Controllable Height Hopping of a Parallel Legged Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To balance requirements of high output, transparency and applicable size of legged robot for vertical hopping motion, a design of integral legged robot system was developed. The actuator used BLDC-harmonic actuator and the main structure is parallel mechanism, which are relatively more suitable for legged robot to perform greater height hopping.
- (2)
- To realize controllable height hopping, a novel height control strategy combined with VMC, using dynamics model construction and function parameter fitting, was proposed, which is appropriate for our mechanical design and can also meet the requirement without extra sensor measurement and online calculation.
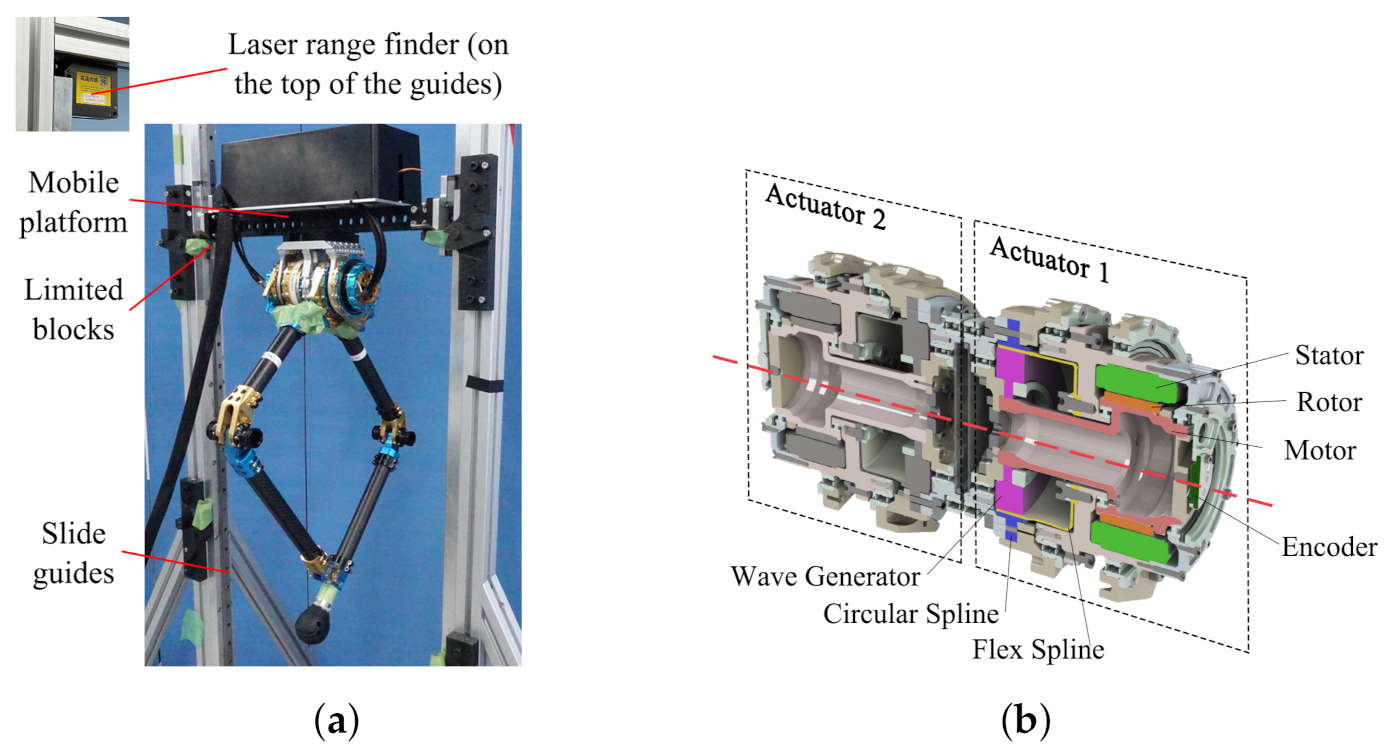
2. Robotic System Design
3. Dynamic Model Analysis
3.1. Actuator Modeling
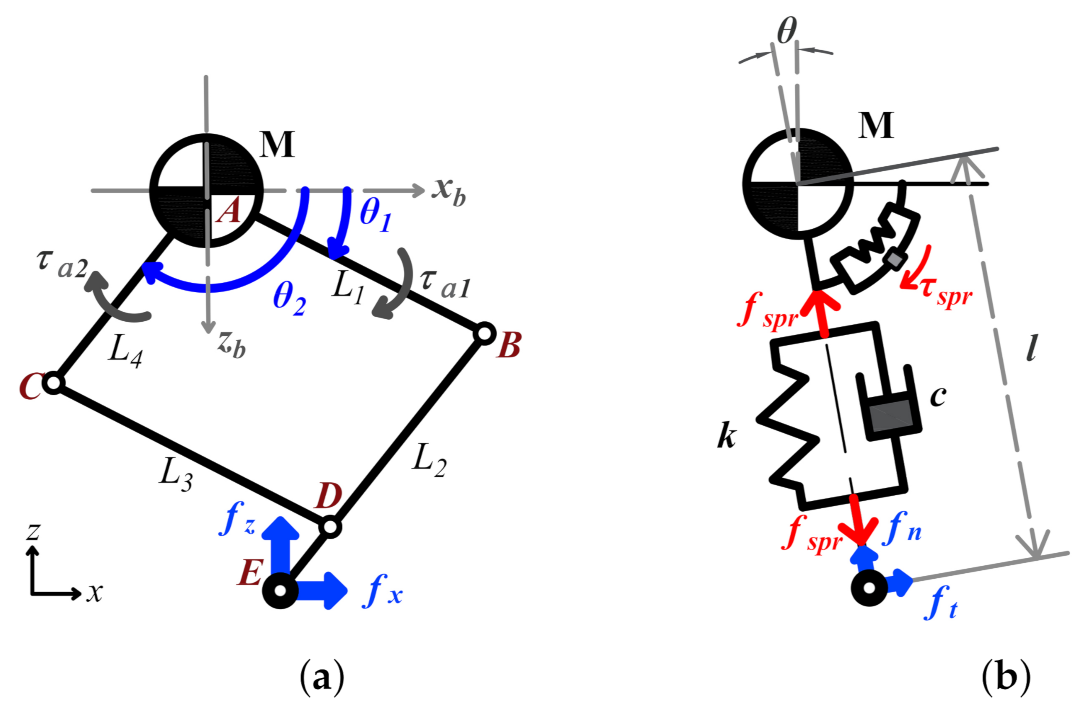
3.2. Leg Structural Modeling
3.3. Integrated Dynamic Modeling
4. Control Strategy
4.1. Virtual Model Controller
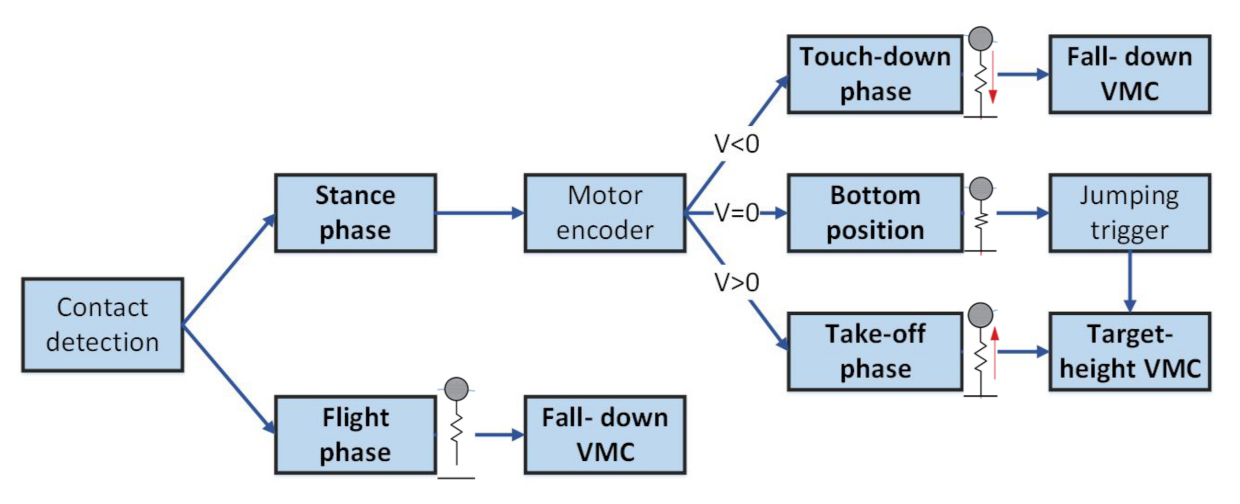
4.2. State Machine Design and Height Measurement
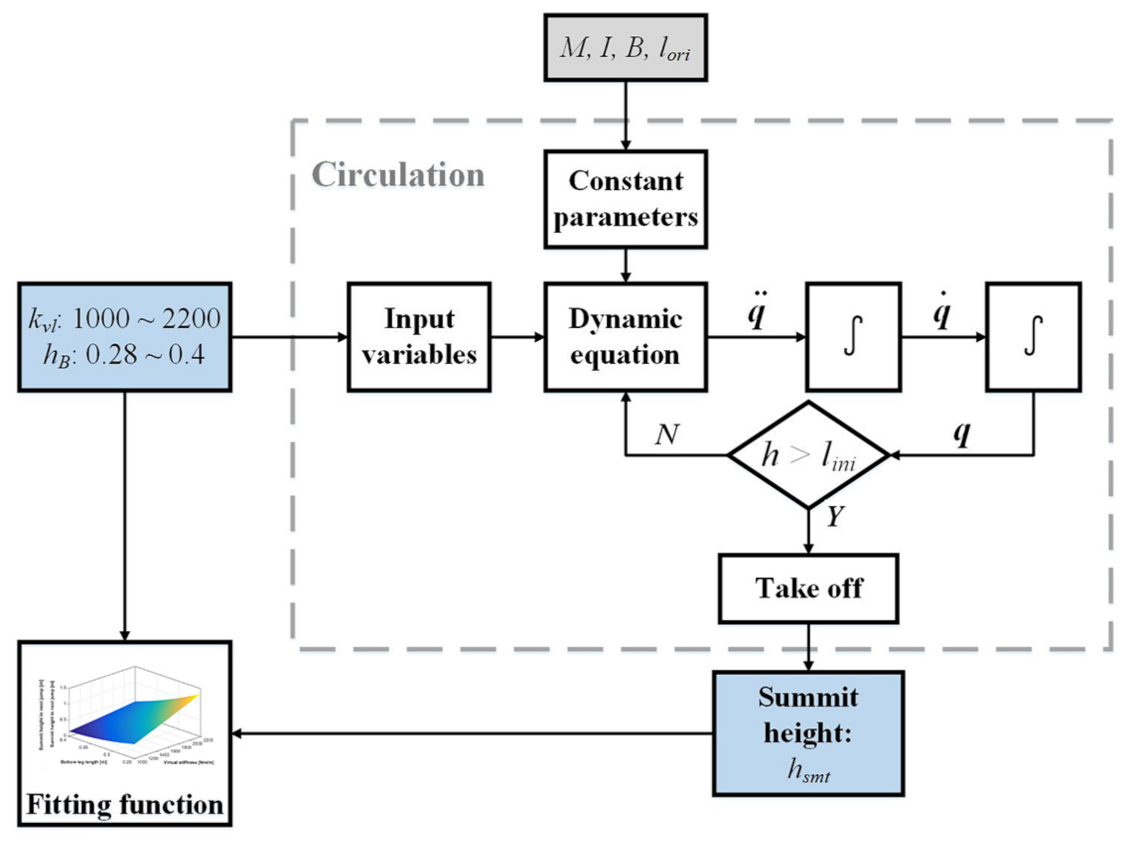
4.3. Height Control Strategy
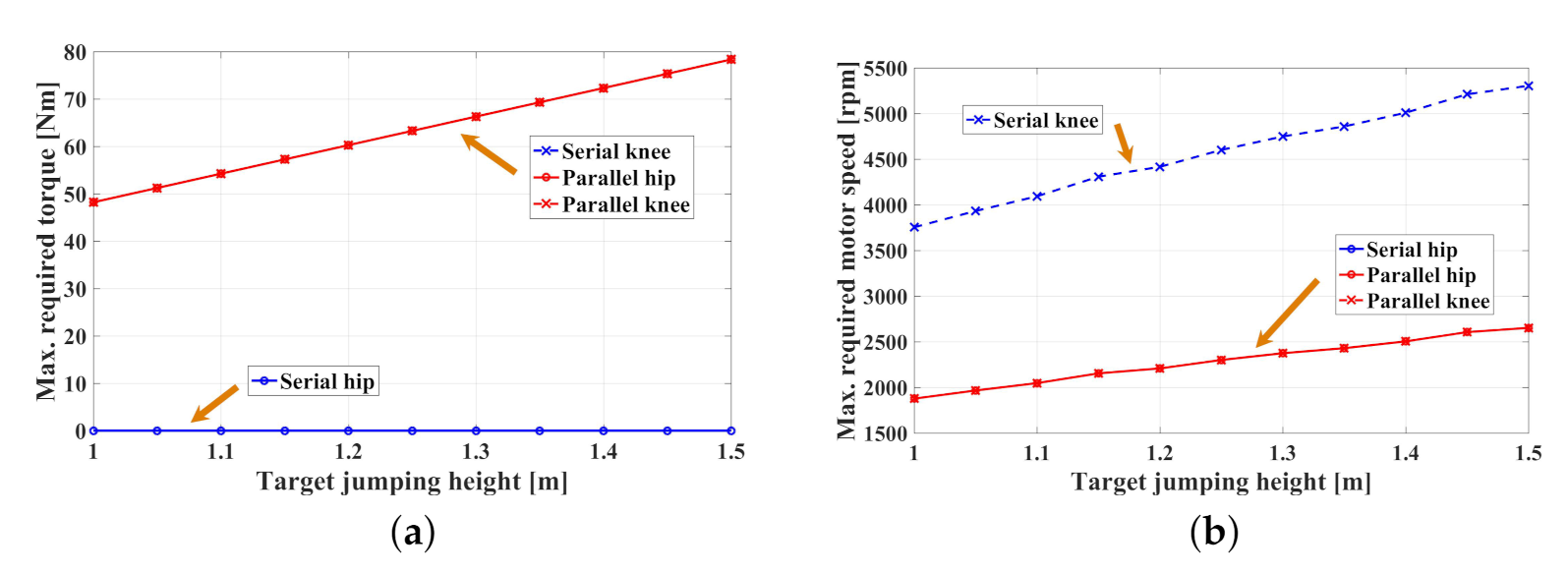
5. Simulation and Experiment
5.1. Simulation and Results
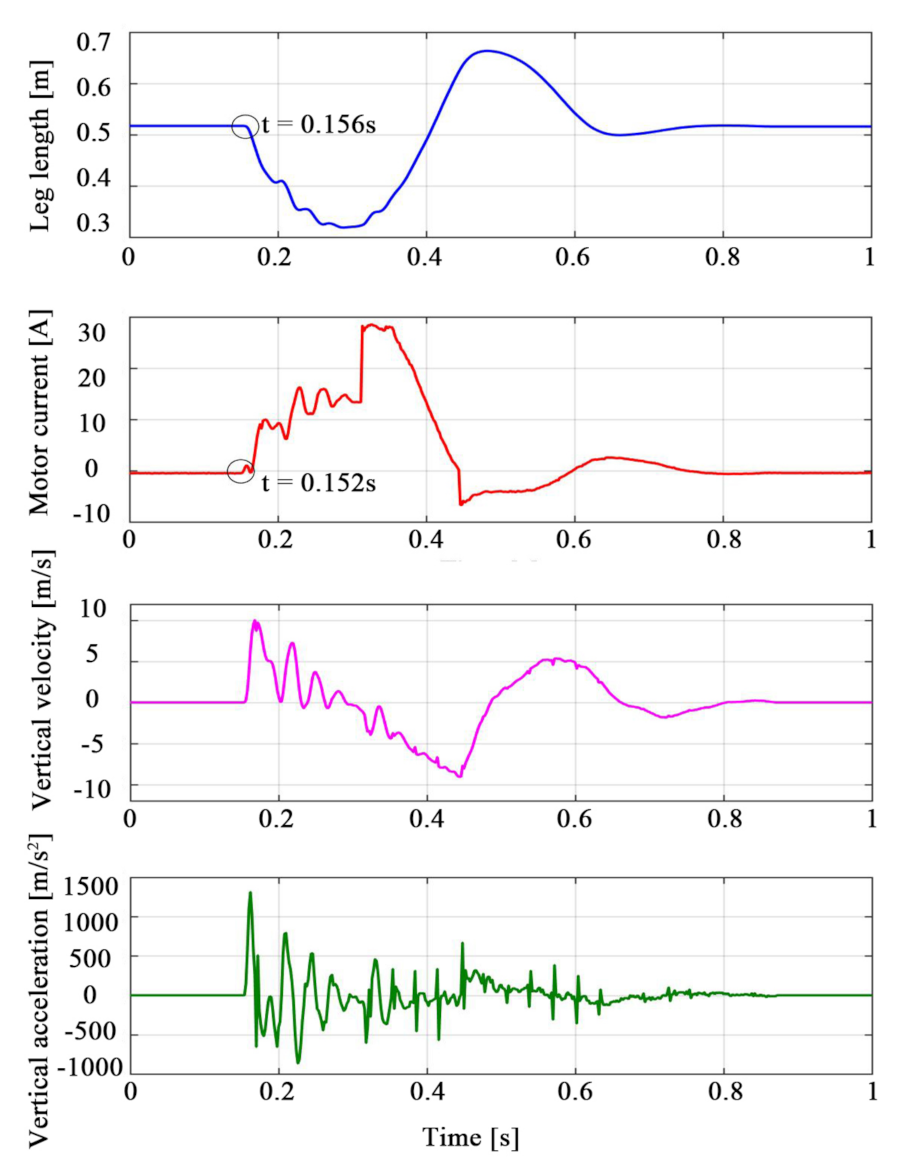
5.2. Single Landing-Jumping Experiment
5.3. Constant Height Hopping
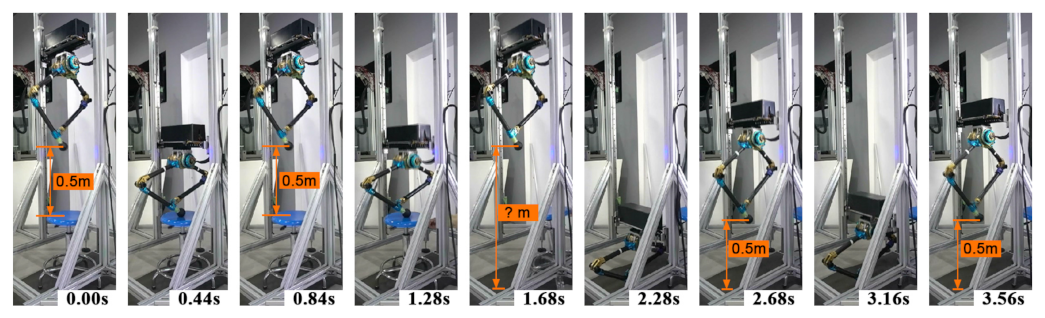
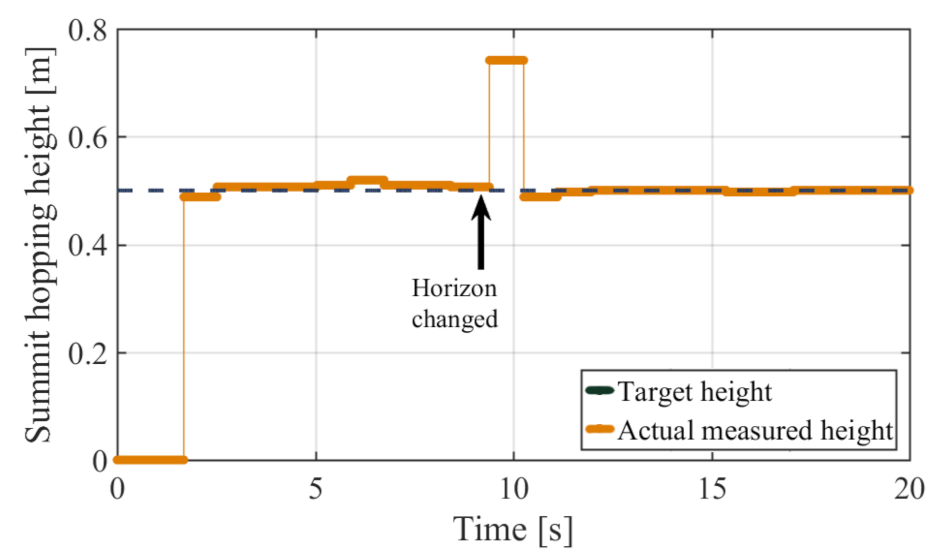
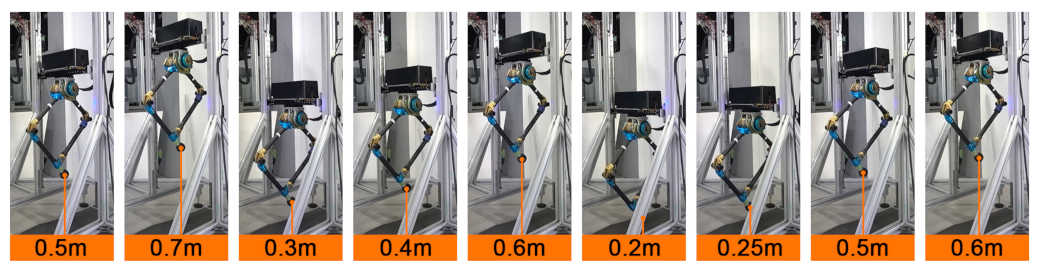
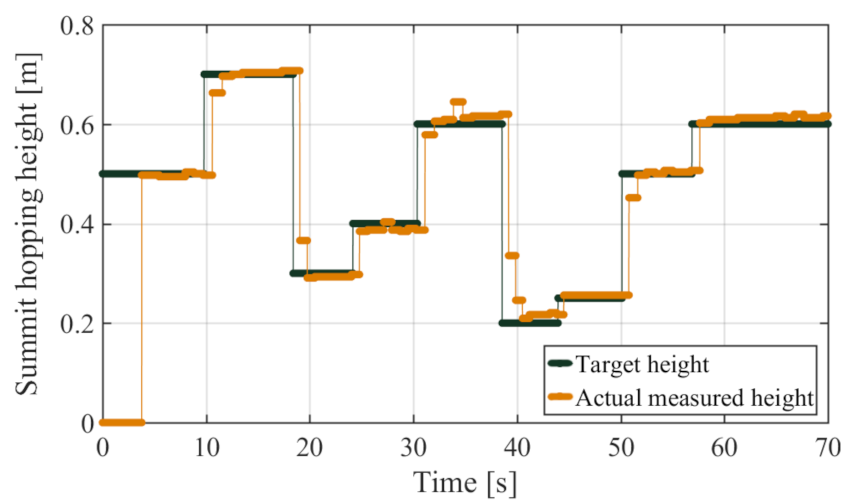
5.4. Variable Height Hopping
5.5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, X.; Ge, W.; Miraglia, M.; Inglese, F.; Zhao, D.; Stefanini, C.; Romano, D. Jumping Locomotion Strategies: From Animals to Bioinspired Robots. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Aoyama, C.; Matsunaga, S.; Higaki, N.; Fujimura, K. The intelligent ASIMO: System overview and integration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 September–4 October 2002; pp. 2478–2483. [Google Scholar]
- Hubicki, C.; Grimes, J.; Jones, M.; Renjewski, D.; Sprowitz, A.; Abate, A.; Hurst, J. ATRIAS: Design and validation of a tether-free 3Dcapable spring-mass bipedal robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 1497–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.; Wang, A.; Chuah, M.; Hyun, D.; Lee, J.; Otten, D.; Lang, J.; Kim, S. Design principles for energy-efficient legged locomotion and implementation on the MIT cheetah robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 20, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, S.; Kim, S. Variable-speed quadrupedal bounding using impulse planning: Untethered high-speed 3D Running of MIT Cheetah 2. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 5163–5170. [Google Scholar]
- Bledt, G.; Powell, M.; Katz, B.; Di Carlo, J.; Wensing, P.; Kim, S. MIT Cheetah 3: Design and control of a robust, dynamic quadruped robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 2245–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, B.; Di Carlo, J.; Kim, S. Mini Cheetah: A platform for pushing the limits of dynamic quadruped control. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 6295–6301. [Google Scholar]
- Seok, S.; Wang, A.; Otten, D.; Kim, S. Actuator design for high force proprioceptive control in fast legged locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 1970–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Wensing, P.; Wang, A.; Seok, S.; Otten, D.; Lang, J.; Kim, S. Proprioceptive actuator design in the MIT Cheetah: Impact mitigation and high-bandwidth physical interaction for dynamic legged robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raibert, M. Legged Robots that Balance; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Blickhan, R. The spring-mass model for running and hopping. J. Biomech. 1989, 22, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kong, K. Realization of Spring Loaded Inverted Pendulum Dynamics with a Two-link Manipulator based on the Bio-inspired Coordinate System. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, H.; Seyfarth, A.; Blickhan, R. Spring-mass running: simple approximate solution and application to gait stability. J. Theoret. Biol. 2005, 232, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, J.; Kam, M. Control of hopping height for a one-legged hopping machine. Mob. Robot. VII 1993, 1831, 604–612. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, J.; Hale, M.; Iravani, P. Adaptive height controller for an agile hopping robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 98, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, J.; Plummer, A; Sahinkaya, M.; Iravani, P.; Guglielmino, E.; Caldwell, D. Fast and adaptive hopping height control of single-legged robot. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 11th Biennial Conference on Engineering Systems Design and Analysis, Nantes, France, 2–4 July 2012; Volume 44861, pp. 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ugurlu, B.; Kawamura, A. Zmp-based online jumping pattern generation for a one-legged robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Meng, L.; Huang, Q. Motion planning for bipedal robot to perform jump maneuver. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurlu, B.; Kawamura, A. On the backward hopping problem of legged robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, J.; Dilworth, P.; Pratt, G. Virtual model control of a bipedal walking robot. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 25 April 1997; pp. 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, B.; Zhu, S.; Pang, Y.; Chen, G. Dynamic Hopping Height Control of Single-Legged Hopping Robot. In Wearable Sensors and Robots; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 20, pp. 365–382. [Google Scholar]
- Kalouche, S. GOAT: A legged robot with 3D agility and virtual compliance. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 4110–4117. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Meng, F.; Fan, X.; Kang, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Yu, Z.; Qin, M.; Ming, A.; Huang, Q. Development of a parallel-elastic robot leg for loaded jumping. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Toyonaka, Japan, 3–5 July 2019; pp. 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D; Pratt, J.; Paluska, D.; Pratt, G. Series elastic actuator development for a biomimetic walking robot. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 September 1999; pp. 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Oh, S. Optimal Landing Strategy for Two-Mass Hopping Leg With Natural Dynamics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Fan, X.; Ming, A.; Huang, Q. Structural Design and Crawling Pattern Generator of a Planar Quadruped Robot for High-Payload Locomotion. Sensors 2020, 20, 6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, H.; Gregorio, P.; Buehler, M. Design, modeling and control of a hopping robot. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 1993 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 26–30 July 1993; pp. 1778–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Taghirad, H.; Belanger, P. Modeling and parameter identification of harmonic drive systems. Trans. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 1998, 120, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total Diameter (mm) | Reduction Ratio | Max. Output Torque (Nm) | Max. Torque– Radius Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIT Cheetah | 125 | 1:5.8 | 174 | 2.8 |
| This paper | 70 | 1:31 | 124 | 3.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Fan, X.; Sato, R.; Ming, A.; Huang, Q. Controllable Height Hopping of a Parallel Legged Robot. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041421
He Z, Meng F, Chen X, Yu Z, Fan X, Sato R, Ming A, Huang Q. Controllable Height Hopping of a Parallel Legged Robot. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041421
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zewen, Fei Meng, Xuechao Chen, Zhangguo Yu, Xuxiao Fan, Ryuki Sato, Aiguo Ming, and Qiang Huang. 2021. "Controllable Height Hopping of a Parallel Legged Robot" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041421
APA StyleHe, Z., Meng, F., Chen, X., Yu, Z., Fan, X., Sato, R., Ming, A., & Huang, Q. (2021). Controllable Height Hopping of a Parallel Legged Robot. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041421







