Analysis of Hydrological Characteristics of Blue Nile Basin, Nashe Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Watershed
2.2. Model Selection
2.3. Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Model Description
2.4. SWAT-CUP (Soil and Water Assessment Tool-Calibration and Uncertainty Programs)
2.4.1. SUFI-2
2.4.2. GLUE
2.4.3. PARASOL
2.4.4. PSO
2.5. Data Collection and Analysis
2.5.1. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
2.5.2. Soil Data
2.5.3. Land Use Land Change (LULC) and Slope Data
2.5.4. Weather Data
2.5.5. Hydrological Data
2.5.6. Model Set Up
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
2.7. Model Calibration and Validation
2.8. Uncertainty Analysis
2.9. Efficiency of Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensitivity Analysis
3.2. Model Calibration
3.3. Model Validation
3.4. Uncertainty Analysis
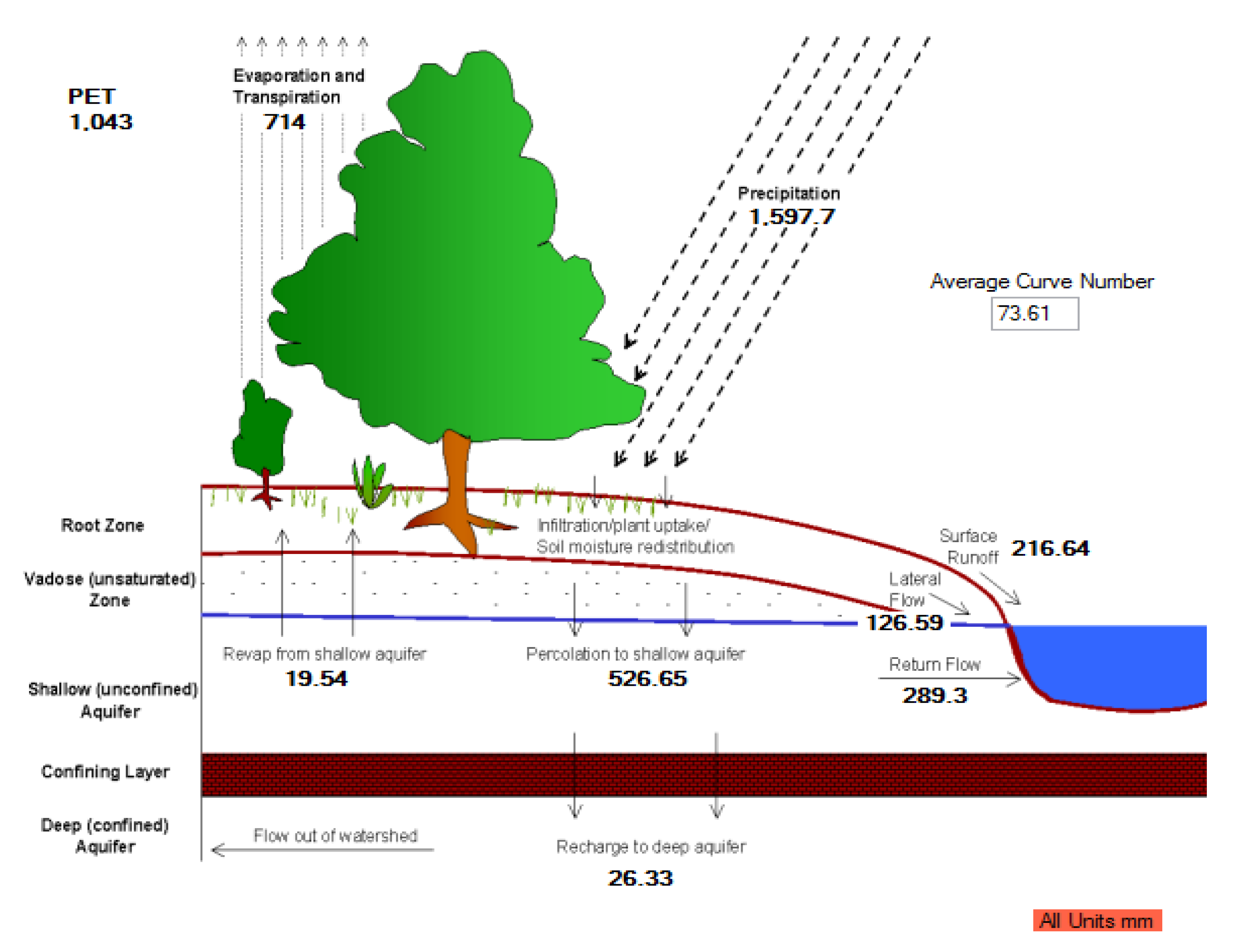
3.5. Hydrological Water Balance of the Watershed
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yazdi, J.; Moridi, A. Interactive Reservoir-Watershed Modeling Framework for Integrated Water Quality Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2105–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, E.B.; Camp, J.V.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Penrod, J.R.; Dobbins, J.P.; Abkowitz, M.D. Watershed Modeling and its Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review. Open Hydrol. J. 2011, 5, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leta, M.K.; Demissie, T.A.; Tränckner, J. Hydrological Responses of Watershed to Historical and Future Land Use Land Cover Change Dynamics of Nashe Watershed, Ethiopia. Water 2021, 13, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, E.I.; Fleifle, A.; Ludwig, R.; Disse, M. Improving SWAT model performance in the upper Blue Nile Basin using meteoro-logical data integration and subcatchment discretization. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4907–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadil, A.; Rhinane, H.; Kaoukaya, A.; Kharchaf, Y.; Bachir, O.A. Hydrologic Modeling of the Bouregreg Watershed (Morocco) Using GIS and SWAT Model. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2011, 3, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UNECA. An Assessment of Africa’s Climatic Records and Recording Networks Including Strategic for Rescuing of Climatic Data; Working paper 3, UNECA: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2011; pp. 2–19. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, K.L.; Polsky, C.; Gober, P.; Chang, H.; Shandas, V. Vulnerability of water systems to the effects of climate change and ur-banization: A comparison of phoenix, Arizona and Portland, Oregon (USA). Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adla, S.; Tripathi, S.; Disse, M. Can we calibrate a daily time-step hydrological model using monthly time-step discharge data? Water 2019, 11, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leta, M.K.; Demissie, T.A.; Trä, J. Evaluation of the Impacts of Land Use Land Cover Change on Hydrology—A Case Study of the Nashe Watershed. In Proceedings of the 6th International Electronic Conference on Water Sciences, Online, 15–30 November 2021; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Bowden, W.B.; Davie, T.; Fenemor, A. Multi-variable and multi-site calibration and validation of SWAT in a large mountainous catchment with high spatial variability. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 20, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megersa, K.; Ankit, C.H.; Tamene, A. Stream Flow and Land Use Land Cover Change in Finchaa Hydropower, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Int. J. Civil. Struct. Environ. Infrastruct. Eng. Res. Dev. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrie, G.D.; Mohamed, Y.A.; van Griensven, A.; Srinivasan, R. Sediment management modelling in the Blue Nile Basin using SWAT model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, M.; Shibata, H. Simulation of watershed hydrology and stream water quality under land use and climate change scenarios in Teshio River watershed, northern Japan. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil & Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation; Blackl Res Center: Temple, TX, USA, 2011; p. 647. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; He, D. Combining the SWAT model with sequential uncertainty fitting algorithm for streamflow pre-diction and uncertainty analysis for the Lake Dianchi Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; Griensven A van Liew MWVan Kannan, N.; Jha, M.K. SWAT: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Sith, R.; Nadaoka, K. Comparison of SWAT and GSSHA for high time resolution prediction of stream flow and sediment con-centration in a small agricultural watershed. Hydrology 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wangpimool, W.; Pongput, K.; Supriyasilp, T.; Sakolnakhon, K.P.; Vonnarart, O. Hydrological Evaluation with SWAT Model and Numerical Weather Prediction for Flash Flood Warning System in Thailand. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2013, 3, 349. [Google Scholar]
- Devia, G.K.; Ganasri, B.P.; Dwarakish, G.S. A review on hydrological models. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysanova, V.; Srinivasan, R. Assessment of climate and land use change impacts with SWAT. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP: SWAT Calibration and uncertainty programs—A User Manual; Eawag: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beven, K.; Binley, A. The future of distributed models: Model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol. Process. 1992, 6, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griensven, A.; Meixner, T. Methods to quantify and identify the sources of uncertainty for river basin water quality models. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, R.; Kennedy, J. A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In Proceedings of the MHS’95, Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 4–6 October 1995; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kassa, T.; Förch, G. Impact of land use/cover change on streamflow: The case of Hare River Watershed, Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the Catchment and Lake Research, Proceedings 2nd Lake Abaya Research Symposium (LARS), Arba Minch, Ethiopia, 7–11 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, T. Analysis of parameter uncertainty in hydrological and sediment modeling using GLUE method: A case study of SWAT model applied to Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Keller, A.A. Uncertainty assessment in watershed-scale water quality modeling and management: 1. Framework and application of generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) approach. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoi, D.N.; Thom, V.T. Parameter uncertainty analysis for simulating streamflow in a river catchment of Vietnam. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 4, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassa, T. Watershed Hydrological Responses to Changes in Land Use and Land Cover, and Management Practices at Hare Watershed, Ethiopia. 2009, p. 229. Available online: http://www.secheresse.info/spip.php?article10823 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Leta, M.; Demissie, T.; Tränckner, J. Modeling and Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Change Dynamics Based on Land Change Modeler (LCM) in Nashe Watershed, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Input/Output File Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tuo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Disse, M.; Chiogna, G. Evaluation of precipitation input for SWAT modeling in Alpine catchment: A case study in the Adige river basin (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Luo, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y. A new parallel framework of distributed SWAT calibration. J. Arid. Land 2014, 7, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercan, M.; Goodall, J.L.; Castronova, A.; Humphrey, M.; Beekwilder, N. Calibration of SWAT models using the cloud. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Ren, L. Assessment of surface water resources and evapotranspiration in the Haihe River basin of China using SWAT model. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27, 1200–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, G.W.; Gowda, P.H.; Evett, S.R.; Baumhardt, R.L.; Brauer, D.K.; Howell, T.A.; Marek, T.H.; Srinivasan, R. Calibration and validation of the SWAT model for predicting daily ET over irrigated crops in the Texas High Plains using lysimetric data. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 611–622. [Google Scholar]
- Megersa, K.L.; Tamene, A.D.; Sifan, A.K. Impacts of Land Use Land Cover Change on Sediment Yield and Stream Flow: A Case of Finchaa Hydropower Reservoir, Ethiopia. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 763–781. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Bardossy, A. Impacts of Data Quantity and Quality on Model Calibration: Implications for Model Parameterization in Data-Scarce Catchments. Water 2020, 12, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.; Wang, X.; Fontane, D.G.; Harmel, R.D.; Arabi, M. A framework for propagation of uncertainty contributed by parameter-ization, input data, model structure, and calibration/validation data in watershed modeling. Environ. Model Softw. 2014, 54, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Parameter Uncertainty Analysis of Surface Flow and Sediment Yield in the Huolin Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coron, L.; Andréassian, V.; Perrin, C.; Lerat, J.; Vaze, J.; Bourqui, M.; Hendrickx, F. Crash testing hydrological models in contrasted climate conditions: An experiment on 216 Australian catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachepsky, Y.A.; Martinez, G.; Pan, F.; Wagener, T.; Nicholson, T. Evaluating hydrological model performance using information theory-based metrics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2016, 46, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Daggupati, P.; Yen, H.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G.; Keitzer, C.S.; Sowa, S.P. Impact of model development, calibration and validation decisions on hydrological simulations in West Lake Erie Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 5307–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.A.; Pereira, S.B.; Pinto, D.B. Calibration and validation of the SWAT hydrological model for the Mucuri river basin. Eng. Agrícola 2018, 38, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, B.; Gong, H. The comparative study of multi-site uncertainty evaluation method based on SWAT model. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 29, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoraba, S.M. Hydrological modeling of the Simly Dam watershed (Pakistan) using GIS and SWAT model. Alex. Eng. J. 2015, 54, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| LULC Types | Area | |
|---|---|---|
| Ha | Watershed (%) | |
| Forest Land | 16,139.47 | 17.06 |
| Grass Land | 7260.56 | 7.68 |
| Rangeland | 9423.44 | 9.96 |
| Agricultural Land | 57,823.41 | 61.14 |
| Built-up area | 785.17 | 0.83 |
| Water body | 3146.00 | 3.33 |
| Total | 94,578.00 | 100 |
| Slope (%) | Area | |
|---|---|---|
| Ha | Watershed (%) | |
| 0–8 | 28,683.68 | 30.33 |
| 8–15 | 23,225.51 | 24.56 |
| 15–30 | 28,660.19 | 30.30 |
| >30 | 14,008.67 | 14.81 |
| Total | 94,578.05 | 100.00 |
| Rates of Performance | NSE | PBIAS | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unsatisfactory | NSE ≤ 0.5 | PBIAS ≥ ±25 | R2 < 0.50 |
| Satisfactory | 0.5 < NSE ≤ 0.65 | ±15 ≤ PBIAS < ±25 | 0.50 < R2 < 0.70 |
| Good | 0.65 < NSE ≤ 0.75 | ±10 ≤ PBIAS < ±15 | 0.70 < R2 < 0.80 |
| Very good | 0.75 < NSE ≤ 1 | PBIAS < ±10 | >0.80 |
| Objective Function | Methods | Calibration | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Sufi-2 | 0.88 | 0.85 |
| Glue | 0.87 | 0.85 | |
| Parasol | 0.87 | 0.84 | |
| PSO | 0.88 | 0.87 | |
| NSE | Sufi-2 | 0.78 | 0.80 |
| Glue | 0.80 | 0.71 | |
| Parasol | 0.82 | 0.72 | |
| PSO | 0.73 | 0.77 | |
| PBIAS | Sufi-2 | −2.70 | 1.60 |
| Glue | −8.70 | 5.70 | |
| Parasol | 10.00 | 8.00 | |
| PSO | 15.00 | 13.30 | |
| P-factor | Sufi-2 | 0.69 | 0.64 |
| Glue | 0.37 | 0.26 | |
| Parasol | 0.22 | 0.15 | |
| PSO | 0.51 | 0.47 | |
| r-factor | Sufi-2 | 1.10 | 1.00 |
| Glue | 0.86 | 0.78 | |
| Parasol | 0.37 | 0.40 | |
| PSO | 0.69 | 0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leta, M.K.; Demissie, T.A.; Waseem, M. Analysis of Hydrological Characteristics of Blue Nile Basin, Nashe Watershed. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411791
Leta MK, Demissie TA, Waseem M. Analysis of Hydrological Characteristics of Blue Nile Basin, Nashe Watershed. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(24):11791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411791
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeta, Megersa Kebede, Tamene Adugna Demissie, and Muhammad Waseem. 2021. "Analysis of Hydrological Characteristics of Blue Nile Basin, Nashe Watershed" Applied Sciences 11, no. 24: 11791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411791
APA StyleLeta, M. K., Demissie, T. A., & Waseem, M. (2021). Analysis of Hydrological Characteristics of Blue Nile Basin, Nashe Watershed. Applied Sciences, 11(24), 11791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411791






