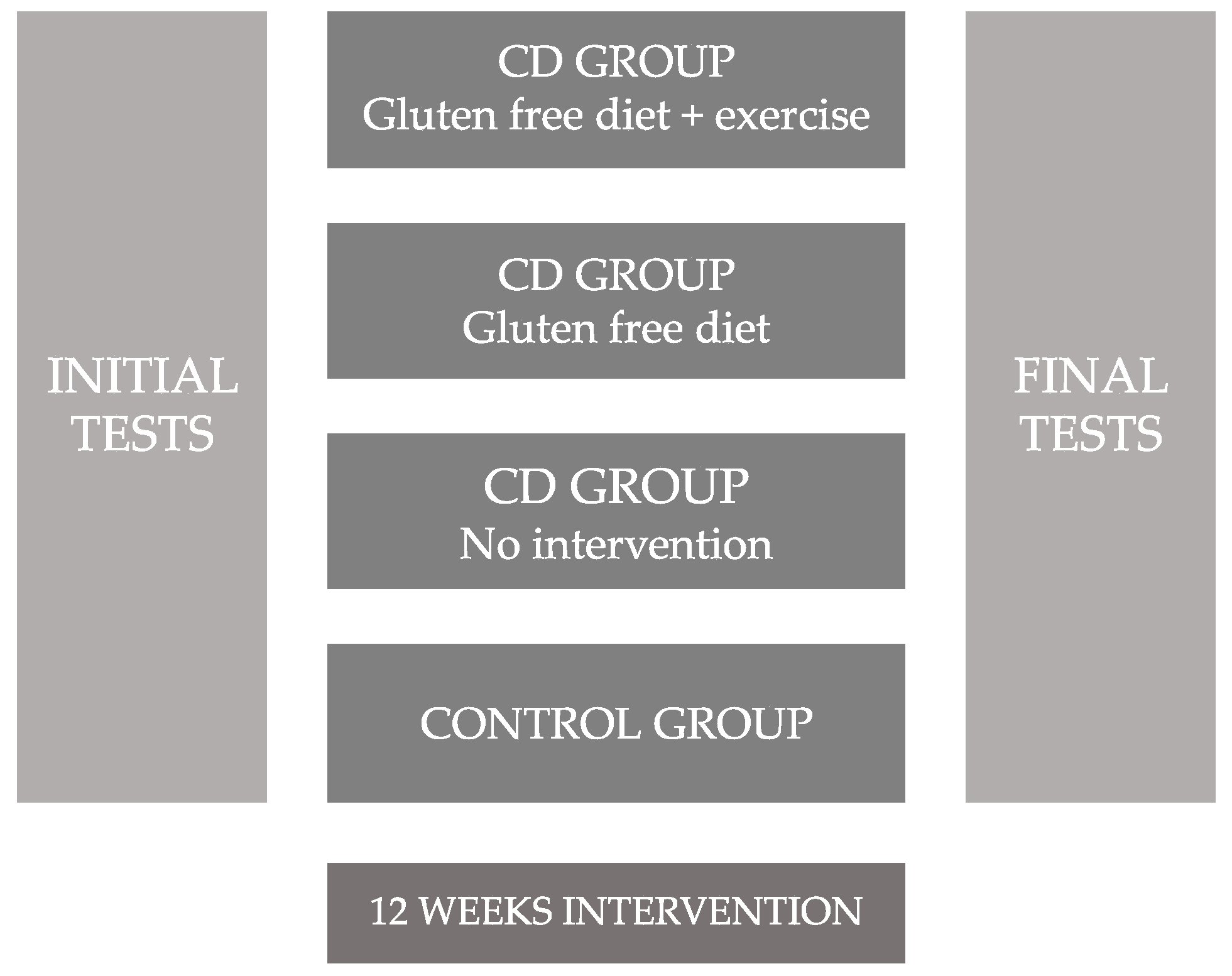
Each of the groups received different types of intervention during 12 weeks as resumed (Figure 2), the distribution was as follows: (1) Menopausal or post-menopausal celiac women will follow a physical exercise program 3/4 times per week and their dietary intake will be gluten-free isocaloric (GFD + E). (2) Menopausal or post-menopausal celiac women will follow a gluten-free isocaloric dietary program (GFD). (3) Menopausal or post-menopausal celiac women in whom all the tests were measured but they did not perform an intervention program with physical exercise or special follow-up of an adapted dietary-nutritional program (NO-GFD). (4) Non celiac menopausal or post-menopausal women in whom all the tests were measured but they did not perform an intervention program with physical exercise or special follow-up of an adapted dietary-nutritional program (CONTROL). Figure 2 shows the study design and it development.
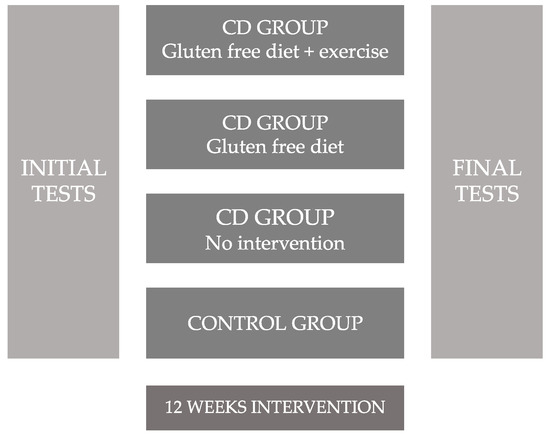
Figure 2.
Design and development of the study. CD = celiac disease.
The prescription of the diets was conducted by professional dietitians. For this purpose they followed the daily intake recommendations of macro and micronutrients for the Spanish population. Each of the participants had an individualized diet adapted to their requirements, paying special attention to the absence of gluten in them. An example of nutritional planning is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Gluten free example diet.
The physical exercise intervention was prescribed by a Physical Activity and Sport Sciences graduate, following the current recommendations of the American College of Sports Medicine. The control of the resistance physical exercise program was carried out by means of pedometers. The control of the physical strength exercise program was executed by means of validated subjective scales of effort perception.
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Quality of Life
A QoL questionnaire was performed; the WHOQOL-BREF of the World Health Organization. The WHOQOL-BREF is a 26-item version of the WHOQOL-100 assessment. It produces four domain scores from 24 items: a “social relationships” domain, a “physical health” domain, a “psychological health” domain, and an “environment” domain. The WHOQOL-BREEF uses a five-point Likert scale with responses from “very dissatisfied” to “very satisfied,” from “not at all” to “an extreme amount,” and from “never” to “always.” The transformed domain scores result in a scale from 0 to 100 with higher scores indicating higher QoL. Previous results [24] indicated that the WHOQOL-BREF is a sound, cross-culturally valid assessment of QoL, as reflected by its four domains: physical, psychological, social, and environment.
2.4.2. Body Composition
The parameters measured were: BC parameters included height (cm), weight (kg), BMI (kg/m2), lean body mass (LBM) (kg), and fat mass (%). A stadiometer (Seca 213, SECA Deutschland, Hamburg, Germany) was used to measure height to the millimeter, with the participant’s head held in the position of the horizontal Frankfort plane. Each participant took an inhalation at the time of measurement, while standing with heels, buttocks, and back in contact with the measuring rod (cm), following the recommendations of the Spanish group of kinanthropometry [25]. The rest of the variables were measured with bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) (Tanita BC-418, Tokyo, Japan), as it is a non-invasive, low-cost, and commonly used method for BC measurements and assessment of clinical status. It was observed that BIA, and many of the anthropometric equations used to estimate LBM change, showed high correlations with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) data [26].
2.4.3. Strength
A calibrated handgrip dynamometer (Takei 5101, Tokyo, Japan) was used to measure isometric grip strength (HGS), the test was performed twice for the dominant hand. Participants sat with 0° of shoulder and elbow flexion, and the forearm and hand in neutral position, and exerted their maximal force for 5 s [27], with 30 s of passive recovery between trials. The highest value for both hands was recorded and used for statistical analysis as the maximum voluntary hand grip strength.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics (mean ± standard deviation) were calculated, and the normality distribution was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk test. To study the equality of variances, the Levene’s test was performed and analysis of variance (ANOVA) (general linear model; time × group) with age as a covariate for the WHOQOL questionnaire to analyze the effects of the intervention on the assessments. For time × group interaction effects, partial eta squared effect sizes (η2p) were calculated (η2p ≥ 0.01 indicates a small effect, ≥0.059 a medium effect, and ≥0.138 a high effect). In the case that significant main effects were found, post hoc (Bonferroni) tests were performed. Moreover, to set up connections between the variables of the study, the Pearson’s correlation test was performed, with 95% confidence intervals. The results were contemplated following the parameters of Salaj and Markovic [28]: low (r ≤ 0.3), moderate (0.3 < r ≤ 0.7), to high (r > 0.7). The statistical significance level was set at p ≤ 0.05. Ultimately, the effect size (ES) was calculated following Cohen’s guidelines [29]. The ES was interpreted as small if it obtained values between 0.2 and 0.5, moderate if 0.5–0.8, and large when >0.8. To perform all statistical analysis, Jamovi 1.1.3.0 software was used.
3. Results
The baseline sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of the study subjects are shown in Table 2. In the study, a total of 28 menopausal or post-menopausal celiac women participated. Except for the NO-GFD group, the mean BMI was between 25.0 and 29.9 kg/m2, therefore, it is within the values corresponding to “overweight”. There were no significant differences between groups in the BMI variable (p = 0.114). BMI was in the normal range in 35% of the cases, 13 participants were overweight and 5 presented obesity. In terms of age, there were significant differences between the different groups (p < 0.001).

Table 2.
Characteristic of celiac participants included in survey.
Table 3 shows the values before and after the intervention for the different variables and the statistics obtained after ANCOVA analysis. As for QoL measured with the WHOQOL-BREF questionnaire, although the differences were not significant, better scores in all domains were observed in GFD + E. In the rest of the groups, depending on the scale observed, the score increased or decreased. In GFD, improvements were observed in the domains “psychological health” and “social relationships”. In NO-GFD, improvements were only observed in the domain “physical health”, in the rest of the domains the scores decreased and therefore the perception was lower. Finally, in the control group there was only a slight increase in the domain “environment”.

Table 3.
Comparison characteristics at baseline and after intervention (ANOVA) presented as mean ± standard deviation.
Regarding BC, Table 3 shows the comparison of fat percentage, fat free mass, and visceral fat of the four different groups; significant differences were observed in the variables % fat (p < 0.001) and fat free mass (p = 0.003) in GFD + E. In the case of fat mass, it decreased significantly, while fat-free mass increased. In terms of grip strength, a difference in effect time (p = 0.010) was observed in the right arm. In addition, a trend was observed between GFD + E and NO-GFD at post-intervention time; p = 0.059, with higher values in GFD + E compared to NO-GFD; 28.7 ± 5.4 kg vs. 25.2 ± 1.8 kg, respectively.
Summary statistics from the ANOVA analysis show that there was a significant time × group difference in fat mass and fat-free mass. There were significant intra-group differences between the variables fat mass (p < 0.01) and fat-free mass (p < 0.005) in GFD + E; celiac women with resistance training + gluten-free nutritional plan.
The ANCOVA analysis for the WHOQOL shows significant time × group differences in “psychological health” and “environment” subscales. Between GFD + E and NO-GFD, post hoc analysis showed an inter-group decreased in the “psychological health” subscale score (p = 0.027). Differences were also observed at time post between GFD and NO-GFD groups (p = 0.18). As for the “environment” subscale, differences were only observed between the NO-GFD and CONTROL groups, with the CONTROL group scoring higher.
As can be seen in the correlations (Table 4), age had a relevant negative relation with WHOQOL total score (p = 0.003) and all its subscales; physical health (p = 0.012), psychological health (p = 0.012), social relationships (p = 0.038), and environment (p = 0.008). This suggests that over the years, the QoL perception is lower.

Table 4.
Matrix of correlations between different variables.
Regarding dynamometry, significant correlations were observed with different variables. Negative correlations were observed between age and upper limb strength (p < 0.001), therefore, the older the age, the lower the strength. However, there are also positive correlations between the results of the handgrip test and the different subscales of the WHOQOL (p < 0.005 in all cases). Furthermore, the positive correlation (p = 0.011) between dynamometric hand strength and kilograms of LBM (kg) should be highlighted.
4. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the QoL, BC, and upper limb strength of a sample of women after undergoing different treatments: (1) gluten-free diet + exercise in celiac women, (2) gluten-free diet in celiac women, (3) celiac controls without a balanced and personalized GFD and exercise, and (4) healthy controls, establishing intragroup differences. Additionally, to study the differences between the different groups at different times (pre and post).
One of the hypotheses was that women with celiac disease would have lower QoL scores, as established research has shown that CD is a disorder that affects almost every system in the body [30]. This result is half confirmed, as the groups of celiac women who received some type of intervention (GFD + exercise or GFD) showed higher scores than healthy women on both the WHOQOL total score and subscales, however, celiac women who did not receive intervention scored lower.
Previous literature reported that the QoL of a patient with CD is mainly related to the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms [31,32]. Although there is no previous research using the same questionnaire, it was observed [33] that scores on other questionnaires significantly decreased after six months of following a gluten-free diet. Furthermore, Deepak C. et al. (2018) [33] also found that patients with clinical symptoms of diarrhea (p = 0.005), mouth ulcer (p = 0.008), generalized weakness (p = 0.009), and fatigue (p = 0.002) had a lower QoL perception than patients with other symptoms. This is also in agreement with Borghini, R. et al. (2016) [34] where they concluded that a gluten-free diet induced an improvement in well-being and a decrease of a depressive state after 12 months of strict diet.
It should be considered that women in the present study (GFD + E) were performing prescribed resistance training. Coinciding with previous studies, Kekäläinen et al. [35], observed that participants who trained twice a week improved their environmental QoL compared to other groups, who did not train or only trained once a week. Therefore, it seems that it can be affirmed that resistance training has positive effects on psychological outcomes. Furthermore, Puciato, D. et al. [36] observed that the highest scores in WHOQOL domains were obtained by respondents with the highest levels of physical activity. Ramirez-Campillo et al. [37] observed high assessments of overall QoL by individuals participating in appropriately dosed resistance training programs compared to controls. Besides, it should be noted that in the present investigation, GFD + E obtained significantly better results in the “psychological” subscale than the women with celiac disease in the control group. Therefore, in accordance with these and more recent studies [12], there is evidence that personalized exercise and lifestyle intervention can also lead to improve the QoL of people, among other things. QoL assessment is fundamental for a proper understanding of the health-disease process.
Concurring with Rodriguez-Almagro et al. [5], age was correlated with lower scores on all WHOQOL dimensions: physical, psychological, social, and environmental. This argument suggests that elder women have a lower perception of their QoL, regardless of the intervention/control group to which they belong. Both lack of movement, which is quite common among elderly people, and a gluten-free diet in elderly celiac patients should be treated as worrying trends.
BC assessment is an important variable for understanding human metabolism in different health conditions, including celiac disease [38]. As mentioned above and confirmed in the review by Costa et al. (2019) [38], celiac women tend to have a lower BMI and fat percentage than healthy women. In the present investigation, the results obtained confirm this statement, since the healthy control group (control group) is the women with the highest BMI values, however, they were not the ones with the highest fat %. Regarding LBM, they report that compared to celiac patients following a GFD, celiac patients not following a GFD had lower LBM in 66% of the studies, and there was no difference in 33.3% of them. This data coincides with the findings of this research, since it is observed that the celiac group with gluten-free diet + physical exercise had an LBM of 27.6 ± 2.3 kg, the celiac group with GFD had 26.1 ± 6.5 kg, and the celiac group without GFD had 25.9 ± 6.9 kg. Coinciding with 100% of the studies analyzed in the review [38], with regards to celiac patients who do not follow a gluten-free diet versus control subjects, it is observed that the values presented are 25.9 ± 6.9 kg and 26.7 ± 5.4 kg, respectively.
Maximal grip strength is one of the most important indicators of upper extremity function in elderly adults. In this cross-sectional study, one finding was that grip strength is inversely associated with age and directly related to both perceived QoL and fat-free mass (p = 0.005 for the left arm). This is consistent with previous studies [39,40] where they observed that QoL was positively associated with HGP. Furthermore, it appears that those celiac women who engage in physical exercise and follow a GFD tend to have better results than celiac women who neither engage in sport nor follow a GFD; 28.7 ± 5.4 and 25.2 ± 1.78 kg in the right arm, respectively. Although there are no data on women with celiac disease with which to compare the results obtained, these results were expected, since it has been seen [41,42] that grip strength is inversely associated with sedentary time in women.
It is important to highlight that the study was an intervention in which four different interventions could be compared, involving both celiac and healthy controls. However, it is necessary to mention some limitations. First, body composition was measured by bioimpedance, although this method is related to bone densitometry (dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry), it was not possible to use this method, which is considered the “gold standard”. In addition, the sample is not homogeneous in terms of age, so it has been included as a covariate in the analyses considered appropriate; in addition, the sample size was not large, as it is limited to a specific patient population (women with CD). Furthermore, in Spain the prevalence of CD is more prevalent among children (1:71) than in adults (1:357), which makes it difficult to have larger study sample sizes. In addition, many pre- and menopausal women have calcific disease but are not diagnosed as such. However, it has been observed that other investigations work with similar sample sizes [42]. It would be interesting to validate these results with a larger cohort.
5. Conclusions
It was found that only the group following a personalized GFD + E, showed a significant improvement in BC. Furthermore, a decrease in fat mass and an increase in muscle mass was observed. This fact was mainly due to the practice of physical activity, specifically resistance training. In addition, this group was the one that presented higher values for handgrip, which was positively related to the perception of QoL. However, the effect of a GFD diet in celiac women and the perception of QoL should not be forgotten, since gastrointestinal symptoms decreased.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.-R.; J.S.-S., S.P.-M. and P.J.M.-P.; methodology, A.M.-R., P.J.M.-P., F.A. and J.A.R.-A.; software, A.M.-R. and D.A.L.-M.; validation, J.S.-S., P.J.M.-P. and S.P.-M.; formal analysis, F.A., R.Y.-S. and J.A.R.-A.; investigation, A.M.-R., J.A.R.-A., M.M.-O., N.A.-M. and D.A.L.-M.; resources, A.M.-R., J.S.-S., P.J.M.-P. and S.P.-M.; data curation, D.A.L.-M., F.A., M.M.-O., R.Y.-S., N.A.-M. and J.A.R.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.-R., D.A.L.-M., J.S.-S. and M.M.-O.; writing—review and editing, S.P.-M., F.A., J.A.R.-A., R.Y.-S. and P.J.M.-P.; visualization, A.M.-R. and J.A.R.-A.; supervision, A.M.-R. and P.J.M.-P.; project administration, A.M.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Generalitat Valenciana (Concelleria D’ Educació, Investigació Cultura I Esport), grant number GV/2017/112.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was conducted according to the standards of the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the University Human Research Ethics Committee of Alicante University (Spain), code UA-2018-10-22. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 27 October 2021) as NCT05052164.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to is personal health information.
Acknowledgments
To all the participants in the present research, administrative personnel of the University of Alicante and to the celiac women’s associations that were involved at the beginning of the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singh, P.; Arora, S.; Singh, A.; Strand, T.A.; Makharia, G.K. Prevalence of celiac disease in Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churruca, I.; Miranda, J.; Lasa, A.; Bustamante, M.Á.; Larretxi, I.; Simon, E. Analysis of body composition and food habits of spanish celiac women. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5515–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalón-Ramon, E.; Juan-García, Y.; Pinzón-Rivadeneira, A. Prevalencia y características de la enfermedad celíaca en la fachada mediterránea peninsular. Med. Fam. Semer. 2016, 42, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, M.; Alonso-Garrido, M.; Lozano, M.; Manyes, L.; Miró, M.; Alonso-Garrido, M.; Lozano, M.; Manyes, L. Estudios clínicos sobre la enfermedad celíaca (2014–2019): Revisión sistemática de la prevalencia de la presentación clínica y enfermedades asociadas por edades. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Hum. Diet. 2020, 24, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Almagro, J.; Hernández-Martínez, A.; Lucendo, A.J.; Casellas, F.; Solano-Ruiz, C.; Siles-González, J. Health-related quality of life and determinant factors in celiac disease. A population-based analysis of adult patients in Spain. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2016, 108, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaukinen, K.; Lindfors, K.; Mäki, M. Advances in the treatment of coeliac disease: An immunopathogenic perspective. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratesi, C.B.; Häuser, W.; Uenishi, R.H.; Selleski, N.; Nakano, E.Y.; Gandolfi, L.; Pratesi, R.; Zandonadi, R.P. Quality of life of celiac patients in Brazil: Questionnaire translation, cultural adaptation and validation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustalahti, K.; Lohiniemi, S.; Collin, P.; Vuolteenaho, N.; Laippala, P.; Mäki, M. Gluten-free diet and quality of life in patients with screen-detected celiac disease. Eff. Clin. Pract. 2002, 5, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ukkola, A.; Mäki, M.; Kurppa, K.; Collin, P.; Huhtala, H.; Kekkonen, L.; Kaukinen, K. Diet improves perception of health and well-being in symptomatic, but not asymptomatic, patients with celiac disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilppula, A.; Kaukinen, K.; Luostarinen, L.; Krekelä, I.; Patrikainen, H.; Valve, R.; Luostarinen, M.; Laurila, K.; Mäki, M.; Collin, P. Clinical benefit of gluten-free diet in screen-detected older celiac disease patients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, S.; Kärner, A.; Hallert, C. Psychological well-being of adult coeliac patients treated for 10 years. Dig. Liver Dis. 2006, 38, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, A.J.; Kronlund, L.; Parmar, C.; Daun, J.T.; Wytsma-Fisher, K.; Reimer, R.A.; Millet, G.Y.; Culos-Reed, S.N. A 12-Week Pilot Exercise Program for Inactive Adults with Celiac Disease: Study Protocol. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2019, 11, 8:2164956119853777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, K.B.; Carlson, S.A.; Gunn, J.P.; Galuska, D.A.; O’Connor, A.; Greenlund, K.J.; Fulton, J.E. physical inactivity among adults aged 50 years and older—United States, 2014. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passananti, V.; Santonicola, A.; Bucci, C.; Andreozzi, P.; Ranaudo, A.; Di Giacomo, D.V.; Ciacci, C. Bone mass in women with celiac disease: Role of exercise and gluten-free diet. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopman, E.G.; le Cessie, S.; von Blomberg, B.M.; Mearin, M.L. Nutritional management of the gluten-free diet in young people with celiac disease in The Netherlands. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, M.; Trandafir, L.; Mîndru, E.; Moraru, E. Variability of nutritional status and of the parameters of lipid metabolism in gluten-free diet. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 2012, 116, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Brar, P.S.; Lee, A.R.; Green, P.H. Body mass index in celiac disease: Beneficial effect of a gluten-free diet. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, W.; Kearney, N. Overweight in celiac disease: Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and effect of a gluten-free diet. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2356–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Della Valle, N.; Rosania, R.; Facciorusso, A.; Trotta, A.; Cantatore, F.P.; Falco, S.; Pignatiello, S.; Viggiani, M.T.; Amoruso, A.; et al. A comparison of the nutritional status between adult celiac patients on a long-term, strictly gluten-free diet and healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardella, M.T.; Fredella, C.; Prampolini, L.; Molteni, N.; Giunta, A.M.; Bianchi, P.A. Body composition and dietary intakes in adult celiac disease patients consuming a strict gluten-free diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodé, S.; Hassager, C.; Gudmand-Høyer, E.; Christiansen, C. Body composition and calcium metabolism in adult treated coeliac disease. Gut 1991, 32, 1342–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Mazure, R.; Mautalen, C.; Vazquez, H.; Bai, J. Body composition and bone mineral density in untreated and treated patients with celiac disease. Bone 1995, 16, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghaei, M. An overview of randomization and minimization programs for randomized clinical trials. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2011, 1, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skevington, S.M.; Lotfy, M.; O’Connell, K.A. The World Health Organization’s WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment: Psychometric properties and results of the international field trial. A report from the WHOQOL group. Qual. Life Res. Int. J. Qual. Life Asp. Treat. Care Rehabil. 2004, 13, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.R.A.; Armesilla, M.D.C.; De Lucas, A.H.; Riaza, L.M.; Pascual, C.M.; Manzañido, J.P.; Quintana, M.S.; Belando, J.E.S. Protocolo de valoración de la composición corporal para el reconocimiento médico-deportivo. documento de consenso del grupo español de cineantropometría (grec)de la federación española de medicina del deporte (femede). Versión 2010. Arch. Med. Deport. 2010, 27, 330–344. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, F.J.; Munguía-Izquierdo, D.; Suárez-Arrones, L. Validity of field methods to estimate fat-free mass changes throughout the season in elite youth soccer players. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Samanes, Á.; Moreno-Pérez, D.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; Domínguez, R.; Pallarés, J.G.; Mora-Rodriguez, R.; Ortega, J.F. Circadian rhythm effect on physical tennis performance in trained male players. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaj, S.; Markovic, G. Specificity of jumping, sprinting, and quick change-of-direction motor abilities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Garatachea, N.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Fiuza-Luces, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Emanuele, E.; Lucia, A. Elite athletes live longer than the general population: A meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F. Epidemiological study of constipation and other gastrointestinal symptoms in 8000 children. Acta Paediatr. 2006, 95, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingone, F.; Swift, G.L.; Card, T.R.; Sanders, D.S.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Bai, J.C. Psychological morbidity of celiac disease: A review of the literature. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, C.; Berry, N.; Vaiphei, K.; Dhaka, N.; Sinha, S.K.; Kochhar, R. Quality of life in celiac disease and the effect of gluten-free diet. JGH Open Open Access J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Borghini, R.; Di Tola, M.; Salvi, E.; Isonne, C.; Puzzono, M.; Marino, M.; Donato, G.; Picarelli, A. Impact of gluten-free diet on quality of life in celiac patients. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2016, 79, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kekäläinen, T.; Kokko, K.; Sipilä, S.; Walker, S. Effects of a 9-month resistance training intervention on quality of life, sense of coherence, and depressive symptoms in older adults: Randomized controlled trial. Qual. Life Res. Int. J. Qual. Life Asp. Treat. Care Rehabil. 2018, 27, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puciato, D.; Borysiuk, Z.; Rozpara, M. Quality of life and physical activity in an older working-age population. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Diaz, D.; Martinez-Salazar, C.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Delgado-Floody, P.; Méndez-Rebolledo, G.; Cañas-Jamet, R.; Cristi-Montero, C.; García-Hermoso, A.; Celis-Morales, C.; et al. Effects of different doses of high-speed resistance training on physical performance and quality of life in older women: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Brito, G.A. Anthropometric parameters in Celiac Disease: A review on the different evaluation methods and disease effects. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 2019, 4586963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L.P.; Confortin, S.C.; Ono, L.M.; Barbosa, A.R.; d’Orsi, E. Quality of life associated with handgrip strength and sarcopenia: EpiFloripa Aging Study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 81, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Y.; Lim, J.; Park, H.S. Relationship between low handgrip strength and quality of life in Korean men and women. Qual. Life Res. 2018, 27, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Son, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-J. Relationship between sedentary time and handgrip strength in healthy Korean women: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2014–2016. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2020, 41, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toselli, S.; Badicu, G.; Bragonzoni, L.; Spiga, F.; Mazzuca, P.; Campa, F. Comparison of the effect of different resistance training frequencies on phase angle and handgrip strength in obese women: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).