Abstract
Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) is a widely consumed seafood in Asian countries. Rich in protein, abalone is consumed for refreshment, pregnancy care, and vitality. Although many studies have found that abalone protein has beneficial effects, the efficiency of the protein extraction method for abalone has rarely been studied. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the effects of various factors of abalone protein extraction, including extraction buffer, sonication, salt (NaCl) concentration, surfactant, and heating. Phosphate buffer showed higher protein yield compared with Tris-HCl buffer. In addition, the highest protein yield for each factor was observed at 60 s of sonication (84.44 µg/mg dw), 0.6 M NaCl (141.9 µg/mg dw), and 16 mM sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (253.15 µg/mg dw). However, a combined effect was not observed. Lower protein extraction efficiency was observed for sous vide-cooked abalone. The electrophoresis assay revealed myofibrillar proteins, including paramyosin, actin, and tropomyosin. Overall, our results demonstrate that various extract conditions affect the protein extraction of abalone.
1. Introduction
Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) is an aquatic organism belonging to gastropod families [1]. Abalones are found in interstitial waters in reefs or kelp forests in the ocean at 5–50 m [2]. Abalone is considered a delicacy and consumed raw or cooked in Asian countries. Furthermore, it is considered a functional food with health benefits in China, Japan, and Korea. With increased life span and economic development, the interest in foods highly associated with promoting health and reducing the prevalence of diseases has markedly increased. Therefore, the nutritional value of foods, especially high-quality proteins that are essential nutrients in the diet and contribute to healthy aging, has been recognized. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimated that the global demand for protein will increase by approximately 40% by 2030 with the increasing population. The high-quality protein in seafood is valued for its nutritional value and functional effects. Abalone is a rich source of high-quality proteins, and nutritional analysis showed that 100 g of the edible part of abalone contained 20 g of protein. The essential amino acids in abalones are arginine, leucine, lysine, glutamic acid, threonine, valine, and isoleucine [1]. The primary free amino acids in abalones are alanine, arginine, and taurine. Taurine, the most abundant amino acid in abalone, has beneficial effects such as protecting liver health, improving fatigue, anti-aging, and preventing myocardial infarction [3,4]. In addition, it is rich in micronutrients such as vitamin B1, vitamin B2, calcium, and phosphorus [1].
Abalone is among the most expensive seafood in the world. The high cost of abalone is attributed to its rarity and the complications of harvesting. The abalone firmly attaches to rocks by its muscular foot, which is responsible for the difficulties of obtaining it from the rocky outcrops where it lives. Therefore, the continuous demand for abalones has shifted the production from wild-caught to aquaculture, and over 95% of commercial abalone is produced by farming. Furthermore, advanced seedling production technology, aquaculture technology, and fishery conditions have increased the supply of abalone. However, shellfish, especially abalones, are vulnerable to harmful algal blooms (HABs). HAB is a typical natural phenomenon resulting from eutrophication, which may affect the global abalone supply chain [5].
As abalone is expensive seafood, it is occasionally consumed as processed food. In particular, it is processed to dried abalone and used as herbal medicine or made into a steamed jerky to enhance the protein and taurine content.
The amount of protein in abalone cultured in Korea is about 10.44–11.10% [6]. Myosin heavy chain, alpha-chain collagen, myofibril, and actin are the primary proteins in the foot muscle of abalone [6]. Various studies have revealed that abalone has a different composition of nutrients, particularly the composition and content of protein and amino acids, depending on the aquaculture environment, farming methods, and feed [6,7].
The extraction method is critical in determining the quantity of protein present in food [8]. Abalone protein is a major nutritional component and constitutes the primary purpose of abalone food processing. Therefore, quality control through accurate protein quantification is critical for processed abalone. Various methods are used to extract proteins from food materials, such as enzyme-assisted extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical extraction, and pulsed electric fields [9]. In addition, various extraction factors are controlled to increase extraction efficiency, including the pH and type of extraction buffer, use of surfactants, and inclusion of salts. The bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay is widely used to quantify protein [10,11]. Different protein extraction methods are adopted depending on the food materials, particularly their protein composition. In addition, the surfactant and salts added during the extraction will affect the downstream protein content analysis, resulting in imprecise estimation of protein contents [11,12]. Therefore, it is critical to develop suitable extraction conditions. Given the limited study on the effects of extraction conditions on shellfish protein, this study aimed to examine the effects of various extraction factors on the efficiency of abalone protein extraction and the composition of the extracted protein.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Fresh abalone was purchased from a local market (Mega Mart, Busan, Korea) (23.80 ± 1.74 g without the shell and viscera). To homogenize the protein components, the abalone sample was freeze-dried for 72 h. The dried abalone was milled, and the abalone powder was stored at −50 °C until further use. To investigate the effects of the types of buffer and surfactant and the salt concentration, phosphate buffer (PB), Tris-HCl, sodium chloride (NaCl), Triton X-100, and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). In addition, the BCA assay reagent was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich to analyze the amounts of protein.
2.2. Protein Extraction from Abalone
Abalone powder (30 mg) was homogenized with 1 mL of extraction buffer at 11,000 rpm for 30 s, followed by ultrasonication at 20 kHz for different time durations. Homogenized samples were centrifuged for 20 min at 14,000 rpm. The supernatants were collected and stored at −70 °C. The entire procedure of protein extraction was carried out on the ice.
2.3. Examination of the Efficiency of Various Protein Extraction Factors
2.3.1. Buffer Selection
The efficiency of the two most commonly used buffers for protein extraction, PB (10 mM) and Tris-HCl (10 mM) with 2 mM EDTA (pH 7.0), was examined in the present study. PB (10 mM) was made using sodium phosphate monobasic and dibasic. Tris-HCl (10 mM) was made by diluting ProNATM 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) (TransLab, Seoul, Korea) with double-distilled water and adjusting the pH to 7.0 using HCl. All buffers were stored at 4 °C and used within two weeks after preparation. The ultrasonication method was applied for 30, 60, and 120 s [13].
2.3.2. The Efficiency of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) for Protein Extraction
The effect of sodium chloride on protein extraction was examined by adding different concentrations of NaCl. Since NaCl in buffer solution was saturated at 6 M, lower concentrations, namely, 0.1, 0.15, 0.3, 0.6, 1.2, 2.4, and 4.8 M, were tested. The amount of protein in abalone extracts was analyzed using BCA assays following the manufacturer’s manual.
2.3.3. The Efficiency of Surfactants for Protein Extraction
SDS and Triton X-100 were used to examine the effects of surfactants. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is the surfactant concentration above which it aggregates to form micelles. It has been reported that the formation of micelles by surfactants can increase the protein extraction rate. Thus, the range of surfactant concentration was determined based on critical micelle concentration (CMC). Based on the CMCs of SDS and Triton X-100, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 mM SDS and 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, and 1.6 mM Triton X-100 were added to extraction buffer.
2.4. Application of Optimal Extraction Conditions to Heat-Treated Abalone
After vacuum packaging of abalone, the packed samples were soaked in a water bath (ANOVA Precision Cooker, San Francisco, CA, USA) at 80 °C for 30 min. Subsequently, the packages were cooled down in ice water for 30 min. The heat-treated abalone was freeze-dried and milled for further use.
2.5. Analysis of Abalone Protein Composition Using Electrophoresis
Abalone proteins were separated by electrophoresis in 5–12% gradient SDS-PAGE gels. Abalone proteins (20 μg) extracted in different conditions, namely, PB only, PB + 0.6 M NaCl, PB + 16 mM SDS, and PB + 8 mM Triton X-100, were mixed with sample buffer and then heated at 90 °C for 5 min in a heating block. Subsequently, electrophoresis was performed at 100 V for 85 min. After electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE gels were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 (TransLab, Seoul, Korea) for 60 min and destained with double-distilled water. Protein bands were tentatively identified by comparison with protein markers (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Extraction and each analysis were performed at least in triplicate. The significance of the difference in the amounts of abalone proteins was analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test or unpaired t-test in Prism 9 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) (p < 0.05).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Assay and Buffer Effects
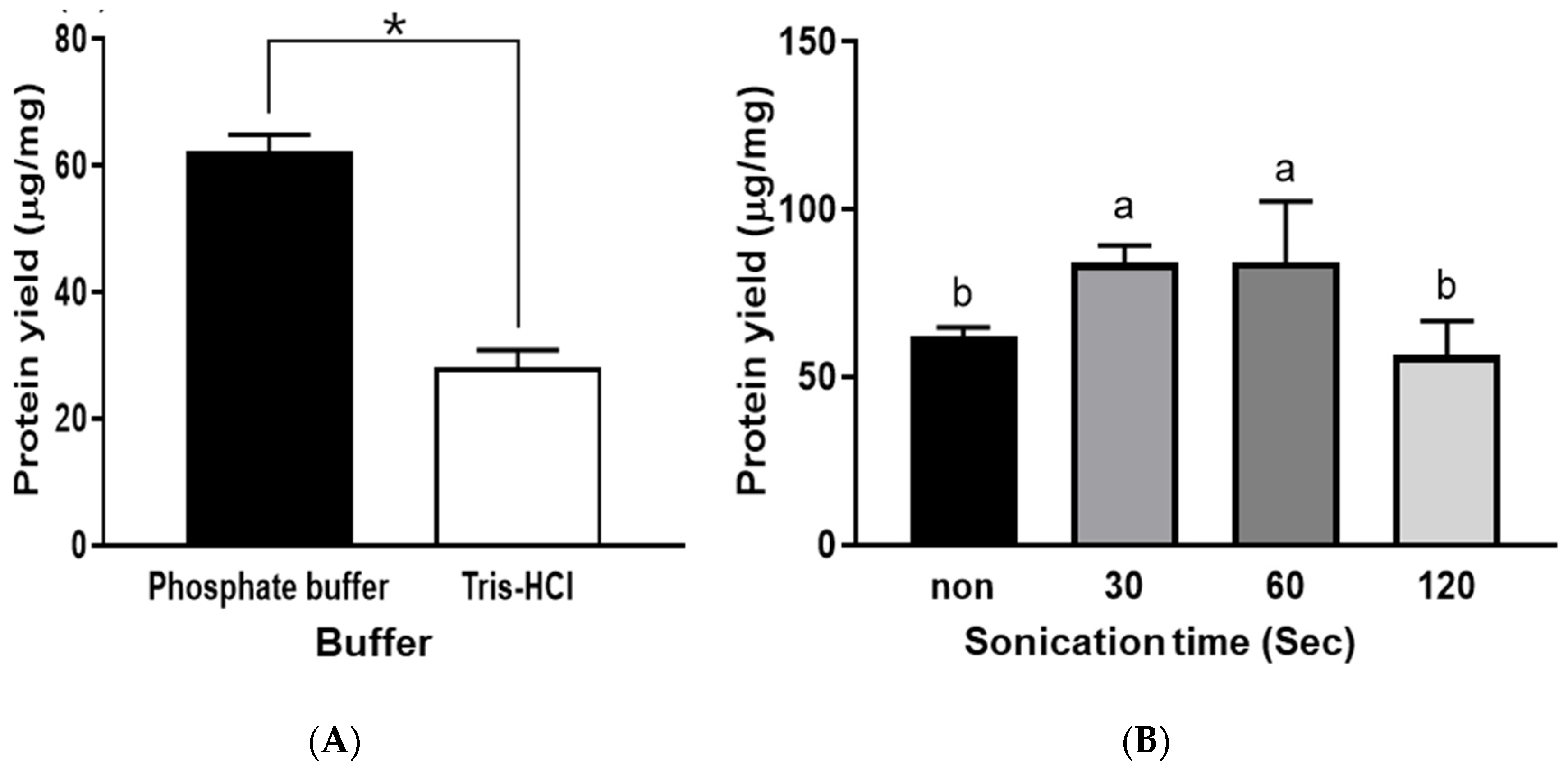
There are significant reasons to use buffer solution for protein extraction, including improving the stability of protein molecules, facilitating the isolation of protein molecules from non-soluble matrix components, and protecting the integrity of the target proteins [14]. In addition, several key factors need to be considered for an appropriate buffer, including solubility, chemical stability, efficiency in the chosen pH, and permeability to the extraction matrix. Generally, PB with a pH range between 5.8 and 8.0 is used to stabilize the proteins and is usually used to solubilize the target proteins. Tris-HCl buffer has a pH range of 7.0–9.0 and can extract cytoplasmic proteins [15]. In addition, Tris-HCl buffer can preserve the physiological ionic strength. However, it is known that the pH of Tris-HCl buffers is highly dependent on the temperature and the concentration. Between PB and Tris-HCl, PB was more effective in extracting protein from abalone. Protein yield was 60.8 µg/mg with PB and 28.7 µg/mg with Tris-HCl (Figure 1A). Therefore, PB was selected to examine the effects of other extraction factors. Our results are in good agreement with another study that compared the effects of PB and Tris-HCl on the extraction of various stress-related biochemical and physiological proteins in Populus deltoids, the eastern cottonwood. In that study, PB showed higher efficiency for soluble proteins, catalase, glutathione reductase, and superoxide dismutase [14].
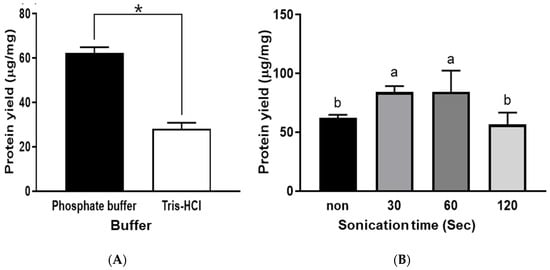
Figure 1.
Protein yields were obtained using different buffer types (A) and the application of various ultrasonication times (B). Bars with symbols (*) or different letters (a and b) are significantly different (p < 0.05).
Regarding sonication time, the protein yield was increased by ultrasonication for up to 60 s. However, sonication for 120 s showed an adverse effect (Figure 1B). This result indicates that the excessive application of ultrasonication could adversely affect the extraction of abalone protein, which could be due to protein denaturation and the occurrence of cavitation in the extraction solution after long-term ultrasonication [16]. Regarding protein denaturation, Siro et al. [17] found that ultrasound energy can denature proteins, especially on the surface of meat. This surface denaturation can rearrange the hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acid groups on the surface, which influences the solubility of proteins [18].
3.2. Sodium Chloride Effects
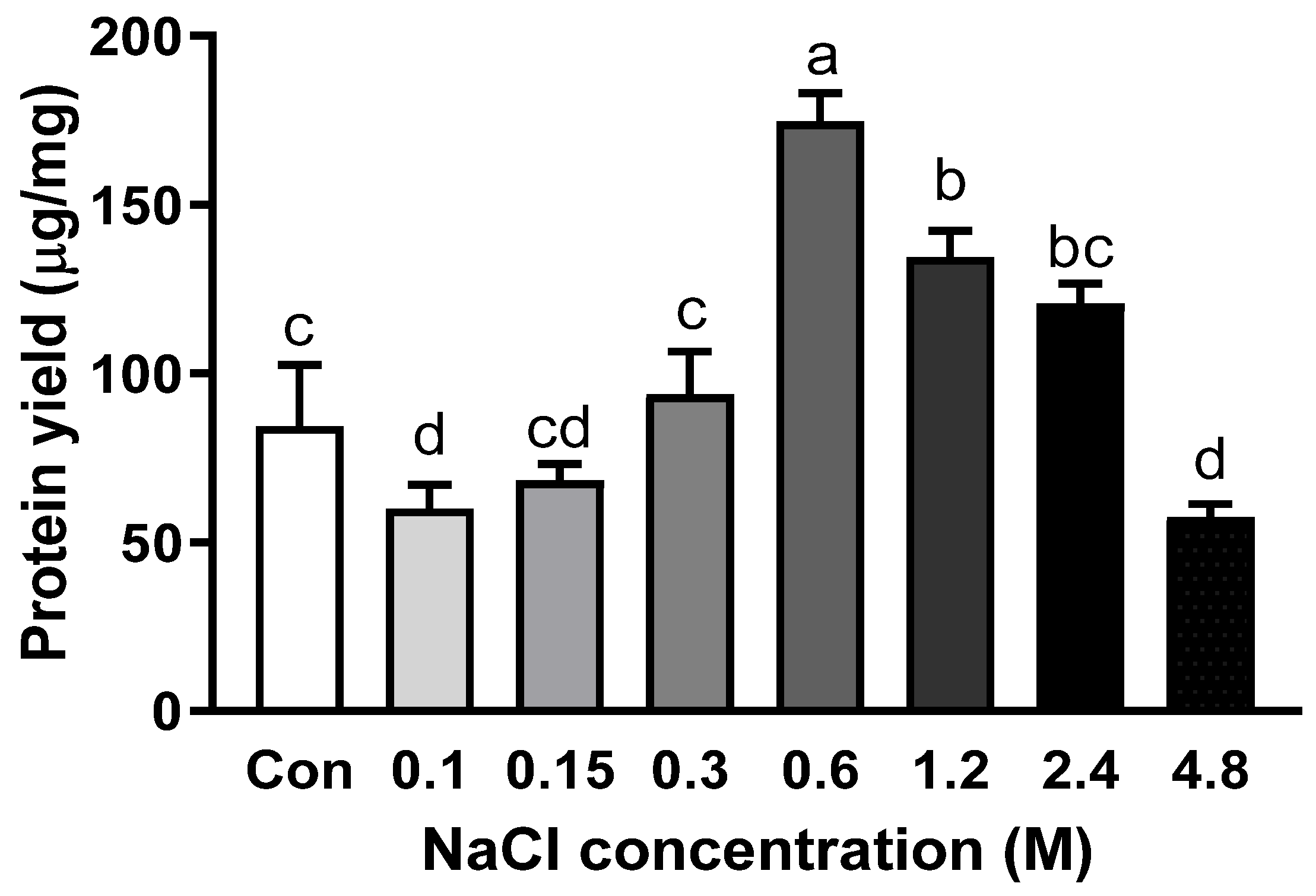
Salt is a significant factor for protein extraction because it is involved in salting-in and salting-out effects [19]. NaCl concentration up to 0.3 M did not alter the abalone protein yield (Figure 2). The extraction yield was significantly increased to 177.5 µg/mg when 0.6 M NaCl was added to PB. However, the extraction yield started to decrease when the concentration of NaCl reached or exceeded 1.2 M. Among various protein components of meat, myofibrillar proteins, including myosin heavy chain, paramyosin, actin, tropomyosin, and myosin light chain, play an essential role in the texture of meat products [20]. In particular, myofibrillar proteins are categorized as salt-soluble proteins, as they are soluble in a solution with an ionic strength of more than 0.3 M [21]. In another study about salt concentration on protein solubility, increasing salt concentration improved the solubility of protein up to a certain level, but not continuously [22]. Myofibrillar proteins are soluble at higher ionic strength compared with sarcoplasmic protein, another type of protein in skeletal muscle, which is soluble at low ionic strength [23]. Therefore, the addition of salt increased the extractability of abalone protein since abalone protein is mainly composed of myofibrillar proteins.
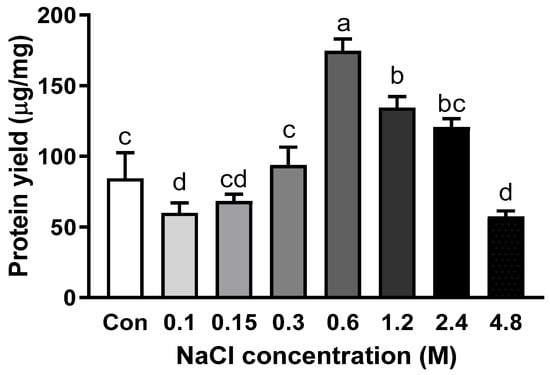
Figure 2.
Protein yield with the addition of different concentrations of NaCl in phosphate buffer with EDTA. Bars with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.3. Surfactant Effects and Synergistic Effects
Increased SDS concentration gradually improved the extraction rate of abalone protein. The maximum yield was reached with 16 mM SDS (Figure 3a). In contrast, Triton X-100 did not alter the extraction rate of abalone protein (Figure 3b). In the presence of 0.6 M NaCl, the SDS concentration also showed a similar trend, but the addition of 32 mM SDS showed the highest protein extraction rate (Figure 4). Surfactants are categorized into ionic and nonionic. There are three types of ionic surfactants, namely, anionic, cationic, and amphoteric [24]. SDS is an anionic surfactant and is negatively charged. An anionic surfactant consists of a negatively charged hydrophilic head group and a hydrophobic tail group, while nonionic surfactants consist of a neutral hydrophilic head group and a hydrophobic tail. SDS is the most frequently used anionic surfactant, while Triton X-100 is a typical nonionic surfactant [25]. The role of surfactants in protein extraction is highly associated with their critical micelle concentration (CMC) [25,26]. In an aqueous solution, surfactants at or over their CMCs preferably form micelle structures. Indeed, over the CMC, the level of monomer surfactants did not increase, but symmetrical spherical micelles dynamically increased. It has been reported that the CMC of SDS was 8.08 mM in water and 1.99 mM in PB [27]. Thus, our results indicate that an increase in the micelle structure of SDS improved the efficiency of abalone protein extraction. On the other hand, Triton X-100 has a lower CMC, so it easily breaks the cell membrane. Although nonionic surfactants are suitable for breaking lipid–lipid and lipid-protein interactions, they are less effective in breaking protein-protein interactions, so the protein yield may not be altered by the addition of Triton-X 100 [28].
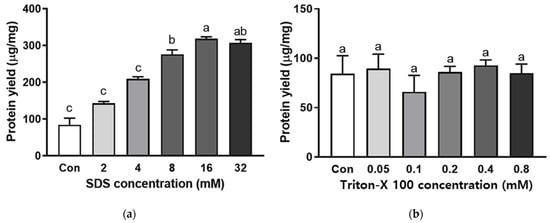
Figure 3.
Protein extraction yield with different surfactant concentrations of (a) SDS and (b) Triton X-100 in phosphate buffer with EDTA. Bars with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).
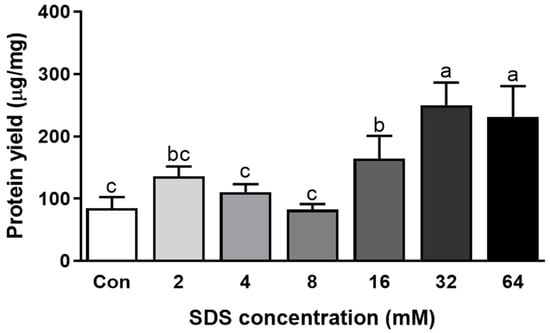
Figure 4.
Protein extraction yield with different concentrations of SDS with 0.6 M NaCl in phosphate buffer with EDTA. Bars with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.4. Application of Extraction Conditions to Thermally Processed Abalone
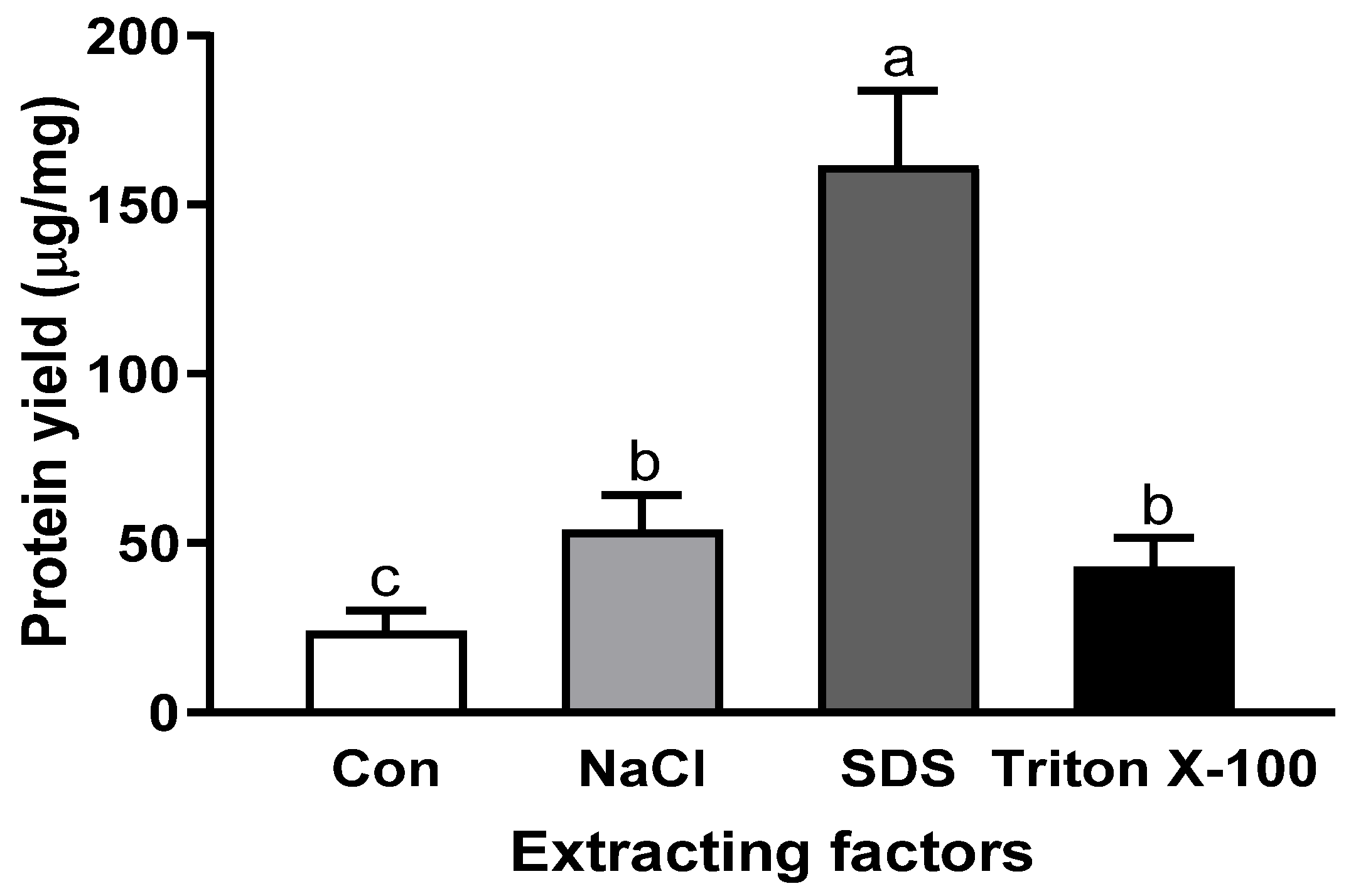
Since the sample condition is also a critical factor for extraction yield, the optimal conditions, including salt and surfactants, were applied to sous vide-cooked abalone. Compared with the raw abalone, protein extraction from thermally processed abalone resulted in significantly lower yields: 53.90 ± 10.2 µg/mg with NaCl, 161.6 ± 22.1 µg/mg with SDS, and 43.0 ± 8.6 µg/mg with Triton X-100 (Figure 5). Our study also shows good agreement with another study, which observed an approximately 80% decrease in the protein concentration of lionfish with 75 °C heating [29]. Our study shows good agreement with another study indicating that thermal treatment of abalone reduced soluble myofibrillar proteins, including myosin heavy chain, paramyosin, actin, and tropomyosin [30]. Temperature can induce changes in the structure and solubility of proteins. Significantly, the temperature-dependent hydrophobic effect, which is the main driving force in protein folding, can cause decreased protein solubility and lower protein extraction efficiency [31]. It has been reported that raising the temperature tends to increase the hydrophobic effects of proteins [12].
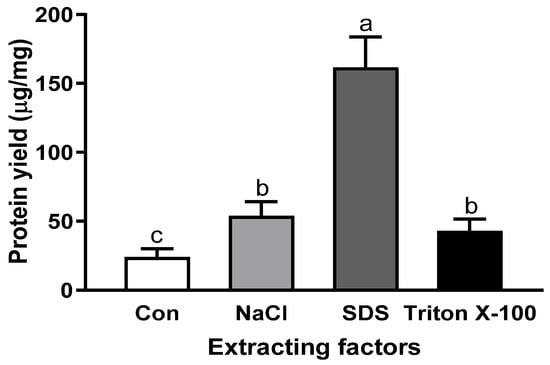
Figure 5.
Protein extraction yield of sous vide-cooked abalone with various optimal extraction factors, including 0.6 M NaCl, 16 mM SDS, and 0.8 mM of Triton X-100. Bars with different letters are significantly different (p < 0.05).
3.5. Abalone Protein Composition
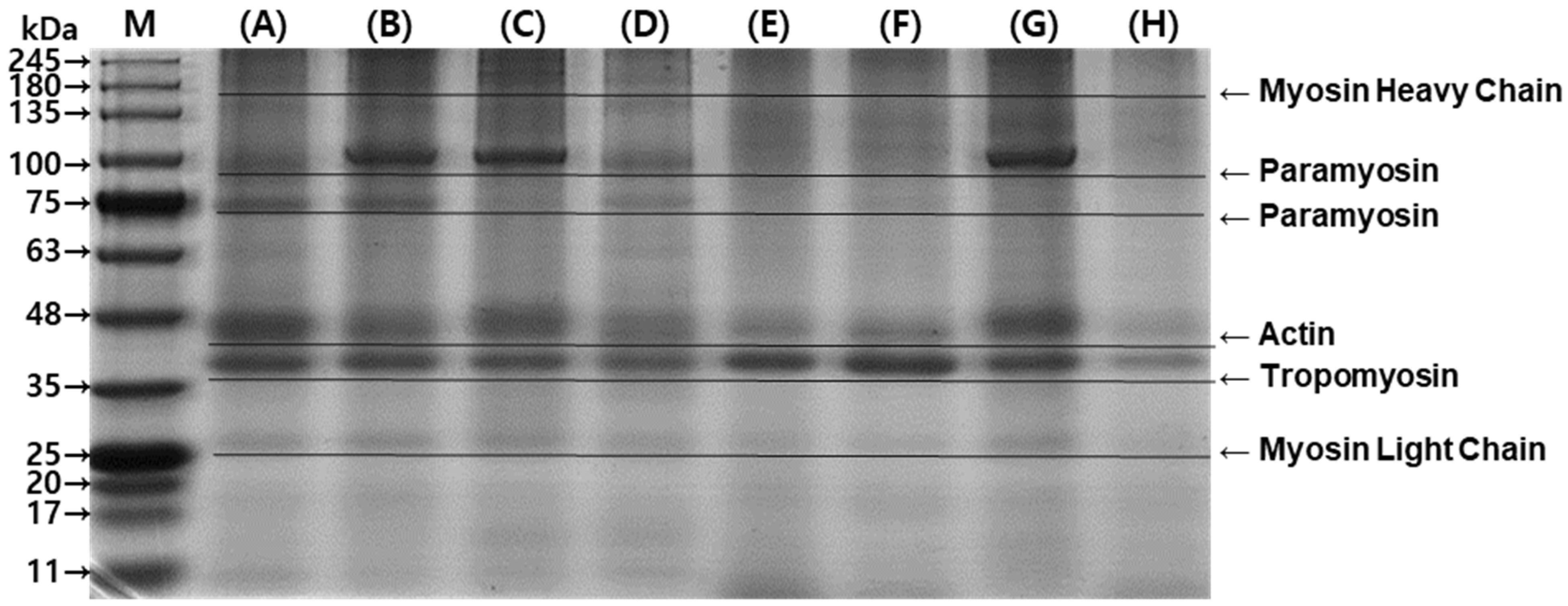
Protein composition was analyzed by electrophoresis. On the SDS-PAGE gel, myosin heavy chain (~200 kDa), paramyosin (~100 kDa and ~75 kDa), actin (~48 kDa), tropomyosin (~37 kDa), and myosin light chain (~25 kDa) were detected (Figure 6) [30]. The most abundant proteins extracted using PB were actin and tropomyosin (Line A). The addition of salt and surfactant changed the composition of extracted protein (Lines B and C), but Triton X-100 did not have the same effect (Line D). Sous vide cooking reduced the extraction of actin and tropomyosin (Line E), which could be due to the denaturation of myofibrillar proteins with thermal treatment [14]. The addition of NaCl did not improve the extraction yield of cooked abalone protein. However, SDS improved the protein extraction, achieving a yield similar to that of the raw abalone sample (Line C), while Triton X-100, another surfactant, did not improve the extraction yield (Line H). SDS was effective in extracting myosin light chain in raw and cooked abalone samples. Since myofibrillar protein is soluble at relatively high ionic strength, the addition of salt improved tropomyosin. In addition, since anionic surfactant effectively breaks protein–protein interaction, SDS showed higher overall myofibrillar protein extraction [27].
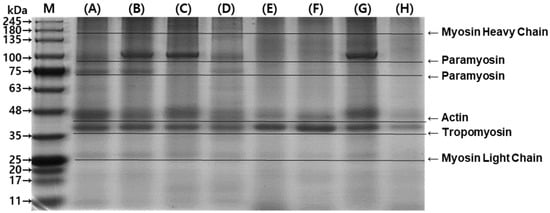
Figure 6.
Composition of raw and sous vide-cooked abalone protein extracted under different extraction conditions. (A) Raw abalone in phosphate buffer (PB) + EDTA, (B) raw abalone in PB + EDTA + 0.6 M NaCl, (C) raw abalone in PB + EDTA + 16 mM SDS, (D) raw abalone in PB + EDTA + 8 mM Triton X-100, (E) sous vide-cooked abalone in phosphate buffer (PB) + EDTA, (F) sous vide-cooked abalone in PB + EDTA + 0.6 M NaCl, (G) sous vide-cooked abalone in PB + EDTA + 16 mM SDS, and (H) sous vide-cooked abalone in PB + EDTA + 8 mM Triton X-100.
4. Conclusions
Haliotis discus hannai (Abalone) is protein-rich seafood that is widely consumed in Asian countries. To diversify our food sources with processed abalone, accurate protein content determination is critical. The present study examined the effects of various factors on abalone protein extraction, including the extraction buffer (PB or Tris-HCl buffer), use of sonication, use of salt (NaCl), and type of detergent (SDS or Triton-X). PB showed greater protein extraction compared with Tris-HCl. With 60 s of sonication, 84.44 µg/mg dw protein was obtained. The inclusion of 0.6 M NaCl or 16 mM SDS increased the protein yield to 141.9 µg/mg dw and 253.15 µg/mg dw, respectively. However, combining these factors did not show a synergistic effect. Cooked abalone showed lower protein extraction efficiency compared with raw abalone. Myosin heavy chain, paramyosin, actin tropomyosin, and myosin light chain were detected by electrophoresis assays. The application of extraction factors altered the protein profile of abalone extract. Our findings demonstrate the effects of various extraction conditions on the protein extraction yield of abalone. The present study supports that the extraction method can affect the protein yield, which is important for the quality of protein in processed food. Furthermore, the present study can provide comprehensive information to researchers who explore methods to increase protein yield and specific protein amounts of shellfish by modulating various factors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.K. and S.L.; validation, B.K. and S.L.; formal analysis, S.L.; investigation, H.-J.Y. and S.-J.J.; methodology, Y.L.; project administration, S.L.; resources, Y.L.; writing—original draft, H.-J.Y.; writing—review and editing, H.-R.K., B.K. and S.L.; supervision, H.-R.K. and B.K.; project administration, S.L.; funding acquisition, B.K. and S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Future Fisheries Food Research Center, the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Republic of Korea under Grant number 201803932 and National Institute of Fisheries Science (NIFS), Republic of Korea under Grant number R2022065.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no relevant financial or non-financial competing interest to report.
References
- Shi, L.; Hao, G.; Chen, J.; Ma, S.; Weng, W. Nutritional evaluation of Japanese abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino) muscle: Mineral content, amino acid profile and protein digestibility. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Miao, X.; Ke, C.; Kong, X.; Li, H.; You, W. Protein changes in abalone foot muscle from three geographical populations of Haliotis diversicolor based on proteomic approach. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 3645–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suleria, H.A.; Masci, P.P.; Gobe, G.C.; Osborne, S.A. Therapeutic potential of abalone and status of bioactive molecules: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tong, T.; Ko, D.O.; Chung, D.O.; Jeong, W.C.; Kim, J.E.; Kang, S.G. Anti-oxidant and Anti-skin-aging Effects of Abalone Viscera Extracts in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2012, 19, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botes, L.; Smit, A.J.; Cook, P.A. The potential threat of algal blooms to the abalone (Haliotis midae) mariculture industry situated around the South African coast. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-J.; Kim, S.Y. Abalone Aquaculture in Korea. J. Shellfish Res. 2013, 32, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.H.; Rayner, C.J.; Kerr, M.; Gorfine, H.K.; McShane, P.E. The composition and amino acid balance of abalone (Haliotis rubra) tissue. Aquaculture 1996, 140, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M. Measuring Protein Content in Food: An Overview of Methods. Foods 2020, 9, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Potkule, J.; Verma, R.; Punia, S.; Mahapatra, A.; Belwal, T.; Dahuja, A.; Joshi, S.; Berwal, M.K.; et al. Advances in the plant protein extraction: Mechanism and recommendations. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mohanna, T.; Bokros, N.T.; Ahsan, N.; Popescu, G.V.; Popescu, S.C. Methods for Optimization of Protein Extraction and Proteogenomic Mapping in Sweet Potato. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2139, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coelho, T.L.; Braga, F.M.; Silva, N.M.; Dantas, C.; Júnior, C.A.; de Sousa, S.A.; Vieira, E.C. Optimization of the protein extraction method of goat meat using factorial design and response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.M.; Chandler, D. Temperature and length scale dependence of hydrophobic effects and their possible implications for protein folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8324–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Jia, J.; Wen, C.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, J. Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of abalone viscera protein and its effect on the iron-chelating activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Chan, Z.; Yang, F. Comparative analyses of universal extraction buffers for assay of stress related biochemical and physiological parameters. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 45, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasekan, A.O.; Nayak, B. Effects of buffer additives and thermal processing methods on the solubility of shrimp (Penaeus monodon) proteins and the immunoreactivity of its major allergen. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukase, H.; Ohdaira, E.; Masuzawa, N.; Ide, M. Effect of Ultrasound in Soybean Protein Extraction. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 33, 3088–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siró, I.; Vén, C.; Balla, C.; Jónás, G.; Zeke, I.; Friedrich, L. Application of an ultrasonic assisted curing technique for improving the diffusion of sodium chloride in porcine meat. J. Food Eng. 2009, 91, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, S.C.d.S.; Miquelim, J.N. Interfacial behavior of food proteins. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 9, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Fan, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H. Influence of pH and salt concentration on functional properties of walnut protein from different extraction methods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çarkcioğlu, E.; Rosenthal, A.J.; Candoğan, K. Rheological and textural properties of sodium reduced salt soluble myofibrillar protein gels containing sodium tri-polyphosphate. J. Texture Stud. 2016, 47, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Joo, S.T.; Ryu, Y.C. Skeletal muscle fiber type and myofibrillar proteins in relation to meat quality. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, M.; Zakaria, Z.; Hashim, U.; Bari, M. Effect of pH and Salt Concentration on Protein Solubility of Slaughtered and Non-Slaughtered Broiler Chicken Meat. Sains Malays. 2017, 46, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.Y.; Morton, J.D.; Clerens, S.; Dyer, J.M. Cooking-Induced Protein Modifications in Meat. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning, P.A.; Mackie, A.R.; Gunning, A.P.; Woodward, N.C.; Wilde, P.J.; Morris, V.J. Effect of surfactant type on surfactant--protein interactions at the air-water interface. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liang, F.; Hu, D.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Zhu, Q. Determining the Critical Micelle Concentration of Surfactants by a Simple and Fast Titration Method. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4259–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y. Surfactant selection principle for reducing critical micelle concentration in mixtures of oppositely charged gemini surfactants. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7968–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuguet, E.; Ràfols, C.; Rosés, M.; Bosch, E. Critical micelle concentration of surfactants in aqueous buffered and unbuffered systems. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 29, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhairi, S.M. Detergent: A Guide to the Properties and Uses of Detergents in Biological Systems; Calbiochem-Novabiochem Corporation: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sommeng, A.N.; Pratiwi, I.; Ginting, M.J.; Sahlan, M.; Hermansyah, H.; Wijanarko, A. The effects of heating process on protein isolation of lionfish (Pterois volitans) spines venom extract to antioxidant activity assay. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2193, 020007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Dong, X.; Sun, L.; Xiao, G.; Chen, X.; Murata, Y.; Yu, C. Effect of Thermal Treatment on the Texture and Microstructure of Abalone Muscle (Haliotis discus). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.; Hoogeveen, A.; Abeln, S. The hydrophobic temperature dependence of amino acids directly calculated from protein structures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).