Mango Leaf Disease Recognition and Classification Using Novel Segmentation and Vein Pattern Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Image resizing and augmentation in order to set query images.
- A method for the segmentation of the diseased part.
- Fusion of color and LBP features by performing canonical correlation analysis (CCA).
- Using classifiers of ten different types to perform identification and recognition.
2. Literature Review
3. Material and Method
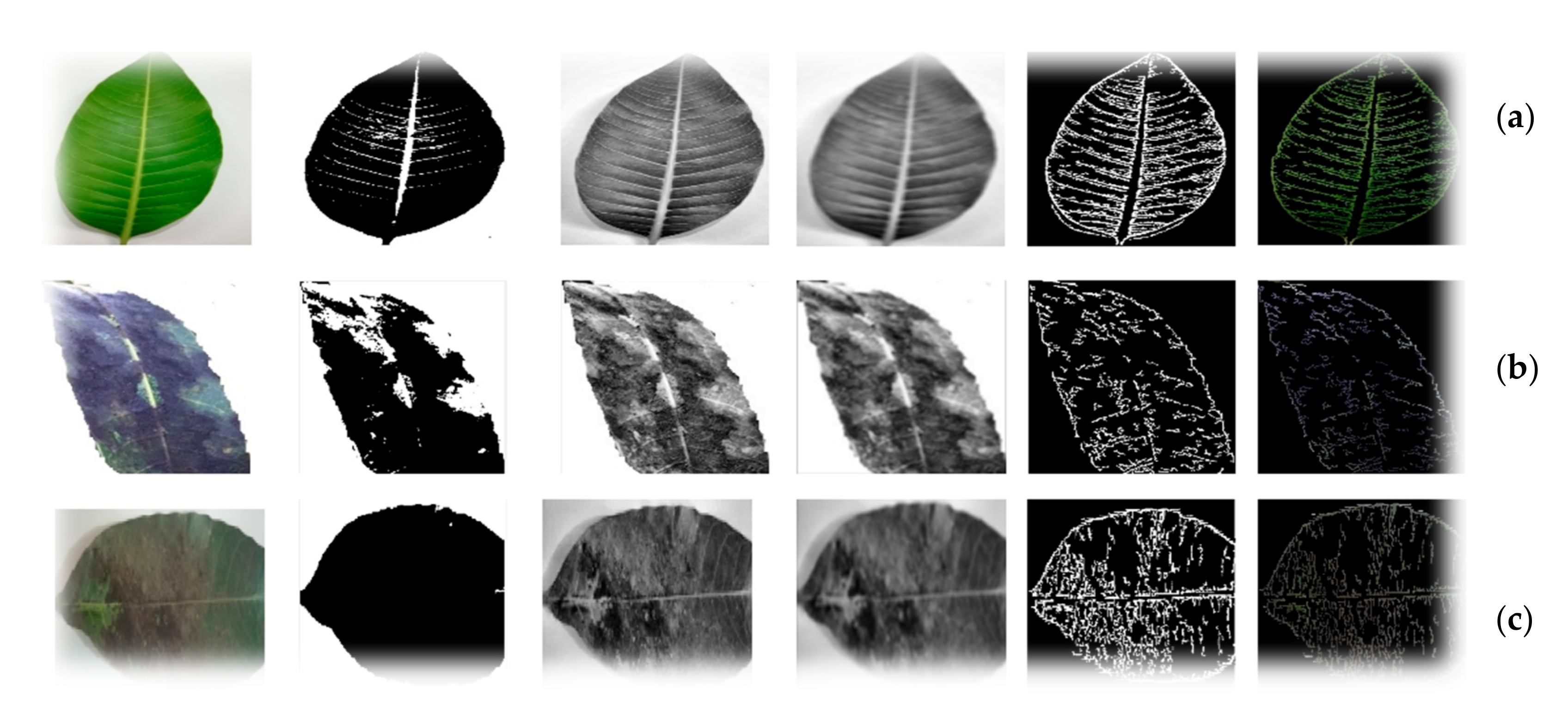
3.1. Preprocessing
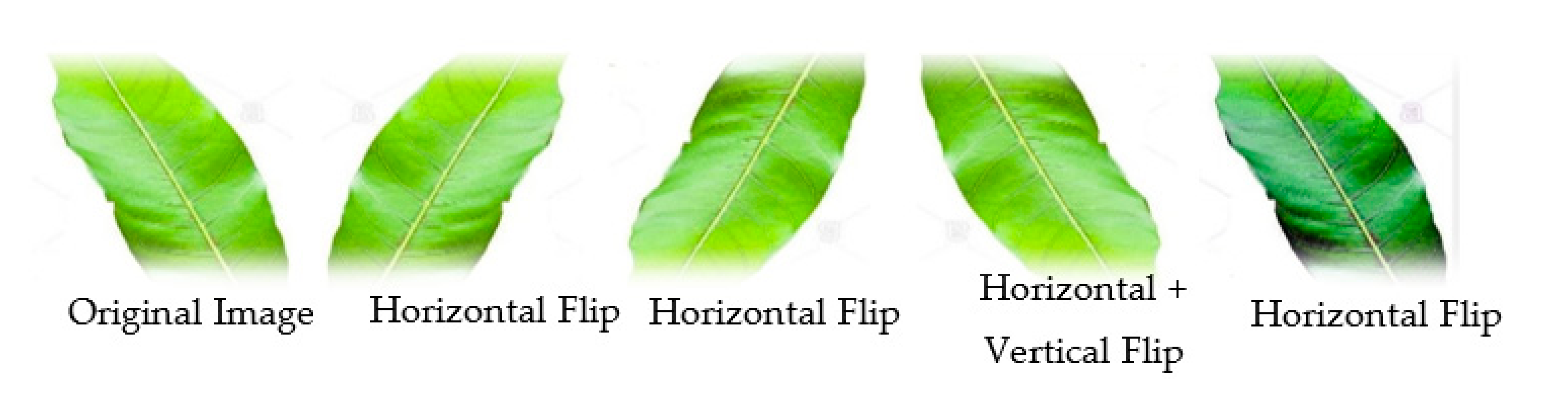
Resizing and Data Augmentation
3.2. Proposed Leaf Vein-Seg Architecture
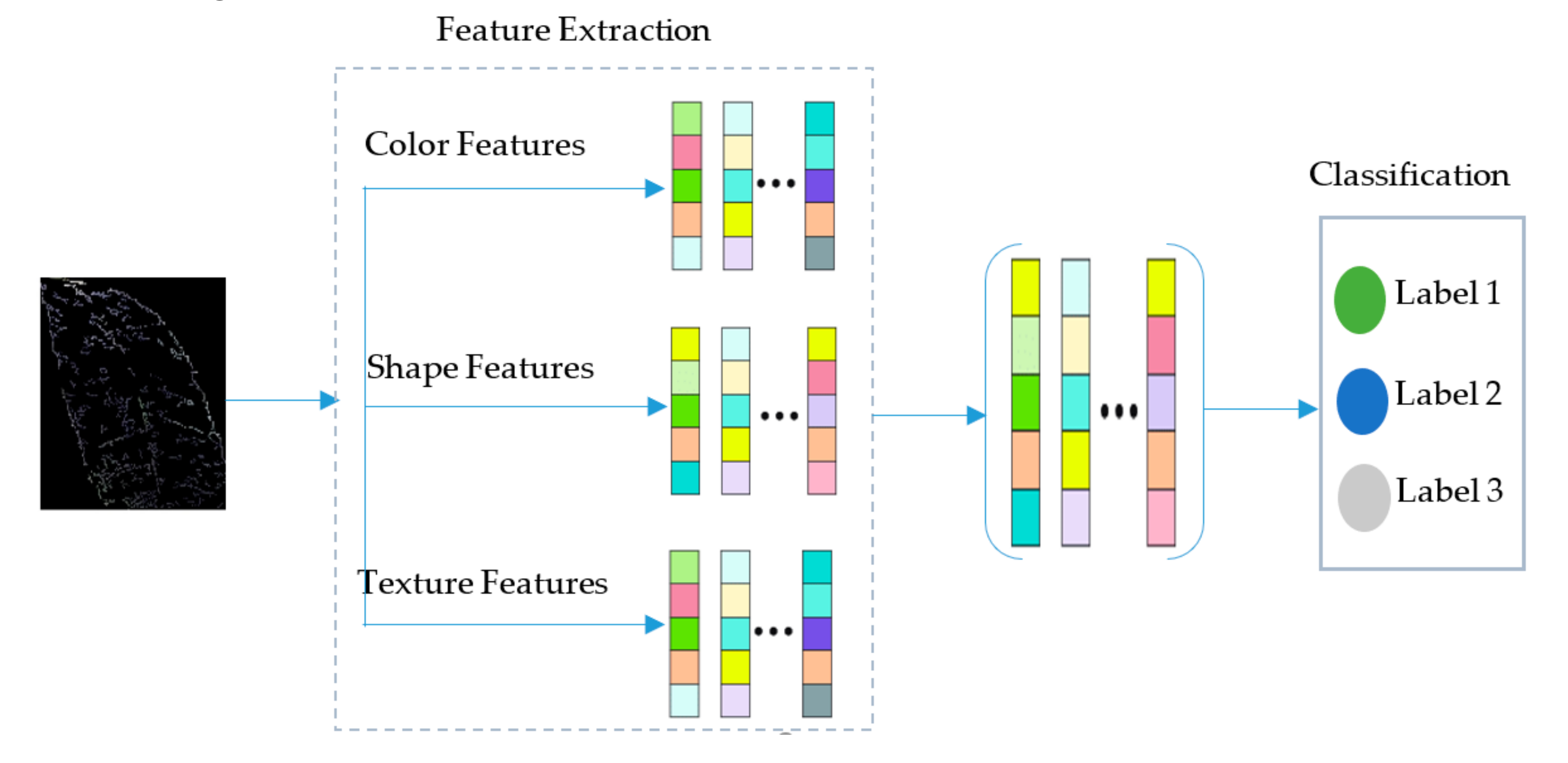
3.3. Features Extraction and Fusion
3.4. Features Fusion and Classification
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Test 1: Powdery Mildew vs. Healthy
4.2. Test 2: Sooty Mold vs. Healthy
4.3. Test 3: Diseased vs. Healthy
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, T.-T.; Choi, J.-W.; Le, T.-T.H.; Kim, J.-W. A comparative study of deep CNN in forecasting and classifying the macronutrient deficiencies on development of tomato plant. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, F.A.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Tariq, U.; Khan, A.; Kadry, S.; Thinnukool, O. A Cascaded Design of Best Features Selection for Fruit Diseases Recognition. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 70, 1491–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Saba, T. Fruits diseases classification: Exploiting a hierarchical framework for deep features fusion and selection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 25763–25783. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.Z.U.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, M.A.; Tariq, U.; Jamal, S.S.; Ahmad, J.; Hussain, I. Classification of Citrus Plant Diseases Using Deep Transfer Learning. CMC Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 1401–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda-Gutierrez, V.; Galvan-Tejada, C.E.; Zanella-Calzada, L.A.; Celaya-Padilla, J.M.; Galván-Tejada, J.I.; Gamboa-Rosales, H.; Luna-Garcia, H.; Magallanes-Quintanar, R.; Guerrero Mendez, C.A.; Olvera-Olvera, C.A. Comparison of convolutional neural network architectures for classification of tomato plant diseases. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, N.; Khan, M.A.; Tariq, U.; Kadry, S.; Yar, M.A.E.; Mostafa, A.M.; Alnuaim, A.A.; Ahmad, S. Multiclass Cucumber Leaf Diseases Recognition Using Best Feature Selection. CMC Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 3281–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.I.; Raza, M.; Anjum, A.; Saba, T.; Shad, S.A. Skin lesion segmentation and classification: A unified framework of deep neural network features fusion and selection. Expert Syst. 2019, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosman, N.F.; Asli, N.A.; Abdullah, S.; Rusop, M. Some common disease in mango. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; p. 020019. [Google Scholar]
- Jogekar, R.N.; Tiwari, N. A review of deep learning techniques for identification and diagnosis of plant leaf disease. In Smart Trends in Computing and Communications: Proceedings of SmartCom 2020; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Runno-Paurson, E.; Lääniste, P.; Nassar, H.; Hansen, M.; Eremeev, V.; Metspalu, L.; Edesi, L.; Kännaste, A.; Niinemets, Ü. Alternaria Black Spot (Alternaria brassicae) Infection Severity on Cruciferous Oilseed Crops. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivazhagan, S.; Ligi, S.V. Mango leaf diseases identification using convolutional neural network. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018, 120, 11067–11079. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, R.; Shah, J.H.; Sharif, M.; Ansari, G.J. Mango Leaf Disease Identification Using Fully Resolution Convolutional Network. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 69, 3581–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.R.; Khan, M.A.; Javed, M.Y.; Masood, H.; Tariq, U.; Nam, Y.; Kadry, S. Cotton Leaf Diseases Recognition Using Deep Learning and Genetic Algorithm. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 69, 2917–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, A.; Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Sharif, A.; Yasmin, M.; Saba, T.; Javed, K. Entropy-controlled deep features selection framework for grape leaf diseases recognition. Expert Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurangzeb, K.; Akmal, F.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Javed, M.Y. Advanced machine learning algorithm based system for crops leaf diseases recognition. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Data Science and Machine Learning Applications (CDMA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 4–5 March 2020; pp. 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, F.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Mittal, M.; Goyal, L.M.; Roy, S. Deep neural network features fusion and selection based on PLS regression with an application for crops diseases classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 103, 107164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, U.; Hussain, N.; Nam, Y.; Kadry, S. An Integrated Deep Learning Framework for Fruits Diseases Classification. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 71, 1387–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Javed, K.; Raza, M.; Saba, T. An automated system for cucumber leaf diseased spot detection and classification using improved saliency method and deep features selection Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 18627–18656. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, C.; Ivanov, S. Robotics, artificial intelligence, and the evolving nature of work. In Digital Transformation in Business and Society; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Adeel, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Azam, F.; Shah, J.H.; Umer, T.; Wan, S. Diagnosis and recognition of grape leaf diseases: An automated system based on a novel saliency approach and canonical correlation analysis based multiple features fusion. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019, 24, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrinanto, F.G.; Dewi, C.; Triwiratno, A. The implementation of k-means algorithm as image segmenting method in identifying the citrus leaves disease. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, East Java, Indonesia, 17–18 November 2019; p. 012024. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Alhaisoni, M.; Saba, T.; Nawaz, N. A probabilistic segmentation and entropy-rank correlation-based feature selection approach for the recognition of fruit diseases. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2021, 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Shah, J.H.; ur Rehman, M.H.; Javed, K. An automated detection and classification of citrus plant diseases using image processing techniques: A review. Comput. Electr. Agric. 2018, 153, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Chang, Y.K.; Heung, B.; Nguyen-Quang, T.; Price, G.W.; Al-Mallahi, A. Effect of directional augmentation using supervised machine learning technologies: A case study of strawberry powdery mildew detection. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 194, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, C.; Manganiello, G.; Nicastro, N.; Cardi, T.; Carotenuto, F. Powdery Mildew Caused by Erysiphe cruciferarum on Wild Rocket (Diplotaxis tenuifolia): Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning Modeling for Non-Destructive Disease Detection. Agriculture 2021, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Chug, A.; Singh, A.P. Statistical analysis of machine learning techniques for predicting powdery mildew disease in tomato plants. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Inform. 2021, 9, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Jain, S. Detection of disease in cotton leaf using artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 Amity International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AICAI), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 February 2019; pp. 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- El Kahlout, M.I.; Abu-Naser, S.S. An Expert System for Citrus Diseases Diagnosis. Int. J. Acad. Eng. Res. (IJAER) 2019, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Azam, M.F.; Lali, M.I.U.; Javed, M.Y. Detection and classification of citrus diseases in agriculture based on optimized weighted segmentation and feature selection. Comput. Electr. Agric. 2018, 150, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Chouhan, S.S.; Jain, S.; Jain, S. Multilayer convolution neural network for the classification of mango leaves infected by anthracnose disease. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 43721–43729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestur, R.; Meduri, A.; Narasipura, O. MangoNet: A deep semantic segmentation architecture for a method to detect and count mangoes in an open orchard. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 77, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srunitha, K.; Bharathi, D. Mango leaf unhealthy region detection and classification. In Computational Vision and Bio Inspired Computing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 422–436. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, Z.; Gimenez, F.; Yi, D.; Rubin, D. Differential data augmentation techniques for medical imaging classification tasks. In Proceedings of the AMIA Annual Symposyum Proceedings, Washington, DC, USA, 6–8 November 2017; pp. 979–984. [Google Scholar]
- Ajitomi, A.; Takushi, T.; Sato, Y.; Arasaki, C.; Ooshiro, A. First report of powdery mildew of mango caused by Erysiphe quercicola in Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2020, 86, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasian, M.; Balachandran, W.; Mares, C. Image enhancement for fingerprint minutiae-based algorithms using CLAHE, standard deviation analysis and sliding neighborhood. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–24 October 2008; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yosinski, J.; Clune, J.; Bengio, Y.; Lipson, H. How transferable are features in deep neural networks? arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1792. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anantrasirichai, N.; Hannuna, S.; Canagarajah, N. Towards automated mobile-phone-based plant pathology management. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.09239. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Alhaisoni, M.; Tariq, U.; Yong, H.-S.; Armghan, A.; Alenezi, F. Human Action Recognition: A Paradigm of Best Deep Learning Features Selection and Serial Based Extended Fusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, F.; Alhaisoni, M.; Tariq, U.; Armghan, A.; Alenezi, F.; Choi, J.-I.; Kadry, S. Human gait recognition: A single stream optimal deep learning features fusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Khan, M.A.; Tariq, U.; Armghan, A.; Alenezi, F.; Younus Javed, M.; Aslam, S.M.; Kadry, S. A Computer-Aided Diagnosis System Using Deep Learning for Multiclass Skin Lesion Classification. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 21, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Sharif, M.; Javed, M.Y.; Saba, T.; Ali, H.; Tariq, J. Melanoma detection and classification using computerized analysis of dermoscopic systems: A review. Curr. Med Imaging 2020, 16, 794–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; Kadry, S. Intelligent fusion-assisted skin lesion localization and classification for smart healthcare. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; Kadry, S.; Hsu, C.H. A two-stream deep neural network-based intelligent system for complex skin cancer types classification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 14, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Kadry, S.; Nam, Y. Computer decision support system for skin cancer localization and classification. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 70, 1–15. [Google Scholar]

| Sooty Mold | Powdery Mildew | Healthy | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 45 | 45 | 135 |
| Methods | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | FNR (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear discriminant | 0.24 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 17.8 | 82.2 |
| Linear SVM | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 5.6 | 94.4 |
| Quadratic SVM | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 6.7 | 93.3 |
| Cubic SVM | 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 3.4 | 96.6 |
| Fine KNN | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 11.2 | 88.8 |
| Medium KNN | 0.18 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 16.7 | 83.3 |
| Cubic KNN | 0.20 | 0.71 | 0.84 | 18.9 | 81.1 |
| Weighted KNN | 0.18 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 11.2 | 88.8 |
| Subspace discriminant | 0.2 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 12.3 | 87.7 |
| Subspace KNN | 0.18 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 16.7 | 83.3 |
| Classification-Class | Classification-Class | |
|---|---|---|
| Powdery Mildew | Healthy | |
| Powdery mildew | 97.7% | <1% |
| Healthy | <1% | 95.6% |
| Methods | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | FNR (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear discriminant | 0.47 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 36.7 | 63.3 |
| Linear SVM | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 4.5 | 95.5 |
| Quadratic SVM | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 6.7 | 93.3 |
| Cubic SVM | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 5.6 | 94.4 |
| Fine KNN | 0.24 | 0.67 | 0.71 | 28.9 | 71.1 |
| Medium KNN | 0.2 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 12.3 | 87.7 |
| Cubic KNN | 0.23 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 11.2 | 88.8 |
| Weighted KNN | 0.20 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 12.5 | 83.3 |
| Subspace discriminant | 0.29 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 18.9 | 81.1 |
| Subspace KNN | 0.24 | 0.6 | 0.75 | 32.2 | 67.8 |
| Classification Class | Classification Class | |
|---|---|---|
| Sooty Mold | Healthy | |
| Sooty mold | 95.5% | <1% |
| Healthy | <1% | 95.5% |
| Methods | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC | FNR (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear discriminant | 0.13 | 0.69 | 0.78 | 27.4 | 72.6 |
| Linear SVM | 0.03 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 6.7 | 93.3 |
| Quadratic SVM | 0.14 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 25.2 | 74.8 |
| Cubic SVM | 0.03 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 4.5 | 95.5 |
| Fine KNN | 0.10 | 0.56 | 0.73 | 33.3 | 66.7 |
| Medium KNN | 0.06 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 11.2 | 88.8 |
| Cubic KNN | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 7.5 | 92.5 |
| Weighted KNN | 0.11 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 20 | 80 |
| Subspace discriminant | 0.13 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 28.1 | 71.9 |
| Subspace KNN | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.77 | 35.6 | 64.4 |
| Classification Class | Classification Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Powdery Mildew | Sooty Mold | |
| Healthy | 97.8% | <1% | - |
| Powdery mildew | - | 97.8% | <1% |
| Sooty mold | - | - | 91.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleem, R.; Shah, J.H.; Sharif, M.; Yasmin, M.; Yong, H.-S.; Cha, J. Mango Leaf Disease Recognition and Classification Using Novel Segmentation and Vein Pattern Technique. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11901. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411901
Saleem R, Shah JH, Sharif M, Yasmin M, Yong H-S, Cha J. Mango Leaf Disease Recognition and Classification Using Novel Segmentation and Vein Pattern Technique. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(24):11901. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411901
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleem, Rabia, Jamal Hussain Shah, Muhammad Sharif, Mussarat Yasmin, Hwan-Seung Yong, and Jaehyuk Cha. 2021. "Mango Leaf Disease Recognition and Classification Using Novel Segmentation and Vein Pattern Technique" Applied Sciences 11, no. 24: 11901. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411901
APA StyleSaleem, R., Shah, J. H., Sharif, M., Yasmin, M., Yong, H.-S., & Cha, J. (2021). Mango Leaf Disease Recognition and Classification Using Novel Segmentation and Vein Pattern Technique. Applied Sciences, 11(24), 11901. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411901






