Parameters Identification of the Fractional-Order Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Models Using Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fractional PMSM Model
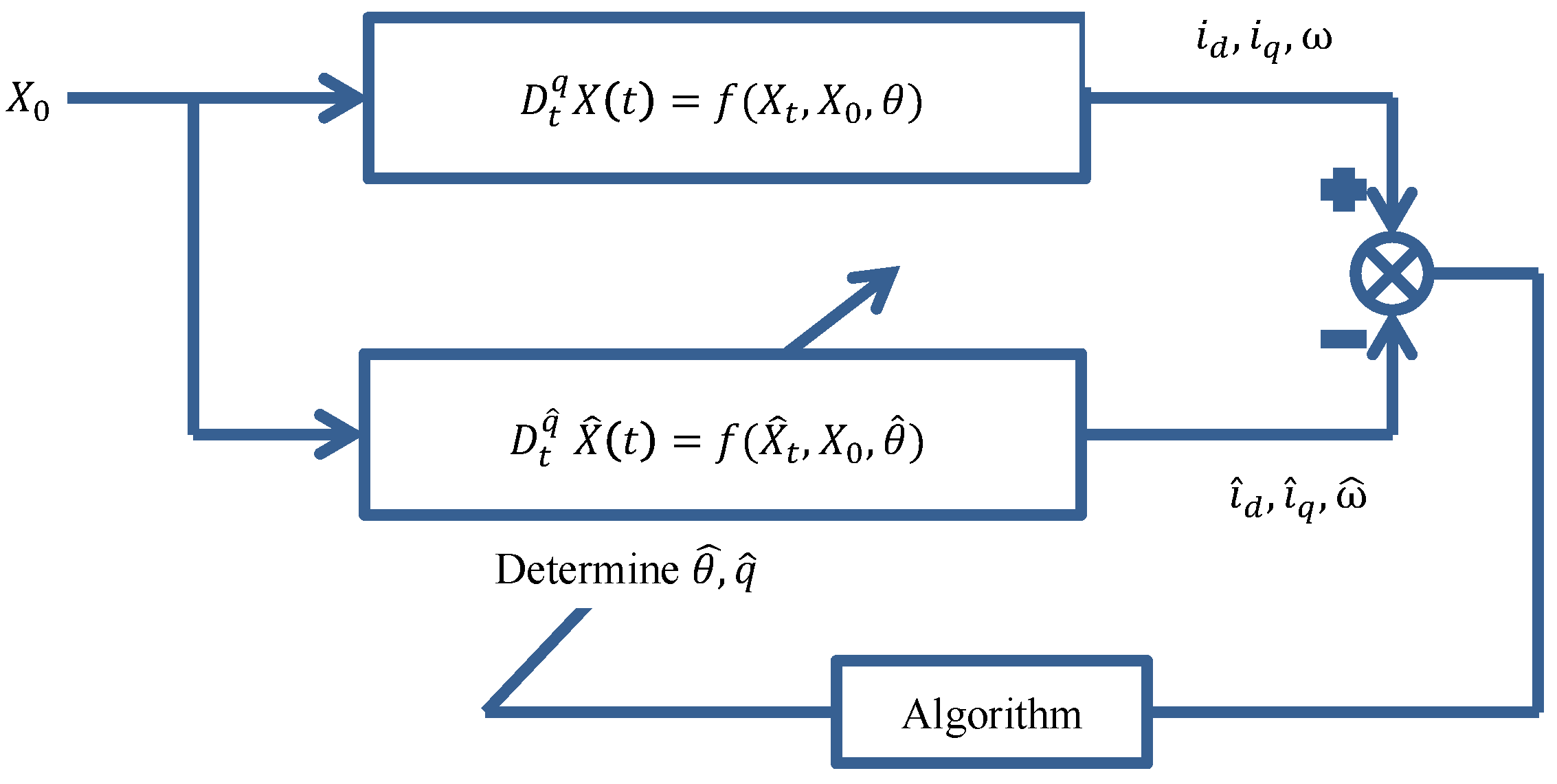
3. Problem Formulation
4. Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer (C.EPSO)
4.1. Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer (EPSO)
4.2. Chaotic Maps
4.3. Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer (C.EPSO)
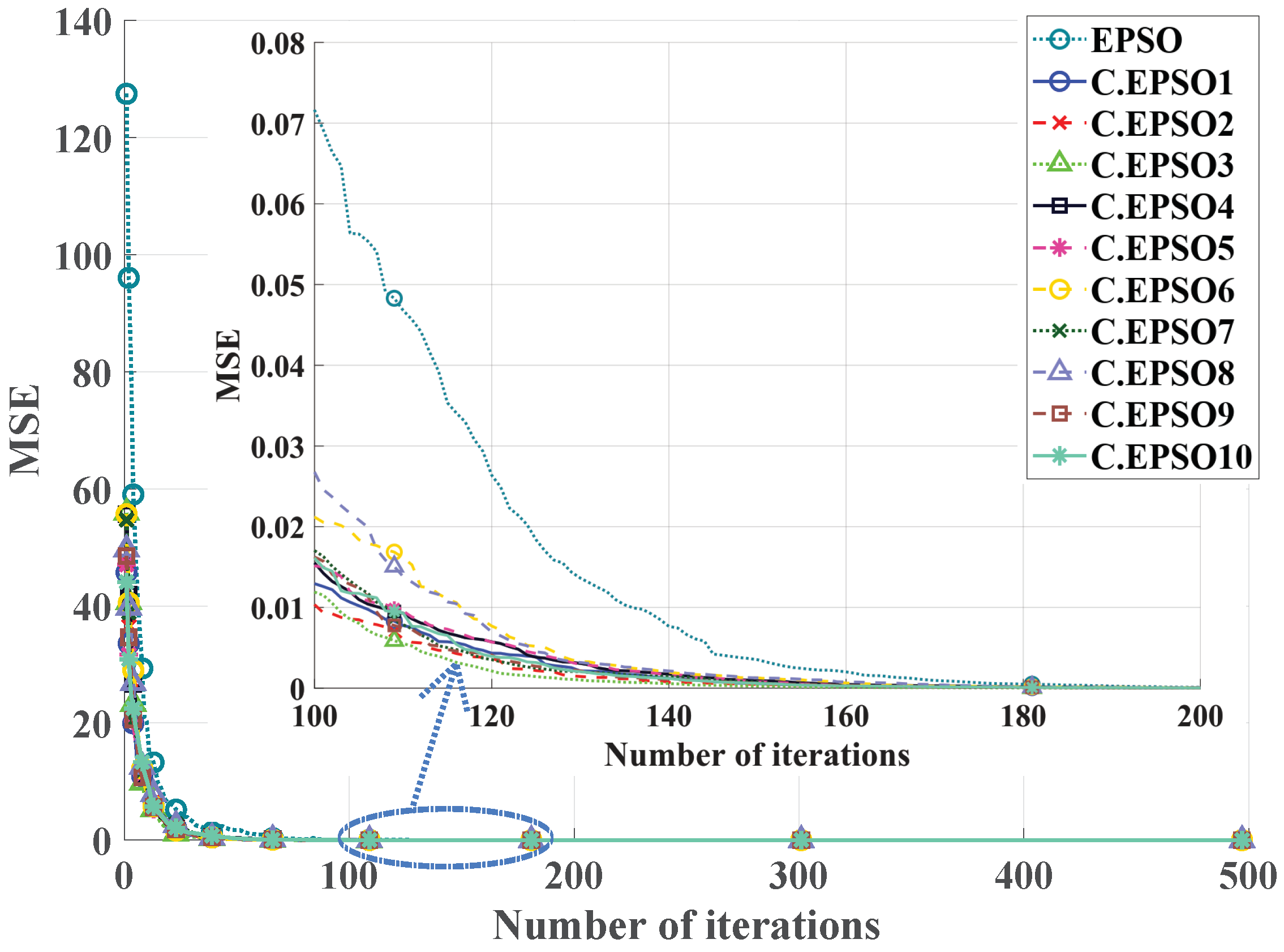
5. Simulation and Results
5.1. Equal Order-Fractional PMSM Model
5.2. Variable Order Fractional PMSM Model
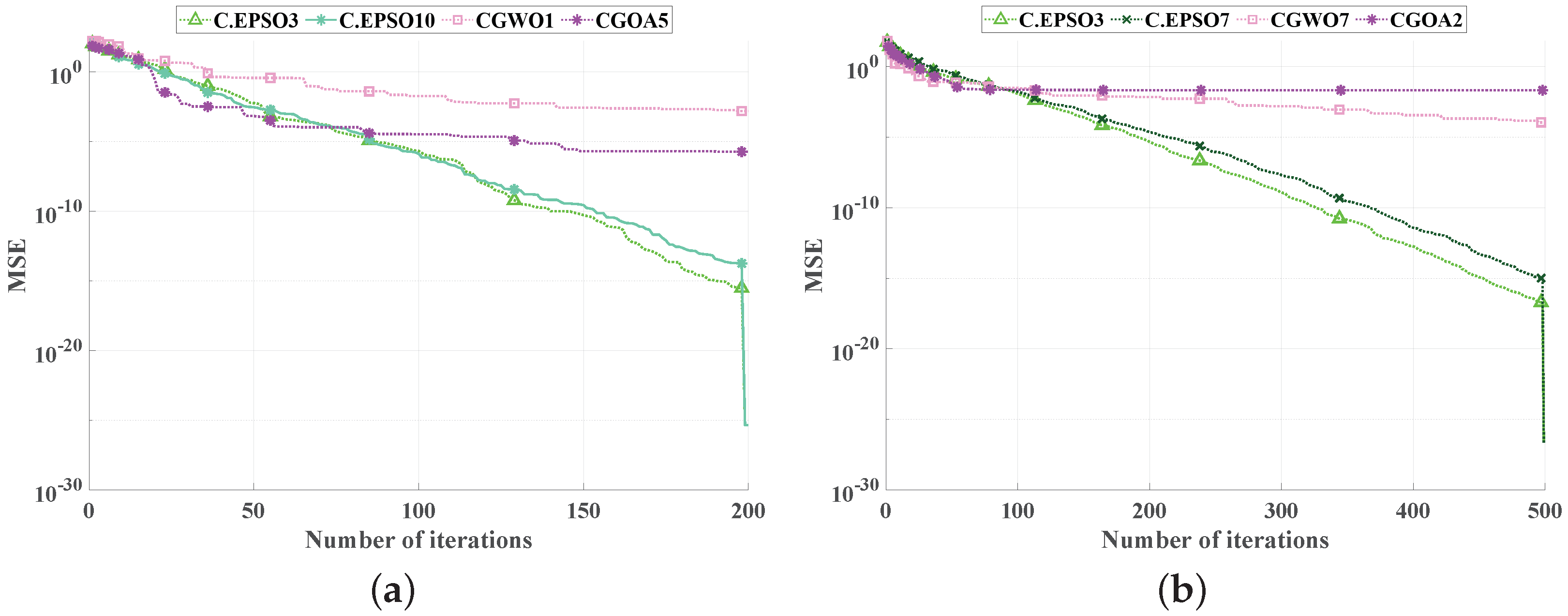
5.3. Comparison with the Latest Published Algorithms in Literature
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dambrauskas, K.; Vanagas, J.; Zimnickas, T.; Kalvaitis, A.; Ažubalis, M. A Method for Efficiency Determination of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Energies 2020, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.L.; Yu, S.M.; Luo, X.S. Fractional-order permanent magnet synchronous motor and its adaptive chaotic control. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.L.; Wu, L. Optik Sliding mode control for synchronization of fractional permanent magnet synchronous motors with finite time. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2016, 127, 3329–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Gao, R. Chaos control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor with time-varying delay by using adaptive sliding mode control based on DSC. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 4147–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, B.; Yu, H.; Gao, J. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications Adaptive fuzzy tracking control for the chaotic permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system via backstepping. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2011, 12, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Vaidhyanathan, S.; Karthikeyan, A.; Duraisamy, P. Dynamic analysis and chaos suppression in a fractional order brushless DC motor. Electr. Eng. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Yu, Y.; Hu, W. Parameter estimation of unknown fractional-order memristor-based chaotic systems by a hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm combined with differential evolution. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 84, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz–Duarte, J.M.; Rosales–Garcia, J.; Correa–Cely, C.R.; Garcia–Perez, A.; Avina–Cervantes, J.G. A closed form expression for the Gaussian–based Caputo–Fabrizio fractional derivative for signal processing applications. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 61, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Cang, S.; Jia, H.; Wang, Z.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Cang, S.; Jia, H.; Wang, Z. Chaotic behavior and circuit implementation of a fractional-order permanent magnet synchronous motor model. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 2887–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.P.; Suganthan, P.N.; Amaratunga, G.A.J. Optimization of Wind Turbine Rotor Diameters and Hub Heights in a Windfarm Using Differential Evolution Algorithm. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.Y.; Liang, J.J.; Zhu, Y.S.; Suganthan, P.N. Solving dynamic economic emission dispatch problem considering wind power by multi-objective differential evolution with ensemble of selection method. Nat. Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, D.; Allam, D.; Eteiba, M. Parameters Identification of Fractional Order Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Models Using Chaotic Meta-Heuristic Algorithms. In Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 529–558. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Yang, Q. Parameter identification of fractional-order chaotic systems without or with noise: Reply to comments. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, N.; Suganthan, P.N. Heterogeneous comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization with enhanced exploration and exploitation. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2015, 24, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaweera, A.; Halgamuge, S.; Watson, H. Self-Organizing Hierarchical Particle Swarm Optimizer With Time-Varying Acceleration Coefficients. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Qin, A.; Suganthan, P.; Baskar, S. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2006, 10, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peram, T.; Veeramachaneni, K.; Mohan, C.K. Fitness-distance-ratio based particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the Swarm Intelligence Symposium, SIS’03, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 26 April 2003; pp. 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, B.Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Das, S. A distance-based locally informed particle swarm model for multimodal optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2013, 17, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, N.; Suganthan, P.N. Ensemble particle swarm optimizer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 55, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Faris, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mirjalili, S. Asynchronous accelerating multi-leader salp chains for feature selection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafarja, M.; Aljarah, I.; Heidari, A.A.; Hammouri, A.I.; Faris, H.; Al-Zoubi, A.M.; Mirjalili, S. Evolutionary Population Dynamics and Grasshopper Optimization approaches for feature selection problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 145, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mafarja, M.; Aljarah, I.; Heidari, A.A.; Faris, H.; Fournier-Viger, P.; Li, X.; Mirjalili, S. Binary dragonfly optimization for feature selection using time-varying transfer functions. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 161, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Khader, A.T.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Yang, X.S. Variants of the flower pollination algorithm: A review. In Nature-Inspired Algorithms and Applied Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 91–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X. A novel hybrid algorithm based on Biogeography-Based Optimization and Grey Wolf Optimizer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 67, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, G.I.; Khoriba, G.; Haggag, M.H. A novel chaotic salp swarm algorithm for global optimization and feature selection. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 3462–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk-Allah, R.M.; Hassanien, A.E.; Bhattacharyya, S. Chaotic crow search algorithm for fractional optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Anand, P. Chaotic grasshopper optimization algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 71, 4385–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, D.; AbdelAty, A.M.; Said, L.A.; Elwakil, A.; Maundy, B.; Radwan, A.G. Chaotic Flower Pollination and Grey Wolf Algorithms for parameter extraction of bio-impedance models. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.J.; Dhillon, J.; Kothari, D. Multi-objective thermal power load dispatch using chaotic differential evolutionary algorithm and Powell’s method. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 2159–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, D.; Allam, D.; Eteiba, M. Chaotic whale optimizer variants for parameters estimation of the chaotic behavior in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 74, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Park, J.B.; Joo, Y.H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, G. Bifurcations and chaos in a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2002, 49, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Chaotic Gravitational Constants for The Gravitational Search Algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 53, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number | Function Name | Chaotic Map |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chebyshev | |
| 2 | Circle | |
| and | ||
| 3 | Gauss/mouse | |
| 4 | Iterative | |
| 5 | Logistic | |
| 6 | Piecewise | |
| 7 | Sine | |
| 8 | Singer | |
| 9 | Sinusoidal | |
| 10 | Tent |
| Algorithms | q | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPSO | |||||
| C.EPSO | C.EPSO1 C.EPSO2 C.EPSO3 C.EPSO4 C.EPSO5 C.EPSO6 C.EPSO7 C.EPSO8 C.EPSO9 C.EPSO10 | ||||
| Algorithms | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPSO | |||||||
| C.EPSO | C.EPSO1 C.EPSO2 C.EPSO3 C.EPSO4 C.EPSO5 C.EPSO6 C.EPSO7 C.EPSO8 C.EPSO9 C.EPSO10 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yousri, D.; Eteiba, M.B.; Zobaa, A.F.; Allam, D. Parameters Identification of the Fractional-Order Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Models Using Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031325
Yousri D, Eteiba MB, Zobaa AF, Allam D. Parameters Identification of the Fractional-Order Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Models Using Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(3):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031325
Chicago/Turabian StyleYousri, Dalia, Magdy B. Eteiba, Ahmed F. Zobaa, and Dalia Allam. 2021. "Parameters Identification of the Fractional-Order Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Models Using Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer" Applied Sciences 11, no. 3: 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031325
APA StyleYousri, D., Eteiba, M. B., Zobaa, A. F., & Allam, D. (2021). Parameters Identification of the Fractional-Order Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Models Using Chaotic Ensemble Particle Swarm Optimizer. Applied Sciences, 11(3), 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031325







