Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Brain Electrical Activity in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
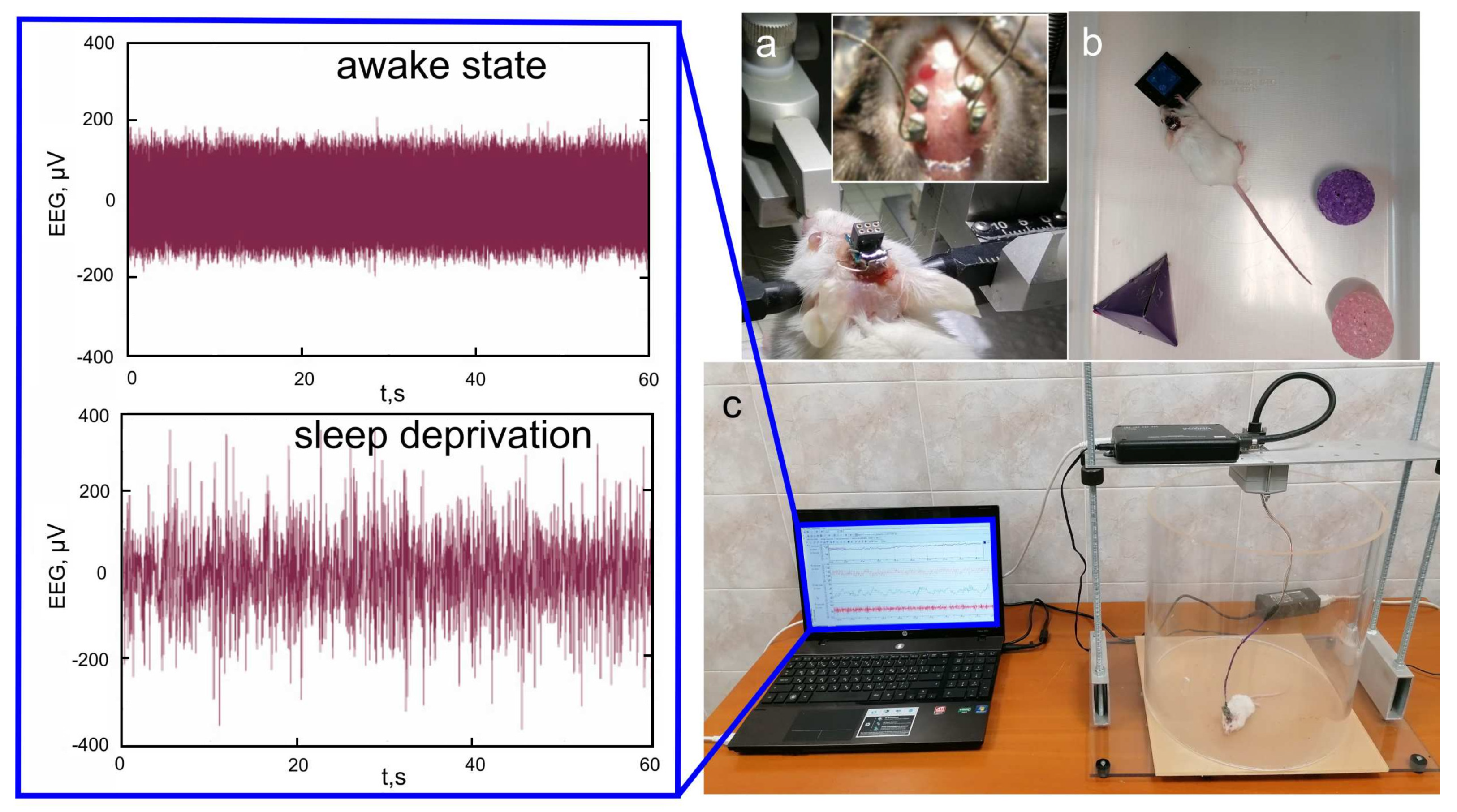
2. Methods and Experiments
2.1. DFA
2.2. EDFA
2.3. Subjects and Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFA | Detrended fluctuation analysis |
| EDFA | Extended detrended fluctuation analysis |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| SD | Sleep deprivation |
| RMS | Root mean square |
References
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depner, C.M.; Stothard, E.R.; Wright, K.P., Jr. Metabolic consequences of sleep and circadian disorders. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fultz, N.E.; Bonmassar, G.; Setsompop, K.; Stickgold, R.A.; Rosen, B.R.; Polimeni, J.R.; Lewis, L.D. Coupled electrophysiological, hemodynamic, and cerebrospinal fluid oscillations in human sleep. Science 2019, 366, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.G. Sleep, circadian rhythms and health. Interface Focus 2020, 10, 20190098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duclos, C.; Beauregard, M.P.; Bottari, C.; Ouellet, M.C.; Gosselin, N. The impact of poor sleep on cognition and activities of daily living after traumatic brain injury: A review. Aust. Occup. Ther. J. 2015, 62, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Someren, E.J.; Cirelli, C.; Dijk, D.J.; Van Cauter, E.; Schwartz, S.; Chee, M.W. Disrupted sleep: From molecules to cognition. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13889–13895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullington, J.M.; Simpson, N.S.; Meier-Ewert, H.K.; Haack, M. Sleep loss and inflammation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 24, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurtado-Alvarado, G.; Pavón, L.; Castillo-Garcia, S.A.; Hernández, M.E.; Dominguez-Salazar, E.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, J.; Gómez-González, B. Sleep loss as a factor to induce cellular and molecular inflammatory variations. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 801341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, A.; Puttonen, S.; Vanttola, P.; Viitasalo, K.; Sulkava, S.; Pervjakova, N.; Joensuu, A.; Salo, P.; Toivola, A.; Hármá, M.; et al. A distinctive DNA methylation pattern in insufficient sleep. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Hsuchou, H.; He, Y.; Kastin, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, W. Sleep restriction impairs blood-brain barrier function. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14697–14706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everson, C.A.; Bergmann, B.M.; Rechtschaffen, A. Sleep deprivation in the rat: III. Total sleep deprivation. Sleep 1989, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.J. Neurological findings after prolonged sleep deprivation. Arch. Neurol. 1965, 12, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.; Postnov, D.; Penzel, T.; Kurths, J. Sleep as a novel biomarker and a promising therapeutic target for cerebral small vessel disease: A review focusing on Alzheimer’s disease and the blood-brain barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.-K.; Havlin, S.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Quantification of scaling exponents and crossover phenomena in nonstationary heartbeat time series. Chaos 1995, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, H.E.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Goldberger, A.L.; Havlin, S.; Ivanov, P.C.; Peng, C.-K. Statistical physics and physiology: Monofractal and multifractal approaches. Phys. A 1999, 270, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, K.; Ausloos, M. Application of the detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA) method for describing cloud breaking. Phys. A 1999, 274, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, C.; McDarby, G. Establishing the relation between detrended fluctuation analysis and power spectral density analysis for stochastic processes. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 6103–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talkner, P.; Weber, R.O. Power spectrum and detrended fluctuation analysis: Application to daily temperatures. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantelhardt, W.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Rego, H.H.A.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A. Detecting long-range correlations with detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys. A 2001, 295, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frolov, N.S.; Grubov, V.V.; Maksimenko, V.A.; Lüttjohann, A.; Makarov, V.V.; Pavlov, A.N.; Sitnikova, E.; Pisarchik, A.N.; Kurths, J.; Hramov, A.E. Statistical properties and predictability of extreme epileptic events. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavlov, A.N.; Runnova, A.E.; Maksimenko, V.A.; Pavlova, O.N.; Grishina, D.S.; Hramov, A.E. Detrended fluctuation analysis of EEG patterns associated with real and imaginary arm movements. Phys. A 2018, 509, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ivanov, P.C.; Chen, Z.; Carpena, P.; Stanley, H.E. Effect of trends on detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 011114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Ivanov, P.C.; Hu, K.; Stanley, H.E. Effect of nonstationarities on detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 041107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryce, R.M.; Sprague, K.B. Revisiting detrended fluctuation analysis. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.H.; Gu, G.F.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Zhou, W.X.; Sornette, D. Comparing the performance of FA, DFA and DMA using different synthetic long-range correlated time series. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlov, A.N.; Pavlova, O.N.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.V.; Kurths, J. Extended detrended fluctuation analysis: Effects of nonstationarity and application to sleep data. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Zschiegner, S.A.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A.; Stanley, H.E. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of nonstationary time series. Phys. A 2002, 316, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castiglioni, P.; Faini, A. A fast DFA algorithm for multifractal multiscale analysis of physiological time series. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlov, A.N.; Abdurashitov, A.S.; Koronovskii, A.A., Jr.; Pavlova, O.N.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.V.; Kurths, J. Detrended fluctuation analysis of cerebrovascular responses to abrupt changes in peripheral arterial pressure in rats. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2020, 85, 105232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.N.; Dubrovsky, A.I.; Koronovskii, A.A., Jr.; Pavlova, O.N.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.V.; Kurths, J. Extended detrended fluctuation analysis of electroencephalograms signals during sleep and the opening of the blood-brain barrier. Chaos 2020, 30, 073138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, A.N.; Dubrovsky, A.I.; Koronovskii, A.A., Jr.; Pavlova, O.N.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.V.; Kurths, J. Extended detrended fluctuation analysis of sound-induced changes in brain electrical activity. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 139, 109989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.C.; Banks, S. Total sleep deprivation, chronic sleep restriction and sleep disruption. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 185, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meerlo, P.; Sgoifo, A.; Suchecki, D. Restricted and disrupted sleep: Effects on autonomic function, neuroendocrine stress systems and stress responsivity. Sleep Med. Rev. 2008, 12, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.A.; Davidson, A.J. Health consequences of circadian disruption in humans and animal models. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 119, 283–323. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, G.D.; Skene, D.J.; Arendt, J.; Cade, J.E.; Grant, P.J.; Hardie, L.J. Circadian rhythm and sleep disruption: Causes, metabolic consequences, and countermeasures. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 584–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medic, G.; Wille, M.; Hemels, M.E. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Sun, Q.; Stκger, F.F.; Sigurdsson, B.; Mortensen, K.N.; Lilius, T.O.; Nedergaard, M. Increased glymphatic influx is correlated with high EEG delta power and low heart rate in mice under anesthesia. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achariyar, T.M.; Li, B.; Peng, W.; Verghese, P.B.; Shi, Y.; McConnell, E.; Benraiss, A.; Kasper, T.; Song, W.; Takano, T.; et al. Glymphatic distribution of CSF-derived apoE into brain is isoform specific and suppressed during sleep deprivation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhan, G.; Fenik, P.; Panossian, L.; Wang, M.M.; Reid, S.; Lai, D.; Davis, J.G.; Baur, J.A.; et al. Extended wakefulness: Compromised metabolics in and degeneration of locus ceruleus neurons. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4418–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Experiment | DFA | EDFA | / |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 2.4 |
| 2 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 3.7 |
| 3 | −0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 2.3 |
| 5 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 1.9 |
| 6 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 2.5 |
| 7 | −0.03 ± 0.01 | −0.04 ± 0.01 | 1.3 |
| 8 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 1.4 |
| 9 | −0.08 ± 0.02 | −0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.8 |
| 10 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 1.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlov, A.N.; Dubrovskii, A.I.; Pavlova, O.N.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.V. Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Brain Electrical Activity in Mice. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031182
Pavlov AN, Dubrovskii AI, Pavlova ON, Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya OV. Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Brain Electrical Activity in Mice. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(3):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031182
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlov, Alexey N., Alexander I. Dubrovskii, Olga N. Pavlova, and Oxana V. Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya. 2021. "Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Brain Electrical Activity in Mice" Applied Sciences 11, no. 3: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031182
APA StylePavlov, A. N., Dubrovskii, A. I., Pavlova, O. N., & Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O. V. (2021). Effects of Sleep Deprivation on the Brain Electrical Activity in Mice. Applied Sciences, 11(3), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031182






