An Integrated Cybernetic Awareness Strategy to Assess Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behaviours in School Context
Abstract
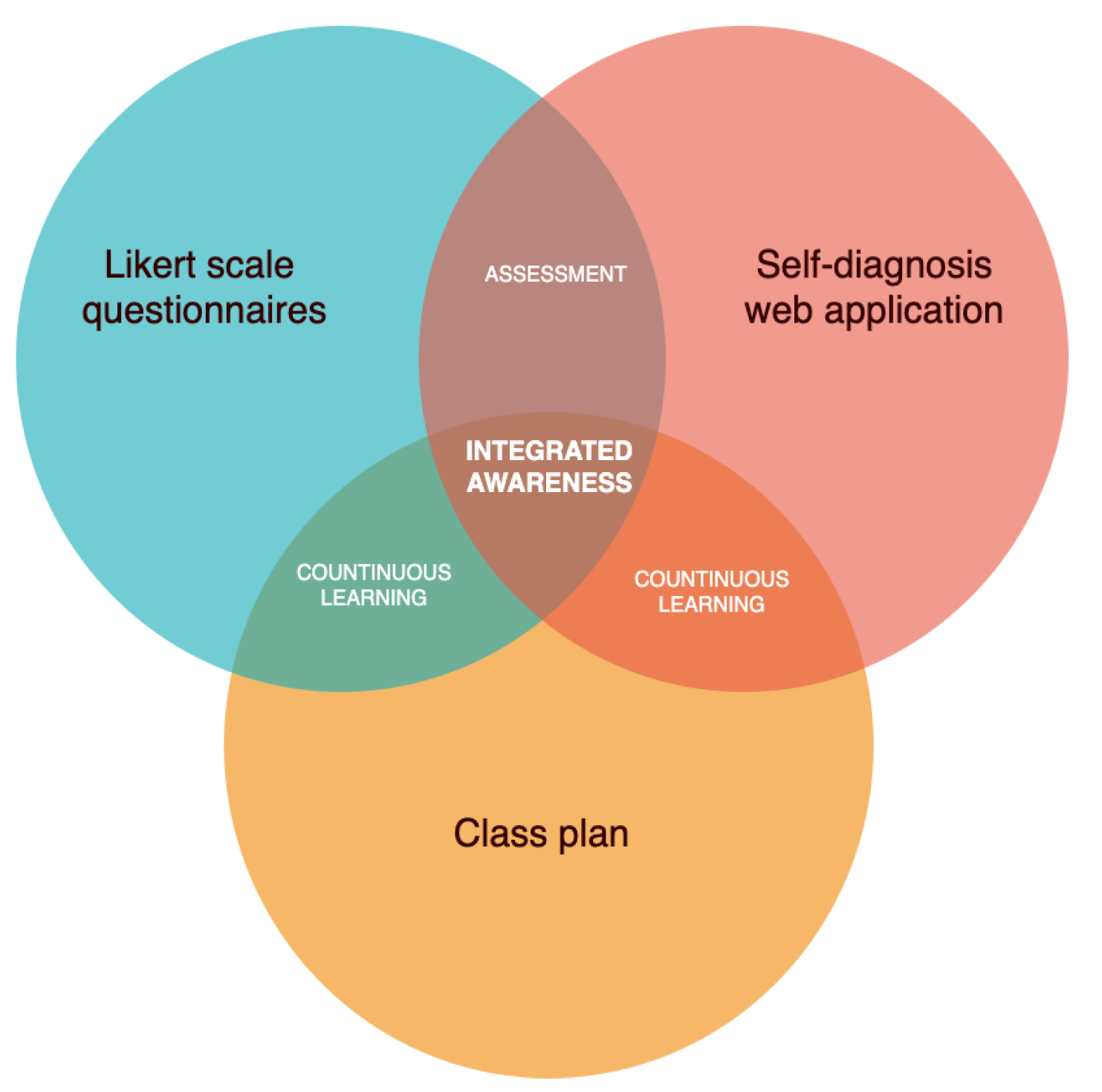
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Risky Attitude and Behaviour Assessment Scales
3.2. Self-Diagnosis Application
- The web application should be user-friendly and easy to use.
- The database of questions should include a vast number of items, and on each interaction, a new randomly generated set of questions should be used.
- The text of each question and its possible answer options should use an understanding, unambiguous, and easy-to-read language.
- The database of questions should follow a predefined layout that meets the published cybersecurity and information security taxonomies and standards.
- There should be provided feedback to the user, according to the answer given for each question. The feedback should include a score, a list of further readings, and a set of tips and hints that should be followed to mitigate some kind of bad behavior that has been observed in the answers.
3.3. Lesson Plan
- A 90-minutes slot was available to apply a lesson plan to briefly accommodate the cyberawareness topics. Further developments should include a deeper lesson plan which should be included in a longer duration slot.
- Two different curricular units were eligible to accommodate these subjects, namely Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs), and Education for Citizenship, being both part of the 6th and 9th grade curricula.
3.4. Statistical Analysis of the Scales
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABIS | ABbreviated Impulsiveness Scale |
| ATC-IB | Attitudes Towards Cybersecurity and Cybercrime in Business |
| CsA-S | Cybersecurity Attitudes in Schools |
| CsB-S | Cybersecurity Behaviors in Schools |
| CSIRT | Computer Security Incident Response Teams |
| ENISA | European Union Agency for Network and Information Security |
| HAIS-Q | Human Aspects of Information Security Questionnaire |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technology |
| KAB | Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behaviors |
| NGO | Non-Governmental Organizations |
| OCS | Online Cognition Scale |
| RScB | Risky Cybersecurity Behaviors Scale |
| SME | Small–Medium Enterprises |
References
- Bellovin, S.M. Layered Insecurity. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2019, 17, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, T. Net of Insecurity: A Flaw in the Design. The Internets Founders Saw Its Promise But Didnt Foresee Users Attacking One Another. USA, 2015. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/sf/business/2015/05/30/net-of-insecurity-part-1/ (accessed on 22 October 2021).
- Dawson, J.; Thomson, R. The future cybersecurity workforce: Going beyond technical skills for successful cyber performance. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goel, S.; Williams, K.; Dincelli, E. Got phished? Internet security and human vulnerability. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancis, J.R. The Age of Cyberpsychology: An Overview. Technol. Mind Behav. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlington, L. Human factors in cybersecurity; examining the link between Internet addiction, impulsivity, attitudes towards cybersecurity, and risky cybersecurity behaviours. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vervier, L.; Zeissig, E.M.; Lidynia, C.; Ziefle, M. Perceptions of Digital Footprints and the Value of Privacy. In Proceedings of the IoTBDS, Prague, Czech Republic, 7–9 May 2017; pp. 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, Y.; Gafni, R. Introducing the concept of cybersecurity footprint. Inf. Comput. Secur. 2021, 29, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaridas-Nalda, F.; Clavel-San Emeterio, M.; Fernández-Ortiz, R.; Arias-Oliva, M. The strategic influence of school principal leadership in the digital transformation of schools. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 112, 106481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demartini, C.G.; Benussi, L.; Gatteschi, V.; Renga, F. Education and digital transformation: The “riconnessioni” project. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 186233–186256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusky, L.; Partow-Navid, P. Students information security practices and awareness. J. Inf. Priv. Secur. 2012, 8, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanus, B.; Wu, Y.A. Impact of users’ security awareness on desktop security behavior: A protection motivation theory perspective. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2016, 33, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.D.; Lemoine, P.A.; Stephens, W.E.; Waller, R.E. Planning for Cyber Security in Schools: The Human Factor. Educ. Plan. 2020, 27, 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tirumala, S.S.; Sarrafzadeh, A.; Pang, P. A survey on Internet usage and cybersecurity awareness in students. In Proceedings of the 2016 14th Annual Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST), Auckland, New Zealand, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Zwilling, M.; Lesjak, D.; Natek, S.; Phusavat, K.; Anussornnitisarn, P. How to deal with the awareness of cyber hazards and security in (Higher) education. In Proceedings of the Thriving on Future Education, Industry, Business and Society. Proceedings of the Makelearn and TIIM International Conference, Piran, Slovenia, 15–17 May 2019; pp. 433–439. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.; Sairi, I.; Zizi, N.; Khalid, F. The importance of cybersecurity education in school. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2020, 10, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livingstone, S.; Haddon, L.; Görzig, A.; Ólafsson, K. Risks and Safety on the Internet: The Perspective of European Children: Full Findings and Policy Implications from the EU Kids Online Survey of 9–16 Year Olds and Their Parents in 25 Countries. Online Report 06.3. 2011. Available online: http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/33731/ (accessed on 22 October 2021).
- Smahel, D.; Machackova, H.; Mascheroni, G.; Dedkova, L.; Staksrud, E.; Ólafsson, K.; Livingstone, S.; Hasebrink, U. EU Kids Online 2020: Survey Results from 19 Countries. Online Report. Available online: https://www.lse.ac.uk/media-and-communications/assets/documents/research/eu-kids-online/reports/EU-Kids-Online-2020-10Feb2020.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- eukidsonline.net. Available online: http://www.eukidsonline.net/ (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Mee, P.; Brandenburg, R.; Lin, W. Oliver Wyman Forum Global Cyber Risk Literacy and Education Index. Oliver Wyman Forum, Octubre, 2020. Available online: https://www.oliverwymanforum.com/cyber-risk/cyber-risk-literacy-education-index.html (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Pfleeger, S.L.; Caputo, D.D. Leveraging behavioral science to mitigate cyber security risk. Comput. Secur. 2012, 31, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormac, A.; Zwaans, T.; Parsons, K.; Calic, D.; Butavicius, M.; Pattinson, M. Individual differences and information security awareness. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 69, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boletsis, C.; Halvorsrud, R.; Pickering, J.B.; Phillips, S.C.; Surridge, M. Cybersecurity for SMEs: Introducing the Human Element into Socio-technical Cybersecurity Risk Assessment. In VISIGRAPP (3: IVAPP); Scitepress: Setúbal, Portugal, 2021; pp. 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, M.; Maximiano, M.; Gomes, R.; Pinto, D. Information Security and Cybersecurity Management: A Case Study with SMEs in Portugal. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2021, 1, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Antunes, M.; Silva, C. Evaluating cybersecurity attitudes and behaviors in Portuguese healthcare institutions. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 181, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENISA. Cybersecurity Culture Guidelines: Behavioural Aspects of Cybersecurity; European Union Agency for Network and Information Security: Athens, Greece, 2018.
- Furnell, S.; Esmael, R.; Yang, W.; Li, N. Enhancing security behaviour by supporting the user. Comput. Secur. 2018, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikh, M. Developing cybersecurity culture to influence employee behavior: A practice perspective. Comput. Secur. 2020, 98, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, F.; Papasalouros, A.; Kambourakis, G.; Gritzalis, S. A comprehensive cybersecurity learning platform for elementary education. Inf. Secur. J. A Glob. Perspect. 2019, 28, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quayyum, F. Cyber security education for children through gamification: Challenges and research perspectives. In International Conference in Methodologies and intelligent Systems for Techhnology Enhanced Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Quayyum, F. Cyber security education for children through gamification: Research plan and perspectives. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM Interaction Design and Children Conference: Extended Abstracts, London, UK, 21–24 June 2020; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Best Security Awareness Training Software in 2021|G2. Available online: https://www.g2.com/categories/security-awareness-training/ (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Zwilling, M.; Klien, G.; Lesjak, D.; Wiechetek, Ł.; Cetin, F.; Basim, H.N. Cyber security awareness, knowledge and behavior: A comparative study. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, H.; Skinner, G. Educating and raising awareness on cyber security social engineering: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Teaching, Assessment, and Learning for Engineering (TALE), Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 4–7 December 2018; pp. 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- ENISA. Reference Incident Classification Taxonomy-Task Force Status and Way Forward; European Union Agency for Network and Information Security: Athens, Greece, 2018.
- ENISA. Material. Available online: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/media/multimedia/material/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS; Sage Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]








| ID | Question |
|---|---|
| A1 * | I believe that it is safe to ignore update warnings from computer software. |
| A2 | I am aware of my role in keeping the school protected from potential cybercriminals. |
| A3 | I believe everyone in the school has a role to play in protecting against threats from cybercriminals. |
| A4 * | It is hard to know how I can help protect the school from cybercrime. |
| A5 * | I don’t have the right skills to be able to protect the school from cybercrime. |
| A6 | I believe that personal information should not be revealed online, namely who I am, where I live or which school I attend. |
| A7 * | Computer systems provide all the protection a school need. |
| A8 * | I think that reporting cybercrime is a waste of time. |
| A9 * | The Police lack the capacity to deal with cybercrime effectively. |
| A10 * | I believe that cybercriminals are more advanced than the people who are supposed to be protecting us. |
| A11 * | I would download copyright material (images, documents, videos). |
| A12 | I believe when I view violence related content in a school, I may have been promoting its sharing and comments. |
| A13 * | I worry that if I report a cyberattack to the Police it might damage the reputation of the school. |
| A14 * | I think more could be done to communicate/disseminate/sensitize the risks from cybercrime to individuals in the school. |
| A15 | I am aware of the schools IT use policy and attempt to follow it. |
| A16 * | I would not know how to report a cyberattack if one happened. |
| A17 * | I don’t think that reporting a cyberattack launched from the school is my responsibility. |
| A18 * | I don’t pay attention to school material about the threats from cybercrime. |
| A19 | I am confident that I would be able to spot the signs of a cyberattack. |
| A20 | I believe that, when inappropriate content appears online, I should ask for help from an adult. |
| A21 | I feel that any individual within the school is at risk of manipulation from confidence tricksters. |
| A22 * | I think that cybercriminals only target a school when there is a substantial financial gain. |
| A23 * | I believe only companies are targeted by hackers and cybercriminals. |
| A24 * | I feel that only companies that take payments using online systems are at risk of being victims of cybercrime. |
| A25 * | I think that I have the right to be always online, with access to all Internet services. |
| ID | Question |
|---|---|
| B1 | Sharing passwords with friends and colleagues. |
| B2 | Using or creating passwords that are not very complicated (e.g., family name and date of birth, letter strings). |
| B3 | Using the same password for multiple websites. |
| B4 | Using online storage systems to exchange and keep personal or sensitive information. |
| B5 | Entering payment information on websites that have no clear security information/certification. |
| B6 | Using free-to-access public Wi-Fi. |
| B7 | Relying on a trusted friend or colleague to advise you on aspects regarding online security. |
| B8 | Downloading free anti-virus software/apps from an unknown source. |
| B9 | Disabling the anti-virus on my computer so that I can download information from websites. |
| B10 | Bringing in my own USB to school in order to transfer data onto it. |
| B11 * | Checking that software in your smartphone/tablet/laptop/PC is up to date. |
| B12 | Downloading digital media (music, films, games) from unlicensed sources. |
| B13 | Sharing my current location on social media. |
| B14 | Accepting friend requests on social media because you recognize the photo. |
| B15 | Clicking on links contained in unsolicited emails from an unknown source. |
| B16 | Sending personal information to unknown people over the Internet. |
| B17 | Clicking on links in an e-mail message that come from a trusted friend or colleague. |
| B18 * | Checking for updates for any anti-virus software you have installed. |
| B19 | Downloading data and material from websites on your computer without checking its authenticity. |
| B20 | Storing personal, family and friend’s information on your personal electronic device (e.g., smartphone/tablet/laptop). |
| ID | Finding | ID |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | The students express some level of awareness regarding their privacy online and the consequences of exposing their personal data? | A6 B5, B13, B14, B16, B20 |
| 02 | Students’ online attitudes and behaviors are tendentiously positive or negative? | A11, A12, A17, A25 B8, B9, B12, B19, A8 |
| 03 | What is the students’ perception about the cybersecurity information provided by the school? | A14, A15, A16, A17, A18 |
| 04 | When contacting with strangers online, are the students’ aware about the concerns involved? | B2, B4, B5, B14, B15, B17 |
| 05 | Are students aware about their attitudes and behaviors towards cybersecurity in school? | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7 B2, B9, B11 |
| 06 | Do students understand the cybercriminals’ motivations? | A19, A22, A23, A24 |
| 07 | Do students reckon on law enforcement and ICT technicians? | A8, A9, A10, A13 |
| 08 | Do students aware about protecting their equipment and data? | B1, B2, B3, B6, B8, B9, B10, B11, B18, B20 |
| 09 | Do students aware about the consequences of using unofficial and copy-write protected software? | B8, B12, B19 |
| ID | Question | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| A1 * | I believe that it is safe to ignore update warnings from computer software | 0.010 |
| A2 | I am aware of my role in keeping the school protected from potential cybercriminals | <0.001 |
| A5 * | I don’t have the right skills to be able to protect the school from cybercrime | 0.016 |
| A6 | I believe that personal information should not be revealed online, namely who I am, where I live or which school I attend | 0.002 |
| A8 * | I think that reporting cybercrime is a waste of time | 0.002 |
| A9 * | The Police lack the capacity to deal with cybercrime effectively | <0.001 |
| A10 * | I believe that cybercriminals are more advanced than the people who are supposed to be protecting us | 0.008 |
| A11 * | I would download copyright material (images, documents, videos) | <0.001 |
| A13 * | I worry that if I report a cyberattack to the Police it might damage the reputation of the school | <0.001 |
| A15 | I am aware of the schools IT use policy and attempt to follow it | <0.001 |
| A16 * | I would not know how to report a cyberattack if one happened | 0.008 |
| A17 * | I don’t think that reporting a cyberattack launched from the school is my responsibility | 0.004 |
| A18 * | I don’t pay attention to school material about the threats from cybercrime | <0.001 |
| A19 | I am confident that I would be able to spot the signs of a cyberattack | 0.023 |
| A20 | I believe that, when inappropriate content appears online, I should ask for help from an adult | <0.001 |
| A25 * | I think that I have the right to be always online, with access to all Internet services | 0.008 |
| B3 | Using the same password for multiple websites | 0.001 |
| B4 | Using online storage systems to exchange and keep personal or sensitive information | 0.029 |
| B5 | Entering payment information on websites that have no clear security information/certification | 0.003 |
| B9 | Disabling the anti-virus on my computer so that I can download information from websites | 0.005 |
| B12 | Downloading digital media (music, films, games) from unlicensed sources | 0.017 |
| B13 | Sharing my current location on social media | <0.001 |
| B19 | Downloading data and material from websites on your computer without checking its authenticity | 0.034 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antunes, M.; Silva, C.; Marques, F. An Integrated Cybernetic Awareness Strategy to Assess Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behaviours in School Context. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311269
Antunes M, Silva C, Marques F. An Integrated Cybernetic Awareness Strategy to Assess Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behaviours in School Context. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(23):11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311269
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntunes, Mário, Carina Silva, and Frederico Marques. 2021. "An Integrated Cybernetic Awareness Strategy to Assess Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behaviours in School Context" Applied Sciences 11, no. 23: 11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311269
APA StyleAntunes, M., Silva, C., & Marques, F. (2021). An Integrated Cybernetic Awareness Strategy to Assess Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behaviours in School Context. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11269. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311269







